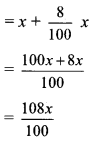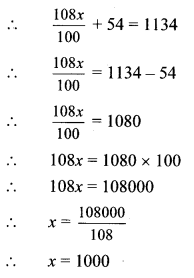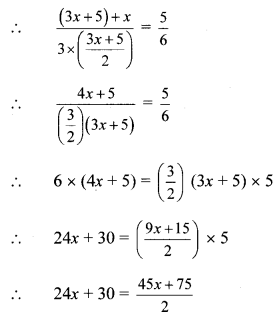Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 12.1 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions Chapter 12 Equations in One Variable.
Equations in One Variable Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Practice Set 12.1 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 8 Maths Practice Set 12.1 Chapter 12 Solutions Answers
Equation in One Variable Practice Set 12.1 Question 1. Each equation is followed by the values of the variable. Decide whether these values are the solutions of that equation.
i. x – 4 = 3, x = – 1, 7, – 7
ii. 9m = 81, m = 3, 9, -3
iii. 2a + 4 = 0, a = 2, – 2, 1
iv. 3 – y = 4, y = – 1, 1, 2
Solution:
i. x – 4 = 3 ….(i)
Substituting x = – 1 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = (-1) – 4
= – 5
R.H.S. = 3
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ x = – 1 is not the solution of the given equation.
Substituting x = 7 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = (7) – 4
= 3
R.H.S. = 3
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴ x = 7 is the solution of the given equation.
Substituting x = – 7 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = (- 7) – 4
= -11
R.H.S. = 3
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴ x = – 7 is not the solution of the given equation.
ii. 9m = 81 …(i)
Substituting m = 3 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 9 × (3)
= 27
R.H.S. = 81
∴L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴m = 3 is not the solution of the given equation.
Substituting m = 9 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 9 × (9)
= 81
R.H.S. = 81
∴L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴m = 9 is the solution of the given equation.
Substituting m = – 3 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 9 × (- 3)
= -27
R.H.S. = 81
∴L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴m = – 3 is not the solution of the given equation.
iii. 2a + 4 = 0 …..(i)
Substituting a = 2 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 2 (2) + 4
= 4 + 4
= 8
R.H.S. = 0
∴L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴a = 2 is not the solution of the given equation.
Substituting a = – 2 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 2 (-2)+ 4
= -4 + 4
= 0
R.H.S. = 0
∴L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴a = – 2 is the solution of the given equation.
Substituting a = 1 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 2(1)+ 4
= 2 + 4
= 6
R.H.S. = 0
∴ L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴a = 1 is not the solution of the given equation.
iv. 3 – y = 4 …(i)
Substituting y = -1 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 3 – (- 1)
= 3 + 1
= 4
R.H.S. = 4
∴L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴y = – 1 is the solution of the given equation.
Substituting y = 1 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 3-(1)
= 2
R.H.S. = 4
∴L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴y = 1 is not the solution of the given equation.
Substituting y = 2 in L.H.S. of equation (i),
L.H.S. = 3-(2)
= 1
R.H.S. = 4
∴L.H.S. ≠ R.H.S.
∴y = 2 is not the solution of the given equation.
Practice Set 12.1 Question 2.
Solve the following equations:
i. 17p – 2 = 49
ii. 2m + 7 = 9
iii. 3x + 12 = 2x – 4
iv. 5 (x – 3) = 3 (x + 2)
v. \(\frac { 9x }{ 8 }+1=10\)
vi. \(\frac{y}{7}+\frac{y-4}{3}=2\)
vii. 13x – 5 = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)
viii. 3 (y + 8) = 10 (y – 4) + 8
ix. \(\frac{x-9}{x-5}=\frac{5}{7}\)
x. \(\frac{y-4}{3}+3 y=4\)
xi. \(\frac{b+(b+1)+(b+2)}{4}=21\)
Solution:
i. 17p – 2 = 49
∴ 17p – 2 + 2 = 49 + 2
…[Adding 2 on both the sides]
∴ 17p = 51
∴ \(\frac{17 p}{17}=\frac{51}{17}\) …[Dividing both the sides by 17]
p = 3
ii. 2m + 7 = 9
∴ 2m + 7 – 7 = 9 – 7
…[Subtracting 7 from both the sides]
∴ 2m = 2
∴ \(\frac{2 m}{2}=\frac{2}{2}\) [Dividing both the sides by 2]
∴ m = 1
iii. 3x + 12 = 2x – 4
∴ 3x + 12 – 12 = 2x – 4 – 12
…[Subtracting 12 from both the sides]
∴ 3x = 2x – 16
∴ 3x – 2x = 2x – 16 – 2x
…[Subtracting 2x from both the sides]
∴ x = – 16
iv. 5 (x – 3) = 3 (x + 2)
∴ 5x – 15 = 3x + 6
∴ 5x – 15 + 15 = 3x + 6 + 15
…[Adding 15 on both the sides]
∴ 5x = 3x + 21
∴ 5x – 3x = 3x + 21 – 3x
…[Subtracting 3x from both the sides]
∴ 2x = 21
∴ \(\frac{2 x}{2}=\frac{21}{2}\) …[Dividing both the sides by 2]
∴ \(x=\frac{21}{2}\)
v. \(\frac { 9x }{ 8 }+1=10\)

vi. \(\frac{y}{7}+\frac{y-4}{3}=2\)


vii. 13x – 5 = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\)

viii. 3 (y + 8) = 10 (y – 4) + 8
∴ 3y + 24 = 10y – 40 + 8
∴ 3y + 24 = 10y – 32
∴ 3y + 24 – 24 = 10y – 32 – 24
…[Subtracting 24 from both the sides]
∴ 3y = 10y – 56
∴ 3y – 10y = 10y – 56
…[Subtracting 10y from both the sides]
∴ – 7y = – 56
∴ \(\frac{-7 y}{-7}=\frac{-56}{-7}\)…[Dividing both the sides by – 7]
∴ y = 8
ix. \(\frac{x-9}{x-5}=\frac{5}{7}\)
∴\(\frac{x-9}{x-5} \times 7(x-5)=\frac{5}{7} \times 7(x-5)\)
…[Multiplying both the sides by 7 (x – 5)]
∴7 (x – 9) = 5 (x – 5)
∴7x – 63 = 5x – 25
∴7x – 63 + 63 = 5x – 25 + 63
…[Adding 63 on both the sides]
∴7x = 5x + 38
∴7x – 5x = 5x + 38 – 5x
…[Subtracting 5x from both the sides]
∴ 2x = 38
∴\(\frac{2 x}{2}=\frac{38}{2}\) …[Dividing both the sides by 2]
∴x = 19
x. \(\frac{y-4}{3}+3 y=4\)
∴\(\frac{y-4}{3} \times 3+3 y \times 3=4 \times 3\)
…[Multiplying both the sides by 3]
∴y – 4 + 9y = 12
∴10y – 4 = 12
∴10y – 4 + 4=12 + 4
…[Adding 4 on both the sides]
∴10y = 16
∴\(\frac{10 y}{10}=\frac{16}{10}\)…[Dividing both the sides by 10]
∴y = \(\frac { 8 }{ 5 }\)
xi. \(\frac{b+(b+1)+(b+2)}{4}=21\)
∴\(\frac{b+(b+1)+(b+2)}{4} \times 4=21 \times 4\)
…[Multiplying both the sides by 4]
∴b + b + 1 + b + 2 = 84
∴3b + 3 = 84
∴3b + 3 – 3 = 84 – 3
…[ Subtracting 3 from both the sides]
∴3b = 81
∴\(\frac{3 b}{3}=\frac{81}{3}[/latex …[Dividing both the sides by 3]
∴b = 27
Maharashtra Board Class 8 Maths Chapter 12 Equations in One Variable Practice Set 12.1 Intext Questions and Activities
Std 8 Maths Practice Set 12.1 Question 1.
Fill in the boxes to solve the following equations. (Textbook pg. no. 75)
i. x + 4 = 9
∴x + 4 – __ = 9 – __
… [Subtracting 4 from both the sides]
∴ x = __
ii. x – 2 = 7
∴x – 2 + __ = 7 + __
… [Adding 2 on both the sides]
∴x = __
iii. [latex]\frac { x }{ 3 }=4\)
∴\(\frac { x }{ 3 }\) × __ = 4 ×__
∴x = __
iv. 4x = 24
∴ __ = __
∴x = __
Solution:
i. x + 4 = 9
∴x + 4 – 4 = 9 – 4
… [Subtracting 4 from both the sides]
∴ x = 5
ii. x – 2 = 7
∴x – 2 + 2 = 7 + 2
… [Adding 2 on both the sides]
∴x = 9
iii. \(\frac { x }{ 3 }=4\)
∴\(\frac { x }{ 3 }\) × 3 = 4 × 3
… [Multiplying both the sides by 3]
∴x = 12
iv. 4x = 24
∴ \(\frac{4 x}{[4]}=\frac{24}{[4]}\)
… [Dividing both the sides by 4]
∴x = 6
Std 8 Maths Digest