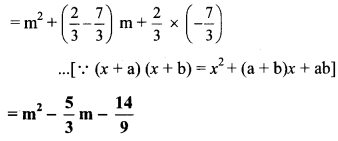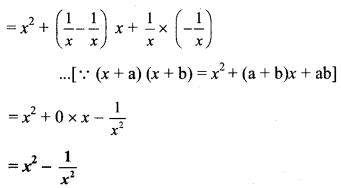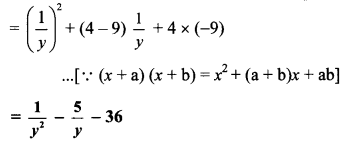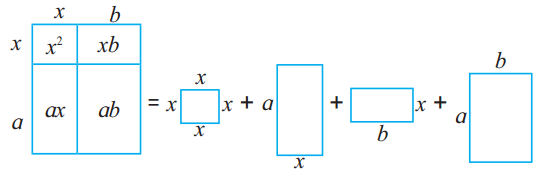Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 5.3 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions Chapter 5 Expansion Formulae.
Expansion Formulae Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Practice Set 5.3 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 8 Maths Practice Set 5.3 Chapter 5 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
Expand:
i. (2m – 5)³
ii. (4 – p)³
iii. (7x – 9y)³
iv. (58)³
v. (198)³
vi. \(\left(2 p-\frac{1}{2 p}\right)^{3}\)
vii. \(\left(1-\frac{1}{a}\right)^{3}\)
viii. \(\left(\frac{x}{3}-\frac{3}{x}\right)^{3}\)
Solution:
i. Here, a = 2m and b = 5
(2m – 5)³
= (2m)³ – 3(2m)² (5) + 3(2m) (5)² – (5)³
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 8m³ – 3(4m²)(5) + 3(2m)(25) – 125
= 8m³ – 60m² + 150m – 125
ii. Here, a = 4 and b = p
(4 – p)³ = (4)³ – 3(4)²(p) + 3(4)(p)² – (p)³
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 64 – 3(16)(p) + 3(4)(p²) – p³
= 64 – 48p + 12p² – p³
iii. Here, a = 7x and b = 9y
(7x – 9y)³
= (7x)³ – 3(7x)² (9y) + 3 (7x)(9y)² – (9y)³
…[(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 343x³ – 3(49x²)(9y) + 3(7x)(81y²) – 729y³
= 343x³ – 1323x²y + 1701xy² – 729y³
iv. (58)³ = (60 – 2)³
Here, a = 60 and b = 2
(58)³ = (60)³ – 3(60)²(2) + 3(60)(2)² – (2)³
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 216000 – 3(3600)(2) + 3(60)(4) – 8
= 216000 – 21600 + 720 – 8
=195112
v. (198)³ = (200 – 2)³
Here, a = 200 and b = 2
(198)³ = (200)³ – 3(200)²(2) + 3(200)(2)² – (2)³
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= 8000000 – 3(40000)(2) + 3(200)(4) – 8
= 8000000 – 240000 + 2400 – 8
= 7762392
vi. Here, a = 2p and b = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2p }\)
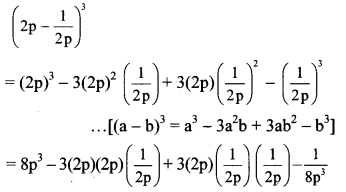
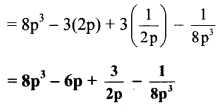
vii. Here, A = 1 and B = \(\frac { 1 }{ a }\)
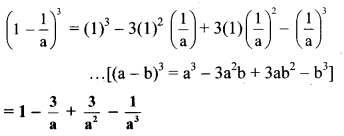
viii. Here, a = \(\frac { x }{ 3 }\) and b = \(\frac { 3 }{ x }\)
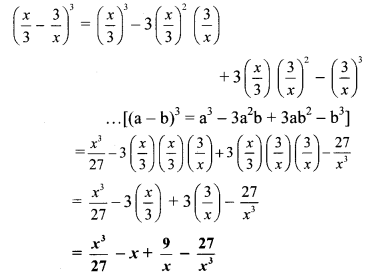
Question 2.
Simplify:
i. (2a + b)³ – (2a – b)³
ii. (3r – 2k)³ + (3r + 2k)³
iii. (4a – 3)³ – (4a + 3)³
iv. (5x – 7y)³ + (5x + 7y)³
Solution:
i. (2a + b)³ – (2a – b)³
= [(2a)³ + 3(2a)²(b) + 3 (2a)(b)² + (b)³] – [(2a)³ – 3(2a)²(b) + 3 (2a)(b)² – (b)³]
… [(a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³, (a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³]
= (8a³ + 12a²b + 6ab² + b³) – (8a³ – 12a²b + 6ab² – b³)
= 8a³ + 12a²b + 6ab² + b³ – 8a³ + 12a²b – 6ab² + b³
= 8a³ – 8a³ + 12a²b + 12a²b + 6ab² – 6ab² + b³ + b³
= 24a²b + 2b³
ii. (3r – 2k)³ + (3r + 2k)³
= [(3r)³ – 3(3r)²(2k) + 3(3r)(2k)² – (2k)³] + [(3r)³ + 3(3r)²(2k) + 3(3r)(2k)² + (2k)³]
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³, (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³]
= (27r³ – 54r²k + 36rk² – 8k³) + (27r³ + 54r²k + 36rk² + 8k³)
= 27r³ – 54r²k + 36rk² – 8k³ + 27r³ + 54r²k + 36rk² + 8k³
= 27r³ + 27r³ – 54r²k + 54r²k + 36rk² + 36rk² – 8k³ + 8k³
= 54r³ + 72rk²
iii. (4a – 3)³ – (4a + 3)³
= [(4a)³ – 3(4a)² (3) + 3(4a)(3)² – (3)³] – [(4a)³ + 3(4a)²(3) + 3(4a)(3)² + (3)³]
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³, (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³]
= (64a³ – 144a² + 108a – 27) – (64a³ + 144a² + 108a + 27)
= 64a³ – 144a² + 108a – 27 – 64a³ -144a² – 108a – 27
= 64a³ – 64a³ – 144a² – 144a² + 108a – 108a – 27 – 27
= -288a² – 54
iv. (5x – 7y)³ + (5x + 7y)³
= [(5x)³ – 3(5x)²(7y) + 3(5x)(7y)² – (7y)³] + [(5x)³ + 3(5x)² (7y) + 3(5x) (7y)² +(7y)³]
… [(a – b)³ = a³ – 3a²b + 3ab² – b³, (a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³]
= (125x³ – 525x²y + 735xy² – 343y³) + (125x³ + 525x²y + 735xy² + 343y³)
= 125x³ – 525x²y + 735xy² – 343y³ + 125x³ + 525x²y + 735xy² + 343y³
= 125x³ + 125x³ – 525x²y + 525x²y + 735xy² + 735xy² – 343y³ + 343y³
= 250x³ + 1470xy²
Maharashtra Board Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Expansion Formulae Practice Set 5.3 Intext Questions and Activities
Question 1.
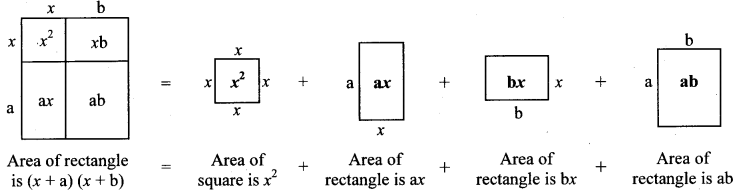
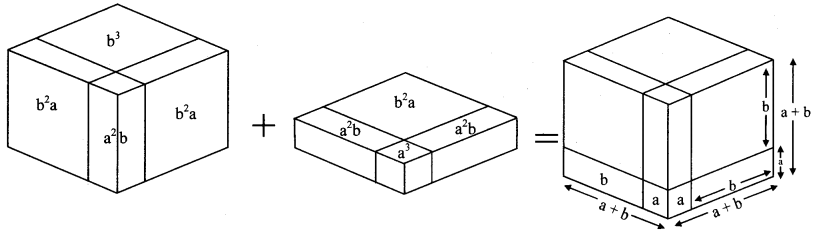
Make two cubes of side a and of side b each. Make six parallelopipeds; three of them measuring a × a × b and the remaining three measuring b × b × a. Arrange all these solid figures properly and make a cube of side (a + b). (Textbook pg. no. 25)
Solution:
(a + b)³ = a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³
= a × a × a + 3 × a × a × b + 3 × a × b × b + b × b × b
Std 8 Maths Digest