Class 7 Hindi Chapter 3 Dadi Maa Ka Parivar Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 3 दादी माँ का परिवार Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Hindi Chapter 3 Dadi Maa Ka Parivar Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 3 दादी माँ का परिवार Textbook Questions and Answers
जरा सोचो ………. बताओ
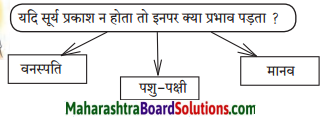
यदि प्राकृतिक संसाधन समाप्त हो जाएँ तो… जैसे-जल, बन आदि। इस पर आधारित अपने विचार लिखिए। (कल्पनात्मक-लेखन)
Answer:
प्रकृति हमारी माता है, वह हमारी जीवनदायिनी है। प्रकृति से हमें कई प्राकृतिक संसाधन प्राप्त होते हैं। जल, वन, खनिज तेल, धातुएँ, कोयला, समुद्र से प्राप्त होनेवाले कई पदार्थ ये सब प्राकृतिक संसाधन हैं। मनुष्य ने अपने स्वार्थ हेतु इन वस्तुओं को अधिक से अधिक मात्रा में उपयोग किया है। अब इनकी संख्या में दिन-प्रतिदिन कमी आती जा रही है। ये सारे प्राकृतिक संसाधन अगर मनुष्य की ऐसी बेपरवाह एवं स्वार्थपरायण वृत्ति से समाप्त हो जाए, तो मनुष्य की आनेवाली पीढ़ियाँ इसका उपभोग न कर पाएंगी और इसका सारा दोष वर्तमान मनुष्य पर डालेंगी।
इसका विचार करते हुए वर्तमान समय में हमें इन सभी प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का उपयोग सोच-समझकर एवं योग्य मात्रा में करना चाहिए। जिस प्रकार पानी के बिना मछली जीवित नहीं रह सकती, उसी प्रकार मनुष्य का संपूर्ण जीवन प्राकृतिक संसाधनों पर आधारित है। इनकी समाप्ति मानव जीवन की सबसे बड़ी हानि होगी। प्रकृति का साथ लेकर ही मनुष्य अपना जीवन अधिक सुंदर व सफल बना सकता है। इसलिए प्रकृति प्रदत्त इस संपदा का प्रयोग हमें भविष्य की सोच एवं संचयन नीति के आधार पर करना चाहिए।

मेरी कलम से
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के आधार पर एक कहानी लिखिए। (पानी, पुस्तक, बिल्ली, राखी।) (कहानी-लेखन)
Answer:
रामपुर नाम का एक गाँव था। वहाँ मोहन नाम का एक लड़का अपने माता-पिता के साथ रहता था। उसकी बहन मीना उनसे दूर रघुपूर नामक गाँव में अपनी शिक्षा पूरी करने के लिए गई थी। मोहन अपनी बहन से बहुत प्रेम करता था। अपनी प्यारी बहन से दूर रहना उसे बिलकुल अच्छा नहीं लगता था। कुछ दिनों बाद राखी का त्योहार आया। मोहन अपनी बहन से मिलने जाना चाहता था किंतु आकाश में छाए बादलों व भारी वर्षा के कारण सब जगह पानी जमा हो गया।
अब मोहन को मीना से मिलने की इच्छा डूबती हुई नज़र आने लगी। उसने अपनी बहन को उपहार देने के लिए कहानियों की एक पुस्तक खरीदी थी। उसे बहुत बुरा लग रहा था। उसने निश्चय किया कि कुछ भी हो वह अपनी बहन से मिलने अवश्य जाएगा। वह बहन को मिलने जाने के लिए जब घर से निकला तब काली बिल्ली रास्ता काटती चली गई। वह बहुत डर गया और सोचने लगा कि अगर रघुपूर जानेवाली बस उसे नहीं मिली, तो वह अपनी बहन से नहीं मिल पाएगा।
वह निराश होकर नीचे बैठ गया और सिसक-सिसककर रोने लगा। तभी उसके सिर को किसी ने प्यार से सहलाया। मोहन ने ऊपर देखा तो उसके सामने उसकी बहन मीना खड़ी थी। मोहन खुशी से फूला न समाया और अपनी बहन से लिपट गया। स्वयं मीना उससे मिलने आई थी। घर के सभी लोग खुश थे। इस प्रकार मोहन-मीना के साथ समस्त परिवार ने खुशीखुशी त्योहार मनाया।

विचार मंथन:
“वृक्षवल्ली आम्हां सोयरे वनचरे” इन पंक्तियों का अर्थ स्पष्ट कीजिए। (अर्थ-स्पष्टीकरण)
Answer:
“वृक्षवल्ली आम्हां सोयरे वनचरे”
वृक्ष अर्थात पेड़-पौधे। वृक्ष महत्त्वपूर्ण प्राकृतिक संसाधन हैं। इनसे मिलनेवाले सारे सुख-साधन हमारे लिए प्रकृति की देन हैं। वन में रहनेवाले सभी पशु-पक्षी, जीव-जंतु, पेड़-पौधे और अपनी मधुर आवाज से अपने भगवान को पुकारने वाले ये रंग-बिरंगे पक्षी प्राकृतिक संबंधों में हमारे परिवार के सदस्य हैं।
इस कारण हमारे परिवार के सभी सदस्यों की देखभाल करना उनके भविष्य के बारे में सोचना उनकी रक्षा करना हमारा परम कर्तव्य है। प्रकृति में स्थित पशु-पक्षी, पेड़-पौधे, नदी-नाले इन सभी प्राकृतिक चीजों पर संपूर्ण मानव जाति का जीवन आधारित है। इनकी रक्षा करना संपूर्ण मानव जाति की रक्षा करना है।
सुने हुए चुटकुले, हास्य प्रसंगों को पुन: स्मरण करके सुनाइए।
Answer:
विदयार्थी स्वयं सुने हुए चुटकुले, हास्य प्रसंग सुनाकर अपेक्षित कृति करेंगे।
आकारिक मूल्यमापन
१. सुनो तो जरा: सुने हुए चुटकुले, हास्य प्रसंगों को पुन: स्मरण करके सुनाओ।
२. वाचन जगत से: स्वामी विवेकानंद का कोई भाषण पढ़ो और प्रमुख वाक्य बताओ।
३. अध्ययन कौशल: अपने और किसी पड़ोसी राज्य के राष्ट्रीय अभ्यारण्यों की शासकीय वीडियो क्लिप्स फिल्म्स आदि देखकर वर्गीकरण करों एवं टिपण्णी बनाओ।

अध्ययन कौशल
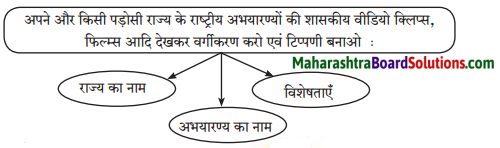
Answer:
१. राज्य का नाम: महाराष्ट्र
अभयारण्य का नाम: संजय गांधी राष्ट्रीय उद्यान
विशेषताएं: यह उद्यान महाराष्ट्र की राजधानी मुंबई के उत्तरी भाग में स्थित है। उद्यान लगभग १०४ वर्ग किलोमीटर तक फैला हुआ है। इस उद्यान में दो मुख्य जलाशय हैं, जिनके आस-पास घिड़याल और पाइथन साँपों का निवास है। इस पार्क के । जंगलों में शेर, बाघ, चमगादड़, माउस डीयर, बोनेट मेकाक, रिसस मेकाक व हनुमान लंगूर आदि भी देखने को मिलते है।
२. राज्य का नाम: केरल
अभयारण्य का नाम: पेरिया वन्य जीव अभयारण्य
विशेषताएं: यह राष्ट्रीय उद्यान एक बाघ संरक्षित क्षेत्र है। यहाँ नदी के गहरे जल में हाथी तैरने का अभ्यास करते हैं। नीलगाय, सांभार, भालू, चीता तथा तेंदुआ आदि जंगली जानवर भी यहाँ पाए जाते हैं।

वाचन जगत से:
स्वामी विवेकानंद का कोई भाषण – पढ़ो और प्रमुख वाक्य बताओ।
Answer:
स्वामी विवेकानंद ने अमेरिका के शिकागो में ११ सितंबर, १८९३ को आयोजित विश्व धर्म सम्मेलन में जो भाषण दिया था, उसमें उन्होंने कहा था, ‘मैं एक ऐसे धर्म का अनुयायी होने में गर्व का अनुभव करता हूँ, जिसने संसार को सहिष्णुता तथा सार्वभौम स्वीकृत दोनों की ही शिक्षा दी है। हम लोग सब धर्मों के प्रति केवल सहिष्णुता में ही विश्वास नहीं करते वरन समस्त धर्मों को सच्चा मानकर स्वीकार करते हैं। मुझे ऐसे देश का व्यक्ति होने का अभिमान है जिसने इस पृथ्वी के समस्त धर्मों और देशों के उत्पिीड़तों और शरणार्थियों को आश्रय दिया है।”
सदैव ध्यान में रखो:
संगठन में ही शक्ति है, इसे जीवन में उतारो ।
भाषा की ओर:
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के वचन बदलकर वाक्य में प्रयोग करके लिखो।
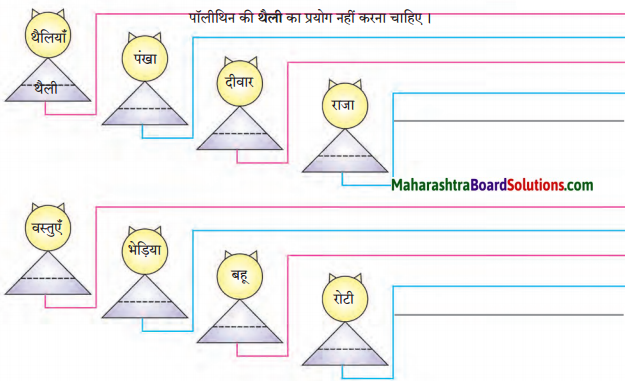
Answer:
१. थैली – पॉलीथिन की थैली का प्रयोग नहीं करना चाहिए।
२. पंखे – आवश्यकता न होने पर पंखे बंद रखकर हमें बिजली की बचत करनी चाहिए।
३. दीवारें – सोना के घर की दीवारें बहुत ही ऊँची हैं।
४. राजा – अपनी प्रजा की रक्षा करना प्रत्येक राजा का कर्तव्य होता है।
५. वस्तु – विजय ने अपनी कीमती वस्तु सँभालकर रखी।
६. भिड़ए – जंगल में भिड़ए दल बनाकर शिकार करते हैं।
७. बहुएँ – मीरा चाची की बहुएँ बहुत ही स्वादिष्ट खाना बनाती हैं।
८. रोटियाँ – समिधा ने अपनी माँ से गोल-गोल रोटियाँ बनाना सीख लिया है।

निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को कहानी के घटना क्रम के अनुसार लिखिए।
Question 1.
चिंकी ने भी दो बेटों का उपहार दिया।
Answer:
घर के आंगन में बरगद का पेड़ था।
Question 2.
एक साथ उड़ने को रहेंगे तैयार।
Answer:
चिंकी ने भी दो बेटों का उपहार दिया
Question 3.
टीनू-मीनू, चुसकू-मुसकू खेलने लगे।
Answer:
एक साथ उड़ने को रहेंगे तैयार।
Question 4.
घर के आँगन में बरगद का पेड़ था।
Answer:
घर के आँगन में बरगद का पेड़ था।

निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.
चिड़िया कहाँ रहती थी?
Answer:
चिड़िया दादी माँ के घर के आँगन के पेड़ पर बने घोंसले में रहती थी।
Question 2.
बहेलिया कब ठगा-सा रह गया?
Answer:
सभी पंछियों को जाल सहित उड़ते देखकर बहेलिया ठगा-सा रह गया।
Question 3.
दादी माँ सुबह उठकर क्या करतीं?
Answer:
दादी माँ सुबह उठकर अपने घर और आँगन की साफ़-सफाई करती। आँगन में अपना आसन लगाकर खाना बनाती व खाती थीं।
Question 4.
चुसकू-मूसकू ने किससे जाल काटा?
Answer:
चुसकू-मुसकू ने अपने पैने दाँतों से जाल काटा।
Question 5.
दादी माँ की दीन-दुनिया में कौन-कौन थे?
Answer:
दादी माँ की दीन-दुनिया में बरगद के पेड़ पर घोंसले में रहने वाली नीलू चिड़िया तथा पेड़ के नीचे बिल बनाकर रहने वाली चिंकी चुहिया थी।
Question 6.
दादी माँ नीलू चिड़िया व चिंकी चुहिया के बच्चों को हमेशा क्या समझाती थीं?
Answer:
दादी माँ नीलू चिड़िया व चिंकी चुहिया के बच्चों को हमेशा यह समझाती थीं कि आपस में लडाई-झगडा मत करो। सभी मिलकर एकता से रहो। एकता में ही खुशहाली है। आपस में किसी प्रकार का मतभेद न रखते हुए खुशहाली से रहो।
Question 7.
चिड़े-चिड़ियों की घर जाने की आस क्यों खत्म हुई?
Answer:
चिड़े-चिड़ियों की घर जाने की आस इसलिए खत्म हो गई क्योंकि सभी पंछी बहेलिए के जाल में फंस गए थे। कई बार निकलने का प्रयास करने के बावजूद भी वे उसमें से नहीं निकल पा रहे थे।
Question 8.
टीनू ने बहेलिए के चंगुल से बच निकलने के लिए कौन-सी योजना बनाई?
Answer:
टीनू ने बहेलिए के चंगुल से बच निकलने के लिए मीनू के एक, दो, तीन, चार कहने पर एक ही दिशा में एक साथ उड़ चलने की योजना बनाई।

व्याकरण और भाषाभ्यास
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के वचन बदलकर वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
Question 1.
थैलियाँ – थैली
Answer:
पॉलीथिन की थैली का प्रयोग नहीं करना चाहिए।
Question 2.
पंखा – पंखे
Answer:
गरमी के दिनों में सभी घरों में पंखे चलाए जाते हैं।
Question 3.
दीवार – दीवारें
Answer:
राजमहल में कई दीवारें होती हैं।
Question 4.
राजा – राजा
Answer:
हमारे भारत में कई वीर राजा हुए हैं।
Question 5.
वस्तुएँ – वस्तू
Answer:
मैने मोहन के हाथ में किमती वस्तू देखी।
Question 6.
भेड़िया – भेड़िए
Answer:
जंगल में कई भेड़िए देखने को मिलते हैं।
Question 7. बहू – बहुएँ
Answer:
मीना की सारी बहुएँ बहुत सुंदर हैं।
Question 8.
रोटी – रोटियाँ
Answer:
मैने भूखे कुत्ते को रोटियाँ खिलाई।
Question 9.
चिड़िया – चिड़ियाँ
Answer:
पेड़ पर चिड़ियाँ चहचहा रही थीं।
Question 10.
लता – लताएँ
Answer:
अंगूर की लताएँ बिखरने लगी हैं।

निम्नलिखित शब्दों के विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए।
- एक
- ठंडा
- रोना
- अच्छा
- मुक्त
- हार
- पास
- आरंभ
Answer:
- अनेक
- गरम
- हँसना
- बुरा
- कैद
- जीत
- दूर
- अंत

Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 3 दादी माँ का परिवार Additional Important Questions and Answers
कोष्ठक में से उचित शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए।
(छोटे-से, आँगन, दाना, एकता, कलरव, ग्यारह, सीख, ताकत)
Question 1.
नीलू …………. चुगने चली गई।
Answer:
दाना
Question 2.
दादी माँ एक ………….. घर में रहती थीं।
Answer:
छोटे-से
Question 3.
उन सब में गजब की ………. थी।
Answer:
एकता
Question 4.
एक और एक .होते हैं।
Answer:
ग्यारह
Question 5.
दादी माँ की ……….. रंग लाई।
Answer:
सीख
Question 6.
आँगन में अचानक …………. हुआ।
Answer:
कलरव
Question 7.
सुबह उठकर दादी ………..” बुहारती थीं।
Answer:
आँगन
Question 8.
हम सब एकता की ………” दिखाएँगे।
Answer:
ताकत

निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के एक वाक्य में उत्तर लिखिए।
Question 1.
दादी माँ कैसी थीं?
Answer:
दादी माँ समझदार व सयानी थीं।
Question 2.
घर के आँगन में कौन-सा पेड़ था?
Answer:
घर के आंगन में बरगद का पेड़ था।
Question 3.
नीलू चिड़िया के बच्चों के नाम क्या थे?
Answer:
नीलू चिड़िया के बच्चों के नाम टीनू और मीनू थे।
Question 4.
चिंकी चुहिया के बच्चों के नाम क्या थे?
Answer:
चिंकी चुहिया के बच्चों के नाम चुसकू-मुसकू थे।
Question 5.
नीलू बच्चों को अपने साथ कहाँ ले गई?
Answer:
नीलू बच्चों को अपने साथ दाना चुगने के लिए ले गई।
Question 6.
चिड़ियाँ कहाँ फँस गई?
Answer:
चिड़ियाँ बहेलिए के जाल में फंस गईं।
Question 7.
चिड़ियों ने अपने भीतर कौन-सी शक्ति भरी?
Answer:
चिड़ियों ने अपने भीतर एकता की शक्ति भरी।
Question 8.
दादी माँ ने किस गोली की बात बताई?
Answer:
दादी माँ ने एकता की गोली की बात बताई।
Question 9.
दादी माँ ने चिड़ियों को किससे याचना करने के लिए कहा?
Answer:
दादी माँ ने चिड़ियों को चिंकी से याचना करने के लिए कहा।
Question 10.
सभी ने एकसाथ मिलकर क्या कहा?
Answer:
सभी ने एकसाथ मिलकर यह कहा कि “अंत भला तो सब भला।”

किसने, किससे कहा?
Question 1.
“एकता पंछियों की ही नहीं, औरों में भी होनी चाहिए वही।”
Answer:
दादी माँ ने पंछियों से कहा।
Question 2.
“हम आजाद हो रहे हैं, अहा!”
Answer:
टीनू-मीनू ने मौसी से कहा।
Question 3.
“मेरे बच्चों, मत लड़ो। झगड़े-टंटों में मत पड़ो।”
Answer:
दादी माँ ने टीनू-मोनू और चुसकू-मुसकू से कहा।
Question 4.
“अरे! हम सब उलझ गए हैं।”
Answer:
मुनमुन ने सभी चिड़ियों से कहा।
Question 5.
“बहेलिए के जाल में फंस गए हैं।”
Answer:
नीलू ने सभी चिड़ियों से कहा।
Question 6.
“बस, इतने में ही डर गई?”
Answer:
टीनू ने सभी चिड़ियों से कहा।
Question 7.
“खैरियत तो है, क्या हुआ था काज?”
Answer:
दादी माँ ने नीलू से कहा।
Question 8.
“टीनू-मीनू हैं समझदार। तभी तो किया खबरदार।”
Answer:
दादी माँ ने पंछियों से कहा।

निमलिखित शब्दों के दो-दो पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
- सुबह
- दुनिया
- स्नेह
- होशियार
- चाह
- आँख
Answer:
- भोर, प्रात:
- संसार, जगत, विश्व
- प्रेम, प्यार
- चालाक, चतुर
- इच्छा, कामना, आकांक्षा
- नयन, नेत्र, चक्षु

निम्नलिखित शब्दों को सही स्थान पर रखकर अर्थपूर्ण शब्द बनाइए।
- चानका
- गऑन
- याटिख
- रककससि
- ईहादु
- ताकए
Answer:
- अचानक
- आँगन
- खटिया
- सिसककर
- दुहाई
- एकता

निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से सर्वनाम शब्द चुनकर लिखिए।
संज्ञा शब्द के बदले प्रयोग किए जानेवाले शब्दों को ‘सर्वनाम कहते हैं। सर्वनाम के मुख्य रूप से छ: भेद होते हैं।
पुरूषवाचक सर्वनाम: जिस सर्वनाम शब्द का प्रयोग व्यक्ति, वक्ता, श्रोता या किसी अन्य के लिए करता है, उसे ‘पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते हैं। जैसे – मैं, तुम, आप, वे इत्यादी।
निश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम : जिस सर्वनाम शब्द से किसी निश्चित व्यक्ति, वस्तु या स्थान का बोध होता हो, उसे ‘निश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते हैं। जैसे – यह, वह, ये, वे आदि।
अनिश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम: जिस सर्वनाम शब्द से किसी अनिश्चित व्यक्ति, वस्तु या स्थान का बोध होता हो, उसे ‘अनिश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते हैं। जैसे – कोई, कुछ, किसी आदि।
संबंधवाचक सर्वनाम : जो सर्वनाम शब्द वाक्य में आए दूसरे संज्ञा या सर्वनाम शब्द से संबंध बताए, उसे ‘संबंधवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते हैं। जैसे – जो-वह, जैसा-वैसा आदि। प्रश्नवाचक सर्वनाम : जिस सर्वनाम का प्रयोग प्रश्न पूछने के लिए किया जाता है, उसे ‘प्रश्नवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते –
जैसे – कौन, क्या, कहाँ आदि।
निजवाचक सर्वनाम: ऐसे सर्वनाम शब्द जो स्वयं के लिए प्रयोग में लाए जाते हैं, उन्हें निजवाचक सर्वनाम’ कहते हैं।
जैसे – स्वयं, खुद, अपने, आप आदि।
- वह दादी माँ की संगिया थी।
- वे सब खुश थे।
- उसने सबको बतलाया।
- हमें एकता से लड़ना चाहिए।
- उन्होंने मिलकर संकट का सामना किया।
Answer:
- वह
- वे
- उसने
- हमें
- उन्होंने

प्रस्तुत पाठ में आए लयात्मक शब्दों को ढूँढ़कर उनका वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
Question 1.
बुहारती – सँवारती
Answer:
मेरी माँ प्रतिदिन घर को बुारती-संवारती रहती है।
Question 2.
फुदकती – चिंचियाती
Answer:
मेरे घर के आँगन में हर दिन चिड़ियाँ फुदकती-चिंचियाती रहती है।
Question 3.
हँसते – खेलते
Answer:
छोटे बच्चे हमेशा हँसते-खेलते रहते हैं।
Question 4.
खाते – गाते
Answer:
मोहन हर पल खाते-गाते रहता है।
Question 5.
आनन- फानन
Answer:
त्योहारों की धूम में कुछ लोग आनन-फानन में नाचते हैं।
Question 6.
टीनू – मीनू
Answer:
टीनू-मीनू दोनों भी चालाक थे।
Question 7.
चुसकू – मुसकू
Answer:
चुसकू-मुसकू के दाँत बड़े तेज थे।

निम्नलिखित मुहावरों एवं कहावतों का अर्थ लिखकर वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
Question 1.
तुनककर बोलना – चिढ़कर बोलना।
Answer:
झगड़े में राजीव का नाम आते ही वह तुनककर बोलने लगा।
Question 2.
अक्ल का पत्ता खोलना – तरकीब बताना।
Answer:
बाढ़ के समय सुनिल ने अपनी अक्ल का पत्ता खोलकर सबकी जान बचाई।
Question 3.
ठगा-सा रहना – चकित होना, सुध-बुध खोकर देखना।
Answer:
उस छोटे बच्चे का करतब देखकर मैं ठगा-सा रह गया।
Question 4.
रंग लाना – मेहनत का फल मिलना।
Answer:
कक्षा में राम का प्रथम क्रमांक आया, आखिर उसकी मेहनत रंग लाई।
Question 5.
मन को बहलाना – प्रेमपूर्वक बातें करना।
Answer:
मेरी दादी माँ हर दिन हम बच्चों के मन को बहलाती हैं।
Question 6.
यत्न करना – बहुत प्रयास करना।
Answer:
कौरवों ने कई प्रकार का यत्न किया किंतु वे पांडवों के साथ युद्ध न जीत सकें।
Question 7.
एक और एक ग्यारह – एकता में बल।
Answer:
कंपनी के मालिक ने मजदूरों को एक-दूसरे से तोड़ने की बहुत कोशिश की किंतु वे बिलकुल डटे रहें, कहते हैं न एक और एक ग्यारह होते हैं।
Question 8.
अंत भला तो सब भला – परिणाम अच्छा तो सब अच्छा।
Answer:
महात्मा गांधी हमेशा सच्चाई की राह पर चलने की सीख देते थे क्योंकि उनका मानना था कि अंत भला तो सब भला।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions पहली इकाई

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()