Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions Chapter 2.6 Chasing the Sea Monster Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 English Lesson 2.6 Chasing the Sea Monster Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 English Chapter 2.6 Chasing the Sea Monster Textbook Questions and Answers
1. From the passage, find all the words and phrases used to describe the ‘monster’.
Question 1.
From the passage, find all the words and phrases used to describe the ‘monster’.
Answer:
Unearthly animal, fearsome creature, unknown creature, huge glowworm, infernal beast, motionless animal.
![]()
2. Form groups of 4. Find all the references to time given In the passage. Then make a chart to show the events described in the passage along with the time when they occur.
Example:
- All night long: The crew stayed on their feet
- Near midnight: …………………………………….
- At 12.53: …………………………………………….
- ………….. : …………………………………………….
- ………….. : …………………………………………….
- ………….. : …………………………………………….
(lise as many lines as you need.)
Question 1.
Form groups of 4. Find all the references to time given in the passage. Then make a chart to show the events described in the passage along with the time when they occur. Example:
Answer:
- All night long: The crew stayed on their feet.
- Near midnight: The sea animal disappeared.
- At 12.53: A deafening hiss was heard.
- Near 2.00 am: The core of a light appeared.
- At 6.00 am: The animals electric glow disappeared.
- At 7.00 am: A dense morning mist spread.
- At 8.00 am: The mist disappeared, the sea animal was seen.
- A few moments later: The frigate headed for the animal.
- Three-quarters of an hour later: They were not getting closer to the animal.
- Next one hour: The frigate gathered speed and so did the sea animal.
- At 10.50 pm: The electric light reappeared.
![]()
3. How long does the whole event described in this passage take? Work it out by reading the passage.
Question 1.
How long does the whole event described in this passage take? Work it out by reading the passage.
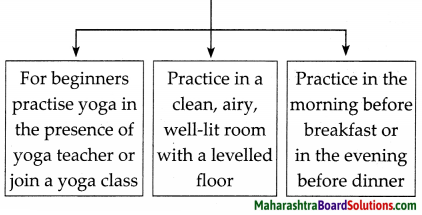
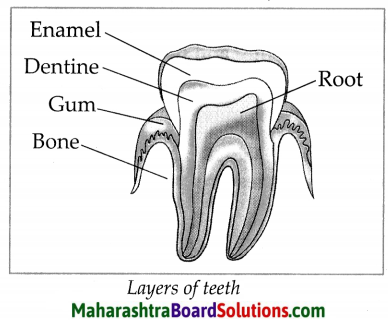
4. Observe the picture and the labels carefully. Then match the words and the meanings given in the foliwing table.
Question 1.
Observe the picture and the labels carefully. Then match the words and the meanings given in the foliwing table.
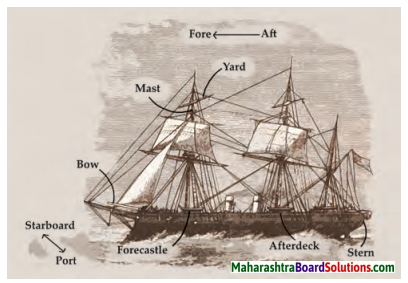
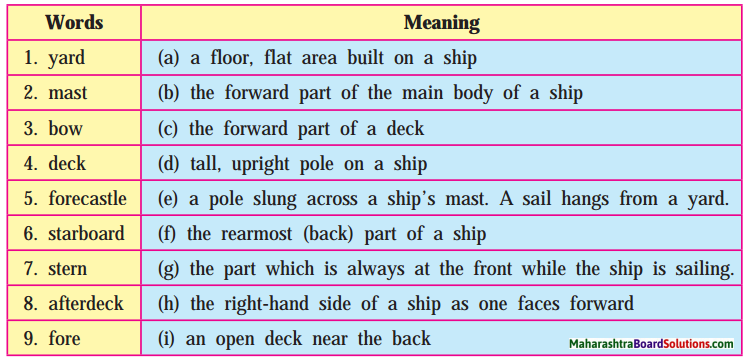
Answer:
| Words | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Yard | (e) A pole slung across a ship’s mast. A sail hangs from a yard |
| 2. Mast | (d) Tall, upright pole on a ship |
| 3. Bow | (b) The forward part of the main body of a ship |
| 4. Deck | (a) A floor, flat area built on a Ship |
| 5. Forecastle | (g) The part which is always at the front while the ship is sailing |
| 6. Starboard | (h) The right-hand side of a ship as one faces forward |
| 7. Stern | (f) The rearmost (back) part of a ship |
| 8. Afterdeck | (i) An open deck near the back |
| 9. Fore | (c) The forward part of a deck |
![]()
5. Form groups of 4-5. Read the following sentences aloud. Using your imagination and with the help of group discussion, write other situations in which the sentences can be used.
- The outcome: disappointment and anger.
- The hour of battle had sounded
- What a chase!
- This was our chance, ……..
Question 1.
Form groups of 4-5. Read the following sentences aloud. Using your imagination and with the help of group discussion, write other situations in which the sentences can be used.
Answer:
- The outcome: disappointment and anger
- The hour of battle had sounded
- What a chase!
- This was our chance
- The outcome: happiness and relief
- The outcome: fun and joy
- The outcome: misery and poverty
- The hour of decision had arrived
- The sound of victory was heard
- What a book!
- What a personality!
- What a movie!
- This was our victory …
- This was our last straw …
- This was our fight…
6. Find the different units of measurement mentioned in the passage and get more information about them from the internet.
Question 1.
Find the different units of measurement mentioned in the passage and get more information about them from the internet.
7. Language Study: Transitive and intransitive verbs : We can classify verbs into two types – transitive and intransitive. Some verbs need on object/objects. When a verb has an object, it is a transitive verb. For example, ‘The boy kicked the football’. Here the verb ‘kick’ has ‘the football’ as its object. ‘Give’, ‘cook’, ‘buy’ are transitive verb.
Some verbs do not need any objects. When a verb does not have an object, it is an intransitive verb. For example, ‘We laughed loudly’. The verb ‘laugh’ in this sentence does not have an object. ‘Laugh’, ‘walk’, ‘dy’ are intransitive verbs.
Some verbs can be transitive or intransitive. For example,
‘Birds fly’. (intransitive) ‘Children fly kites’. (transitive)
Class 7 English Chapter 2.6 Chasing the Sea Monster Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Guess what order the commander must have given.
Answer:
The order given by the commander must have been to advance slowly towards the monster and to be ready to attack.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did the Abraham Lincoln slow down? Answer: The Abraham Lincoln slowed down because
it was
unable to compete with the monster’s speed.
Question 3.
What is the monster compared to when it disappeared?
Answer:
The monster is compared to a huge glow-worm when it disappeared.
Question 4.
What did the deafening hiss resemble?
Answer:
The deafening hiss resembled the sound made by a water spout expelled with tremendous intensity.
Question 5.
Who would get $ 500?
Answer:
The man who would pierce the infernal beast would get $ 500.
![]()
Question 6.
Describe the gunner who accepted the challenge.
Answer:
The gunner who accepted the challenge was a calm, cool, old and gray bearded man.
Question 7.
What was Ned Land doing?
Answer:
Ned Land was brandishing his dreadful weapon.
Reading Skills, Vocabulary and Grammar
Simple Factual Questions:
Fill in the blanks.
Question i.
Let’s wait for daylight and then we’ll play a …………… role.
Answer:
different
Question ii.
Unable to compete with the monster’s speed, our frigate, the ………………. slowed down.
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
What is the name of the narrator?
Answer:
The name of the narrator is Professor Aronnax.
Question 2.
What is the name of the ship?
Answer:
The name of the ship is ‘Abraham Lincoln’.
![]()
Question 3.
At what time is this event taking place?
Answer:
This event is taking place sometime near midnight.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Give two words as phrases used to describe ‘monster’ in this passage.
Answer:
fear some creature, cetacean
Grammar:
Question 1.
The animal mimicked the frigate. (End with ’… the animal’)
Answer:
The frigate was mimicked by the animal.
Question 2.
No one thought of sleeping. (Make it affirmative)
Answer:
Everyone remained awake.
Question 3.
The animal mimicked the frigate. (Change into interrogative)
Answer:
Didn’t the animal mimic the frigate?
![]()
Question 4.
Pick out the verb and state whether it is transitive or intransitive.
- Rama rang the bell loudly.
- The bell rang loudly.
- The baby sleeps on a bed.
- The birds fly in the air.
- Close the door.
- He wrote a letter to his friend.
Answer:
- rang – transitive verb
- rang – intransitive verb
- sleeps – intransitive verb
- fly – intransitive verb
- dose – transitive verb
- wrote – transitive verb
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
Write whether True or False.
Question i.
We stayed on the alert until night and were getting ready for action.
Answer:
False
Question ii.
The mist was very dense.
Answer:
True.
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
What can the blunderbusses do?
Answer:
The blunderbusses can launch harpoons as far as a mile.
![]()
Grammar:
Question 1.
Ned had a dreadful weapon. (Add a question tag)
Answer:
Ned had a dreadful weapon, didn’t he?
Question 2.
Pick out two abstract nouns from the extract.
Answer:
Disappointment, anger.
Personal Response:
Question 1.
Do you like travelling on sea? Why?
Answer:
No, I do not like travelling on sea. I don’t know how to swim and I am very scared of drowning.
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Fill in the blanks.
Question i.
………… stayed at his post, harpoon in hand.
Answer:
Ned Land
![]()
Question ii.
The animal is faster than the ………….. .
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Explain why the author uses the words “what a chase!”.
Answer:
It was an exciting chase no doubt. The author says that the excitement shook his very being. The animal was so smart, it let the frigate get a little closer to it and then picked up speed and kept its distance. The animal was playing tricks with the frigate.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Pick out the words from the extract that mean the following.
i. person who fires the cannon
ii. moved faster
Answer:
i. cannoneer
ii. gathered speed
![]()
Question 2.
Give the meanings of the following.
i. harpooner
ii. mate
Answer:
i. person who handles the harpoon
ii. assistant
Grammar:
Question 1.
what a chase no i can’t describe the excitement that shook my very being (Punctuate)
Answer:
What a chase! No, It can’t describe the excitement that shook my very being.
Question 2.
The cannoneer fired a shot. (Add a question tag)
Answer:
The cannoneer fired a shot, didn’t he?
Language Study
Do as directed.
Question 1.
There was a mighty explosion. (Pick out the verb and state its kind)
Answer:
was – transitive verb.
![]()
Question 2.
The monster seemed motionless. (Frame a ’Wh1 question so as to get the underlined words as the answer)
Answer:
Who seemed motionless?
Question 3.
Barely twenty feet separated him from the motionless animal. (Pick out the adjectives from the sentence)
Answer:
Twenty, motionless
Question 4.
The electric light suddenly went out. (Identify the part of speech of the underlined word)
Answer:
Suddenly – adverb
Question 5.
Pick out the verb and state whether it is transitive or intransitive.
Question i.
The hunter killed the wolf.
Answer:
killed – transitive verb
![]()
Question ii.
Leena saw a monster.
Answer:
saw – transitive verb
Question iii.
Rains spoilt the picnic.
Answer:
spoilt – transitive verb
Question iv.
The baby cried loudly.
Answer:
cried – intransitive verb
Question v.
The bird flew away.
Answer:
flew – intransitive verb
![]()
Writing Skills
Question 1.
Write an essay on ‘A Sea Journey’.
Answer:
A sea journey is something I had never experienced. I used to look at the majestic sea and wonder what it would be like to travel by sea. I got the chance of a life time to travel on a ship.
The ship was filled with people from different states of India. At the beginning all was wonderful, the people, the sea, the sky, the weather. I was told that the journey would take many on board. But as time passed, the journey which I felt would be a pleasant one, wasn’t all that pleasant. There was nothing to see except water, water and more water. The movement of the ship on the water gave me a nauseating/nauseous feeling.
I was praying and hoping for the journey to end. At last after about eight long hours we touched land. I was so happy to be on firm landing once again. The journey by sea was an experience I wouldn’t want to repeat. This journey by sea was my first and last one.
Chasing the Sea Monster Summary in English
The lesson ‘Chasing the Sea Monster’ is an extract from the novel ‘20,000 Leagues under the Sea’ written by Jules Verne. The story in this extract is about spotting a mysterious sea monster by the inmates on a warship. The story revolves round the relentless chase between the warship (frigate) and the sea monster.
The warship (frigate) named Abraham Lincoln captained by Commander Farragut along with Professor Pierre Aronnax, a French marine biologist and narrator of the story, a master harpoonist Ned Land and other crew members chase the sea monster and in the end Ned Land succeeds in hitting the sea monster. The collision between the frigate and the sea monster is so hideous that Commander Farragut, Professor Pierre Aronnax and Ned Land are hurled into the sea.
Introduction:
The lesson ‘Chasing The Sea Monster7 is a science fiction written by Jules Verne, a French writer. He is known as the ‘Father of Science Fiction’. This is a passage, from his novel ‘20,000 Leagues under the Sea’. He describes how people on a ship think of the submarine as an animal and try to chase and hunt it.
![]()
Glossary:
- frigate (n) – small, speedy ship used in war
- unearthly (adj) – strange, not like those found on earth
- luminous (adj) – bright, full of light
- fearsome (adj) – scary, frightening
- crew (n) – people working on the ship
- cetaceans (n) – marine animals like a whale
- lurking (v) – hiding
- whaling gear (n) – equipment used to hunt whales
- mate (n) – assistant
- armour (n) – protective metal covering
- profound (adj) – deep
- astern to port (v) – towards the hinder part or stem; backward
- blunderbusses (n) – a short, large bored gun firing metal balls, slugs or nails
- duck guns (n) – large shot guns used for hunting ducks in large number
- harpoon (n) – a barbed spear attached to a rope and thrown or fired from a gun to hunt whales or large fish
- cannoneer (n) – an artillery man who uses cannon
- harpooner (n) – a person who uses harpoons especially to hunt whales
- enormous (adj) – huge
- hideous (adj) – dreadful, horrid
- mute (adj) – dumb; not having the power of speech
- alert (adj) – attentive
- informed (adj) – having information, based on information.
- target (n) – a person, object or place selected as the aim of attack
- weariness (n)- tiredness
- brandishing (v) – to move or swing back and forth particularly demonstrating skill
- collision (n)- clash
7th Std English Questions And Answers:
- From a Railway Carriage Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- The Souvenir Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- Abdul Becomes a Courtier Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- How Doth the Little Busy Bee Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- Learn Yoga from Animals Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- Chasing the Sea Monster Class 7 English Questions And Answers
- Great Scientists Class 7 English Questions And Answers










 Answer:
Answer: