Class 7 Hindi Chapter 6 Prithvi Se Agni Tak Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 6 ‘पृथ्वी’ से ‘अग्नि’ तक Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Hindi Chapter 6 Prithvi Se Agni Tak Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 6 ‘पृथ्वी’ से ‘अग्नि’ तक Textbook Questions and Answers
स्वयं अध्ययन:
किसी महान विभूति क्रम जीवनक्रम वर्षानुसार बनाकर लाओ और पड़ो। जैसे: जन्म, शालेय शिक्षा आदि।
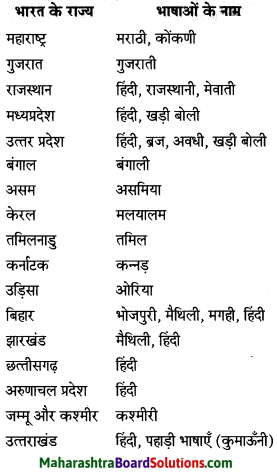
अंतरजाल के माध्यम से भारतीय वैज्ञानिकों और उनके कार्यों की सूची बनवाएँ।
डॉ. ए. पी. जे अब्दुल कलाम की जीवनी पढ़ने के लिए प्रेरित करें।
खोजबीन:
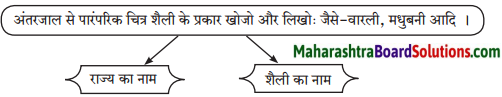
अंतरजाल से पद्मभूषण से विभूषित विभूतियों की जानकारी का संकलन करके सुनाओ।
सुनो तो जरा:
विज्ञान प्रदर्शनी के लिए बनाए गए उपकरण बनाने की विधि एवं उपयोग सुनो और सुनाओ।

जरा सोचो….. चर्चा करो:
“यदि मैं अंतरिक्ष यात्री बन जाऊँ तो…” विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए। (कल्पनात्मक-लेखन)
Answer:
मेरे जीवन का एक सबसे बड़ा सपना है कि मैं एक अंतरिक्ष यात्री बने। अगर मैं अंतरिक्ष यात्री बन गया, तो मुझे स्वयं पर गर्व महसूस होगा क्योंकि यह मेरे जीवन का सबसे बड़ा लक्ष्य है। मैं भी आसमान में पक्षियों की भाँति उड़ जाऊँगा। ऊपर से हमारी सुंदर पृथ्वी का नजारा देखूगा। कई ग्रह, तारे, धूमकेतु इनका बारीकी से अवलोकन व अध्ययन करूँगा। कई प्रकार की नई बातें देश व देशवासियों के लिए खोज लाऊँगा। चंद्रमा के बारे में इसके पहले लोगों ने जो कथन किए हैं। मैं उनका प्रत्यक्ष अनुभव प्राप्त करूंगा। अपने यान से पृथ्वी, सूर्य, चंद्रमा और अन्य दूसरे दुर्लभ ग्रहों के चित्र संशोधन के लिए लूंगा। अपने अवलोकन व संशोधन से कई प्रकार का महत्त्वपूर्ण ज्ञान मैं देशवासियों और विश्व के लिए ले आऊँगा। मैं कुछ इस प्रकार के कारनामें करूँगा, जिससे विश्व में अपने देश का नाम ऊँचा हो। मैं सदैव एक सफल अंतरिक्ष यात्री बनकर लौटना चाहूँगा।
विचार मंथन:
“हम विज्ञान लोक के वासी’ विषय पर अपने विचार लिखिए। (विचारात्मक-लेखन)
Answer:
आज का युग विज्ञान का युग है। आज का कोई भी क्षेत्र विज्ञान से अछूता नहीं है। प्राचीन काल से असंभव समझे जानेवाले सभी कार्यों को विज्ञान ने संभव करके दिखाया है। छोटी सुई से लेकर आकाश की दूरी नापने वाले हवाई जहाज व रॉकेट इस विज्ञान की ही देन हैं। हम अपने प्रतिदिन के जीवन में विज्ञान निर्मित वस्तुओं का ही प्रयोग करते हैं। विद्युत की निर्मिती, कल-कारखाने, अंतरिक्ष की खोज, जीवन में बदलाव, आधुनिक खेती की सामग्री पूरा जीवन विज्ञान निर्मित वस्तुओं से घिरा हुआ है।
प्राचीन काल से हम कहते व सुनते आ रहे हैं कि मनुष्य “धरती का वासी है’, परंतु विज्ञान के इन चमत्कारों और मनुष्य द्वारा विज्ञान निर्मित वस्तुओं के उपयोग किए जाने पर हम अगर कहें कि ‘हम विज्ञान लोक के वासी’ हैं, तो यह गलत न होगा। विज्ञान ही है जिसने धरती के प्रत्येक असंभव कार्य को संभव करके दिखाया है। किंतु आज के इस आधुनिक युग में हमें इस बात का जरूर ध्यान रखना चाहिए कि विज्ञान से मनुष्य को कई हानियाँ भी हो रही हैं। इन सब बातों को ध्यान में रखते हुए हमें विज्ञान की तरक्की का उपयोग मानव जाति के भले के लिए ही करना चाहिए। तभी हम असल में ‘विज्ञान लोक के वासी’ कहलाएंगे।

मेरी कलम से:
निम्नलिखित संकेत बिंदुओं के आधार पर कहानी लिखिए। (कहानी-लेखन)

Answer:
शीर्षक बेगुसराय नाम का एक राज्य था। उस राज्य में विभूति नारायण नामक राजा राज्य करते थे। राजा बड़े ही कर्मठ, परोपकारी व न्यायी थे। उन्हें अपने दरबार के लिए एक ऐसे राजमंत्री की तलाश थी, जो परोपकारी व निस्वार्थी हो। एक दिन रामपुर नामक गाँव में एक मेला लगा। मेला देखने के लिए लोगों की भीड़ उमड़ पड़ी। राजा विभूतिनारायण ने अपने सैनिकों को बताया कि आज हम अपने राज्य के लिए राजमंत्री की खोज करेंगे। वे अपने सेवकों को सड़क के प्रवेशद्वार पर एक बड़ा-सा पत्थर रखवाने के लिए कहते हैं तथा वेश बदलकर स्वयं वहाँ खड़े हो जाते हैं। कई लोग उस रास्ते से जाते हैं। उस पत्थर से टकराते हैं, गिरते हैं, किंतु किसी ने भी उस पत्थर को उठाकर रास्ते से दूर नहीं किया। अजय नाम का एक लड़का बहुत रही थी।
कुछ देर बाद उससे न रहा गया। वह स्वयं उस बड़े भारी पत्थर के पास गया और पत्थर को ढंकेलकर रास्ते के किनारे से सरकाकर हटा दिया। राजा की नज़र इस लड़के पर पड़ी। राजा खुशी से प्रसन्न हो उठे। पर वे कुछ देर देखते रहे। अजय को उस पत्थर के नीचे एक चिट्ठी मिली। उसमें लिखा था “आज से तुम इस राज्य के राजमंत्री हो।” इतने में राजा विभूतिनारायण उसके समीप आए और उससे कहा कि “मैं तुम्हारी परोपकारी भावना व निस्वार्थ सेवा बृत्ति से प्रसन्न हूँ। आज से मैं तुम्हें इस राज्य का राजमंत्री घोषित करता हूँ।” अजय के लिए यही सबसे बड़ा पुरस्कार था। राजा ने अपनी ओर से हजार सुवर्ण मुद्राएँ देकर उसे सम्मानित किया और अपने दरबार में राजमंत्री का पद प्रदान किया।
सीख – इस कहानी से हमें यह सीख मिलती है कि हमें किसी भी कार्य को छोटा या बड़ा नहीं समझना चाहिए बल्कि परोपकारी भावना से प्रत्येक सामाजिक कार्य को हमें करना चाहिए। जो समाज व जनता के हित में हों।
शीर्षक – “जनसेवा ही सच्ची ईश्वर सेवा है।” अथवा
“कर भला तो हो भला।”

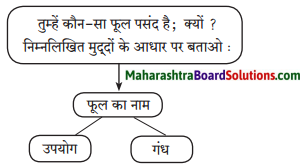
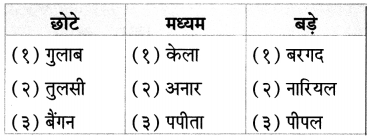
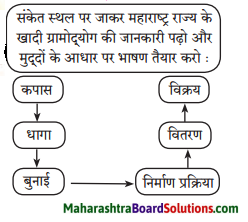
बताओ तो सही

वाचन जगत से :
गणतंत्र दिवस पर सम्मनित बच्चों के बहादुरी के प्रसंग पढ़ो और पसंदीदा किसी एक का वर्णन करो।
अध्ययन कौशल:
अपना दैनिक नियोजन बताओ तथा उसपर अमल करो।
सदैव ध्यान में रखो:
दैनिक जीवन में विज्ञान का उपयोग करना श्रेयस्कर होता है।
सही विकल्प चुनकर वाक्य फिर से लिखो:
(श्रीहरिकोटा, सेकंड्स, वैज्ञानिक, स्थगित, रॉकेट, चक्रवात, शोर, महानतम)
Question 1.
‘अग्नि’ टीम में पाँच सौ से अधिक …………” थे।
Answer:
अग्नि’ टीम में पाँच सौ से अधिक वैज्ञानिक थे।
Question 2.
‘पृथ्वी’ प्रक्षेपण के लिए ………….” अंतरिक्ष केंद्र में विशेष सुविधाएँ स्थापित की।
Answer:
‘पृथ्वी’ प्रक्षेपण के लिए श्रीहरिकोटा अंतरिक्ष केंद्र में विशेष सुविधाएँ स्थापित की।
Question 3.
यह मेरे जीवन के ………. क्षणों में से एक था।
Answer:
यह मेरे जीवन के महानतम क्षणों में से एक था।

Question 4.
सिर्फ छह सौ ………की भव्य उड़ान ने हमारी सारी
Answer:
सिर्फ छह सौ सेकंड्स की भव्य उड़ान ने हमारी सारी
Question 5.
थकान को एक पल में धो डाला। हमें प्रक्षेपण ……….करना पड़ा।
Answer:
थकान को एक पल में धो डाला। हमें प्रक्षेपण स्थगित करना पड़ा।
Question 6.
एक ………. का खतरा मँडरा रहा था।
Answer:
एक चक्रवात का खतरा मँडरा रहा था।
Question 7.
……… विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में इस तरह की चीजें बहुत आम
Answer:
रॉकेट विज्ञान के क्षेत्र में इस तरह की चीजें बहुत आम
Question 8.
ज्वार के कारण लहरें किनारों से टकराकर और अधिक ………….. मचा रही थीं।
Answer:
ज्वार के कारण लहरें किनारों से टकराकर और अधिक शोर मचा रही थीं।

तीन-चार वाक्यों में उत्तर लिखो:
Question 1.
भारत को चुनिंदा राष्ट्रों के समूह में किसने पहुँचा दिया?
Answer:
भारत को सामर्थ्यशील नागरिक अंतरिक्ष उद्योग और व्यवहार्य मिसाइल आधारित सुरक्षा प्रणालियों ने चुनिंदा राष्ट्रों के समूह में पहुंचा दिया।
Question 2.
टीम के साथ डॉ. कलाम ने कौन-सा अनुभव बाँटा?
Answer:
अपनी टीम के साथ डॉ. कलाम ने यह अनुभव बाँटा कि मेरा प्रक्षेपणयान तो गिरकर समुद्र में खो गया था, लेकिन उसकी वापसी सफलता के साथ हुई। आपकी मिसाइल तो अभी तक आपके सामने है। वास्तव में आपने कुछ भी ऐसा नहीं खोया है, जिसे एक-दो हफ्तों के काम से सुधारा न जा सके।
Question 3.
‘अग्नि’ का प्रक्षेपण पहले स्थगित क्यों करना पड़ा?
Answer:
कंप्यूटर द्वारा उपकरण ठीक ढंग से काम न करने के निर्देश तथा निचली रेंज केंद्र द्वारा ‘होल्ड’ करने के संकेत प्राप्त होने के कारण ‘अग्नि’ का प्रक्षेपण पहले स्थगित करना पड़ा।
Question 4.
रक्षामंत्री ने डॉ. कलाम जी से कब और क्या पूछा था?
Answer:
रक्षामंत्री महोदय ने डॉ. कलाम से ‘अग्नि’ के प्रक्षेपण करने की पहली रात पूछा, “अग्नि की कामयाबी का जश्न मनाने के लिए तुम मुझसे क्या उपहार चाहोगे?”

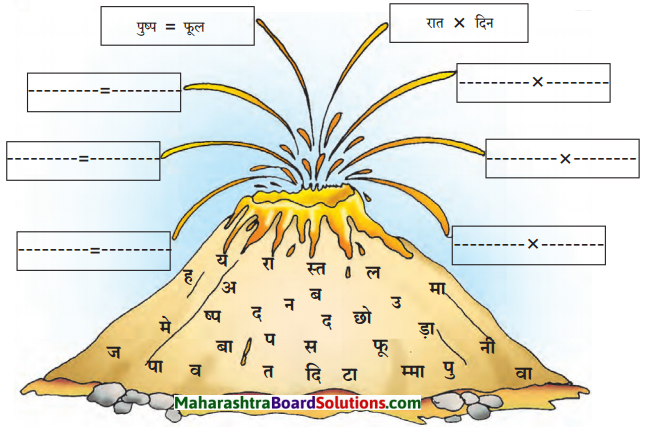
भाषा की ओर:
दाएँ पंख में उपसर्ग तथा बाएँ पंख में प्रत्यय लगाकर शब्द लिखो तथा उनके वाक्य बनाओ।

निम्नलिखित शब्दों में उपसर्ग व प्रत्यय लगाकर नए शब्द का निर्माण कीजिए तथा उनका वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
उपसर्ग (pefix): वे शब्दांश जो किसी शब्द के आगे लगकर उसके अर्थ में परिवर्तन लाते हैं तथा नया शब्द बनाते हैं उन्हें ‘उपसर्ग’ कहते है। जैसे – धन + वान = धनवान, मानव + ता = मानवता आदि।
प्रत्यय: वे शब्दांश जो किसी शब्द के पीछे जुड़कर उसके अर्थ को विशिष्ट बनाते हैं, उसे प्रत्यय (suffix) कहा जाता है।
जैसे = आवश्यक + ता = आवश्यकता
(१) दिन
उपसर्ग – प्रतिदिन प्रत्यय – दिनभर
Answer:
मैं प्रतिदिन खेलता हूँ।
दिनभर नहीं खेलना चाहिए।
(२) नम्र
उपसर्ग – विनम्र प्रत्यय – नम्रता
Answer:
सुनिल विनम्र लड़का है।
हमें सभी के साथ नम्रता से व्यवहार करना चाहिए।
(३) डर
उपसर्ग – निडर प्रत्यय – डरपोक
Answer:
मेरे पिताजी बड़े निडर है।
मोहन बड़ा डरपोक है।

(४) जल
उपसर्ग – निर्जल प्रत्यय – जलमय
Answer:
मेरी माँ निर्जल व्रत करती है।
पूरा तालाब जलमय है।
(५) साहस
उपसर्ग – दु:साहस प्रत्यय – साहसिक
उत्तरः
रावण के सभी कार्य दु:साहस से भरे थे।
राजन ने बड़ा साहसिक कार्य किया।
(६) सत्य
उपसर्ग – असत्य प्रत्यय – सत्यवादी
उत्तर :
गांधी जी कभी असत्य नहीं बोलते थे।
राजा हरिश्चंद्र बड़े सत्यवादी थे।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions Chapter 6 ‘पृथ्वी’ से ‘अग्नि’ तक Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक वाक्य में लिखिए।
Question 1.
देश के रॉकेट विज्ञान के इतिहास में कौन-सी युगांतरकारी घटना हुई।
Answer:
‘पृथ्वी’ उपग्रह को अंतरिक्ष में छोड़ना देश के रॉकेट विज्ञान के इतिहास में युगांतरकारी घटना हुई।
Question 2.
‘अग्नि’ टीम में कुल कितने वैज्ञानिक काम करते थे?
Answer:
‘अग्नि’ टीम में कुल पाँच सौ वैज्ञानिक काम करते थे।
Question 3.
डॉ. कलाम ने अपने टीम के सदस्यों को किस हालत में पाया?
Answer:
डॉ. कलाम ने अपने टीम के सदस्यों को सदमे और शोक की हालत में पाया।

Question 4.
प्रक्षेपणयान कहाँ खो गया था?
Answer:
प्रक्षेपणयान समुद्र में गिरकर कहीं खो गया था।
Question 5.
डॉ. कलाम व उनकी टीम को कौन-सा महान अवसर दिया गया था?
Answer:
डॉ. कलाम व उनकी टीम को ‘अग्नि’ जैसी प्रणाली विकसित करने का अवसर दिया गया था।
Question 6.
अंत में प्रक्षेपण कब निर्धारित किया गया?
Answer:
अंत में प्रक्षेपण बाईस मई उन्नीस सौ नवासी (२२ मई, १९८९) को निर्धारित किया गया।
Question 7.
रक्षामंत्री ने डॉ. कलाम से क्या पूछा?
Answer:
रक्षामंत्री ने डॉ. कलाम से यह पूछा कि “कलाम! कल ‘अग्नि’ की कामयाबी का जश्न मनाने के लिए तुम मुझसे क्या उपहार चाहोगे?”
Question 8.
डॉ. कलाम ने अपने उपहार के बदले में किस चीज़ की माँग की?
Answer:
डॉ. कलाम ने अपने उपहार के बदले में आर.सी.आई. में लगाने के लिए एक लाख पौधों की मांग की।
Question 9.
अगले दिन कितने बजे ‘अग्नि’ मिसाइल प्रज्वलित हो उठी?
Answer:
अगले दिन सुबह सात बजकर दस मिनट पर ‘अग्नि’ मिसाइल प्रज्वलित हो उठी।
Question 10.
डॉ. कलाम और उनके सदस्यों की थकान को किसने धो डाला?
Answer:
डॉ. कलाम और उनके सदस्यों की थकान को ‘अग्नि’ की सिर्फ छह सौ सेकंड्स की भव्य उड़ान ने धो डाला।

निम्नलिखित वाक्य सही है या गलत लिखिए।
Question 1.
डॉ. कलाम ने रक्षामंत्री से दस लाख रूपये की मांग की।
Answer:
गलत
Question 2.
‘अग्नि’ की उड़ान के लिए छह सौ सेकंड्स का समय लगा।
Answer:
सही
Question 3.
‘पृथ्वी’ उपग्रह २९ फरवरी १९२७ को छोड़ा गया।
Answer:
गलत
Question 4.
‘अग्नि’ का प्रक्षेपण ठीक ढंग से न होने पर डॉ. कलाम जी के टीम के सदस्य बहुत खुश हुए।
Answer:
गलत
Question 5.
समस्याओं को हमें हराने का मौका उन्हें नहीं देना चाहिए।
Answer:
सही
Question 6.
ज्वार के कारण लहरें शोर मचा रही थीं।
Answer:
सही
Question 7.
‘अग्नि’ की सफल उड़ान डॉ. कलाम के जीवन का एक महान क्षण था।
Answer:
सही
Question 8.
श्री हरिकोटा हमारे देश का एक प्रसिद्ध अंतरिक्ष केंद्र है।
Answer:
सही
डॉ. कलाम ने आर.डी.एल – आर.सी.आई परिवार के सदस्यों को संबोधित करते हुए क्या कहा?
Answer:
डॉ. कलाम ने आर.डी.एल व आर.सी.आई परिवार के सदस्यों को संबोधित करते हुए यह कहा कि स्वाभाविक रूप से बड़े अवसर अपने साथ बराबर की चुनौतियाँ लेकर आते हैं। हमें हिम्मत नहीं हारनी चाहिए, समस्याओं को हमें हराने का मौका नहीं देना चाहिए।

निम्नलिखित शब्दों का वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए।
Question 1.
उपग्रह
Answer:
हमारे देश ने आज तक कई उपग्रह अंतरिक्ष में भेजे हैं।
Question 2.
आत्मनिर्भर
Answer:
मनुष्य को हमेशा आत्मनिर्भर बनने का प्रयास करना चाहिए।
Question 3.
सदमा
Answer:
पिता के मृत्यु की खबर सुनकर मोहन को बड़ा सदमा पहुंचा।
Question 4.
हिम्मत
Answer:
मुसीबत के समय हमें अपनी हिम्मत नहीं हारनी चाहिए।
Question 5.
पूर्णिमा
Answer:
पूर्णिमा के दिन चाँद पूरा होता है।
Question 6.
प्रज्वलित
Answer:
साहित्यिक कार्यक्रम के पहले अतिथियों के हाथों से दीप प्रज्वलित किया गया।
Question 7.
नतीजा
Answer:
संजय की मेहनत का उसे शानदार नतीजा प्राप्त हुआ।

व्याकरण और भाषाभ्यास
निम्नलिखित शब्दों का विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
- एक
- कम
- देश
- भीतर
- विशाल
- दिन
- सफलता
- पूर्णिमा
Answer:
- अनेक
- ज्यादा
- विदेश
- बाहर
- लघु
- रात
- असफलता
- अमावस्या

निम्नलिखित संज्ञा शब्दों से विशेषण शब्दों की रचना कीजिए।
- विज्ञान
- इतिहास
- संसार
- व्यवहार
- दिन
- जोश
- राष्ट्र
- स्वभाव
- भारत
Answer:
- वैज्ञानिक
- ऐतिहासिक
- सांसारिक
- व्यावहारिक
- दैनिक
- जोशीला
- राष्ट्रीय
- स्वाभाविक
- भारतीय

निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समान अर्थवाले शब्द लिखिए।
- समुद्र
- रात
- अवधि
- विज्ञान
- अवसर
- अग्नि
- मौसम
- सवाल
- नींद
Answer:
- सागर
- निशा
- समय
- शास्त्र
- मौका
- आग
- ऋतु
- प्रश्न
- निद्रा

निम्नलिखित शब्दों का शुद्ध रूप लिखिए।
- पृथवी
- स्वदयेशी
- सनगठन
- सुरकक्षा
- समुदर
- परीवार
- समबोधन
- परिक्षा
Answer:
- पृथ्वी
- स्वदेशी
- संगठन
- सुरक्षा
- समुद्र
- परिवार
- संबोधन
- परीक्षा

पाठ में आए दस अनुस्वार व अनुनासिक शब्दों को ढूंढकर लिखिए।
Answer:
अनुस्वार – अंतरिम, संगठन, अंतरिक्ष, तुरंत, सेकंडों, केंद्र, संस्थान, लोगों, संचार, दिमागों, सुंदर, लंबी, रक्षामंत्री, श्रृंखला, सेकंड्स, क्षणों। अनुनासिक – पाँच, यहाँ, बाधाएँ, मैंडरा, आँकड़े, बाँटा, जाँच, चुनौतियाँ, बनाएँ, सुविधाएँ, दाँव, गतिविधियाँ।।
पाठ में आए सर्वनाम शब्दों को पहचानकर उनका भेद लिखिए तथा अपने वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए।
Question 1.
मेरा (पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम) (उत्तम पुरुष)
Answer:
मेरा प्रक्षेपणयान तो समुद्र में गिरकर कहीं खो गया था।
Question 2.
यह (निश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम)
Answer:
यह देश के रॉकेट विज्ञान के इतिहास में युगातरकारी घटना थी।
Question 3.
कुछ (अनिश्चयवाचक सर्वनाम)
Answer:
आने वाले कुछ पलों में जगह-जगह रूकने की जरूरत पड़ी।
क्या (प्रश्नवाचक)
Answer:
रक्षामंत्री ने कलाम से कहा, “तुम मुझसे क्या उपहार चाहोगे?”

Question 5.
जिस – उसी (संबंधवाचक सर्वनाम)
Answer:
जिस समय हम टी-१४ सेकंड पर थे, उसी समय कंप्यूटर ने संकेत दिया।
Question 6.
कोई (अनिश्चवाचक सर्वनाम)
Answer:
हमें संकेत मिला कि उपकरणों में से कोई एक ठीक काम नहीं कर रहा है।
Question 7.
हम (पुरुषवाचक सर्वनाम) (उत्तम पुरुष)
Answer:
हम पाँच साल की कड़ी मेहनत के बाद सफल हुए।
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 7 Solutions पहली इकाई
![]()

![]()

![]()