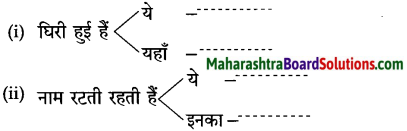
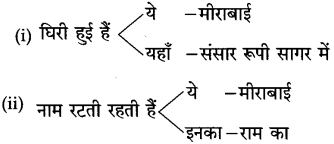
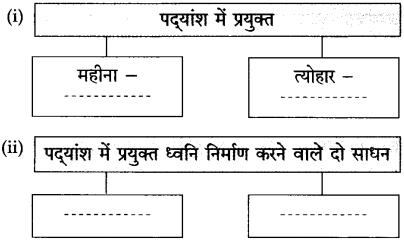
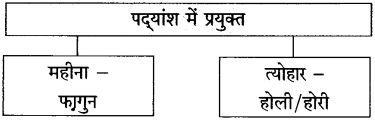
Std 10 Hindi Chapter 3 Shram Sadhana Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Hindi Solutions Lokbharti Chapter 3 श्रम साधना Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Digest Chapter 3 श्रम साधना Questions And Answers
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Std Digest Chapter 3 श्रम साधना Textbook Questions and Answers
कृति
(कृतिपत्रिका के प्रश्न 1 (अ) तथा प्रश्न 1 (आ) के लिए
*सूचना के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
प्रश्न 1.
उत्तर लिखिए:
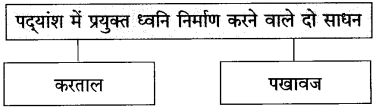
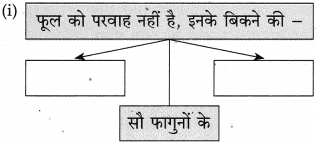
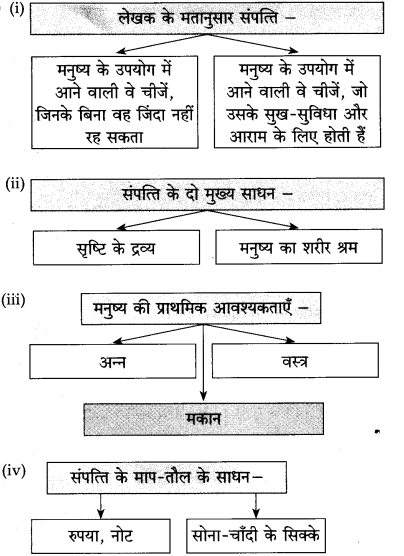
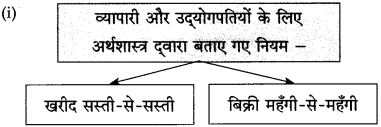
१. व्यापारी और उद्योगपतियों के लिए अर्थशास्त्र द्वारा बनाए गए नये नियम –
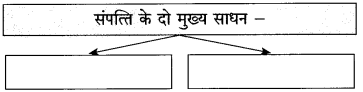
२. संपत्ति के दो मुख्य साधन –
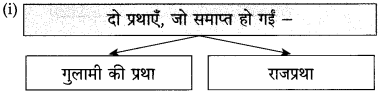
३. समाप्त हुईं दो प्रथाएँ –
४. कल्याणकारी राज्य का अर्थ –
उत्तर:
कल्याणकारी राज्य का अर्थ – सब तरह के दुर्बलों को राजसत्ता द्वारा मदद दिया जाना।
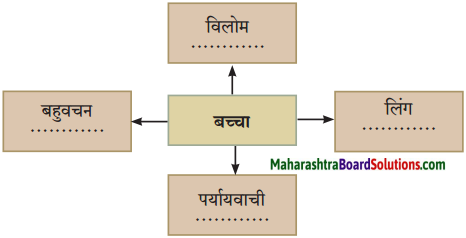
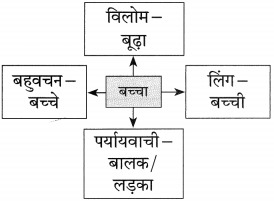
प्रश्न 2.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए:

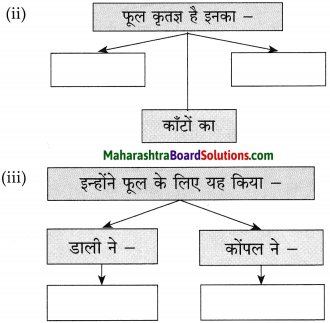
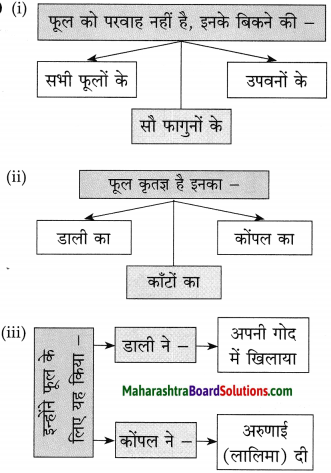
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 3.
तुलना कीजिए:
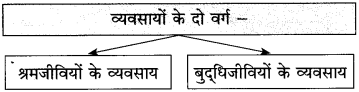
बुद्धिजीवी – श्रमजीवी
1. …………………. 2. ………………….
1. …………………. 2. ………………….
उत्तर:
बुद्धिजीवी – श्रमजीवी
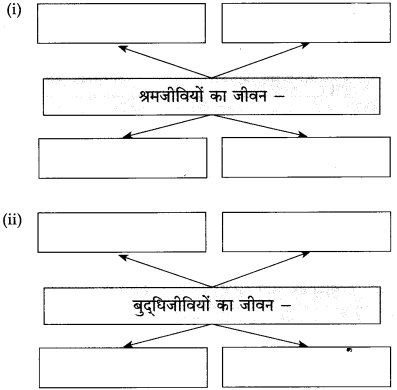
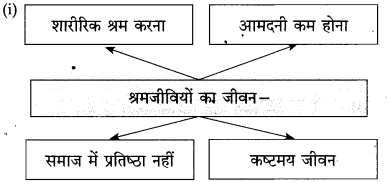
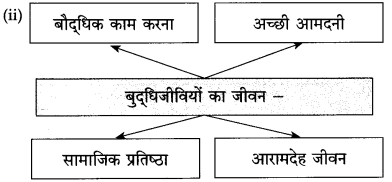
1. बौद्धिक काम करना। -1. शारीरिक श्रम करना।
2. अधिक आमदनी, प्रतिष्ठित एवं सुखमय जीवन। – 2. आमदनी कम, प्रतिष्ठा नहीं, कष्टमय जीवन।

प्रश्न 4.
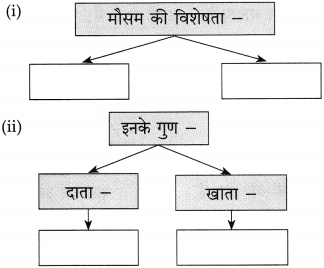
लिखिए:

उत्तर:
प्रश्न 5.
पाठ में प्रयुक्त ‘इक’ प्रत्यययुक्त शब्दों को ढूँढ़कर लिखिए तथा उनमें से किन्हीं चार का स्वतंत्र वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए।
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 6.
पाठ में कुछ ऐसे शब्द हैं, जिनके विलोम शब्द भी पाठ में ही प्रयुक्त हुए हैं, ऐसे शब्द ढूँढ़कर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
(i) हाड़ × माँस
(ii) प्रत्यक्ष × अप्रत्यक्ष
(iii) देश × विदेश
(iv) हाथ × पैर
(v) स्वार्थ × परार्थ
(vi) अमीर × गरीब।
अभिव्यक्ति
‘समाज परोपकार वृत्ति के बल पर ही ऊँचा उठ सकता है’, इस कथन से संबंधित अपने विचार लिखिए।
उत्तर:
हमारे शास्त्रों में परोपकार को बहुत महत्त्व दिया गया है। पेड़ों में फल लगना, नदियों के जल का बहना परोपकार का ही एक रूप है। इसी तरह सज्जन व्यक्तियों की संपत्ति और इस शरीर को भी परोपकार में लगा देने के लिए कहा गया है। हमारे समाज में गरीब-अमीर हर प्रकार के व्यक्ति होते हैं। अनेक लोग ऐसे हैं जिन्हें भरपेट भोजन भी नहीं मिलता और कुछ लोग ऐसे हैं, जिनके पास इतनी संपत्ति है कि उन्हें स्वयं इसकी पूरी जानकारी नहीं है। मनुष्य में परोपकार की प्रवृत्ति जन्मजात होती है। प्यासे को पानी पिलाना और किसी भूखे को खाना खिला देना कौन नहीं चाहता।

यही परोपकार भावना है। हमारे देश में अनेक अस्पताल, अनेक शिक्षा संस्थाएँ परोपकार करने वाले लोगों के धन से चल रही हैं। समाज के कमजोर वर्ग के लिए तरह-तरह की संस्थाएँ काम कर रही हैं। इनका संचालन दान अथवा सहायता के रूप में प्राप्त धन से हो रहा है। हर युग में समाज के उत्थान के लिए परोपकारियों का सहयोग प्राप्त होता रहा है। यह सहयोग इसी तरह मिलता रहना चाहिए तभी हमारे समाज का उत्थान होगा।
भाषा बिंदु
प्रश्न 1.
निम्न वाक्यों में अधोरेखांकित शब्द समूह के लिए कोष्ठक में दिए गए मुहावरों में से उचित मुहावरे का चयन कर वाक्य फिर से लिखिए:
[इज्जत उतारना, हाथ फेरना, काँप उठना, तिलमिला जाना, दुम हिलाना, बोलबाला होना]
१. करामत अली हौले-से लक्ष्मी से स्नेह करने लगा।
वाक्य = ………………………………………
उत्तर:
वाक्य: करामत अली हौले-से लक्ष्मी पर हाथ फेरने लगा।
२. सार्वजनिक अस्पताल का खयाल आते ही मैं भयभीत हो गया ।
वाक्य = ………………………………………
उत्तर:
वाक्य: सार्वजनिक अस्पताल का ख्याल आते ही मैं काँप उठा।
३. क्या आपने मुझे अपमानित करने के लिए यहाँ बुलाया था ?
वाक्य = ………………………………………
उत्तर:
वाक्य: क्या आपने मेरी इज्जत उतारने के लिए यहाँ बुलाया था?
४. सिरचन को बुलाओ, चापलूसी करता हुआ हाजिर हो जाएगा।
वाक्य = ………………………………………
उत्तर:
वाक्य: सिरचन को बुलाओ, दुम हिलाता हुआ हाजिर हो जाएगा।
५. पंडित बुद्धिराम काकी को देखते ही क्रोध में आ गए।
वाक्य = ………………………………………
उत्तर:
वाक्य: पंडित बुद्धिराम काकी को देखते ही तिलमिला उठे।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित मुहावरों का अर्थ लिखकर उनका अर्थपूर्ण वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए
१. गुजर-बसर करना: ………………………………………
२. गला फाड़ना: ………………………………………
३. कलेजे में हूक उठना: ………………………………………
४. सीना तानकर खड़े रहना: ………………………………………
५. टाँग अड़ाना: ………………………………………
६. जेब ढीली होना: ………………………………………
७. निजात पाना: ………………………………………
८. फूट-फूटकर रोना: ………………………………………
९. मन तरंगायित होना: ………………………………………
१०. मुँह लटकाना: ………………………………………
उत्तर:
(i) गुजर-बसर करना।
अर्थ: जीविका चलाना।
वाक्य: पंडित घनश्याम किसी तरह गुजर-बसर कर लेते हैं।

(ii) गला फाड़ना।
अर्थ: ऊँची आवाज में बोलना।
वाक्य: बेटे ने पिता से कहा, “मैं आपकी बात सुन रहा हूँ,आप
नाहक गला फाड़ रहे हैं।”
(iii) कलेजे में हूक उठना।
अर्थ: कसक होना।
वाक्य: सेठ लक्खूमल जब भी जवान बेटे की हत्या की बात याद करते हैं, उनके कलेजे में हूक उठती है।
(iv) सीना तानकर खड़े रहना।
अर्थ: दृढ़तापूर्वक अड़े रहना।।
वाक्य: वह समाजसेवक निर्दोष लोगों की सहायता के लिए सीना तानकर खड़ा रहता हैं।
(v) टाँग अड़ानां।
अर्थ: कार्य में बाधा डालना।
वाक्य: किसी के बनते हुए काम में टाँग अड़ाना अच्छी बात नहीं है।
(vi) जेब ढीली होना।
अर्थ: काफी खर्च होना।
वाक्य: मरीज की बीमारी तो ठीक हो गई, पर अस्पताल का बिल भरने में जेब ढीली हो गई।
(vii) निजात पाना।
अर्थ: मुक्त होना।
वाक्य: आखिरकार लंबे अरसे बाद सेठजी लेन-देन के मुकदमे से निजात पा गए।
(viii) फूट-फूटकर रोना।
अर्थ: बिलखते हुए रोना।
वाक्य: बेटे के गायब हो जाने पर माँ फूट-फूटकर रोई थी।
(ix) मन तरंगित होना।
अर्थ: मौज में आना।
वाक्य: बेटे की अच्छे वेतनवाली नौकरी लग जाने की बात सुनकर पिता का मन तरंगित हो गया।
(x) मुँह लटकाना।
अर्थ: चिंता, दुख से सिर नीचा कर लेना।
वाक्य: पिता जब निकम्मे बेटे को फटकारता है, तो वह मुँह लटकाकर सुनता रहता है।
प्रश्न 3.
पाठ्यपुस्तक में आए मुहावरों का अपने वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए।
उत्तर:
(इसके लिए विद्यार्थी ‘नवनीत हिंदी (LL) उपयोजित लेखन, कक्षा दसवीं’ पुस्तक देखें।)
उपयोजित लेखन
निम्न शब्दों के आधार पर कहानी लेखन कीजिए
मिट्टी, चाँद, खरगोश, कागज।
उत्तर:
एक छोटा-सा गाँव था। गाँव के लोग खेती-बारी से अपना गुजारा करते थे। लोगों के पास छोटे-छोटे खेत थे। वे अपने खेतों में साल में दो फसलें उगाते थे। खेतों में उत्पन्न अनाज से साल भर बड़ी मुश्किल से उनका काम चलता था। इस गाँव के लोगों में आपस में बहुत प्रेम-भाव था। गाँव में कुछ लोग ऐसे थे, जिनके पास खेत भी नहीं थे। उनका जीवन बहुत कष्टमय था। इन्हीं में से एक था आत्माराम। आत्माराम गाँव के किसानों के खेत में काम करके कुछ कमा लिया करता था।

एक दिन गाँव में एक साधु महाराज आए। आत्माराम ने साधु के सामने अपनी समस्या रखते हुए कहा, “महाराज कुछ ऐसा उपाय बताइए, जिसमें मैं चार पैसे कमाकर अपना और अपने परिवार का पेट पाल सकूँ।” साधु महाराज ने कहा, “ले यह मिट्टी। यह मिट्टी तेरे लिए सोना बनेगी।” आत्माराम बोला, “मैं समझा नहीं, महाराज। ऐसी मिट्टी तो गाँव में बहुत है, क्या करूँ इसका?” साधु ने कहा, “मिट्टी खोद। उससे खिलौने बना और बाजार में बेच। तेरा भला होगा।” आत्माराम ने साधु को धन्यवाद दिया।
वह मिट्टी से खरगोश, चूहा, तोता, गुड़िया, गुड्डा बनाता और बाजार में बेच आता। इससे उसे अच्छी आय होने लगी। अब उसकी जिंदगी आराम से चलने लगी।
एक दिन बाजार में एक लड़के ने उससे चाँद के खिलौने की माँग की। यह खिलौना तो उसने कभी बनाया ही नहीं था। बात आई-गई हो गई।
एक दिन आत्माराम ने चाँद की शक्ल का पतंग आकाश में उड़ते हुए देखा। फिर क्या था! अब आत्माराम ने मिट्टी के खिलौने बनाने बंद कर दिए और कागज के पतंग, खरगोश, तोते, बिल्ली, गुड़िया, गुड्डा आदि बनाने लगा। अब उसके खिलौनों का वजन हल्का हो गया और उसकी कमाई भारी हो गई।
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Textbook Solutions Chapter 3 श्रम साधना Additional Important Questions and Answers
गद्यांश क्र.1
प्रश्न. निम्नलिखित पठित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
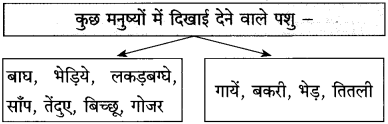
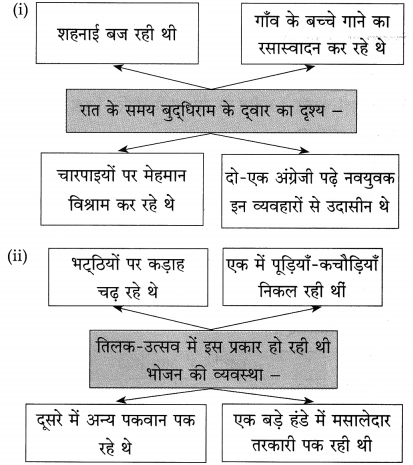
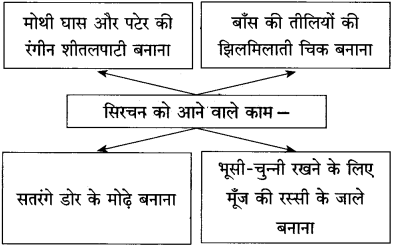
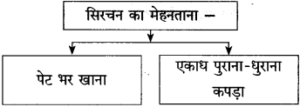
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
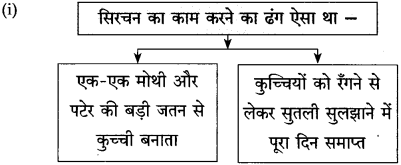
(स्वाध्याय में दिए गए ‘उत्तर लिखिए’ प्रश्न को कृतिस्वरूप में दिया गया है।)
उत्तर:
(ii)
(iii)

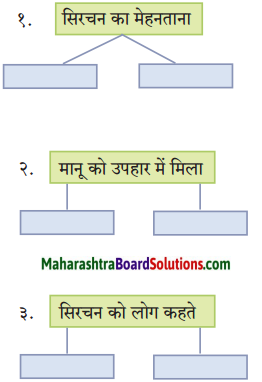
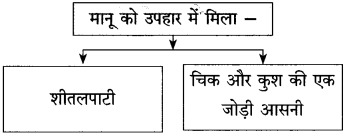
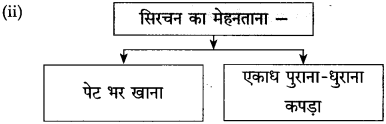
कृति 2: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
(i) संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:
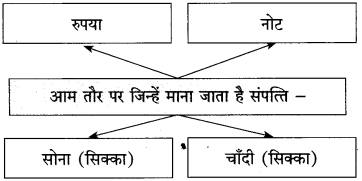
(ii) लिखिए:
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
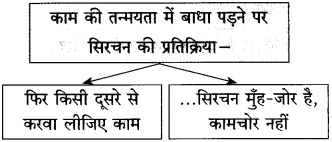
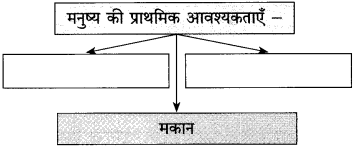
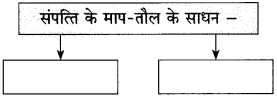
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
उत्तर:
कृति 3: (शब्द संपदा)
प्रश्न 1.
शब्दों के समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) प्रथा =
(ii) युद्ध =
(iii) हुकूमत =
(iv) गुलामी =
उत्तर:
(i) प्रथा = रिवाज
(ii) युद्ध = लड़ाई
(iii) हुकूमत = शासन
(iv) गुलामी = दासता।

प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) गौण x
(ii) अनेक x
(iii) अप्राकृतिक x
(iv) बादशाह x
उत्तर:
(i) गौण x मुख्य
(ii) अनेक x एक
(iii) अप्राकृतिक x कृत्रिम
(iv) बादशाह x भिखारी।
प्रश्न 3.
लिंग पहचान कर लिखिए:
(i) मकान – ………………………
(i) संपत्ति – …………………………
उत्तर:
(i) मकान – पुल्लिग
(ii) संपत्ति – स्त्रीलिंग।
कृति 4: (स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति)
प्रश्न.
‘राजाओं और बादशाहों का राज’ के बारे में अपने विचार 25 से 30 शब्दों में व्यक्त कीजिए।
उत्तर:
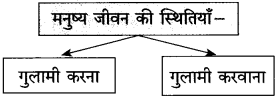
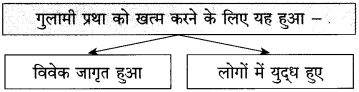
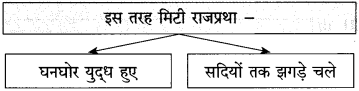
स्वतंत्रता प्राप्ति के पहले हमारे देश में छोटी-बडी अनेक रियासतें थीं। राजा, बादशाह और तालुकेदार इन रियासतों के मालिक थे। इनके राज में रहने वाली जनता इनकी प्रजा कहलाती थी। राजा और बादशाह जनता से तरह-तरह के कर वसूल करते थे और कर अदा न कर पाने पर जनता पर तरह-तरह के अत्याचार करते थे। एक तरह से जनता को ये अपना गुलाम समझते थे और उसका शोषण करने में जरा भी नहीं झिझकते थे। जनता इनसे त्रस्त थी।
इसके अलावा ये राजा और बादशाह अपने स्वार्थ के लिए आपस में लड़ते-भिड़ते थे और मौका मिलने पर एक-दूसरे की रियासतों पर कब्जा कर जनता में लूटपाट किया करते थे। असहाय जनता की कोई सुनने वाला नहीं था। आजादी मिलने के बाद इन छोटी-छोटी रियासतों को खत्म कर भारत संघ में मिला लिया गया। इसके बाद इन राजाओं और बादशाहों का राज खत्म हो गया। इसके साथ ही समाप्त हो गया जनता पर इनका अत्याचार। फिर तो प्रजातंत्र में न कोई किसी का राजा रहा न कोई किसी की प्रजा। सबको समान अधिकार उपलब्ध हो गए।

गद्यांश क्र. 2
प्रश्न निम्नलिखित पठित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
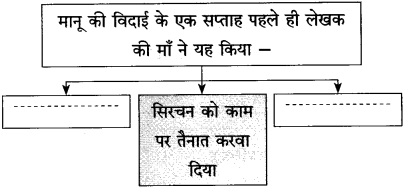
प्रश्न 1.
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
अकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:
कृति 2: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
संजाल पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
उत्तर लिखिए:
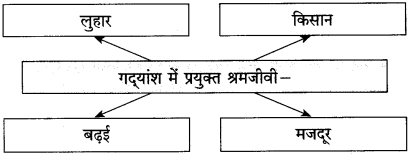
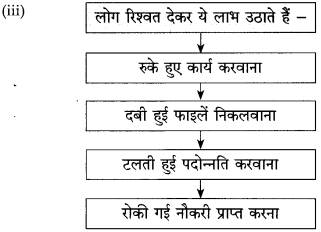
(i) जो संपत्ति का निर्माण करते हैं, वे – [ ]
(ii) धन इकट्ठा होता है इनके पास – [ ]
(iii) बौद्धिक काम से अपना भरण-पोषण करने वाले लोग – [ ]
(iv) समाज के लिए ये दोनों जरूरी हैं – [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) जो संपत्ति का निर्माण करते हैं, वे माण – [मजदूर]
(ii) धन इकट्ठा होता है इनके पास – [व्यवस्था करने वाले]
(iii) बौद्धिक काम से अपना भरण-पोषण करने वाले लोग – [मंत्री, राज्य के कर्मचारी, क्लर्क, न्यायाधीश, वकील, डॉक्टर, अध्यापक, व्यापारी]
(iv) समाज के लिए ये दोनों जरूरी है – [श्रमजीवी और बुद्धिजीवी]

प्रश्न 3.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
(i)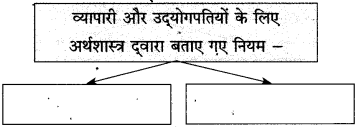
उत्तर:
(ii) दो ऐसे प्रश्न बनाकर लिखिए, जिनके उत्तर निम्नलिखित शब्द हों:
(1) अन्न
(2) श्रम जीवियों पर
उत्तर:
(1) वर्षभर मेहनत कर किसान क्या पैदा करता है?
(2) बुद्धिजीवियों का जीवन किन लोगों पर आधारित है?
कृति 3: (शब्द संपदा)
प्रश्न 1.
गद्यांश में आए शब्द-युग्म ढूँढ़कर लिखिए।
(i) ……………………..
(ii) ……………………..
(iii) ……………………..
(iv) ……………………..
उत्तर:
(i) लेन – देन
(ii) राज – काज
(iii) ऊँचे – ऊँचे
(iv) भरण – पोषण।
प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) प्रत्यक्ष × ……………………..
(ii) धनवान × ……………………..
(iii) ऊँचा × ……………………..
(iv) दुर्भाग्य × ……………………..
उत्तर:
(i) प्रत्यक्ष × परोक्ष
(ii) धनवान × निर्धन
(iii) ऊँचा × नीचा
(iv) दुर्भाग्य × सौभाग्य।

कृति 4: (स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति)
प्रश्न.
‘शारीरिक श्रम का महत्त्व’ विषय पर अपने विचार 25 से 30 शब्दों में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
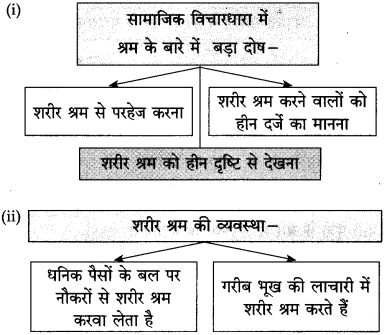
श्रम दो प्रकार का होता है। शारीरिक श्रम और बौद्धिक श्रम। पुराने जमाने में पढ़े-लिखे लोगों की संख्या कम थी, इसलिए लोगों को शारीरिक श्रम का ही सहारा था। वे जीवन-यापन के लिए छोटा-मोटा काम करके अपना गुजारा कर लेते थे। शिक्षा की समुचित व्यवस्था हो जाने के बाद पढ़े-लिखे लोगों की संख्या में अंधाधुंध वृद्धि हुई है। हर शिक्षित व्यक्ति चाहता है कि उसे ऐसी नौकरी मिले, जिसमें उसे शारीरिक श्रम न करना पड़े। शारीरिक श्रम वाला काम कोई करना नहीं चाहता। इसलिए देश में लाखों नवयुवक बेरोजगार हैं। यह लोगों के शारीरिक श्रम से परहेज रखने का परिणाम है।
लोगों को शारीरिक श्रम का महत्त्व समझना जरूरी है। बुद्धि के बल पर बड़ीबड़ी योजनाएँ बनाई जा सकती हैं, पर उनका कार्यान्वयन करने के लिए शारीरिक श्रम की ही आवश्यकता होती है। छोटी-छोटी चीजों से लेकर बड़ी-बड़ी चीजों का निर्माण केवल शारीरिक श्रम से ही हो सकता है। जो व्यक्ति इस रहस्य को समझते हैं, वे शारीरिक श्रम को महत्त्व देते हैं। अनेक पढ़े-लिखे लोग अपना व्यवसाय अथवा छोटा-मोटा काम शुरू करके अपना जीवन-यापन कर रहे हैं और बौद्धिक श्रम के साथ शारीरिक श्रम उनका साथ दे रहा है। स्वरोजगार के द्वारा वे स्वयं भी काम कर रहे हैं और दूसरों को भी रोजगार दे रहे हैं।
गद्यांश क्र. 3
प्रश्न. निम्नलिखित पठित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
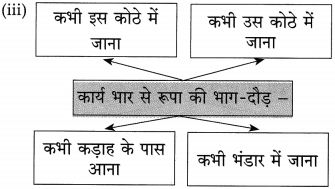
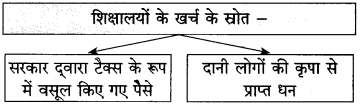
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:

कृति 2: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
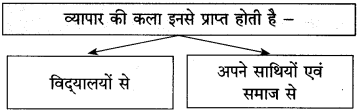
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
(i)
(ii)
उत्तर:
(ii)
कृति 3: (शब्द संपदा)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के समानार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) आम = …………………….
(ii) श्रम = …………………….
(iii) हिस्सा = …………………….
(iv) जगत = …………………….
उत्तर:
(i) आम = सामान्य
(ii) श्रम = मेहनत
(iii) हिस्सा = भाग
(iv) जगत = संसार।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से प्रत्यय और मूल शब्द अलग करके लिखिए:
(i) योग्यता
(i) अल्पतम
(ii) बुनियादी
(iv) सामाजिक
उत्तर:
(i) योग्य + ता (ता)
(ii) अल्प + तम (तम)
(iii) बुनियाद + ई (ई)
(iv) समाज + इक (इक)।

कृति 4: (स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति)
प्रश्न.
‘समाज परोपकार वृत्ति के बल पर ही ऊँचा उठ सकता है’- इस कथन से संबंधित अपने विचार 25 से 30 शब्दों में लिखिए।
गद्यांश क्र.4
प्रश्न. निम्नलिखित पठिक अट्यार पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
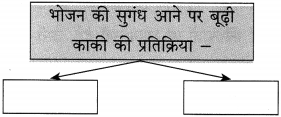
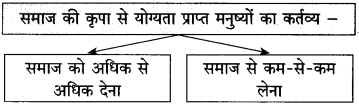
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
(iii) 
उत्तर:
कृति 2: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
(i) अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार उत्पादन की प्रेरणा के लिए यह करना होगा – [ ]
(ii) पूँजी के बारे में अनुभव यह बताता है – [ ]
(iii) लेखक के अनुसार स्वार्थ का अर्थ – [ ]
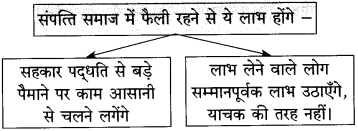
(iv) समाज इस वृत्ति के बल पर ऊँचा उठ सकता है – [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) अर्थशास्त्रियों के अनुसार उत्पादन की प्रेरणा के लिए यह करना होगा – [व्यक्ति को स्वार्थ के लिए अवसर देने होंगे।
(ii) पूँजी के बारे में अनुभव यह बताता है – [पूँजी गरीबी या बेकारी की समस्या हल नहीं कर सकी है]
(iii) लेखक के अनुसार स्वार्थ का अर्थ – [परार्थ की हानि]
(iv) समाज इस वृत्ति के बल पर ऊँचा उठ सकता है – [परोपकार की वृत्ति]
प्रश्न 3.
गद्यांश के वाक्यों को उचित क्रम से लिखिए:
(i) देखना है कि समाज का कल्याण किस वृत्ति से होगा।
(ii) बिना शरीर श्रम किए उस सामग्री का उपयोग करने का न्यायोचित अधिकार हमें नहीं मिलता।
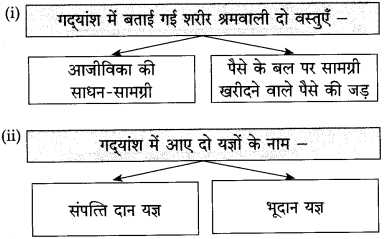
(iii) आजीविका की साधन-सामग्री किसी-न-किसी के श्रम के बिना हो ही नहीं सकती।
(iv) नैतिक दृष्टि से स्वार्थवृत्ति का पोषण करना योग्य नहीं है।
उत्तर:
(i) आजीविका की साधन-सामग्री किसी-न-किसी के श्रम के बिना हो ही नहीं सकती।
(ii) बिना शरीर श्रम किए उस सामग्री का उपयोग करने का न्यायोचित अधिकार हमें नहीं मिलता।
(iii) नैतिक दृष्टि से स्वार्थवृत्ति का पोषण करना योग्य नहीं है।
(iv) देखना है कि समाज का कल्याण किस वृत्ति से होगा।
कृति 3: (शब्द संपदा)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्द समूह के लिए गद्यांश से चुनकर एक-एक शब्द लिखिए:
(i) वह दौलत, जो किसी के अधिकार में हो और जो खरीदी या बेची जा सकती हो-
(ii) दूसरों के उपकार या भलाई का काम’ –
(iii) ऐसी बात-जिसमें केवल अपना हित हो –
(iv) वह धन-जिससे कोई व्यवसाय आरंभ किया गया हो –
उत्तर:
(i) संपत्ति
(ii) परोपकार
(iii) स्वार्थ
(iv) पूँजी।

प्रश्न 2.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिखिए:
(i) थोड़ा × ……………………
(ii) दोषपूर्ण × ……………………
(iii) योग्य × ……………………
(iv) गरीबी × ……………………
उत्तर:
(i) थोड़ा × बहुत
(ii) दोषपूर्ण × निर्दोष
(iii) योग्य × अयोग्य
(iv) गरीबी × अमीरी।
कृति 4: (स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति)
प्रश्न.
‘मेवे फलते श्रम की डाल’ विषय पर 25 से 30 शब्दों में अपनी लिखित अभिव्यक्ति दीजिए।
उत्तर:
श्रम दो प्रकार का होता है। एक शारीरिक श्रम और दूसरा बौद्धिक श्रम। दोनों प्रकार के श्रम का अपना-अपना महत्त्व है। श्रम को सदा महत्त्व दिया गया है। श्रम करने वाला व्यक्ति परिश्रम करके अपना भरण-पोषण करता है और शान से रहता है। जो श्रम करता है, वह स्वयं अपने भाग्य का निर्माण करता है। वह अपना खून-पसीना एक कर मेहनत की पवित्र रोटी खाता है। मेहनत की जिंदगी ही सच्ची जिंदगी है।
श्रम करने वाला व्यक्ति काम से कभी नहीं घबराता। उसके सामने जैसा भी काम आता है, उसे वह लगन और मेहनत से पूरा करता है। विद्यार्थी श्रम द्वारा ही परीक्षा में सफलता प्राप्त करते हैं। मजदूर, किसान, इंजीनियर, वैज्ञानिक, व्यापारी, खिलाड़ी आदि सबकी प्रगति में श्रम का ही हाथ होता है। हमें याद रखना चाहिए कि श्रम कभी बेकार नहीं जाता। ईमानदारी से किए गए श्रम का तुरंत लाभ भले न मिले, पर कभी-न-कभी उसका फल मिलकर ही रहता है। श्रम करने वाले ही मेवों का स्वाद चखते हैं।
गद्यांश क्र. 5
प्रश्न. निम्नलिखित पठित गद्यांश पढ़कर दी गई सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
कृति 1: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
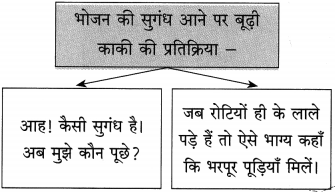
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए:
(i) शरीर श्रम के लिए क्या जरूरी है?
(ii) श्रम की प्रतिष्ठा बढ़ाना किसके हाथ है?
उत्तर:
(i) शरीर श्रम के लिए जरूरी है दिल में प्रीति होना।
(ii) श्रम की प्रतिष्ठा बढ़ाना श्रमिक के हाथ है।
कृति 2: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
आकृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
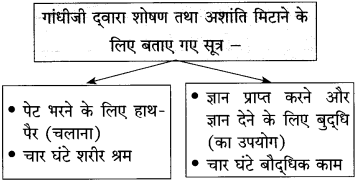
(i) गांधीजी की मान्यता के अनुसार। हर व्यक्ति को यह करना चाहिए – [ ]
(ii) अब कुछ समय से जगत के सामने दया की जगह यह विचार आया है – [ ]
(iii) महात्माजी द्वारा दी गई प्रसिद्ध विचारधारा – [ ]
(iv) अहिंसा के मार्ग से यह प्रश्न हल हो सकता है – [ ]
उत्तर;
(i) गांधीजी की मान्यता के अनुसार हर व्यक्ति को यह करना चाहिए – [उत्पादक श्रम]
(ii) अब कुछ समय से जगत के सामने दया की जगह यह विचार आया है – [समता का]
(iii) महात्माजी द्वारा दी गई गई प्रसिद्ध विचारधारा – [अहिंसा]
(iv) अहिंसा के मार्ग से यह प्रश्न हल हो सकता है – [विषमता का]
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के आधार पर प्रश्न बनाइए:
(i) गांधीजी ने श्रम और श्रमिक की प्रतिष्ठा स्थापित करने के लिए ही रचनात्मक कार्यों को लोक चेतना का माध्यम बनाया।
(ii) कानून से मानवोचित गुणों का विकास नहीं हो सकता?
(iii) अहिंसा के प्रभाव का कुछ अनुभव भी हम कर सकते हैं।
(iv) आर्थिक सामाजिक समता का प्रश्न अहिंसा के मार्ग से सुलझेगा।
उत्तर:
(i) गांधीजी ने किन बातों की प्रतिष्ठा स्थापित करने के लिए रचनात्मक कार्यों को लोक चेतना का माध्यम बनाया?
(ii) कानून से किन गुणों का विकास नहीं हो सकता?
(iii) किसके प्रभाव का अनुभव हम कर सकते हैं?
(iv) आर्थिक सामाजिक समता का प्रश्न किस मार्ग से सुलझेगा?

कृति 3: (शब्द संपदा)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के वचन पहचान कर लिखिए:
(i) बच्चा – ………………….
(ii) विषमताएँ – ………………….
(iii) पैसे – ………………….
(iv) धनिक – ………………….
उत्तर:
(i) बच्चा – एकवचन
(ii) विषमताएँ – बहुवचन
(ii) पैसे – बहुवचन
(iv) धनिक – एकवचन।
प्रश्न 2.
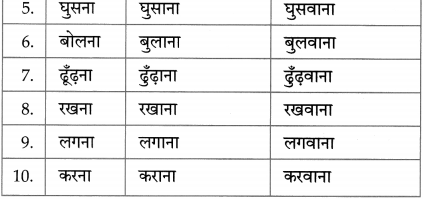
गद्यांश में प्रयुक्त ‘इक’ प्रत्यययुक्त शब्दों को ढूँढ़कर स्वतंत्र वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए:
(i) ………………….
(ii) ………………….
(iii) ………………….
(iv) ………………….
(v) ………………….
(vi) ………………….
उत्तर:
(i) आर्थिक
(ii) प्राकृतिक
(iii) श्रमिक
(iv) सामाजिक
(v) प्राथमिक
(vi) बौद्धिक
(i) आर्थिक: किसानों की आर्थिक दशा सुधारने के लिए कुछ करो।
(ii) प्राकृतिक: कश्मीर की घाटी प्राकृतिक दृश्यों से भरी पड़ी है।
(iii) श्रमिक: कारखाने में काम करने वाले श्रमिक का काम बहुत मेहनत का होता है।
(iv) सामाजिक: मनुष्य एक सामाजिक प्राणी है।
(v) प्राथमिक: घायल व्यक्ति को तुरंत प्राथमिक चिकित्सा की जरूरत होती है।
(vi) बौद्धिक: हर व्यक्ति की बौद्धिक क्षमता भिन्न-भिन्न होती है।

कृति 4: (स्वमत अभिव्यक्ति)
प्रश्न.
शारीरिक श्रम स्वास्थ के लिए अति उत्तम’ विषय पर अपने। विचार 25 से 30 शब्दों में लिखिए।
उत्तर:
शारीरिक श्रम का अर्थ है, वह मेहनत, जिसमें हाथ-पैर के सहयोग से काम संपन्न हो। किसान, मजदूर, क्ली, ठेलेवाले, शारीरिक मेहनत करते हैं। वैसे हर व्यक्ति जाने-अनजाने थोड़ी बहुत शारीरिक मेहनत करता ही है। अपने घर की सफाई करना, खाना बनाना, बरतन धोना और बाजार-हाट से सामान-सब्जी लाना भी श्रम है। कुछ शारीरिक काम करने वाले लोग धूप में खेतों में काम करते हैं।
कुछ कारखानों में पसीना बहाकर मेहनत करते हैं। कुछ अनाज के बोरे ३ गाड़ियों पर चढ़ाते-उतारते हैं। कुछ सड़कों पर हथौड़े लेकर पत्थर तोड़ते ३ या खुदाई करते हैं। ये मोटा खाते और मोटा पहनते हैं, पर शारीरिक ३ रूप से स्वस्थ होते हैं। दूसरी ओर वे लोग हैं, जो कोई शारीरिक श्रम ३ नहीं करते। वे पौष्टिक भोजन करते हैं, नर्म गद्देदार बिछौनों पर सोते B हैं, पर बीमारी के कारण उन्हें नींद नहीं आती। भोजन नहीं पचता।
डॉक्टर इन्हें कम भोजन करने और ज्यादा दवाइयाँ लेने के लिए कहते हैं। शारीरिक श्रम के अभाव में इनका जीवन कष्टप्रद बन जाता है।
डॉक्टर इन्हें हाथ-पैर चलाने और व्यायाम करने की सलाह देते हैं। ऐसे 3 लोगों को शारीरिक श्रम करने वालों से सबक लेना चाहिए, जो
अपनी मेहनत के बल पर भले-चंगे बने रहते हैं। इस प्रकार शारीरिक , श्रम अच्छे स्वाथ्य की कुंजी है।
भाषा अध्ययन (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न, सूचनाओं के अनुसार कृतियाँ कीजिए:
1. शब्द भेद:
प्रश्न.
अधोरेखांकित शब्दों के शब्दभेद पहचानकर लिखिए:
(i) गांधीजी ने यह काम श्रम और श्रमिक की प्रतिष्ठा कायम करने के लिए किया।
(ii) विषमता दूर करने के लिए प्रभावशाली उपाय करना चाहिए।
उत्तर:
(1) गांधीजी – व्यक्तिवाचक संज्ञा।
(ii) प्रभावशाली – गुणवाचक विशेषण।
2. अव्यय:
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित अव्ययों का अपने वाक्यों में प्रयोग कीजिए:
(i) फिर
(ii) कभी-कभी।
उत्तर:
(i) संपत्ति रूपी ये सब चीजें फिर कैसे बनती हैं?
(ii) बुद्धिजीवियों को भी कभी-कभी शरीर श्रम करना पड़ता है।

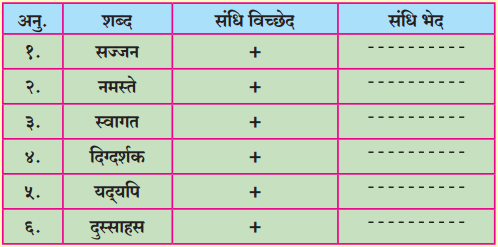
3. संधि:
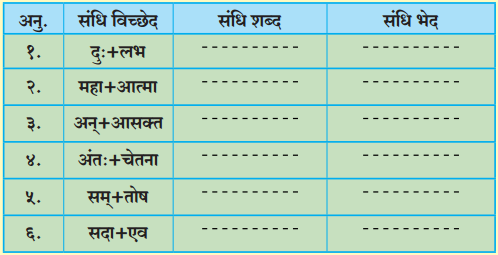
प्रश्न.
कृति पूर्ण कीजिए:
| संधि शब्द |
संधि विच्छेद |
संधि भेद |
| …………………… |
स्व + अर्थ |
…………………… |
| अथवा |
| …………………… |
सम् + पूर्ण |
…………………… |
उत्तर:
| संधि शब्द |
संधि विच्छेद |
संधि भेद |
| स्वार्थ |
स्व + अर्थ |
स्वर संधि |
| अथवा |
| सपूर्ण |
सम् + पूर्ण |
व्यंजन संधि |
4. सहायक क्रिया:
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में से सहायक क्रियाएँ पहचानकर उनका मूल रूप लिखिए:
(i) प्रतिदिन समय पर अपना काम किया करो।
(ii) वह अपनी जमा-पूँजी भी गंवा बैठा।
उत्तर:
सहायक क्रिया – मूल रूप
(i) करो – करना
(ii) बैठा – बैठना
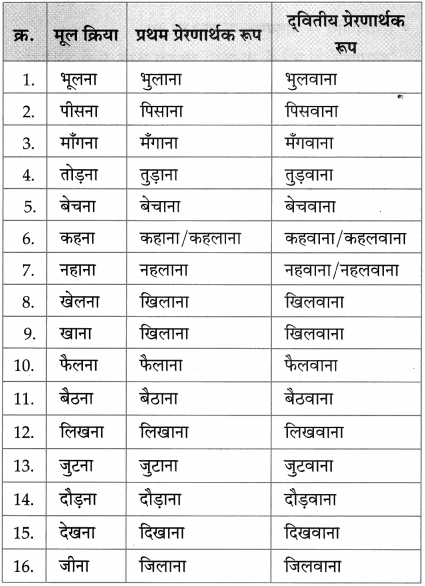
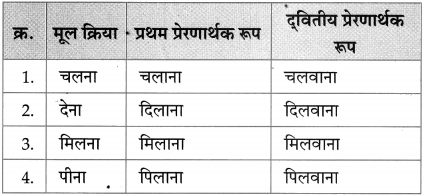
5. प्रेरणार्थक क्रिया:
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित- क्रियाओं के प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक और द्वितीय प्रेरणार्थक रूप लिखिए:
(i) खौलना
(ii) डूबना।
उत्तर:
क्रिया – प्रथम प्रेरणार्थक रूप – दवितीय प्रेरणार्थक रूप
(i) खौलना – खौलाना – खौलवाना
(ii) डूबना – डुबाना – डुबवाना

6. मुहावरे:
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित मुहावरों का अर्थ लिखकर वाक्य में प्रयोग कीजिए:
(i) मुंह फेरना
(ii) रट लगाना।
उत्तर:
(i) मुँह फेरना।
अर्थ: उपेक्षा करना।
वाक्य: कर्मचारी अपनी माँग लेकर सेठ जी के पास जाते तो वे उनसे बात करने के बजाय मुँह फेर लेते।
(ii) रट लगाना।
अर्थ: एक ही बात बार-बार कहना।
वाक्य: मुर्गा बहुत सबेरे ‘कुकड़-फूं’ की रट लगाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
अधोरेखांकित वाक्यांश के लिए उचित मुहावरे का चयन करके वाक्य फिर से लिखिए: (फूला न समाना, भार होना, कान में डालना)
(i) मुनीम जी ने बड़े बाबू को बात पहुँचाई।
(ii) मेडिकल में प्रवेश मिल जाने पर नकुल बहुत प्रसन्न हुआ।
उत्तर:
(i) मुनीम जी ने बात बड़े बाबू के कान में डाल दी।
(ii) मेडिकल में प्रवेश मिल जाने पर नकुल फूला न समाया।
7. कारक:
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में प्रयुक्त कारक पहचानकर उसका भेद लिखिए:
(i) गुलामी की प्रथा संसार भर में हजारों वर्षों तक चलती रही।
(ii) गांधीजी ने श्रम और श्रमिकों की प्रतिष्ठा स्थापित करने का काम किया।
उत्तर:
(i) गुलामी की-संबंध कारक
(ii) गांधीजी ने-कर्ता कारक।
8. विरामचिह्न:
प्रश्न.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में यथास्थान उचित विरामचिह्नों का प्रयोग करके वाक्य फिर से लिखिए:
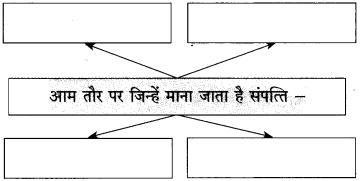
(i) आम तौर से माना जाता है कि रुपया नोट और सोना-चाँदी का सिक्का ही संपत्ति है
(ii) अर्थशास्त्र ने यह नियम बताया है कि खरीद सस्ती से सस्ती हो और बिक्री महँगी से महँगी
उत्तर:
(i) आम तौर से माना जाता है कि रुपया, नोट और सोना-चाँदी का सिक्का ही संपत्ति है।
(ii) अर्थशास्त्र ने यह नियम बनाया है कि खरीद सस्ती-से-सस्ती हो और बिक्री महँगी से महँगी।

9. काल परिवर्तन:
प्रश्न.
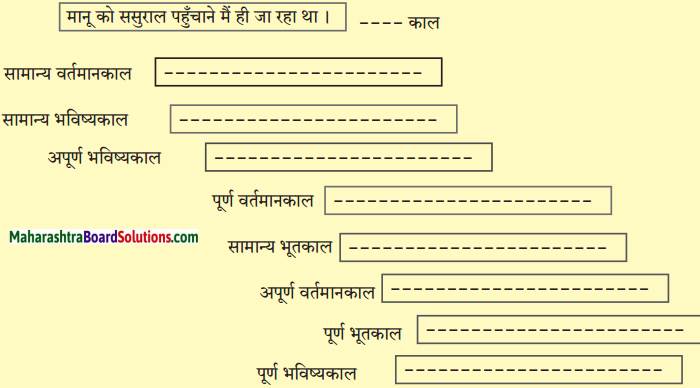
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का सूचना के अनुसार काल परिवर्तन कीजिए:
(i) बहुत से लोग अपनी आजीविका शरीर श्रम से चलाते हैं। (अपूर्ण भूतकाल)
(ii) जिनके पास संपत्ति है, वे आराम से रह रहे हैं। (सामान्य भविष्यकाल)
उत्तर:
(i) बहुत से लोग अपनी आजीविका शरीर श्रम से चला रहे थे।
(ii) जिनके पास संपत्ति है, वे आराम से रहेंगे।
10. वाक्य भेद:
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का रचना के आधार पर भेद पहचानकर लिखिए:
(i) हमारी विचारधारा में बड़ा भारी दोष है।
(ii) लोग शरीर श्रम करना नहीं चाहते और इसे हीन दृष्टि से देखते हैं।
(iii) जिस श्रम में समाज को जिंदा रखने की क्षमता है, उस श्रम का सही मूल्य श्रमिक जान लेगा तो देश में आर्थिक क्रांति होने में देर नहीं लगेगी।
(iv) सामाजिक समता का प्रश्न अहिंसा के मार्ग से सुलझेगा।
उत्तर:
(i) सरल वाक्य
(ii) संयुक्त वाक्य
(iii) मिश्र वाक्य
(iv) सरल वाक्य।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों का दी गई सूचना के अनुसार अर्थ के आधार पर परिवर्तन कीजिए:
(i) गरीब भूख की लाचारी से श्रम करता है। (संदेहवाचक वाक्य)
(ii) अब राजप्रथा मिट गई। (आज्ञावाचक वाक्य)
उत्तर:
(i) शायद गरीब भूख की लाचारी से श्रम करता है।
(ii) अब’राजप्रथा मिटा दो। 11. वाक्य शुद्धिकरण:
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित वाक्य शुद्ध करके वाक्य फिर से लिखिए:
(i) इस सम्बन्ध में कुछ भाई अमेरिका का उदाहरण पेस करते हैं।
(ii) वही आधार पे भारत को कल्याणकारी राज्य बनाने की बात चली है
उत्तर:
(i) इस संबंध में कुछ भाई अमेरिका का उदाहरण पेश करते हैं।
(ii) उसी आधार पर भारत को कल्याणकारी राज्य बनाने की बात चली है।

उपक्रम/कृति/परियोजना
पठनीय
महात्मा गांधी के श्रमप्रतिष्ठा और अहिंसा संबंधी विचार पढ़कर चर्चा कीजिए।
श्रवणीय
आर्थिक विषमता को दूर करने वाले उपायों के बारे में सुनकर कक्षा में सुनाइए।
संभाषणीय
‘वर्तमान युग में सभी बच्चों के लिए खेल-कूद और शिक्षा के समान अवसर प्राप्त हैं’ विषय पर चर्चा करते हुए अपना मत प्रस्तुत कीजिए।
श्रम साधना Summary in Hindi
विषय-प्रवेश : प्राचीन काल से आज तक सामाजिक और राजनैतिक व्यवस्था में अनेक परिवर्तन हुए हैं। इसके साथ ही संपत्ति तथा उसके निर्माण में लगने वाली शक्तियों के बीच तरह-तरह की असमानताएँ भी रही हैं। श्रमजीवियों तथा व्यापारियों की आर्थिक स्थिति में जमीन-आसमान का अंतर रहा है। प्रस्तुत निबंध में लेखक ने मानवीय जीवन, संपत्ति, संपत्ति के स्वामित्व, मनुष्य की प्राथमिक आवश्यकताओं तथा शारीरिक एवं बौद्धिक श्रम आदि का विस्तृत विवेचन किया है। प्रस्तुत वैचारिक निबंध में श्रम की प्रतिष्ठा स्थापित करते हुए सामाजिक एवं आर्थिक समानता पर बल दिया गया है।
Hindi Lokbharti 10th Textbook Solutions दूसरी इकाई

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()