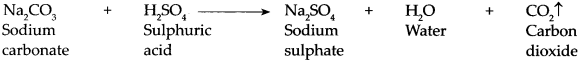
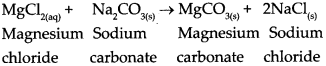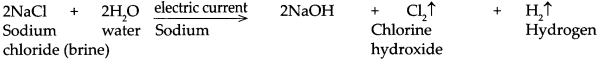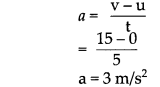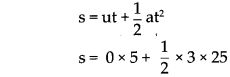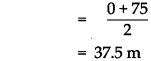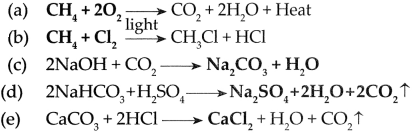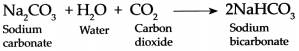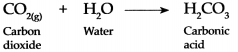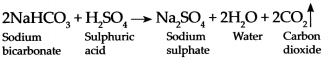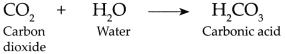Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 9 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Identify the odd one out and justify.
(a) Chloride, nitrate, hydride, ammonium
Answer:
Ammonium is the odd one out as it is a basic radical and rest all are acidic radicals. Generally, basic radicals are formed by the removal of electrons from the atom of metals such as Na+, Cu2+. But there are some exceptions, such as NH4+.
![]()
(b) Hydrogen chloride, sodium hydroxide, calcium oxide, ammonia
Answer:
Hydrogen chloride is the odd one out. It is acidic and rest all are basic.
(c) Acetic acid, carbonic acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid
Answer:
Carbonic acid is the odd one out. It is a dibasic acid and rest are all monobasic acids.
(d) Ammonium chloride, sodium chloride, potassium nitrate, sodium sulphate
Answer:
Ammonium chloride is the odd one out, as it is made up of a strong acid and weak base and rest all are formed from strong acid and strong base.
(e) Sodium nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium sulphate, sodium chloride
Answer:
Sodium carbonate is the odd one out, as it is made up of a weak acid and strong base, and rest all are formed from strong acid and strong base.
(f) Calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, sodium oxide.
Answer:
Zinc oxide is the odd one out, as it is an amphoteric oxide, and rest all are basic oxides.
(g) Crystalline blue vitriol, crystalline common salt, crystalline ferrous sulphate, crystalline sodium carbonate.
Answer:
Crystalline common salt is the odd one out, as it does not contain water of crystallisation. It is an ionic compound and ionic compounds are crystalline in nature and rest all have their crystalline structure because of their water of crystallization.
![]()
(h) Sodium chloride, potassium hydroxide, acetic acid, sodium acetate.
Answer:
Acetic acid is the odd one out. It is an acid, the rest are all salts.
2. Write down the changes that will be seen in each instance and explain the reason behind it.
(a) 50ml water is added to 50ml solution of copper sulphate.
Answer:
- Copper sulphate solution is blue. It is a concentrated solution.
- When 50 ml of water is added to this concentrated solution, it becomes a diluted solution.
- The intensity of the blue colour is now different in this homogenous mixture.
(b) Two drops of the indicator phenolphthalein were added to 10ml solution of sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
- Sodiumhy droxide is a base and phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator.
- Sodium hydroxide solution will turn pink if phenolphthalein is added to it.
- It is a test for identifying bases.
(c) Two or three filings of copper were added to 10ml dilute nitric acid and stirred.
Answer:
When copper metal reacts with dilute nitric acid, the metal does not displace hydrogen from the acid like reaction with other metals. Instead the reaction produces nitric oxide, (NO).

(d) A litmus paper was dropped into 2ml dilute HCl. Then 2ml concentrated NaOH was added to it and stirred.
Answer:
Blue litmus Paper:
- HCl is hydrochloric acid, so the blue litmus turns red.
- When equal amount of NaOH is added the colour again changes to blue and remains the same.
Red litmus paper:
- Red litmus paper shows no colour change in hydrochloric acid.
- When some amount of NaOH is added the colour changes to blue initially but when the amount of NaOH is sufficient the blue colour dissappears.
- Equal amounts of HC1 and NaOH results in the formation of NaCl, a salt, and the solvent water. This reaction is called the neutralization reaction.
![]()
(e) Magnesium oxide was added to dilute HCl and magnesium oxide was a added to dilute NaOH.
Answer:
(i) Magnesium oxide + dil HCl.
This is a neutralization reaction. Magnesium oxide is an insoluble base, it reacts with dilute HCl to produce a soluble salt MgCl2 and water H2O.
\(\mathrm{MgO}_{(\mathrm{s})}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(n)}\)
(ii) Magnesium oxide + NaOH.
No chemical reaction takes place between magnesium oxide and sodium hydroxide.
(f) Zinc oxide was added to dilute HCl and zinc oxide was added to dilute NaOH.
Answer:
- Zinc oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and water. It is a neutralization reaction.
\(\mathrm{ZnO}_{(\mathrm{s})}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow \mathrm{ZnCl}_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})}\) - Zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium zincate and water.
\(\mathrm{ZnO}_{(\mathrm{s})}+2 \mathrm{NaOH}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{ZnO}_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{t})}\)
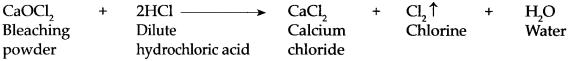
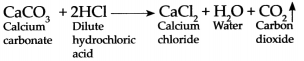
(g) Dilute HCl was added to limestone.
Answer:
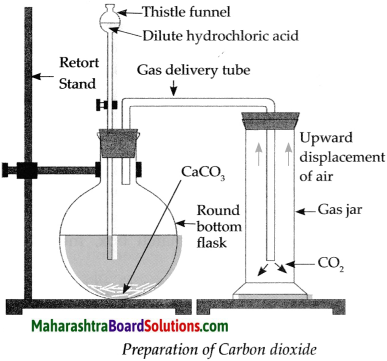
- When hydrochloric acid is added to limestone, carbon dioxide is liberated. Limestone is calcium carbonate.
CaCO3 + 2 HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O - Carbon dioxide is prepared in the laboratory using these chemicals.
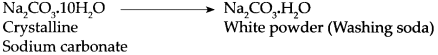
(h) Pieces of blue vitriol were heated in a test tube. On cooling, water was added to it.
Answer:
- On heating, the crystalline structure of blue vitriol breaks down to form a colourless powder and water is released.
- This water is part of the crystal structure of blue vitriol.
- It is called water of crystallization.
- On adding water to the white powder, a solution was formed which has the same colour as the copper sulphate salt solution.
![]()
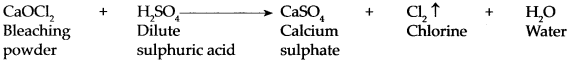
(i) Dilute H2SO4 was taken in an electrolytic cell and electric current was passed through it.
Answer:
- If pure water is used in the electrolytic cell, current does not flow even on putting on the switch.
- Pure water is a bad conductor of electricity. Dilute H2SO4 is acidulated water.
- The electrical conductivity of water increases on mixing with strong acid or base in it due to their dissociation and electrolysis of water takes place.
- H2SO4 is fully dissociated in aqueous solution. \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\)
- H2O is a weak electrolyte and is only slightly dissociated \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}^{+}+\mathrm{OH}^{-}\)
- During electrolysis, the hydrogen ions migrate towards the cathode and are discharged there.
[H+ ions gains electrons and are converted to hydrogen gas]
\(2 \mathrm{H}^{+}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\)
Cathode reaction:
\(2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{i})}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+2 \mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
Anode reaction:
\(2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})} \longrightarrow \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+4 \mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+4 \mathrm{e}\)
- For every hydrogen ion discharged at the anode, another hydrogen ion is formed at the cathode.
- The net result is that the concentration of the sulphuric acid remains constant and electrolysis of water is overall reaction. \(2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{H}_{2}+\mathrm{O}_{2}\)
- The volume of the hydrogen gas formed near the cathode is double that of the oxygen gas formed near the anode.
3. Classify the following oxides into three types and name the types.
CaO, MgO, CO2, SO3, Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, Fe2O3
Answer:
There are three types of oxides : Basic oxides, Acidic oxides and Amphoteric oxides.
| Basic oxides | Acidic oxides | Amphoteric oxides |
| CaO | CO2 | ZnO |
| MgO | SO3 | Al2O3 |
| Na2O | ||
| Fe2O3 |
Generally metal oxides are basic in nature.
Exception : Al2O3 and ZnO are amphoteric oxides.
Generally non-metal oxides are acidic in nature.
![]()
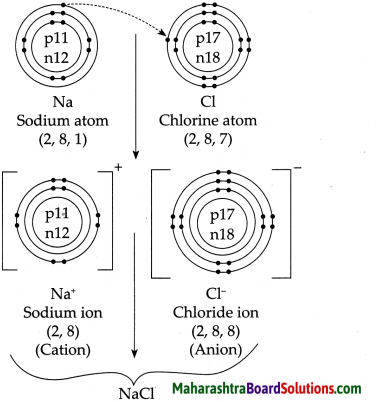
4. Explain by drawing a figure of the electronic configuration.
a. Formation of sodium chloride from sodium and chlorine.
Answer:
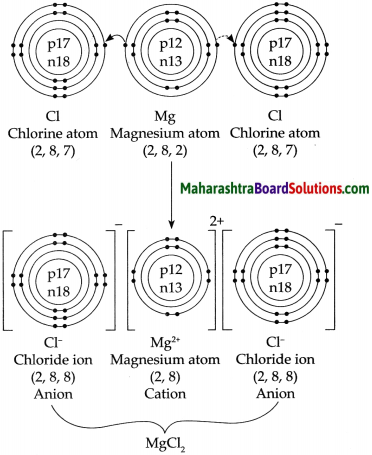
b. Formation of a magnesium chloride from magnesium and chlorine.
Answer:
5. Show the dissociation of the following compounds on dissolving in water, with the help of chemical equation and write whether the proportion of dissociation is small or large.
Hydrochloric acid, Sodium chloride, Potassium hydroxide, Ammonia, Acetic acid, Magnesium chloride, Copper sulphate.
Answer:
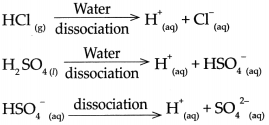
(a) Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- \(\mathrm{HCl}_{(g)} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }}>\mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+\mathrm{Cl}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
- Hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, as on dissolving in water, it dissociates almost completely and the resulting aqueous solution contains mainly H ions and the concerned acidic radical.
- The proportion of dissociation is large.
![]()
(b) Sodium chloride (NaC1)
- \(\mathrm{NaCl}_{(s)} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }}>\mathrm{Na}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+\mathrm{Cl}_{\text {(aq) }}^{-}\)
- When an ionic compound begins to dissolve in water, the water molecules push themselves in between the positive and negative ions of the compound and separate them from each other.
- The proportion of dissociation is large.
(c) Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- \(\mathrm{KOH}_{(n)} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }} \mathrm{K}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+\mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}\)
- Potassium hydroxide is a strong base, as on dissolving in water, it dissociates almost completely and the resulting aqueous solution contains mainly OH+ ions and the concerned basic radical.
- The proportion of dissociation is large.
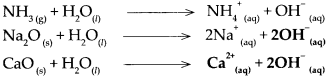
(d) Ammonia (NH3)
(i) \(\mathrm{NH}_{3(\mathrm{~g})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{n}}-\frac{\text { Water }}{\text { uissociation }}>\mathrm{NH}_{4 \text { (aq) }}^{+}+\mathrm{OH}_{\text {(aq) }}^{-}\)
(ii) Ammonia dissolves in water to form NH4OH (ammonium hydroxide). NH4OH does not dissociate completely as it is a weak base. The aqueous solution contains a small proportion of OH– ions and the concerned basic radical along with a large proportion of undissociated molecules of the base i.e. NH4OH.
(iii) The proportion of dissociation is small.
(e) Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH}_{(l)} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }} \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COO}_{(\text {aq) }}+\mathrm{H}_{(a z)}+{ }^{+}\)
- Acetic acid is a weak acid, on dissolving in water it does not dissociate completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains H+ ion and the concerned acidic radical in small proportion along with large proportion of the undissociated molecules of the acid.
- The proportion of dissociation is small.
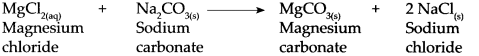
(f) Magnesium chloride (MgCl2)
- \(\mathrm{MgCl}_{2(\mathrm{~s})} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }}>\mathrm{Mg}^{2+} \text { (aq) }+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \text {(aq) }\)
- Magnesium chloride dissolves in water and forms magnesium ions and chloride ions. When an ionic compound begins to dissolve in water, the water molecules push themselves in between the ions of the compound and separate them from each other.
- The proportion of dissociation is large.
![]()
(g) Copper sulphate (CuSO4)
- \(\mathrm{CuSO}_{4(s)} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }}>\mathrm{Cu}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{2+}+\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\)
- When Copper sulphate is dissolved in water it forms copper ions and sulphate ions. When an ionic compound begins to dissolve in water, water molecules push themselves in between the ions of the compound and separate them from each other.
- The proportion of dissociation is large.
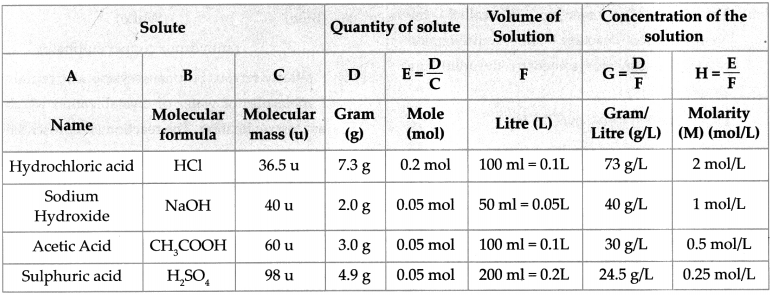
6. Write down the concentration of each of the following solutions in g/L and mol/L.
a. 7.3g HCl in 100ml solution
b. 2g NaOH in 50ml solution
c. 3g CH3COOH in 100ml solution
d. 4.9g H2SO4 in 200ml solution
Answer:
To find : The concentration in g/L.
Solution:
7. Obtain a sample of rainwater. Add to it a few drops of universal indicator. Meausre its pH. Describe the nature of the sample of rainwater and explain the effect if it has on the living world.
Answer:
- pH of rain water is 6.5 that means rain water is slightly acidic.
- When we add universal indicator to rain water it turns orangish red, indicating pH value is between 0 to 7, which tells us that rain water is acidic in nature.
- Most of the plants grow best when pH of soil is close to 7. If the soil is too acidic or too basic, it affects plant growth.
![]()
8. Answer the following questions.
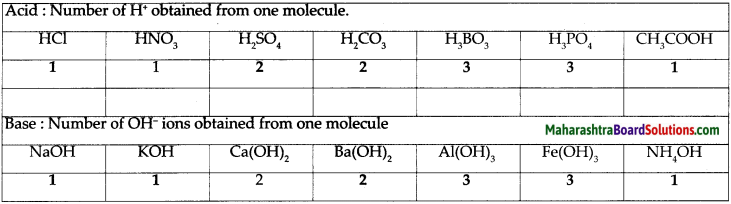
a. Classify the acids according to their basicity and give one example of each type.
Answer:
- Basicity of acids : The number of H+ ions obtainable by the dissociation of one molecule of an acid is called its basicity. The acids are classified as monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acids based on the number of H+ ions present.
- Examples of monobasic acid : HCl, HNO3, CH3COOH
- Examples of dibasic acid: H2SO4, H2CO3
- Examples of tribasic acid: H3BO3, H3PO4
b. What is meant by neutralization? Give two examples from everyday life of the neutralization reaction.
Answer:
- In neutralization reaction, an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
- In a neutralisation reaction the acid dissociates to form H+ ions and base dissociates to form OH ions.
- They combine to form H2O molecules which mixes with the solvent.
Examples in daily life:
- When people suffer from acidity, they take some antacids to neutralise the acid in their stomach.
- If an ant stings us the pain is due to formic acid. It is neutralised by rubbing moist baking soda which is basic in nature.
c. Explain what is meant by electrolysis of water. Write the electrode reactions and explain them.
Answer:
Electrolysis of water:
- Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas due to an electric current being passed through acidified water.
- Cathode reaction:
\(2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)}+2 \mathrm{e}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+2 \mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq}}\) - Anode reaction:
\(2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(l)} \longrightarrow \mathrm{O}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}+4 \mathrm{H}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+4 \mathrm{e}^{-}\) - It is found that the volume of gas formed near the cathode is double that of the gas formed near the anode.
- Hydrogen gas is formed near the cathode and oxygen gas near the anode.
- From this, it is clear that electrolysis of water has taken place and its constituent element have been released.
9. Give a reason for the following.
a. Hydronium ions are always in the form H3O+.
Answer:
- Acids in water gives H+ ions. These H+ ions do not exist freely in water.
- This is because H+ is a single proton, a hydrogen atom has only one proton and one electron.
- If the electron is removed to make H+, all that is left is an extremely tiny positively charged nucleus.
- This H ion will immediately combine with the surrounding water (H2O) molecules to form (H3O4) hydronium ion.
![]()
b. Buttermilk spoils if kept in a copper or brass container.
Answer:
- Buttermilk contains an organic acid called as lactic acid.
- The lactic acid reacts with copper and brass and forms toxic compounds which are not fit for consumption.
- They are harmful and may cause food poisoning.
- So it is not advisable to keep buttermilk in brass or copper containers.
10. Write the chemical equations for the following activities.
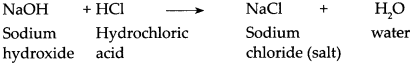
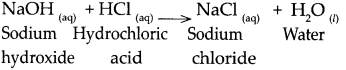
(a) NaOH solution was added to HCl solution.
Answer:
When NaOH reacts with HCl, it gives NaCl and water.
(b) Zinc dust was added to dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
When zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, it forms zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas is liberted.
![]()
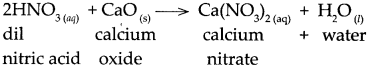
(c) Dilute nitric acid was added to calcium oxide.
Answer:
When dilute nitric acid reacts with calcium oxide, it forms calcium nitrate and water.
(e) Carbon dioxide gas was passed through KOH solution.
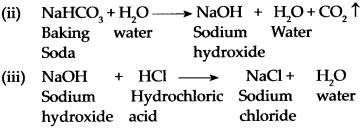
(f) Dilute HCl was poured on baking soda.
11. State the differences.
a. Acids and bases
Answer:
| Acids | Bases |
| (i) A substance which liberates H+ ions when dissolved in water is an acid (ii) Blue litmus turns red in an acid. (iii) The pH of an acid is less than 7. (iv) Acids are sour to taste (v) e.g. HCl, H2SO4 |
A substance which liberates OH– ions when dissolved in water is called a base. Red litmus turns blue in a base The pH of a base is greater than 7. Bases are bitter to taste, e.g. NaOH, KOH. |
b. Cation and anion
Answer:
| Cations | Anions |
| (i) Cations are ions with a net positive charge. | Anions are ions with a net negative charge. |
| (ii) Cations are generally formed by metals. When metals donate electrons, they have excess of protons, hence they form cations. | Anions are generally formed by non-metals. When non-metals accept electrons, they have excess of electrons, hence they form anions. |
| (iii) Cations are attracted towards the cathode which are negatively charged electrodes. | Anions are attracted towards the anode which are positively charged electrodes. |
| (iv) e.g.: Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ etc. | e.g.: O2 , S2-, Cl–, Br– etc. |
![]()
c. the Negative electrode and the positive electrode.
Answer:
| Negative Electrode | Positive Electrode |
| (i) Negatively charged electrodes are called as a cathode. | Positively charged electrodes are called as Anode. |
| (ii) Positively charged cations move towards the cathode or negative electrode. | Negatively charged anions move towards the anode or positive electrode. |
| (iii) Cathode accepts electrons from cations | Anode gives electrons to anions |
12. Classify aqueous solutions of the following substances according to their pH into three groups : 7, more than 7, less than 7.
Common salt, sodium acetate, hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide, potassium bromide, calcium hydroxide, ammonium chloride, vinegar, sodium carbonate, ammonia, sulphur dioxide.
Answer:
| pH = 7 | pH > 7 | pH < 7 |
| (a) common salt. | sodium acetate. | sulphur dioxide. |
| (b) potassium bromide. | sodium carbonate | hydrochloric acid. |
| (c) | ammonia. | carbon-dioxide. |
| (d) | calcium hydroxide. | ammonium chloride. |
| (e) | vinegar |
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
How are the following substances classified into three groups with the help of litmus?
Lemon, tamarind, baking soda, buttermilk, vinegar, orange, milk, lime, tomato, milk of magnesia, water, alum.
Answer:
| Basic Substance: Turns Red Litmus Blue | Acidic Substance: Turns Blue Litmus Red | Neutral Substance: No change in the colour of litmus |
| Baking Soda | Lemon | water |
| Lime | Tamarind | |
| Milk of Magnesia | Buttermilk | |
| Vinegar | ||
| Orange | ||
| Milk | ||
| Tomato | ||
| Alum |
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the columns in the part of the following table:
Answer:
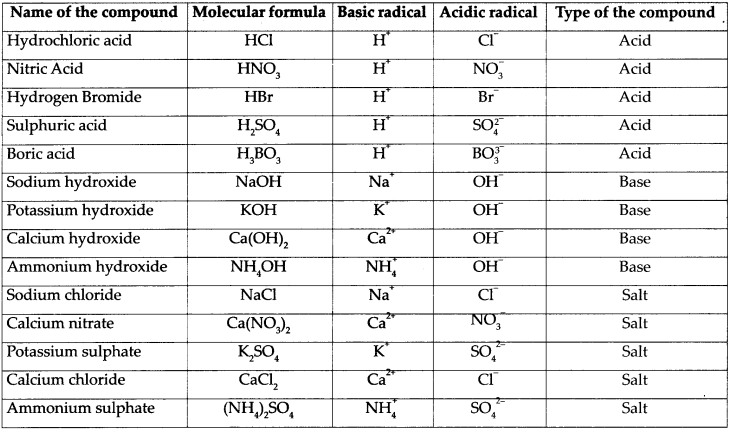
Question 3.
Complete the following table of the concentration of various aqueous solutions.
Answer:
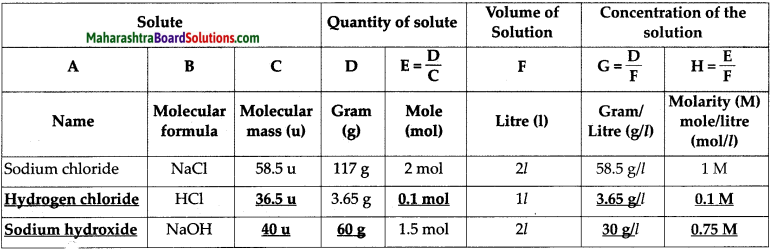
Question 4.
Complete the following table of neutralization reactions and also write down the names of the acids, bases and salts in it.
Answer:
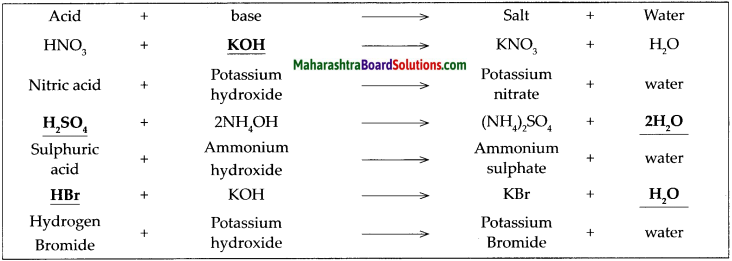
![]()
Question 5.
What are the names of the following compounds? NH3, Na2O, CaO.
Answer:
NH3 : Ammonia
Na2O : Sodium oxide
CaO : Calcium oxide
Question 6.
Into which type will you classify the above compounds, acid, base or salt?
Answer:
NH3 : base
Na2O : base
CaO : base
Question 7.
ive examples of monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acids.
Answer:
Monobasic acid examples: HNO3, HCl, CH3COOH
Dibasic acid examples: H2SO4, H2CO3
Tribasic acid examples: H3BO3, H3PO4
Question 8.
Give the three types of bases with their examples.
Answer:
Types of bases:
Monoacidic base examples : NaOH, KOH, NH4OH
Diacidic base examples: Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2
Triacidic base examples: A(OH)3, Fe(OH)3
Question 9.
What are the colours of the following natural and synthetic indicators in acidic and basic solutions? Litmus, turmeric, jamun, methyl orange, phenolphthalein?
Answer:
| Indicator | Colour in Acidic Solution | Colour in basic Solution |
| Litmus | Red | Blue |
| Turmeric | Yellow | Red |
| Jamun | Red | Blue-Green |
| Methyl orange | Red | Yellow |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | Pink |
![]()
Question 10.
On mixing the substances as shown here, what are the resulting mixtures formed by mixing the following substances called?
(a) Water and salt
(b) Water and sugar
(c) Water and sand
(d) Water and sawdust
Answer:
(a) Water and salt – Homogeneous mixture
(b) Water and sugar – Homogeneous mixture
(c) Water and sand – Heterogeneous mixture
(d) Water and sawdust – Heterogeneous mixture
Question 11.
What would be the definition of an acid and a base with reference to the neutralization reaction?
Answer:
- Acid: An acid is a substance which neutralises a base to form salt and water.
- Base: A base is a substance which neutralises an acid to form salt and water.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
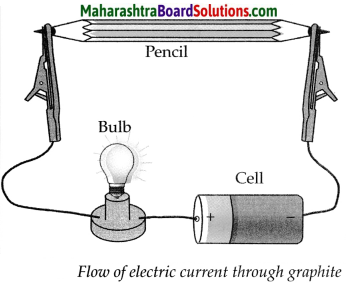
Take aqueous solution of sodium chloride, copper sulphate, glucose, urea, dil.H2SO4 and dil.NaOH in a beaker and test the electrical conductivity of the solutions. Answer the given below questions.
(a) With which solutions did the bulb glow?
Answer:
Solutions with which bulb glows: Aqueous solution of NaCl, CuSO4, H2SO4 and NaOH.
(b) Which solutions are electrical conductors?
Answer:
Solutions which are electrical conductors:
NaCl, CuSO4, H2SO4 and NaOH.
Question 2.
During electrolysis of copper sulphate, if electric current is passed through the electrolytic cell for a long time, what change would be seen at the anode?
Answer:
- When electricity is passed for a long time through copper sulphate solution, the following reaction is seen at the anode: Anode Reaction: Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e–
- All the copper atoms will get converted into copper ions and get deposited on the cathode. This process continues till the copper anode exists.
![]()
Question 3.
Would water be a good conductor of electricity?
Answer:
Pure water is not a good conductor of electricity.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
(i) With which solutions did the bulb glow?
(ii) Which solutions are electrical conductors?
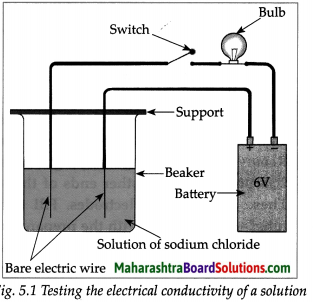
Answer:
(i) The bulbs glows when the wire are immersed in NaCl solution.
(ii)
| Solution | Results | |
| 1g Copper Sulphate Solution | Bulb glow | |
| 1g Glucose Solution | Bulb does not glow | |
| 1g Urea Solution | Bulb does not glow | |
| 5ml dil.H2SO4 Solution | Bulb glows | |
| 5ml dil. NaOH Solution | Bulb glows | |
Question 2.
What would be the definition of an acid and a base with reference to the neutralization reaction?
Answer:
- Acid: An acid is a substance which neutralises a base to form salt and water.
- Base: A base is a substance which neutralises an acid to form salt and water.
![]()
Question 3.
Dissolve 2g salt in 500ml pure water. Take 250 ml of this solution in a 500ml capacity beaker. Connect two electrical wires to the positive and negative terminals of a power supply. Remove the insulating cladding from about 2cm portions at the other ends of the wires. These are the two electrodes. Fill two test tubes upto the brim with the prepared dilute salt solution. Invert them on the electrodes without allowing any air to enter. Start the electric current under 6V potential difference from the power supply. Observe what happens in the test tubes after some time.
(a) Did you see the gas bubbles forming near the electrodes in the test tubes?
(b) Are these gases heavier or lighter than water?
(c) Are the volumes of the gases collected over the solution in the two test tubes the same or different?
(d) Test the solutions in the two test tubes with litmus paper, what do you see?
(e) Repeat the activity by using dilute H2SO4 as well as dilute NaOH as the electrolyte.
Answer:
(a) Yes, gas bubbles can be seen forming near the electrodes in the test tube.
(b) These gases are lighter than water.
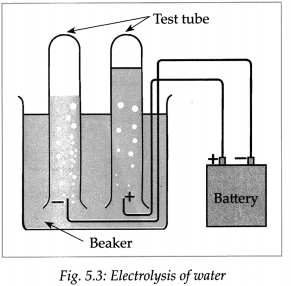
(c) The volumes of gases collected over the solution in the two test tubes are different.
(d) The solution in the cathode turns red litmus blue while solution in anode turns blue litmus red.
(e) When the above experiment is repeated with dil H2SO4 and dil NaOH, Hydrogen gas is liberated at cathodes and oxygen gas is liberated at anode.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Cut a lemon into two equal parts. Take the juice of each part into two separate beakers. Pour 10 ml of drinking water in one beaker and 20 ml in the second. Stir the solutions in both the beakers and taste them. Is there any difference in the tastes of the solutions in the two beakers? What is that difference?
Answer:
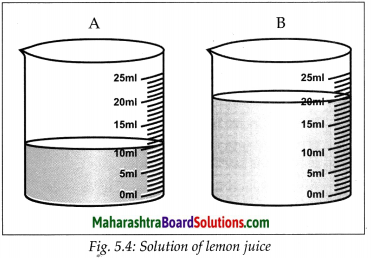
- In the above activity, the sour taste of the solutions is because of the solute, lemon juice in them.
- The quantity of the lemon juice is the same in both the solutions. Yet their tastes are different.
- The solution in the first beaker is more sour than the one in the second.
- Although the quantity of the solute is the same in both the solutions, the quantity of the solvent is different.
- Ratio of the quantity of the solute to the quantity of the resulting solution is different. This ratio is larger for the solution in the first beaker and therefore that solution tastes more sour.
- On the other hand, the proportion of the lemon juice in the total solution in the second beaker is smaller and taste is less sour.
- The taste of foodstuff depends upon the nature of the taste-giving ingredient and its proportions in the foodstuff.
- Similarly, all the properties of a solution depend on the nature of the solute and solvent and also on the proportion of the solute in a solution
- The proportions of a solute in a solution is called the concentration of the solute in the solution.
![]()
Question 2.
Take a big test tube. Choose a rubber stopper in which a gas tube can be fitted. Take a few pieces of magnesium ribbon in the test tube and add some dilute HCl to it. Take a lighted candle near the end of the gas tube and observe. What did you observe?
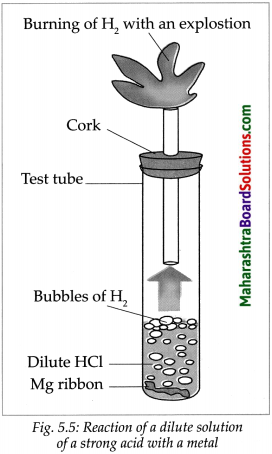
Answer:
- Magnesium metal reacts with dilute HCl and an inflammable gas, hydrogen, is formed.
- During this reaction, the reactive metal displaces hydrogen from the acid to release hydrogen gas.
- At the same time, the metal is converted into basic radical which combines with the acidic radical from the acid to form the salt.
\(\mathrm{Mg}_{(\mathrm{s})}+2 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq}) \longrightarrow} \underset{\rightarrow}{\mathrm{MgCl}_{2(\mathrm{aq})}}+\mathrm{H}_{2(\mathrm{~g})}\)
Question 3.
Take some water in a test tube and add a little red oxide (the primer used before painting iron articles) to it. Now add a small quantity of dilute HCl to it, shake the test tube and observe.
(a) Does the red oxide dissolve in water?
(b) What change takes place in the particles of red oxide on adding dilute HCl?
Answer:
(a) The chemical formula of red oxide is Fe2O3. It is insoluble in water.
(b) The water-insoluble red oxide reacts with HCl to produce a water-soluble salt FeCl3.
- This gives a yellowish colour to the water.
- The following chemical equation can be written for this chemical change.
\(\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3(\mathrm{~s})}+6 \mathrm{HCl}_{(\mathrm{aq})} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{3(\mathrm{aq})}+3 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})}\)
![]()
Question 4.
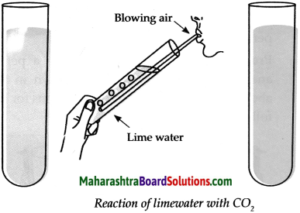
Fit a bent tube in a rubber cork. Take some lime water in a test tube and keep it handy. Take some baking soda in another test tube and add some lemon juice to it. Immediately fit the bent tube over it. Insert its other end into the lime water. Note down your observations of both the test tubes. Repeat the procedure using washing soda, vinegar and dilute HC1 properly. What do you see?
Answer:
- In this activity, when limewater comes in contact with the gas released in the form of an effervescence, it turns milky.
- This is a chemical test for carbon dioxide gas.
- When lime water turns milky, we infer that the effervescence is of CO2.
- This gas is produced on the reaction of acids with carbonate and bicarbonate salts of metals.
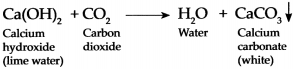
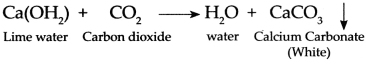
- A precipitate of CaCO3 is produced on its reaction with the lime water Ca(OH)2.
- This reaction can be represented by the following chemical equation.
\(\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_{2(\mathrm{aq})}+\mathrm{CO}_{2(\mathrm{~g})} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CaCO}_{3(\mathrm{~s})}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{(\mathrm{l})}\) - Washing soda is sodium carbonate Na2CO3. It will react same as baking soda (NaHCO3).
- Vinegar and HCl are acids, they do not react chemically with lemon juice.
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 Acids, Bases and Salts Additional Important Questions and Answers
Select the correct option
Question 1.
…………………. acid is present in lemon.
(a) malic acid
(b) tartaric acid
(c) citric acid
(d) butyric acid
Answer:
(c) Citric acid
Question 2.
Tamarind contains …………………. acid.
(a) Lactic acid
(b) tartaric acid
(c) matlic acid
(d) butyric acid
Answer:
(b) tartaric
Question 3.
Butter milk contains …………………. acid.
(a) butyric acid
(b) Lactic acid
(c) matlic acid
(d) citric acid
Answer:
(a) Butyricacid
![]()
Question 4.
If the basic radical is H+ the type of compound is ………………… .
(a) neutral
(b) base
(c) acid
(d) alkali
Answer:
(c) Acid
Question 5.
The name of compound NH3 is ………………… .
(a) nitric acid
(b) ammonium
(c) nitride
(d) ammonia
Answer:
(b) ammonia
Question 6.
The bases which are soluble in water are called as ………………… .
(a) indicators
(b) acids
(c) alkalis
(d) salts
Answer:
(c) alkalis
Question 7.
H3PO4 is a …………………. acid.
(a) monobasic
(b) tribasic
(c) tetrabasic
(d) dibasic
Answer:
(b) tribasic
Question 8.
According to pH scale pure water has a pH of ………………… .
(a) 6
(b) 7
(c) 5
(d) 8
Answer:
(b) 7
![]()
Question 9.
With reference to neutralization, metallic oxides are ………………… in nature.
(a) basic
(b) neutral
(c) acidic
(d) saline
Answer:
(a) basic
Question 10.
Molecular formula of blue vitriol is ………………… .
(a) CuSO3 5H2O
(b) CuSO4 4H2O
(c) CUSO3 4H2O
(d) CUSO4 5H2O
Answer:
(d) CUSO4 5H2O
Question 11.
Molecular formula of crystalline alum is ………………… .
(a) KSO4, AISO4, 24H2O
(b) K2SO4, ALSO4, 24H2O
(c) K2SO4, AL2(SO4)3, 24H2O
(d) KSO4, Al2(SO4)3, 24H2O
Answer:
(c) K2SO4, AL2(SO4)3, 24H2O
Question 12.
Molecular formula for sodium oxide is ………………… .
(a) Na2O
(b) NaO2
(c) NaO
(d) Na2O2
Answer:
(a) Na2O
Question 13.
H2CO3 is …………………. acid.
(a) monobasic
(b) dibasic
(c) tribasic
(d) tetrabasic
Answer:
(b) dibasic
![]()
Question 14.
Molecular formula of Red oxide is ………………… .
(a) Fe2O3
(b) CuO
(c) Fe3O4
(d) Na2O
Answer:
(a) Fe2O3
Question 15.
The positive terminal electrode is called as ………………… .
(a) anode
(b) cathode
(c) anion
(d) cation
Answer:
(a) anode
Question 16.
…………………. produced in stomach helps in digestion.
(a) Hydrochloric acid
(b) Oxalic acid
(c) Sulphuric acid
(d) Nitric acid?
Answer:
(a) Hydrochloric acid
Question 17.
The solution turns blue litmus red, its pH is likely to be ………………… .
(a) 7
(b) 4
(c) 14
(d) 9
Answer:
(b) 4
![]()
Question 18.
An ionic compound NaCl is formed by ………………… .
(a) Na+ and Cl–
(b) Na+ and Cl+
(c) Na– and Cl–
(d) Na– and Cl+
Answer:
(a) Na+ and Cl–
Question 19.
pH of strong acid is ………………… .
(a) 0
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 14
Answer:
(a) 0
Question 20.
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O is a …………………. reaction.
(a) neutralization
(b) crystallisation
(c) electrolysis
(d) dissociation
Answer:
(a) neutralization
Question 21.
Adding water to acid is an …………………. reaction.
(a) endothermic
(b) exothermic
(c) neutralisation
(d) crystallisation
Answer:
(b) exothermic
Find the odd one out:
(a) Rose Petal, Turmeric, Phenolphthalein, Indigo.
Answer:
Phenolphthalein is odd one out as rest are natural indicators while phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator.
![]()
(b) Lime water, Vinegar, Acetic acid, Tartaric acid.
Answer:
Lime water is odd one out as this is basic in nature while rest are acidic.
(c) NaHCO3, HCl, H2SO4, HNO3
Answer:
NaHCO3 is odd one out as it is base while rest are acids.
(d) Oxalic acid, Nitric acid, Citric acid, acetic acid.
Answer:
Nitric acid is odd one out as others are weak acids while Nitric acid is a strong acid.
(e) Crystalline, Liquid, Gases, Solid.
Answer:
Crystalline is odd one out as this is nature of a compound while others are physical states of compounds.
(f) Ca(OH)2, Mg (OH)2, NaOH, NH4OH.
Answer:
NaOH is odd one out even though all are bases but NaOH is highly soluble in water compared to others.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Name the three types of ionic compounds.
Answer:
The three types of ionic compounds are acids, bases and salts.
Question 2.
Name the two constituents of molecule of an ionic compound.
Answer:
- Cation (positive ion/ basic radical)
- Anion (negative ion/acidic radical).
Question 3.
Name any three acids with their molecular formula.
Answer:
- Hydrochloric acid – HC1
- Sulphuric acid – H2SO4
- Nitric acid – HNO3
![]()
Question 4.
Name any three bases with their molecular formula.
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide – NaOH
- Potassium hydroxide – KOH
- Calcium hydroxide – Ca(OH)2
Question 5.
Name any three salts with their molecular formula.
Answer:
- Sodium chloride – NaCl
- Potassium sulphate – K2 SO4
- Calcium chloride – CaCl2
Question 6.
Name any two strong acids.
Answer:
- Hydrochloric acid – HC1
- Sulphuric acid – H2 SO4
Question 7.
Name any two weak acids.
Answer:
- Acetic acid – CH3 COOH
- Carbonic acid – H2 CO3
Question 8.
Name any two strong bases.
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide – NaOH
- Potassium hydroxide – KOH
![]()
Question 9.
Name a weak base.
Answer:
Ammonium hydroxide – NH4OH
Question 10.
Name any two alkalis.
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide – NaOH
- Potassium hydroxide – KOH
Question 11.
Name any two acids with their basicity 1 (monobasic)
Answer:
- Hydrochloric acid – HC1
- Nitric acid – HNO3
Question 12.
Name any two acids with their basicity 2 (dibasic)
Answer:
- Sulphuric acid – H2 SO4
- Carbonic acid – H2CO3
Question 13.
Name any two acids with their basicity 3 (tribasic)
Answer:
- Boric acid – H3BO3
- Phosphoric acid – H3PO4
Question 14.
Name any two bases with their acidity 1 (monoacidic)
Answer:
- Sodium hydroxide – NaOH
- Potassium hydroxide – KOH
![]()
Question 15.
Name any two bases with their acidity 2 (diacidic)
Answer:
- Calcium hydroxide – Ca(OH)2
- Barium hydroxide – Ba(OH)2
Question 16.
Name any two bases with their acidity 3 (triacidic)
Answer:
- Aluminium hydroxide – Al(OH)3
- Ferric hydroxide – Fe(OH)3
Question 17.
Name the two units to express the concentration of the solution.
Answer:
- mass of solute in grams dissolved in one litre of the solution grams per litre, (g/L).
- Number of moles of the solute dissolved in one litre of the solution. Molarity (M) of the solution.
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) HNO3 (2) H3PO4 (3) CH3COOH (4) H2CO3 |
(a) Acetic acid (b) Carbonic acid (c) Phosphoric acid (d) Nitric acid |
Answer:
(1-d),
(2- c),
(3 – a),
(4 – b)
![]()
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) NH4OH (2) Ca(OH)2 (3) Al(OH)3 (4) Ba(OH)2 |
(a) Aluminium Hydroxide (b) Barium Hydroxide (c) Calcium Hydroxide (d) Ammonium Hydroxide |
Answer:
(1-d),
(2- c),
(3 – a),
(4 – b)
Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ Solution | Column ‘B’ pH | ||
| (1) | Milk | (a) | 0 |
| (2) | Milk of Magnesia | (b) | 14 |
| (3) | 1 M HCl | (c) | 10.5 |
| (4) | 1 M NaOH | (d) | 6.5 |
Answer:
(1-d),
(2- c),
(3 – a),
(4 – b)
![]()
Question 4.
| Column ‘A’ | Column’B’ |
| (1) Urine (2) Apples (3) Orange (4) Butter |
(a) Butyric acid (b) Uric acid (c) Malic acid (d) Citric acid |
Answer:
(1 – b),
(2 – c),
(3 – d),
(4 – a)
Question 5.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Crystalline blue vitriol (2) Crystalline green vitriol (3) Crystalline (4) washing soda Crystalline alum |
(a) FeS04-7H20 (b) K2S04-A12(S04)3.24H20 (c) CuS04-5H20 (d) Na2CO310H2O |
Answer:
(1-c),
(2- a),
(3 – d),
(4 – b)
![]()
State whether the following statements are true or false and if false. Correct the false statement:
(1) The separation of H and CI in HCI is in absence of water.
(2) \(\mathrm{NaOH}_{(\mathrm{s})} \frac{\text { Water }}{\text { dissociation }}>\mathrm{Na}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{+}+\mathrm{OH}_{(\mathrm{aq})}^{-}\)
(3) H2SO4 is a strong acid.
(4) NaC1 is an ionic compound.
(5) Turmeric is synthetic indicator.
(6) Metal + Dilute acid forms salt and water.
(7) Copper oxide is called red primer.
(8) Oxide of non-metal + Acid → Salt + Water.
(9) Zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium zincate.
(10) Al2O3 is an amphoteric oxide.
(11) Blue vitriol ZnSO4. 7H2O.
(12) Molecular formula for crystalline Ferrous sulphate is Fe5O4. 5H2O.
(13) NaCl in water does not conduct electricity.
(14) Phenolphthalein is colourless in base.
Answer:
(1) False. The separation of H+ and Cl– in HC1 is in presence of water.
(2) True
(3) True
(4) True
(5) False. Turmeric is a natural indicator.
(6) False. Metal + Dilute acid forms salt and hydrogen gas.
(7) False. Iron oxide is called red primer.
(8) False. Oxide of izan-metal + Base → Salt + Wafer.
(9) True
(10) True
(11) False. Blue Vitriol is CuSO4. 5H2O.
(12) False. Molecular formula for crystalline Ferrous sulphate is FeSO4. 7H2O.
(13) False. NaCl in water conducts electricity.
(14) False, Phenolphthalein is colourless in acid and pink in base.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Acid
Answer:
An acid is a substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to H ion as the only cation. For example, HC1, H2 SO4, H2CO3.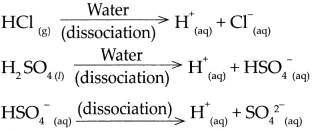
Question 2.
Base
Answer:
A base is a substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to the OW ion as the only anion. For, NaOH, Ca(OH)2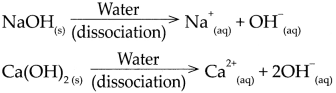
![]()
Question 3.
Strong Acid
Answer:
On dissolving in water, a strong acid dissociates almost completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains mainly H ions and the concerned acidic radical. e.g. HC1, HBr, HNO3, H2SO4.
Question 4.
Weak Acid
Answer:
On dissolving in water a weak acid does not dissociate completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains H+ ion and the concerned acidic radical in small proportion along with large proportion of the undissociated molecules of the acid, e.g., H2CO3 (Carbonic acid), CH3COOH (Acetic acid)
Question 5.
Strong Base
Answer:
On dissolving in water, a strong base dissociates almost completely and the resulting aqueous solution contains mainly OH ions and the concerned basic radicals, e.g. NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2, Na2O.
Question 6.
Weak Base
Answer:
On dissolving in water, a weak base does not dissociate completely and the resulting aqueous solution contains a small proportion of OH ions and the concerned basic radical along with a large proportion of undissociated molecules of the base. e.g. NH4 OH.
Question 7.
Alkali
Answer:
The bases which are highly soluble in water are called alkali, e.g. NaOH, KOH, NH3. Here, NaOH and KOH are strong alkalis while NH3 is a weak alkali.
Question 8.
Basicity of acids
Answer:
The number of H+ ions obtainable by the dissociation of one molecule of an acid is called its basicity.
![]()
Question 9.
Acidity of bases
Answer:
The number of OH ions obtainable by the dissociation of one molecule of a base is called its acidity.
Question 10.
Concentration of solute in the solution.
Answer:
The proportion of a solute in a solution is called the concentration of the solute in the solution.
Question 11.
Concentrated solution.
Answer:
When the concentration of a solute in its solution is high, it is a concentrated solution.
Question 12.
Dilute solution
Answer:
When the concentration of a solute in its solution is low, it is a dilute solution.
Question 13.
Neutralization
Answer:
A reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water is called a neutalization reaction.
NaOH + HC1 → NaCl + H2O
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
Question 14.
Cathode
Answer:
The electrode connected to the negative terminal of a battery by means of a conducting wire is called a cathode.
![]()
Question 15.
Anode
Answer:
The electrode connected to the positive terminal of a battery by means of a conducting wire is called an anode.
Question 16.
Cations
Answer:
Cations are positively charged ions which are attracted towards negative electrode (cathode) when electricity is passed into a solution of an ionic compound.
Question 17.
Anions
Answer:
Anions are negatively charged ions which are attracted towards the positive electrode (anode) when electricity is passed into a solution of an ionic compound.
Question 18.
Electrolytic cell
Answer:
An assembly that consists of a container with an electrolyte and the electrodes dipped in it, is called an electrolytic cell.
Question 19.
Molarity of a solution
Answer:
The number of moles of the solute dissolved in one litre of the solution is called the molarity of that solution. The molarity of a solute is indicated by writing its molecular formula inside a square bracket for example [NaCl] = 1
Question 20.
Acid – base indicators
Answer:
Some natural and synthetic dyes show two different colours in acidic and basic solution, and such dyes are acid base indicators.
Explain the following chemical reactions with the help of balanced equations:
Question 1.
Magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas is liberated.
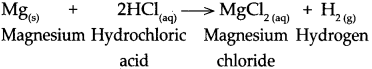
![]()
Question 2.
When copper reacts with nitric acid.
Answer:
When copper reacts with nitric acid, it forms copper nitrate and hydrogen gas is liberated.
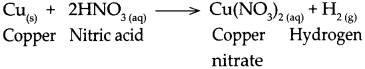
Question 3.
When ferric oxide reacts with diluted hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When Ferric oxide reacts with diluted hydrochloric acid, it forms ferric chloride and water.
Question 4.
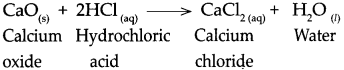
When calcium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When calcium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms calcium chloride and water.
Question 5.
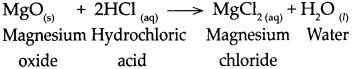
When Magnesium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When magnesium oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms magnesium chloride and water.
Question 6.
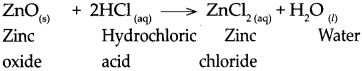
When zinc oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When zinc oxide reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms zinc chloride and water.
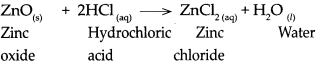
Question 7.
When aluminium oxide reacts with hydrogen fluoride
Answer:
When aluminium oxide reacts with hydrogen fluoride, it forms Aluminium fluoride arid water.
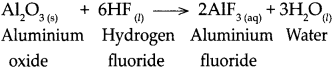
![]()
Question 8.
When carbon dioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
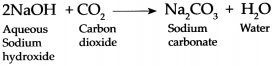
Answer:
When carbon dioxide reacts with Sodium hydroxide, it forms Sodium carbonate and water.
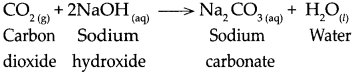
Question 9.
When carbon dioxide reacts with potassium hydroxide.
Answer:
When carbon dioxide reacts with potassium hydroxide, it forms potassium carbonate and water.
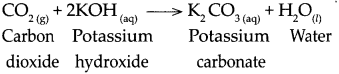
Question 10.
When sulphur trioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
When sulphur trioxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it forms sodium sulphate and water.
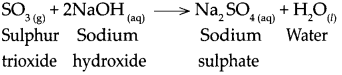
Question 11.
When calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide.
Answer:
When calcium hydroxide reacts with carbon dioxide, it forms calcium carbonate and water.
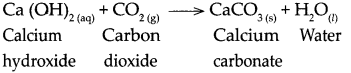
Question 12.
When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When sodium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, it forms sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and water.

Question 13.
When sodium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid.
Answer:
When sodium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid, it forms sodium sulphate, carbon dioxide and water.
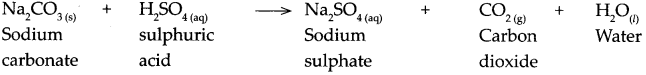
![]()
Question 14.
When calcium carbonate reacts with nitric acid.
Answer:
When calcium carbonate reacts with nitric acid, it forms calcium nitrate, carbon dioxide and water.

Question 15.
When potassium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid.
Answer:
When potassium carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid, it forms potassium sulphate, carbon dioxide and water.
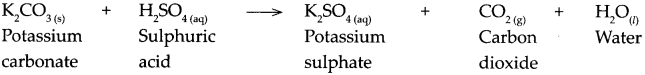
Question 16.
When sodium bicarbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid. OR Dilute HC1 was poured on baking soda
Answer:
When sodium bicarbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, it forms sodium chloride, carbon dioxide and water.

Question 17.
When potassium bicarbonate reacts with nitric acid.
Answer:
When potassium bicarbonate reacts with nitric acid, it forms potassium nitrate, carbon dioxide and water.

Question 18.
When sodium bicarbonate reacts with acetic acid.
Answer:
When sodium bicarbonate reacts with acetic acid, it forms sodium acetate, carbon dioxide and water.
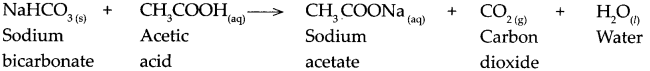
![]()
Question 19.
When copper sulphate is heated.
Answer:
When copper sulphate is heated it loses it’s water of crystallization to form white anhydrous copper sulphate.
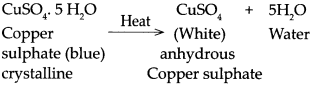
Question 20.
When Ferrous sulphate is heated.
Answer:
When ferrous sulphate is heated it loses its water of crystallization to form white anhydrous ferrous sulphate.
![]()
![]()
Q.2. (B)-3. Complete the following table.
Question 1.
Complete the following table.
Answer:
Complete the following reactions.
Question 1.
Answer:
Question 2.
Metal + Dilute acid → Salt + Hydrogen
Answer:
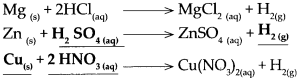
![]()
Question 3.
Metal oxide + Dilute acid → SaIt + Water
Answer:
![]()
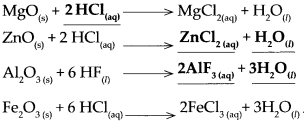
Question 4.
Oxide of non-metal + base → salt + water
Answer:
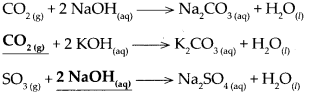
Question 5.
Carbonate salt of metal + dilute acid → Another salt of metal + Carbon dioxide + water
Answer:
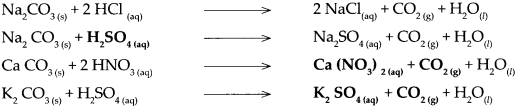
Question 6.
Bicarbonate salt of metal + dilute acid → Another salt of metal + carbon dioxide + water
Answer:

Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Ionic compound NaCl has very high stability.
Answer:
- The outermost shell of both Na+ and Cl– ions is a complete octet.
- An electronic configuration with a complete octet indicates a stable state.
- A molecule of NaCl has Na+ and Cl– ions. An ionic bond is formed between these ions.
- The force of attraction between them is very strong as it is formed between the oppositely charged Na+ and Cl– ions.
- Therefore NaCl, an ionic compound has very high stability.
![]()
Question 2.
Ionic compound dissociates while forming an aqueous solution.
Answer:
- On dissolving in water, an ionic compound forms an aqueous solution.
- In the solid state, the oppositely charged ions in the ionic compound are sitting side by side.
- When an ionic compound being to dissolve in water, the water molecules push themselves in between the ions of the compound and it separates them from each other, that is to say, an ionic compound dissociates while forming an aqueous solution.
Question 3.
Blue coloured copper sulphate crystals become colourless on heating.
Answer:
- Copper sulphate crystals are blue in colour and crystalline in form due to presence of water of crystallisation.
- Each molecule of crystalline copper sulphate contains five molecules of water of crystallisation (CuSO4.5H2O).
- On heating, the copper sulphate crystals lose the water of crystallisation and turns into white amorphous powder called as anhydrous copper sulphate.
- Therefore, blue coloured copper sulphate crystals become colourless on heating.
Question 4.
During electrolysis of water, a few drops of sulphuric acid are added to it.
Answer:
- Pure water is a covalent compound and hence it is a non-electrolyte and does not conduct electricity.
- When a few drops of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) are added to water.
- Being a strong acid it dissociates almost completely in its solution forming H+ cations and \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}\) anions.
- The movement of these ions in the solution towards the respective electrodes amount to the conduction of electricity through the solution.
- Therefore, during electrolysis of water, a few drops of sulphuric acid are added to it.
Question 5.
Glucose is a non-electrolyte.
Answer:
- Glucose is a covalent compound
- It does not form any ions in its aqueous solution.
- Due to this aqueous solution of glucose does not conduct electronic current.
- Hence, glucose is a non-electrolyte.
![]()
Question 6.
Pure water is a poor conductor of electricity but aqueous solution of sodium chloride conducts electricity.
Answer:
- Pure water does not contain any free ions.
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) is an ionic compound made up of sodium cation (Na+) and chloride anion (Cl)
- When sodium chloride is dissolved in water , these ions dissociates in its aqueous solution. ‘
- These ions are free to move in the solution and conduct electricity.
- Therefore, pure water is a poor conductor of electricity but aqueous solution of sodium Chloride conducts electricity.
Question 7.
When carbon dioxide gas is passed through freshly prepared lime water, the limewater turns milky.
Answer:
- Limewater traditionally means a weak solution of the alkali calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2.
- When CO2 is passed through limewater, it reacts with calcium hydroxide to form insoluble particulates (precipitate of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- Calcium carbonate is weak basic salt and this gives a milky white precipitate.
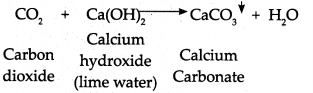
- Hence, lime water turns milky when CO2 gas is passed through it.
Q.3.1. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Write down chemical equations for
(a) Zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide
(b) Aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
(a) When zinc oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it forms sodium zincate and water
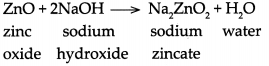
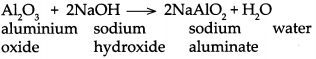
(b) When Aluminium oxide reacts with sodium hydroxide, it forms sodium aluminate and water.
Question 2.
Can we call Al2O3 and ZnO acidic oxides on the basis of above reactions.
Answer:
- No, because they also react with acids to form their respective salts and water.
- So, they show the properties of basic oxides also.
![]()
Question 3.
Define ‘amphoteric oxides’ and give two examples.
Answer:
- Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which react with both adds as well as bases to form their respective salts and water.
- Amphoteric oxides show the properties of both acidic oxides as well as basic oxides. ZnO and Al2 O3 are amphoteric oxides.?
Question 4.
Take a solution of 1g copper sulphate in 50ml water in a 100 ml capacity beaker. Use a thick plate of copper as anode and a carbon rod as cathode. Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure and pass an electric current through the circuit for some time. Do you see any changes?
Answer:
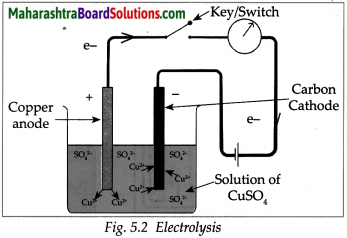
- A thin film of copper metal is deposited on cathode which is immersed in solution. There is no change in colour of solution
- The electrons from cathode combines with Cu2+ ion from the solution forming Cu atoms which were then deposited on the cathode.
Q.3.5. Answer in brief:
Question 1.
What are acids, bases and salts?
Answer:
- Compounds having H+ as the basic radical in their molecules are called Acids.
- Compounds having OH– as the acidic radical in their molecule are called Bases.
- Ionic compounds which have a basic radical other than H+ and an acidic radical other than OH– are called salts.
Question 2.
What is an ionic bond?
Answer:
- The molecule of an ionic compound has two constituents namely cation (positive ion / basic radical) and anion (negative ion / acidic radical).
- There is a force of attraction between these ions as they are oppositely charged, and that is called the ionic bond.
- The force of attraction between one positive charge on a cation and one negative charge on an anion makes one ionic bond.
![]()
Question 3.
Give examples to show that proportions of H+ and OH– ions in aqueous solution determines the properties of those solutions.
Answer:
The examples to show that proportions of H+ and OH– ions in aqueous solution determines the properties of those solutions are :
- The proportions of H+ and OH ions divides soil into the acidic, neutral and basic, types of soil.
- It is necessary for blood, cell sap etc to have H+ and OH– ions in certain definite proportions for their proper functioning.
- Fermentation carried out with the help of micro-organisms, other biochemical processes and also many chemical processes require the proportion of H+ and OH– ions to be maintained within certain limits.
Question 4.
What is pH scale?
Answer:
- In 1909, the Danish scientist Sorensen introduced a convenient new scale of expressing H+ ion concentration which is found to be useful in chemical and biochemical processes.
- It is the pH scale (pH: power of hydrogen). The pH scale extends from 0 to 14. According to this scale pure water has a pH of 7. pH 7 indicates a neutral solution. This pH is the midpoint of the scale.
- The pH of an acidic solution is less than 7 and?
Question 5.
Give the pH of following solutions.
Answer:
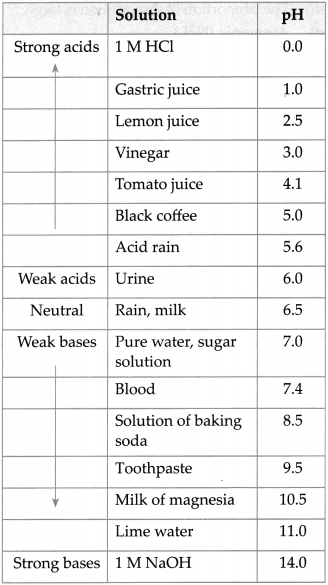
![]()
Question 6.
What is universal indicator? Which is the most accurate method of measuring the pH of a solution?
Answer:
- In the pH scale, the pH of solutions varies from 0 to 14 in accordance with the strength of the acid or base.
- To show these variations in pH, a universal indicator is used.
- A universal indicator shows different colours at different values of pH. A universal indicator is made by mixing several synthetic indicators in specific proportions.
- The pH of a solution can be determined by means of a universal indicator solution or the pH paper made from it.
- However, the most accurate method of measuring the pH of a solution is to use an electrical instrument called pH meter.
- In this method, pH is measured by dipping electrodes into the solution.
Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases.
Answer:
The Swedish scientist Arrhenius put forth a theory of acids and bases in the year 1887. This theory gives definitions of acids and bases as follows:
Acid : An acid is a substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to H ion as the only cation. For example, HCl, H2SO4, H2CO3
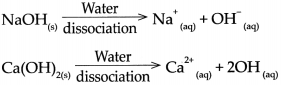
Base: Abase is a substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to the OH ion as the only anion, For example, NaOH, Ca(OH)2
Question 2.
Write a short note on Neutralization.
Answer:
- Take 10 ml of dilute HCl in a beaker, go on adding dilute NaOH drop by drop and record the pH.
- Stop adding the NaOH when the green colour appears on the pH paper, that is when the pH of solution becomes 7.
- Both HCl and NaOH dissociate in their aqueous solutions.

- Addition of NaOH to HCl solution is like adding a large concentration of OH ions to a large concentration of H+ ions.
- However water dissociates into H+ and OH ions to a very small extent.
- Therefore on mixing the excess OH– ions combines with excess H+ ions and forms H2O molecules which mix with solvent water.
- This change can be represented by the ionic equation shown as follows. H+ + Cl– + Na+ + OH– → Na+ + Cl– + H2O
- It can be observed that Na+ and CT ions are there on both the sides. Therefore the net ionic reaction is H+ + OH– → H2O
- As NaOH solution is added drop by drop to the HCl solution, the concentration of ff goes on decreasing due to combination with added OH ions, and that is how the pH goes on increasing.
- When enough NaOH is added to HCl, the resulting aqueous solution contains only Na+ and Cl– ions, that is, NaCl, a salt, and the solvent water. The only source of H+ and OH– ions in this solution is a dissociation of water.
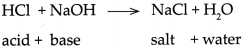
- Therefore, this reaction is called the Neutralization reaction. The Neutralization reaction is also represented by the following simple equation.
Question 3.
Explain the water of Crystallization.
Answer:
- Take some crystals of blue vitriol (CuSO4. 5H2O) in a test tube. Heat the test tube on a low flame of a burner.
- It was observed that on heating, the crystalline structure of blue vitriol broke down to form a colourless powder and water came out.
- This water was part of the crystal structure of blue vitriol. It is called water of crystallization.
- On adding water to the white powder a solution
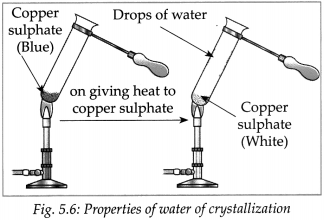
was formed which had the same colour as the solution in the first test tube. - From this we come to know that no chemical change has occurred in the crystals of blue vitriol due to heating.
- Losing water on heating blue vitriol, breaking down of the crystal structure, losing blue colour and regaining blue colour on adding water are all physical changes.
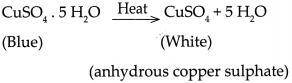
- Similarly, ferrous Sulphate crystals also contain 7 molecules of water of crystallization which are lost on heating.
- The reaction is represented as
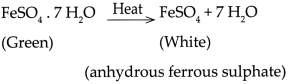
- Ionic compounds are crystalline in nature. These crystals are formed as a result of definite arrangement of ions.
- In the crystals of some compounds, water molecules are also included in this arrangement.
- That is the water of crystallization. The water of crystallization is present in a definite proportion of the chemical formula of the compound.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the conduction of electricity through solutions of ionic compounds
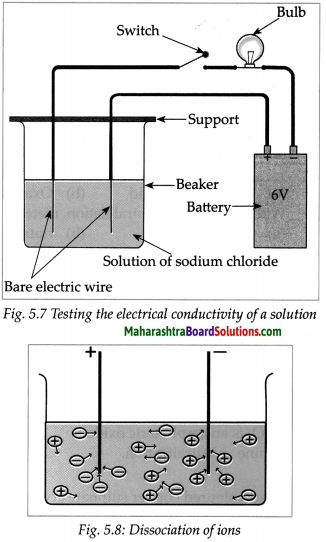
Answer:
- Electrons conduct electricity through electrical wires, and ions conduct electricity through a liquid or a solution.
- Electrons leave the battery at the negative terminal, complete the electric circuit and enter the battery at the positive terminal.
- When there is a liquid or a solution in the circuit, two rods, wires or plates are immersed in it. These are called electrodes.
- Electrodes are made of conducting solid. The electrode connected to negative terminal of a battery by means of a conducting wire is called a cathode and the electrode connected to the positive terminal of a battery is called anode.
- We have seen that salts, strong acids and strong bases dissociates almost completely in their aqueous solutions.
- Therefore the aqueous solutions of all these three contain large number of cations and anions.
- A characteristic of liquid state is the mobility of its particles. Due to its mobility the positive charged ions of the solution are attracted to the negative electrode or cathode.
- On the other hand, the negative charged ions of the solution are attracted to the positive electrode or anode.
- The movement of ions in the solution towards the respective electrodes accounts to the conduction of electricity through the solution.
- From this we can understand that those liquids or solutions which contain a large number of dissociated ions conduct electricity.

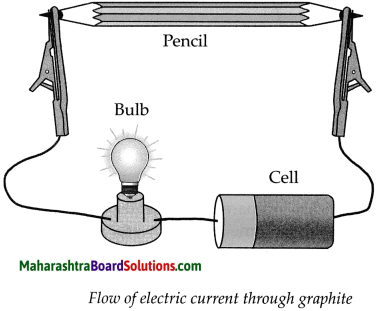
9th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- Laws of Motion Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Work and Energy Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Current Electricity Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Measurement of Matter Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Acids, Bases and Salts Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Classification of Plants Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Energy Flow in an Ecosystem Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Useful and Harmful Microbes Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Environmental Management Class 9 Questions And Answers
- Information Communication Technology (ICT) Class 9 Questions And Answers