Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Aksharbharati Chapter 3 शाल Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 10th Marathi Aksharbharati Chapter 3 शाल Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 3 Question Answer
Marathi Aksharbharati Std 10 Digest Chapter 3 शाल Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न 1.
उत्तरे लिहा.
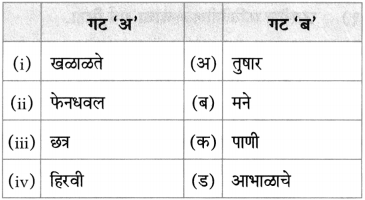
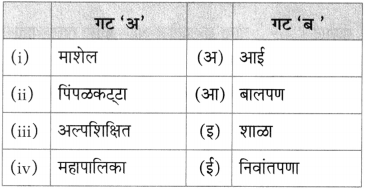
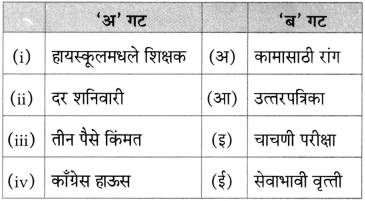
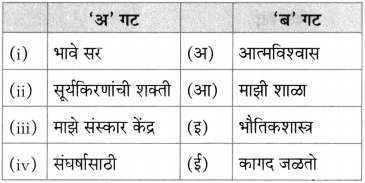
(अ) पु. ल. व सुनीताबाई यांनी दिलेल्या शालीचा लेखकाने पाठात केलेला उल्लेख – [ ]
(आ) २००४ च्या मराठी साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष – [ ]
(इ) पाठात उल्लेख असणारी नदी – [ ]
(ई) सभासंमेलने गाजवणारे कवी – [ ]
उत्तर:
(अ) पु. ल. व सुनीताबाई यांनी दिलेल्या शालीचा लेखकाने पाठात केलेला उल्लेख – [पुलकित शाल]
(आ) २००४च्या मराठी साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष – [लेखक रा. ग. जाधव]
(इ) पाठात उल्लेख असणारी नदी – [कृष्णा]
(ई) सभा संमेलने गाजवणारे कवी – [नारायण सुर्वे]
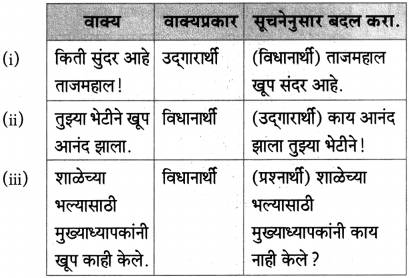
प्रश्न 2.
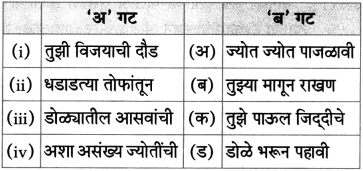
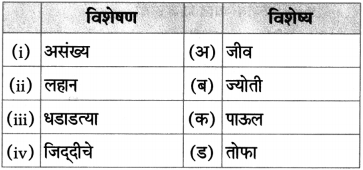
शालीचे पाठात आलेले विविध उपयोग लिहा.
उत्तर:
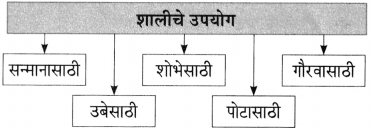
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
खालील प्रसंगी लेखकाने केलेली कृती लिहा.
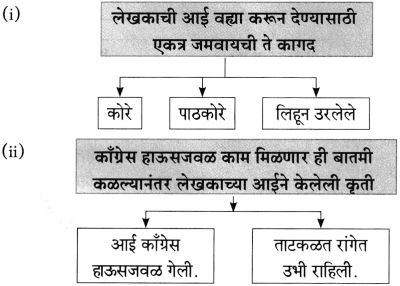
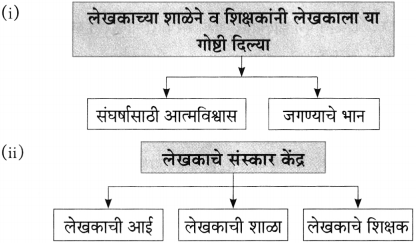
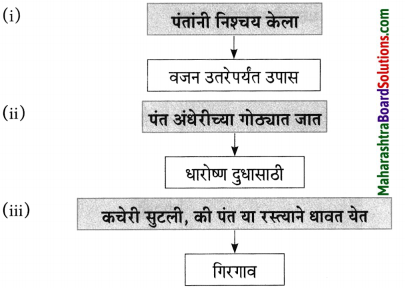
(अ) एका बाईचे बाळ कडाक्याच्या थंडीने कुडकुडत होते.
उत्तर:
लेखकाने बाईला हाक मारून खिडकीतून शाल व पाचपन्नास रुपयांच्या नोटा दिल्या.
(आ) म्हातारा, अशक्त भिक्षेकरी कट्ट्याला लागूनच चिरगुटे टाकून व पांघरून कुडकुडत बसल्याचे पाहिले.
उत्तर:
लेखकाने त्याला आपल्याजवळील दोन शाली दिल्या.
प्रश्न 4.
कारणे शोधून लिहा.
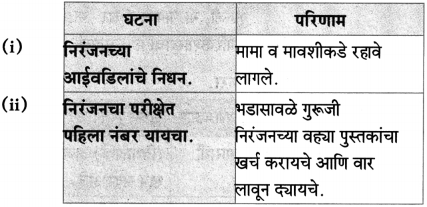
(अ) एका बाईच्या बाळासाठी शाल दिल्याच्या घटनेची ऊब पुलकित शालीच्या उबेपेक्षा जास्त होती, कारण ………………………… .
उत्तर:
त्यामागे लेखकाची आपुलकीची, माणुसकीची भावना होती. शिवाय त्या शालीच्या उबेची त्यावेळी त्या बाळाला जास्त गरज होती.
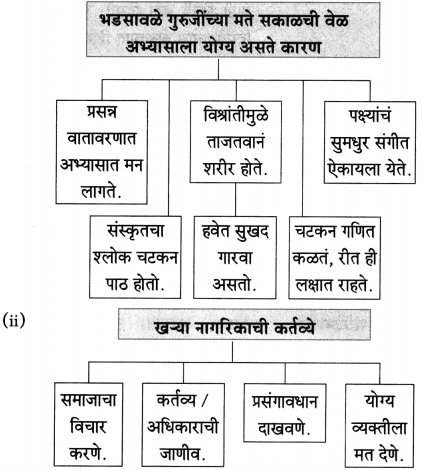
(आ) शालीच्या वर्षावामुळे नारायण सुर्वे यांची शालीनता हरवली नाही, कारण ………………………… .
उत्तरः
ते स्वभावत:च शालीन होते.
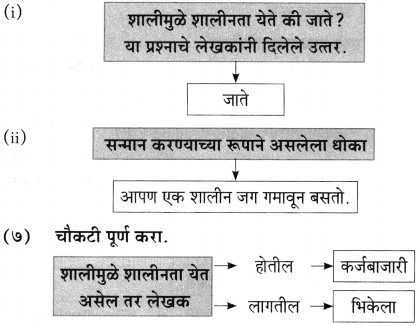
(इ) लेखकांच्या मते शालीमुळे शालीनता जाते, कारण ………………………… .
उत्तर:
सन्मान करण्याच्या रूपाने आपण खरे तर एक शालीन जग गमावून बसण्याचा मोठा धोकाच त्यात असतो.
प्रश्न 5.
आकृती पूर्ण करा.

उत्तर:

![]()
प्रश्न 6.
खालील वाक्यांतील कृतींतून किंवा विचारांतून कळणारे लेखकाचे गुण शोधा.
(अ) बाईला हाक मारून खिडकीतून शाल व नोटा दिल्या.
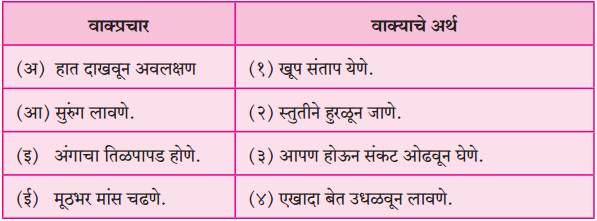
(आ) खरे तर, खरीखुरी शालीनता शालीविनाच शोभते!
(इ) हळूहळू मी सगळ्या शाली वाटून टाकल्या.
उत्तर:
(अ) बाईला हाक मारून खिडकीतून शाल व नोटा दिल्या – [माणूसकी]
(आ) खरे तर, खरीखुरी शालीनता शालीविनाच शोभते! – [नम्रता]
(इ) हळूहळू मी सगळ्या शाली वाटून टाकल्या – [उदारता]
प्रश्न 7.
खालील शब्दांतील अक्षरांपासून अर्थपूर्ण शब्द तयार करा.
(अ) जवळपास
(आ) उलटतपासणी
उत्तर:
(i) जवळ, पास, वळ, पाव, पाळ, पाज, पाजळ इ.
(ii) उलट, तपासणी, पास, पाणी, पाट, पाल, पालट, पात इ.
प्रश्न 8.
अधोरेखित शब्दासाठी योग्य समानार्थी शब्द वापरून वाक्ये पुन्हा लिहा.
(अ) नारायण सुर्वे यांच्या कार्यक्रमांना अहोरात्र भरतीच असे.
उत्तर:
नारायण सुर्वे यांच्या कार्यक्रमांना रात्रंदिवस भरतीच असे.
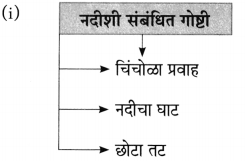
(आ) खोलीच्या दक्षिणेकडील खिडक्या कृष्णा नदीच्या चिंचोळ्या प्रवाहावर होत्या.
उत्तरः
खोलीच्या दक्षिणेकडील खिडक्या कृष्णा नदीच्या अरुंद/निमुळत्या प्रवाहावर होत्या.
(इ) मी सगळ्या शालींचे गाठोडे बांधून निकटवर्ती मित्राकडे ठेवले.
उत्तरः
मी सगळ्या शालींचे गाठोडे बांधून जवळच्या मित्राकडे ठेवले.
![]()
प्रश्न 9.
‘पुलकित’ हे उत्तर येईल असा प्रश्न तयार करा.
उत्तरः
(i) लेखकाने सूटकेसमधील कोणती शाल काढली?
(ii) लेखकाने खिडकीतून बाईला नोटा व पैसे दिले या घटनेची ऊब कोणत्या शालीच्या ऊबेपेक्षा अधिक होती?
प्रश्न 10.
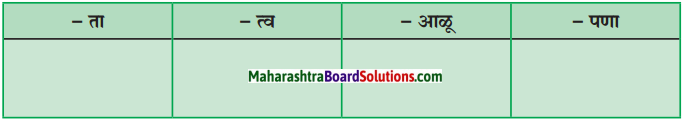
शालीनपासून शालीनता भाववाचक नाम तयार होते. त्याप्रमाणे ‘ता’, ‘त्व’, ‘आळू’ आणि ‘पणा’ हे प्रत्यय लावून तयार झालेली भाववाचक नामे लिहा.
प्रश्न 11.
अधोरेखित शब्दांचे लिंग बदलून वाक्ये पुन्हा लिहा.
(अ) लेखक सुंदर लेखन करतात.
उत्तर:
लेखिका सुंदर लेखन करतात.
(आ) तो मुलगा गरिबांना मदत करतो.
उत्तरः
ती मुलगी गरिबांना मदत करते.
प्रश्न 12.
स्वमत.
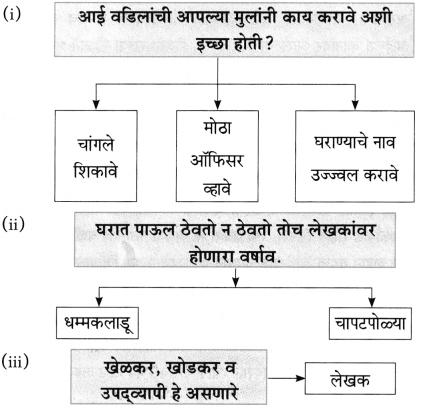
(अ) ‘शाल व शालीनता’ यांचा पाठाच्या आधारे तुम्हांला कळलेला अर्थ स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
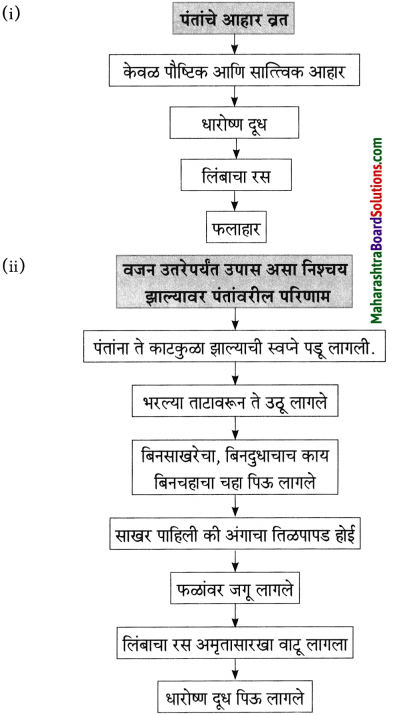
‘शाल’ ही प्रतीकात्मक आहे. तर शालीनता ही ‘चरित्रात्मक’ आहे. आपल्या मनात असलेली, एखाद्या व्यक्तिबद्दलची आदराची भावना. आपण त्या व्यक्तीबद्दलचा सन्मान शाल हे प्रतीक देऊन प्रकट करतो. त्यातून त्या व्यक्तिमध्ये असलेला गुण दिसून येतो. तो म्हणजे शालीनता (नम्रता). व्यक्तीचे चारित्र्य हे शालीनतेमध्ये दडलेले असते, त्याच व्यक्तीचे चरित्र लिहिले जाते, ज्या व्यक्तीचे चारित्र्य चांगले आहे. चारित्र्याचे एक अंग आहे ‘शालीनता’! आणि म्हणून मला वाटते की, ‘शाल’ ही प्रतीकात्मक आहे; तर शालीनता ही चरित्रात्मक आहे.
![]()
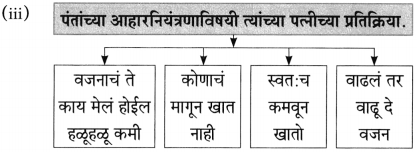
(आ) “भिक्षेकऱ्याने केलेला शालीचा उपयोग’, याविषयी तुमचे मत लिहा.
उत्तर:
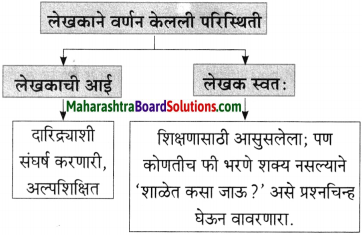
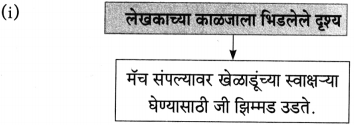
मानवाच्या तीन मुलभूत गरजा – अन्न, वस्त्र, निवारा. या पाठातील भिक्षेकऱ्याकडे या तिन्ही गोष्टी नाहीत, निवारा म्हणजे राहायला घर नाही म्हणून तो ओंकारेश्वर मंदिराबाहेर भिक्षा मागतो. थंडीत कुडकुडताना पाहिल्यावर लेखकाला त्याची दया आली व त्याने त्याचे थंडीपासून संरक्षण व्हावे म्हणून आपल्याजवळील एक नाही तर दोन शाली दिल्या. पण दोन दिवसापासून भुकेला असलेल्या भिक्षेकऱ्याने शाली विकून आपल्या पोटाची आग विझवली, भूक शांत केली. माणूस श्रीमंत असो की गरीब त्याला जगण्यासाठी अन्नाची आवश्यकता असतेच. एक वेळ कपडे नसतील, निवारा नसेल तर चालवून घेईल; पण वेळेला खायला हे मिळालेच पाहिजे आणि त्यामुळे भिक्षेकऱ्याने शाली विकून आपल्या पोटाची आग शांत केली हे माझ्या मते योग्यच आहे.
(इ) लेखकाच्या भावना जशा ‘शाल’ या वस्तूशी निगडित आहेत तशा तुमच्या आवडीच्या वस्तूशी निगडित असलेल्या भावना, तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
उत्तरः
आमचे एकत्र कुटुंब, १५ जणांचा हसता खेळता परिवार कुटुंबप्रमुख-आजी आजोबा नंतर आई-बाबा, काका-काकी, भाऊ-बहिणी. लहानपणी आजीने माझ्यासाठी तिच्या जुन्या लुगड्यांची, आईच्या जुन्या साड्यांची शिवलेली गोधडी मी आजही वापरतो. आज आजी नाही-शरीराने; पण गोधडीच्या स्वरूपात आजही ती सतत माझ्यासोबत आहे. त्या गोधडीत ऊब आहे, आजीचे प्रेम आहे, वात्सल्य आहे. थंडीच्या दिवसात तर मग सूर्य कितीही वर आला तरी सोडावीशी वाटत नाही. हां! आता त्या गोधडीला आजीच्या तपकिरीचा वास येतो तो भाग वेगळा! पण तरीही आजीची गोधडी आजही माझ्या जीवनाचे अविभाज्य अंग आहे.
Marathi Akshar Bharati Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 3 शाल Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न १. पुढील उताऱ्याच्या आधारे दिलेल्या सूचनेनुसार कृती करा,
कृती १: आकलन कृती
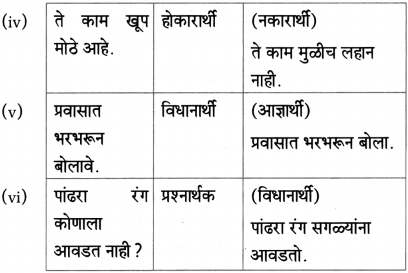
प्रश्न 1.
आकृतिबंध पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
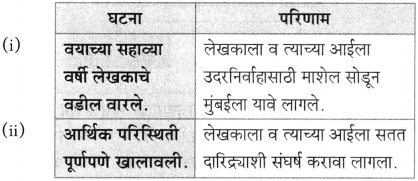
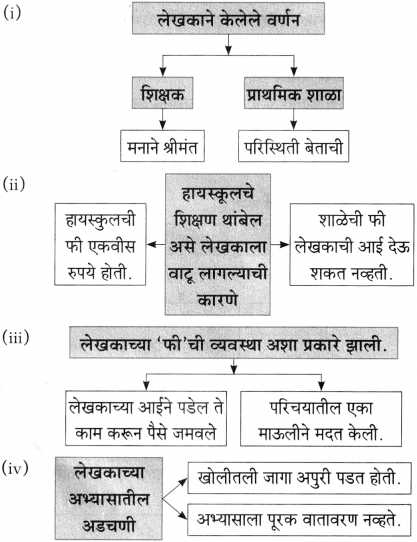
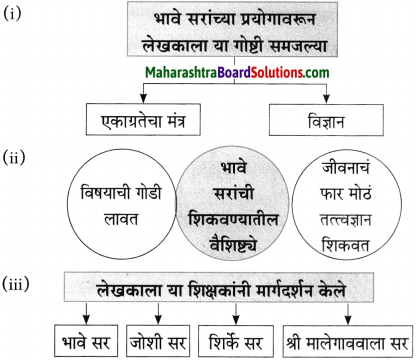
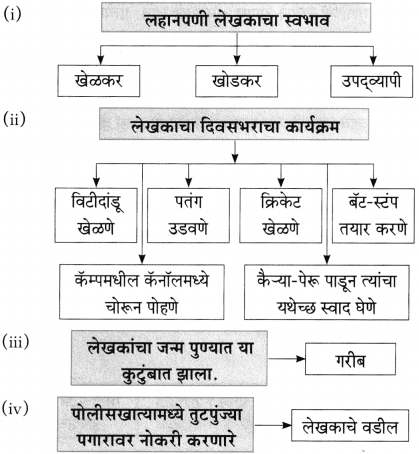
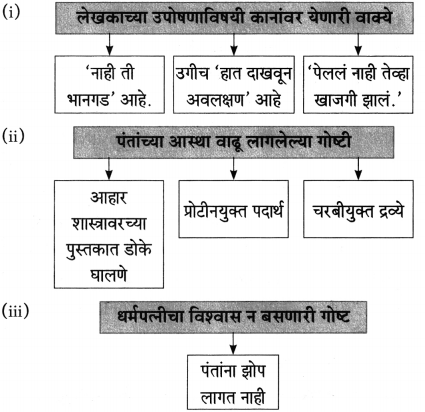
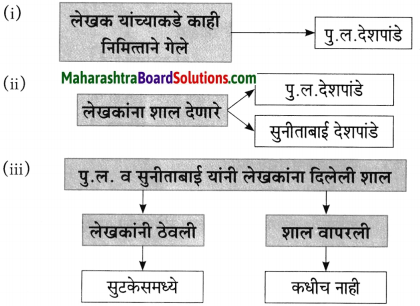
(i) एकदा लेखक पु.ल.देशपांडे यांच्याकडे कशासाठी गेले होते?
उत्तर:
एकदा लेखक पु.ल. देशपांडे यांच्याकडे काही एक निमित्ताने गेले होते.
(ii) सुनिताबाईंनी शालीबद्दल विचारताच लेखकाने लगेच हो का म्हटले?
उत्तर:
पु.ल, व सुनीताबाईंनी लेखकाला शाल दयावी हा त्यांना त्यांचा गौरव वाटला, म्हणून लेखकांनी लगेच त्यांना हो म्हटले.
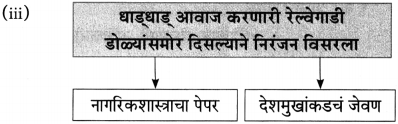
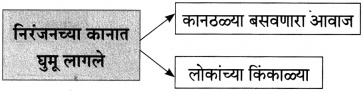
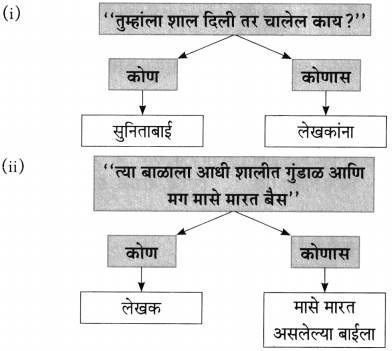
(iii) कडाक्याच्या थंडीने कोण कुडकुडत रडत होते ?
उत्तर:
कडाक्याच्या थंडीने मासे पकडणाऱ्या बाईचे बाळ कुडकुडत होते.
प्रश्न 3.
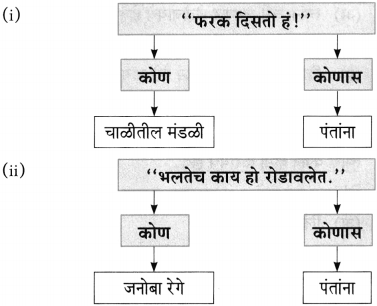
कोण कोणास म्हणाले ते लिहा.
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
कोण ते लिहा
उत्तर:
(i) लेखकांना थांबवणाऱ्या – [सुनीताबाई]
(ii) काम झाल्यावर निघण्याच्या बेतात असणारे – [लेखक]
(iii) एका पायावर हो म्हणणारे – [लेखक]
प्रश्न 5.
चूक की बरोबर लिहा.
(i) ती शाल लेखकांनी सुटकेसमध्ये ठेवली.
(ii) ती शाल वापरली मात्र कधीच नाही.
उत्तर:
(i) बरोबर
(ii) बरोबर
कृती २: आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
कारण लिहा.
(i) बाळ थंडीने कुडकुडत रडत असतानाही आई तिकडे बघतही नव्हती, कारण…
उत्तर:
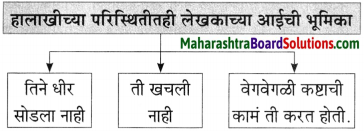
बाळ थंडीने कुडकुडत रडत असतानाही आई तिकडे बघतही नव्हती, कारण ती मासे पकडण्याच्या उद्योगात होती.
प्रश्न 2.
नावे लिहा.
उत्तर:
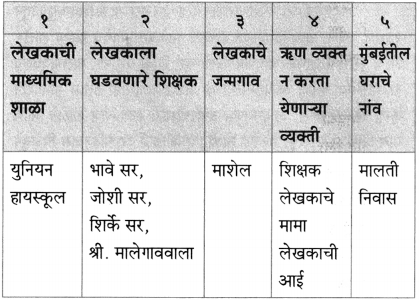
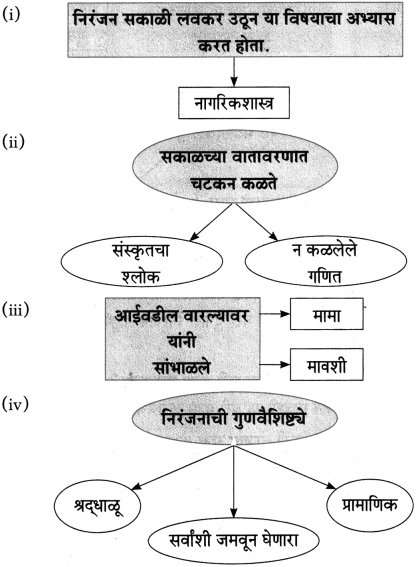
(i) लेखक विश्वकोशाचा अध्यक्ष म्हणून गेले ते ठिकाण – [वाई]
(ii) लेखक या शाळेत राहत होते – [प्राज्ञ पाठशाळा]
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
सहसंबंध लिहा.
(i) खोलीच्या खिडक्या: दक्षिणेकडे: चिंचोळा प्रवाह: ………………………………
(ii) पुलकित: शाल: पाचपन्नास रुपयांच्या: ………………………………
उत्तर:
(i) कृष्णा नदीचा
(ii) नोटा
प्रश्न 4.
खालील कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
(ii) लेखकाने सुटकेसमधील ही शाल काढली – [पुलकित]
प्रश्न 5.
आकृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 6.
खालील प्रश्नांची प्रत्येकी एका वाक्यात उत्तरे लिहा.
(i) एका बाईने तिचे छोटे मूल कशात ठेवले होते?
उत्तरः
एका बाईने तिचे छोटे मूल एका टोपलीत ठेवले होते.
(ii) वाईला लेखक कोण म्हणून गेले होते?
उत्तरः
वाईला विश्वकोशाचा अध्यक्ष म्हणून लेखक गेले होते.
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
कंसातील योग्य शब्दांचा वापर करून रिकाम्या जागा पूर्ण करा.
(i) तिचे बाळ कडाक्याच्या ……………………………… कुडकुडत रडत होते. (उन्हाने, पावसाने, थंडीने, वाऱ्याने)
(ii) या घटनेची ……………………………… पुलकित शालीच्या उबेपेक्षा अधिक (गरमी, नरमी, ऊब, मजा)
(iii) “त्या बाळाला आधी ……………………………… गुंडाळ आणि मग मासे मारत बैस.” (कापडात, साडीत, शालीत, फडक्यात)
उत्तर:
(i) थंडीने
(ii) ऊब
(iii) शालीत
प्रश्न २. पुढील उताऱ्याच्या आधारे दिलेल्या सूचनेनुसार कृती करा.
कृती १: आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
उत्तरे लिहा.
उत्तर:
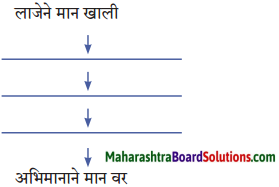
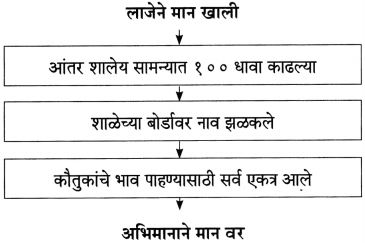
(i) सभा संमेलने गाजवणारे साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष – [नारायण सुर्वे]
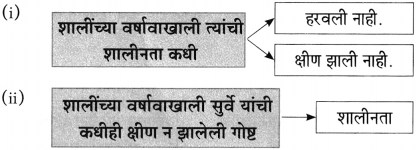
(ii) शालींच्या वर्षावाखाली कधीच हरवली नाही की क्षीणही झाली नाही – [शालीनता]
प्रश्न 2.
चूक की बरोबर लिहा.
(i) शालीमुळे शालीनता येते.
(ii) कविवर्य, नारायण सुर्वे साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष झाले,
उत्तर:
(i) चूक
(ii) बरोबर
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 4.
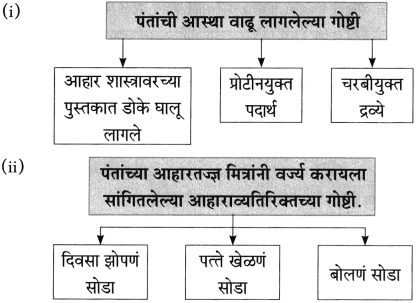
खालील गोष्टींचा परिणाम लिहा.
(i) नारायण सुर्वे साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष झाले.
(ii) प्रत्येक कार्यक्रमात त्यांना शाल व श्रीफळ मिळे.
उत्तर:
(i) त्यांच्या कार्यक्रमांना अहोरात्र भरती असायची.
(ii) या शाली घेऊन ते ‘शालीन’ बनू लागले.
प्रश्न 5.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 6.
कंसातील योग्य शब्द निवडून रिकाम्या जागा भरा,
(i) “या शाली घेऊन घेऊन मी आता ………………………………….. बनू लागलो आहे.’ (शालीन, कुलीन, मलीन, आदर्श)
(ii) शाल व ………………………………….. यांचा संबंध काय? (शालीनता, कुलीनता, मलीनता, शाली)
(iii) प्रत्येक कार्यक्रमात सन्मानाची शाल व ………………………………….. त्यांना मिळत राही. (नारळ, श्रीफळ, सन्मानचिन्ह, ढाल)
उत्तर:
(i) शालीन
(ii) शालीनता
(iii) श्रीफळ
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

कृती २: आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
सहसंबंध लिहा.
(i) शाल: शालीनता:: उपरोधिक: …………………………………..
(ii) साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष: नारायण सुर्वे:: …………………………………..
कार्यक्रमांना अहोरात्र:
उत्तर:
(i) खोच
(ii) भरती
प्रश्न 2.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 3.
चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
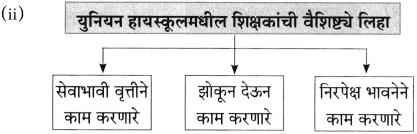
(i) नारायण सुर्वे यांचा मुळातला स्वभाव → [शालीन]
(ii) कविवर्य नारायण सुर्वे यांच्यावर शालींचा झालेला → [वर्षाव]
प्रश्न 4.
विधाने पूर्ण करा.
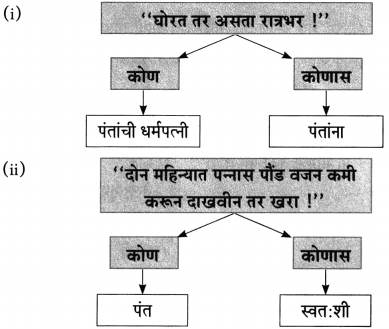
(i) “शालीमुळे शालीनता येत असेल तर …………………………………..
(ii) “पण शेकडो शाली खरेदी करून सर्वांना एकेक शाल …………………………………..
उत्तर:
(i) मी कर्जबाजारी होईन, भिकेला लागेन.
(ii) लगेचच नेऊन देईन.
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
दिलेल्या पर्यायापैकी योग्य पर्यायांची निवड करून वाक्य पूर्ण करा. त्यांच्या बोलण्यातील उपरोधिक खोच माझ्याच नव्हे तर
(अ) कोणाच्याही सहजपणे लक्षात येणारी होती.
(आ) सर्वांच्या सहजपणे लक्षात येणारी होती.
(इ) समाजाच्या सहजपणे लक्षात येणारी होती.
(ई) इतरांच्याही सहजपणे लक्षात येणारी होती.
उत्तरः
त्यांच्या बोलण्यातील उपरोधिक खोच माझ्याच नव्हे तर कोणाच्याही सहजपणे लक्षात येणारी होती.
(ii) शालींच्या वर्षावाखाली त्यांची शालीनता कधी …………………………………. .
(अ) नाहिशी झाली नाही.
(आ) उफाळून आली नाही.
(इ) हरवली नाही.
(ई) गायब झाली नाही.
उत्तर:
शालींच्या वर्षावाखाली त्यांची शालीनता कधी हरवली नाही.
प्रश्न 6.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
प्रश्न ३. पुढील उताऱ्याच्या आधारे विचारलेल्या कृती सोडवा.
कृती १: आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
एका शब्दात उत्तरे लिहा.
(i) लेखक साहित्य संमेलनाचे अध्यक्ष झाले ते साल.
(ii) लेखकाची खोली.
(iii) लेखकाने शालींचे गाठोडे याच्याकडे ठेवले.
उत्तर:
(i) २००४
(ii) आठ बाय सहाची
(iii) निकटवर्ती मित्राकडे,
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
खालील कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
(i) लेखकाने मित्राला दिलेले अधिकार → [शाली वापरण्याचे वगैरे]
(ii) शालींचे बांधले → [गाठोडे]
(iii) लेखकाने यांना शाली वाटल्या → [गरीब श्रमिकांना]
प्रश्न 3.
चूक की बरोबर ते लिहा.
(i) लेखक साहित्य संमेलनाचे बिनविरोध अध्यक्ष झाले.
(ii) लेखकांनी सर्व शालींचे गाठोडे बांधून मित्राकडे दिले.
(iii) मित्र अप्रमाणिक होता.
उत्तर:
(i) बरोबर
(ii) बरोबर
(iii) चूक
प्रश्न 4.
चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
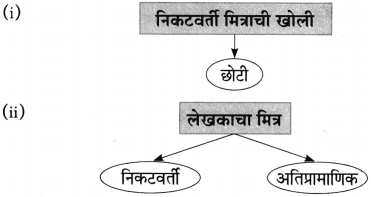
(i) निकटवर्ती मित्राचा स्वभाव – अतिप्रामाणिक
(ii) तत्कालीन एक-दोन वर्षांत लेखकावर झालेला वर्षाव – शालींचा
प्रश्न 5.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
खालील गोष्टींचा झालेला परिणाम लिहा.
(i) तत्कालीन एक-दोन वर्षांत लेखकावर शालींचा वर्षाव झाला.
(ii) आठ बाय सहाच्या खोलीत जमलेल्या शाली ठेवणे शक्य नव्हते.
उत्तर:
(i) एवढ्या शाली जमत गेल्या, की लेखकांच्या आठ बाय सहाच्या खोलीत त्यांना ठेवणे शक्य नव्हते.
(ii) त्याचे गाठोडे बांधून निकटवर्ती मित्राकडे ते ठेवण्यास दिले.
प्रश्न 7.
सहसबंध लिहा.
(i) निकटवर्ती: मित्र:: गरीब: …………………………
(ii) शालीचे: गाठोडे:: आठ बाय सहा: …………………………
उत्तर:
(i) श्रमिक
(ii) खोली
कृती २: आकलन कृती।
प्रश्न 1.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
कृती पूर्ण करा,
उत्तर:
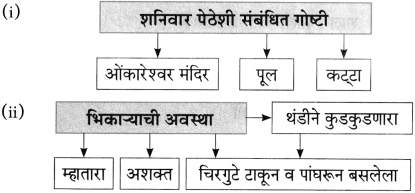
(i) लेखकांना आवडणारी गोष्ट – कट्ट्यावर बसणे
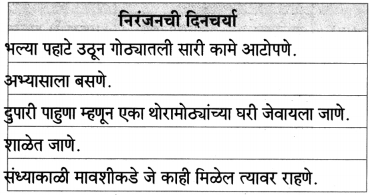
(ii) लेखक रोज संध्याकाळी शनिवार पेठेतील ओंकारेश्वर येथे जात असत – मंदिराच्या पुलावर
प्रश्न 3.
फक्त नावे लिहा.
(i) शनिवार पेठेतील मंदीर – ओंकारेश्वर
(ii) चिरगुटे टाकून व पांघरून कुडकुडत बसलेला – म्हातारा
(iii) कट्ट्यावर बसणारे – लेखक
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
सहसंबंध लिहा
(i) शनिवार: पेठ:: मंदीर: …………………………
दिवस: थंडीचे:: म्हातारा: …………………………
उत्तर:
(i) ओंकारेश्वर
(i) भिक्षेकरी
प्रश्न 5.
योग्य पर्याय निवडून अपूर्ण वाक्य पूर्ण करून लिहा.
(i) लेखक शनिवार पेठेतील ओंकारेश्वर मंदिराच्या पुलावर बहुधा ……………………….. .
(अ) रोज सकाळी जात असे.
(ब) रोज दुपारी जात असे.
(क) रोज संध्याकाळी जात असे.
(ड) रोज रात्री जात असे.
उत्तर:
लेखक शनिवार पेठेतील ओंकारेश्वर मंदिराच्या पुलावर बहुधा रोज संध्याकाळी जात असे.
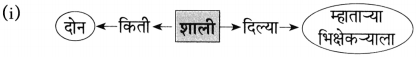
(ii) दुसऱ्या दिवशी मी दोन शाली घेऊन ओंकारेश्वराच्या ……………………….. .
(अ) कट्ट्यावर आलो.
(ब) पायऱ्यांवर आलो.
(क) मंदिरात आलो.
(ड) बागेत आलो.
उत्तर:
दुसऱ्या दिवशी मी दोन शाली घेऊन ओंकारेश्वराच्या कट्ट्यावर आलो.
प्रश्न 6.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

![]()
प्रश्न 7.
कंसातील योग्य पर्याय निवडून रिकाम्या जागा भरा.
(i) हळूहळू मी सगळ्या शाली ………………………… टाकल्या, गरीब श्रमिकांना! (देऊन, वाटून, फेकून, विकून)
(ii) त्याने थरथरत्या हातांनी मला ………………………… केला. (नमस्कार, अभिवादन, नमस्ते, सलाम)
उत्तर:
(i) वाटून
(ii) नमस्कार
प्रश्न ४. पुढील उताऱ्याच्या आधारे दिलेल्या सूचनेनुसार कृती करा.
कृती १: आकलन कृती
प्रश्न 1.
कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
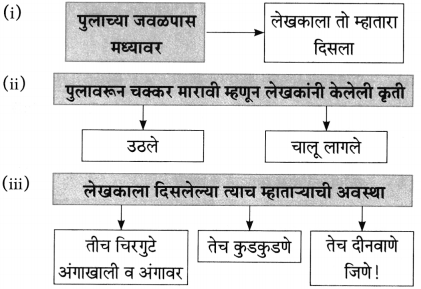
प्रश्न 2.
कारण लिहा.
(i) लेखक चार-पाच दिवस संध्याकाळी ओंकारेश्वराला गेले नाहीत, कारण …
उत्तर:
लेखक चार-पाच दिवस संध्याकाळी ओंकारेश्वराला गेले नाहीत, कारण त्यांना कामांमुळे उसंत लाभली नाही.
प्रश्न 3.
घटनेचा परिणाम लिहा.
उत्तर:
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
योग्य पर्याय निवडून विधान पूर्ण करा.
(i) पुढे चार-पाच दिवस मला काही कामांमुळे संध्याकाळी ओंकारेश्वरला जाण्यास ………………………… .
(अ) वेळ मिळाला नाही.
(ब) उसंत लाभली नाही.
(इ) सवड मिळाली नाही.
(ई) फुरसत मिळाली नाही.
उत्तरः
पुढे चार-पाच दिवस मला काही कामांमुळे संध्याकाळी ओंकारेश्वरला जाण्यास उसंत लाभली नाही.
(ii) तेथील पुलावर चक्कर मारावी म्हणून मी उठलो व ………………………… .
(अ) रस्त्यावरून चालू लागलो.
(ब) कट्ट्यावरून चालू लागलो.
(इ) पुलावरून चालू लागलो.
(ई) पायवाटेवर चालू लागलो.
उत्तरः
तेथील पुलावर चक्कर मारावी म्हणून मी उठलो व पुलावरून चालू लागलो.
प्रश्न 5.
चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
(i) त्यानंतर लेखक नेहमीप्रमाणे करत राहिले – ये-जा
(ii) लेखकांना काही कामामुळे एवढे दिवस ओंकारेश्वरला जाण्यास उसंत लाभली नाही – चार-पाच दिवस
प्रश्न 6.
फक्त नावे लिहा.
उत्तर:
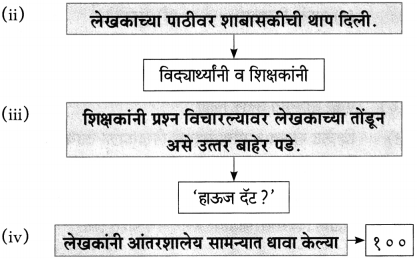
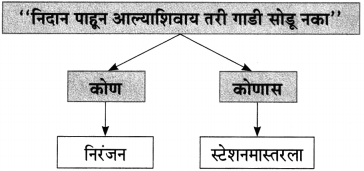
(i) लेखकांना एकदम आठवण झाली – [भिक्षेकरी वृद्धाची]
(i) भिक्षेकरी म्हाताऱ्याकडे लगबगीने जाणारे – [लेखक]
![]()
कृती २: आकलन कृती
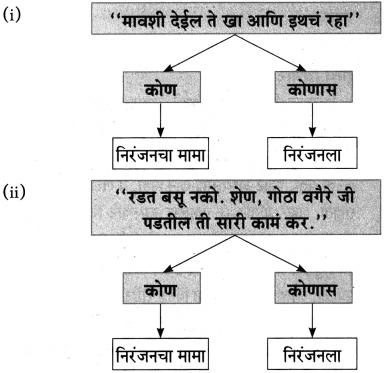
प्रश्न 1.
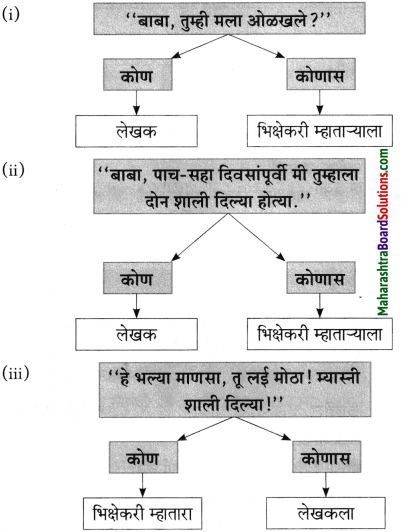
कोण कोणास म्हणाले ते लिहा.
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
घटनेचा परिणाम लिहा.
उत्तर:

![]()
प्रश्न 3.
वाक्याचा योग्य क्रम लावून वाक्ये पुन्हा लिहा.
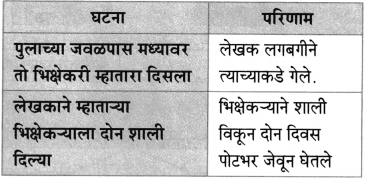
(i) तुझं लई उपकार हायेत बाबा.
(ii) त्या शोभेपेक्षा पोटाची आग लई वाईट!
(iii) आमचं हे असलं बिकट जिणं।
(iv) मी शाली इकल्या व दोन-तीन दिवस पोटभर जेवून घेतलं बाबा!
उत्तर:
(i) त्या शोभेपेक्षा पोटाची आग लई वाईट!
(ii) मी शाली इकल्या व दोन-तीन दिवस पोटभर जेवून घेतलं बाबा!
(iii) आमचं हे असलं बिकट जिणं!
(iv) तुझं लई उपकार हायेत बाबा.
प्रश्न 4.
खालील कृती पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 5.
सहसबंध लिहा.
(i) भला: माणूस:: शालीची: …………………. .
(ii) बिकट: जिणं:: पोटाची: …………………. .
उत्तर:
(i) शोभा
(ii) आग
प्रश्न 6.
चौकटी पूर्ण करा.
उत्तर:
(i) भिकाऱ्यास न शोभणाऱ्या → [शाली]
(ii) शाली विकून पोटभर जेवणारा → [म्हातारा भिक्षेकरी]
(iii) म्हाताऱ्यावर उपकार करणारा → [लेखक]
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
उताऱ्यात आलेल्या शरीराच्या तीन अवयवांची नावे लिहा.
उत्तर:
मान, हात, पोट
प्रश्न 8.
कंसातील योग्य शब्द वापरून रिकाम्या जागा भरा.
(i) पुलाच्या जवळपास मध्यावर तो …………………. म्हातारा दिसला. (वयस्कर, सभ्य, भिक्षेकरी, नम्र)
(ii) अभाग्यांना सन्मानाच्या …………………. तरी दयाव्यात! (शाली, चादरी, पोथ्या, गोधडी)
उत्तर:
(i) भिक्षेकरी
(ii) शाली
कृती ३: स्वमत
प्रश्न 1.
तुम्हांला समाजात असणाऱ्या गरीब, दीनदुबळ्या लोकांना कशी मदत करावी वाटते ते लिहा.
उत्तर:
आजकाल घरातून बाहेर पडल्यावर समाजात वावरताना.
कुठे प्रवास करताना, वेगवेगळ्या धार्मिक स्थळांना भेटी देताना ठिक-ठिकाणी आपणास गरीब, लाचार, दीन लोकं दिसतात. ज्यांच्या अंगावर साधे स्वच्छ, नीटनेटके कपडेही नसतात. त्यांना राहायला व्यवस्थित जागाही नसते. अंथरण्यास पांघरण्यास काही कपडेही नसतात.
अशा सर्व प्रकारच्या लोकांना पाहिल्यावर वाटते, की त्यांना योग्य आश्रमात नेऊन आश्रय दयावा. घरातील काही, न वापरण्याजोगे परंतु चांगले स्वच्छ न फाटलेले कपडे त्यांना यावेत. घरातील ठेवणीच्या शाली, चादरी ज्या आपण उपयोगात आणत नाही, त्या अशा लोकांना याव्यात, भुकेल्यांना दोन घास भरवावेत. तहानलेल्यांना पाणी पाजून शांत करावे. जेणेकरून त्यांचे थोडेतरी दुःख कमी व्हावे.
प्रश्न 2.
स्वमत.
(i) ‘शाल व शालीनता’ यांचा पाठाच्या आधारे तुम्हाला कळलेला अर्थ स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तरः
‘शाल’ ही प्रतीकात्मक आहे. तर शालीनता ही ‘चरित्रात्मक’ आहे. आपल्या मनात असलेली, एखाद्या व्यक्तिबद्दलची आदराची भावना. आपण त्या व्यक्तीबद्दलचा सन्मान शाल हे प्रतीक देऊन प्रकट करतो. त्यातून त्या व्यक्तिमध्ये असलेला गुण दिसून येतो. तो म्हणजे शालीनता (नम्रता). व्यक्तीचे चारित्र्य हे शालीनतेमध्ये दडलेले असते, त्याच व्यक्तीचे चरित्र लिहिले जाते, ज्या व्यक्तीचे चारित्र्य चांगले आहे. चारित्र्याचे एक अंग आहे ‘शालीनता’! आणि म्हणून मला वाटते की, ‘शाल’ ही प्रतीकात्मक आहे; तर शालीनता ही चरित्रात्मक आहे.
![]()
(ii) ‘भिक्षेकऱ्याने केलेला शालीचा उपयोग’, याविषयी तुमचे मत लिहा.
उत्तर:
मानवाच्या तीन मुलभूत गरजा – अन्न, वस्त्र, निवारा. या पाठातील भिक्षेकऱ्याकडे या तिन्ही गोष्टी नाहीत, निवारा म्हणजे राहायला घर नाही म्हणून तो ओंकारेश्वर मंदिराबाहेर भिक्षा मागतो. थंडीत कुडकुडताना पाहिल्यावर लेखकाला त्याची दया आली व त्याने त्याचे थंडीपासून संरक्षण व्हावे म्हणून आपल्याजवळील एक नाही तर दोन शाली दिल्या. पण दोन दिवसापासून भुकेला असलेल्या भिक्षेकऱ्याने शाली विकून आपल्या पोटाची आग विझवली, भूक शांत केली. माणूस श्रीमंत असो की गरीब त्याला जगण्यासाठी अन्नाची आवश्यकता असतेच. एक वेळ कपडे नसतील, निवारा नसेल तर चालवून घेईल; पण वेळेला खायला हे मिळालेच पाहिजे आणि त्यामुळे भिक्षेकऱ्याने शाली विकून आपल्या पोटाची आग शांत केली हे माझ्या मते योग्यच आहे.
(iii) लेखकाच्या भावना जशा ‘शाल’ या वस्तूशी निगडीत आहेत तशा तुमच्या आवडीच्या वस्तूशी निगडित असलेल्या भावना, तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
उत्तरः
आमचे एकत्र कुटुंब, १५ जणांचा हसता खेळता परिवार कुटुंबप्रमुख-आजी आजोबा नंतर आई-बाबा, काका-काकी, भाऊ-बहिणी. लहानपणी आजीने माझ्यासाठी तिच्या जुन्या लुगड्यांची, आईच्या जुन्या साड्यांची शिवलेली गोधडी मी आजही वापरतो. आज आजी नाही-शरीराने; पण गोधडीच्या स्वरूपात आजही ती सतत माझ्यासोबत आहे. त्या गोधडीत ऊब आहे, आजीचे प्रेम आहे, वात्सल्य आहे. थंडीच्या दिवसात तर मग सूर्य कितीही वर आला तरी सोडावीशी वाटत नाही. हां! आता त्या गोधडीला आजीच्या तपकिरीचा वास येतो तो भाग वेगळा! पण तरीही आजीची गोधडी आजही माझ्या जीवनाचे अविभाज्य अंग आहे.
शाल शब्दार्थ
- शाल – खांदयावरून पांघरण्याचे उबदार वस्त्र, महावस्त्र – (a Shawl)
- निमित्त – कारण – (a purpose, a reason)
- चिंचोळ्या – निमुळत्या – (narrow)
- प्रवाह – वाहण्याचा ओघ – (a flow)
- कडाक्याची थंडी – खूप थंडी – (very cold)
- कुडकुडणे – थरथर कापणे, थंडीने गारठून थरथरणे – (shiver from cold)
- हाक मारणे – बोलावणे (to call)
- शालीन – नम्र, लीन – (gentle, humble)
- उपरोधिक – टोमणा असलेले, मनाला लागेल अस – (Sarcastic, ironical)
- क्षीण – कमी, दुर्बल – (weak)
- शेकडो – शंभर – (hundred)
- तत्कालीन – त्या काळातील – (of that time)
- गाठोडे – कपडे इत्यादीचे बोचके – (a bundle)
- निकटवर्ती – जवळचा – (very close)
- सर्वाधिकार – सर्व अधिकार – (full power)
- श्रमिक – काम करणारे, कष्ट करणारे – (hard worker)
- बहुधा – बहुतेक करून – (most probably)
- कट्टा – दगडांचा चौकोनी ओटा – (a raised platform of stones)
- चिरगुटे – कपड्यांच्या चिंध्या चिंध्या – (a shred of cloth)
- पांघरून – अंग झाकून, अंगावर घेऊन – (a coverlet)
- वृद्ध – म्हातारा, वय झालेला माणूस – (aged)
- भिक्षेकरी – भीक मागणारा – (a beggar)
- लगबगीने – त्वरीत, जलद – (hurriedly)
- भल्या माणसा – मोठ्या माणसा, सज्जन – (good natured person)
- इकल्या – विकल्या – (to sold)
- बिकट – वाईट – (bad)
- जिणं – आयुष्य – (life)
- लई – खूप – (many, much)
- अभागी – गरीब, दीन, लाचार (unlucky)
Marathi Aksharbharati Std 10 Digest Pdf भाग-१