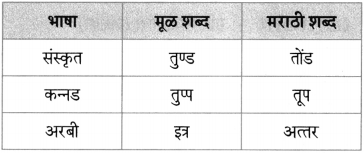
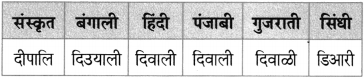
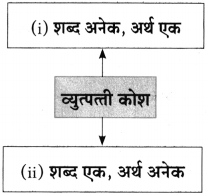
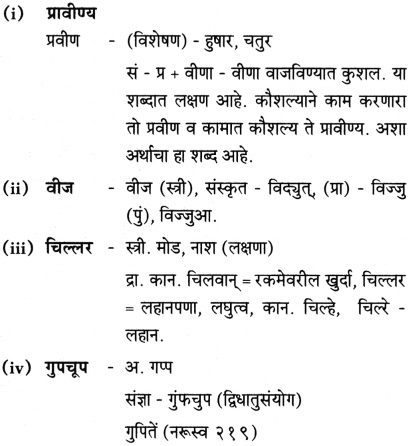
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Kumarbharti Chapter 8 वाट पाहताना Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 10th Marathi Kumarbharti Chapter 8 वाट पाहताना Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 8 Question Answer
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Digest Chapter 8 वाट पाहताना Textbook Questions and Answers
कृति
कतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न १ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी…
प्रश्न 1.
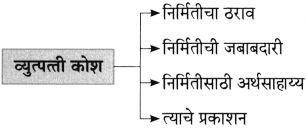
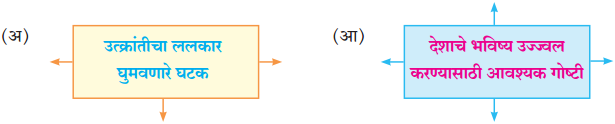
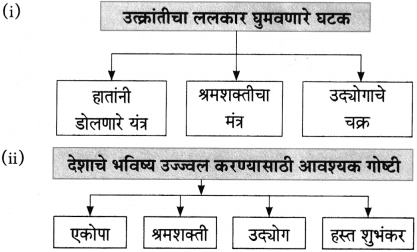
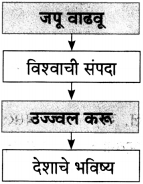
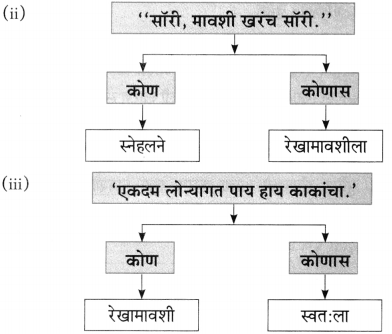
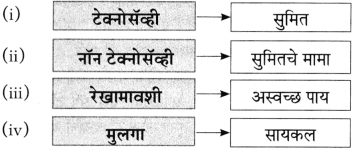
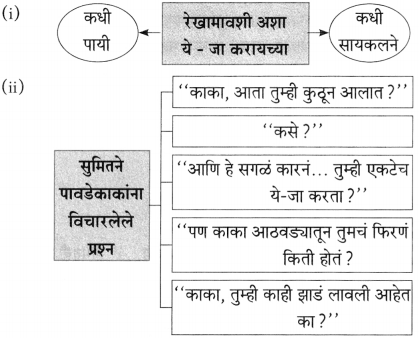
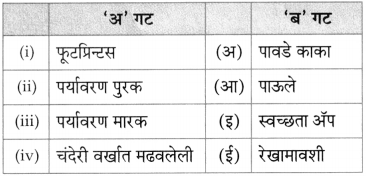
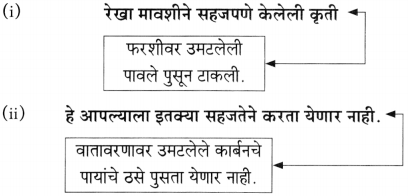
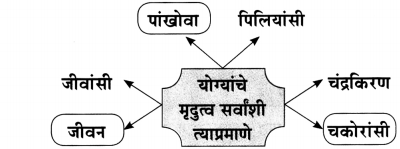
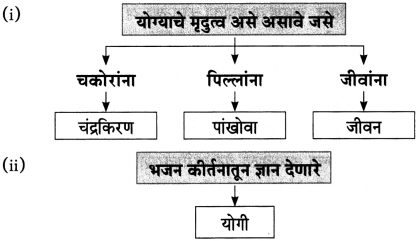
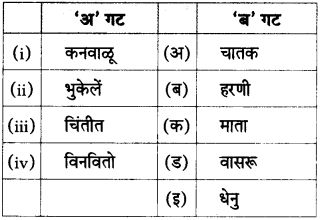
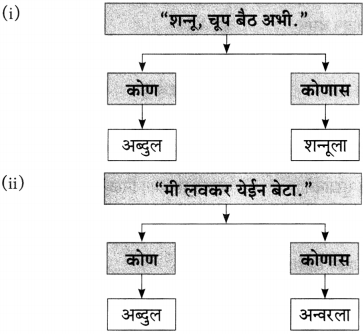
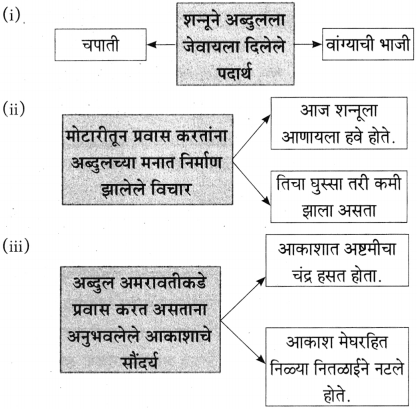
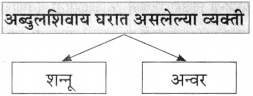
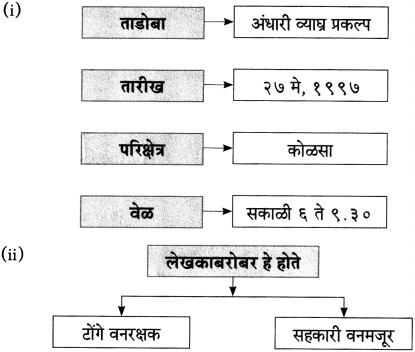
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा.
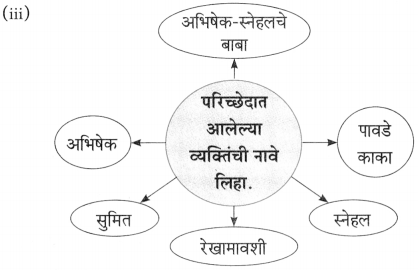
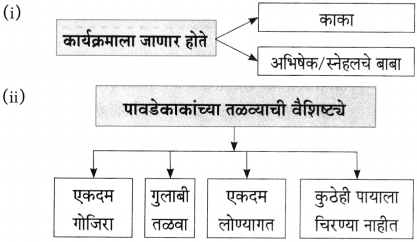
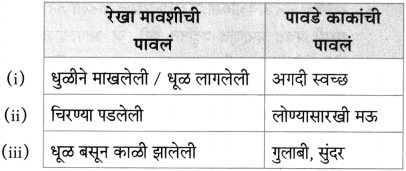
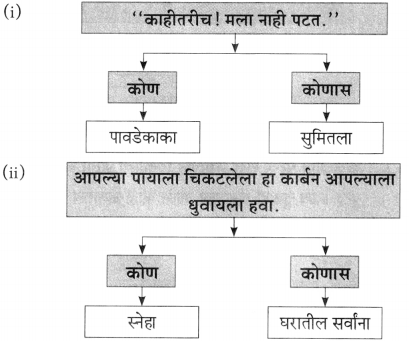
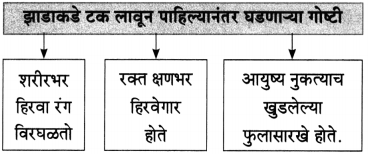
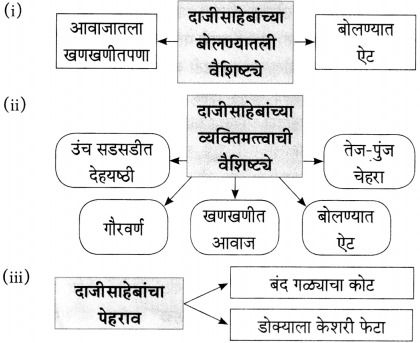
(i) 
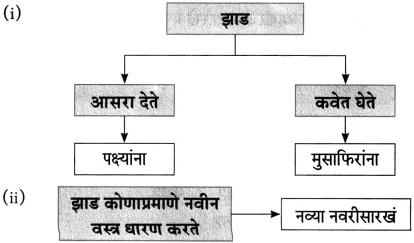
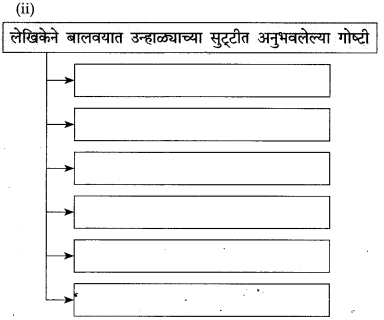
(ii) 
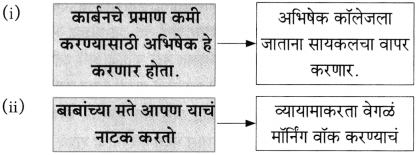
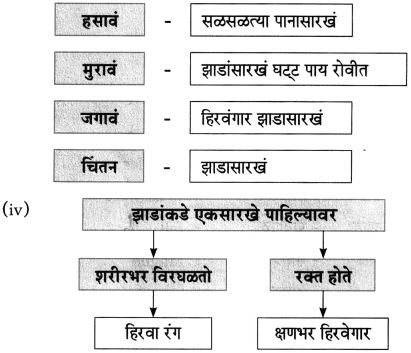
(iiii) 
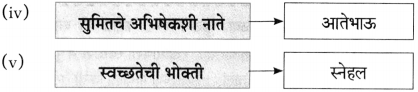
(iv) 
उत्तर:
(i) 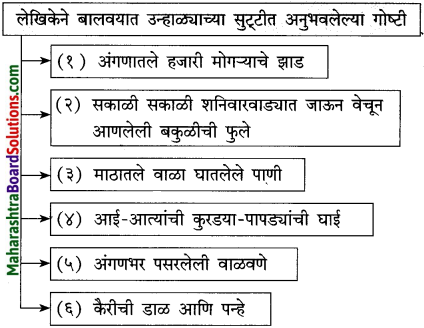
(ii) 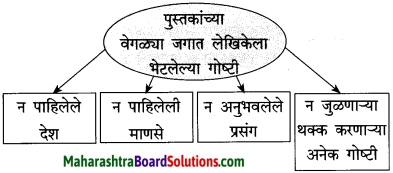
(iii)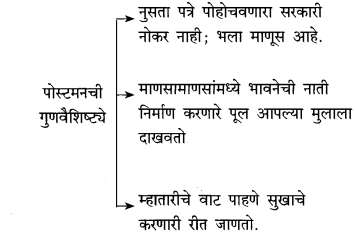
(iv) 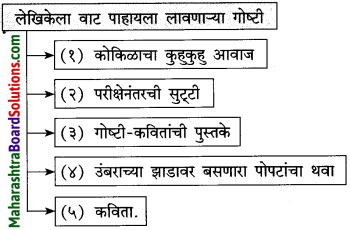
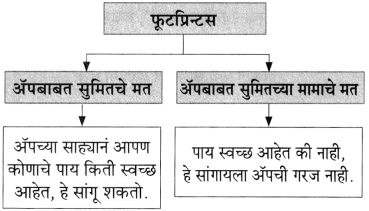
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
कारणे शोधा
(अ) आवाजाची वाट पाहण्याचं सार्थक व्हायचं, कारण ……………………………………
(आ) म्हातारीच्या तोंडावर समाधान पसरायचं, कारण ……………………………………
(इ) पुस्तक वाचण्याची वाट पाहण्यात उन्हाळ्याच्या आधीचा काळ लेखिकेला वेड लावायचा, कारण ……………………………………
(ई) पोस्टमन मनानंच कोरं पत्र वाचतो, कारण ……………………………………
उत्तर:
(अ) आवाजाची वाट पाहण्याचं सार्थक व्हायचं, कारण पहाटे कुहुकुहु ऐकू यावा, ही रात्री झोपताना बाळगलेली इच्छा पहाटे पहाटे पूर्ण होई.
(आ) म्हातारीच्या तोंडावर समाधान पसरायचं; कारण दूर परगावी राहणारा आपला मुलगा आपली आठवण काढतो, आपल्याला तो त्याच्याकडे नेणार आहे, या कल्पने- तेचे मन सुखायचे,
(इ) पुस्तक वाचण्याची वाट पाहण्यात उन्हाळ्याच्या आधीचा काळ लेखिकेला वेड लावायचा, कारण पुस्तकांतून भाषेची शक्ती, लेखकांच्या प्रतिभेची शक्ती समजू लागली होती.
(ई) पोस्टमन मनानंच कोरं पत्र वाचतो; कारण त्या म्हातारीला पुत्रभेटीचा आनंद मिळावा आणि तिचे शेवटचे दिवस समाधानात जावेत, अशी पोस्टमनची इच्छा होती.
प्रश्न 3.
तुलना करा.
| व्यक्तीशी मैत्री | कवितेशी मैत्री |
| …………………….. | …………………….. |
| …………………….. | …………………….. |
| …………………….. | …………………….. |
उत्तर:
| व्यक्तीशी मैत्री | कवितेशी मैत्री |
| आपण त्या व्यक्तीला हाक मारतो. तिच्याकडे धावतो. मनसोक्त गप्पा मारतो. ती व्यक्ती प्रतिसादही देते. व्यक्ती हवी तेव्हा भेटू शकते. | कविता तिच्याकडे धाव घेऊनही भेटत नसे. मात्र ती प्रसन्न झाली तर कधीही धावत येऊन भेटे. कविता मात्र खूप वाट पाहायला लावते. |
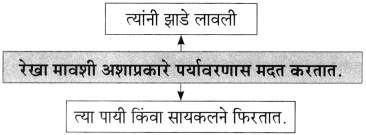
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
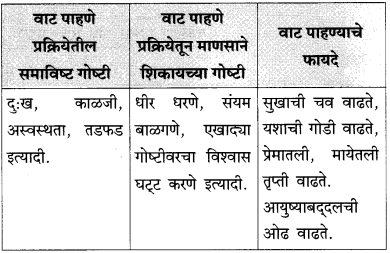
‘वाट पाहणे’ या प्रक्रियेबाबत पुढील मुद्द्यांना अनुसरून लेखिकेचे मत लिहून तक्ता पूर्ण करा.
| वाट पाहणे प्रक्रियेतील समाविष्ट गोष्टी | वाट पाहणे प्रक्रियेतून माणसाने शिकायच्या गोष्टी | वाट पाहण्याचे फायदे |
| …………………….. | …………………….. | …………………….. |
| …………………….. | …………………….. | …………………….. |
| …………………….. | …………………….. | …………………….. |
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 5.
स्वमत.
(अ) पाठाच्या शीर्षकाची समर्पकता तुमच्या शब्दांत सांगा.
उत्तर :
अरुणा ढेरे यांचा ‘वाट पाहताना’ हा अत्यंत हृदय ललित लेख आहे. जीवनातील एक मूलभूत महत्त्वाचे तत्त्व या लेखात त्या उलगडून दाखवतात. तसे पाहिले तर माणूस वाट पाहत पाहतच वाटचाल करीत असतो. प्रत्येक पावलावर त्याच्या मनात ‘नंतर काय होईल?’, ‘माझ्या स्वप्नांप्रमाणे, कल्पनेप्रमाणे घडेल ना?’ अशी तगमग असते. हीच तगमग त्याला पुढे जायला, जीवन जगायला लावते. हे तत्व लेखिकांनी अनेक उदाहरणांच्या साहाय्याने स्पष्ट केले आहे.
सुट्टीतल्या सगळ्या गोष्टी जगायला मिळतील या आशेने लेखिका सुट्टीची वाट पाहत. अनेक अनोळखी प्रदेश, माणसे, प्रसंग यांचा सहवास घडवणाऱ्या पुस्तकांची वाट पाहणे अत्यंत रमणीय होते. उंबराच्या झाडावर बसणाऱ्या पोपटांच्या थव्यामुळे हिरवेगार बनलेले ते झाड पाहून लेखिकांचे मन हळवे, कोमल होऊन जाते. त्यातच त्यांच्या कवितांची मुळे रुजतात. वाट पाहण्याने त्यांची निर्मितिशीलता जागृत होते. आत्याची वाट पाहताना त्यांचे मन अस्वस्थता आणि अनामिक भीती यांनी भरून जाते. या सर्वात जगण्याचाच अनुभव होता. अस्वस्थता, हुरहुर, दुःख, तगमग, शंकाकुलता हे सारे भाव पोस्टमनला भेटलेली म्हातारी, तसेच शेतकरी, वारकरी भक्त यांच्या चेहऱ्यांवर लेखिकांना गवसतात. अशा प्रकारे जगण्याच्या मुळाशीच वाट पाहण्याची भावना असल्याचे भान लेखिका या लेखातून वाचकांना देतात. म्हणून वाट पाहताना’ हे शीर्षक अत्यंत समर्पक आहे.
![]()
(आ) म्हातारीचं वाट पाहणं सुखाचं करण्यासाठी पोस्टमनने केलेल्या युक्तीबाबत तुमचे मत लिहा.
उत्तर:
एखादी निर्जीव वस्तू पोहोचती करावी, त्याप्रमाणे तो पोस्टमन पत्रे देत नसे. कारण पत्रे ही निर्जीव वस्तू नसतात. ती माणसांच्या सुखदुःखांनी, आशा-आकांक्षांनी भरलेली असतात. त्यात माणसांचे मन असते, हृदय असते. पत्रांचे हे स्वरूप चित्रपटातल्या त्या पोस्टमनने जाणले होते. म्हणून तो अंध म्हातारीला मुलाचे काल्पनिक पत्र वाचून दाखवतो. ते पत्र खोटे असते. मजकूर खोटा असतो. त्या अंध म्हातारीच्या मुलाचा स्पर्शसुद्धा त्या पत्राला झालेला नसतो. पण म्हातारी सुखावते. तिचे उरलेले दिवस आनंदात जातात. या विपरीत स्थितीने पोस्टमनचे मन कळवळते. पण म्हातारी सुखावणे हे अधिक मूल्ययुक्त होते. आपल्या मुलालाही तो पोस्टमन हीच उदात्त शिकवण देतो. मुलातला माणूस जागा करतो. माणसाशी माणसासारखे वागण्याची ही महान शिकवण होती. प्रत्येक आई-वडिलांनी आपल्या मुलांना असे माणूसपण शिकवले पाहिजे; तरच मानवी समाजाला भविष्य आहे.
(इ) ‘वाट पाहणे एरवी सुखाची गोष्ट नसली तरी अनेक गोष्टींचे मोल जाणवून देणारी आहे’. या विधानाची सत्यता पटवून दया.
उत्तर:
‘वाट पाहताना’ या पाठात लेखिकांनी जीवनाचा एक सुखमंत्रच सांगितला आहे. वाट पाहणे हा तो मंत्र होय. कोणत्याही गोष्टीसाठी पाहायला शिकले पाहिजे, असे त्यांचे सांगणे आहे. वाद पाहणे हे तसे कधीच सुखाचे नसते. आपल्या आशा-आकांक्षा पूर्ण करण्यासाठी, एखादी गोष्ट मिळवण्यासाठी आपले मन अधीर झालेले असते. मन शंकेने व्याकुळ होते. हवी ती गोष्ट आपल्याला मिळेल का? असा प्रश्न मचात काहूर माजवतो.
एखादी गोष्ट वाट न पाहता, चटकन मिळाली, तर ती गोष्ट आपली जिवाभावाची आहे की वरवरची आहे, हे कळायला मार्ग राहत नाही. इच्छा तत्काळ पूर्ण झाल्यास आपल्याला आनंद मिळेल, हे खरे आहे.
पण आपण कदाचित वरवरच्या गोष्टींमध्ये बुडून जाण्याची शक्यता असते. अधिकाधिक वाट पाहिल्यामुळे आपली खरी ओढ कुठे आहे, हे कळते. म्हणजेच आपल्याला खरोखर काय हवे आहे, नेमकी कशाची गरज आहे, हे कळून चुकते. जे आपल्या दृष्टीने मोलाचे आहे, हे शोधण्याची दृष्टी या वाट पाहण्यातून मिळते. आपल्या दृष्टीने मोलाच्या असलेल्या गोष्टी मिळाल्या तर आपले जीवन समृद्ध होते. समृद्घ जीवन जगणे हेच तर प्रत्येक माणसाचे ध्येय असते. म्हणून वाट पाहणे त्रासाचे असले तरी अनेक गोष्टींचे मोल ओळखण्यासाठी ते उपयोगी ठरते, हे खरे आहे.
![]()
भाषासौंदर्य
मराठी भाषेतील शब्दसामर्थ्य शब्दातीत आहे. ‘वाट’ या एकाच शब्दाचा वापर विविध अर्थानी करून एक अर्थपूर्ण मनोगत तयार झाले आहे.
नमस्कार,
तू वाट दाखवणार,
म्हणून काल तुझ्या पत्राची वाट पाहत होतो.
त्या वाटेने पत्र आलेच नाही.
नेहमी त्या वाटेवरून धावणारी
पोस्टमन दादाची सायकलही त्या दिवशी धावली नाही.
शेवटी सगळा दिवस वाट पाहण्यात गेला,
साऱ्या दिवसाचीच वाट लागली
आणि मी माझ्या घरच्या वाटेने माघारी फिरलो
मनात आले आपण पत्राचीच वाट पाहत होतो
आता कशाचीच वाट पाहू नये
आपणच आपली वाट निर्माण करावी
जी वाट नवनिर्मितीची ठरेल.
वरील मनोगताचा अभ्यास करा व त्यातील भाषिक सामर्थ्य जाणून घ्या. एका शब्दाचे वेगवेगळ्या संदर्भात वेगवेगळे अर्थ असणारे इतर काही शब्द वापरून तुम्हांलाही असे मनोगत लिहिता येईल.
आपल्या भाषिक क्षमता वाढवण्यासाठी याचा सराव करा.
उतारा क्र. १
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या
सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १: (आकलन)
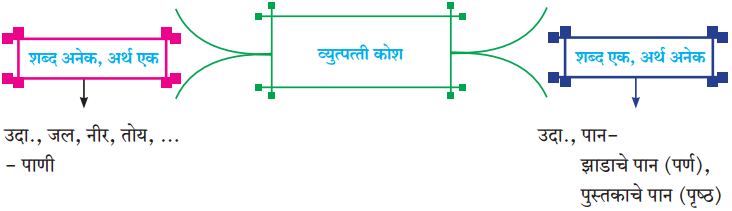
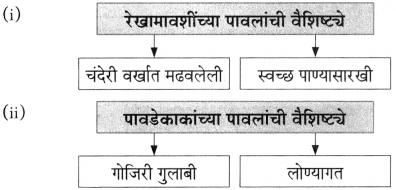
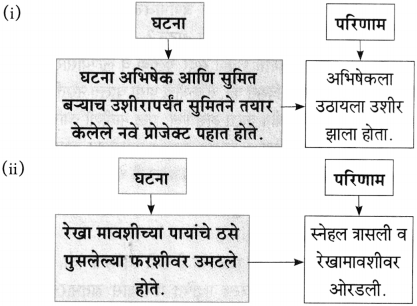
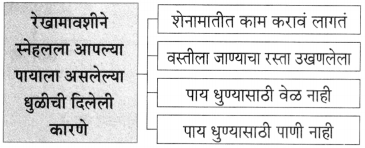
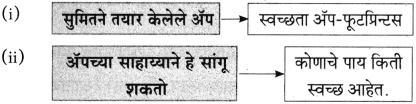
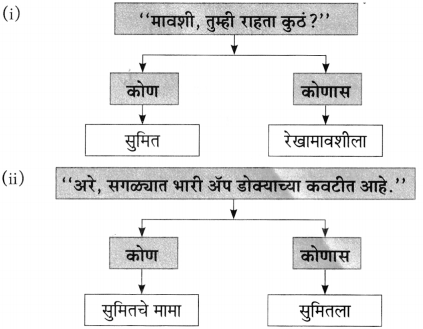
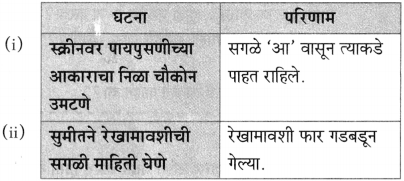
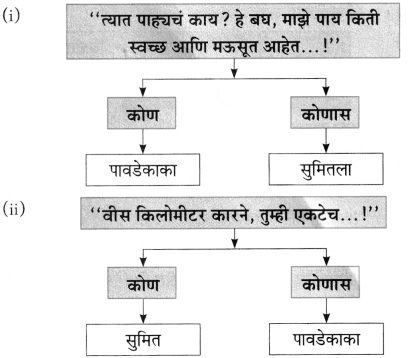
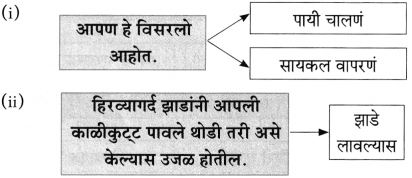
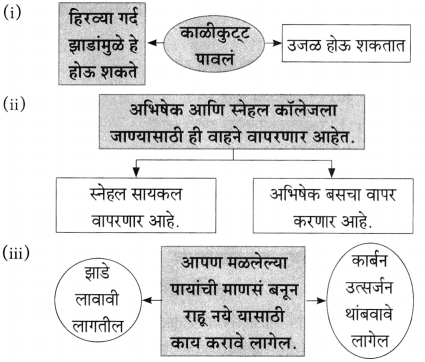
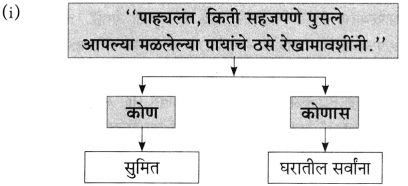
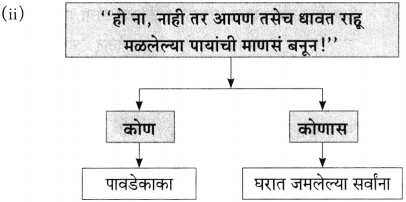
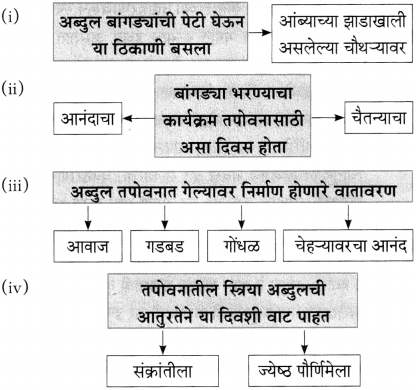
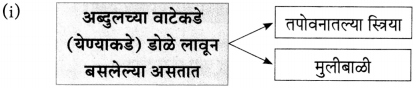
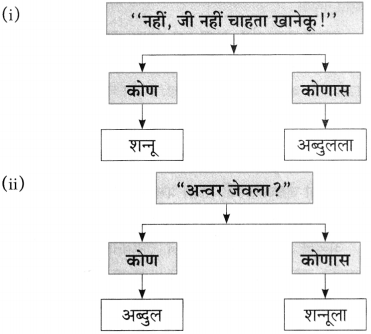
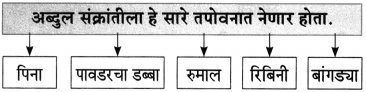
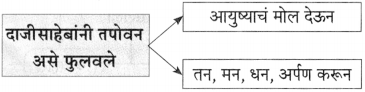
प्रश्न 1.
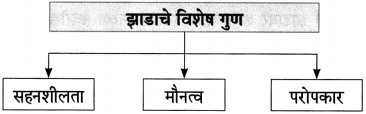
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा :

उत्तर:
![]()
कृती २ : (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
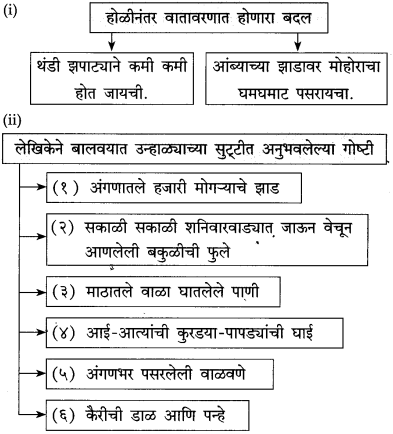
अंगणात मोकळ्या वातावरणात झोपायला मिळण्यापर्यंतचा घटनाक्रम :
(i) होळीनंतर थंडी झपाट्याने कमी होत जायची आणि आंब्याचा मोहोर नुसता घमघमत असायचा.
(ii) ………………………..
(iii) ………………………..
उत्तर:
(i) होळीनंतर थंडी झपाट्याने कमी होत जायची आणि आंब्याचा मोहोर नुसता घमघमत असायचा.
(ii) मार्च-एप्रिलमध्ये मुलांना गॅलरीत झोपायला मिळे.
(iii) सुट्टी लागल्यावर अंगणात अंथरुणे पडत.
प्रश्न 2.
लेखिकांचा वाट पाहण्याचा पहिला अनुभव :
(i) ………………………..
(ii) ………………………..
(iii) ………………………..
(iv) ………………………..
उत्तर:
(i) अंगणात रात्रीच्या थंड वातावरणात हळूहळू झोप येई.
(ii) उदया कुहुकुहु ‘ ऐकू येईल का, ही हुरहुर लागे.
(iii) पहाटे पहाटे झोपेत असतानाच कुहुकुहु ऐकू येई.
(iv) त्या आवाजाची वाट पाहिली, याची धन्यता वाटे.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
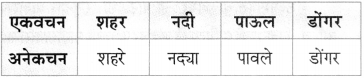
प्रश्न 1.
भांडे ‘ या शब्दातील पहिल्या अक्षरावरील अनुस्वार काढला की ‘भाडे’ हा शब्द मिळतो. दोन्ही अर्थपूर्ण शब्द आहेत. असे उताऱ्यातून दोन शब्द शोधा आणि अनुस्वारसहित व अनुस्वारविरहित असे प्रत्येकी दोन्ही शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
पाठातील शब्द : थंडी. दोन शब्द : थंडी, थडी. तोंड. दोन शब्द : तोंड, तोड.
प्रश्न 2.
कंसात दिलेला प्रत्यय जोडून प्रत्ययासहितचे पूर्णरूप लिहा :
(i) झपाटा (ने)
(ii) झोप (चा)
(iii) भाषा (ला)
(iv) पुस्तके (त)
उत्तर:
(i) झपाट्याने
(ii) झोपेचा
(iii) भाषेला
(iv) पुस्तकांत.
प्रश्न 3.
अधोरेखित नामांच्या जागी अन्य योग्य नामे लिहून वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा :
आमच्या भल्यामोठ्या वाड्यात पुष्कळ बिहाडे होती.
उत्तर:
आमच्या भल्यामोठ्या इमारतीत पुष्कळ कुटुंबे होती.
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
घमघमाट’ यासारखे तुम्हांला ठाऊक असलेले चार शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
चमचमाट, दणदणाट, ठणठणाट, फडफडाट.
Marathi Kumarbharti Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 8 वाट पाहताना Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १ : (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
कारणे लिहा :
(i) पण तेव्हा जीव नुसता फुटून जायचा; कारण ……………………………….
(ii) पोस्टमनचे काम वाटते तितके सोपे नव्हते; कारण ……………………………….
उत्तर:
(i) पण तेव्हा जीव नुसता फुटून जायचा; कारण आत्याला घरी यायला रात्र होई म्हणून लेखिकांचे मन अनामिक भीतीने व्यापून जायचे.
(ii) पोस्टमनचे काम वाटते तितके सोपे नव्हते; कारण पत्रांचा थैला पाठीवर घेऊन वाहनांची सोय नसलेल्या वाड्या वस्त्यांवर पायी चालत जावे लागे.
प्रश्न 2.
अर्थ स्पष्ट करा :
(i) तो नुसता पत्र पोहोचवणारा सरकारी नोकर नाही. तो माणूस आहे.
(ii) पावसाची वाट पाहणाऱ्या शेतकऱ्याचे डोळे आठवा जरा.
उत्तर:
(i) तो पोस्टमन एक वस्तू नेऊन दुसऱ्याला दयावी, इतक्या कोरडेपणाने काम करणारा हमाल नव्हता. तो त्या पत्रात दडलेल्या माणसांच्या भावभावना ओळखू शकत होता, त्या माणसांशी तो मनाने जोडला जायचा.
(ii) पाऊस पडण्याचे दिवस आले की शेतकरी आतुरतेने पावसाची वाट पाहतो. त्या वेळी त्याच्या मनात पाऊस पडेल की नाही, पडला तर पुरेसा पडेल की नाही, ही धाकधुकी असते. आणि पडलाच नाही तर? ही जिवाची तडफड करणारी भीतीही असते. हे सर्व भाव शेतकऱ्यांच्या डोळ्यांत दिसतात.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
‘रडू गळ्याशी दाटून येणे’ या वाक्प्रचारात ‘गळा’ या अवयवाचा उपयोग केलेला आहे, असे शरीराच्या अवयवांवर आधारित आणखी चार वाक्प्रचार लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) राग नाकावर असणे,
(ii) पाऊल वाकडे पडणे.
(iii) छाती पिटणे.
(iv) नाकातोंडात पाणी जाणे.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
‘वाड्यावस्त्या’ यासारखे आणखी चार जोडशब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) गल्लीबोळ
(ii) बाजारहाट
(iii) नदीनाले
(iv) झाडेझुडपे.
प्रश्न 3.
अधोरेखित सर्वनाम कोणाला उद्देशून योजले आहे, ते लिहा :
(i) पोस्टमन आल्याचे तिला बरोबर समजते.
(ii) त्याच्या येण्याची वाट पाहत आहे.
(iii) तो त्याला माणसे दाखवतो.
उत्तर:
(i) तिला – अंध म्हातारी.
(ii) त्याच्या – म्हातारीचा मुलगा.
(iii) तो – पोस्टमन, त्याला – पोस्टमनचा मुलगा.
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न ४ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी…
व्याकरण घटकांवर आधारित कृती :
१. समास:
विग्रहावरून सामासिक शब्द लिहा :
विग्रह – सामासिक शब्द
(i) कानापर्यंत
(ii) राजाचा वाडा
(iii) सात सागरांचा समूह
(iv) दहा किंवा बारा
उत्तर:
विग्रह – सामासिक शब्द
(i) कानापर्यंत – आकर्ण
(ii) राजाचा वाडा – राजवाडा
(iii) सात सागरांचा समूह – सप्तसिंधू
(iv) दहा किंवा बारा – दहाबारा
![]()
२. अलंकार :
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील ओळींमधील अलंकार ओळखा व स्पष्टीकरण दया :
‘कुटुंबवत्सल इथे फणस हा।
कटिखांदयावर घेऊनि बाळे।।’
उत्तर :
अलंकार → चेतनगुणोक्ती
स्पष्टीकरण : फणसाच्या झाडाला लगडलेली फळे म्हणजे फणसाची लेकरे आहेत, अशा मानवी भावनांचे आरोपण फणसाच्या निर्जीव झाडावर केल्यामुळे हा चेतनगुणोक्ती अलंकार आहे.
प्रश्न 2.
पुढील वैशिष्ट्यावरून अलंकार ओळखा व समर्पक उदाहरण दया : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका -३)
(i) उपमेय व उपमान या दोघात भेद नाही.
(ii) उपमेय हे उपमानच आहे.
(अ) अलंकाराचे नाव → [ ]
(आ) अलंकाराचे उदाहरण → [ ]
उत्तर :
(अ) अलंकाराचे नाव → [रूपक]
(आ) अलंकाराचे उदाहरण → [वारणेचा ढाण्या वाघ बाहेर पडला]
३. वृत्त :
पुढील ओळींचे गण पाडून वृत्त ओळखा :
तदितर खग भेणे वेगळाले पळाले
उपवन जल केली जे कराया मिळाले
उत्तर :
वृत्त : हे मालिनी वृत्त आहे.
![]()
४. शब्दसिद्धी :
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील शब्दांना ‘खोर’ हा प्रत्यय लावून शब्द तयार करा :
(i) भांडण –
(i) चुगली –
उत्तर:
(i) भांडखोर
(ii) चुगलखोर
प्रश्न 2.
पुढील शब्दांच्या आधी ‘अव’ हा उपसर्ग लावून शब्द तयार करा :
(i) गुण – (ii) लक्षण –
उत्तर:
(i) अवगुण
(ii) अवलक्षण
प्रश्न 3.
वर्गीकरण करा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका -१).
शब्द : सामाजिक, अभिनंदन, नम्रता, अपयश.
प्रत्ययघटित – उपसर्गघटित
(i) ……………………………
(ii) ……………………………
उत्तर:
प्रत्ययघटित – उपसर्गघटित
(i) सामाजिक – (ii) नम्रता
(i) अभिनंदन – (ii) अपयश
![]()
५. सामान्यरूप :
पुढील शब्दांची सामान्यरूपे लिहा :
(i) रात्रीचे –
(ii) पंखांनी –
(iii) आंब्यावर –
(iv) म्हातारीला –
(v) संगीताने –
(vi) हाताला –
उत्तरे :
(i) रात्रीचे – रात्री
(ii) पंखांनी – पंखां
(iii) आंब्यावर – आंब्या
(iv) म्हातारीला – म्हातारी
(v) संगीताने – संगीता
(vi) हाताला – हाता
६. वाक्प्रचार :
प्रश्न 1.
जोड्या जुळवा :
वाक्प्रचार – अर्थ
(i) चाहूल येणे – (अ) चौकशी करणे
(ii) सार्थक होणे – (आ) गुंग होणे
(iii) थक्क होणे – (इ) अंदाज येणे
(iv) विचारपूस करणे – (ई) धन्य वाटणे
(v) भान विसरणे – (उ) चकित होणे
उत्तरे :
(i) चाहूल येणे – अंदाज येणे
(ii) सार्थक होणे – धन्य वाटणे
(iii) थक्क होणे – चकित होणे
(iv) विचारपूस करणे – चौकशी करणे
(v) भान विसरणे – गुंग होणे.
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
दिलेल्या वाक्यांत योग्य वाक्प्रचारांचा उपयोग करून वाक्ये पुन्हा लिहा : (कपाळाला आठी पडणे, सहीसलामत बाहेर पडणे, भान विसरणे) (सराव कृतिपत्रिका -१)
(i) त्सुनामीच्या तडाख्यात सापडलेल्या लोकांना भारतीय जवानांनी सुखरूप बाहेर काढले.
(ii) दिवाळीसाठी आणलेले नवीन कपडे नमिताला न आवडल्यामुळे तिने नाराजी व्यक्त केली.
उत्तर:
(i) त्सुनामीच्या तडाख्यात सापडलेले लोक भारतीय … जवानांच्या मदतीने सहीसलामत बाहेर पडले.
(ii) दिवाळीसाठी आणलेले नवीन कपडे पाहून नमिताच्या कपाळालां आठी पडली.
भाषिक घटकांवर आधारित कृती:
१. शब्दसंपत्ती :
प्रश्न 1.
गटात न बसणारा शब्द लिहा :
(i) कोकीळ, पोपट, कावळा, गाय, मोर,
(ii) कुरड्या, पापड्या, शेवया, चकल्या, वाळवण.
उत्तर:
(i) गाय
(ii) वाळवण,
प्रश्न 2.
पुढील पक्ष्यांसमोर त्यांची घरे लिहा :
जसे : कोकिळा – घरटे; तसे
(i) पोपट – …………………….
(ii) कोंबडा – …………………….
उत्तर:
(i) पोपट – ढोली
(ii) कोंबडा – खुराडे.
प्रश्न 3.
जसे : पोपटांचा – थवा; तसे –
(i) गुरांचा – …………………….
(ii) फुलांचा – …………………….
उत्तर:
(i) गुरांचा – कळप
(ii) फुलांचा – गुच्छ,
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
पुढील शब्दांचे भिन्न अर्थ लिहा :
← माळा →
← गार →
उत्तर:
मजला ← माळा → हार
थंड ← गार → गारगोटी
प्रश्न 5.
गटात न बसणारा शब्द शोधा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-३)
(i) खाणे, जेवणे, जेवण, करणे →
(ii) मधुर, स्वस्त, पाणी, स्वच्छ →
उत्तर:
(i) जेवण
(ii) पाणी
प्रश्न 6.
विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा :
(i) मऊ x …………………..
(ii) गार x …………………..
(iii) धाकटा x …………………..
(iv) अलीकडे x …………………..
(v) अंध x …………………..
(vi) दूर x …………………..
(vii) पक्की x …………………..
(viii) शहर x …………………..
उत्तर:
(i) मऊ x टणक
(ii) गार x गरम
(iii) धाकटा x थोरला
(iv) अलीकडे x पलीकडे
(v) अंघ x डोळस
(vi) दूर x जवळ
(vii) पक्की x कच्ची
(viii) शहर x खेडे
वाट पाहताना शब्दार्थ
- घमघमणे – सुगंध दाटून येऊन पसरणे.
- हजारी मोगरा – अनेक फुलांचा गुच्छ येणारे मोगऱ्याचे झाड.
- गराडा – गर्दी करून घातलेला वेढा.
- प्रतिमा – नवनवीन कल्पना योजून निर्मिती करण्याची क्षमता.
- दिंडी दरवाजा – (दिंडी = मोठ्या दरवाजात असलेला लहान दरवाजा.) दिंडी असलेला मोठा दरवाजा.
- शोष – कोरडेपणा, सुकलेपणा, घशास पडलेली कोरड.
- भला – चांगला, सज्जन.
- डोळस – डोळे-दृष्टी शाबूत असलेला, आंधळेपणाने विश्वास न ठेवणारा.
- धीर धरणे – अधीरता, उत्सुकता दाबून ठेवून संयम बाळगणे.
वाट पाहताना वाक्प्रचार व त्यांचे अर्थ
- तोंडावर येणे : (एखादी भावी घटना) नजीक येऊन ठेपणे.
- सार्थक होणे : धन्यता वाटणे, परिपूर्ती होणे.
- मन आतून फुलून येणे : मनातल्या मनात अमाप आनंद होणे.
- जीव फुटून जाणे : अतोनात कासावीस होणे, भयभीत होणे.
- नाटक चालू ठेवणे : सोंग, बतावणी चालू ठेवणे.
Must Read:
FINNIFTY Pivot Point Calculator
Marathi Kumarbharti Class 10 Textbook Solutions भाग-२