Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Civics Solutions Chapter 6 Bureaucracy Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 8 Civics Chapter 6 Bureaucracy Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
Bureaucracy Class 8 Questions And Answers Chapter 6 Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Civics Chapter 6 Bureaucracy Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Identify if the following statements are correct or wrong and rewrite the wrong statements in their correct form:
Question 1.
In a Parliamentary democracy, representatives elected by the people and ministers bear the administrative responsibility.
Answer:
Correct.
Question 2.
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) recruits candidates for civil services in Maharashtra.
Answer:
Wrong – Maharashtra Public Service Commission recruits candidates for civil services in Maharashtra.
![]()
2. Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Reservation policy is followed even in Civil Services.
Answer:
- A part of the society comprising of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Women, Other Backward Castes and specially-abled is termed as the weaker section of the society.
- It was essential to empower these weaker sections.
- They were left out of civil services due to social inequality.
- In order to establish social justice and provide opportunities to weaker sections of the society, reservation policy is followed even in civil services.
Question 2.
It is necessary for civil servants to be politically neutral.
Answer:
- In Parliamentary democracy, in India, a new government comes in power after every five years. But the bureaucracy is permanent, i.e. they remain same.
- Bureaucracy is expected to implement the policies and decisions of the earlier government with same efficiency and commitment.
- Civil servants are expected to keep away from taking a political stand and remain neutral while discharging their duties.
- If civil servants work according to their political views it will lead to chaos. Hence, they should be politically neutral.
3. Answer the following questions in 25 to 30 words:
Question 1.
Explain the role of the ministers and civil servants in the efficient administration of the department.
Answer:
- The efficiency of a particular department depends upon the inter-relationship between the Minister and his Secretary and Deputy secretary.
- The decisions taken by the Ministers are based on the necessary information provided by the bureaucracy.
- The bureaucracy, i.e. civil servants have complete information about the financial provisions for a particular scheme or plan and also about the history of successes and failures of policies.
- Hence, if the Ministers develop mutual trust and transparency with the civil servants, it will help in the efficient administration of the department.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain how the bureaucracy provides stability to the political system.
Answer:
- Bureaucracy does the work of implementing decisions taken by the ministers.
- Several important reforms introduced during the post-independent period have been effectively implemented by the bureaucracy.
- It consistently provides services like water supply, public cleanliness, transport, electricity, etc. to the people and brings stability in their day-to-day life.
- It acts as an instrument of social transformation and democratisation. In this way, it gives stability to the political system.
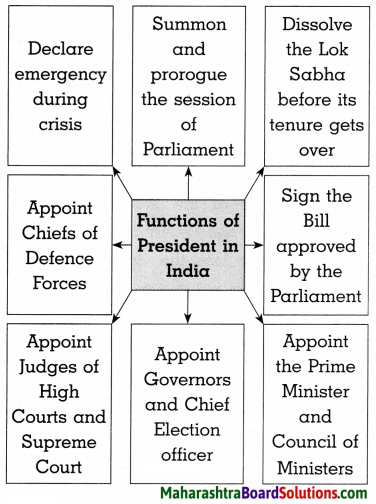
4. Complete the concept picture.
Question 1.
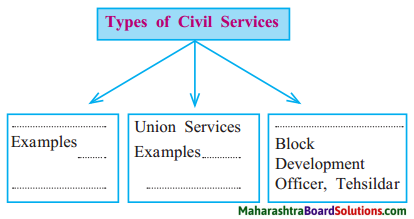
Answer:
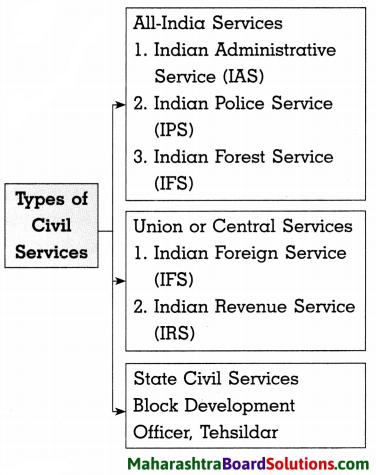
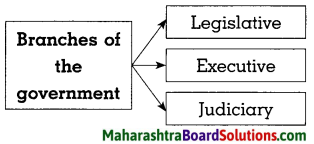
5. Discuss characteristics of bureaucracy.
Question 1.
Bureaucracy:
Answer:
- It is the administrative system that works under the Union Executive.
- As this administrative system includes civil servants i.e. bureaucrats, it is called Bureaucracy.
- It has the responsibility of actual implementation of government’s policies.
- Though the ministers control the bureaucracy, they are dependent on the bureaucracy for information and efficient functioning.
![]()
Question 2.
Armed Forces and Civil Services:
Answer:
- Defending the country from external aggression and internal threats and ensuring security of the country is carried out by the Armed Forces.
- Services provided to the citizens for making their daily lives comfortable and enabling them to develop themselves and the society are called Civil Services.
- The administrative system developed to provide services to citizens are called Civil Services.
- The armed forces help the civil services for internal security.
Meaning of the Headlines given In the box:

- In the box, a few posts like District Collector, Municipal Commissioner, flnance Secretary, and Divisional Commissioner are mentioned.
- They are civil servants in the government’s administrative system, working for the welfare of the people.
Project:
Question 1.
Prepare a questionnaire and interview a civil servant in your locality
Class 8 Civics Chapter 6 Bureaucracy Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct options and complete the statements:
Question 1.
…………….. is permanent in nature.
(a) Election Commission
(b) Bureaucracy
(c) President
(d) Prime Ministers
Answer:
(b) Bureaucracy
![]()
Question 2.
The bureaucracy is politically ……………….. .
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) biased
(d) neutral
Answer:
(d) neutral
Question 3.
The Parliament holds the ……….. responsible for malpractices.
(a) bureaucracy
(b) Prime Minister
(c) minister
(d) President
Answer:
(c) minister
Question 4.
The ………….. has established autonomous institutions like the Public Service Commissions for selecting efficient civil servants.
(a) Constitution
(b) Council of Ministers
(c) Parliament
(d) President
Answer:
(a) Constitution
Question 5.
The ‘Indian Foreign Service’ is included under ……………
(a) All India Services
(b) Union or Central Services
(c) State Civil Services
(d) Armed Forces
Answer:
(b) Union or Central Services
Identify if the following statements are correct or wrong and rewrite the wrong statements in their correct form:
Question 1.
Bureaucracy is an important instrument of social transformation.
Answer:
Correct.
![]()
Question 2.
Civil servants are not aware of the history of successes and failures of policies.
Answer:
Wrong – Civil servants are aware of the history of successes and failures of policies.
Question 3.
Civil servants are never publicly criticised.
Answer:
Correct.
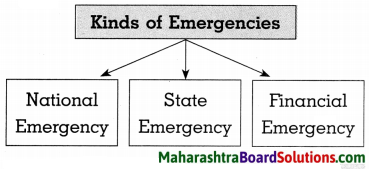
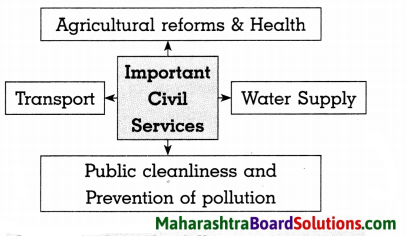
Complete the following concept maps:
Question 1.
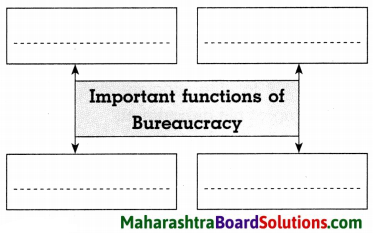
Answer:
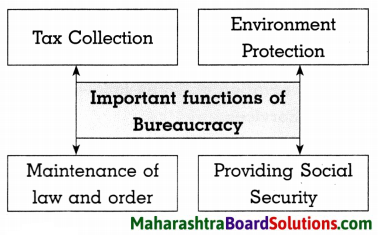
Question 2.
Answer:
Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
Coordination between the Civil Servants and Ministers help in efficient functioning of the government.
Answer:
- In Parliamentary democracy, the Executive is responsible for the efficient governance of the country.
- The decisions relating to the concerned department are made by the minister-in-charge, but necessary information to make such decisions is given by the civil servants.
- The ministers are dependent on the civil servants for many reasons.
Hence, coordination and mutual trust between the civil servants and ministers help in efficient functioning of the government.
![]()
Question 2.
The Bureaucracy is not held directly responsible for any success or failure of policy.
Answer:
- It is the Minister who is responsible for the efficient and smooth functioning of his department.
- Though providing necessary information and giving advice is the function of the bureaucracy, it is not accountable for any inefficiency.
- The Parliament holds the Minister responsible for inefficiency and malpractices.
- In such case, the Minister bears the responsibility and protects the bureaucracy.
Thus, the anonymity of bureaucracy is preserved, which means they are not held directly responsible for any success or failure of policy. ‘
Question 3.
Bureaucracy is considered as an important instrument of social transformation.
Answer:
- Many laws are enacted by the government for empowerment of women, protection of children and marginalised sections of the society.
- Social change is brought through the implementation of such policies.
- These laws are successfully implemented by the bureaucracy.
Hence, Bureaucracy is considered as an important instrument of social transformation.
Answer the following questions in 25 to 30 words:
Question 1.
Explain the characteristics of Bureaucracy.
Answer:
- Bureaucracy is the administrative system which actually implements the government’s policies.
- Though the government changes, bureaucracy remains constant. Thus, it is permanent in nature.
- It has to remain politically neutral and discharge its duties.
- Its anonymity is maintained, i.e. it is not held directly responsible for any success or failure of policies and it is never publicly criticized.
Thus, the structure of Bureaucracy in India is extensive and complex.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the significance of Indian bureaucracy.
Answer:
- The Indian bureaucracy implements the policies made by the government for the welfare of the people effectively.
- It provides several essential services to the people consistently and brings stability in their day to day life.
- It provides stability to the political system.
- It acts as an important instrument of social transformation and democratization of society.
Question 3.
Explain the role of bureaucracy in the democratisation of society.
Answer:
- Equality and social justice are important values of democracy.
- Bureaucracy has helped in bringing marginalised sections of society into the mainstream by implementing the reservation policy effectively.
- Their participation has been increased in the process of decision¬making.
- Democratisation of society not only requires progressive laws and policies but also effective participation of bureaucracy in implementing it.
Thus, bureaucracy plays an important role in the democratisation of society.
![]()
Question 4.
Why have autonomous institutions like Public Service Commissions been established?
Answer:
The Constitution of India has established autonomous institutions like Public Service Commissions for following reasons:
- To select civil servants.
- To conduct competitive exams for selecting candidates on the criteria of merit and efficiency.
- To decide other aspect to like the nature of the exam, syllabus, eligibility, etc.
- To select efficient and deserving candidates through interviews and recommend them to the government for appointment.
Open-Ended Question:
Question 1.
Express your views on ‘ideal bureaucracy’.
Answer:
Bureaucracy includes civil servants and all the employees working in various government offices. In India, bureaucracy is criticised most of the times and is seldom praised.
According to me, an ideal bureaucracy should function as follows:
- The bureaucracy should advise and force the ministers to adopt policies of public welfare.
- It should give full cooperation to the ministers for implementing policies effectively.
- It should adopt the principle of equality and an unbiased approach while implementing the policies so that maximum people are benefitted.
- It should make the people aware of different beneficial policies.
- It should strictly keep away from ill- practices like corruption, unnecessary delay, cheating and frauds, etc.
- It should aim at establishing social justice by extending maximum benefits to weaker sections.
- It should function as an effective medium for development of the country, social transformation and democratisation of society.
![]()
(B) Oral Examination:
Answer the following questions orally:
Question 1.
Who is the Chief Civil Servant of your district?
Question 2.
Name any two schemes/plans implemented by the government officers for your village/city.
Question 3.
How do armed forces help the civil servants?
Question 4.
Who is the Chief Civil Servant of a taluka/tehsil?
Formative Evaluation:
Oral Work:
1. Interview:
Prepare a questionnaire and interview a civil servant in your locality.
2. Group discussion:
Conduct a group discussion in your class on the topic ‘Role of bureaucracy in the development of city/village.’
![]()
Project:
Question 1.
Collect information about the working of bureaucracy at taluka/tehsil level.
8th Std Civics Questions And Answers:
- Introduction to the Parliamentary System Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Indian Parliament Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Union Executive Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Indian Judicial System Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
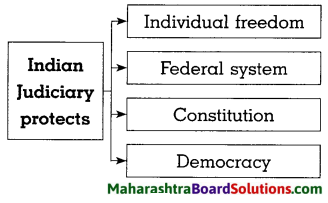
- The State Government Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- Bureaucracy Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers