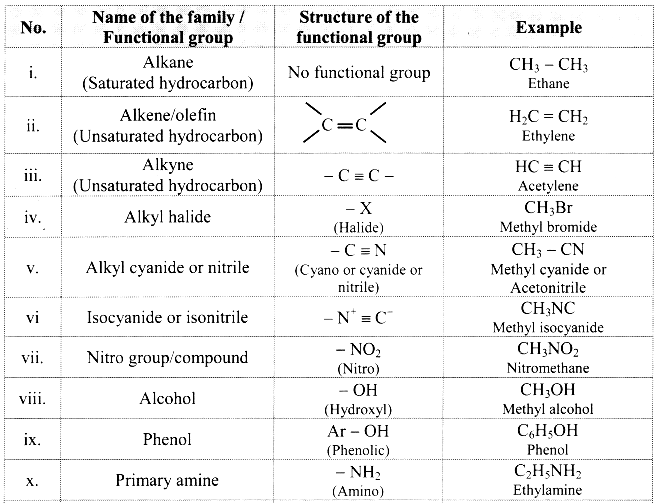
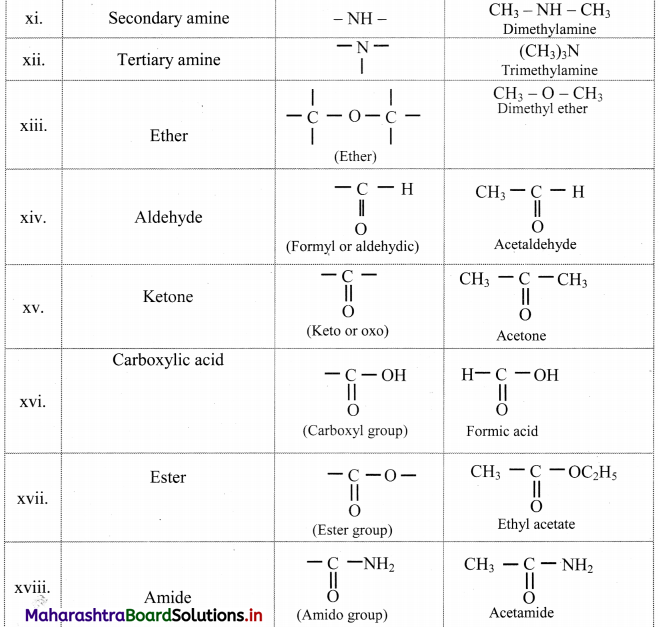
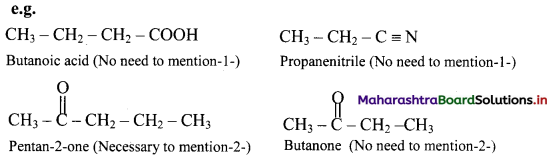
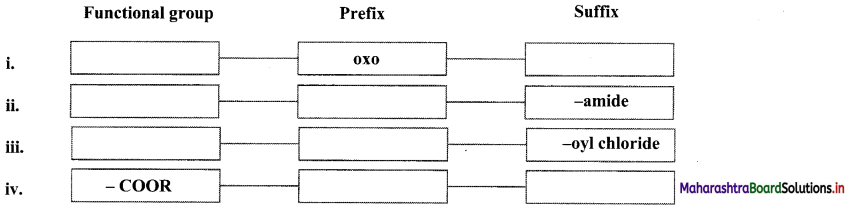
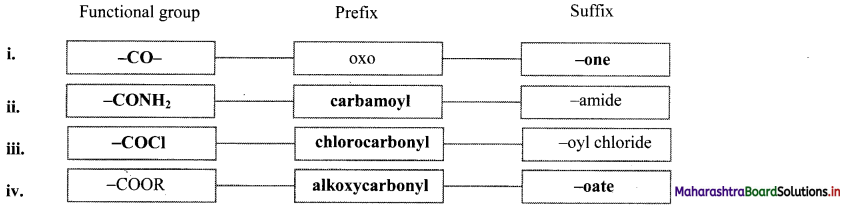
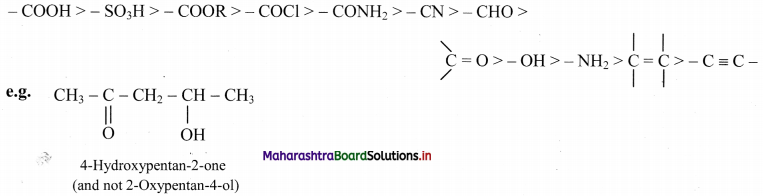
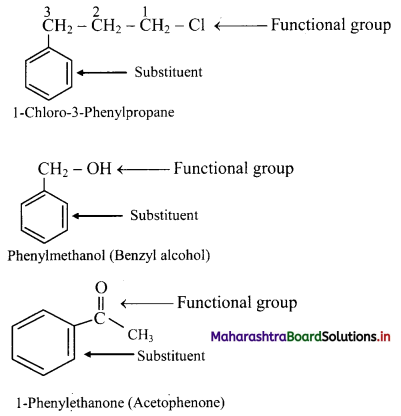
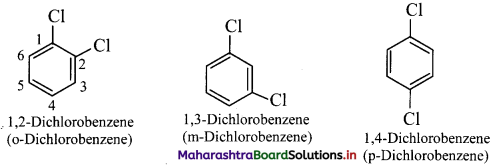
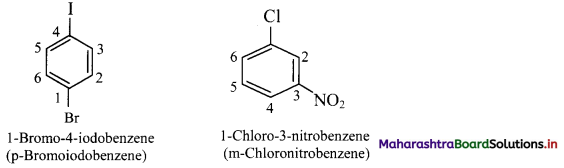
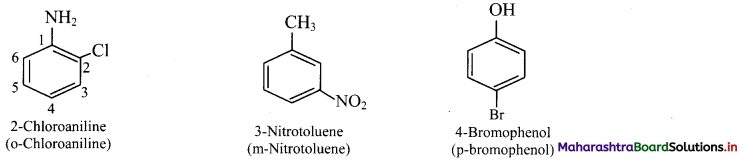
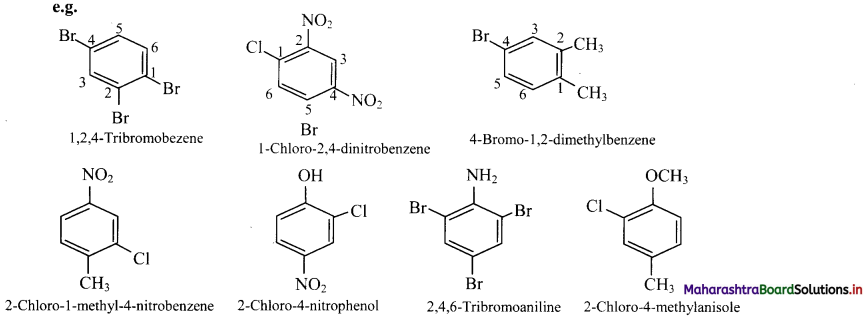
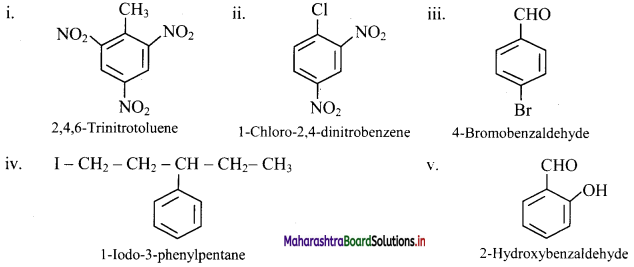
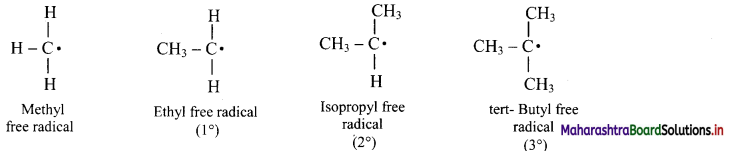
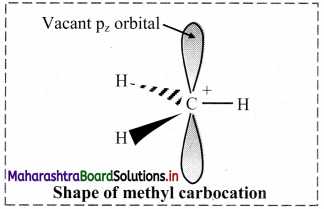
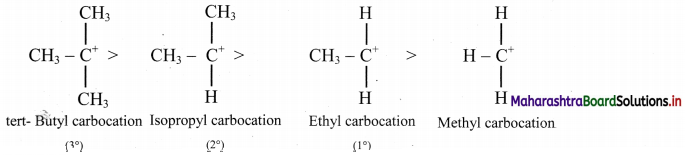
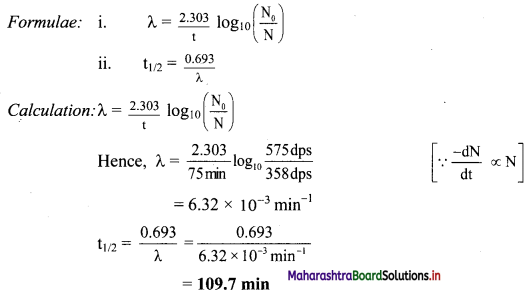
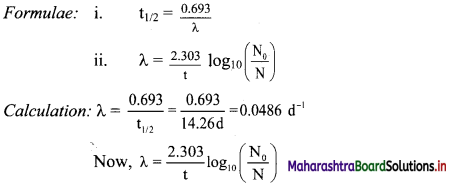
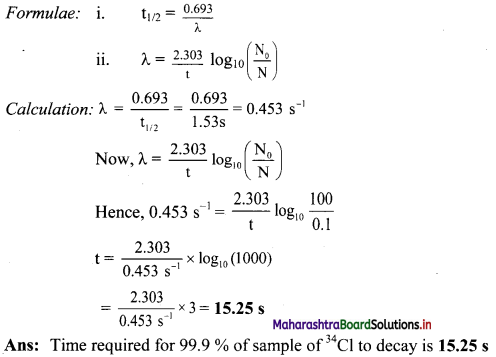
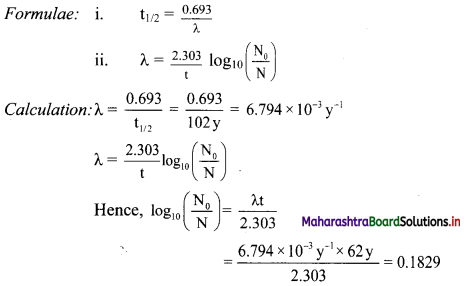
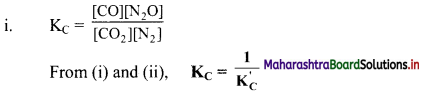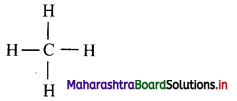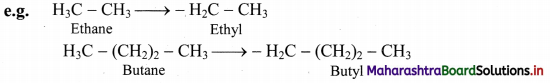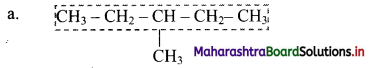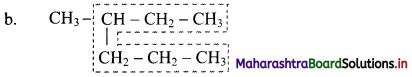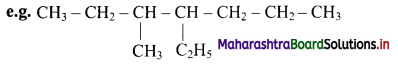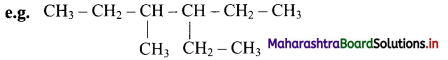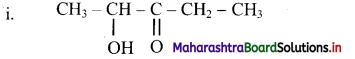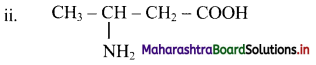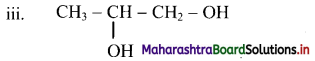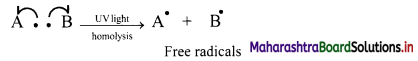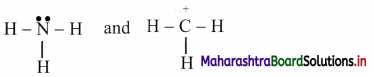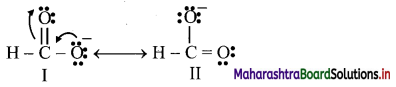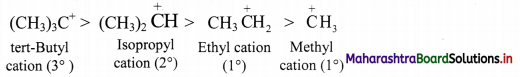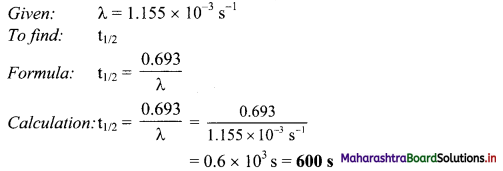Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Hydrocarbons Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 15 Hydrocarbons
Question 1.
What are unsaturated and saturated hydrocarbons?
Answer:
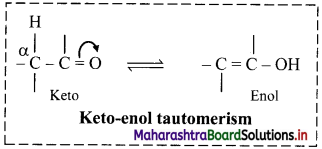
Hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon multiple bond (C=C or C≡C) are called unsaturated hydrocarbons, whereas those which contain carbon-carbon single bond (C-C) are called saturated hydrocarbons.
Question 2.
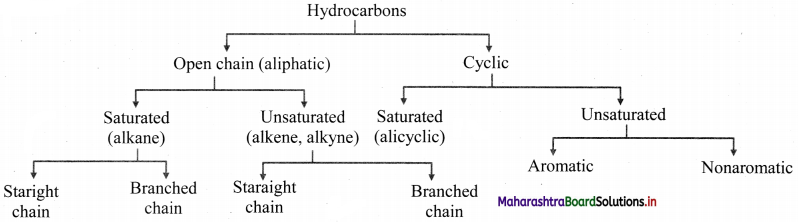
How are hydrocarbons classified?
Answer:
Question 3.
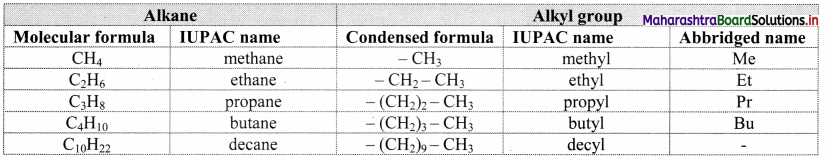
Define alkanes. Write general formula of alkanes.
Answer:
- Alkanes are aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons containing carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single
covalent bonds. - They have a general formula CnH2n+2 where, ‘n’ stands for number of carbon atoms in the alkane molecule.
![]()
Question 4.
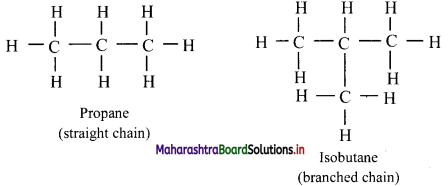
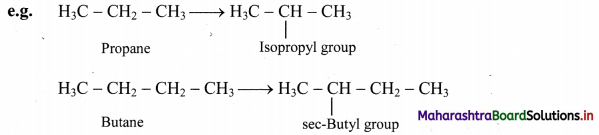
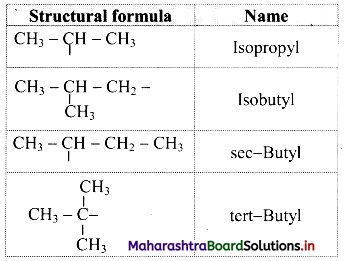
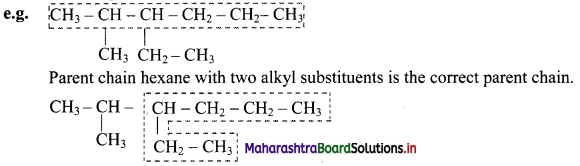
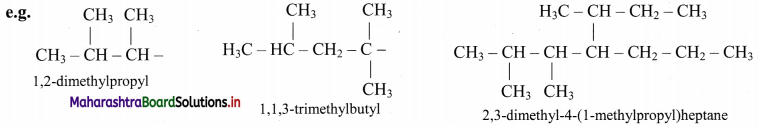
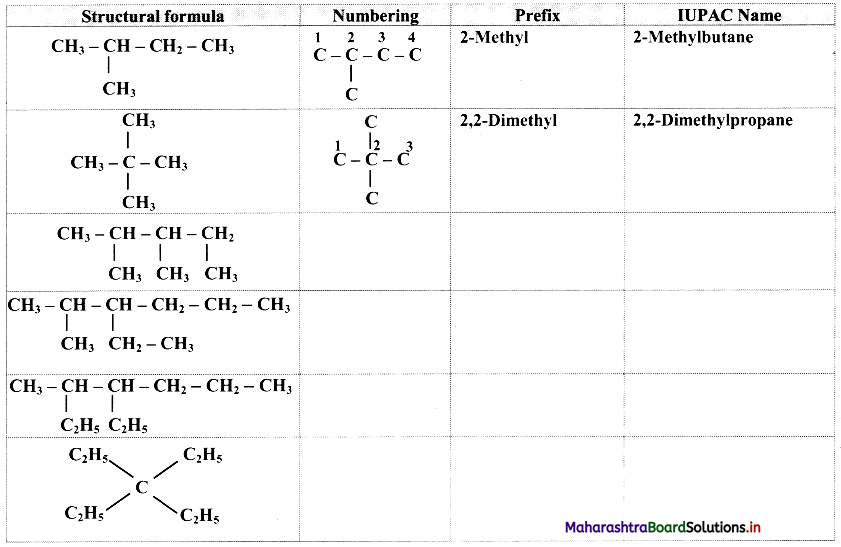
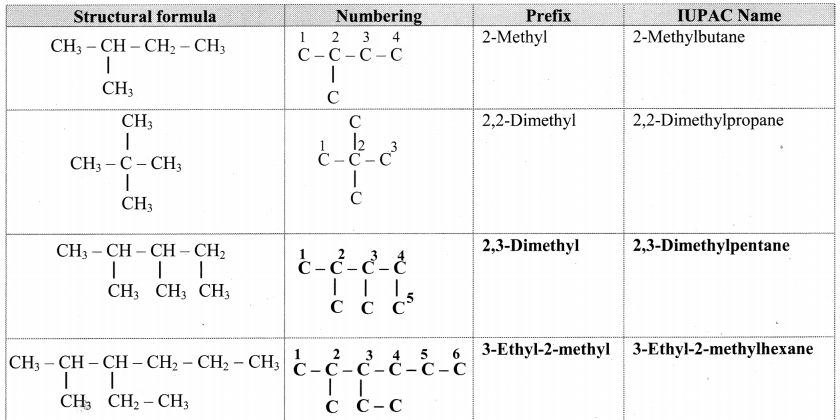
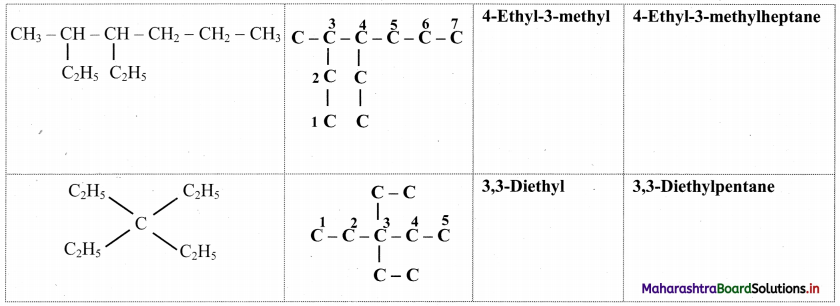
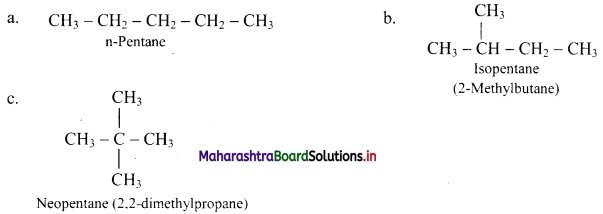
Give information about isomerism in alkanes. Write the all possible structural isomers of a saturated hydrocarbon containing four carbon atoms along with their IUPAC names.
Answer:
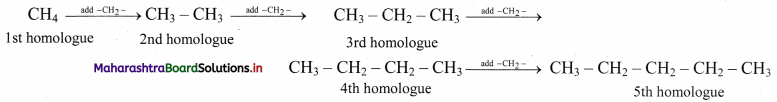
i. Alkanes with more than three carbon atoms generally exhibit, structural isomerism and in particular, the chain isomerism.
ii. The number of possible structural isomers increase rapidly with the number of carbon atoms.
iii. Structural isomers of a saturated hydrocarbon containing four carbon atoms along with their IUPAC names.

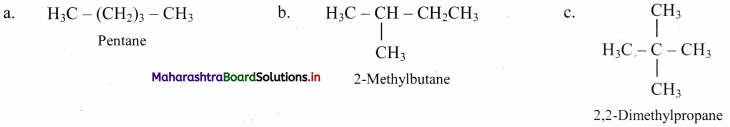
Question 5.
Write all the possible structural isomers of a saturated hydrocarbon having molecular formula C5H12.
Answer:
Question 6.
Define sigma bond.
Answer:
A single covalent bond formed by the coaxial overlap of orbitals is called sigma (σ) bond.
Question 7.
i. Why do C – C bonds in alkanes undergo rotation?
ii. What are conformations?
Answer:
i. a. Alkanes have single covalent bonds (sigma bonds) formed by the coaxial overlap of orbitals.
b. As a direct consequence of coaxial overlap of orbitals, a sigma bond is cylindrically symmetrical and the extent of orbital overlap is unaffected by rotation about the single bond and therefore, C – C bonds undergo rotation.
ii. a. In alkanes, the atoms bonded to one carbon of a C – C single bond change their relative position with reference to the atoms on the other carbon of that bond on rotation of that C – C single bond.
b. The resulting arrangements of the atoms in space about the C – C single bond are called conformations or conformational isomers. Innumerable conformations result on complete rotation of a C – C single bond through 360°.
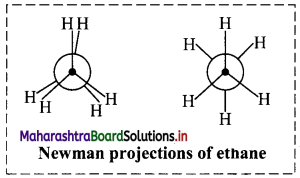
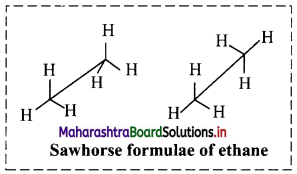
Question 8.
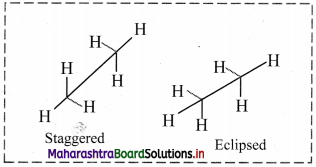
i. What is conformational isomerism?
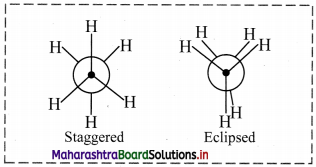
ii. Name the two extreme conformations shown by ethane molecule.
Answer:
i. The phenomenon of existence of conformation is a type of stereoisomerism and is known as conformational isomerism.
ii. Ethane molecule shows the following two extreme conformations:
- Staggered conformation
- Eclipsed conformation
![]()
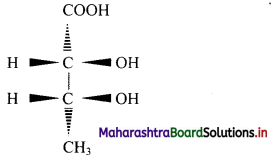
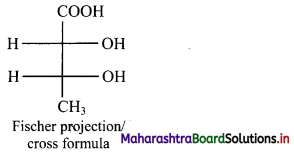
Question 9.
Draw structures representing staggered and eclipsed conformations of ethane using:
i. Sawhorse projection
ii. Newman projection
Answer:
i. Sawhorse projection of ethane:
ii. Newman projection of ethane:
Question 10.
How are alkanes obtained from crude oil?
Answer:
Alkanes are obtained by fractional distillation of crude oil in oil refineries.
Question 11.
How are alkanes obtained from alkenes and alkynes?
OR
How are alkanes obtained from catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes?
Answer:
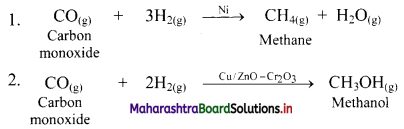
i. Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes or alkynes with dihydrogen gas gives corresponding alkanes.
ii. Finely divided powder of platinum (Pt) or palladium (Pd) catalyse the hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes at room temperature.
iii. Relatively high temperature and pressure are required with finely divided nickel as the catalyst.
e.g. a. Propene to propane:

b. Ethyne to ethane:

Question 12.
Write the general reactions for the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes and alkynes.
Answer:
General reaction for catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes:

General reaction for catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes:

Question 13.
Write the structures of alkenes that on catalytic hydrogenation give n-butane.
Answer:

Question 14.
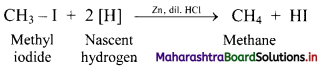
Explain the preparation of alkanes by reduction of alkyl halides with the help of an example.
Answer:
i. Alkanes can be prepared by reduction of alkyl halides using zinc and dilute hydrochloric acid.
ii. The reduction of alkyl halides is due to nascent hydrogen obtained from the reaction between reducing agent Zn and dilute HCl.
e.g. Reduction of methyl iodide to methane.
![]()
Question 15.
How are alkanes obtained by Wurtz reaction?
Answer:
Alkyl halides on treatment with reactive sodium metal in dry ether, gives higher alkanes having double the number of carbon atoms. This is called as Wurtz coupling reaction.
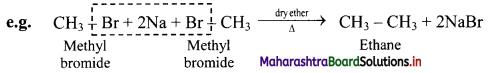
Question 16.
How will you convert ethyl chloride into n-butane?
Answer:
Ethyl chloride on heating with sodium metal in presence of dry ether gives n-butane.
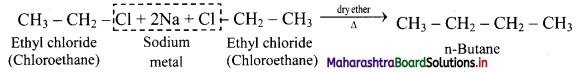
Question 17.
Write chemical equations for reactions that take place on treating ethereal solutions of:
i. Methyl iodide with sodium metal
ii. Ethyl iodide with sodium metal
Answer:
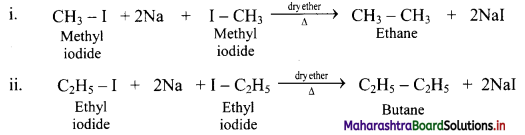
Question 18.
Explain the preparation of Grignard reagents.
OR
What is Grignard reagent? Explain its preparation.
Answer:
Grignard reagent are alkyl magnesium halides obtained by treating alkyl halides with dry magnesium metal in the presence of dry ether.
General Reaction:
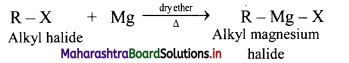
Question 19.
State the action of water on methyl magnesium bromide in dry ether with the help of a chemical reaction.
Answer:
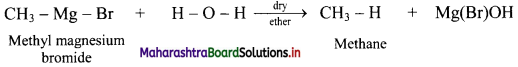
Question 20.
Write the reagents involved in the following conversions.
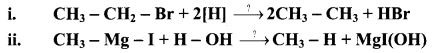
Answer:
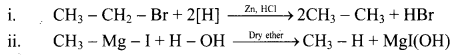
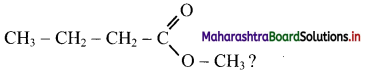
Question 21.
Straight chain alkanes have higher melting and boiling points as compared to branched isomeric alkanes. Give reason.
Answer:
i. The electronegativity of carbon and hydrogen is nearly the same. Therefore, C-H and C-C bonds are nonpolar covalent bonds and hence, alkanes are nonpolar.
ii. Alkane molecules are held together by weak intermolecular van der Waals forces.
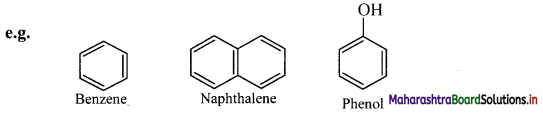
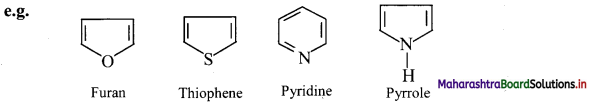
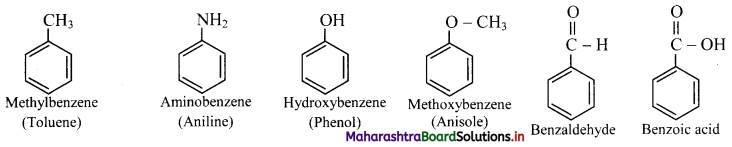
iii. Larger the surface area of molecules, stronger are such intermolecular van der Waals forces.
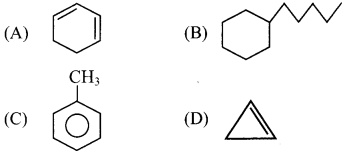
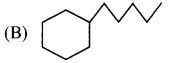
iv. In straight chain alkane molecules, surface area is relatively larger as compared to branched chain alkanes and as a result, the intermolecular forces are relatively stronger in straight chain alkanes than in branched chain alkanes.
Hence, straight chain alkanes have higher melting and boiling points as compared to branched alkanes.
![]()
Question 22.
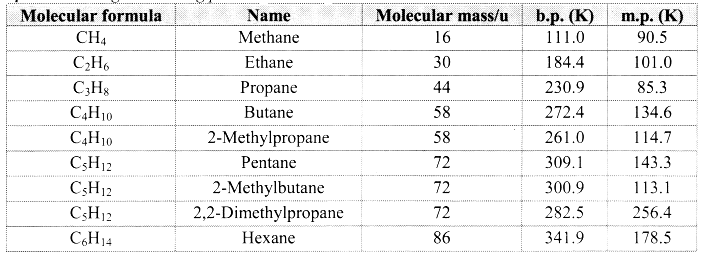
State physical properties of alkanes.
Answer:
- Alkanes are colourless and odourless.
- At room temperature, the first four alkanes are gases, alkanes having 5 to 17 carbon atoms are liquids while the rest all are solids.
- Alkanes are readily soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, ether or ethanol while they are insoluble in water.
- Alkanes have low melting and boiling points which increases with an increase in the number of carbon atoms for straight chain molecules. But for branched chain molecules, more the number of branches, lower is the boiling/melting point.
Note: [Melting and boiling points of alkanes]
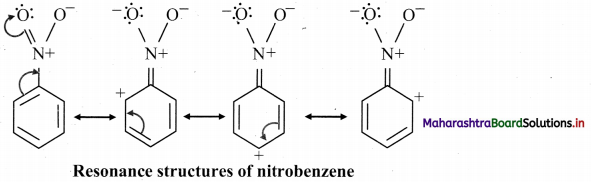
Question 23.
Define substitution reactions.
Answer:
The reactions in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms is called as substitution reactions.
e.g. Halogenation of alkanes.
Question 24.
i. What is halogenation of alkanes?
ii. Write the order of reactivity of halogens towards alkanes.
Answer:
i. Substitution of H atoms of alkanes by X (halogen, X = Cl, Br, I and F) atom is called halogenation of alkanes.
ii. The reactivity of halogens toward alkanes follows the order: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
[Note: The ease of replacement of hydrogen atoms from the carbon in alkanes is in the order: 3 > 2 > 1.]
Question 25.
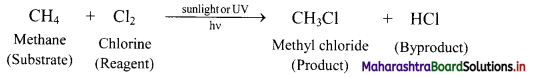
Explain reactions involved in chlorination of methane.
Answer:
Alkanes react with chlorine gas in presence of UV light or diffused sunlight or at a high temperature (573-773 K) to give a mixture of alkyl halides.
Chlorination of methane:
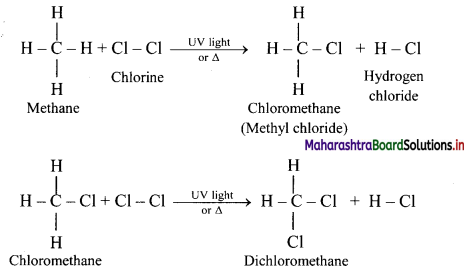
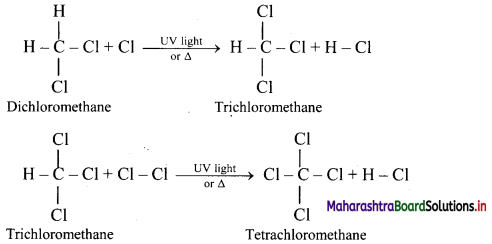
Tetrachloromethane is a major product when excess of chlorine is used. Chloromethane is obtained as major product when excess of methane is employed.
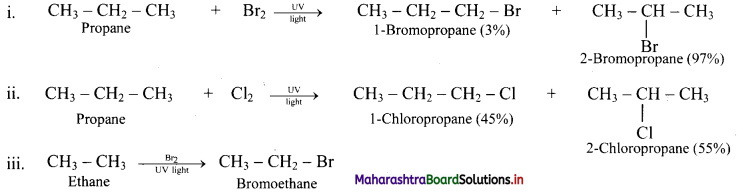
Question 26.
Predict the products in the following set of reactions.

Answer:
Question 27.
What is the action of Cl2 and Br2 on 2-methylpropane?
Answer:
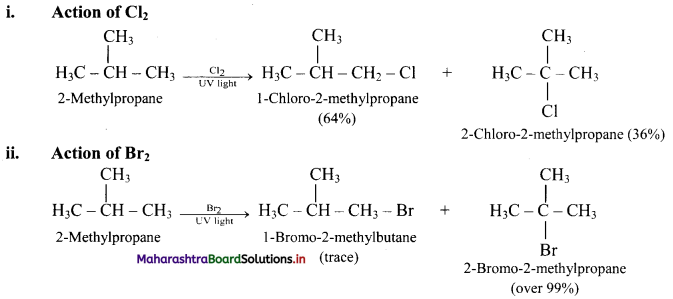
[Note: In bromination, there is high degree of selectivity as to which hydrogen atoms are replaced.]
![]()
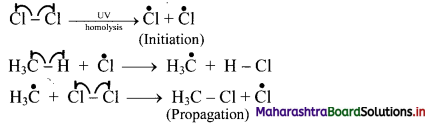
Question 28.
Explain mechanism of halogenation of alkanes.
Answer:
i. Halogenation of alkanes follows the free radical mechanism.
ii. Homolysis of halogen molecule (X2) generates halogen atoms, i.e., halogen free radicals.
iii. The mechanism of the first step of chlorination of methane is shown below:
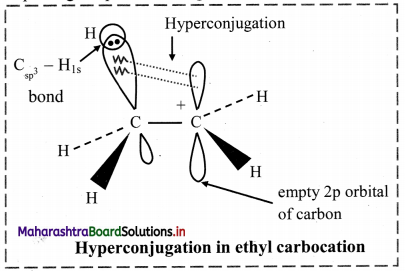
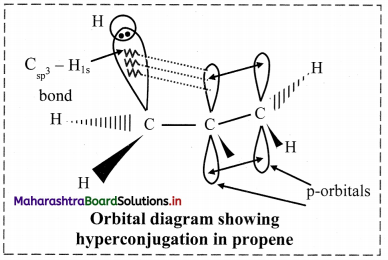
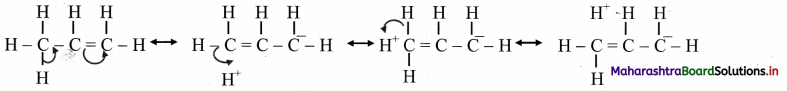
Question 29.
Why are alkanes used as fuels?
Answer:
On heating in the presence of air or dioxygen, alkanes are completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water with the evolution of a large amount of heat. Hence, alkanes are used as fuels.
Question 30.
What is combustion of alkanes? Write a general equation for alkane combustion.
Answer:
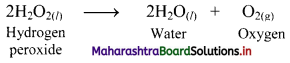
On heating in the presence of air or dioxygen, alkanes are completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water with the evolution of a large amount of heat. This is known as combustion reaction of alkanes.
General representative equation for combustion is:
![]()
Question 31.
Write chemical equations for combustion of butane and methane.
Answer:
i. Combustion of butane:

ii. Combustion of methane:

Question 32.
Write a short note on pyrolysis of alkanes.
Answer:
Alkanes on heating at higher temperature in absence of air decompose to lower alkanes, alkenes and hydrogen, etc. This is known as pyrolysis or cracking.
e.g. Pyrolysis of hexane
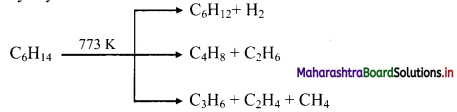
Question 33.
Explain aromatization reaction of alkanes. Give its one application.
Answer:
i. Straight chain alkanes containing 6 to 10 carbon atoms are converted to benzene and its homologues, on heating under 10 to 20 atm pressure at about 773 K in the presence of V2O5, Cr2O3, MO2O3, etc. supported over alumina.
ii. The reaction involves simultaneous dehydrogenation and cyclization. This reaction is known as aromatization or reforming.

This process is used in refineries to produce high quality gasoline which is used in automobiles as fuel.
![]()
Question 34.
Collect the information on CNG and LPG with reference to the constituents and the advantages of CNG over LPG.
Answer:
Constituents of CNG (Compressed Natural Gas):
It mainly consists of methane compressed at a pressure of 200-248 bar.
Constituents of LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas):
It contains a mixture of propane and butane liquefied at 15°C and a pressure of 1.7 – 7.5 bar.
Advantages of CNG over LPG:
- CNG is cheaper and cleaner than LPG.
- CNG produces less pollutants than LPG.
- It does not evolve gases containing sulphur and nitrogen.
- Octane rating of CNG is high, hence thermal efficiency is more.
- Vehicles powered by CNG produces less carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emission.
[Note: Students are expected to collect additional information on their own.]
Question 35.
Write the uses of alkane.
Answer:
Uses of alkanes:
- First four alkanes are used as a fuel mainly for heating and cooking purpose. For example, LPG and CNG.
- CNG, petrol and diesel are used as fuel for automobiles.
- Lower liquid alkanes are used as solvent.
- Alkanes with more than 35 C atoms (tar) are used for road surfacing.
- Waxes are high molecular weight alkanes. They are used as lubricants. They are also used for the preparation of candles and carbon black that is used in manufacture of printing ink, shoe polish, etc.
Question 36.
i. Write the general molecular formula of alkenes.
ii. Why are alkenes also known as olefins?
Answer:
i. Alkenes have general formula CnH2n, where, n = 2,3,4… etc.
ii. Alkenes are also known as olefins because the first member ethene/ethylene reacts with chlorine to form oily substance.
[Note: Alkenes with one carbon-carbon double bond, contain two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkanes.]
Question 37.
Define alkadienes and alkatrienes. Give one example for each.
Answer:
i. The aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing two carbon-carbon double bonds are called as alkadienes.
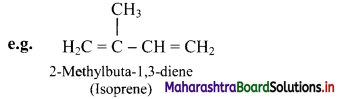
ii. The aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing three carbon-carbon double bonds are called as alkatrienes.
Question 38.
Explain structural isomerism in alkenes by giving an example.
Answer:
Alkenes with more than three carbon atoms show structural isomerism.
e.g. Alkene with molecular formula C4H8 is butene. The structural formulae for C4H8 can be drawn in three different ways:
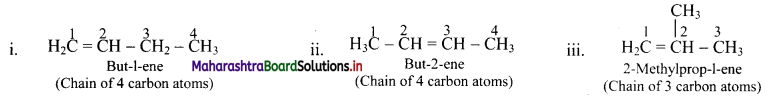
![]()
Question 39.
Draw structures of chain isomers of butene.
Answer:
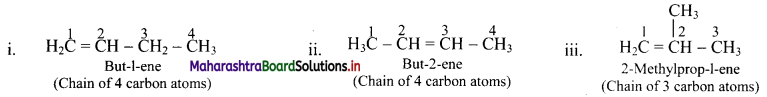
Question 40.
Draw structures of position isomers of butene.
Answer:
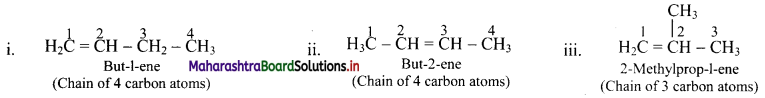
Question 41.
Define geometrical isomerism.
Answer:
The isomerism which arises due to the difference in spatial arrangement of atoms or groups about doubly bonded carbon (C=C) atoms is called geometrical isomerism.
Question 42.
Explain geometrical isomerism using a general example.
Answer:
i. If the two atoms or groups bonded to each end of the C=C double bond are different, then the molecule can be represented by two different special arrangements of the groups as follows:

ii. In structure (A), two identical atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond.
The geometrical isomer in which two identical or similar atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond is called cis-isomer.
iii. In structure (B), two identical atoms or groups lie on the opposite side of the double bond.
The geometrical isomer in which two identical or similar atoms or groups lie on the opposite side of the double bond is called trans-isomer.
iv. Due to different arrangement of atoms or groups in space, these isomers differ in their physical properties like melting point, boiling point, solubility, etc.
Question 43.
i. Define cis- and trans-isomer.
ii. Draw geometrical isomers of but-2-ene.
Answer:
i. a. Cis isomer: The geometrical isomer in which two identical or similar atoms or groups lie on the same side of the double bond is called a cis-isomer.
b. Trans isomer: The geometrical isomer in which two identical or similar atoms or groups lie on the opposite side of the double bond is called a trans-isomer.
ii. Geometrical or cis-trans isomers of but-2-ene are represented as:
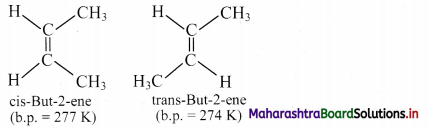
Question 44.
State whether the following alkenes can exhibit geometrical (or cis-trans) isomerism or not. Give reason for the answer.
i. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH = CH2
ii. CH3 – CH2 – CH = C(CH3)2
Answer:
Both the alkenes (i) and (ii) cannot exhibit geometrical isomerism, since 1 alkene is a terminal alkene (containing two H-atoms on the same side of the double bond) while the 2nd alkene is a 1,1-disubstituted alkene (containing two identical alkyl groups on the same side of the double bond).
![]()
Question 45.
Write the general formulae of alkenes which exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
Answer:
Alkenes having the following general formulae exhibit cis-trans isomerism:
RCH=CHR, R1R2C=CR1R3, R1CH=CR1R2, R1CH=CR2R3, R1CH=CHR2 and R1R2C=CR3R4
Question 46.
Draw structures of cis-trans isomers for the following:
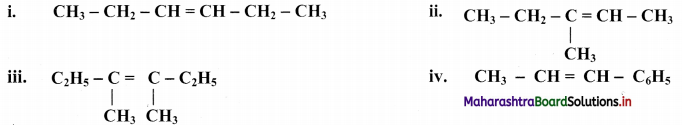
Answer:
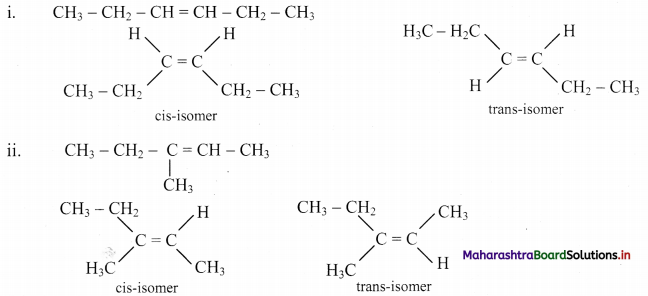
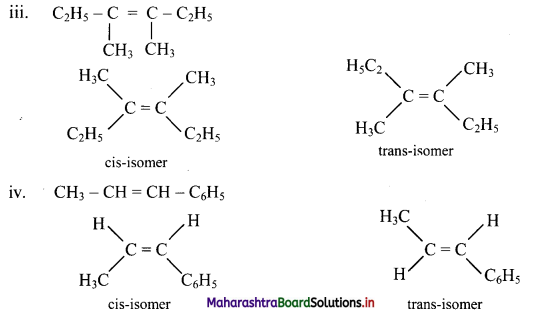
Question 47.
Which of the following compounds will show geometrical isomerism?
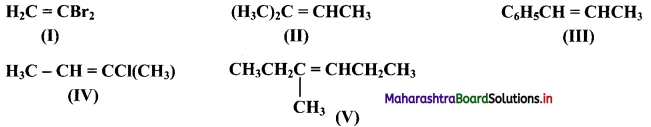
Answer:
Compounds (III), (IV) and (V) will show geometrical isomerism as they have each of the doubly bonded carbon atoms in their structures, attached to different atoms/groups of atoms.
Question 48.
Alkenes can be obtained from which industrial sources?
Answer:
- The most important alkenes for chemical industry are ethene, propene and buta-1,3-diene.
- Alkenes containing up to four carbon atoms can be obtained in pure form from the petroleum products.
- Ethene is produced from natural gas and crude oil by cracking.
Question 49.
What is β-elimination reaction? Explain in brief.
Answer:
The reactions in which two atoms or groups are eliminated from adjacent carbon atoms are called 1,2-elimination reactions. Since the atom/group is removed from β-carbon atom (β to the leaving group) it is called as β-elimination reaction.
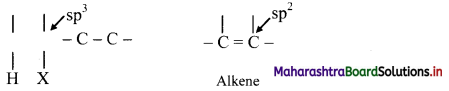
The hybridization of each C in the reactant is sp3 while that in the product is sp2. This means elimination reactions cause change in hybridization state while forming multiple bonds from single bond.
![]()
Question 50.
i. What is dehydrohalogenation reaction?
ii. How is it carried out. Explain with an example.
Answer:
i. a. The reactions in which there is removal of hydrogen (H) atom and halogen (X) atom from adjacent carbon atoms are known as dehydrohalogenation reactions.
b. The carbon carrying X is called α-carbon atom. The hydrogen atom from adjacent carbon called β-carbon atom, is removed and hence, the reaction is known as β-elimination.
ii. When an alkyl halide is boiled with a hot concentrated alcoholic solution of a strong base like KOH or NaOH, alkene is formed with removal of water molecule.
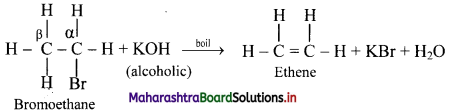
[Note: The ease of dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides is in the order 3 > 2 > 1.]
Question 51.
State Saytzeff rule.
Answer:
In dehydrohalogenation the preferred product is the alkene that has the greater number of alkyl groups attached to doubly bonded carbon atoms.
Question 52.
Write and explain dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-chlorobutane.
Answer:
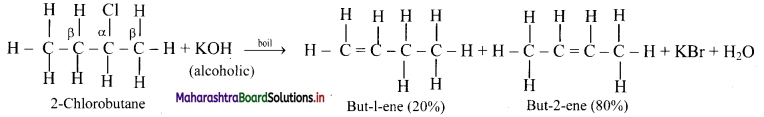
In dehydrohalogenation of 2-chlorobutane, but-2-ene (disubstituted alkene) is the preferred product because it is formed faster than but-1-ene (monosubstituted alkene) which is in accordance with Saytzeff rule.
Question 53.
Write the CORRECT order of stability of alkenes with respect to Saytzeff rule.
R CH = CH2, CH2 = CH2, R2C = CH2, R2C = CR2, RCH = CHR, R2C = CHR
Answer:
R2C = CR2 > R2C = CHR > R2C = CH2, RCH = CHR > RCH = CH2 > CH2 = CH2
Question 54.
Explain dehydration reaction of alcohols.
Answer:
i. Alcohols on heating with sulphuric acid form alkenes with elimination of water molecule. The reaction is known as catalysed dehydration of alcohols.
ii. The exact conditions of dehydration depend upon the alcohol.
iii. Dehydration of alcohol is an example of β-elimination since -OH group from α-carbon along with H-atom from β-carbon is removed.
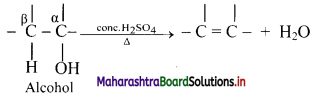
The ease of dehydration of alcohol is in the order 3° > 2° > 1°.
![]()
Question 55.
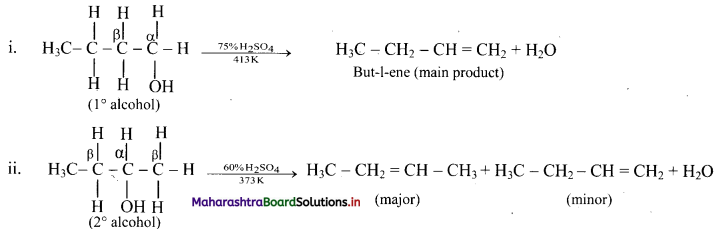
Write dehydration reaction of 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols giving one example for each.
Answer:
The ease of dehydration of alcohols is in the order 3° > 2° > 1°.
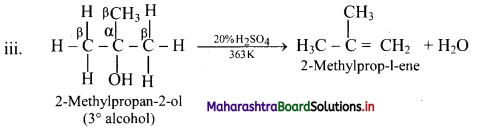
Question 56.
Explain isomerism with structure in the product obtained by acid catalysed dehydration of pentan-2-ol.
Answer:
i. Pentan-2-ol on acid catalysed dehydration, forms the following isomers.
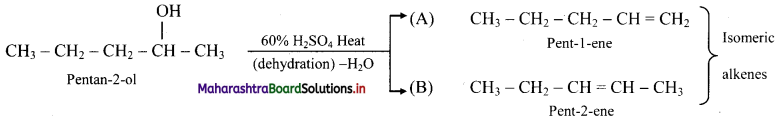
ii. A and B are position isomers.
iii. Pent-2-ene has the following geometrical isomers:

Question 57.
What is dehalogenation? Write the general reaction for dehalogenation of vicinal dihalides.
Answer:
i. Removal of two halogen atoms from adjacent carbon atoms is called dehalogenation.
ii. The dihalides of alkane in which two halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms are called vicinal dihalides.
iii. Vicinal dihalides on heating with zinc metal form an alkene.
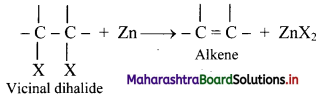
Question 58.
How is propene obtained by dehalogenation reaction?
Answer:
![]()
Question 59.
How are geometrical isomers of alkenes obtained from alkynes?
Answer:
Alkenes are obtained by partial reduction of alkynes wherein C = C triple bond of alkynes is reduced to a C = C double bond by:
i. using calculated quantity of dihydrogen in presence of Lindlar’s catalyst (palladised charcoal deactivated partially with quinoline or sulphur compound) to give the cis-isomer of alkene.
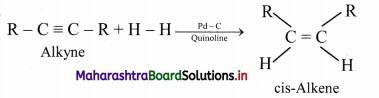
ii. using sodium in liquid ammonia to give trans-isomer of alkene.
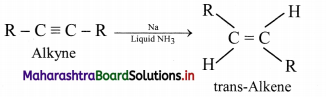
Question 60.
Write physical properties of alkenes.
Answer:
- Alkenes are nonpolar or weakly polar compounds that are insoluble in water, and soluble in nonpolar solvents like benzene, ether, chloroform.
- They are less dense than water.
- The boiling point of alkene rises with increasing number of carbons.
- Branched alkenes have lower boiling points than straight chain alkenes.
- The boiling point of alkene is very nearly the same as that of alkane with the same carbon skeleton.
![]()
Question 61.
Arrange the following alkenes in increasing order of their boiling points.
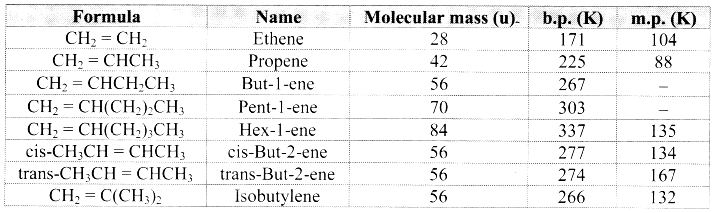
But-1-ene, 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene, 2-methylpropene, propene, 2-methylbut-2-ene.
Answer:
Propene < 2-methylpropene < but-1-ene < 2-methylbut-2-ene < 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene.
Note: Melting points and boiling points of alkenes.
Question 62.
What kind of reactions do alkenes undergo? Give reason.
Answer:
Alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reactions since they are unsaturated and contain pi (π) electrons.
Question 63.
Write a note on halogenation of alkenes.
OR
Explain the formation of vicinal dihalides from alkenes with the help of examples.
Answer:
Alkenes are converted into the corresponding vicinal dihalides by addition of halogens (X2 = Cl2 or Br2).

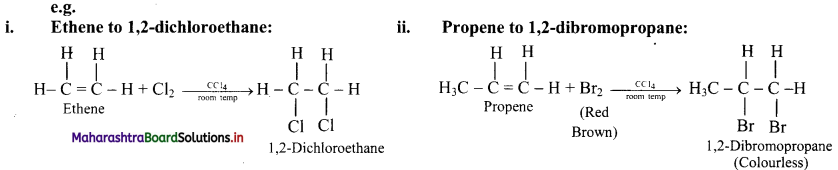
Question 64.
How is carbon-carbon double bond in a compound detected by bromination?
Answer:
When an alkene like ethene is treated with bromine in presence of CCl4, the red-brown colour of bromine disappears due to following reaction.
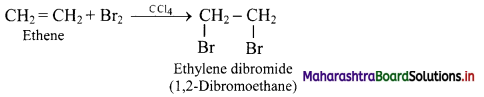
Hence, decolourisation of bromine is used to detect the presence of C = C bond in unknown compounds.
![]()
Question 65.
Explain the formation of alkyl halides from alkenes.
Answer:
i. Alkenes react with hydrogen halides (HX) like hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide and hydrogen iodide to give corresponding alkyl halides (haloalkanes). This reaction is known as hydrohalogenation of alkenes.
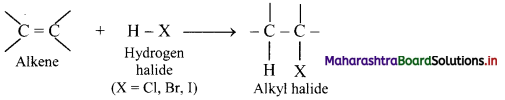
ii. The order of reactivity of halogen acids is HI > HBr > HCl.
Question 66.
State Markovnikov’s rule and explain it with the help of an example.
Answer:
i. Markovnikov’s rule: When an unsymmetrical reagent is added to an unsymmetrical alkene, the negative part (X-) of the reagent gets attached to the carbon atom which carries less number of hydrogen atoms.
ii. For example, addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes yield two isomeric products.
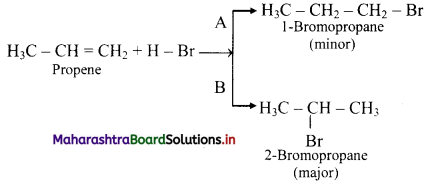
iii. Experimentally it has been found that 2-Bromopropane is the major product.
[Note: Addition of HBr to symmetrical alkenes yields only one product.]
Question 67.
Explain Anti-Markovnikov’s addition or peroxide effect or Kharasch-Mayo effect.
Answer:
In 1933, M. S. Kharasch and F. R. Mayo discovered that the addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkene in the presence of organic peroxide (R-O-O-R) takes place in the opposite orientation to that suggested by Markovnikov’s rule.
![]()

Question 68.
Write the structure of major alkyl halide obtained by the action of HCl on pent-1-ene
i. in presence of peroxide
ii. in absence of peroxide.
Answer:
The structures of alkyl halides obtained by the action of hydrogen bromide on pent-1-ene are as follows:
i. In presence of peroxide:
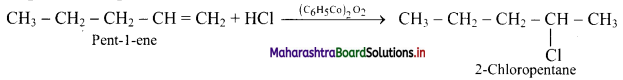
ii. In absence of peroxide:

[Note: Presence/absence of peroxide has no effect on addition of HCl or HI.]
Question 69.
Explain the formation of alcohols from alkenes using conc. sulphuric acid with the help of an example.
Answer:
i. Alkenes react with cold concentrated sulphuric acid to form alkyl hydrogen sulphate (ROSO3H). The addition takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule as shown in the following steps.
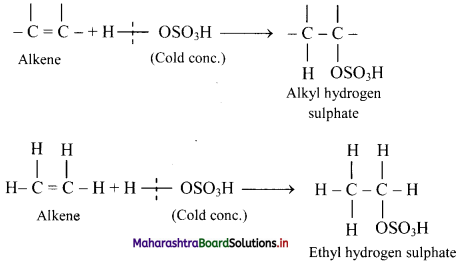

ii. If alkyl hydrogen sulphate is diluted with water and heated, then an alcohol having the same alkyl group as the original alkyl hydrogen sulphate is obtained.
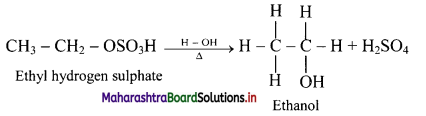
iii. This is an excellent method for the large-scale manufacture of alcohols.
![]()
Question 70.
What is hydration of alkenes?
Answer:
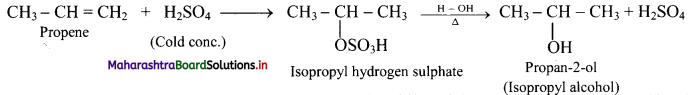
i. Reactive alkenes on adding water molecules in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid, form alcohol.
ii. The addition of water takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule. This reaction is known as hydration of alkenes.
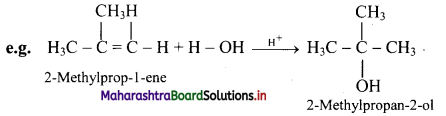
Question 71.
Complete the following conversion.
![]()
Answer:
Question 72.
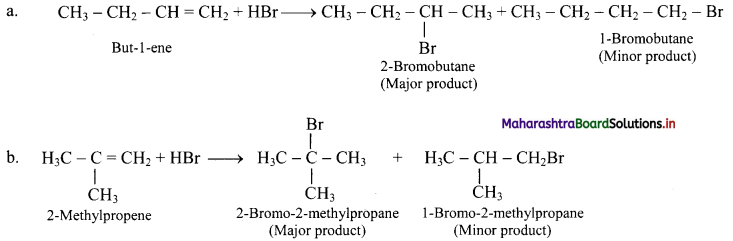
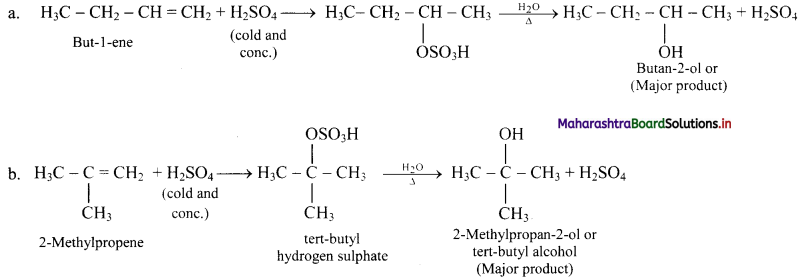
But-1-ene and 2-methylpropene are separately treated with following reagents. Predict the product/products. Indicate major/minor product,
i. HBr
ii. H2SO4 / H2O
Answer:
i. HBr:
ii. H2SO4 / H2O:
Question 73.
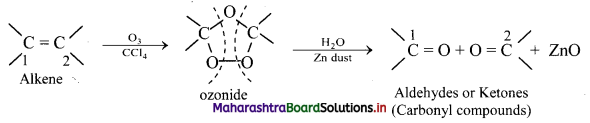
Explain: Ozonolysis
Answer:
i. The C = C double bond in alkenes, gets cleaved on reaction with ozone followed by reduction.
ii. The overall process of formation of ozonide by reaction of ozone with alkene in the first step and then decomposing it to the carbonyl compounds by reduction in the second step is called ozonolysis.
iii. When ozone gas is passed into solution of the alkene in an inert solvent like carbon tetrachloride, unstable alkene ozonide is obtained.
iv. This is subsequently treated with water in the presence of a reducing agent zinc dust to form carbonyl compounds, namely, aldehydes and/or ketones.
Question 74.
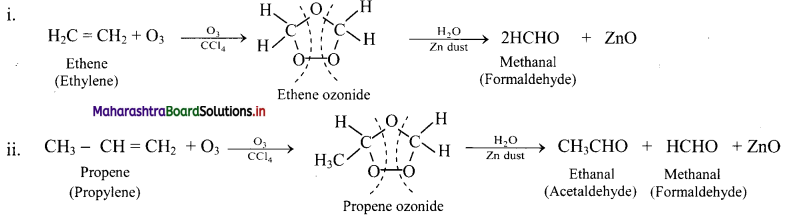
Write reactions for the ozonolysis of the following alkenes:
i. Ethene
ii. Propene
Answer:
Question 75.
What is the role of zinc dust, in ozonolysis reaction?
Answer:
In ozonolysis, the role of zinc dust is to prevent the formation of hydrogen peroxide which oxidizes aldehydes to corresponding acids.
![]()
Question 76.
State TRUE or FALSE. If false, correct the statement.
i. In the cleavage products of ozonide, a carbonyl group (C=O) is formed at each of the original doubly bonded carbon atoms.
ii. In ozonolysis, the structure of original alkene reactant cannot be identified by knowing the number and arrangement of carbon atoms in aldehydes and ketones produced.
iii. Ozonolysis reaction is used to locate the position and determine the number of double bonds in alkenes.
Answer:
i. True
ii. False
In ozonolysis, knowing the number and arrangement of carbon atoms in aldehydes and ketones produced, we can identify the structure of original alkene.
iii. True
Question 77.
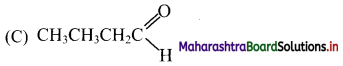
Identify the alkene which produces a mixture of methanal and propanone on ozonolysis. Write the reactions involved.
Answer:
i. The structure of alkene which produces a mixture of methanol and propanone on ozonolysis is
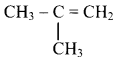
ii. Reactions:
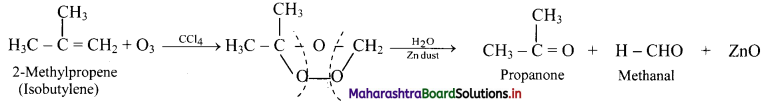
Question 78.
Explain the process of hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes.
Answer:
i. Alkenes with diborane in tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvent undergo hydroboration to form trialkylborane, which on oxidation with alkaline peroxide forms primary alcohol.
ii. The overall reaction gives anti-Markovnikov’s product from unsymmetrical alkenes.
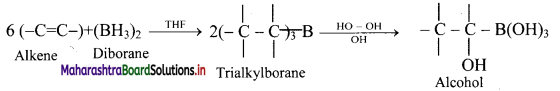
Question 79.
Write reactions for the following conversion by hydroboration-oxidation reaction.
Ethene to ethanol
Answer:
Ethene to ethanol:
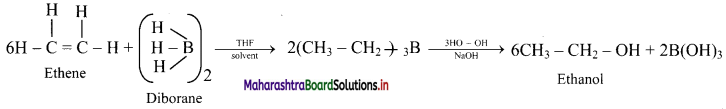
Question 80.
Define: Polymerization
Answer:
The process in which large number of small molecules join together and form very large molecules with repeating units is called polymerization.
Question 81.
What is the difference between monomer and polymer?
Answer:
The compound having very large molecules made of large number of repeating small units is called polymer while the simple compound forming the repeating units in the polymer is called monomer.
![]()
Question 82.
How is ethene converted to polyethene?
Answer:
Ethene at high temperature and under high pressure interacts with oxygen, and undergoes polymerization giving high molecular weight polymer called polyethene.
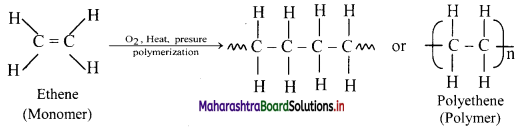
Here, n represents the number of repeating units and is a large number.
Question 83.
Explain the process of hydroxylation of alkenes.
OR
What is the action of alkaline KMnO4 on alkenes?
Answer:
Alkenes react with cold and dilute alkaline potassium permanganate to form glycols.
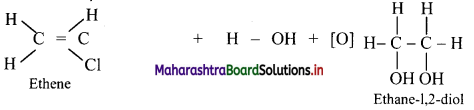
Question 84.
Explain Baeyer’s test giving one example.
Answer:
i. During hydroxylation of alkenes the purple colour of KMnO4 disappears.
ii. Hence, such reaction serves as a qualitative test for detecting the presence of double bond in the sample compound. This is known as Baeyer’s test.
e.g. As propene contains a double bond, it reacts with alkaline KMnO4 to give colourless propane-1,2-diol as product. Therefore, the purple colour of alkaline KMnO4 disappears.

Question 85.
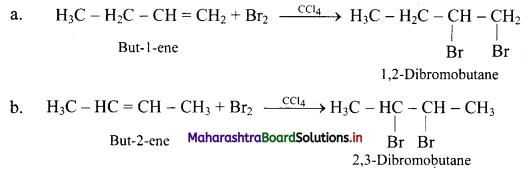
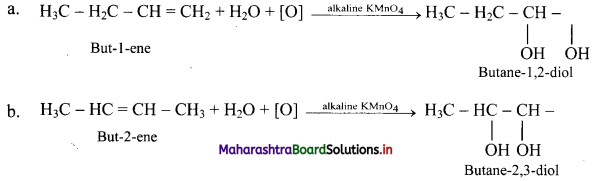
What is the action of following reagents on but-1-ene and but-2-ene?
i. Bromine
ii. Cold and dilute alkaline KMnO4.
Answer:
i. Action of Br2:
ii. Action of cold and dilute alkaline KMnO4:
Question 86.
Describe the action of acidic potassium permanganate on alkenes.
Answer:
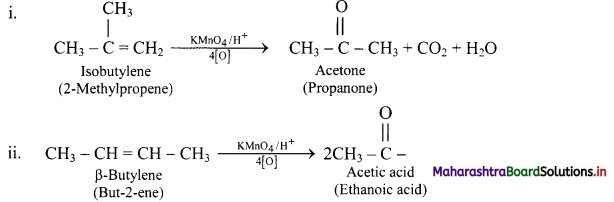
Acidic potassium permanganate or acidic potassium dichromate oxidizes alkenes to ketones or acids depending upon the nature of the alkene and the experimental conditions. This is called oxidative cleavage of alkenes.
e.g.
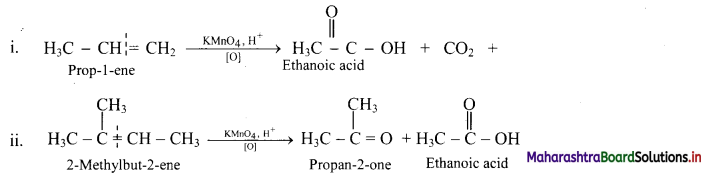
Question 87.
Complete the following conversions.

Answer:
Question 88.
State some important uses of alkenes.
Answer:
- Alkenes are used as starting materials for preparation of alkyl halides, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, acids, etc.
- Ethene and propene are used to manufacture polythene, polypropylene which are used in polyethene bags, toys, bottles, etc.
- Ethene is used for artificial ripening of fruits, such as mangoes.
![]()
Question 89.
What are alkynes? Write their general formula.
Answer:
- Alkynes are aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing at least one C = C.
- Their general formula is CnH2n-2.
Question 90.
Explain position isomerism in alkyne.
Answer:
Alkynes show position isomerism which is a type of structural isomerism.
e.g. But-1-yne and but-2-yne, both are represented by C4H6, however, both of them differ in position of triple bond in them.
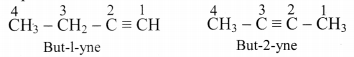
[Note: 1-Alkynes are also called terminal alkynes.]
Question 91.
Draw the structural isomers of isomers of C5H8. Identify position isomers amongst them.
Answer:
i. Structural isomers of C5H10 (fourth member of homologous series of alkynes):
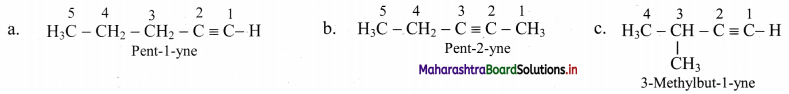
ii. The compounds pent-1-yne and pent-2-yne are position isomers of each other.
Question 92.
What are alkadiynes and alkatriynes? Give one example of each.
Answer:
The aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing two and three carbon-carbon triple bonds in their structure are called alkadiynes and alkatriynes, respectively.
e.g. CH ≡ C – CH2 – C ≡ CH
Alkadiyne (Penta-1,4-diyne)
HC ≡ C- C ≡ C- C ≡ CH
Alkatriyne (Hexa-1,3,5-triyne)
Question 93.
Complete the following table:
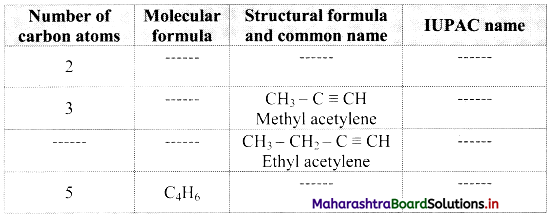
Answer:
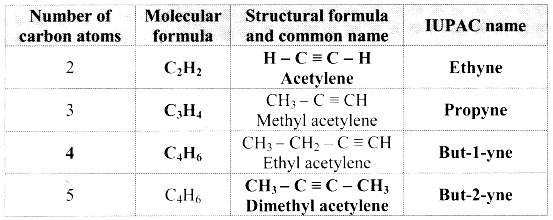
![]()
Question 94.
How is acetylene prepared from the following compounds?
i. Methane
ii. Calcium carbide
Answer:
i. From methane: Ethyne is industrially prepared by controlled, high temperature, partial oxidation of methane.
![]()
ii. From calcium carbide: Industrially, ethyne is prepared by reaction of calcium carbide with water.
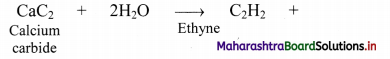
Question 95.
How are alkynes prepared by dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides? Write general reaction and explain it using an example.
Answer:
Vicinal dihalides react with alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide to form alkenyl halide which on further treatment with sodamide forms alkyne.
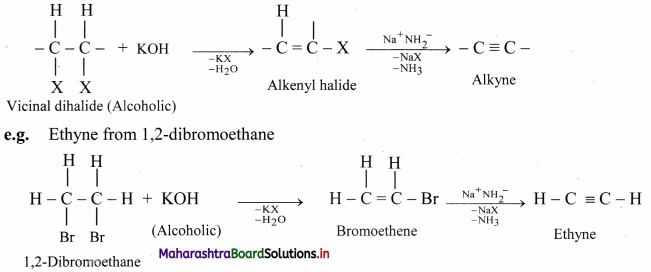
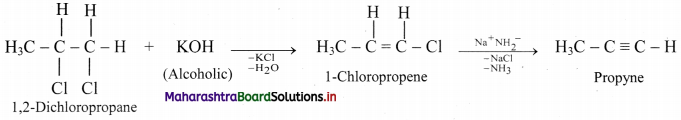
Question 96.
Convert 1,2-dichloropropane to propyne.
Answer:
Question 97.
i. What are terminal alkynes?
ii. How are they converted to higher nonterminal alkynes? Give one example.
Answer:
i. Terminal alkynes are the compounds in which hydrogen atom is directly attached to triply bonded carbon atom.
ii. a. A smaller terminal alkyne first reacts with a very strong base like lithium amide to form metal acetylide (lithium amide is easier to handle than sodamide).
b. Higher alkynes are obtained by reacting metal acetylides (alkyn-1-yl lithium) with primary alkyl halides.
![]()
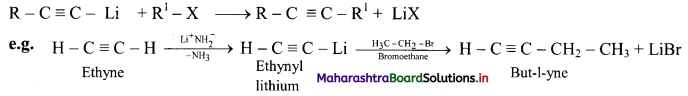
Question 98.
How is pent-2-yne prepared from propyne?
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 99.
Enlist physical properties of alkenes.
Answer:
The physical properties of alkynes are similar to those of alkanes and alkenes.
- They are less dense than water.
- They are insoluble in water and quite soluble in less polar organic solvents like ether, benzene, carbon tetrachloride.
- The melting points and boiling points of alkynes increase with an increase in molecular mass.
Question 100.
Lithium amide (LiNH2) is very strong base and it reacts with terminal alkynes to form lithium acetylides with the liberation of hydrogen indicating acidic nature of terminal alkynes. Why is it so?
Answer:
- The hydrogen bonded to C ≡ C triple bond has acidic character.
- In terminal alkynes, hydrogen atom is directly attached to sp hybridized carbon atom.
- In sp hybrid orbital, the percentage of s-character is 50%. An electron in s-orbital is very close to the nucleus and is held tightly.
- The sp hybrid carbon atom in terminal alkynes is more electronegative than the sp2 carbon in ethene or the sp3 carbon in ethane.
- Due to high electronegative character of carbon in terminal alkynes, hydrogen atom can be given away as proton (H+) to very strong base.
Question 101.
Give reason: Acidic nature of alkynes is used to distinguish between terminal and non-terminal alkynes.
Answer:
- Acidic alkynes react with certain heavy metal ions like Ag+ and Cu+ and form insoluble acetylides.
- On addition of acidic alkyne to the solution of AgNO3 in alcohol, it forms a precipitate, which indicates that the hydrogen atom is attached to triply bonded carbon.
Hence, this reaction is used to differentiate terminal alkynes and non-terminal alkynes.
Question 102.
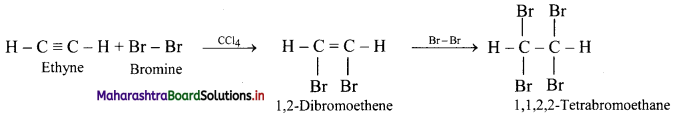
Predict the product in the following reactions.
\(\mathbf{H C} \equiv \mathbf{C H}+\mathbf{2 B r}_{2} \stackrel{\mathrm{CCl}_{4}}{\longrightarrow} ?\)
Answer:
Ethyne reacts with bromine in inert solvent such as carbon tetrachloride to give tetrabromoethane.
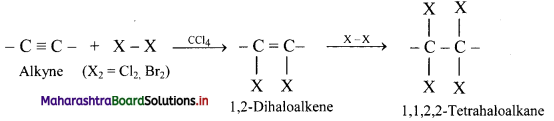
Question 103.
Write the general reaction for addition of halogens to alkynes.
Answer:
Question 104.
Explain the addition of hydrogen halides to alkynes using a general reaction.
Answer:
i. Hydrogen halides (HCl, HBr and HI) add to alkynes across carbon-carbon triple bond in two steps to form geminal dihalides (in which two halogen atoms are attached to the same carbon atom).
ii. The addition of HX in both the steps takes place according to Markovnikov’s rule as shown in below.
General reaction:
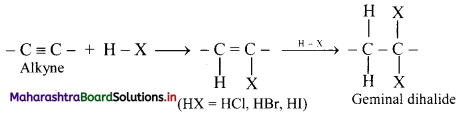
iii. The order of reactivity of hydrogen halides is HI > HBr > HCl.
![]()
Question 105.
State the action of HBr on acetylene and methyl acetylene.
Answer:
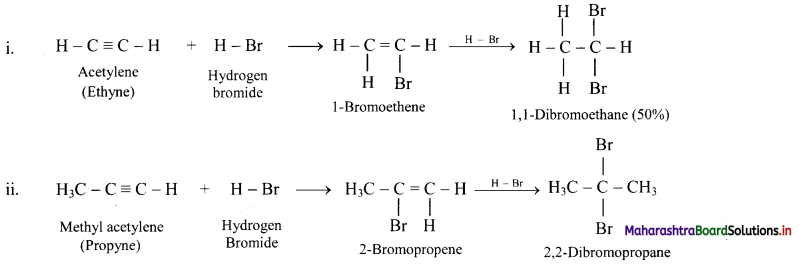
Question 106.
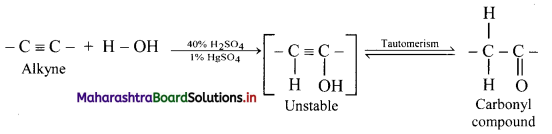
Explain reactions of alkynes with water using general reaction.
Answer:
Alkynes react with water in presence of 40% sulphuric acid and 1% mercuric sulphate to form aldehydes or ketones, i.e., carbonyl compounds.
General reaction:
Question 107.
Predict the products when ethyne and propyne are treated with 1% mercuric sulphate in H2SO4.
Answer:
i. Ethyne:
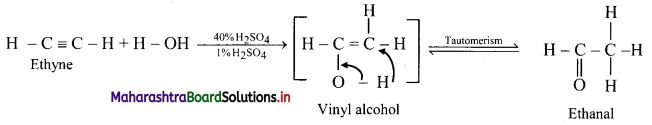
ii. Propyne:
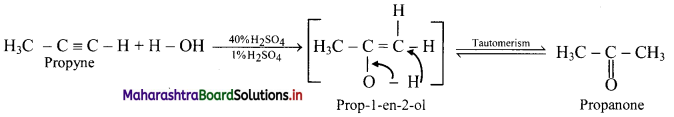
Question 108.
Convert:
i. But-1-yne to butan-2-one
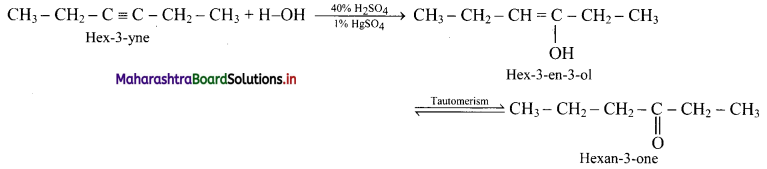
ii. Hex-3-yne to hexan-3-one
Answer:
i. But-l-yne to butan-2-one:
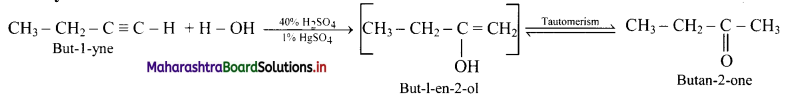
ii. Hex-3-yne to hexan-3-one:
Question 109.
What are products obtained on hydration of but-1-yne and but-2-yne? Are they same or different? Explain.
Answer:
i. Hydration of but-1-yne:
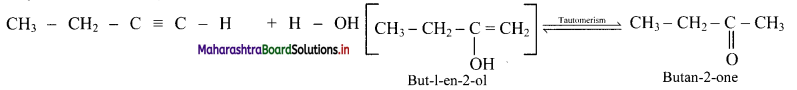
Hydration of but-2-yne:
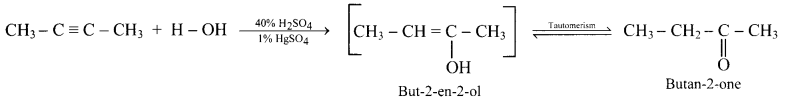
The products obtained on hydration of but-1-yne and but-2-yne are same i.e., butan-2-onc since the addition of water to alkyncs takes place according to Markovnikovs rule.
![]()
Question 110.
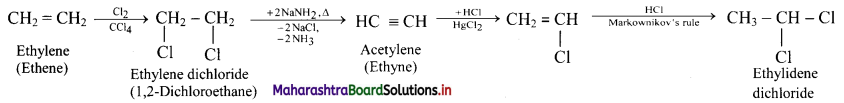
How is ethylene converted into ethylidene dichloride?
Answer:
Question 111.
Write some important uses of acetylene.
Answer:
- Ethyne (acetylene) is used in preparation of ethanal (acetaldehyde), propanone (acetone), ethanoic acid (acetic acid).
- It is used in the manufacture of polymers, synthetic rubber, synthetic fibre, plastic, etc.
- For artificial ripening of fruits.
- In oxy-acetylene (mixture of oxygen and acetylene) flame for welding and cutting of metals.
Question 112.
Many organic compounds obtained from natural sources such as resins, balsams, oil of wintergreen, etc. have pleasant fragrance or aroma. Such compounds are named as aromatic compounds.
i. Name the simplest aromatic compound.
ii. Write the names of any two aromatic compounds.
Answer:
i. Benzene is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon.
ii. Toluene and naphthalene
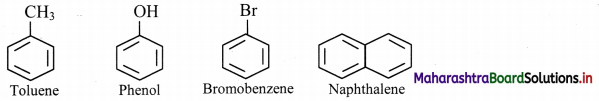
Question 113.
Draw structures of any four aromatic hydrocarbons.
Answer:
Question 114.
Write the molecular formula of benzene. Give its boiling point.
Answer:
The molecular formula for benzene is C6H6. Its boiling point is 353 K.
Question 115.
State TRUE or FALSE. Correct the false statement.
i. Aromatic hydrocarbons are also called as arenes.
ii. Toluene is a non-aromatic hydrocarbon.
iii. Benzene is colourless liquid having characteristic odour.
Answer:
i. True
ii. False
Toluene is an aromatic hydrocarbon.
iii. True
![]()
Question 116.
Name any two large-scale sources of benzene.
Answer:
Coal-tar and petroleum are the two large-scale sources of benzene.
[Note: Other aromatic compounds like toluene, phenol, naphthalene, etc. are also obtained from coal-tar and petroleum.]
Question 117.
Draw the structure of an aromatic compound that resembles benzene but does not have pleasant odour.
Answer:
Question 118.
Name and draw the structures of any three compounds that have pleasant odour but do not resemble benzene.
Answer:
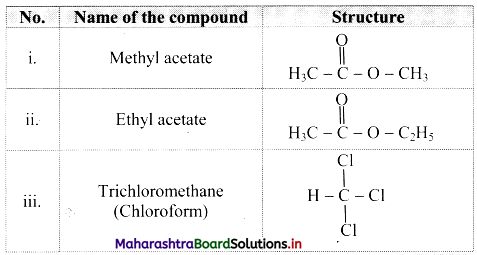
Question 119.
Differentiate between aromatic and aliphatic compounds.
Answer:
Aromatic compounds:
- Aromatic compounds contain higher percentage of carbon.
- They bum with sooty flame.
- They are cyclic compounds with alternate single and double bonds.
- They are not attacked by normal oxidizing and reducing agents.
- They do not undergo addition reactions easily. They do not decolourise dilute alkaline aqueous KMnO4 and Br2 in CCl4, though double bonds appear in their structure.
- They prefer substitution reactions.
Aliphatic compounds:
- Aliphatic compounds contain lower percentage of carbon.
- They bum with non-sooty flame.
- They are open chain compounds.
- They are easily attacked by oxidizing and reducing agents.
- Unsaturated aliphatic compounds undergo addition reactions easily. They decolourise dilute aqueous alkaline KMnO4 and Br2 in CCl4.
- The saturated aliphatic compounds give substitution reactions.
Question 120.
Benzene cannot have open chain structure. Explain this statement.
Answer:
- The molecular formula of benzene is C6H6. This indicates high degree of unsaturation.
- Open chain or cyclic structure having double and triple bonds can be written for C6H6.
- However, benzene does not behave like alkenes or alkynes. This indicates that benzene cannot have the open chain structure.
![]()
Question 121.
Compare the reactivity of benzene and alkenes with the following reagents:
i. Dilute alkaline KMnO4
ii. Br6 in CCl4
iii. H6O in acidic medium
Answer:
| Reagent | Alkenes | Benzene |
| Dilute alkaline aqueous KMnO4 | Decolourisation of KMnO4 | No decolourisation |
| Br2 in CCl4 | Decolourisation of red brown colour of bromine | No decolourisation |
| H2O in acidic medium | Addition of H2O molecule | No reaction |
Question 122.
Give the evidence for the cyclic structure of benzene.
Answer:
Evidence for the cyclic structure of benzene:
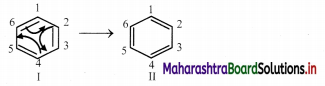
i. Benzene yields only one and no isomeric monosubstituted bromobenzene (C6H5Br) when treated with equimolar bromine in FeBr3. This indicates that all six hydrogen atoms in benzene are identical.
![]()
ii. This is possible only if benzene has cyclic structure of six carbons bound to one hydrogen atom each.
iii. Benzene on catalytic hydrogenation gives cyclohexane.
![]()
This confirms the cyclic structure of benzene and three C = C in it.
Question 123.
Write a short note on the Kekule structure of benzene.
Answer:
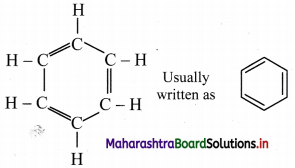
Kekule structure of benzene:
i. August Kekule in 1865 suggested the structure for benzene having a cyclic planar ring of six carbon atoms with alternate single and double bonds and hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom.
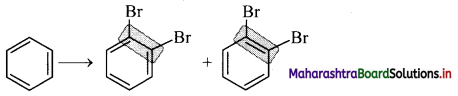
ii. The Kekule structure indicates the possibility of two isomeric 1,2-dibromobenzenes. In one of the isomers, the bromine atoms would be attached to the doubly bonded carbon atoms whereas in the other, they would be attached to single bonded carbons.
iii. However, benzene was found to form only one ortho-disubstituted benzene. This problem was overcome by Kekule by suggesting the concept of oscillating nature of double bonds in benzene as given below.
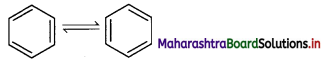
iv. Even with this modification, Kekule structure of benzene failed to explain unusual stability and preference to substitution reactions rather than addition reactions, which was later explained by resonance.
Question 124.
Explain the resonance phenomenon with respect to benzene.
OR
Explain the resonance hybrid structure of benzene.
Answer:
- Benzene is a hybrid of various resonance structures. The two structures, (A) and (B) given by Kekule are the main contributing structures.
- The resonance hybrid is represented by inserting a circle or a dotted circle inscribed in the hexagon as shown in (C).
- The circle represents six electrons delocalized over the six carbon atoms of benzene ring.
- A double headed arrow between the resonance structures is used to represent the resonance phenomenon.
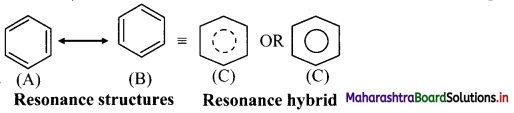
Question 125.
Why does benzene not prefer to undergo addition reactions?
Answer:
- Benzene is highly unsaturated molecule but despite of this feature, it does not give addition reaction.
- The actual structure of benzene is represented by the resonance hybrid which is the most stable form of benzene than any of its resonance structures.
- This stability due to resonance (delocalization of π electrons) is so high that π-bonds of the molecule becomes strong and thus, resist breaking.
Thus, benzene does not prefer to undergo addition reactions.
![]()
Question 126.
Explain the resonance structures of benzene using the orbital overlap concept.
Answer:
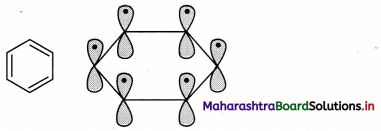
The structure of benzene can be better explained by the orbital overlap concept,
i. All six carbon atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridized. Two sp2 hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom overlap and form carbon-carbon sigma (σ) bond and the remaining third sp2 hybrid orbital of each carbon overlaps with s orbital of a hydrogen atom to form six C – H sigma bonds.
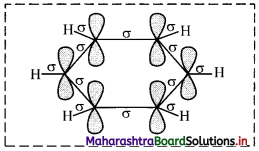
ii. The unhybridized p orbitals of carbon atoms overlap laterally forming π bonds. There are two possibilities of forming three π bonds by overlap of p orbitals of C1 – C2, C3 – C4, C5 – C6 or C2 – C3, C4 – C5, C6 – C1, respectively, as shown in the following figure. Both the structures are equally probable.
According to resonance theory, these are two resonance structures of benzene.
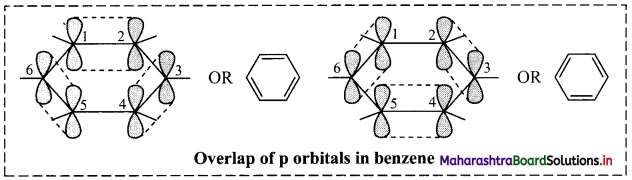
Question 127.
Explain the structure of benzene with respect to molecular orbital theory.
Answer:
i. According to molecular orbital (MO) theory, the six p orbitals of six carbons give rise to six molecular orbitals of benzene.
ii. Shape of the most stable MO is as show in the figure below. Three of these π molecular orbitals lie above and the other below those of free carbon atom energies.
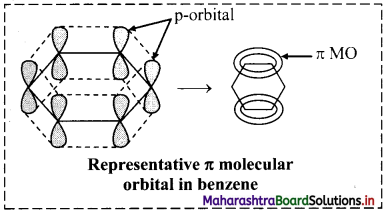
iii. The six electrons of the p orbitals cover all the six carbon atoms and are said to be delocalized. Delocalization of π electrons results in stability of benzene molecule.
Question 128.
Give the carbon-carbon bond length in benzene. Explain why benzene shows unusual behaviour.
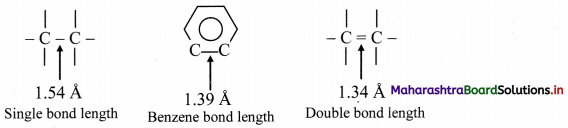
Answer:
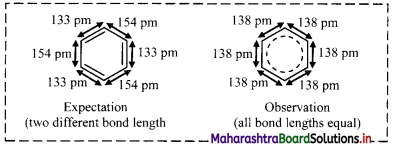
i. X-ray diffraction data indicate that all C – C bond lengths in benzene are equal (139 pm) which is an intermediate between C – C (154 pm) and C = C bond (133 pm).
ii. Thus, absence of pure double bond in benzene accounts for its reluctance to addition reactions under normal conditions, which explains unusual behaviour of benzene.
Question 129.
Write a short note on aromaticity.
Answer:
i. All aromatic compounds undergoes substitution reactions rather than addition reactions and this property is referred to as aromaticity or aromatic character.
ii. The aromatic character of benzene is correlated to its structure.
iii. Aromaticity is due to extensive cyclic delocalization of p electrons in the planar ring structure.
iv. Three rules of aromaticity that is used for predicting whether a particular compound is aromatic or non-aromatic are as follows:
- Aromatic compounds are cyclic and planar (all atoms in ring are sp2 hybridized).
- Each atom in aromatic ring has a p orbital. The p orbitals must be parallel so that continuous overlap is possible around the ring.
- Huckel rule: The cyclic π molecular orbital formed by overlap of p orbitals must contain (4n + 2) p electrons, where n = integer 0, 1, 2, 3, … etc.
Question 130.
State and explain the Huckel rule of aromaticity.
Answer:
Huckel rule: The cyclic π molecular orbital formed by overlap of p orbitals must contain (4n + 2) p electrons, where n = integer 0, 1,2,3, … etc.
Explanation:
According to Huckel rule, a cyclic and planar compound is aromatic if it the number of π electrons is equal to (4n + 2), where n = integer 0, 1, 2, 3, … etc.
| n | Number of π electrons |
| n = 0 | (4 × 0) – 2 = 2 |
| n = 1 | (4 × 1) + 2 = 6 |
| n = 2 | (4 × 2) + 2 = 10 |
e.g. Consider benzene molecule:
Benzene has 6π electrons. According to Huckel rule, if n = 1, then (4n + 2)π = 6π electrons. Hence, benzene is aromatic.
![]()
Question 131.
By using the rules of aromaticity, explain whether the following compounds are aromatic or non-aromatic.
i. Benzene
ii. Naphthalene
iii. Cycloheptatriene
Answer:
i. Benzene:
a. It is cyclic and planar.
b. It has three double bonds and six π electrons.
c. It has a p orbital on each carbon of the hexagonal ring. Hence, a continuous overlap above and below the ring is possible.
d. According to Huckcl rule, this compound is aromatic if, 4n + 2 = Number of π electrons.
4n + 2 = 6,
∴ 4n = 6 – 2 = 4
n = 4/4 = 1, here, ‘n’ comes out to be an integer.
Hence, benzene is aromatic.
ii. Naphthalene:
a. It is cyclic and planar.
b. It has 5 double bonds and 10 n electrons.
c. It has a p orbital on each carbon atom of the ring. Hence, a continuous overlap around the ring is possible.
d. According to Huckel rule, this compound is aromatic if, 4n + 2 = Number of π electrons.
4n + 2 = 10,
∴ 4n = 10 – 2 = 8
n = 8/4 = 2, Here ‘n’ comes out to be an integer.
Hence, naphthalene is aromatic.
iii. Cycloheptatriene:
a. It is cyclic and planar.
b. It has three double bonds and 6 π electrons.
c. But one of the carbon atoms is saturated (sp3 hybridized) and it does not have a p orbital.
d. Hence, a continuous overlap around the ring is not possible in cycloheptatriene. Hence, it is non-aromatic.
Question 132.
How does Huckel rule help in determining the aromaticity of pyridine?
Answer:
i. Pyridine has three double bonds and 6 π electrons.
ii. The six p orbitals containing six electrons form delocalized π molecular orbital.
iii. The unused sp2 hybrid orbital of nitrogen containing two non-bonding electrons is as it is.
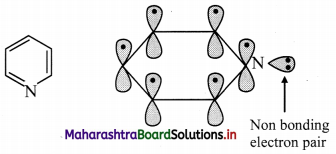
iv. According to Huckel rule, this compound is aromatic if, 4n + 2 = Number of π electrons
4n + 2 = 6,
∴ 4n = 6 – 2 = 4
n = 4/4 = 1, here ‘n’ comes out to be an integer. Hence, pyridine is aromatic.
Question 133.
How is benzene prepared from ethyne/acetylene?
Answer:
From ethyne (By trimerization): Alkynes when passed through a red hot iron tube at 873 K, polymerize to form aromatic hydrocarbons. Ethyne when passed through a red hot iron tube at 873 K undergoes trimerization to form benzene.

Question 134.
How is benzene prepared from sodium benzoate?
OR
Explain preparation of benzene by decarboxylation.
Answer:
From sodium benzoate (by decarboxylation): When anhydrous sodium benzoate is heated with soda lime, it undergoes decarboxylation and gives benzene.
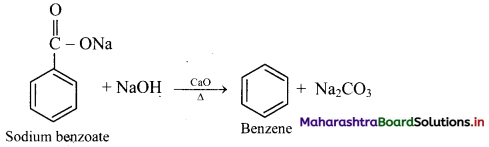
[Note: This reaction is useful for decreasing the length of a carbon chain by one C-atom]
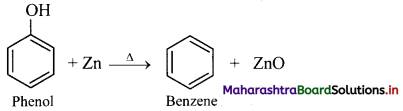
Question 135.
How will you convert phenol to benzene?
Answer:
From phenol (By reduction): When vapours of phenol are passed over heated zinc dust, it undergoes reduction and gives benzene.
Question 136.
Enlist physical properties of benzene.
Answer:
Physical properties of benzene:
- Benzene is a colourless liquid.
- Its boiling point is 353 K and melting point is 278.5 K.
- It is insoluble in water. It forms upper layer when mixed with water.
- It is soluble in alcohol, ether and chloroform.
- Its vapours are highly toxic which on inhalation lead to unconsciousness.
![]()
Question 137.
What is the action of chlorine on benzene in the presence of UV light?
Answer:
Addition of chlorine: When benzene is treated with chlorine in the presence of bright sunlight or UV light, three molecules of chlorine gets added to benzene to give benzene hexachloride.
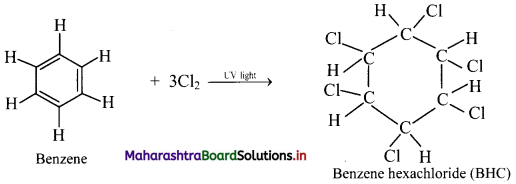
Question 138.
Name the γ-isomer of benzene hexachloride which is used as insecticide.
Answer:
The γ-isomer of benzene hexachloride which is used as insecticide is called as gammaxene or lindane.
Question 139.
How will you convert benzene to cyclohexane?
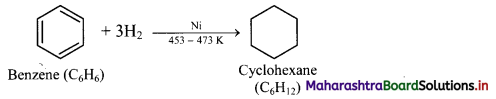
Answer:
Addition of hydrogen: When a mixture of benzene and hydrogen gas is passed over heated catalyst nickel at 453 K to 473 K, cyclohexane is formed.
Question 140.
What is the action of ozone on benzene?
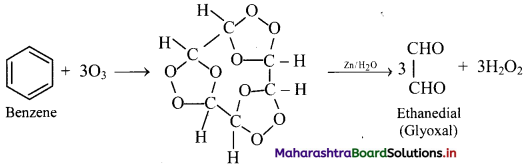
Answer:
Addition of ozone: When benzene is treated with ozone in the presence of an inert solvent carbon tetrachloride, benzene triozonide is formed, which is then decomposed by zinc dust and water to give glyoxal.
Question 141.
What are the different types of electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene?
Answer:
i. Benzene shows electrophilic substitution reactions, in which one or more hydrogen atoms of benzene ring are replaced by groups like – Cl, – Br, – NO2, – SO3H, -R, -COR, etc.
ii. Different types of electrophilic substitution reactions of benzene are as follows:
- Halogenation (chlorination and bromination)
- Nitration
- Sulphonation
- Friedel-Craft’s alkylation and
- Friedel-Craft’s acylation
Question 142.
Write a short note on chlorination reaction of benzene.
Answer:
Chlorination of benzene:
i. In chlorination reaction, hydrogen atom of benzene is replaced by chlorine atom.
ii. Chlorine reacts with benzene in dark in the presence of iron or ferric chloride or anhydrous aluminium chloride or red phosphorus as catalyst to give chlorobenzene (C6H5Cl).
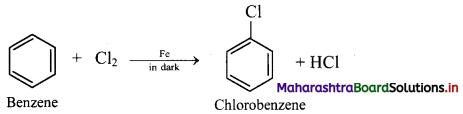
iii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: Cl+, chloronium ion,
Formation of the electrophile: Cl – Cl + FeCl3 → Cl+ + [FeCl4]–
![]()
Question 143.
Write a short note on bromination reaction of benzene.
Answer:
Bromination of benzene:
i. In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of benzene is replaced by bromine atom.
ii. Bromine reacts with benzene in dark in presence of iron or ferric bromide or anhydrous aluminium bromide or red phosphorus as catalyst to give bromobenzene (C6H5Br).
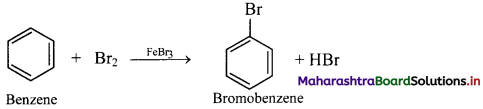
iii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: Br+
Formation of the electrophile: Br – Br + FeBr3 → Br+ + [FeBr4]–
Question 144.
Why direct iodination of benzene is not possible?
Answer:
Direct iodination of benzene is not possible as the reaction is reversible.
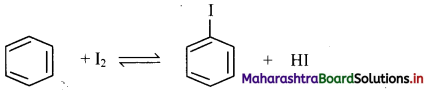
[Note: Iodination of benzene can be carried out in the presence of oxidising agents like HIO3 or HNO3.]
Question 145.
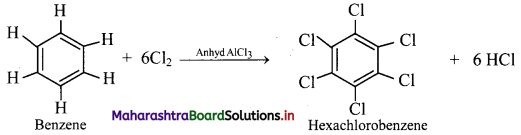
How will you convert benzene to hexachlorobenzene?
Answer:
When benzene is treated with excess of chlorine in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it gives hexachlorobenzene.
Question 146.
State true or false. Correct the false statement.
i. In halogenation reaction, hydrogen atom of benzene ring is replaced by halogen atom.
ii. The molecular formula of hexachlorobenzene is C6H6Cl6.
iii. Benzene forms the lower layer when mixed with water.
Answer:
i. True
ii. False
The molecular formula of hexachlorobenzene is C6Cl6
iii. False
Benzene forms the upper layer when mixed with water.
![]()
Question 147.
Explain the nitration reaction of benzene.
Answer:
Nitration of benzene:
i. When benzene is heated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid (nitrating mixture) at about 313 K to 333 K, it gives nitrobenzene.
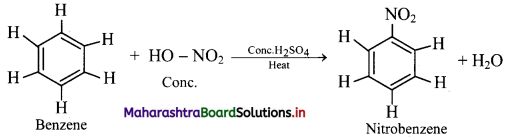
ii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{+}\), nitronium ion
Formation of the electrophile: HO – NO2 + 2H2SO4 ⇌ \(2 \mathrm{HSO}_{4}^{-}\) + H3O+ + \(\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\)
Question 148.
Write a short note on sulphonation of benzene.
Answer:
Sulphonation of benzene:
i. When benzene is heated with fuming sulfuric acid (oleum) at 373 K, it gives benzene sulfonic acid.
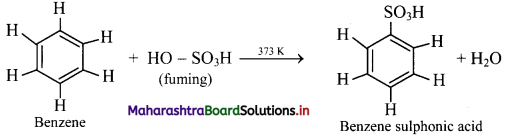
ii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: SO3, free sulphur trioxide
Formation of the electrophile: 2H2SO4 → H3O+ + \(\mathrm{HSO}_{4}^{-}\) + SO3
Question 149.
Write a short note on Friedel-Craft’s alkylation reaction of benzene.
Answer:
Friedel-Craft’s alkylation reaction of benzene:
i. When benzene is treated with an alkyl halide like methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it gives toluene.

ii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: R+
Formation of the electrophile: R – Cl + AlCl3 → R+ + \(\mathrm{AlCl}_{4}^{-}\)
iii. Friedel-Craft’s alkylation reaction is used to extend the chain outside the benzene ring.
Question 150.
Explain Friedel-Craft’s acylation reaction of benzene. Give example reactions.
Answer:
Friedel-craft’s acylation reaction of benzene:
i. When benzene is heated with an acyl halide or acid anhydride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride, it gives corresponding acyl benzene.
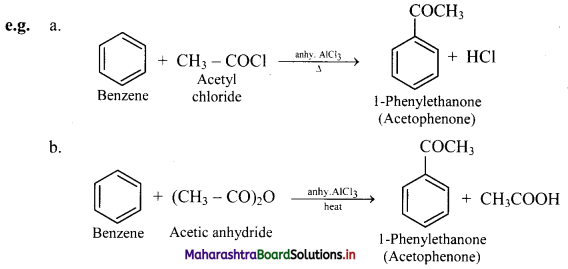
ii. Electrophile involved in the reaction: R – C- = O, acylium ion
Formation of the electrophile: R – COCl + AlCl3 → R – C+ = O + \(\mathrm{AlCl}_{4}^{-}\)
Question 151.
Write the general combustion reaction for hydrocarbons.
Answer:
General combustion reaction for any hydrocarbon (CxHy) can be represented as follows:
![]()
![]()
Question 152.
Write the combustion reaction of benzene.
Answer:
When benzene is heated in air, it bums with sooty flame forming carbon dioxide and water.
C6H6 + \(\frac {15}{2}\)O2 → 6CO2 + 3H2O
Question 153.
Write a note on the directive influence of substituents (functional groups) in monosubstituted benzene.
Answer:
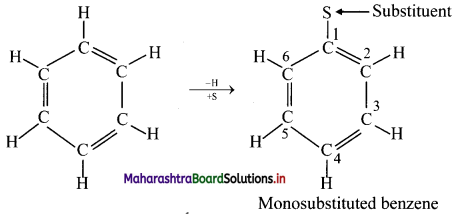
i. In benzene, all hydrogen atoms are equivalent and so, when it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions, only one monosubstituted product is possible.
Monosubstituted benzene:
ii. When monosubstituted benzene undergoes further electrophilic substitution, the second substituent (electrophile, E) can occupy any of the five positions available and give three disubstituted products.
But these disubstituted products are not formed in equal amounts.
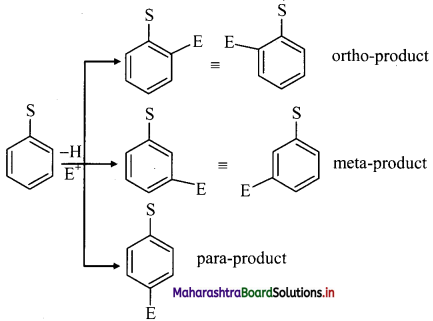
iii. The position of second substituent (E) is determined by the nature of substituent (S) already present in the benzene ring and not on the nature of second substituent (E).
iv. The groups which direct the incoming group to ortho and para positions are called ortho and para directing groups. The groups which direct the incoming group to meta positions are called meta directing groups. Thus, depending on the nature of the substituent (S) either ortho and para products or meta products are formed as major products.
Question 154.
What are ortho and para directing groups? Enlist few ortho and para directing groups.
Answer:
The groups which direct the incoming group to ortho and para positions are called ortho and para directing groups.
Ortho and para directing groups:
![]()
Question 155.
Explain the directive influence of ortho, para directing groups in monosubstituted benzene using suitable example.
OR
Explain the directive influence of -OH group in benzene.
Answer:
i. The directive influence of ortho, para directing groups can be explained with the help of inductive and resonance effects.
ii. phenol has the following resonating structures:
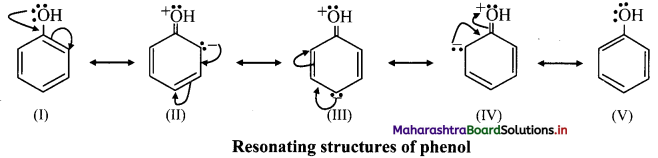
iii. It can be seen from the above resonating structures, that the ortho (o-) and para (p-) positions have a greater electron density than the meta positions.
iv. Therefore, -OH group activates the benzene ring for the attack of second substituent (E) at these electron rich centres. Thus, phenolic -OH group is activating and ortho, para-directing group.
v. In phenol, -OH group has electron withdrawing inductive (-I) effect which slightly decreases the electron density at ortho positions in benzene ring. Thus, resonance effect and inductive effect of -OH group act opposite to each other. However, the strong resonance effect dominates over inductive effect.
![]()
Question 156.
Explain the o, p-directive effect of methyl group.
Answer:
- All ortho and para directing groups possess nonbonding electron pair on the atom which is directly attached to the aromatic ring; however, methyl group is an exception.
Methyl (or alkyl groups) is ortho and para directing, although it has no nonbonding electron pair on the key atom. This is explained on the basis of special type of resonance called hyperconjugation or no bond resonance.
Question 157.
Explain why halide group is an ortho and para directing group.
Answer:
i. In aryl halides, halogens are moderately deactivating. Because of their strong -I effect, overall electron density on the benzene ring decreases, which makes the electrophilic substitution difficult.
ii. However, halogens are ortho and para directing. This can be explained by considering resonance structures.
iii. e.g. Chlorobenzene has the following resonating structures:
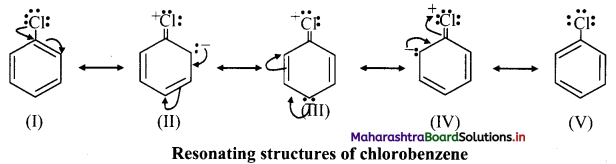
iv. Due to resonance, the electron density on ortho and para positions is greater than meta positions and hence, -Cl is ortho and para directing.
Question 158.
What are meta directing groups? Enlist few of them.
Answer:
The groups which direct the incoming group to meta positions are called meta directing groups.
[Note: All meta directing groups have positive (or partial positive) charge on the atom which is directly attached to an aromatic ring.]
Question 159.
Explain the directive influence of nitro group in nitrobenzene.
OR
Explain why nitro group is a meta-directing group.
Answer:
i. Meta directing group withdraws electrons from the aromatic ring by resonance, making the ring electron-deficient. Therefore, meta groups are ring deactivating groups.
ii. Due to -I effect, -NO2 group reduces electron density in benzene ring on ortho and para positions. So, the attack of incoming group becomes difficult at ortho and para positions. The incoming group can attack on meta positions more easily.
iii. The various resonance structures of nitrobenzene are as shown below:
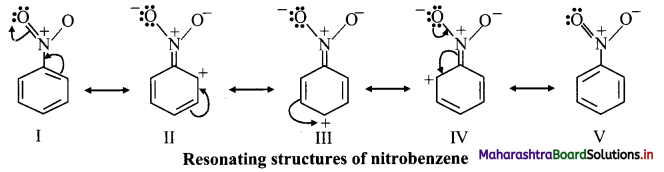
iv. It is clear from the above resonance structures that the ortho and para positions have comparatively less electron density than at meta positions. Hence, the incoming group/electrophile attacks on meta positions.
Question 160.
What are polycyclic aromatic compounds? How are they produced?
Answer:
- Polycyclic aromatic compounds are the hydrocarbons containing more than two benzene rings fused together.
- They are produced by incomplete combustion of tobacco, coal and petroleum.
Question 161.
Write the harmful effects of benzene.
Answer:
- Benzene is both, toxic and carcinogenic (cancer causing).
- In fact, it might be considered “the mother of all carcinogens” as a large number of carcinogens have structures that include benzene rings.
- In liver, benzene is oxidized to an epoxide and benzopyrene is converted into an epoxy diol. These substances are carcinogenic and can react with DNA and thus, can induce mutation leading to uncontrolled growth of cancer cells.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Alkanes are represented by the general formula ………….
(A) CnH2n-2
(B) CnH2n+2
(C) CnH2n
(D) CnHn
Answer:
(B) CnH2n+2
2. Which of the following compound is alkanes?
(A) C5H10
(B) C10H22
(C) C15H28
(D) C9H16
Answer:
(B) C10H22
3. Alkanes are commonly called …………
(A) arenes
(B) paraffins
(C) olefins
(D) acetylenes
Answer:
(B) paraffins
4. Every carbon atom in alkanes is …………..
(A) sp hybridized
(B) sp2 hybridized
(C) sp3 hybridized
(D) sp3d hybridized
Answer:
(C) sp3 hybridized
5. Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more organic compounds have ………….
(A) same molecular formula but different structural formula
(B) same structural formula but different molecular formula
(C) same general formula, but different structural formula
(D) same empirical formula, same structural formula
Answer:
(A) same molecular formula but different structural formula
![]()
6. Pentane exhibits …………. chain isomers.
(A) two
(B) three
(C) four
(D) five
Answer:
(B) three
7. Which of the following is NOT an isomer of hexane?
(A) 2-Methylpentane
(B) 2,2-Dimethylbutane
(C) 2,2-Dimethylpentane
(D) 3-Methylpentane
Answer:
(C) 2,2-Dimethylpentane
8. Alkanes can be prepared by ………… of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(A) hydrogenation
(B) oxidation
(C) hydrolysis
(D) cracking
Answer:
(A) hydrogenation
9. Catalytic hydrogenation of ethene or acetylene gives …………..
(A) ethane
(B) propylene
(C) methane
(D) propane
Answer:
(A) ethane
10. Ethyl iodide when reduced by zinc and dilute HCl, leads to the formation of …………..
(A) Methane
(B) Ethane
(C) Ethylene
(D) Butane
Answer:
(B) Ethane
![]()
11. The reaction of alkyl halides with sodium in dry ether to give higher alkanes is called ………..
(A) Wurtz reaction
(B) Kolbe’s reaction
(C) Frankland’s reaction
(D) Williamson’s reaction
Answer:
(A) Wurtz reaction
12. Methane is ………… molecule.
(A) polar
(B) nonpolar
(C) highly polar
(D) none of these
Answer:
(B) nonpolar
13. Alkanes are ………… in water.
(A) soluble
(B) sparingly soluble
(C) insoluble
(D) none of these
Answer:
(C) insoluble
14. As branching increases, boiling point of alkanes ………….
(A) increases
(B) decreases
(C) remains same
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) decreases
15. Halogenation of alkane is an example of …………. reaction.
(A) dehydration
(B) substitution
(C) addition
(D) elimination
Answer:
(B) substitution
![]()
16. Order of reactivity of halogens in halogenation of alkanes is ………….
(A) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
(B) I2 > Br2 > Cl2 > F2
(C) Br2 < I2 < F2 < Cl2
(D) Cl2 < I2 < Br2 < F2
Answer:
(A) F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2
17. The thermal decomposition of alkanes in absence of air to give lower alkanes, alkenes and hydrogen is called ………….
(A) vapour phase nitration
(B) pyrolysis
(C) polymerisation
(D) combustion
Answer:
(B) pyrolysis
18. But-1-ene and But-2-ene are …………
(A) chain isomers
(B) position isomers
(C) geometrical isomers
(D) metamers
Answer:
(B) position isomers
19. Hex-2-ene and 2-Methylpent-2-ene exhibit …………
(A) chain isomerism
(B) position isomerism
(C) geometrical isomerism
(D) optical isomerism
Answer:
(A) chain isomerism
20. Which of the following shows position isomerism?
(A) Propene
(B) Ethene
(C) 2-Methylpropene
(D) Pent-2-ene
Answer:
(D) Pent-2-ene
![]()
21. When identical atoms or group of atoms are attached to the two carbon atoms on the same side of the double bond, the isomer is called ………… isomer.
(A) cis
(B) trans
(C) position
(D) chain
Answer:
(A) cis
22. Which of the following does NOT exhibit geometrical isomers?
(A) But-2-ene
(B) Pent-2-ene
(C) But-1-ene
(D) Hex-2-ene
Answer:
(C) But-1-ene
23. When ethyl bromide is heated with alcoholic KOH, ………… is formed.
(A) ethane
(B) ethanol
(C) ethene
(D) acetylene
Answer:
(C) ethene
24. Alkenes are insoluble in …………
(A) benzene
(B) water
(C) ether
(D) chloroform
Answer:
(B) water
25. Markownikov’s rule is applicable to …………
(A) symmetrical alkenes
(B) alkanes
(C) unsymmetrical alkenes
(D) alkynes
Answer:
(C) unsymmetrical alkenes
![]()
26. When propene is treated with HBr in the dark and in absence of peroxide, then the main product formed is …………
(A) 1-bromopropane
(B) 2-bromopropane
(C) 1,2-dibromopropane
(D) 1,3-dibromopropane
Answer:
(B) 2-bromopropane
27. The product formed by the addition of HCl to propene in presence of peroxide is …………..
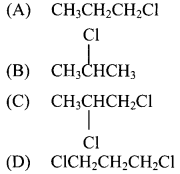
Answer:
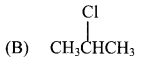
28. Propene reacts with HBr in presence of peroxide, to form …………..
(A) 2-bromopropane
(B) 1-bromopropane
(C) 3-bromopropane
(D) 1,2-dibromopropane
Answer:
(B) 1-bromopropane
29. Markovnikov’s rule is applicable for …………..
(A) CH2 = CH2
(B) CH3CH = CHCH3
(C) CH3CH2CH = CHCH2CH3
(D) (CH3)2C = CH2
Answer:
(D) (CH3)2C = CH2
30. The addition of HCl in presence of peroxide does not follow anti-Markownikov’s rule because …………..
(A) HCl bond is too strong to be broken homolytically
(B) Cl atom is not reactive enough to add on to a double bond
(C) Cl atom combines with H atom to form HCl
(D) HCl is a reducing agent
Answer:
(A) HCl bond is too strong to be broken homolytically
![]()
31. An alkene on ozonolysis produces a mixture of acetaldehyde and acetone. Identify the alkene.
(A) But-1-ene
(B) But-2-ene
(C) 2-Methylbut-1-ene
(D) 2-Methylbut-2-ene
Answer:
(D) 2-Methylbut-2-ene
32. The ozonolysis of (CH3)2C = C(CH3)2 followed by treatment with zinc and water will give ……………
(A) acetone
(B) acetone and acetaldehyde
(C) formaldehyde and acetone
(D) acetaldehyde
Answer:
(A) acetone
33. The compound which forms only acetaldehyde on ozonolysis is …………..
(A) ethene
(B) propyne
(C) but-1-ene
(D) but-2-ene
Answer:
(D) but-2-ene
34. Treatment of ethylene with ozone followed by decomposition of the product with Zn/H2O gives two moles of ………….
(A) formaldehyde
(B) acetaldehyde
(C) formic acid
(D) acetic acid
Answer:
(A) formaldehyde
35. Ozonolysis of 2,3-Dimethylbut-1-ene followed by reduction with zinc and water gives ………….
(A) methanoic acid and 3-methylbutan-2-one
(B) methanal and 2-methylbutan-2-one
(C) methanal and 3-methylbutan-2-one
(D) methanoic acid and 2-methylbutan-2-one
Answer:
(C) methanal and 3-methylbutan-2-one
![]()
36. The reaction, CH2 = CH2 + H2O + [O]
![]()
is called ……………
(A) hydroxylation
(B) decarboxylation
(C) hydration
(D) dehydration
Answer:
(A) hydroxylation
37. An alkene on vigorous oxidation with KMnO4 gives only acetic acid. The alkene is …………..
(A) CH3CH2CH = CH2
(B) CH3CH = CHCH3
(C) (CH3)2C = CH2
(D) CH3CH = CH2
Answer:
(B) CH3CH = CHCH3
38. Ethylene reacts with Baeyer’s reagent to give a/an ………….
(A) glycol
(B) aldehyde
(C) acid
(D) alcohol
Answer:
(A) glycol
39. Baeyer’s reagent is ………….
(A) aqueous KMnO4
(B) neutral KMnO4
(C) alkaline KMnO4
(D) aqueous bromine water
Answer:
(C) alkaline KMnO4
40. Alkynes have general formula ………….
(A) CnH2n-2
(B) CnH2n
(C) CnH2n+2
(D) CnH2n+1
Answer:
(A) CnH2n-2
![]()
41. Aliphatic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing two carbon-carbon triple bonds in their structure are called as ………….
(A) alkadiynes
(B) alkatriynes
(C) alkynes
(D) alkanes
Answer:
(A) alkadiynes
42. Acetylene is prepared in the industry by the action of water on ………….
(A) calcium carbonate
(B) calcium carbide
(C) mercuric chloride
(D) calcium oxide
Answer:
(B) calcium carbide
43. The dihalogen derivatives of alkanes when heated with …………. form corresponding alkynes.
(A) alcoholic water
(B) sodamide
(C) zinc
(D) acids
Answer:
(B) sodamide
44. Alkynes readily undergo …………. reaction.
(A) addition
(B) substitution
(C) elimination
(D) rearrangement
Answer:
(A) addition
45. Liquid bromine reacts with acetylene to form ………….
(A) 1,2-dibromoethene
(B) 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane
(C) 1,1-dibromoethene
(D) methyl chloride
Answer:
(B) 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane
![]()
46. When acetylene is passed through dil H2SO4 in the presence of 1% mercuric sulphate, the compound formed is ………….
(A) ethanol
(B) acetone
(C) acetaldehyde
(D) acetic acid
Answer:
(C) acetaldehyde
47. The compounds which contain at least one benzene ring are ………….
(A) aliphatic compounds
(B) aromatic compounds
(C) cycloalkanes
(D) both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(B) aromatic compounds
48. Which of the following compounds does NOT contain any benzene rings in their structure?
(A) Benzaldehyde
(B) Benzoic acid
(C) Naphthalene
(D) Furan
Answer:
(D) Furan
49. Benzene undergoes ………….
(A) only addition reaction
(B) only substitution reaction
(C) both addition and substitution reactions
(D) nucleophilic substitution reactions
Answer:
(C) both addition and substitution reactions
50. If the substituents are on the adjacent carbon atoms in the benzene ring, it is called ………….
(A) meta
(B) para
(C) ortho
(D) beta
Answer:
(C) ortho
![]()
51. How many molecules of acetylene are required to form benzene?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer:
(B) 3
52. Which of the following compound on reduction gives benzene?
(A) Sodium benzoate
(B) Acetylene
(C) Cyclohexane
(D) Phenol
Answer:
(D) Phenol
53. X-Ray diffraction reveals that benzene is a …………. structure.
(A) triangular
(B) planar
(C) co-planar
(D) 3D
Answer:
(B) planar
54. γ-isomer of BHC is known as ………….
(A) gammene
(B) gammaxane
(C) chlorobenzene
(D) hexachlorobenzene
Answer:
(B) gammaxane
55. Benzene when treated with ozone forms ………….
(A) glyoxal
(B) acetic acid
(C) formaldehyde
(D) benzaldehyde
Answer:
(A) glyoxal
![]()
56. …………. is formed as intermediate product in ozonolysis of benzene.
(A) Benzaldehyde
(B) Phenol
(C) Benzene triozonide
(D) Cyclohexane
Answer:
(C) Benzene triozonide
57. Electrophile in chlorination of benzene is ………….
(A) Cl
(B) Cl+
(C) Cl–
(D) Cl2
Answer:
(B) Cl+
58. Benzene when treated with fuming. H2SO4 at 373 K forms ………….
(A) ethylbenzene
(B) toluene
(C) benzene sulphonic acid
(D) acetophenone sulphonic acid
Answer:
(C) benzene sulphonic acid
59. Ethyl chloride reacts with benzene in presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride to form ………….
(A) ethyl benzene
(B) chlorobenzene
(C) toluene
(D) acetophenone
Answer:
(A) ethyl benzene
60. The electrophile in Friedel-Craft’s alkylation reaction is ………….
(A) R+
(B) R–
(C) Cl+
(D) RCO+
Answer:
(A) R+