Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions Chapter 2.2 The Souvenir Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 English Lesson 2.2 The Souvenir Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 English Chapter 2.2 The Souvenir Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Guess the meaning of the following words:
exorbitantly, precautions, unauthorised, repeatedly, enthusiastically
Write the smaller and related words that you see within these words.
Question 1.
Guess the meaning of the following words. Write the smaller and related words that you see within these words.
Answer:
(i) exorbitantly (adv) – excessively, smaller words – orbit, bit, ant.
related words – exorbitant.
(ii) precaution (n) – to take care beforehand.
smaller words – caution, cat, rat, pet, ear, action, reaction.
related word – caution
(iii) unauthorised (adj) – having no authority.
smaller word – author, ant, rise, his, this, north, said
related words – authorise, authorised.
(iv) repeatedly (adv) – done several times; again and again.
smaller words – repeat, pet, eat, ate, pat, rat, tape, trade
related words – repeat, repeated.
(v) enthusiastically (adv) – done in an excited and motivated manner.
smaller words – enthusiastic, thus, ally, silly, thin, ten
related words – enthusiast, enthusiastic, enthusiastical.
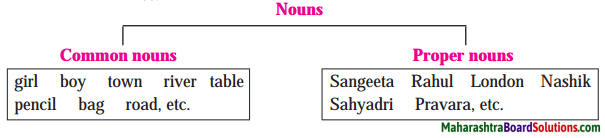
Collective nouns also have singular and plural forms.
Examples:
class – classes, herd – herds, team – teams.
Some more examples-
- arrm armies council – councils
- school – schools group – groups
- society – societies cabinet – cabinets
- department – departments, etc
Collective Nouns (examples)
- an army ol ants
- a flight of birds
- a school of hsh
- a shoal ol hsh
- a choir ot singers
- a band of musicians
- a crew of sailors
- a troupe of artists/dancers
- an audience of listeners
- a litter of puppies/kittens
- a galaxy of stars
- a group of islands
- a forest of trees
- an album of stamps/autographs/photographs
2. Use the details given in the story and your imagination and prepare a timetable for the trip to the moon.
Question 1.
Use the details given in the story and your imagination and prepare a timetable for the trip to the moon.

3. Say whether the following statements are right or wrong.
Question a.
Sayali was travelling in space for the first time.
Answer:
Wrong.
Question b.
Many changes had occurred on the earth in the hundred years before Sayali’s trip to the moon.
Answer:
Correct
Question c.
There were no old cities left on the earth.
Answer:
Correct

Question d.
Sayali’s mother did not want her to go on the trip.
Answer:
Correct
Question e.
There were no human settlements on the moon.
Answer:
Correct
Question f.
Sayali made a hasty purchase.
Answer:
Wrong
Question g.
Sayali did not understand the mistake she had made.
Answer:
Correct

4. Imagine you are Sayali. Write your diary for eveiy day of your trip to the moon, and for the day you gave the earrings to your mother.
Question 1.
Imagine you are Sayali. Write your diary for eveiy day of your trip to the moon, and for the day you gave the earrings to your mother.
Answer:
Monday
28th May, 2018
11.30 pm
Dear Diary,
After spending the day on walking the soil of the moon, it feels joyous and I am pleases to have such a trip.
The weather there is cold, so every time I go there. I carry some warm clothes with me.
Today I bought an earning for my mother. When I gave it to her she was very happy and thrilled to see them. She even said ‘Sayali’, ‘I am proud of you’.
She said that it was the most beautiful gift. She has ever got. The earnings was also very beautiful. Well t was a peaceful day for me.
Good night
5. Discuss: In the story, human settlements are mentioned but not cities or villages. Why is it so?
6. Gather more information about the following from your Science textbook, the internet and other sources.
Gravitational force
View of the sky when you are on the moon.
Chandrayaan mission of India.

7. You want to start human settlement somewhere else other than the earth, in the universe. Will you select a star or a planet? Why? What features supporting life will you look for? Try to find answers to such questions and make a presentalion using scientific information and your imagination.
8. Language Study: Common nouns – 2: Some nouns stand for a number of persons
or things taken together. They are called collective nouns.
Examples: class (a class of sixty students), a herd of cattle, a flock of sheep,
a team of players, a list of names.
Collective nouns also have singular and plural forms.
Examples: class-classes, herd-herds, team-teams
Make a collection of collective nouns.
Class 7 English Chapter 2.2 The Souvenir Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
In what time periods is the story taking place? given to the children?
Answer:
The story is taking place in 2069, somewhere closer to the 22nd century.
Question 2.
Where does Sayali live?
Answer:
Sayali lives on the earth.
Question 3.
What were the two important instructions
Answer:
The two important instructions were:
1. To be extremely careful while roaming outside the human settlements on the moon because a gravitational force equivalent to that of the earth had been artificially maintained in the human settlements but outside the settlements the gravitational force of the moon was at work.
2. To buy articles only from the shops which were inside the dome shaped settlements because there the articles would be genuine and not to buy anything from the unauthorised shops outside the settlement.

Question 4.
Imagine you are landing on the moon. What would be your feelings?
Answer:
For me the moon always looked like a huge cotton ball. Now that I have got a chance to go on the moon and as I am getting closer, I can see the moon has a lot of craters. I am so excited to be landing on the moon and anxious too as to what it would be like when I step on the moon. I am looking forward to walking on the moon; I have heard that we do not actually walk but bounce on the moon because of its lack of gravitational force. I am waiting to walk on the moon and experience the feel of flying while walking.
Question 5.
Was Sayali making a mistake when she bought earrings?
Answer:
Yes, Sayali was making a mistake when she bought the earrings.
Question 6.
What instructions had she ignored?
Answer:
She had been instructed to buy articles only from the shops which were inside the dome shaped settlements which were genuine and not to buy anything from the unauthorised shops outside the settlement. She ignored these instructions and purchased from outside the settlement.

Question 7.
Why had the earrings become so heavy on the earth?
Answer:
Sayali purchased the earrings from outside the human settlement where the moon’s gravitational force was at work. The gravitational force of the moon made the earrings light on the moon, but it became very heavy on the earth because of the earth’s gravitational force.
Question 8.
Which was the longest trip during mummy’s childhood?
Answer:
During mummy’s childhood the longest trip meant going to Europe.
Question 9.
What did the dome shaped settlements on the moon resemble?
Answer:
The dome shaped settlements on the moon resembled the igloos of the Eskimos.
Question 10.
Where were the children escorted to, on the moon?
Answer:
The children were escorted through an airtight tunnel to the settlement at the Neil Armstrong base on the moon.

Question 11.
Quote the first words uttered by a human on the moon. Who uttered them and when?
Answer:
The first words uttered by a human on the moon was, ‘One small step, for a man, one giant leap for mankind’.
These words were uttered by Neil Armstrong who was the first man to put his foot on the moon.
Question 12.
Say whether the following statements are right or wrong.
- Sayali was travelling in space for the first time.
- Many changes had occurred on the earth in the hundred years before Sayali’s trip to the moon.
- There were no old cities left on the earth.
- Sayali’s mother did not want her to go on the trip.
- There were no human settlements on the moon.
- Sayali made a hasty purchase.
- Sayali did not understand the mistake she had made.
Answer:
- Right
- Right
- Wrong
- Wrong
- Wrong
- Right
- Wrong.
Question 13.
Discuss: In the story, human settlements are mentioned but not cities or villages. Why is it so?
Answer:
There are no cities or villages on the moon but just human settlements because according to me people have just started settling on the moon, making it their home.
I Reading Skills, Vocabulary and Grammar
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
Question 1.
State whether the statements true or false.
1. The three days of the trip were going to be part of the daytime on the moon.
2. The stars are seen rarely and very brightly on the earth.
Answer:
1. False
2. False.

Question 2.
Choose the correct answer.
In the moon sky the earth looked times bigger than the moon in the earth sky.
(a) Seventy
(b) Thirteen
(c) Seventeen
Answer:
(b) Thirteen
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
What did the beautiful enchanting view make Sayali and her friends feel?
Answer:
The beautiful enchanting view made Sayali and her friends feel ecstatic.
Question 2.
What was special about the sky watch on the moon?
Answer:
The speciality about the sky watch was that the stars shone dazzling bright against the dark background of the moon sky because there is no atmosphere on the moon.
Question 3.
What does it tell you about the conditions on the earth at that time?
Answer:
The conditions on the earth at that time was usually foggy and the stars were seen rarely and only very faintly.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Pick out a word from the extract which means – ‘not clear’.
Answer:
Foggy

Question 2.
Find the odd man out:
Moon, stars, earth, bright
Answer:
Bright – the rest are nouns.
Grammar:
Question 1.
Pick out the adjective.
They fell asleep feeling happy, excited and comfortable at the same time.
Answer:
Asleep, happy, excited, comfortable.
Question 2.
The most attractive view was that of the disc of the earth! (State the kind of sentence)
Answer:
Exclamatory.
Question 3.
Pick out two compound words from the extract.
Answer:
background, comfortable, daylight, night-time.

Question 4.
It was seventy times brighter. (Adda question tag)
Answer:
It was seventy times brighter, wasn’t it?
Personal Response:
Question 1.
How does the moon look to you from the earth?
Answer:
To me the moon looks like a round shiny ball of cotton. Sometimes, I feel that the moon looks like a pizza layered with cheese. I love to look at the full moon and dream of being there someday.
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
1. The second day’s attraction was a ………. on the moon!
2. ………… and her friends had travelled far and wide and had done a lot of sight-seeing.
Answer:
1. circus
2. Sayali

Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. One unique feature of the circus was the seating arrangement.
2. The guide had assigned them the task of writing stories about the circus.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Where did the teacher take the students on the second day?
Answer:
The teacher took the students to the circus on the moon on the second day.
Question 2.
What was the unique feature of the circus?
Answer:
The unique feature of the circus was the seating arrangement.
Question 3.
What were the special attractions of the circus?
Answer:
The special attractions of the circus were high jumps and long jumps.

Question 4.
What could be the reason behind the unique seating arrangement?
Answer:
The unique seating arrangement with the spectators sitting inside the tent and the circus going on outside could be because the gravitational force in the tents was artificially maintained according to the earth’s gravitational force which helped the spectators to remain in one place without bouncing around and watching the circus which was taking place outside the tent where the gravitational force of the moon was at work. This helped the performers perform unique stunts as well.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Identify the plurals of the following words.
- friend
- metre
- feature
- tent
- teacher.
Answer:
- friends
- metres
- features
- tents
- teachers.
Question 2.
Pick out compound words from the passage.
Answer:
outside, self-study, sight-seeing.
Grammar:
Question 1.
One gymnast jumped twenty seven metres high! (Add a question tag)
Answer:
One gymnast jumped twenty seven metres high, didn’t he?

Question 2.
It was expected that the students should spend some time for self-study.
(Frame a ‘Wh’ question so as to get the underlined
words as the answer.)
Answer:
What was expected from they students?
Personal Response:
Question 1.
What would be the overall effects of having no atmosphere?
Answer:
Atmosphere is a protective layer of gases that envelopes the earth. It consists of a number of gases including nitrogen, oxygen and many more.
Life depends on the atmosphere.
- If there was no atmosphere the intense light and harmful radiation of the sun would harm life.
- Every creature depending on oxygen from the smallest ant to the biggest whales would perish. There
- would be no oceans because in the absence of atmosphere, oceans would just evaporate due to the scorching heat of the sun.
- No water for living because there would be no water-cycle.
- The temperature would be so high that everything would get burnt.
- Atmosphere protects asteroid strikes on the earth.
- To sum it up, without atmosphere there would be no life.

Answer the following.
Question 1.
Collective noun: Collective noun is the name given to a number of persons, animals or things taken as a whole, (one single collective unit)
Examples:
- Persons – staff, team, crowd, jury, committee, gang, crew, choir, class
- Animals- flock, herd, shoal, swarm, pride, pack, brood
- Things – bunch, pile, stack, flight, pile collection, bouquet, library
Make a collection of collective nouns.
- an army of soldiers
- a fleet of ships
- a brood of chickens
- a collection of pictures/stamps
- a flight of steps
- a pride of lions
- apackof wolves
- a litter of puppies/kittens
- a bunch of keys/flowers
- a gang/band of thieves
Question 2.
Punctuate the following sentences.
- a Jam packed three day’s programme awaited the children on the moon
- be careful when you walk dear children don’t run or sprint you will fall
- she exclaimed hello dear how am i going to wear such heavy earrings
- everyone was looking forward to this visit to the historical monument it was the oldest place in the history of man on the moon
Answer:
- A jam-packed three day’s programme awaited the children on the moon.
- “Be careful when you walk, dear children; don’t run, or sprint, you will fall!”
- She exclaimed, “Hello dear, how am I going to wear such heavy earrings?”
- Everyone was looking forward to this visit to the historical monument – it was the oldest place in the history of man on the moon.

Question 3.
Find out the collective words for the following:
1. A …….. of shoes.
2. A ………. of mountains.
3. A ………… of ships.
4. A ………….. of flowers.
5. A ……….. of lies.
6. A ………… of wild animals.
Answer:
pair, range, fleet, bouquet, pack, zoo
Question 4.
Identify the plurals of the following.
- company
- firm
- family
- crowd
- gang
Answer:
- companies
- firms
- families
- crowds
- gangs
Do as directed.
Question 1.
Remembering the incident made her laugh even now. (Frame a ‘Wh’ question so as to get the underlined words as the answer)
Answer:
What made her laugh even now?

Question 2.
She had read the description. (Change the voice)
Answer:
The description had been read by her.
Question 3.
The clouds had disappeared, the stars were shining bright. (Use ‘not only … but also’)
Answer:
Not only had the clouds disappeared but also the stars were also shining bright.
Question 4.
Sayali immediately realized her mistake. (Identify the part of speech for the underlined word)
Answer:
immediately – adverb.
Question 5.
Her mother picked up the earrings. (Change the voice)
Answer:
The earrings were picked up by her mother.
Question 6.
Give me those red earrings. (Kind of sentence)
Answer:
Imperative sentence.

Question 7.
High jumps and long jumps were the special attractions. (Use ‘not only … but also’)
Answer:
Not only high jumps but also long jumps were the special attractions.
Question 8.
A hundred years ago Neil Armstrong had landed at this place. (Frame a question – begin with ’When …’)
Answer:
When had Neil Armstrong landed at this place?
Question 9.
Give me those red earrings. (Add a question tag)
Answer:
Give me those red earrings, will you/won’t you?
Question 10.
Use a prefix to get the opposite of:
Answer:
- experience × inexperience
- contented × discontented
- appeared × disappeared
- visible × invisible
- comfortable × uncomfortable
- happy × unhappy
- paid × unpaid
- spent × unspent

Writing Skills
Diary Writing
Question 1.
Write your diary everyday describing your trip to the moon, and also about the day you gifted the earrings to your mother.
Answer:
11th June, 2019
Sunday
We landed safely on the moon. It was a wonderful experience. In the space shuttle I was excited as well as anxious. When we alighted from the space shuttle on the moon, it was a feeling which cannot be expressed in words. On the first day we were taken to the Neil Armstrong base. We were instructed about the things we could and could not do.
We were told about the differences in the gravitational force on the moon and in the human settlement on the moon. We were a part of the night time on the moon. The stars shone brightly like diamonds. We also saw the earth from the moon. The earth looked thirteen times bigger than the moon and seventy times brighter. The view was so enchanting that we were ecstatic.
12th June, 2019
Monday
We woke up early and got ready for our second day’s attraction. We saw a circus show on the moon! The unique feature of the circus was the seating arrangement. We were made to sit inside the tent and the circus was going on outside the tent. High jumps and long jumps were the main attraction. We also visited various settlements and jotted down important points which would help us in writing an essay on our trip to the moon. My friends and I travelled a lot and did a lot of sight-seeing.
13th June, 2019
Tuesday
Being excited, we were ready before the others. Our teacher took us to that place of historical importance where Neil Armstrong had landed in Apollo II on 20th July, 1969, the space flight that helped the 1st two humans walk on the moon. It was Neil Armstrong who was the first human being to put his foot on the moon. We got to see the first footprint of Neil Armstrong which has been preserved on the moon land. The first words uttered by a human on the moon is also carved at the base of Neil Armstrong’s statue.
We were made to wear space suits for the first time as we were going to roam on the moon experiencing its gravitational force. My friends purchased souvenirs for their families and friends because the next day we were to start our return journey. How these three days have flown by! I am carrying back memories to last a life time.
15th June, 2019
Thursday
I was so excited on the moon that I had not thought of any of my family members, not even mummy! How could I forget her! I remembered mummy just before leaving for the earth, I felt very guilty. In my haste to please my mother, I forgot the instructions given by our escorts and purchased a beautiful pair of red earrings from a shopkeeper outside the settlement. After returning to the earth, the first thing I did was to show mummy the earrings I had brought for her. Mummy picked up the earrings to admire it and found them very heavy. It was then that I realised the blunder I had done. Now those earrings are kept as souvenirs from the moon in our show case.

Formative Assessment:
Question 1.
Prepare a timetable for a trip to the moon. Use your imagination.
Answer:
- Plan ahead before making the trip.
- Research your destination and know what to expect.
- Get the necessary passport/documents.
- Check and get immunization if necessary.
- Keep updated with the current happenings on the moon.
- Learn and understand what should be done/ not done on the moon.
- Have a communication plan with family and friends at home.
- Pack wisely. The lighter the better. Take things you like to wear and plan on wearing it several times.
- Have a good attitude. Keep your mind open.
- Don’t complain.
- Be an observer not a judge. Enjoy your trip.
The Souvenir Summary in English
Introduction:
‘The Souvenir’ written by Lakshman Londhe is a story in the form of a science fiction.
Paraphrase:
‘The Souvenir’ is a story which is a science fiction. A science fiction deals with world that differs from our own as a result of new scientific discoveries, new technologies or different social systems. It is sometimes hard to distinguish science fiction from fantasy. Through this story the writer has tried to tell us the changes which would have taken place by 2069 because of new technologies.

Glossary:
- souvenir (n) – a thing that is kept as a reminder of a person, place or event
- awe (n) – amazement
- abate (v) – subside, to reduce
- azure (n) – clear blue colour
- unauthorized (v) – not legal unauthorised (adj) – having no authority
- enthusiastically (adv) – happily
- repeatedly (adv) – again and again
- exorbitantly (adv) – excessively
- shuttle (n) – a form of transport that travels between two places
- panorama (n) – an unbroken view of an entire surrounding area, a very wide view, usually a 360° view
- succession (n) – following in sequence
- escorted (v) – carefully accompanied
- genuine (adj) – real
- ecstatic (adj) – extremely happy
- unique (adj) – unusual
- sprint (v) – a short race at top speed
- jam-packed (adj) – extremely crowded
- out of the world – extraordinary; not found on the earth
- far and wide – across a large area
- precaution (n) – care taken before hand
- captured (v)- recorded
- receptionist (n) – a person who greets and deals with visitors
- outset (v) – start
- dazzling (adj) – extremely bright
- foggy (adj) – unclear
- uttered (v) – said
7th Std English Questions And Answers:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()