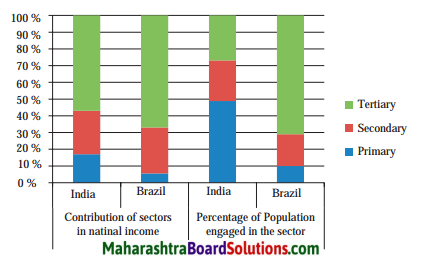
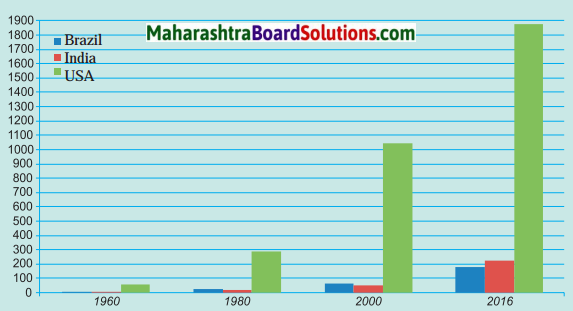
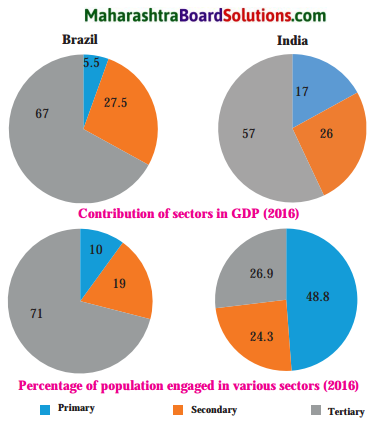
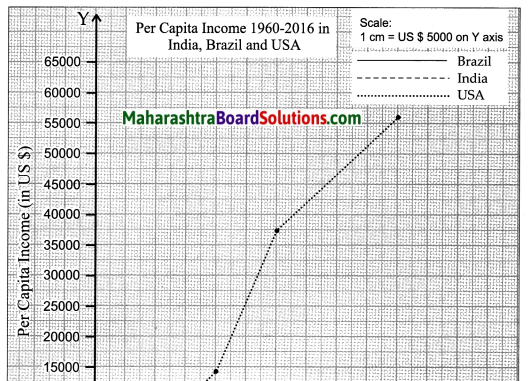
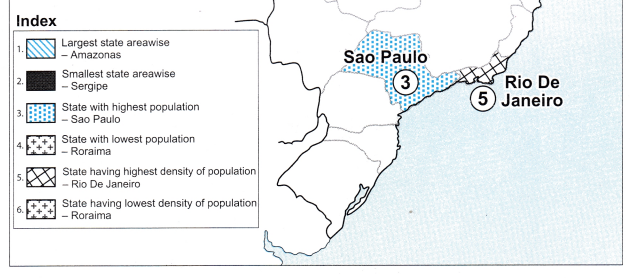
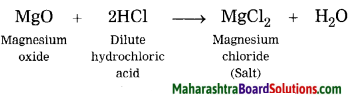
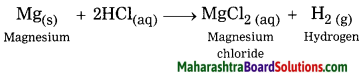
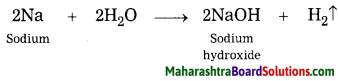
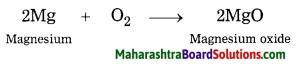Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Geography Solutions Chapter 3 Physiography and Drainage Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 Geography Chapter 3 Question Answer Physiography and Drainage Maharashtra Board
Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Physiography and Drainage Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Geography Class 10 Chapter 3 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Complete the sentences by choosing the right option :
Question a.
Brazil is covered mainly by _________.
(a) highlands
(b) mountainous region
(c) plains
(d) dissected hills
Answer:
(a) highlands
![]()
Question b.
Like Brazil, India too has __________.
(a) high mountains
(b) west flowing rivers
(c) ancient plateau
(d) snow-capped mountains
Answer:
(c) ancient plateau
Question c.
The Amazon Basin is mainly ________.
(a) characterized by droughts
(b) filled by swamps
(c) covered by dense forests
(d) fertile
Answer:
(c) covered by dense forests
Question d.
Amazon is a large river in the world. Near its mouth ___________.
(a) deltaic regions are found
(b) no deltas are found
(c) deposition of sediment occurs
(d) fishing is done
Answer:
(b) no deltas are found
Question e.
The Lakshadweep Islands of the Arabian Sea are _________.
(a) made from the part separated by mainland
(b) coral islands
(c) volcanic islands
(d) continental islands
Answer:
(b) coral islands
Question f.
To the foothills of the Aravalis _________.
(a) lies the Budelkhand Plateau
(b) lies the Malwa Plateau
(c) lies the Mewad Plateau
(d) lies the Deccan Plateau
Answer:
(c) lies the Mewad Plateau
![]()
2. Answer the following Questions:
Question a.
Differentiate between the physiography of Brazil and India
Answer:
| The Physiography of India | The Physiography of Brazil |
| The physiographic divisions of India are the Himalayas, the North Indian Plains and the Peninsula, Coastal Plains, and the Islands. | The physiographic divisions of Brazil are: The Highlands, The Great Escarpment, The Coastal region, The Plains and The Islands. |
| There are long and high mountain ranges in northern and north eastern part of India in the form of Himalayan ranges. The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats lie to the west and east of the Peninsular region. The average altitude of the Greater Himalayas is around 6000m. | In Brazil there are no high and continuous mountain ranges. The eastern side of the Highlands is demarcated because of the Escarpment. The Great Escarpment located in south-eastern part of the Highlands has an altitude of 790m in this region with the height gradually decreasing. |
| In India the Plains occupy a wide area in the north. The Plains lie between the Himalayas in the North and the Peninsula in the South. It extends from Rajasthan in the West to Assam in the East. The Coastal Plains lie to the west and east of the Peninsula. | In Brazil the Amazon Basin in the North and the Parana-Paraguay Basin to the South West constitutes the Plains. Also a narrow coastal plain is confined to the North and the East. |
| The Peninsular Plateau region of India lies to the South of the North Indian Plains and is divided into 2 groups, the The Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau. | In Brazil the Highlands occupy an extensive area in the South and is described as the Brazilian Highlands or the Brazilian Shield. Also to the North lies the Guyana Highland. |
| The islands in India are either volcanic or coral in origin. | The islands in Brazil are mainly depositional and some of them are coral in nature. |
Question b.
What measures are being taken to control pollution in the rivers of India?
Answer:
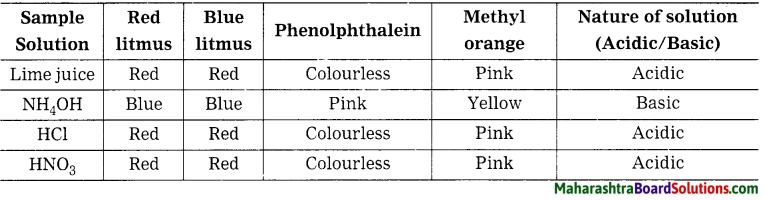
Rivers in India are getting polluted due to the sewage and effluents being added to it and thus affecting its quality. Following measures are being taken to control pollution in the rivers in India.
(i) Treating of the sewage before draining it into the rivers.
(ii) Reducing the use of pesticides and insecticides as they drain into the water sources and pollute it.
(iii) Discharge of industrial effluents into rivers without proper treatment is now controlled.
(iv) Reusing the water for different purposes which reduces the overuse and pollution of water.
(v) Carrying out the cleaning and purification of the river water under the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP).
(vi) Creating awareness in the people about the importance of rivers and harmful effects of pollution.
(vii) Setting up of Pollution Control Boards (PCB) at the state and national level to curb pollution.
Question c.
Explain the characteristics of the North Indian Plains.
Answer:
(i) This division lies between Himalayan Mountains in the north and the Peninsula in the south.
(ii) Similarly, it extends from Rajasthan and Punjab in the west to Assam in the east.
(iii) It is mostly a flat low lying area.
(iv) The North Indian Plains are divided into two parts. The part lying to the east of the Aravalis is the basin of the river Ganga and is therefore known as the Ganga Plains. It slopes eastward.
(v) Most of the Indian state of West Bengal and Bangladesh together constitute the delta of Ganga-Brahmaputra system. It is known as the Sunderbans. It is considered to be the world’s largest delta.
(vi) The western part of the North Indian Plains is occupied by desert known as the Thar Desert or Marusthali. Most of Rajasthan is occupied by this desert.
(vii) To the north of the desert lie the plains of Punjab.
(viii) This region is spread to the west of Aravalis and Delhi ranges. These plains have formed as a result of the depositonal work by river Satluj and its tributaries. The slope of the plains is towards the west.
Because the soil here is very fertile, agriculture is largely practised in this region.
Question d.
What could be the reasons behind the formation of swamps in the extensive continental location of Pantanal?
Answer:
Pantanal is one of the largest wetlands in the world, lying in the south west part of the highland areas.
It is a region of swamps and marshes in northwestern part of Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil and it extends into Argentina too.
This region is drained by the river Paraguay and its tributaries.
They collect the water from the highland areas and deposit the sediments in the low lying Pantanal region.
Pantanal is a gently sloped basin which is submerged throughout the year due to the filling of the sediments and water in the depression area of the Pantanal.
Question e.
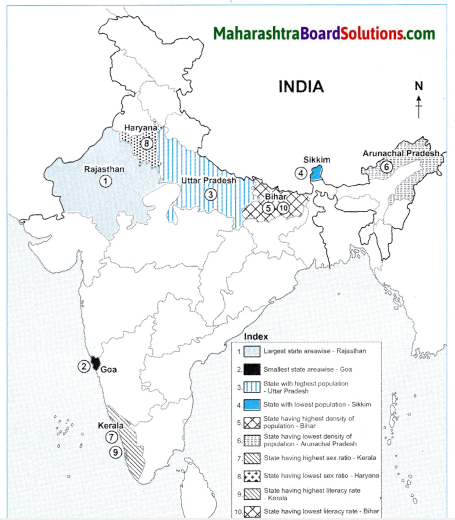
Which are the major water divides of India give examples.
Answer:
A mountain or an upland which separates two drainage basins is known as a Water Divide. The major Water Divides of India are :
Western Ghats: The Western Ghats acts as a water divide and separates the west flowing rivers like Zuari, Mandvi, Vaitama draining into the Arabian Sea, from the east flowing rivers like the Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri draining into the Bay of Bengal.
Vindhya ranges: It divides the drainage basin of the River Ganga and the River Narmada.
Aravali ranges : The Aravali ranges separate the west flowing river Luni from the east flowing river Banas.
Satpuda ranges: The Satpudas separate the Narmada drainage basin and the Tapi drainage basin.
Question 3.
Write notes on :
Answer:
a. Amazon River Basin:
(i) Amazon collects its headwaters from the eastern slopes of Andes Mountains in Peru.
(ii) Amazon River receives huge discharge. This is about 2 lakh m³/s.
(iii) As a result, Amazon washes off the load supplied to it from the catchment
(iv) Consequently, sediments are not deposited even at the mouth.
(v) A dense network of distributaries, which is a characteristic feature of river mouth areas, is by and large absent in the mouth region of Amazon.
(vi) Instead, we find a series of islands developed along the mouth of Amazon, beyond the coastline into the Atlantic Ocean.
(vii) At the mouth, the width of Amazon channel is 150 km.
(viii) Most of the course of the Amazon river is suitable for navigation.
b. Himalayas:
(i) The Himalayas is one of the young fold mountains in the world.
(ii) The Himalayas extend from Pamir Knot in Tajikistan to the east. It is a major mountain system of the Asian continent.
(iii) In India, it extends from Jammu and Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh.
(iv) The Himalayas is not a single mountain range. There are many parallel ranges in the system.
(v) The southernmost range of Himalayas is known as the Siwaliks. It is also the youngest range.
(vi) Beyond the Siwaliks are Lesser Himalayas (Himachal), Greater Himalayas (Himadri) and Trans Himalayan ranges from south to north.
(vii) These ranges are young to old respectively.
(viii) These mountain ranges can also be divided into Western Himalayas (or Kashmir Himalayas), Central Himalayas (or Kumaun Himalayas) and Eastern Himalayas (or Assam Himalayas).
![]()
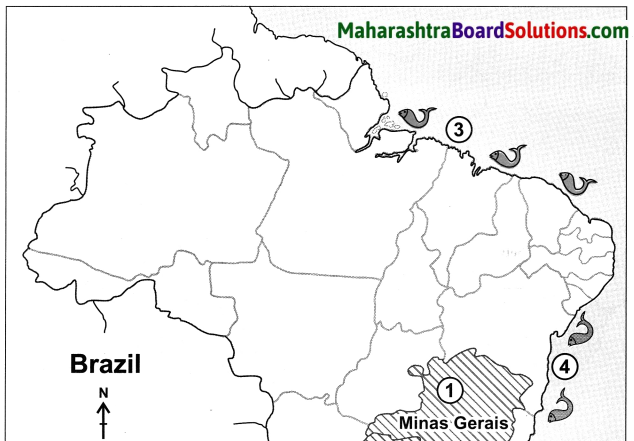
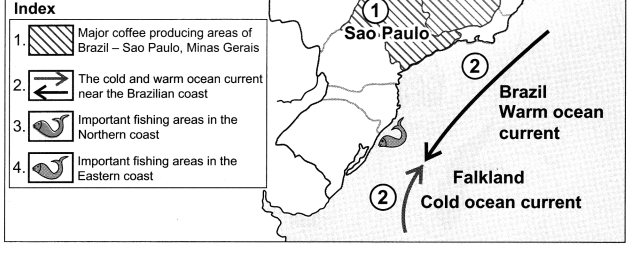
c. The coasts of Brazil:
(i) Brazil has a coastline of about 7400 km. They are divided into two parts namely northern coast and the eastern coast.
(ii) The northern coast extends from Amapa province in the north to Rio Grande Do Norte in the east. This coast can be called as North Atlantic Coast. From here, the eastern coast extends towards the south.
(iii) The northern coast is characterized by mouths of many rivers including the Amazon. Therefore, this region is a low-lying region.
(iv) On this coast lie the Marajo island, Marajo and Sao Marcos Bays.
(v) Marajo, a large coastal island located between River Amazon and River Tocantins, lies on the northern coast.
(vi) The eastern coast receives a large number of smaller rivers. The only major river which meets the Atlantic Ocean here is Sao Francisco.
(vii) The Brazilian Coast is characterized by a large number of beaches and sand dune complexes.
(viii) The Brazilian Coast is protected in some areas by coral reefs and atoll islands.
d. The Indian Peninsula:
(i) The area lying to the south of North Indian Plains and tapering towards the Indian Ocean is called Indian Peninsula.
(ii) It consists of many plateaus and hill ranges.
(iii) The Aravalis in the north west are the oldest fold mountains here.
(iv) It includes a series of plateaus bordering the Plains, Vindhyas and Satpuda ranges in the central part and the hilly regions of Western and Eastern Ghats.
e. The Great Escarpment:
(i) An Escarpment is a long, steep slope especially one at the edge of a plateau.
(ii) Though the Great Escarpment occupies a I very small area, the nature of its slope and the effect it has on the climate makes is a separate
physiographic region.
(iii) The eastern side of the Brazilian Highland is demarcated because of the escarpment.
(iv) In this region, the altitude of the escarpment is 790 m.
(v) In some regions, the height decreases gradually.
(vi) The escarpment is very steep particularly from Sao Paulo to Porto Alegre.
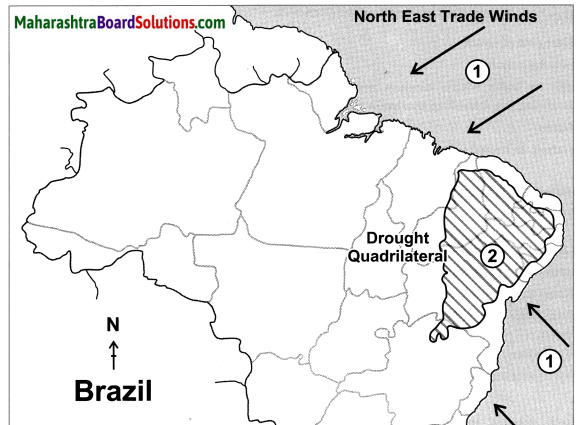
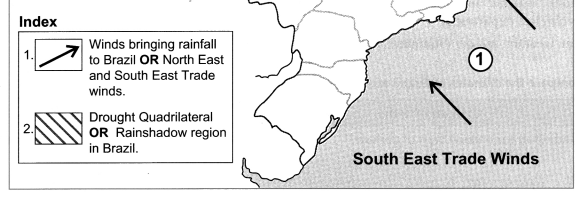
(vii) The escarpment acts as a barrier to the Southeast Trade Winds giving rise to the rainshadow area in the northeast part of the highlands. The region to the north of this area is called ‘Drought Quadrilateral’.
![]()
4. Write geographical reasons:
Question a.
There are no west flowing rivers in Brazil.
Answer:
(i) Many rivers originating from the terminal portion of the Brazilian highlands flow northwards to meet the Amazon river and finally terminate in the Atlantic Ocean.
(ii) Sao Francisco River flows 1000 kms towards the north and then turns east to join the Atlantic Ocean.
(iii) The rivers Parana, Paraguay and Uruguay originating from the southern part of Brazilian highlands flow southwest and enter Argentina.
(iv) The Amazon river, originating from the Andes mountain in the west flows eastwards to meet the Atlantic Ocean.
(v) Thus, there are no west flowing rivers in Brazil.
Question b.
There are dissimilarities between the eastern and the western coast of India.
Answer:
(i) The western coast borders the Arabian Sea and the eastern coast borders the Bay of Bengal.
(ii) The western coast is by and large a rocky coast. At places, spurs starting from the Western Ghats have extended right up to the coast. The eastern coast has been formed as a result of depositional work of rivers.
(iii) The width of the western coast is narrow, whereas that of the eastern coast is wide.
(iv) Short and swift rivers originating from Western Ghats form estuaries on the western coast, whereas, because of the gentle slope the east flowing rivers flowing at low speed deposit sediments and form deltas on the eastern coast.
(v) Thus there are dissimilarities between the eastern and the western coasts of India.
Question c.
There are fewer natural ports on the eastern coast of India.
Answer:
(i) The eastern coast borders the Bay of Bengal. It has been formed as a result of depositional work of rivers.
(ii) Many east flowing rivers have formed deltas at their mouth due to the gentle slope.
(iii) Sediments deposited by the river makes the coast shallow.
(iv) Therefore there are fewer natural ports on the eastern coast of India.
Question d.
As compared to Amazon, the pollution in river Ganga affects human life greatly.
Answer:
(i) The Amazon Basin is a sparsely populated region of Brazil.. Unfavourable climate, heavy rainfall, inaccessibility and dense forest are the barriers for development of human settlements and industrialisation here.
(ii) On the other hand, the Ganga Plain region is one of the most densely populated regions of India.
(iii) Due to flat fertile plains, availability of water, suitable climate, dense human settlements have been established in this region.
(iv) Mining activities in the Amazon Basin causes pollution in the Amazon River, whereas industrial and domestic sewage adds to the pollution of
River Ganga. Thus as compared to Amazon, the pollution in River Ganga affects human life greatly, as the Ganga Plain is more densely populated as compared to the Amazon Plains.
5. Identify the correct group:
Question a.
The order of the physiographic units in Brazil while going from North West to South East
(i) Parana River basin – Guyana Highlands – Brazilian Highlands
(ii) Guyana Highlands – Amazon river basin – Brazilian Highlands
(iii) Coastal plains – Amazon River basin – Brazilian Highlands
Answer:
Guyana Highlands – Amazon River basin – Brazilian Highlands
Question b.
These Rivers of Brazil are north-flowing
(i) Juruaka – Xingu – Aragua
(ii) Negro – Branco – Paru
(iii) Japura – Jurua – Purus
Answer:
Juruaka – Xingu – Aragua
Question c.
The order of plateaus of India from south to north.
(i) Karnataka – Maharashtra – Bundelkhand
(ii) Chhota Nagpur – Malwa – Marwad
(iii) Telangana – Maharashtra – Marwad
Answer:
Karnataka – Maharashtra – Bundelkhand
![]()
Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Physiography and Drainage Intext Questions and Answers
Observe the map and answer the following questions.
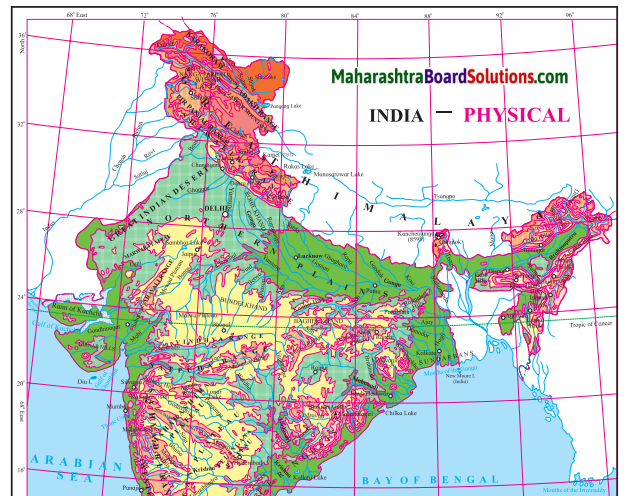
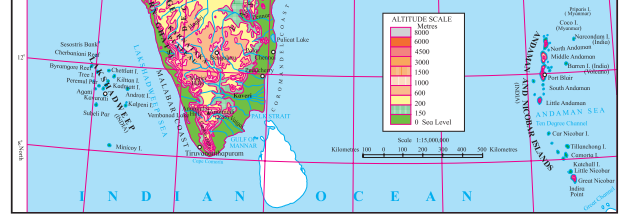
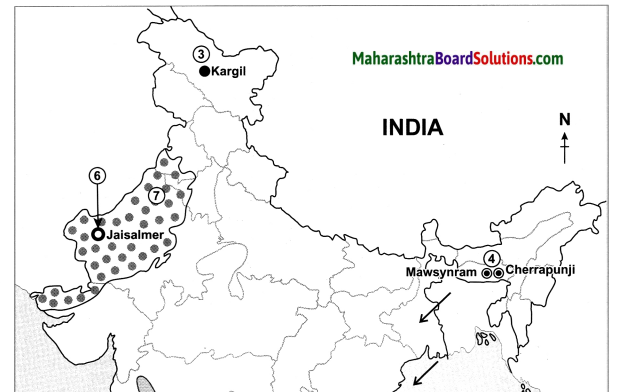
Physiography And Drainage Map Questions And Answers Question 1.
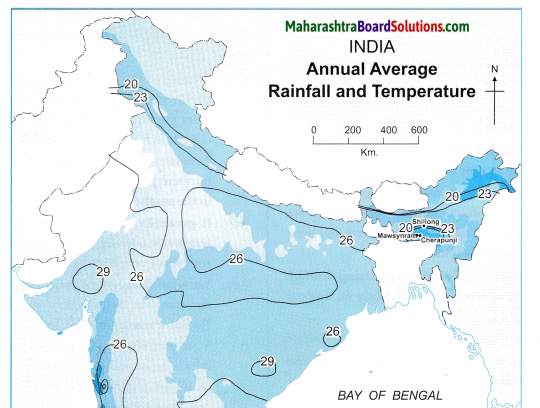
In which direction does the region with an altitude of more than 6000m lie in India ?
Answer:
The region with an altitude of more than 6000m lies part of India towards the north and north eastern.
Physiography And Drainage Questions And Answers Question 2.
Look for the south-flowing river in the peninsular region. In which river basin does it lie?
Answer:
River Wardha and Vainganga are the south flowing river in the peninsular region. These lie in the Godavari river basin.
Physiography And Drainage Question 3.
In which direction is the slope of the region in the north shown in dark green.
Answer:
The region in the north shown in dark green is the North Indian Plain. It slopes towards the east.
Geography Class 10 Chapter 3 Physiography And Drainage Question 4.
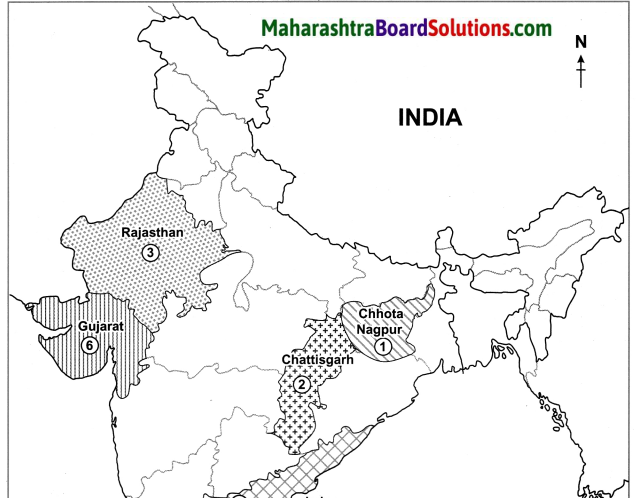
Make a list of plateaus located in between Aravalli ranges and Chhota Nagpur Plateau.
Answer:
Plateaus located in between Aravalli ranges and Chhota Nagpur Plateau are Mewad Plateau, Bundelkhand, Baghelkhand and Malwa Plateau.
Physiography And Drainage Of India And Brazil Notes Question 5.
Name the peak shown in the Eastern Ghats.
Answer:
Mahendragiri (1600m) and Malayagiri (1187m) are the peak shown in the Eastern Ghats.
Physiography And Drainage 10th Question 6.
Which mountains demarcate the deep plains of Brahmaputra?
Answer:
Dafla Hills, Naga Hills, Garo, Khasi and Jaintia Hills demarcate the deep plains of Brahmaputra.
Physiography And Drainage Class 10 Question 7.
Give the relative location of the Nilgiri Hills.
Answer:
Nilgiri Hills lie at the convergence of Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats in the southern part of the Deccan Pleateau.
10th Physiography Chapter 3 In Marathi Question Answer Question 8.
In which direction does the height of Sahyadri hills increase?
Answer:
The height of Sahayadri hills increase towards the south.
Question 9.
The Vindhyas act as a water divide between which two river basins?
Answer:
The Vindhyas acts as a water divide between Ganga river system and Narmada river system.
![]()
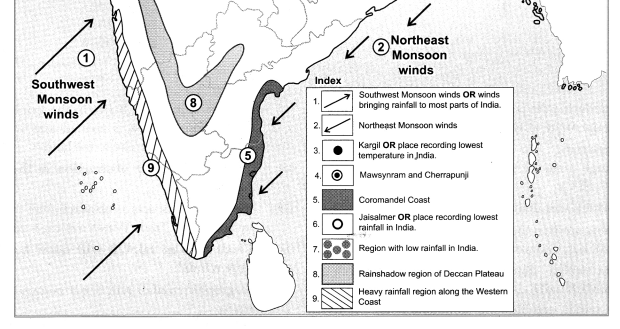
Observe the map and answer the following questions.
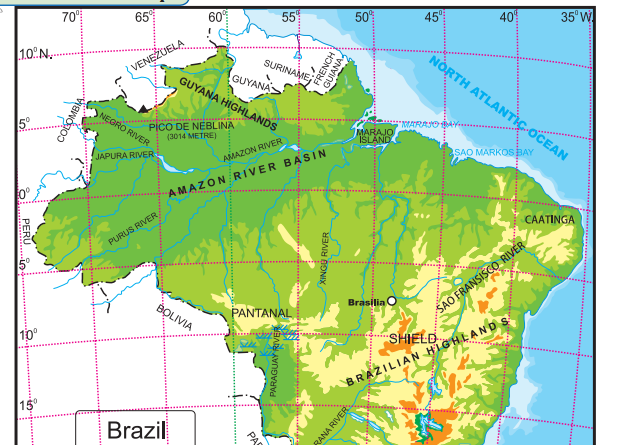
Question 1.
What is the range of altitude of the Amazon river basin?
Answer:
The range of altitude of the Amazon river basin is from 0 metres to 200 metres.
Question 2.
Between which two highlands is the Amazon river basin located?
Answer:
The Amazon river basin is located between the Guyana Highlands and the Brazilian Highlands.
Question 3.
Observe the region with the altitude of 500 to 1000 metres. Describe the locational extent of this region in yellow with reference to the direction.
Answer:
The region in yellow represents the Brazilian Highlands. They cover most of the eastern and southern parts of Brazil.
Question 4.
What do the isolated regions shown in yellow indicate?
Answer:
The isolated region shown in yellow indicate the Brazilian Highlands or the Brazilian Plateau or the Brazilian Shield.
Question 5.
Besides the Amazon river basin, where else do you find regions with an altitude of less than 200m?
Answer:
Besides the Amazon basin the other regions with an altitude of less than 200m are the Pampas, Parana and Paraguay basin, as well as the Eastern and Northen coastal region.
Question 6.
Describe the plateau region with height of 200 to 500m through which tributaries of Amazon flow in your own words.
Answer:
The highlands here gradually slope towards north and slopes are not very steep. The tributaries of Amazon, eg. Xingu river flowing through this region make rapids and waterfalls.
Question 10.
Enumerate the characteristics of the Western Ghats.
Answer:
(i) The Western Ghats are a continuous chain of mountains extending from north to south for about 1600 km. They run parallel to the west cost of India.
(ii) In the north, i.e., in Maharashtra and Karnataka these mountain ranges are referred as Sahyadris and in the south they are referred as Annamalai hills.
(iii) The height of the Western Ghats increases towards the south.
(iv) These hill ranges comprise of many peaks such as Kalsubai Peak (1646 m) located to the north and Anaimudi Peak (2695 m) located to the south of Western Ghats.
(v) The highest peak of Western Ghats is Anaimudi Peak (2695 m) located in Annamalai hills.
(vi) The western slope of the Western Ghats is steep while the eastern slope is gentle
(vii) The Western Ghats acts as a water divide for the rivers flowing towards Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal.
Question 11.
Compare the Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats
Answer:
| S.no | Eastern Ghats | Western Ghats | ||
| (i) | The Eastern Ghats run along the eastern coast of India in the north east to south west direction. | (i) | The Western Ghats also known as Sahyadris run in the north-south direction along the western coast of India. | |
| (ii) | It forms the eastern boundary of the Deccan Plateau. . | (ii) | It forms the western boundary of Deccan Plateau. | |
| (hi) | It is not continuous, but is broken at many places by rivers like Godavari and Krishna. | (iii) | The Western Ghats is like a continuous wall like structure, but is broken at same places by passes. | |
| (iv) | Comparatively less number of rivers originate from the Eastern Ghats. | (iv) | It is a source of many westward and eastward flowing rivers. | |
| (v) | The average altitude of the Eastern Ghats is low (600 mts) but they are wider than Western Ghats. | (v) | The average altitude of the Western Ghats is high (900-1600 mts) but it is narrower in width than Eastern Ghats. | |
| (vi) | Highest peak of Eastern Ghats is Jindhagada (1690 m) | (vi) | Highest peak of Western Ghats is Anaimudi Peak (2695 m) | |
Question 12.
Why are the Western Ghats called a water divide ?
Answer:
The Western Ghats divide the basins of the west flowing rivers like Vaitama, Mandovi, etc. flowing towards the Arabian sea from those of the east flowing rivers like Godavari, Krishna, etc. flowing towards the Bay of Bengal.
![]()
Answer the following Questions:
Question 1.
Differentiate between the Physiography of Brazil and India.
Answer:
| The Physiography of India | The Physiography of Brazil |
| (i) The physiographic divisions of India are the Himalayas, the North Indian Plains and the Peninsula, Coastal Plains, and the Islands. | (i) The physiographic divisions of Brazil are: The Highlands, The Great Escarpment, The Coastal region, The Plains and The Islands. |
| (ii) There are long and high mountain ranges in northern and north eastern part of India in the form of Himalayan ranges. The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats lie to the west and east of the Peninsular region. The average altitude of the Greater Himalayas is around 6000m. | (ii) In Brazil there are no high and continuous mountain ranges. The eastern side of the Highlands is demarcated because of the Escarpment. The Great Escarpment located in south-eastern part of the Highlands has an altitude of 790m in this region with the height gradually decreasing. |
| (iii) In India the Plains occupy a wide area in the north. The Plains lie between the Himalayas in the North and the Peninsula in the South. It extends from Rajasthan in the West to Assam in the East. The Coastal Plains lie to the west and east of the Peninsula. | (iii) In Brazil the Amazon Basin in the North and the Parana-Paraguay Basin to the South West constitutes the Plains. Also a narrow coastal plain is confined to the North and the East. |
| (iv) The Peninsular Plateau region of India lies to the South of the North Indian Plains and is divided into 2 groups, the The Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau. | (iv) In Brazil the Highlands occupy an extensive area in the South and is described as the Brazilian Highlands or the Brazilian Shield. Also to the North lies the Guyana Highland. |
| (v) The islands in India are either volcanic or coral in origin. | (v) The islands in Brazil are mainly depositional and some of them are coral in nature. |
Question 2.
What measures are being taken to control pollution in the rivers of India?
Answer:
Rivers in India are getting polluted due to the sewage and effluents being added to it and thus affecting its quality. Following measures are being taken to control pollution in the rivers in India.
- Treating of the sewage before draining it into the rivers.
- Reducing the use of pesticides and insecticides as they drain into the water sources and pollute it.
- Discharge of industrial effluents into rivers without proper treatment is now controlled.
- Reusing the water for different purposes which reduces the overuse and pollution of water.
- Carrying out the cleaning and purification of the river water under the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP).
- Creating awareness in the people about the importance of rivers and harmful effects of pollution.
- Setting up of Pollution Control Boards (PCB) at the state and national level to curb pollution.
Question 3.
Explain the characteristics of the North Indian Plains.
Answer:
(i) This division lies between Himalayan Mountains in the north and the Peninsula in the south.
(ii) Similarly, it extends from Rajasthan and Punjab in the west to Assam in the east.
(iii) It is mostly a flat low lying area.
(iv) The North Indian Plains are divided into two parts. The part lying to the east of the Aravalis is the basin of the river Ganga and is therefore known as the Ganga Plains. It slopes eastward.
(v) Most of the Indian state of West Bengal and Bangladesh together constitute the delta of Ganga-Brahmaputra system. It is known as the Sunderbans. It is considered to be the world’s largest delta.
(vi) The western part of the North Indian Plains is occupied by desert known as the Thar Desert or Marusthali. Most of Rajasthan is occupied by this desert.
(vii) To the north of the desert lie the plains of Punjab.
(viii) This region is spread to the west of Aravalis and Delhi ranges. These plains have formed as a result of the depositonal work by river Satluj and its tributaries. The slope of the plains is towards the west.
(ix) Because the soil here is very fertile, agriculture is largely practised in this region.
Question 4.
What could be the reasons behind the formation of swamps in the extensive continental location of Pantanal?
Answer:
Pantanal is one of the largest wetlands in the world, lying in the south west part of the highland areas.
It is a region of swamps and marshes in northwestern part of Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil and it extends into Argentina too.
This region is drained by the river Paraguay and its tributaries.
They collect the water from the highland areas and deposit the sediments in the low lying Pantanal region.
Pantanal is a gently sloped basin which is submerged throughout the year due to the filling of the sediments and water in the depression area of the Pantanal.
Question 5.
Which are the major water divides of India give examples.
Answer:
A mountain or an upland which separates two drainage basins is known as a Water Divide. The major Water Divides of India are :
Western Ghats: The Western Ghats acts as a water divide and separates the west flowing rivers like Zuari, Mandvi, Vaitama draining into the Arabian Sea, from the east flowing rivers like the Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri draining into the Bay of Bengal.
Vindhya ranges: It divides the drainage basin of the River Ganga and the River Narmada.
Aravali ranges: The Aravali ranges separate the west flowing river Luni from the east flowing river Banas.
Satpuda ranges: The Satpudas separate the Narmada drainage basin and the Tapi drainage basin.
![]()
( Colours of Both )
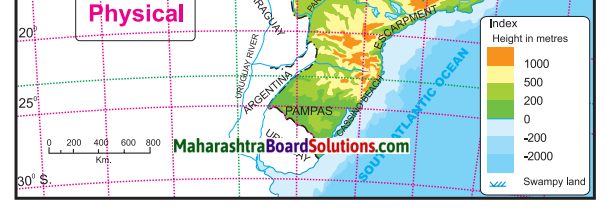
Use the physical maps of India, Brazil and the indices to answer the following:
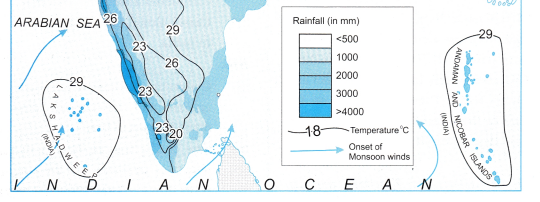
Question 1.
In which parts do the areas with highest altitude lie in both the countries, respectively?
Answer:
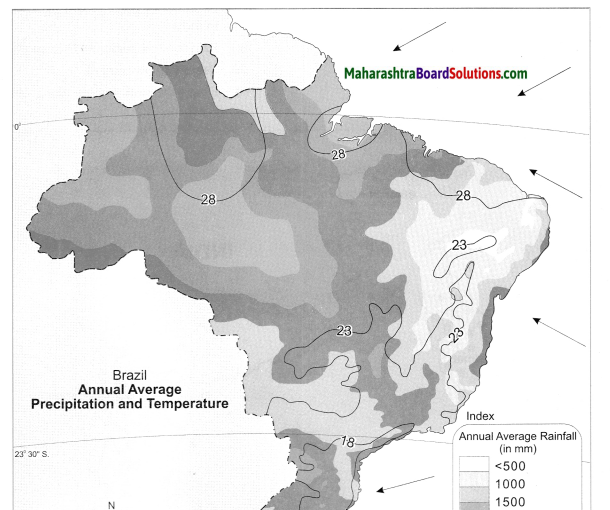
In India, the Himalayas occupying the northern and the north eastern part name highest altitude. In Brazil, the Escarpment occupying the southern part has highest altitude and the highest peak Pico de Neblina lies to the north in the Guyana Highlands.
Question 2.
In which country is the range of altitude higher?
Answer:
India has higher range of altitude as compared to Brazil.
Question 3.
Compare the highest range of altitudes given in both the countries. What difference do you see?
Answer:
The highest range of altitude in Brazil is more than 1000m, whereas in India, the highest range of altitude is more than 8000 m.
Question 4.
In which direction is the slope of the Amazon river basin region?
Answer:
The slope of Amazon Basin is towards the east.
Question 5.
In which direction is the slope of the Deccan Plateau of India ?
Answer: The slope of Deccan Plateau is towards the east.
Question 6.
Tell the regions of rain shadow in both the countries.
Answer:
The rain shadow regions of India are eastern side of Western Ghats on the Deccan Plateau and western side of Eastern Ghats. The rain shadow region of Brazil lies in the north eastern part of the Great Escarpment.
Question 7.
Write a comparative note on the basins of Ganga and Amazon river. You may consider following points for the comparison.
Answer:
| Points for comparison | Ganga River Basin | Amazon River Basin |
| (1) Size of catchment area | Spreading across the northern and eastern parts of India the Ganga River basin has a total catchment area of 10,16,124 sq. km. | Spreading across the northern parts of Brazil the Amazon River basin has a total catchment area of 70,50,000 sq. km. |
| (2) Their relative location within respective countries | The Ganga river basin lies to the south of the Himalayas in the North Indian plains and also occupies the northern part of the peninsula, i.e. the Central Highlands. | The Amazon river basin occupies the entire region in the north of Brazil right from the Guyana Highlands to the northern part of the Brazilian Highlands. |
| (3) Headwater regions of rivers. | Ganga river originates from the Gangotri Glacier in Uttarakhand. | The Amazon river originates from the eastern slopes of Andes Mountains in Peru. |
| (4) Orientation of the rivers | The Ganga flows eastwards passing through the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal and terminates into the Bay of Bengal. One of its branch enters into Bangladesh. | The Amazon river flows from the west to the east entirely through the states of Amazonas and Para in northern Brazil and terminates into the North Atlantic Ocean. |
| (5) Major tributaries and their orientation | (i) Yamuna is the major right bank tributary of the river Ganga originating from the Yamunotri Glacier and meeting river Ganga at Allahabad. Other right bank tributaries originating from the Peninsula like river Chambal, Ken, Shon, Damodar, etc. flow northwards and join river Ganga.
(ii) The left bank tributaries like river Gomati, Ghagra, Gandak, and Kosi flow south and meet river Ganga. |
(i) Rivers like Negro, Branka, Paru flow south from the Guyana Highlands and meet the Amazon river as left bank tributaries.
(ii) River Madeira, Juruaka, Xingu and Tocantins flow northwards and join the Amazon river at its right bank. |
| (6) Any other point(s) | (i) The Ganga river basin is densely populated due to the deposition of fertile alluvial soil and plenty of water available for agriculture.
(ii) Fertile plains and deltas are formed. (iii)River Ganga is 2525 km long. (iv)Water discharge is 16,648 cu.m, per sec. |
(i) Amazon river basin is sparsely populated due to dense equatorial rain forests, unfavourable climate and lack of transport links.
(ii) No deltas are formed but islands have developed along the mouth of the Amazon River. (iii) River Amazon is 6400 km long. (iv) Water discharge is 2,09,000 cu.m, per sec. |
Question 8.
Distinguish between:
Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats.
Answer:
| S.no | Eastern Ghats | Western Ghats | ||
| (i) | The Eastern Ghats run along the eastern coast of India in the north east to south west direction. | (i) | The Western Ghats also known as Sahyadris run in the north-south direction along the western coast of India. | |
| (ii) | It forms the eastern boundary of the Deccan Plateau. . | (ii) | It forms the western boundary of Deccan Plateau. | |
| (hi) | It is not continuous, but is broken at many places by rivers like Godavari and Krishna. | (iii) | The Western Ghats is like a continuous wall like structure, but is broken at same places by passes. | |
| (iv) | Comparatively less number of rivers originate from the Eastern Ghats. | (iv) | It is a source of many westward and eastward flowing rivers. | |
| (v) | The average altitude of the Eastern Ghats is low (600 mts) but they are wider than Western Ghats. | (v) | The average altitude of the Western Ghats is high (900-1600 mts) but it is narrower in width than Eastern Ghats. | |
| (vi) | Highest peak of Eastern Ghats is Jindhagada (1690 m) | (vi) | Highest peak of Western Ghats is Anaimudi Peak (2695 m) | |
![]()
Class 10 Geography Chapter 3 Physiography and Drainage Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option and rewrite the statements:
Question 1.
The part of North Indian Plains lying to the east of the Aravalis is called ____.
(a) Ganga Plains
(b) Brahmaputra Plains
(c) Kaveri Plains
(d) Krishna Plains
Answer:
(a) Ganga Plains
Question 2.
The delta of Ganga-Brahmaputra system is called ________.
(a) Sunderbans
(b) Parnaiba
(c) Amazon
(d) Marajo
Answer:
(a) Sunderbans
Question 3.
The western part of the North Indian Plains occupied by deserts known as ________.
(a) Thar Desert or Marusthali
(b) Gobi Desert
(c) The Deccan Thorn scrub Desert
(d) Spiti Valley Cold Desert
Answer:
(a) Thar Desert or Marusthali
Question 4.
The area lying to the south of North Indian Plains and tapering towards Indian Ocean is called _____.
(a) Himalayas
(b) Peninsula
(c) Western Ghats
(d) Indira Point
Answer:
(b) Peninsula
Question 4.
The in the north west of Peninsular India are the oldest fold mountains.
(a) Aravalis
(b) Satpudas
(c) Karakoram range
(d) Vindhya range
Answer:
(a) Aravalis
Question 6.
The ______ rivers in India are seasonal in nature.
(a) Northern
(b) Peninsular
(c) Himalayan
(d) Mountainous
Answer:
(b) Peninsular
Question 6.
River _______ is the second largest river system in India in terms of catchment area.
(a) Krishna
(b) Godavari
(c) Brahmaputra
(d) Ganga
Answer:
(b) Godavari
Question 7
The major river of Peninsula flows through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu,
(a) Kaveri
(b) Indus
(c) Ganga
(d) Brahmaputra
Answer:
(a) Kaveri
Question 8.
India is blessed with a long coastline extending for approximately
(a) 8000 km
(b) 5000 km
(c) 7500 km
(d) 7900 km
Answer:
(c) 7500 km
Question 9.
The islands in the Arabian sea are called _______ islands.
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Barren
(c) Marajo
(d) Lakshadweep
Answer:
(d) Lakshadweep
Question 10
_____ is the southernmost range of the Himalayas.
(a) Himadri
(b) Lesser Himalayas
(c) Siwaliks
(d) Kumaon Himalayas
Answer:
(c) Siwaliks
Question 12.
The Islands in the Bay of Bengal are called _______ islands.
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Maldives
(c) Corsela
(d) Lakshadweep
Answer:
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
![]()
Question 13.
The highest peak of Brazil is called _______.
(a) Pico de Neblina
(b) Mount Everest
(c) Kanchenjunga
(d) Mount Roraima
Answer:
(a) Pico de Neblina
Question 14.
The acts as a barrier to the south-east trade winds giving rise to the rain shadow area in the north – eastern part of the highlands in Brazil.
(a) Coastal Plains
(b) Escarpment
(c) Plateaus
(d) Pantanal wetlands
Answer:
(b) Escarpment
Question 15.
Amazon collects its headwaters from the eastern
slopes of Andes mountains in
(a) Uruguay
(b) Peru
(c) Ecuador
(d) Columbia
Answer:
(b) Peru
Question 16.
The Island is the only active volcano of India.
(a) Majuli
(b) St. Mary’s
(c) Barren
(d) Lakshadweep
Answer:
(c) Barren
Question 17.
______ is a large coastal island located between the mouths of river Amazon and river Tocantins,
(a) Pantanal
(b) Plata
(c) Paraniba
(d) Marajo
Answer:
(d) Marajo
Question 18.
_______ is one of the largest wetlands in the world.
(a) Plata
(b) Marajo
(c) Pantanal
(d) Paraniba
Answer:
(c) Pantanal
Question 19.
The Paraguay and the Parana rivers form the catchment of River in Argentina.
(a) Paraniba
(b) Plata
(c) Pantanal
(d) Marajo
Answer:
(b) Plata
Question 20.
____ River enters the Atlantic Ocean near Salvador town.
(a) Marajo
(b) Puraguaco
(c) Plata
(d) Parana
Answer:
(b) Puraguaco
Question 21.
The river ______ flows through Pakistan and then meets the Arabian Sea.
(a) Ganga
(b) Chambal
(c) Indus
(d) Brahmaputra
Answer:
(c) Indus
Question 22.
Ganga receives as its tributary in its lower reaches in Bangladesh.
(a) Satluj
(b) Indus
(c) Brahmaputra
(d) Ravi
Answer:
(c) Brahmaputra
Identify the correct group:
Question 1.
Parallel ranges of Himalayas from south to north
(i) Siwaliks – Lesser Himalayas – Greater Himalayas
(ii) Trans Himalayas – Kumaun – Shiwaliks
(iii) Kashmir Himalayas – Kumaun Himalayas – Assam Himalayas
Answer:
Siwaliks – Lesser Himalayas – Greater Himalayas
Question 2.
Physiographic division of India from north to south
(i) The Himalayas – The North Indian Plains – The Peninsula
(ii) The Peninsula – The Great Escarpment – The North Indian Plains
(iii) Coastal Plains – Islands – Himalayas
Answer:
The Himalayas – The North Indian Plains – The Peninsula .
Question 3.
Physiographic divisions of Brazil
(i) The Himalayas – The North Indian Plain – The Peninsula
(ii) The Highlands – The Great Escarpment – The Plains
(iii) Islands – Peninsula – Coastal Plains
Answer:
The Highlands – The Great Escarpment – The Plains
![]()
Question 4.
Three major River Basins of Brazil
(i) Ganga Basin – Brahmaputra Basin – Narmada Basin.
(ii) Paraguay Parana Basin – Amazon Basin – Sao Francisco
(iii) Godavari Basin – Krishna Basin – Kaveri Basin.
Answer:
Paraguay Parana Basin – Amazon Basin – Sao Francisco
Question 5. The order of subdivisions of North Indian Plains from west to east.
(i) Marusthali – Ganga Plains – Sunderbans
(ii) Pamir; Knot – Punjab Plains – Marusthali
(iii) Sunderbans – Vindhyas – Western Ghats
Answer:
Marusthali – Ganga Plains – Sunderbans
Match the column:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Western Himalayas
(2) Central Himalayas (3) Eastern Himalayas |
(a) Siwaliks
(b) Assam Himalayas (c) Kashmir Himalayas (d) Kumaun Himalayas |
Answer:
1-c
2-d
3-b
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Himalayas | (a) the western and eastern part of the Peninsula. |
| (2) North Indian Plains | (b) consists of many plateaus and hill ranges |
| (3) The Peninsula | (c) one of the young fold mountains in the world. |
| (4) The Coastal Plains | (d) lies between Himalayan mountains in the north and the Peninsula in the south. |
| (5) The Island group | (e) are located more than 300 km away from the mainland in the Atlantic ocean. |
| (f) small and large islands along the coast of the mainland. |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – d
3 – b
4 – a
5 -f
Question 3.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) The southernmost point of India | (a) Gangotri |
| (2) The highlands in eastern Brazil | (b) Andes mountains |
| (3) The origin of Ganga | (c) Guyana Highlands |
| (4) The origin of Amazon | (d) Indira Point |
| (5) The southern most point of mainland India | (e) Kanyakumari |
| (f) The Great Escarpment |
Answer:
1 – d
2 -f
3 – a
4 – b
5 – e
Question 4.
| S.no | Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. | Longest river of India | (a) Sao Francisco |
| 2. | Second largest river of India | (b) Godavari |
| 3 | Longest river of Brazil | (c) Ganga
(d) Brahmaputra (e) Amazon |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – b
3 – e
Answer the following in one sentence:
Question 1.
Which mountain is considered as one of the young fold mountains in the world?
Answer:
The Himalayas are considered as one of the young fold mountains in the world.
Question 2.
What is the southernmost range of Himalayas called?
Answer:
The southernmost range of Himalayas is called the Siwaliks.
![]()
Question 3.
Where are the North Indian Plains located?
Answer:
The North Indian Plains lies between Himalayan Mountains in the north and the Peninsula in the south.
Question 4.
Where are the Ganga Plains located?
Answer:
The Ganga Plains lie to the east of the Aravalli in the North Indian Plain.
Question 5.
What constitutes the delta of Ganga-Brahmaputra system?
Answer:
Most of the West Bengal state of India and Bangladesh together constitute the delta of Ganga Brahmaputra system.
Question 6.
What are Sunderbans?
Answer:
The delta region of Ganga-Brahmaputra system are called the Sunderbans and it extends from Indian state of West Bengal to Bangladesh.
Question 7.
What is the length of the coastline of India?
Answer:
The length of the coastline of India is approximately 7500 km.
Question 8.
Why do the rivers originating from Western Ghats form estuaries?
Answer:
Rivers originating from Western Ghats are short and swift, hence they form estuaries.
Question 9.
What are the islands located in the Arabian Sea called?
Answer:
The Islands located in the Arabian sea are called Lakshadweep Islands.
Question 10.
What are the islands located in the Bay of Bengal called?
Answer:
The islands located in the Bay of Bengal are called Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Question 11.
Name the only active volcano in India.
Answer:
Barren Island is the only active volcano in India located in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Question 12.
Which is the highest peak in Brazil?
Answer:
The highest peak in Brazil is Pico de Neblina.
Question 13.
What acts as a barrier to the South East trade winds giving rise to rainshadow area in the northeastern part of the highlands in Brazil?
Answer:
The Escarpment acts a barrier to the South East Trade winds giving rise to rainshadow area in the northeastern part of the highlands in Brazil.
Question 14.
Name the coastal island located between the mouths of river Amazon and river Tocantins.
Answer:
Marajo is a large coastal island located between the mouths of River Amazon and River Tocantins.
Question 15.
What are most of the Amazon Plains covered with?
Answer:
Most of the Amazon Plains are covered with tropical rainforests.
Question 16.
Where is Pantanal located?
Answer:
Pantanal is located in the northwestern part of Mato Grosso Do Sul in Brazil and it extends into Argentina.
Question 17.
What is a ‘Drought Quadrilateral’?
Answer:
The rain shadow region of Trade Winds lying in the northern part of Brazil is called ’Drought Quadrilateral’.
Question 18.
What is the Brazilian coast characterized by?
Answer:
The Brazilian coast is characterised by a large number of beaches and sand dune complexes.
Question 19.
What protects the Brazilian coast?
Answer:
The Brazilian coast is protected in some areas by coral reefs and atoll islands.
Question 20.
What is Pantanal?
Answer:
Pantanal, which is a region of swamps and marshes is one of the largest wetlands in the world. Located in the northwestern part of Mato Grosso Do Sul in Brazil.
Question 21.
From where does Amazon collect its head waters?
Answer:
Amazon collects its headwaters from the eastern slopes of the Andes Mountains in Peru.
Question 22.
Where does the river Sao Francisco flow?
Answer:
The river flows towards the north for a distance of about 1000 km. over the Brazilian plateau and takes a sharp eastward turn to enter the coastal : strip along the Atlantic Ocean.
Question 23.
Which rivers meet the North Atlantic Ocean?
Answer:
River Paraniba and River Itapecuru meet the North Atlantic Ocean.
Question 24.
Which two river systems are covered under the Himalayan Drainage System?
Answer:
The Himalayan Drainage System cover two major river systems such as the Indus river system and the Ganga river system.
Question 25.
What are ’Kayals’?
Answer:
The coastal rivers in Kerala have long extending backwaters near their mouths, which are locally known as ’Kayals.’
Question 26.
Name the three major river basins of Brazil.
Answer:
The three major river basins of Brazil are Amazon Basin, Paraguay-Parana system in the southwest and Sao Francisco in the eastern part of the highland.
Question 27.
What is the approximate discharge of Amazon river?
Answer:
The approximate discharge of Amazon river is about 2 lakh m3/s.
Question 28.
Where are the rivers Paraguay-Parana located?
Answer:
The rivers Paraguay and Parana are located in the south-western part of Brazil.
Question 29.
Which is the third important river of Brazil?
Answer:
Sao Francisco is the third important river of Brazil.
![]()
Question 30.
How are Indian rivers classified?
Answer:
The rivers in India are classified into Himalayan and Peninsular rivers.
Question 31.
Name the major tributary of river Ganga.
Answer:
Yamuna, originating at Yamunotri is a major tributary of Ganga.
Question 32.
From where do Himalayas extend?
Answer:
The Himalayas extend from Pamir Knot in Tajikistan to the east.
Question 33.
Which physical division lies between the Himalayas and the Peninsula?
Answer:
The North Indian Plains lie between the Himalayas in the north and the Peninsula in the south.
Question 34.
Which physical division forms the core of the South American continent?
Answer:
The Brazilian and Guyana Highlands forms the core of the South American continent.
Question 35.
The Guyana highlands cover, which states of Brazil?
Answer: The Guyana highlands cover the states of Roraima, Para and Amapa in Brazil.
Question 36.
Because of which physical division is the eastern side of Brazilian highlands are demarcated?
Answer:
The eastern side of Brazilian highlands are demarcated because of the Great Escarpment.
Question 37.
Which is the largest plain land of Brazil?
Answer:
The Amazon plains lying in the northern part is the largest plain land of Brazil.
Question 38.
On which coast of India are deltas found?
Answer:
Deltas are found on the eastern coast of India.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Five major physiographic divisions of India.
Answer:
The Himalayas, The North Indian Plains, The Peninsula, Coastal Plains and Island groups.
Question 2.
West-East division of Himalayas.
Answer:
Western Himalayas (Kashmir Himalayas),
Central Himalayas (Kumaun Himalayas) and Eastern Himalayas (Assam Himalayas).
Question 3.
Region constituting delta of Ganga-Brahmaputra system or world’s largest delta. .
Answer:
Sunderbans.
Question 4.
Coast bordering Arabian sea.
Answer:
Western Coast.
Question 5.
Coast bordering Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
Eastern Coast.
Question 6.
Islands in the Arabian Sea.
Answer:
Lakshadweep Islands.
Question 7.
Islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
![]()
Question 8.
Other name of Thar Desert.
Answer:
Marusthali.
Question 9.
Ranges in the central part of India.
Answer:
Vindhyas and Satpuda.
Question 10.
Physiographic divisions of Brazil.
Answer:
The Highlands, The Great Escarpment, The Coasts, The Plains, The Island group.
Question 11.
Length of coastline of Brazil.
Answer:
Approximately 7400 km
Question 12.
Major river basins of Brazil.
Answer:
Amazon Basin, Paraguya-Parana system, Sao Francisco.
Question 13.
Two main Himalayan river basins of India.
Answer:
Ganga river basin and Indus river basin.
Question 14.
Origin of Ganga in Himalayas
Answer:
Gangotri Glacier
Question 15.
Major tributary of Ganga
Answer:
Yamuna river.
Question 16.
Tributaries of River Indus.
Answer:
Rivers Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Satluj.
Question 17.
Origin of River Satluj.
Answer:
Mansarovar.
Question 18.
Rivers flowing into the Gulf of Khambhat.
Answer:
Rivers Tapi, Narmada, Mahi, and Sabarmati.
Question 19.
River basin located to the south of River Godavari.
Answer:
Basin of River Krishna.
Question 20.
Plains formed due to depositional work of river Satluj.
Answer:
Punjab Plains.
Question 21.
Tributaries of Peninsula joining the Ganga basin.
Answer:
Rivers Chambal, Ken, Betawa, Shon, and Damodar.
Question 22.
States having short and swift river systems.
Answer:
Kerala, Karnataka, Goa and Maharashtra.
Question 23.
River originating from the eastern slopes of Western Ghats.
Answer:
Rivers Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri.
Question 24.
Largest wetlands in the world.
Answer:
Pantanal.
Question 25.
Highest peak of Brazil
Answer:
Pico de Neblina.
Question 26.
Western border of Indian Peninsula.
Answer:
Western Ghats.
Question 27.
Eastern border of Indian Peninsula.
Answer:
Eastern Ghats.
Question 28.
Oldest fold mountains of India.
Answer:
Aravallis.
Question 29.
Major mountain system of Asia.
Answer:
Himalayas.
![]()
Identify the type on the basis of the statement
Question 1.
A landform formed due to deposition of sediment carried by a river as the flow leaves its mouth and enters slower-moving or standing water.
Answer:
Delta.
Question 2.
The area where land meets the sea or ocean, or a line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake.
Answer:
Coast.
Question 3.
Portion of land drained by a river and its tributaries.
Answer:
River Basin.
Question 4.
majority of its border, (Usually three sides) while being connected to a mainland from which it extends.
Answer:
The Peninsula.
Question 5.
A steep slope or long cliff that forms as an effect of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively leveled areas having differing elevations.
Answer:
Escarpment.
Question 6.
Any piece of land that is surrounded by water all the sides.
Answer:
Island.
Mark the following on the map with the given information:
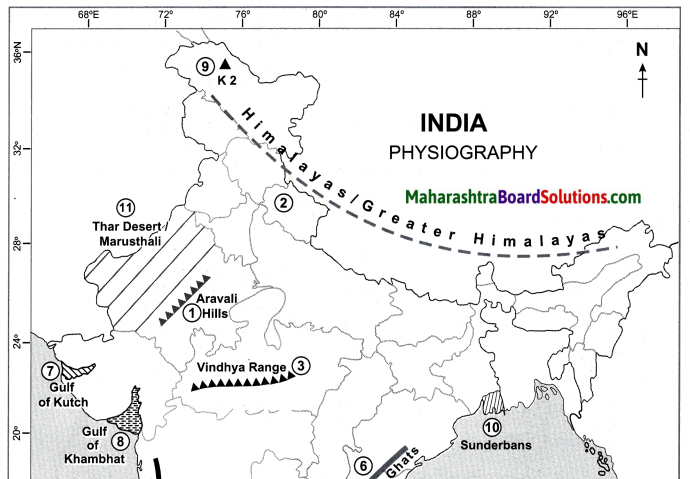
Question 1.
On the outline map of India.
(a) Aravali hills
(b) Himalayas/Greater Himalayas
(c) Vindhya Range and Satpuda Range
(d) Gulf of Mannar
(e) Western Ghats
(f) Eastern Ghats
(g) Gulf of Kutch
(h) Gulf of Khambhat
(i) K2
(j) Sunderbans
(k) Thar Desert/Marusthali
Answer:
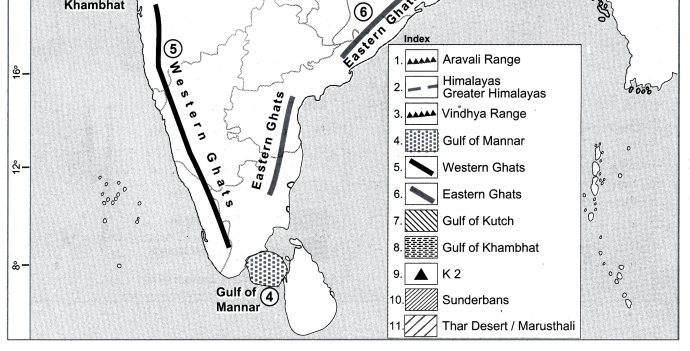
Question 2.
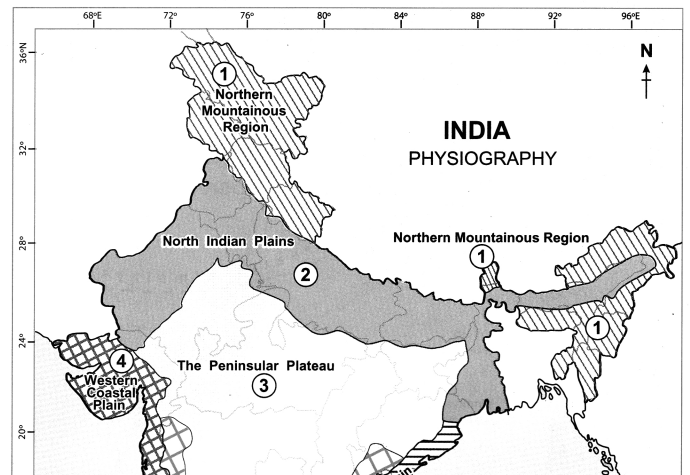
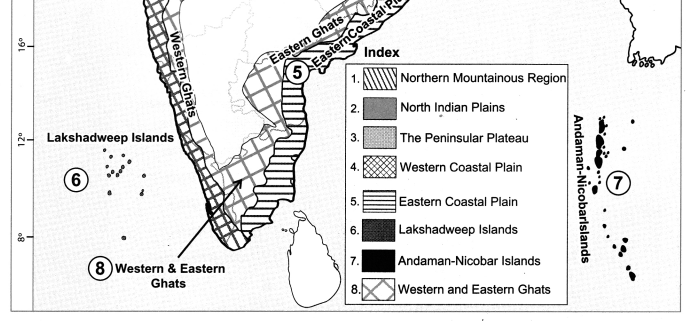
On the outline map of India mark the following.
(a) Northern Mountainous Region
(b) North Indian Plains
(c) The Peninsular Plateau
(d) Western Coastal Plain
(e) Eastern Coastal Plain
(f) Lakshadweep Island
(g) Andman-Nicobar Islands
(h) Western and Eastern Ghats
Answer:
![]()
Question 3.
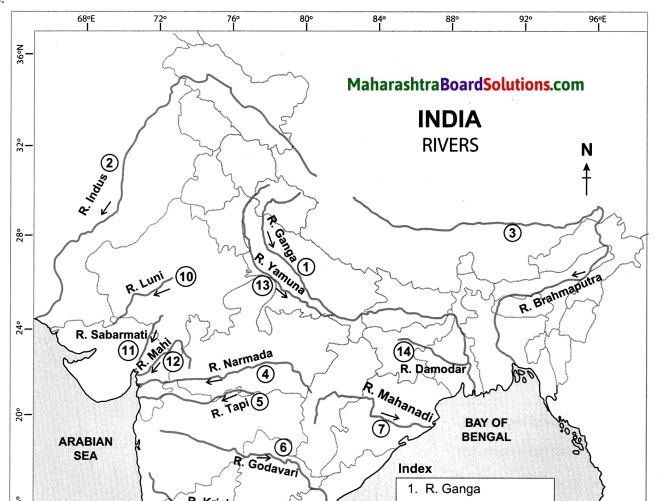
Show the following on the outline map of India.
(a) R. Ganga
(b) R. Indus
(c) R. Brahmaputra
(d) R. Narmada
(e) R. Tapi
(f) R. Godavari
(g) R. Mahanadi
(h) R. Krishna
(i) R. Kaveri
(j) R. Luni
(k) R. Sabarmati
(l) R. Mahi
(m) R. Yamuna
(n) R. Damodar
Answer:
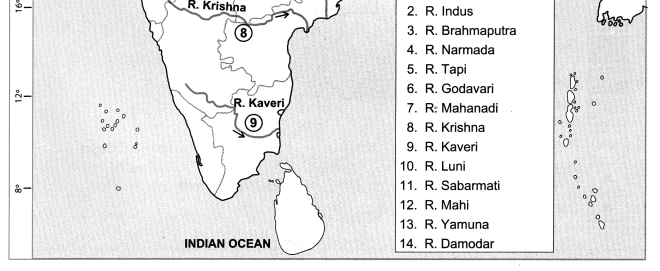
Question 4.
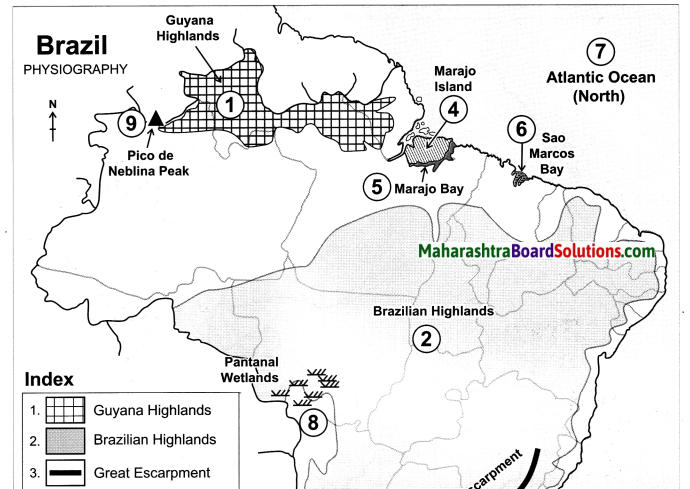
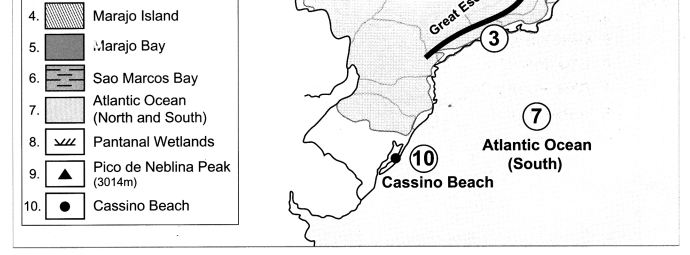
On the outline map of Brazil, mark the following:
(a) Guyana Highlands
(b) Brazilian Highlands
(c) Great Escarpment
(d) Marajo Island
(e) Marajo Bay
(f) Sao Marcos Bay
(g) Atlantic Ocean
(h) Pantanal Wetlands
(i) Pico De Neblina Peak
(j) Cassino Beach
Answer:
Question 5.
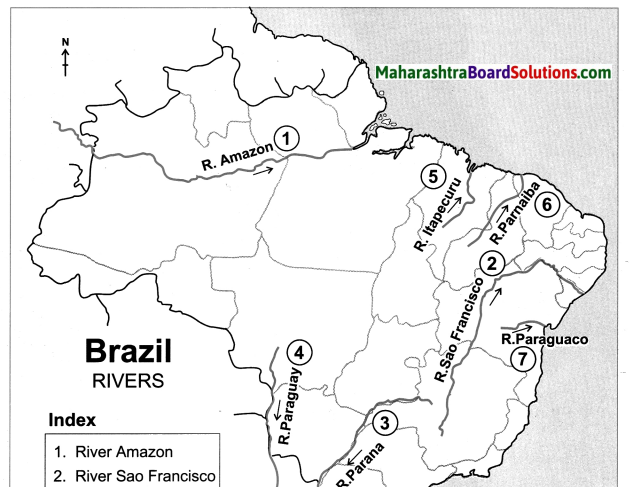
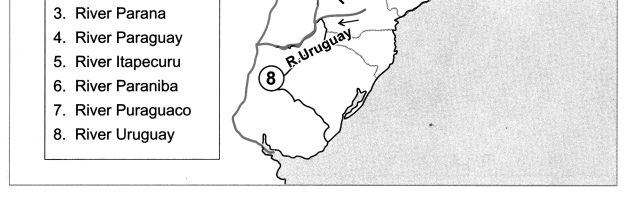
On an outline map of Brazil, show all major rivers of Brazil.
(a) River Amazon
(b) River Sao Francisco
(c) River Parana
(d) River Paraguay
(e) River Itapecuru
(f) River Paraniba
(g) River Puraguaco
(h) River Uruguay
Answer:
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
There are no deltas on the western coast of India.
Answer:
(i) Deltas are formed in the coastal areas where there is gentle slope, because the rivers slow down forming distributaries and channels.
(ii) The western coast bordering the Western Ghats are by and large rocky coasts having a narrow width.
(iii) Many short and swift seasonal rivers originate from the steep western slopes of the Western Ghats.
(iv) As the rivers flow through steep slopes, their velocity increases. So there is very little deposition
made by them.
(v) Hence, there are no deltas on the western coast of India.
![]()
Question 2.
Many deltas are found along the Eastern coast of India.
Answer:
(i) The eastern coast borders the Bay of Bengal. It has been formed as a result of depositional work of rivers.
(ii) Many east flowing rivers rising from the Western and Eastern Ghats after travelling a long distance join the Bay of Bengal at this coast.
(iii) Because of the gentle slope of the land, rivers flow at lower velocities and deposit the sediments brought with them at the coast.
Therefore, this coast is comparatively wider than the west.
(iv) As a result, deltas are found along the eastern coast of India.
Question 3.
The region to the north of the Escarpment is called Drought Quadrilateral.
Answer:
(i) The eastern side of the Highlands is demarcated because of the Escarpment having an altitude of 790 m.
(ii) The Escarpment acts as a barrier to the Southeast trade winds and cause orographic type of rainfall in the coastal region.
(iii) Beyond the highlands the effect of these winds gets reduced leading to minimal rainfall.
(iv) A rain shadow region is formed to the north east of the Escarpment. Thus, the region to the north of this area is called “Drought Quadrilateral”.
Question 4.
The Amazon Plains are covered by inaccessible tropical rainforest.
Answer:
(i) The northern part of Brazil lying between the Equator and the Tropic of Capricorn, i.e. in the Tropical zone is covered largely by the Amazon Plains.
(ii) Amazon plains lying between the Guyana highlands and the Brazilian highlands form the largest plain land of Brazil.
(iii) The Amazon valley receives very heavy rainfall of around 2000 mm and the average temperature here is 25 to 28°C.
(iv) These conditions favor the dense growth of tropical rain forests. Due to frequent flooding and dense undergrowth, these forests are largely inaccessible.
Question 5.
Pantanal is called the largest wetlands in the world.
Answer:
(i) Pantanal lies towards the south western part of the highland area in Brazil.
(ii) Roughly 80% of the Pantanal flood plains are submerged during the rainy season.
(iii) This region is filled with swamps and marshes from the northwestern part of Mato Grosso Do Sul in Brazil till Argentina.
(iv) Hence Pantanal is called the largest wetland in the world.
Question 6.
Agriculture is widely practised in the plains of Punjab region.
Answer:
(i) Plains of Punjab lie to the north of Rajasthan. This region is spreads to the west of Aravalis and Delhi ranges.
Question 1. These plains have formed as a result of the depositional work by river Sutluj and its tributaries.
(iii) Since the soil here is very fertile, agriculture is largely practised in this region.
(iv) Thus, due to.the availability of fertile soil and ample water suppy agriculture is practised here.
Question 7.
Write notes on :
Answer:
The Western Ghats:
(i) Western Ghats also known as Sahyadri (Benevolent Mountains) is a mountain range that runs parallel to the western coast of the Indian peninsula.
(ii) The range runs north to south along the western : edge of the Deccan Plateau, and separates the plateau from a narrow coastal plain, called West coastal plan, along the Arabian Sea.
(iii) The range starts near the border of Gujarat and Maharashtra, south of the Tapi river, and runs approximately 1,600 km through the states of Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu ending near Kanyakumari, at the southern tip of India.
(iv) The altitude of the western Ghats increases towards the south.
Island group of India:
(i) India has many small and large islands along the coast of the mainland. These are included in the coastal island group.
(ii) Besides, India has two large group of islands, one each in the Arabian Sea and in the Bay of Bengal.
(iii) The islands in the Arabian Sea are known as Lakshadweep whereas the islands in the Bay of Bengal are called the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(iv) Most of the islands in Lakshadweep are atoll islands.
(v) They are small in extent and not very high.
(vi) Islands in the Andaman group are mainly volcanic islands.
(vii) They are large with hills in their interior parts, which includes an island called Barren Island which has the only active volcano in India. There are atolls in the Nicobar group too.
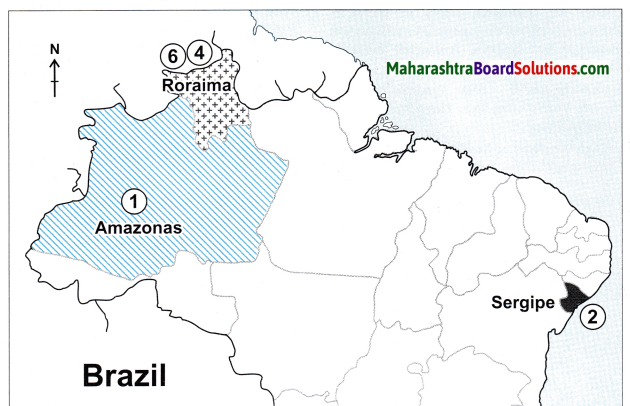
Brazilian Highlands:
(i) Southern Brazil is occupied by an extensive plateau. It is known as the Brazilian Highlands or the Brazilian Shield or the Brazilian Plateau.
(ii) Brazilian and Guyana Highlands together form the core of South American continent.
(iii) The main part of the Guyana Highlands is in Venezuela and it extends up to French Guiana. In Brazil, it covers the states of Roraima, Para and Amapa in the north.
(iv) The lower part of these highlands is found in Brazil. But the highest peak of Brazil, Pico de Neblina, 3014 m lies on the border between Brazil and Venezuela.
(v) The regions to the east and south of the Brazilian highlands have an altitude of more than 1000m. But in other parts, the altitude is between 500 to 1000m.
(vi) The highlands gradually slope towards north and the slopes are not very steep.
(vii) The tributaries of Amazon flowing through this region make rapids and waterfalls. Towards the north the slopes are steep but not abrupt. A number of rivers originate from the terminal portion of the highlands and flow northwards to meet Atlantic Ocean.
(viii) Some major rivers like Uruguay, Paraguay and Parana originate from the southern slopes of the highlands and enter Argentina. Its slope towards the east is steep and it appears in the form of an escarpment.
![]()
Coastal Plains of India:
(i) India is blessed with a long coastline extending for approximately 7500 km.
(ii) It lies to the western and eastern part of the Peninsula. Its western and eastern coastlines show remarkable dissimilarities.
(iii) The western coast borders the Arabian Sea. It is by and large a rocky coast.
(iv) At places, spurs starting from the Western Ghats have extended right up to the western coast. Its width is also less.
(v) Rivers originating from Western Ghats are short and swift and hence they form estuaries and not deltas.
(vi) The eastern coast borders the Bay of Bengal. It has formed as a result of depositional work of rivers.
(vii) Many east flowing rivers rising from the Western and Eastern Ghats meet the eastern coast.
(viii) Because of the gentle slope of the land, rivers flow at lower velocities and deposit the sediments brought with them at the eastern coast. As a result, deltas are found along this coast.
The Plains of Brazil:
(i) The plains in Brazil are confined to two areas namely the Amazon basin in the north and Paraguay-Parana source region in the southwest.
(ii) Amazon plains lying between the two highlands form the largest plain land of Brazil.
(iii) Amazon plains lying in the northern parts of Brazil generally slope eastwards.
(iv) The Amazon basin is quite wide in the west (about 1300 km) and it narrows eastward. Its width is minimum where the Guyana Highlands and Brazilian Highland come closer. (240 km.)
(v) As the river approaches the Atlantic Ocean, the width of the plains increases.
(vi) These are mostly forested areas and largely inaccessible due to frequent flooding and dense undergrowth. Most of the Amazon plains are covered by tropical rainforests.
(vii) The other plains in Brazil are located to the southwestern part of the highlands. They form the source region of Paraguay and Parana rivers.
(viii) The source region of Paraguay slopes towards the south while the source region of Parana slopes towards the southwest.
(ix) Pantanal is one of the largest wetlands in the world. It lies towards the southwest part of the highland areas. It is a region of swamps and marshes in northwestern part of Mato Grosso Do Sul in Brazil and it extends into Argentina.
Coastal Rivers of Brazil:
(i) Brazil has a number of short coastal rivers.
Question 1. The coastal area being densely populated these rivers attain significance.
(iii) River Pamaiba and River Itapecuru flowing northwards meet the North Atlantic Ocean.
(iv) The rivers that enter South Atlantic Ocean collect their headwaters along the escarpment.
(v) River Puraguaco enters the Atlantic Ocean near Salvador town.
Paraguay – Parana system:
(i) These two rivers are located in the southwestern part of Brazil.
(ii) Both the rivers form the catchment of River Plata in Argentina.
(iii) These two rivers and river Uruguay in extreme south of the highlands collect their headwaters from the southern portion of the highlands.
Indus River System:
(i) Indus and its tributaries (Jhelum, Beas, Chenab, Ravi and Satluj) drain the Western Himalayas i.e., they flow through the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
(ii) They flow almost parallel to each other.
(iii) A major tributary of river Indus, the Satluj, originates near Mansarovar and flows westwards.
(iv) Punjab Plains have formed from the depositional work of this river and its tributaries.
(v) Indus flows through Pakistan and then meets the Arabian Sea.
Ganga River System:
(i) The river Ganga originates from the Gangotri glacier and crosses the Himalayas to become an east-flowing river.
(ii) Many tributaries of the Ganga also flow in a similar manner.
(iii) River Yamuna, originating at Yamunotri, is a major tributary of Ganga.
(iv) Another major tributary of the Ganga flows through the northern part of the Greater Himalayas, crosses the Himalayas to enter India.
(v) When it flows through the Himalayas it is called Tsang Po.
(vi) When it crosses the Himalayas, it is called Dihang and its eastward flow thereafter is called as Brahmaputra.
(vii) From time to time, Ganga meets its tributaries, hence its discharge increases.
(viii) Ganga receives Brahmaputra as its tributary in its lower reaches in Bangladesh. The huge volume of water and huge deposition has led to the formation of a large delta.
(ix) Besides these Himalayan rivers, Ganga receives a number of tributaries from Peninsula like Shon, Damodar, etc.
Rivers Meeting the Arabian Sea:
(i) The west flowing rivers occupying the area between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea are short in length but swift.
10th Std Geography Questions And Answers:
- Field Visit Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Location and Extent Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Physiography and Drainage Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Climate Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Natural Vegetation and Wildlife Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Population Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Human Settlements Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Economy and Occupations Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers
- Tourism, Transport and Communication Class 10 Geography Questions And Answers