Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 Science Chapter 3 Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Match the pairs.
diversity in living things and their classification class 6 exercise Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Amphibians | a. A monkey |
| 2. Vertebrates | b. A snake |
| 3. With scales | c. A frog |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Amphibians | c. A frog |
| 2. Vertebrates | a. A monkey |
| 3. With scales | b. A snake |
![]()
2. Who is the odd one out?
Question a.
Fungus, mushroom, chrysanthemum, spirogyra
Answer:
Chrysanthemum (only flowering plants)
or
Spirogyra (only aquatic plant)
Question b.
Mango, banyan, palm, chickpea
Answer:
Chickpea (shrub, others are not)
or
Palm (tall tree without any branches, others have branches)
![]()
Question c.
Grape, orange, lemon, hibiscus
Answer:
Grape (only creeper, others are not)
or
Hibiscus (flower, others are fruits)
Question d.
Sunflower, banyan, jowar, bajra
Answer:
Banyan (perinnial, others are not)
Question e.
Guava, radish, carrot, beetroot
Answer:
Gauva (fruit, others are roots)
![]()
Question f.
Deer, fish, man, worms
Answer:
Worms (invertebrate, others are not)
or
Fish (aquatic animal, others are terristrial animals
3. What is the difference?
Question a.
Flowering plant and Non-flowering plant
Answer:
| Flowering plant | Non-flowering plant |
| 1. Plants that bear flowers are called flowering plants. | 1. Plants that do not bear flowers are called nonflowering plants. |
| 2. They have roots, stems and leaves. | 2. They may not have roots, stems or leaves. |
| e.g. Rose, sunflower, lotus | e.g. Pine, fern, algae |
![]()
Question b.
A Tree and a Shrub
Answer:
| Tree | Shrub |
| 1. They have branches at some height above the ground. | 1. They give out branches close to the ground. |
| 2. They grow very tall compared to shrubs. | 2. They grow upto 2 to 3 metres in height. |
| 3. They have strong and hard stems. | 3. They have thick hard stems. |
| e.g. Mango tree, banyan tree | e.g. Hibiscus, oleander |
![]()
Question c.
Vertebrates and Invertebrates
Answer:
| Vertebrates | Invertebrates |
| 1. They have vertebral column. | 1. They do not have vertebral column. |
| 2. The brain is well developed. | 2. The brain if present may not be developed. |
| e.g. Human, dog, fishes etc. | e.g. earthworm, insects etc. |
4. True or false?
Question a.
The snail is an aquatic animal.
Answer:
False
Question b.
Amphibians can live in air and in water.
Answer:
False
Question c.
The function of the brain is well developed in vertebrate.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question d.
The amoeba is a multicellular animal.
Answer:
False
5. Write two names of each.
Question a.
A flowering plant
Answer:
Rose, hibiscus
Question b.
A non-flowering plant
Answer:
Fern, algae
Question c.
A tree
Answer:
Mango, banyan
Question d.
A shrub
Answer:
Oleander, hibiscus
Question e.
A creeper
Answer:
Pumpkin, watermelon
![]()
Question f.
An annual plant
Answer:
Jowar, sunflower
Question g.
A biennial plant
Answer:
Carrot, beetroot
Question h.
A perennial plant
Answer:
Mango, gulmohar
6. Write answers to the following.
Question a.
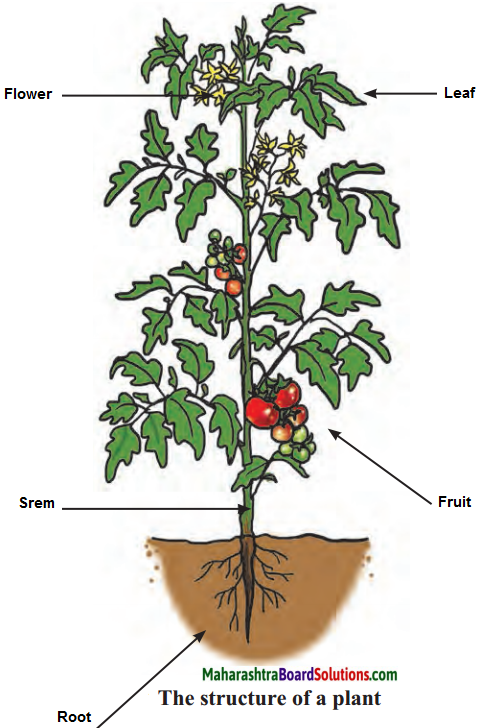
What are the parts of a plant?
Answer:
The parts of a plant are: root, stem, leaves, flowers, fruit and seed.
Question b.
What are the functions of root?
Answer:
The functions of root are:
- The root hold the soil firmly and anchor the plant.
- They absorb water, salt and minerals from the soil and transport it to stem.
- Some roots store food. e.g. Carrot, radish.
![]()
Question c.
Why is it necessary to classify living things?
Answer:
- There is a great diversity in living things- both plants and animals on the earth.
- In order to identify them and to study their characteristics, systematic classification is necessary.
Question d.
What are the criteria used to classify living things?
Answer:
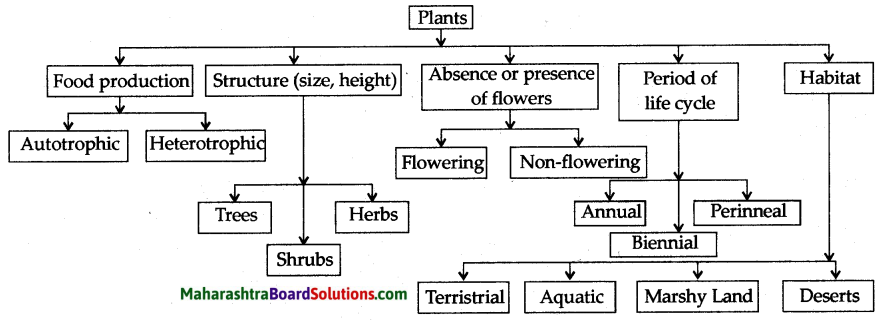
Following are the criteria used to classify living things:
a. Plants:
- Mode of nutrition.
- Similarities and differences in structure.
- Presence of flowers or not.
- Period of life cycles.
- Habitat.
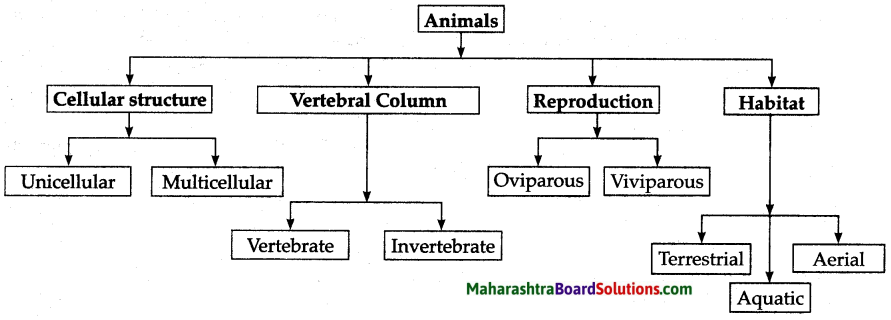
b. Animals:
- Cell structure.
- Presence of vertebral column.
- Method of reproduction.
- Habitat.
![]()
Question e.
Tell some characteristics of creepers.
Answer:
The characteristics of creepers are:
- The stem of a creeper is very flexible, soft and green and need support to climb.
- Some climbers spread on the ground, e.g. Pumpkin
- Some have aerial roots, e.g. Money plant
- Some climbers develop tendrils, e.g. Cucumber
Question f.
Explain the characteristics of herbs with examples.
Answer:
- Herbs grow 1 to 1.5 m tall.
- Their stem is green and quite flexible.
- They may live for a few months or upto two years, e.g. Tulsi, oregano, etc.
Question g.
How is the body of animals protected?
Answer:
Body of animals are protected by special covering such as skins, feathers, scales, hair fur, etc.
![]()
Question h.
On the basis of which criteria will you classify plants and animals?
Answer:
7. Draw figures.
Question a.
Draw the figure of a plant to show the parts, namely, the root, stem and leaves in it.
Answer:
Activity:
Question 1.
Visit a plant nursery and classify the plants there.
Question 2.
Visit a zoo and obtain information about the diversity in animals.
![]()
Question 3.
Write an essay on diversity in plants.
Question 4.
Collect seeds of various plants during summer and throw them in open spaces (fallow land, moorland, hill, etc.) during the rainy season.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Plants that can prepare their own food are called ………….. plants.
Answer:
autotrophic
Question 2.
Pitcher plants are ………….. .
Answer:
insectivorous
![]()
Question 3.
The ………….. is an important means of reproduction.
Answer:
flower
Question 4.
Animals that lay eggs are ………….. animals.
Answer:
oviparous
Question 5.
Animals that can live on land as well as water are called ………….. .
Answer:
amphibians
Choose the correct alternative:
Question 1.
The ………….. is a perennial.
(a) beetroot
(b) gulmohar
(c) grass
Answer:
(b) gulmohar
![]()
Question 2.
The sunflower is a / an ………….. plant.
(a) annual
(b) biennial
(c) perennial
Answer:
(a) annual
Question 3.
Cactus is a ………….. plant.
(a) land
(b) water
(c) desert
Answer:
(c) desert
Question 4.
The …………….. is a unicellular animal.
(a) cockroach
(b) snail
(c) paramoecium
Answer:
(c) paramoecium
Question 5.
Hen is a …………….. animal.
(a) oviparous
(b) viviparous
(c) none of above
Answer:
(b) oviparous
![]()
Question 6.
Earthworm is a / an ……………. animal.
(a) vertebrate
(b) invertebrate
(c) unicellular
Answer:
(b) invertebrate
True or False:
Question 1.
The pods of beans and peas are actually fruits.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Fungus is heterotrophic.
Answer:
True
Write two names of each.
Question 1.
An invertebrate animal
Answer:
Earthworm, cockroach
![]()
Question 2.
An oviparous animal.
Answer:
Hen, sparrow
Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Autotrophic plant and Heterotrophic plant
Answer:
| Autotrophic plant | Heterotrophic plant |
| 1. They can produce their own food. | 1. They cannot produce their own food. They depend on other things for their food. |
| 2. They are green in colour. | 2. They are nongreen in colour. |
| e.g. Periwinkle, pomegranate etc. | e.g. Dodder, loranthus etc |
Classify as directed.
Question 1.
Into annual, biennial, perennial
Sunflower, carrot, bajra, mango, jowar, oleander, beetroot, coconut
Answer:
| Annual | Biennial | Perennial |
| Sunflower | Carrot | Mango |
| bajra | beetroot | oleander |
| jowar | coconut |
![]()
Question 2.
Into vertebrates and invertebrates
Fish, cat, earthworm, snail, hen, cockroach
Answer:
| Vertebrates | Invertebrates |
| Fish | Earthworm |
| cat | snail |
| hen | cockroach |
![]()
Define.
Class 6 Science Chapter 3 Diversity In Living Things and Their Classification Question 1.
Unicellular animal
Answer:
Animals which have a single cell body performing all functions, are called unicellular animals, e.g. Amoeba
Diversity In Living Things And Their Classification Exercise Question 2.
Multicellular animals
Answer:
Animals which have many cells in their body, are called multicellular animals, e.g. Cat
Diversity In Living Things and Their Classification Question 3.
Vertebrates
Answer:
Animals with vertebral column are called vertebrates, e.g. Man
![]()
Question 4.
Invertebrate animals
Answer:
Animals without vertebrate column are called invertebrate animals, e.g. Earthworm
Question 5.
Oviparous animals
Answer:
Animals which lay eggs and hatch them are called oviparous animals, e.g. Hen
Question 6.
Viviparous animals
Answer:
Animals which give birth to their young ones are called viviparous animals, e.g. Dog
Answer the following:
Question 1.
Give the functions of:
Answer:
a. Stem:
1. The stem gives support to the other parts of the plant.
2. The stem carries out the function of production, conduction and storage of the food.
3. In some cases it stores food.
b. Leaves: They play an important role in the production of food.
c. Flowers: The flowers are reproductive organ of plant.
d. Fruits: Fruits have seeds which give rise to new plant.
e. Seeds: From the seeds arise new plants.
![]()
Answer the following in short.
Question 1.
What type of plants are toolstools and mushrooms?
Answer:
Toolstools and mushrooms are heterotrophs.
Question 2.
What type of plant is a fig?
Answer:
Fig is a tree.
Question 3.
Do ferns, algae and money plant bear flowers?
Answer:
Ferns, algae and money plants do not bear flowers. They are non-flowering plants.
Question 4.
Which is the largest flower and where is it found?
Answer:
Rafflesia Arnoldi is the world’s largest flower. It is found in Indonesia.
![]()
Question 5.
Where does pomegranate grow?
Answer:
Pomegranate is a shrub which grows on land in soil.
Question 6.
Where do bulrushes and railroad creepers grow?
Answer:
Bulrushes is a water plant and railroad creepers grow along the ground.
Question 7.
Where does lotus grow?
Answer:
Lotus grows in water.
Question 8.
Where does the dodder plant grow?
Answer:
Dodder is a parasitic plant and grows on other plants.
Question 9.
Why does water hyacinth float?
Answer:
The stem of water hyacinth is filled with air and its leaves are specially modified, which helps it to float in water.
![]()
Question 10.
Why is the stem of a cactus plant fleshy?
Answer:
Cactus is a desert plant. As there is a shortage of water, cactus stores water in its stem and hence, stem of cactus is fleshy.
Question 11.
Which spheres of the earth do living things exist?
Answer:
Living things exists in all three spheres of earth, i.e. Atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere.
Question 12.
Are the plants and animals that you have seen all alike?
Answer:
No. They are all of different types.
Question 13.
What are the similarities between a mango, a banyan and a tamarind tree?
Answer:
They are tall, big and perennial plants.
Question 14.
What are the similarities between the hibiscus, oleander and lantana plants?
Answer:
They are shorter and smaller than trees.
![]()
Question 15.
What are the similarities between fenugreek and periwinkle plants?
Answer:
They are smaller and shorter than trees and shrubs.
Question 16.
Have you seen vines like the pumpkin, the railroad creeper, kavali, watermelon or the grapvine? How do they grow?
Answer:
They have very soft, green and flexible stem. They grow with the help of a support.
Question 17.
For how many years do crops like bajra, wheat, corn, radish, marigold live?
Answer:
They live for about one year.
Question 18.
To which part of plants are butterflies and insects attracted?
Answer:
Butterflies and insects are attracted towards the flower of the plants.
![]()
Question 19.
What is the chain of bones in the centre of our back called?
Answer:
A vertibral column.
6th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land Class 6 Questions And Answers
- The Living World Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Diversity in Living Things and their Classification Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Substances in the Surroundings – Their States and Properties Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Substances in Daily Use Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Nutrition and Diet Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Our Skeletal System and the Skin Class 6 Questions And Answers
- Motion and Types of Motion
- Force and Types of Force Class 6 Questions And Answers
