Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Solutions Chapter 9 Money Market and Capital Market in India Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Std 12 Economics Chapter 9 Question Answer Money Market and Capital Market in India Maharashtra Board
Class 12 Economics Chapter 9 Money Market and Capital Market in India Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Economics Class 12 Chapter 9 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Complete the following statements:
Question 1.
Development financial institutions were established to …………………
a) provide short-term funds.
b) develop industry, agriculture, and other key sectors.
c) regulate the money market.
d) regulate the capital market.
Answer:
b) develop industry, agriculture, and other key sectors.
![]()
Question 2.
The money market faces a shortage of funds due to
a) inadequate savings.
b) growing demand for cash.
c) presence of unorganized sector.
d) financial mismanagement.
Answer:
a) inadequate savings.
Question 3.
Individual investors have lost confidence in the
capital market due to
a) lack of financial instruments.
b) high transaction costs.
c) low returns.
d) financial scams.
Answer:
d) financial scams.
Question 4.
Commercial banks act as intermediaries in the financial system to
a) make profits
b) accelerate the country’s economic growth.
c) mobilize the savings and allocating them to various sectors of the economy.
d) control the credit.
Answer:
c) mobilize the savings and allocating them to various sectors of the economy.
2. Complete the correlation:
1) Money market : Short term funds :: …………….. : Long term funds
2) …………….. : Central Bank:: SBI : Commercial Bank
3) Co-operative banks : Organized sector :: Indigenous bankers : ……………..
4) Primary market : …………….. :: Secondary market : Old issues
Answers:
- Capital market
- RBI
- Unorganised sector
- New issue
![]()
3. Find the odd word:
Question 1.
Types of Bank Accounts:
Answer:
Saving A/c, D-mat A/c, Recurring A/c, Current A/c.
Question 2.
Unregulated Financial Intermediates:
Answer:
Mutual fund, Nidhi, Chit fund, Loan Companies.
Question 3.
Financial Assets:
Answer:
Bonds, Land, Government Securities,
Derivatives.
Question 4.
Quantitative Tools:
Answer:
Bank Rate, Open Market Operation, Foreign Exchange Rate, Variable Reserve Ratio.
4. Assertion and Reasoning:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Money market economizes use of cash
Reasoning (R) : Money market deals with financial instruments that are close substitutes of money
Options: 1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Regional stock exchanges have witnessed a sharp decline in the volume of trade.
Reasoning (R) : Investors prefer to trade in securities listed in premier stock exchanges like BSE, NSE etc.
Options:
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : The unorganized sector of the money market lacks transparency.
Reasoning (R) : Activities of the unorganized sector are largely confined to rural areas.
Options:
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : Foreign exchange management and control is undertaken by commercial banks.
Reasoning (R) : RBI has to maintain the official rate of exchange of rupee and ensure its stability.
Options:
1) (A) is True, but (R) is False
2) (A) is False, but (R) is True
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
4) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Answer:
3) Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
![]()
5. Identify and explain the concepts from the given illustrations:
Question 1.
Raghu’s father regularly invests his money in stocks and bonds.
Answer:
Concept: Financial Market
Explanation : Financial Market refers to a market where financial assets such as bonds, stocks, derivatives, government securities foreign currency, etc. are sold and purchased.
Question 2.
Sara makes a monthly contribution to a fund jointly created by her friends. The collected fund is then given to a chosen member through lucky draw.
Answer:
Concept: Chit fund
Explanation : Under chit fund, members make regular contribution to the fund, bids or draws are made on the basis of a criteria mutually agreed upon by members.
Question 3.
Tina deposited a lurnpsurn amount of 50,000 in the bank for a period of one year.
Answer:
Concept: Fixed deposit
Explanation : Fixed deposit refers to a lumpsum amount deposited by a customer for a specified period of time. Compared to all other deposits, fixed deposits carry a high rate of interest.
Question 4.
ABC bank provides d-mat facility, safe deposit lockers, internet banking facilities to its customers.
Answer:
Concept: Ancillary function of Commercial Bank
Explanation : Ancillary services are those services of commercial banks which are provided beside the primary services of bank. Ancillary services are transfer of j funds collection of money, making periodical payments on behalf of the customer, merchant banking, foreign exchange, safe deposits lockers, D-mat facility, internet banking.
![]()
6. Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Money market and Capital market.
Answer:
| Money Market | Capital Market |
| (a) Money market is a market for lending and borrowing of short term funds. It is a market for “near money”. | (a) Capital market is a market for long-term funds both equity and debt, raised within and outside the country. |
| (b) Money market is divided into 2 structure Organised sector of money market Unorganised sector of money market | (b) Capital market is divided into 4 parts. Government securities
|
Question 2.
Demand deposit and Time deposit.
Answer:
| Demand Deposits | Time Deposits |
| (a) Deposits that are withdrawable on demand are known as demand deposits. | (a) Deposits that are repayable after a certain period of time are known as time deposits. |
| (b) Example : 1. Current Account 2. Saving Account |
(b) Example : 1. Recurring Deposits 2. Fixed Deposits |
Question 3.
Organized sector and Unorganized sector of money market.
Answer:
| Organized Sector | Unorganized Sector |
| (a) The organized sector of the money market is within the direct purview of RBI regulation. | (a) This market is unorganized because its activities are not systematically co-ordinated by the RBI. |
| (b) It consist of Reserve Bank of India. Commercial Bank, Co-operative Bank, Regulated Financial Intermediaries, etc. | (b) The unorganized Indian Money market is largely made up of indigenous bankers, money lenders and unregulated non-bank financial intermediaries. |
7. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Explain the problems faced by the money market in India.
Answer:
Following are the problems of money market in India:
(a) Shortages of Funds : Generally, there is shortage of funds in Indian Money Market on account of various factors like inadequate banking facilities, low savings, lack of banking habits, existence of parallel economy,- etc. have also been responsible for the paucity of funds in the money market.
(b) Existence of Unorganised Money Market : This is one of the major defects of Indian Money Market. It does distinguish between short term and long term finance, and also between the purposes of finance. Since it is outside the control and supervision of RBI. It limits the RBI’s control over money market.
(c) Delays in technological up-gradation: Use of advanced technology is a pre requisite for the development and smooth functioning of financial markets. Delays in up-gradation of technology hampers the working of the money market.
(d) Absence of Well Organized Banking Sector : Branch expansion was very slow before bank nationalization in 1969. Even now the banks are largely concentrated in large towns and small cities. There is lack of movement of funds. Indian banking system is not yet a well organized sector.
(e) No Uniformity in the rates of interest:
There exists too many rates of interest in the Indian Money Market such as the borrowing rate of government, deposits and lending rates of co-operatives and commercial banks, lending rates of financial institutions, etc. This is due to lack of mobility of funds from one section of the money market to another.
(f) Seasonal fluctuations : The seasonal stringency of money and high rate of interest during the busy season (November to June) is striking feature of Indian Money market. There are wide fluctuation in the interest rates from one season to another. Money Market add money into the money market during the busy season and withdraw funds during the slack seasons.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the functions of commercial bank.
Answer:
(A) Meaning A bank is a dealer in credit. Any institution that accepts deposits from public who have more cash than it needs immediately and gives loans to those who are need is called as a bank. Commercial bank performs all these functions for earning profit. Commercial banks play an important role in mobilizing savings and allocating ) them to various sectors of the economy. It includes both scheduled commercial banks l and non scheduled commercial banks.
(B) Definition of Commercial Bank :
Banking Regulation Act 1949 “”Banking means the accepting for the purpose of lending or investment of deposits of money from public repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, demand draft, order or otherwise.
The above definition clearly indicates the essential function of a bank is mainly dealing in money and credit.
(C) Functions of a Commercial Bank :
Commercial Bank performs a variety of functions to satisfy the needs of the various S sectors of the economy.
The functions of Commercial Banks are as follows:
(I) Accepting Deposits:
The most significant and traditional function of commercial bank is accepting ? deposits from public. A commercial bank acts as the custodian of public deposits. This l function is very important because it helps in the mobilisation of funds from households to businessman for production purposes, Commercial banks act as intermediary by accepting deposits and paying interest on them and giving loans and charging interest) from borrowers at a high rate. The difference j between the two is the profit of the bank. Commercial bank accepts the following types of deposits :
(A) Demand Deposits
(B) Time Deposits
(A) Demand Deposits : The deposits which ; are withdrawable on demand, are known as demand deposits. They are of two types (1) Current Account Deposits (2) Saving) Account Deposits
(1) Current Account Deposits : Current j account deposits are usually held by businessmen, industrial enterprises, public bodies for business transactions. Money deposited in current account can be withdrawn in part or full at any time and any number of times by the depositors without any prior notice. Overdraft facilities and agency service are provided by the bank to the current account holders. Very low or no interest is paid on these accounts as the banks cannot utilise these short term deposits. Banks may charge certain amount of service charges on account holders.
(2) Saving Account Deposits : Saving account deposits are opened by salaried class or people with fixed income for holding their short term savings. Money deposited in these accounts retain high degree of liquidity. At the same time it earns nominal interest. It is a kind of demand deposits which is generally kept by people for sake of safety.
(B) Time Deposits : These are deposits, which are repayable after a certain period of time. They are of two types – (1) Recurring Deposits (2) Fixed Deposits
(1) Recurring Deposits : These are deposits under which people deposit a fixed amount at regular interval for specified period of time. These deposits encourage savings and carry high rate of interest.
(2) Fixed Deposits : Fixed deposits are time deposits or term deposits, which attract fund for a specific period. It is a time bound deposit as the amount deposited cannot be withdrawn before the maturity of the period. However, loans can be taken from the bank against the security of this deposit, within that period. These deposits earn a higher rate of interest.
(II) Advancing / Granting Loans :
The second major function of a commercial bank is to make loans and advances out of the money, which comes to it from the public by way of deposits. Direct loans and advances are given to all types of persons particularly to businessmen and investors against personal security, gold, silver and other assets. The profit earning capacity of commercial banks depends on this function of lending. Generally banks grant loans and advances to the borrowers in the following forms :
(1) Loans (2) Cash Credit (3) Overdraft facility (4) Discounting of bills.
(III) Ancillary Functions :
Commercial Banks also provide variety of ancillary services like – transfer of funds, j collection of money, making periodical ( payments on behalf of the customer, merchant banking, foreign exchange, safe deposit lockers, D-mat facility, internet banking, mobile banking, ATM facility, purchase and sale of securities, etc.
(IV) Credit Creation :
It is an important function of commercial banks. Commercial banks are the creators of credit.
Commercial Bank collects deposits from public which is called as primary deposits. After deducting required reserves, bank lends money to the borrower which is called j as secondary deposits or derivative deposits. This procedure is followed by entire banking [ system in a country leading to creation of credit.
Thus, every loan creates deposits and every deposits creates loans.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the role of capital market in India.
Answer:
Role of Capital Market:
- Mobilizes long term savings : Capital market helps to mobilize long term savings from various section of the population through the sale of securities.
- Provides equity capital : Capital market provides equity capital or share capital to entrepreneurs which will be used by entrepreneurs to purchase business assets and also to fund the business operations.
- Operational efficiency : Capital market helps to achieve operational efficiency by lowering the transaction costs, simplifying transaction procedures, lowering settlement timings in purchase and sale of stocks.
- Quick valuation : Capital market helps to determine a fair and quick value of both equity (shares) and debt (bonds, debentures) instruments.
- Integration : Capital market brings integration among real and financial sectors, equity and debt instruments, government and private sector, domestic and external funds, etc.
Question 4.
Explain the problems of capital market in India.
Answer:
Following are the problems of capital market in India :
- Scams : It is observed that different types of financial scams in the stock exchange have affected the confidence of individual investors in the securities market. Scams involve manipulation of larger amount of money, which results in public distrust and loss of confidence among the individual investors.
- Inadequate debt instruments : There is less trading in debt securities due to narrow investor base, high cost of issue, lack of accessibility to small and medium enterprises.
- Lack of informational efficiency : Indian stock markets lacks informational efficiency as compared to advanced countries.
- Decline in volume of trade : There is sharp decline in the volume of trade in regional stock exchanges. This is due to investors preferring trading in securities listed in premier stock exchanges like BSE and NSE.
8. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the role of money market in India.
Answer:
(A) Meaning:
Money market is a market for lending and borrowing short term funds.
It is a market for near money.
It deals in short term instruments like trade bills, government securities, promissory notes, etc.
Money market centres are located at Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata. Money market consists of organised as well as unorganised j sector.
Role of Money Market in India :
(a) Portfolio Management : Money market deals with different types of financial instruments which are designed to suit the risk and return preferences of the investors. This enables the investors to hold a portfolio of different financial assets which in turn, j helps in minimizing risk and maximizing returns.
(b) Implementation of monetary policy :
Various monetary policies are implemented by the Central Bank, with an aim to manage the quantity of money, to meet the requirements of different sectors of the economy and to increase the pace of economic growth. Money market ensures successful implementation of these monetary policies. It also guides the central bank in developing an appropriate interest policy.
(c) Growth of Commerce, Industry and Trade : Money market facilitates discounting bills of exchange to local and international traders who are in urgent need of short-term funds. It also provides working capital for agriculture and small scale industries.
(d) Financial requirements of the Government : Money market helps the Government to fulfil its short term financial requirements on the basis of Treasury Bills.
Economizes the use of cash : Money market deals with various financial instruments that are close substitutes of money and not actual money. Thus, it economizes the use of cash.
Equilibrating mechanism : Money
market helps to establish equilibrium between the demand for and supply of short term funds by allocating rationally the available resources and thus mobilizing the savings of public into fruitful investment channels.
Liquidity Management : Money Market, through the monetary authorities facilitates better management of liquidity and money in the economy. This, in turn, leads to economic stability and development of the country.
Short-term requirements of borrowers :
Money market provides short-term financial needs of the borrowers at reasonable prices.
Question 2.
Explain the functions of RBI.
Answer:
(A) Introduction: Central Bank is the apex or the supreme monetary banking authority and occupies an important position in the monetary and banking structure of the country.
The guiding principle of a Central Bank is to act only in public interest and for the welfare of the country without regards to profit as primary consideration.
In India, The Reserve Bank of India is the Central Bank. It was established as shareholder’s bank on 1st April, 1935. It was nationalized on 1st January, 1949.
(B) Definitions :
(1) According to M. H. de Kock –
“A Central Bank is one which constitutes the apex of the monetary and banking structure of the country. ”
“(2) According to Prof. W. A. Shaw –
“Central Bank is a bank which controls credit.”
(C) Functions of Central Bank :
(1) Issue of Currency Notes : The Central i Bank has been authorised to print and issue ; currency notes. The RBI enjoys the monopoly of note issue of all denominations except one rupee note. The one rupee note and coins are issued by the Ministry of Finance of the government of India but their distribution is undertaken by RBI.
(2) Banker to the Government: The Central Bank acts as (A) a banker, (B) advisor, and (C) agent to the government. It performs all these functions which commercial banks do for their customers.
As a banker to the government, central bank transacts the business of Central and State governments. It accepts money and makes payments on behalf of these governments.
As an advisor, central bank advises the government on various economic issues and policies.
As an agent, central bank acts as a representative of central bank and attends l the international meetings of IMF and World Bank.
In short, it is a friend, philosopher and guide to the government.
(3) Bankers’ Bank : It supervises, co-ordinates j and controls the operations and activities of the commercial banks. As their bank it undertakes the following functions:
(a) acts as custodian of cash reserve.
(b) acts a lender of the last resort.
(c) provides clearing house function.
(4) Controller of Credit or Money Supply : Central Bank regulates the volume of credit and money supply in the country. The main objective behind this is to maintain price and ; economic stability in the country.
There are various methods which Central Bank uses to control the supply of credit in : the economy. They are –
- Quantitative Measures control the quantity or volume of credit created by the commercial banks. They are bank rate, open market operation and cash reserve ratio.
- Qualitative Measures or Selective Measures deal with the purpose and direction of credit. They are – varying margin requirements, regulation of credit, moral suasion and direct action.
(5) Custodian of Foreign Exchange Reserve of the Country: The Central Bank is also a custodian of country’s gold and major foreign currencies like US dollar, Euro the British Pound, etc. obtained by government from international trade.
The central bank also maintains international liquidity.
(6) Developmental and Promotional Functions : In developing countries like India, a very important function of Central Bank is to promote economic development.
- To promote banking habits among the poor people.
- To provide agriculture finance through NABARD and to promote rural and agricultural development.
- To provide industrial finance through IDBI, SFC and IFCI and boost the growth of industrial sector.
- To provide export – import finance through EXIM bank.
- To encourage small savings through Unit Trust of India.
(7) Data Collection and Publicity : The Central Bank also collects and publishes information relating to agriculture, industrial and financial sectors of the economy, exports and imports, banking, trends in money and capital market, etc.
Its main publications include – Report on Currency and Finance, RBI Bulletin, RBI Journals and various research papers.
Intext Questions
Try this (Textbook Page 81)
Identify the type of finance into – Personal finance, Corporate finance or Public finance.
Answer:
| Personal Finance | Corporate Finance | Public Finance |
| Building a retirement corpus. | Raising share capital through sale of equity shares. | Collection of tax revenue. |
| Clearing home loan through EMI (Equated Monthly Instalment) | Managing working capital needs. | Expenditure on social infrastructure such as health and education. |
Find out (Textbook Page 83)
Find out names of the Central Banks of the following countries.
(1) USA
(2) Canada
(3) Russia
(4) Germany
(5) China
(6) UK (United Kingdom)
(7) Sweden
(8) France
(9) Japan
(10) Australia
Answer:
(1) USA : Federal Reserve System ;
(2) Canada : Bank of Canada
(3) Russia : Central Bank of Russia
(4) Germany : Deutsche Bundes bank
(5) China : People’s Bank of China
(6) UK (United Kingdom) : Bank of England
(7) Sweden : Sveriges Riksbank
(8) France : Banque de France
(9) Japan : Bank of Japan
(10) Australia : Reserve Bank of Australia
Try this (Textbook Page 85)
Pair the logos given with their respective banks as given in the bracket below :
(State Bank of India, HSBC Bank, Union Bank of India, Axis Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, HDFC Bank)
Answer:
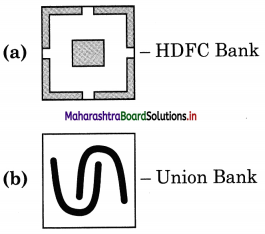
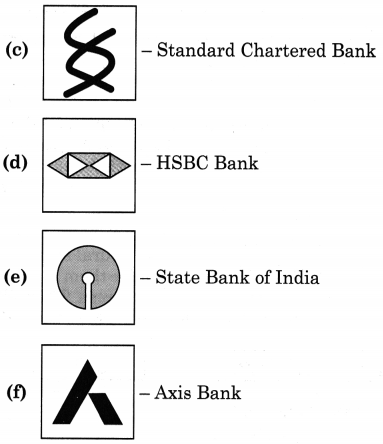
Try this (Textbook Page 85)
Collect information of Co-operative banks in your region at different levels.
Answer:
[Students should do this activity by themselves]
Find out (Textbook Page 90):
List the regional stock exchanges in India.
Answer:
- Regional Stock Exchanges in India :
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)
- National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- Calcutta Stock Exchange (CSE) Metropolitan Stock Exchange (MSE)
- India International Exchange (India INX)
- NSE IFSC Ltd.
12th Std Economics Questions And Answers:
- Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Utility Analysis Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Demand Analysis Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Elasticity of Demand Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Supply Analysis Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Forms of Market Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Index Numbers Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- National Income Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Public Finance in India Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Money Market and Capital Market in India Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers
- Foreign Trade of India Class 12 Economics Questions And Answers