Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Science Solutions Part 2 Chapter 2 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 1 Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 10 Science Part 2 Chapter 2 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 10 Science Part 2 Chapter 2 Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 1 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
a. After complete oxidation of a glucose molecules, ……….. number of ATP molecules are formed.
Answer:
After complete oxidation of a glucose molecules, 38 number of ATP molecules are formed.
b. At the end of glycolysis, ……………… molecules are obtained.
Answer:
At the end of glycolysis, pyruvate molecules are obtained.
c. Genetic recombination occurs in ………… phase of prophuse of meiosis-I.
Answer:
Genetic recombination occurs in pachytene phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
d. All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in …………. phase of mitosis.
Answer:
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equutorial plane of cell in metaphase phase of mitosis.
e. For formation of plasma membrane, phospholipid molecules are necessary.
Answer:
For formation of plasma membrane, …………… molecules are necessary.
f. Our muscle cells perform ……………… type of respiration during exercise.
Answer:
Our muscle cells perform anaerobic type of respiration during exercise.
![]()
Question 2.
Write definitions.
a. Nutrition.
Answer:
Nutrition: The process of taking nutrients in the body and utilizing them by an organism is known as nutrition.
b. Nutrients.
Answer:
Nutrients: The substances like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals etc. which are components of the food are called nutrients.
c. Proteins.
Answer:
Proteins: Protein is a macromolecule which is formed by many amino acids which are joined by peptide bonds.
d. Cellular respiration.
Answer:
Cellular respiration: Oxidation of glucose and other food components which takes place inside the cell in presence or absence of oxygen, is known as cellular respiration.
e. Aerobic respiration.
Answer:
Aerobic respiration: Cellular respiration taking place in presence of oxygen is known as aerobic respiration.
f. Glycolysis.
Answer:
Glycolysis: The process occurring in the cell where a molecule of glucose is oxidized in step by step process forming two molecules of each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water, is called glycolysis.
Question 3.
Distinguish between
a. Glycolysis and TCA cycle
Answer:
Glycolysis:
- The process of glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- In glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is oxidized step-by-step to produce two molecules each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water.
- Glycolysis can take place in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- The first step in cellular respiration is glycolysis where glucose is converted into pyruvate.
- Two molecules of pyruvate are obtained in glycolysis.
- Two molecules of ATP are used up in glycolysis.
- Four molecules of ATP are produced in glycolysis.
- CO2 is not produced during glycolysis.
TCA cycle:
- TCA cycle takes place in mitochondria.
In TCA cycle, molecule of acetyl-co-A is completely oxidized and in the process CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 and ATP is produced. - TCA cycle takes place only during aerobic respiration.
- The second step in cellular respiration is TCA cycle.
- Pyruvate is converted into CO2 and H2O during TCA cycle.
- ATP molecules are not used up in TCA cycle.
- Two molecules of ATP are produced in TCA cycle.
- CO2 is produced in TCA cycle.
b. Mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:
Mitosis:
- In mitosis the chromosome number does not change. Diploid cells remain diploid, without change.
- One cell gives rise to two daughter cells in mitosis.
- Karyokinesis of mitosis has four stages, viz. prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- Prophase of mitosis is not lengthy.
- Genetic recombination does not happen in mitosis as there is no crossing over.
- Mitosis is essential for growth and development.
- Mitosis takes place both in somatic cells and germinal cells.
meiosis:
- In meiosis, the chromosome number is reduced to half. The diploid cells become haploid.
- One cell gives rise to four daughter cells in meiosis.
- Meiosis has two major stages, viz. meiosis-I and meiosis-II. Each is further subdivided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
- Prophase of meiosis-I is very lengthy.
- Genetic recombination takes place in homologous chromosomes as there is crossing over during prophase-I.
- Meiosis is essential for formation of gametes in sexual reproduction.
- Meiosis takes place in only germinal cells. It does not take place in somatic cells.
c. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
Aerobic respiration:
- Oxygen is required for aerobic respiration.
- Aerobic respiration takes place in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm.
- At the end of aerobic respiration CO2 and H2O is formed.
- Energy is produced in large amount in aerobic respiration.
- Glucose is completely oxidized in aerobic respiration.
- 38 molecules of ATP are formed during aerobic respiration.
- Chemical reaction:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6H2O + 6 CO2 + 686 Kcal
Anaerobic respiration:
- Oxygen is not required for anaerobic respiration.
- Anaerobic respiration occurs only in the cytoplasm.
- At the end of anaerobic respiration CO2 and C2H5OH are formed.
- Energy is produced in lesser amount in anaerobic respiration.
- Glucose is incompletely oxidized in anaerobic respiration.
- 2 molecules of ATP are formed during anaerobic respiration.
- Chemical reaction:
C6H12O6 → 2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2 + 50 Kcal
![]()
Question 4.
Give scientific reasons.
a. Oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
Answer:
- When glucose is completely oxidized in aerobic cellular respiration, it produces 38 molecules of ATP.
- In cellular respiration, three processes take place one after the other, these are glycolysis, Krebs cycle and electron transport chain reactions.
- In absence of oxygen only glycolysis can occur but further two reactions will not take place.
- If glycolysis occurs in absence of oxygen, it produces alcohol.
- By anaerobic glycolysis only two molecules of ATP are produced.
- This results in less energy supply to the body. Therefore, oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
b. Fibres are one of the important nutrients. (Board’s Model Activity Sheet)
Answer:
- Fibres are indigestible substance.
- They are thrown out along with other useless and undigested matter.
- This aids in egestion. Some fibres also help in digestion of other substances.
- Green leafy vegetables, fruits, cereals, etc. are considered as important in diet as they supply nutritious fibres.
- Thus, fibres are considered as one of the important nutrients.
c. Cell division is one of the important properties of cells and organisms.
Answer:
- Cell division is very essential for all the living organisms.
- The growth and development is possible only due to cell division.
- The emaciated body can be restored only through the cell division which adds new cells.
- Offspring is produced only through the cell division that take place in parents.
- In asexual reproduction, mitosis helps to give rise to new generation.
- In sexual reproduction, meiosis helps to form haploid gametes.
- All such functions show that cell division is one of the important properties of cells and organisms.
d. Sometimes, higher plants and animals too perform anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
- When there is deficiency of oxygen in the surrounding, the aerobic respiration is not possible.
- In such case, to survive, higher plants switch over to anaerobic respiration.
- In some animal tissues in case of oxygen deficiency cells perform anaerobic respiration.
e. Krebs cycle is also known as citric acid cycle.
Answer:
- Sir Hans Kreb proposed this cycle and hence it is called Krebs cycle.
- These are series of cyclic chain reactions which begins with acetyl-coenzyme-A molecules which act with molecules of oxaloacetic acid.
- The reactions are catalysed with the help of specific enzymes.
- The first molecule formed in this reaction is called citric acid. Therefore, Krebs cycle is also called citric acid cycle.
![]()
Question 5.
Answer in detail.
a. Explain the glycolysis in detail.
Answer:
- Carbohydrates are converted to glucose after the process of digestion is completed. The oxidation of glucose for releasing energy is called glycolysis which takes place in cytoplasm.
- Glycolysis can occur in presence of oxygen or without oxygen too. The first type of glycolysis takes place in aerobic respiration and the second type is in anaerobic respiration.
- In aerobic respiration, there is step-wise oxidation of glucose molecule forming two molecules each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water.
- Later the pyruvic acid formed in this process is converted into molecules of Acetyl-Coenzyme-A along with two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of CO2.
- During anaerobic respiration along with glycolysis there is fermentation too. This is incomplete oxidation of glucose and thus it results in formation of lesser energy.
- The process of glycolysis was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jacob Parnas. Therefore, in their honour, glycolysis is also called as Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway (EMP pathway). For the discovery they had performed experiments on muscles.
b. With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the mitosis in detail.
Answer:
(1) There are two stages of mitosis. These are
(a) Karyokinesis or nuclear division and
(b) Cytokinesis or cytoplasmic division. Karyokinesis takes place in further four phases, viz prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
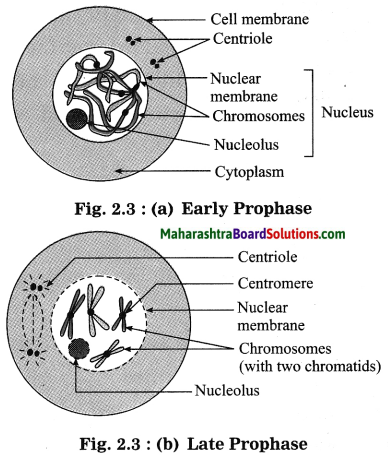
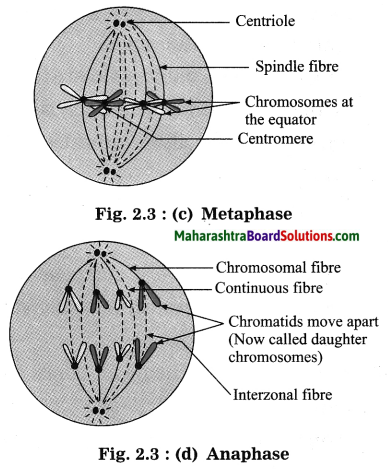
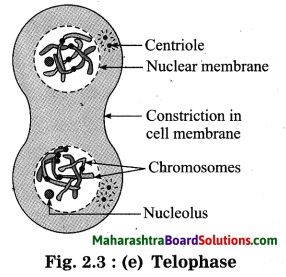
(a) Karyokinesis:
(i) Prophase: During prophase, condensation of chromosomes starts. The thin and thread like chromosomes start thickening. They are seen with their pair of sister chromatids. In animal cells the centrioles are seen to duplicate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
(ii) Metaphase: Chromosomes complete their condensation and each one is seen with its sister chromatids. The chromosomes are seen in equatorial plane of the cell. The spindle fibres are formed from polar region, where centrioles are present, and they attach themselves to the centromere of each chromosome. Nuclear membrane now disappears completely.
(iii) Anaphase: The centromeres of the chromosomes now divide forming two daughter chromosomes. The spindle fibres pull apart the chromosomes from equatorial region to the opposite poles. Chromosomes moving to the poles appear like bunch of bananas. One set of chromosomes reach each pole by the end of the anaphase.
(iv) Telophase: Telophase is reverse of events that occurred in prophase. The thickened chromosomes decondense. They again assume the thin and thread like appearance. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus appear again. The spindle fibres are completely lost. The cell looks as if it has two nuclei in one cytoplasm.
(b) Cytokinesis: In animal cells a notch develops in the middle of the cell. This notch goes on deepening down and later the cytoplasm divides into two. In plant cells, cell plate formation takes place and then cytokinesis takes place.
c. With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the five stages of prophase-I of meiosis.
Answer:
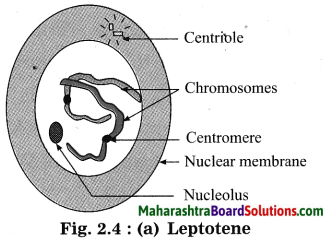
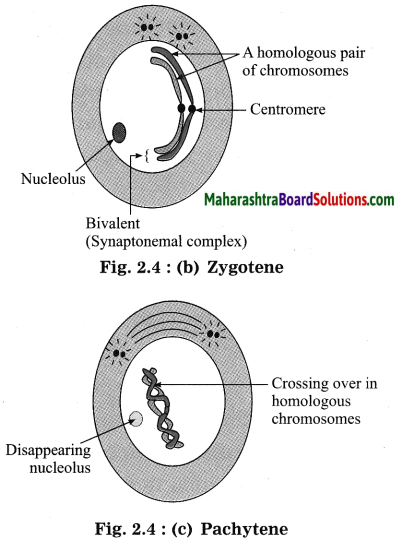
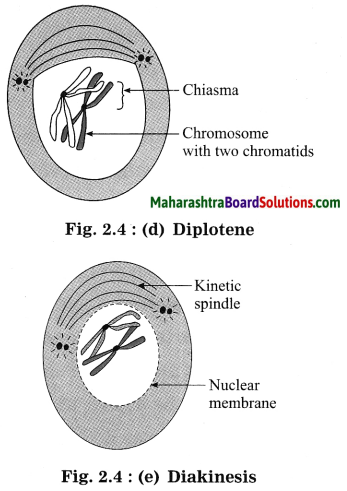
Prophase-I: Prophase – I of meiosis is much longer phase of the meiosis.
It is subdivided into 5 substages, namely leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis.
(1) Leptotene: Initially the chromosomes start condensation and they become compact during leptotene.
(2) Zygotene: In zygotene, homologous chromosomes start pairing. This pairing is called synapsis. The structure called synaptonemal complex develops to hold chromosomes in place during this pairing. Each chromosome’s chromatid arm divides and forms structure called bivalent or tetrad.
(3) Pachytene: During pachytene stage, crossing over of non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes takes place. Genetic recombination is produced due to such exchange. The homologous chromosomes still remain paired together at the sites of crossing over.
(4) Diplotene: During diplotene, synaptonemal complex dissolves and the homologous chromosomes of the bivalents separate except at the point of crossing over. Thus, it looks like X-shaped structures called the chiasmata.
(5) Diakinesis: The last phase of prophase is for termination of chiasmata. The spindle fibres originate, and the cross-over homologous chromosomes are now separated. The nucleQlus disappears, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
d. How do all the life processes contribute to the growth and development of the body?
Answer:
- Different systems work in co-ordination with each other in the body of the living organisms. In human body the homoeostasis is very advanced.
- Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, excretory system, nervous system and all the external and internal organs in the bodywork independently but in coordination with each other.
- The digested and absorbed nutrients of the food are transported to various cells with the help of circulatory system due to pumping of the heart. Simultaneously, the oxygen absorbed in the blood by lungs is also transported to each cell by RBCs.
- Mitochondria in every cell brings about oxidation of nutrients and produce energy required for all of these functions.
- The control is exercised by the nervous system on all these actions. This keeps the organism alive and helps in growth and development of the same.
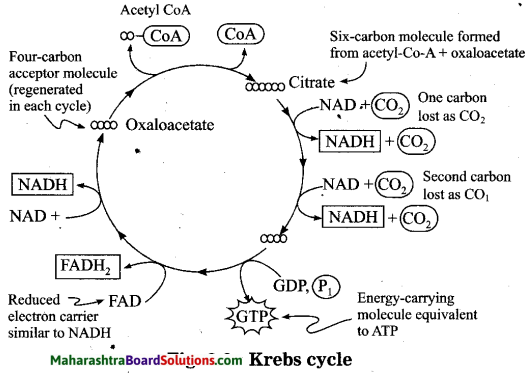
e. Explain the Krebs cycle with reaction.
Answer:
- Krebs cycle was proposed by Sir Hans Kreb. This cycle is named after him. It is also called tricarboxylic acid cycle or citric acid cycle.
- The acetyl-coenzyme-A molecules enter the mitochondria located in the cytoplasm.
- They participate in the chemical reactions taking place in Krebs cycle.
- In the cyclic chemical reactions, acetyl- coenzyme-A is completely oxidised
- It yields molecules of CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 and ATP upon complete oxidation.
![]()
Question 5.
How energy is formed from oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins?
Correct the dagram below.
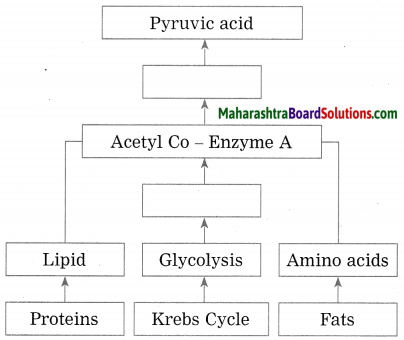
Answer:
(1) First of all the dietary carbohydrates are digested in the digestive system with the help of various enzymes and converted into glucose. Similarly, proteins are converted into amino acids and fats are broken down into fatty aid and glycerol (alcohol).
(2) Oxidation of carbohydrates takes place during cellular respiration. Glucose is oxidized by three steps during aerobic respiration, viz. glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle or Krebs cycle and electron transfer chain.
(3) From one molecule of glucose two molecules of each pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water are formed during glycolysis. Pyruvic acid which is formed in this process is converted into Acetyl-Coenzyme-A along with release of two molecules each of NADH2 and CO2.
(4) In the next step, i.e. in TCA cycle, molecules of Acetyl-Co-A enter the mitochondria and a cyclic chain of reactions take place. Acetyl part of Acetyl- Co-A is completely oxidized through this cyclical process. The molecules CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 are released in this process.
(5) In third step, i.e. in ETC reaction, NADH2 and FADH2 formed during first two steps are used for obtaining ATP molecules. 3 molecules of ATP are obtained from each NADH2 molecule and 2 molecules of ATP from each FADH2.
(6) Thus, one molecule of glucose upon complete oxidation in presence of oxygen yields 38 molecules of ATP. This is how from carbohydrates, energy is obtained.
(7) If carbohydrates are insufficient in diet, then proteins or lipids are used for energy production. Fatty acids derived from fats and amino acids derived from proteins are converted into Acetyl- Co-A. Acetyl-Co-A once again can yield energy through TCA cycle.
Corrected diagram:
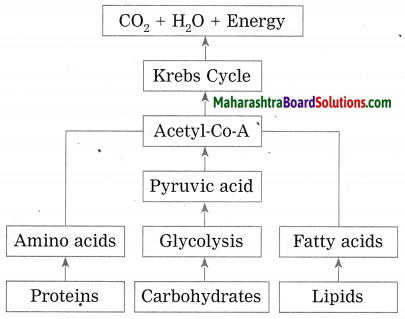
Project:
With the help of information collected from internet, prepare the slides of various stages of mitosis and observe under the compound microscope.
Can you recall? (Text Book Page No. 12)
Question 1.
How are the food stuffs and their nutrient contents useful for body?
Answer:
The food stuffs are digested and converted into soluble nutrients. These nutrients are carried by blood to every cell of the body. The oxygen inhaled at the time of respiration is also carried to every cell. In the body cells, this oxygen carries out oxidation of nutrients and thus energy is produced. The energy helps the body to carry out all its functions. The nutrients help in the growth and development of the body.
Question 2.
What is the importance of balanced diet for body?
Answer:
Balanced diet has carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals in the right proportion. Each nutrient carries a specific important function. In balanced diet all these nutrients are in right proportion. Since balanced diet is required for energy and nutrition, it is very important to maintain our health.
![]()
Question 3.
Which different functions are performed by muscles in body?
Answer:
There are three 4ypes of muscles in our body. The voluntary muscles bring about all the movements according to our will. Involuntary muscles bring about all vital activities of the body. The visceral organs are under the control of involuntary muscles. The cardiac muscles control the movements of heart. Carbohydrates and proteins are stored in muscles.
Question 4.
What is the importance of digestive juices in digestive system?
Answer:
Digestive juice contains different enzymes. Enzymes act as catalysts and bring about the chemical reactions at faster pace. The digestive juices of stomach make pH of digestive tract acidic while that of intestinal juice make it alkaline.
Question 5.
Which system is in action for removal of waste materials produced in human body?
Answer:
Excretory system helps in the removal of nitrogenous waste materials produced in the human body.
Question 6.
What is the role of circulatory system in energy production?
Answer:
Due to circulatory system, glucose from digestive system and oxygen from respiratory system is transported to every cell. Red blood cells carry the oxygen as the blood is pumped by the heart. In every cell with the help of oxygen, glucose molecules yield the energy by the process of oxidation.
Question 7.
How are the various processes occurring in the human body controlled? In how many ways?
Answer:
The nervous system and the endocrine system brings about control by nervous and chemical coordination in the body. Due to such coordination different functions of the body are carried out in sequential and controlled manner.
Use your barain power:
Question 1.
Many players are seen consuming some food stuffs during breaks of the game. Why may be the players consuming these food stuffs? (Text Book Page No. 12)
Answer:
- Players require energy in greater amount.
- They perspire heavily at the time of game or sport which results in the loss of water and electrolytes from their body.
- This may affect their performance in sport. To prevent such unfavourable effect, they are given, juices or drinks.
- This helps them to restore the balance of water and electrolytes in their body. It also gives enhanced energy required for the performance.
![]()
Question 2.
Many times, we experience dryness in mouth. (Text Book Page No. 17)
Answer:
- In our body there is 65-70% water. This proportion is always maintained.
- Sometimes we lose lots of water either through perspiration or due to unavailability of water for a long time. In such situations, we experience dryness in our mouth.
- Dryness is a natural feeling which creates urge in us to drink water, thereby the proportion of water in the body is brought back to its normal levels.
Question 3.
Oral rehydration solution (Salt-sugar- water) is frequently given to persons experiencing loose motions. (Text Book Page No. 17)
Answer:
- Loose motions cause lot of loss of water from the body.
- This may result in dehydration. This can be lethal if ignored.
- Especially in case of young children this is a very serious fatal problem.
- Thus, to bring back the normal proportion of water and electrolytes, oral rehydration solution or ORS is given to the patient who suffers from loose motions.
Question 4.
We sweat during summer and heavy exercise. (Text Book Page No. 17)
Answer:
- During summer, the environmental temperatures are high.
- This causes rise in our body temperature. Exercising also cause rise in the temperature. But since we can regulate our body temperature to a constant level, the sweat, glands g6t automatically stimulated.
- This induces perspiration.
- The sweat evaporates and causes fall in the body temperature. Thus, for regulation of body temperature, we sweat during summer or even after heavy exercise.
Question 5.
What do you mean by diploid (2n) cell? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
- The cells in which chromosome number is double are known as diploid cells.
- Male and female gametes unite together in the process of fertilization. Their chromosomes mix together in the zygote, therefore, the chromosome number is always diploid.
- E.g. Diploid chromosome no. in human beings is 46. We hate 46 chromosomes in each of our body cells.
Question 6.
What do you mean by haploid (n) cell? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
- The cells with only one set of chromosomes is known as haploid cell.
- At the time of sexual reproduction, there is meiosis. In meiosis chromosome number of the parental germ cells are reduced to half. Therefore, gametes are haploid.
- The haploid chromosome number (n) in human beings is 23.
- Sperm and ovum both are haploid carrying 23 chromosomes each.
Question 7.
What do you mean by homologous chromosomes? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
- Every species has definite number of chromosome pairs in their diploid cells.
- In every pair, the two chromosomes are alike in shape, type and genes located over them.
- Such chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
- E.g. In human diploid cell, pair of chromosome no. 1 shows chromosome no. 1 from mother and chromosome no. 1 from father. These two chromosomes are homologous to each other.
Question 8.
Whether the gametes are diploid or haploid? Why? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
The cells that give rise to gametes are diploid (2n). But by meiosis they give rise to gametes which are haploid (n). Two haploid gametes undergo fertilization and the zygote formed becomes once again diploid (2n).
Question 9.
How are the haploid cells formed? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
Diploid cells undergo meiosis, which is a reduction division. In this way haploid cells are formed.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the importance of haploid cells? (Text Book Page No. 20)
Answer:
- The gametes that take part in the sexual reproduction should be haploid.
- Otherwise the chromosome number will not be maintained at constancy. E.g. Parents have 2n = 46 chromosomes in their cells.
- If meiosis does not take place in them, the gametes formed will also contain 46 chromosomes.
- The resultant offspring will have 46 + 46 = 92 chromosomes.
- Such skewed number will produce large scale abnormalities.
- But due to meiosis, the gametes formed are haploid and thus the chromosome number is maintained constant for every species. Gametes are haploid cells, this is the most important fact.
Internet is my friend. (Text Book Page No. 17)
Collect information.
(a) What are symptoms of diseases like night blindness, rickets, beriberi, neuritis, pellagra, anaemia, scurvy?
Answer:
| Disease | Symptoms |
| Night blindness |
|
| Rickets |
|
| Beriberi |
|
| Neuritis |
|
| Pellagra |
|
| Anaemia |
|
| Scurvy |
|
(b) What do you mean by coenzymes?
Answer:
Co-enzyme is a non-protein compound that is necessary for the functioning of an enzyme. It is bound to the enzyme as a catalyst. This increases the rate of reaction. Co-enzymes always act along the enzymes. They cannot work independently. But the same molecule of coenzyme can be used again and again.
Many co-enzymes are vitamins or derived from vitamins. When vitamin intake is too low, then an organism also lacks the co-enzymes that catalyse reactions. Water-soluble vitamins, which include all B complex vitamins and vitamin C, lead to the production of co-enzymes. Two of the most important and widespread vitamin-derived coenzymes are Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) and co-enzyme A.
(c) Find the full forms of FAD, FMN, NAD, NADP.
Answer:
| FAD | Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide |
| FMN | Flavin Mono Nucleotide |
| NAD | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide |
| NADP | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate |
(d) How much quantity of each vitamin is required every day?
Answer:
| Vitamin | Daily requirement |
| A | 700 and 900 μ grams |
| B Complex | 100 mg/day for adults. |
| C | 75 mg |
| D | 5 μg |
| E | 10 mg |
| K | 80 μg |
![]()
Choose the correct alternative and write its alphabet against the sub-question number:
Question 1.
The process of glycolysis occurs in ……….
(a) cytoplasm
(b) mitochondria
(c) nucleus
(d) cell membrane
Answer:
The process of glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm.
Question 2.
ATP is called ………. of the cell.
(a) energy currency
(b) combustion fuel
(c) storage of glucose
(d) protein depot
Answer:
ATP is called protein depot of the cell.
Question 3.
Excess of carbohydrates are stored in liver and muscles in the form of ………….
(a) sugar
(b) glucose
(c) glycogen
(d) protein
Answer:
Excess of carbohydrates are stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Question 4.
Chemically vitamin B2 is ………….
(a) Riboflavin
(b) Nicotinamide
(c) Cyanacobalomine
(d) Pantothetic acid
Answer:
Chemically vitamin B2 is Riboflavin
Question 5.
Somatic and stem cells undergo type of ………… division. (March 2019)
(a) meiosis
(b) mitosis
(c) budding
(d) cloning
Answer:
Somatic and stem cells undergo type of mitosis division.
Question 6.
We get ……….. energy from carbohydrates.
(a) 9 kcal/gm
(b) 9 cal/gm
(c) 4 cal/gm
(d) 4 kcal/gm
Answer:
We get 4 cal/gm energy from carbohydrates.
Question 7.
Which of the following vitamins is necessary for synthesis of NADH2?
(a) Vitamin B2
(b) Vitamin B3
(c) Vitamin
(d) Vitamin K
Answer:
(b) Vitamin B3
Write whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
Glucose is oxidized step by step in the cells during the process of respiration at the body level.
Answer:
False. (Glucose is oxidized step by step in the cells during the process of cellular respiration.)
Question 2.
In aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidized in three steps.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Glycolysis is also called Embden-Meyerhof-Paarnas pathway.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Molecules of pyruvic acid formed in this glycolysis are converted into molecules of acetyl-co-enzyme A.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Excess of ATP molecules obtained from proteins are not stored in the body.
Answer:
False. (Excess of ammo acids obtained from proteins are not stored in the body.)
Question 6.
Proteins of animal origin are called ‘first class’ proteins.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 7.
The disease related with the deficient synthesis of insulin is heart disease.
Answer:
False. (The disease related with the deficient synthesis of insulin is diabetes.)
Match the columns:
| Protein | Part of the body (July 2019) |
| (1) Haemoglobin | (a) muscles |
| (2) Ossein | (b) skin |
| (c) bones | |
| (d) blood |
Answer:
(1) Haemoglobin – blood
(2) Ossein – bones.
| Protein | Part of the body |
| (1) Keratin | (a) muscles |
| (2) Myosin | (b) skin |
| (c) bones | |
| (d) blood |
Answer:
(1) Keratin – skin
(2) Myosin – muscles.
![]()
Find the odd one out:
Question 1.
Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Insulin
Answer:
Insulin. (All the others are hormones produced with the help of fatty acids.)
Question 2.
Actin, Ossein, Myosin, Melanin
Answer:
Melanin. (All the others are proteins concerned with locomotion of the body.)
Question 3.
Lipids, Carbohydrates, Fatty acids, Proteins
Answer:
Fatty acids. (All the others are food constituents; fatty acid is soluble nutrient.)
Question 4.
Alcohol, Vinegar, Pyruvic acid, Lactic acid.
Answer:
Pyruvic acid. (All the others are chemical substances formed by the process of fermentation.)
Question 5.
Tricarboxylic acid cycle, Citric acid cycle, Krebs cycle, EMP pathway.
Answer:
EMP pathway. (All the other terms are synonymous to each other.)
Considering the relationship in the first pair, complete the second pair by using a word or group of words:
Question 1.
Process that occurs in the cytoplasm : Glycolysis :: Process that occurs in the mitochondria ………
Answer:
Krebs cycle
Question 2.
Skin : Keratin :: Blood : …………
Answer:
Haemoglobin
Question 3.
Energy obtained from protein : 4 kcal :: Energy obtained from fats / lipids : …………
Answer:
9 Kcal
Question 4.
Breakdown of glucose molecule : Glycolysis :: Formation of glucose from proteins : …………….
Answer:
Gluconeogenesis
![]()
Question 5.
Condensation of chromosomes : Prophase :: Formation of spindle fibres : …………
Answer:
Metaphase
Question 6.
Division of nucleus : Karyokinesis :: Division of cytoplasm :: ………..
Answer:
Cytokinesis.
Write definitions:
Question 1.
Gluconeogenesis.
Answer:
Gluconeogenesis: Formation of glucose through non-carbohydrate sources such a protein is called gluconeogenesis.
Question 2.
Fermentation.
Answer:
Fermentation: Conversion of pyruvic acid produced in the process of glycolysis into other organic acids or alcohol with the help of some enzymes is called fermentation.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Products formed after complete oxidation of acetyl part present in the molecule of acetyl-coenzyme-A.
Answer:
Molecules of CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 and ATP.
Question 2.
Place where electron transfer chain reaction take place.
Answer:
Mitochondria present in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Question 3.
Two co-enzymes involved in cellular respiration.
Answer:
NAD → Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide and FAD Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide.
Question 4.
Scientist who discovered the TCA cycle.
Answer:
Sir Hans Krebs.
![]()
Question 5.
Steps of anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
Glycolysis and fermentation.
Question 6.
Most abundantly found protein nature.
Answer:
An enzyme RUBISCO present in plant chloroplasts.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
We feel exhausted after exercising.
Answer:
- When we undertake constant exercises, there may be shortage of oxygen for the cells.
- Therefore, our muscles and other tissues perform anaerobic respiration in such condition.
- In this process, lactic acid is formed.
- Molecules of ATP produced in oxidation of food are also much less.
- Thus, there is less energy in the body and accumulation of lactic acid too. All this brings about a feeling of exhaustion.
Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
Write the forms to which the following food materials are converted after digestion:
(a) Milk (b) Potato (c) Oil (d) Chapati.
Answer:
(a) Milk: Proteins (casein) are converted into amino acids. Lactose sugar is converted into glucose. Lipids are converted into fatty acids and glycerol.
(b) Potato: Carbohydrates (starch) are converted into glucose.
(c) Oil: Lipids are converted into fatty acids and glycerol.
(d) Chapati: Carbohydrates (starch) are converted into glucose.
Question 2.
On which two levels does respiration take place in living organisms?
Answer:
- In organism respiration takes place at two levels, viz. Body level and Cellular level.
- Respiration at body level: The exchange of respiratory gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide between body and surrounding is called respiration at body level.
- Cellular respiration: Oxidation of nutrients inside the cell with or without oxygen is called cellular respiration.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions: (July 2019)
(a) Write main types of vitamins.
Answer:
A, B, C, D, E and K are main types of vitamins.
(b) Name water soluble vitamins.
Answer:
Water soluble vitamins are B and C.
(c) Name fat soluble vitamins.
Answer:
Fat soluble vitamins are A, D, E and K.
Question 4.
Answer the following questions:
(a) Why some living organisms have to perform anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
Some bacteria and lower organisms do not live in the presence of oxygen. In order to survive, they have to perform anaerobic respiration. Sometimes, muscle cells and erythrocytes also perform anaerobic respiration when there is lack of enough oxygen.
(b) Give two examples of such living organisms.
Answer:
Yeast and bacteria.
(c) What are the two steps of anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
Glycolysis and fermentation are the two steps of anaerobic respiration.
Question 5.
Which is the energy currency of the cell? Explain it in detail.
Answer:
- ATP or Adenosine triphosphate is the ‘energy currency’ of the cell.
- Chemical composition of ATP is as follows: it is a triphosphate molecule having adenosine ribonucleoside. The nitrogenous compound-adenine, pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups are present in ATP.
- In this energy-rich molecule the energy remains trapped in the bonds by which phosphate groups are attached to each other.
- ATP molecules are stored in the cells. As per the need, energy is derived by breaking the phosphate bond of ATP.
- During cellular respiration, the oxidation of glucose yields 38 molecules of ATP. Whenever required they are consumed to liberate energy.
![]()
Question 6.
How is energy obtained during starvation or hunger?
Answer:
- Due to starvation or hunger, there is less supply of nutrients and energy to the body. In such condition, the stored carbohydrates in the body also deplete.
- In such condition, fats and proteins present in the body are utilized.
- Fats or lipids are converted into fatty acids and proteins are broken down to amino acids.
- Fatty acids and amino acids both are converted to acetyl-coenzyme-A.
- Acetyl-coenzyme-A can undergo series of cyclic reactions and oxidised to liberate energy in the form of ATP molecules.
Question 7.
Why glycolysis is also called EMP pathway?
Answer:
Process of glycolysis was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jacob Pamas along with their colleagues. They performed experiments on muscles to understand glycolysis. Hence, in their honour, glycolysis is also edited Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway or EMP pathway.
Question 8.
How are proteins obtained? What are the components of the proteins?
Answer:
- Protein, is a macromolecule which is formed by amino acids.
- When digestion of protein takes place, it forms different amino acids. These amino acids are transported to each cell by blood circulation.
- By protein synthesis, these amino acids are again used to make different kinds of proteins which our body needs.
- Animal proteins are said to be ‘first class proteins’ as they contain good quality amino acids.
- 4 Kcal/gm energy is obtained from the proteins.
Question 9.
Where and in which forms the amino acids formed after digestion of food are used in the body?
Answer:
(1) After digestion of proteins, amino acids are formed. These amino acids are used to synthesise proteins in different forms. e.g.
- In blood-Haemoglobin and antibodies are formed.
- In skin – Melanin and keratin are formed.
- In bones – Ossein is formed.
- In pancreas-Insulin and trypsin are synthesized.
- Pituitary and all other glands produce hormones by utilising amino acids.
- In muscles – Actin and myosin are formed.
- In all the cells, plasma membrane is formed by proteins. All enzymes are also synthesised using the amino acids.
![]()
Question 10.
What are fatty acids? What are the different uses of fatty acids ?
Answer:
(1) The fatty acids are components of the lipids. When lipids are digested, it forms fatty acids and alcohol (glycerol).
(2) There are certain chemical bonds between fatty acids and alcohol.
(3) Fatty acids are very essential for the health.
(4) After digestion, fatty acids are absorbed into the blood and transported to the cells.
(5) Different types of cells produce their own substances from these fatty acids.
E.g. (a) Plasma membrane is produced from phospholipids.
(b) Hormones like testosterone, progesterone, estrogen, aldosterone are produced from fatty acids.
(c) The axonal coverings around the neurons are also made from fatty acids.
Give explanations for the following statements:
Question 1.
After complete oxidation of a glucose molecules, 38 number of ATP molecules are formed.
Answer:
I. Glycolysis: No. of ATP molecules formed = 4
No. of ATP molecules used = 2
II. Krebs cycle : No. of ATP molecules formed = 2
III. ETC Reaction :
NADH2: 10 NAD2 x 3 ATP = 30 ATP
FADH2 : 2 FADH2 x 2 ATP = 4 ATP
Total ATP molecules produced = (4+2+34)
= 40 ATP
ATP molecules used = 2 ATP
Therefore, total ATP molecules = 38 ATP
Question 2.
At the end of glycolysis, pyruvate molecules are obtained.
Answer:
The process of glycolysis takes place m the cytoplasm of the cell. One molecule of glucose is gradually oxidized step by step forming two molecules of each pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water. Of these, pyruvate or pyruvic acid takes part in the further reactions.
Question 3.
Genetic recombination occurs in pachytene phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
Answer:
In prophase of meiosis I there are total 5 stages. Of these in pachytene the process of crossing over takes place between homologous chromosomes as chromosomes come near each other forming synapsis.
Question 4.
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in metaphase of mitosis.
Answer:
In mitosis, the metaphase is the stage when dividing chromosomes lie on the equatorial plane of the cell. They are later pulled by the spindle fibres to the opposite poles.
Question 5.
For formation of plasma membrane, phospholipid molecules are necessary.
Answer:
Upon the digestion of fats, fatty acids and glycerol are formed. The fatty acids can be converted into phospholipid which are essential molecules for development of plasma membrane.
![]()
Question 6.
Our muscle cells perform anaerobic type of respiration during exercise.
Answer:
When the proportion of oxygen is less, then the cells switch over to anaerobic respiration. When we are exercising there is increased demand of oxygen for muscle cells. If this is not fulfilled, they perform anaerobic respiration during exercise.
Question 7.
Excess of carbohydrates are stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Answer:
The carbohydrates which are not used to produce energy cannot be stored in the body in the form of glucose. This glucose is therefore converted into complex compound called glycogen. Glycogen is stored in muscles and liver.
Complete the paragraph by choosing the appropriate words given in the brackets:
Question 1.
(gamete, crossing over, haploid, Meiosis-II, meiosis-I, diploid)
……….. is just like mitosis. In this stage, the two haploid daughter cells formed in ……… undergo division by separation of recombined sister chromatids and four ……….. daughter cells are formed. Process of …………… production and spore formation occurs by meiosis. In this type of cell division, four haploid (n) daughter cells are formed from one ……….. cell. During this cell division, ………… occurs between, the homologous chromosomes.
Answer:
Meiosis-II is just like mitosis. In this stage, the two haploid daughter cells formed in meiosis-I undergo division by separation of recombined sister chromatids and four haploid daughter cells are formed. Process of gamete production and spore formation occurs by meiosis. In this type of cell division, four haploid (n) daughter cells are formed from one diploid cell. During this cell division, crossing over occurs between the homologous chromosomes.
Question 2.
(external, inhalation, alveolar, breathing, respiration, exhalation)
Release of energy from the assimilated food is called …………. Inhalation and exhalation is called …….. When ……….. is done, air enters the lungs. The oxygen from this air enters the blood while carbon dioxide from the blood exits from the blood. Through exhalation, CO2 is given out. This gaseous exchange occurs through ……….. membrane. This is called ………….. respiration. The RBCs carry oxygen to every cell.
Answer:
Release of energy from the assimilated food is called respiration. Inhalation and exhalation is called breathing. When inhalation is done, air enters the lungs. The oxygen from this air enters the blood while carbon dioxide from the blood exits from the blood. Through exhalation, CO2 is given out. This gaseous exchange occurs through alveolar membrane. This is called external respiration. The RBCs carry oxygen to every cell.
Read the paragraph and answer the questions given below:
1. Dietary fibre — found mainly in fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes — is probably best known for its ability to prevent or relieve constipation. But foods containing fibre can provide other health benefits as well, such as helping to maintain a healthy weight and lowering your risk of diabetes, heart disease and some types of cancer. Dietary fibre, also known as roughage or bulk, includes the parts of plant foods your body can’t digest or absorb. Unlike other food components, such as fats, proteins or carbohydrates — which your body breaks down and absorbs — fibre isn’t digested by your body. Instead, it passes relatively intact through your stomach, small intestine and colon and out of your body.
Questions and Answers :
Question 1.
Which food items provide rich fibre content?
Answer:
Fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes give rich amount of dietary fibre.
Question 2.
Enlist the advantages of fibres in diet.
Answer:
Fibres help to relieve constipation and help in maintaining a healthy weight and lowering risk of diabetes, heart disease and some types of cancer.
Question 3.
Are fibres digested in the body?
Answer:
No, fibres are not digested in the body but are passed on without any alteration.
Question 4.
Which is the path through which fibres pass in the digestive tract?
Answer:
Fibres pass through stomach, small intestine and colon.
Question 5.
What is a roughage?
Answer:
Roughage is the fibre content of the food which consists of plant matter which cannot be digested by the human enzymes, hence form undigested bulk matter in the faeces.
![]()
2. The substances formed by specific chemical bond between fatty acids and alcohol are called lipids. Digestion of lipids consumed by us is nothing but their conversion into fatty acids and alcohol. Fatty acids are absorbed and distributed everywhere within the body. From those fatty acids, different cells produce various substances necessary to themselves. Ex. the molecules called phospholipids which are essential for producing plasma membrane are formed from fatty acids. Besides, fatty acids are used for producing hormones like progesterone, estrogen, testosterone, aldosterone, etc. and the covering around the axons of nerve cells. We get 9 Kcal of energy per gram of lipids. Excess of lipids are stored in adipose connective tissue in the body.
Questions and Answers:
Question 1.
Define lipids.
Answer:
Lipids are molecules formed of fatty acids and glycerol (alcohol) which have specific bonds between them.
Question 2.
What happens to fats that are eaten in excess?
Answer:
When excess of fats are eaten, they are stored in adipose connective tissue.
Question 3.
Which hormones regulating reproductive functions are produced from fatty acids?
Answer:
Progesterone, estrogen and testosterone are the reproductive hormones produced from fatty acids.
Question 4.
How is plasma membrane of the cells formed?
Answer:
The digested fats are absorbed in the form of fatty acids. These are converted back to phospholipids from which plasma membrane of cells is formed.
Question 5.
What happens to lipids when their digestion is completed? How much energy do they provide?
Answer:
After complete digestion of lipids they are converted to fatty acids and glycerol. 1 gm of lipid provides 9 kcal of energy.
Diagram based questions:
Question 1.
Draw a neat diagram of the structure of chromosome and label the parts:
(a) Centromere (b) p-arm (March 2019)
Answer:
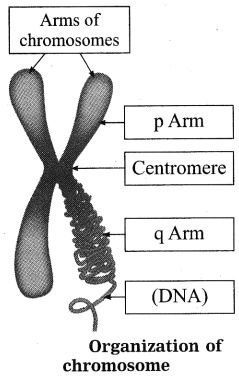
Question 2.
Sketch and label the diagram to show ATP – the energy currency of the cell.
Answer:
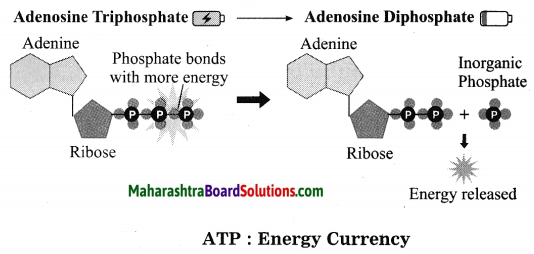
![]()
Question 3.
Mitochondria and Krebs cycle:
Answer:
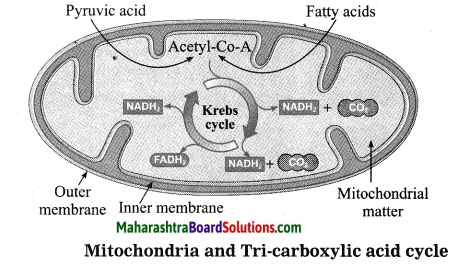
(a) Which co-enzymes are shown in the diagram?
Answer:
The co-enzymes NADH2 and FADH2 are shown in the above diagram.
(b) Which chemical reaction takes place in the mitochondria? Which molecules are produced in this reaction?
Answer:
The chemical reaction that takes place in the mitochondria is called Electronic Transport Chain reaction. The molecules of H2O, carbon dioxide and energy in the form of ATP are produced in this reaction.
Question 4.
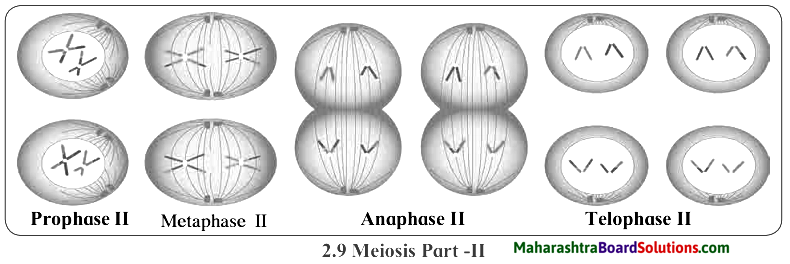
Observe the diagrams 2.8 and 2.9 given on the Textbook page no. 19 and answer the following questions.
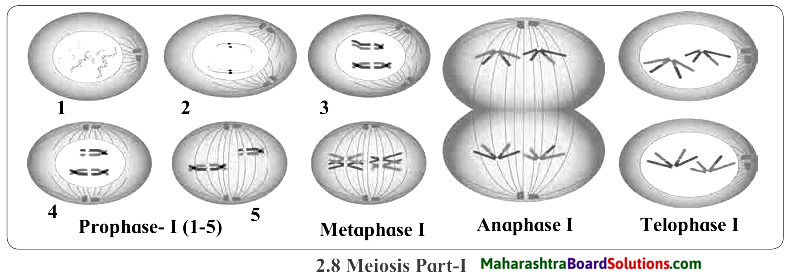
(a) Which peculiarity do you observe in the figure of Metaphase-I of meiosis ?
Answer:
The chromosomes are seen lying on the equatorial plane in the metaphase-I of meiosis.
(b) What is the important difference between Telophase-I and Telophase-II of meiosis?
Answer:
In figure of Telophase-I the diploid chromosomes are seen in two daughter cells. In Telophase-II four daughter cells are seen with haploid chromosomes in them.
(c) Which figure shows phenomena of crossing over?
Answer:
The third figure of Prophase-I shows phenomena of crossing over.
![]()
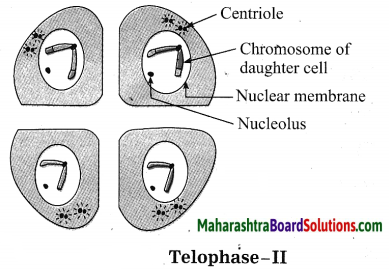
Question 5.
Label the diagram below? Which phase of cell division is seen in the above diagram?
Answer:
The above figure shows Telophase-II of Meiosis-II.
Question 6.
Observe and label the diagram: (Text Book Page No. 13)
Answer:
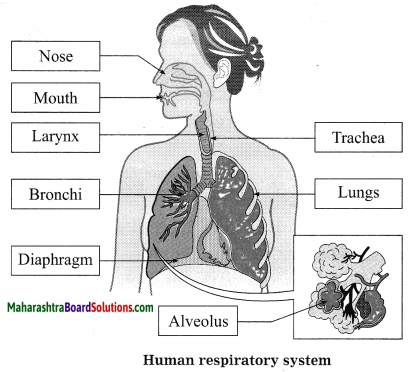
Activity based questions:
Question 1.
Complete the following chart and state which process of energy production it represents: (March 2019)
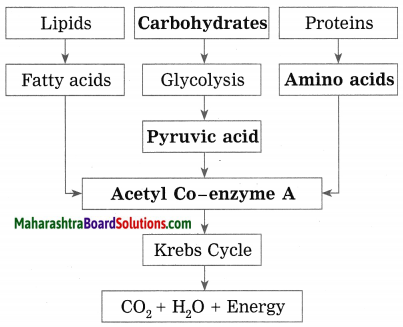
Answer:
The chart shows process of energy production through aerobic respiration of carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
(Answers to the blanks in chart are given in bold.)
![]()
Project:
Project 1.
Use of ICT: (Text Book Page No. 20)
Collect videos and photographs of different life processes in living organisms. Prepare a presentation and present it on the occasion of science exhibition.
Project 2.
Books are my friend: (Text Book Page No. 20)
Read different Encyclopaedias of technical terms in biology and anatomy and other reference books.
10th Std Science Part 2 Questions And Answers:
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 1 Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part – 2 Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Environmental management Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Towards Green Energy Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Animal Classification Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Introduction to Microbiology Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Cell Biology and Biotechnology Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Social health Class 10 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 10 Questions And Answers