Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Maths Solutions covers the Practice Set 1.4 8th Std Maths Answers Solutions Chapter 1 Rational and Irrational Numbers.
Rational and Irrational Numbers Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Practice Set 1.4 Solutions Maharashtra Board
Std 8 Maths Practice Set 1.4 Chapter 1 Solutions Answers
Question 1.
The number √2 is shown on a number line. Steps are given to show √3 on the number line using √2. Fill in the boxes properly and complete the activity.
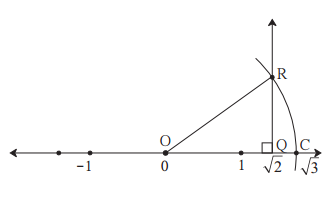
The point Q on the number line shows the number ……….
A line perpendicular to the number line is drawn through the point Q. Point R is at unit distance from Q on the line.
Right angled ∆OQR is obtained by drawing seg OR.
l(OQ) = √2, l(QR) = 1
∴By Pythagoras theorem,
[l(OR)]² = [l(OQ)]² + [l(QR)]²
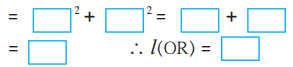
Draw an arc with centre O and radius OR. Mark the point of intersection of the line and the arc as C. The point C shows the number √3
Solution:
The point Q on the number line shows the number √2
A line perpendicular to the number line is drawn through the point Q. Point R is at unit distance from Q on the line.
Right angled ∆OQR is obtained by drawing seg OR.
l(OQ) = √2, l(QR) = 1
∴By Pythagoras theorem,
[l(OR)]² = [l(OQ)]² + [l(QR)]²
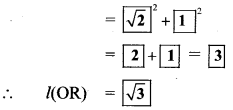
.. .[Taking square root of both sides]
Draw an arc with centre O and radius OR. Mark the point of intersection of the line and the arc as C. The point C shows the number √3.
Question 2.
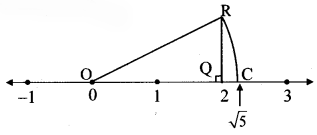
Show the number √5 on the number line.
Solution:
Draw a number line and take a point Q at 2
such that l(OQ) = 2 units.
Draw a line QR perpendicular to the number line through the point Q such that l(QR) = 1 unit.
Draw seg OR.
∆OQR formed is a right angled triangle.
By Pythagoras theorem,
[l(OR)]² = [l(OQ)]² + [l(QR)]²
= 2² + 1²
= 4 + 1
= 5
∴l(OR) = √5 units
…[Taking square root of both sides]
Draw an arc with centre O and radius OR. Mark the point of intersection of the number line and arc as C. The point C shows the number √5.
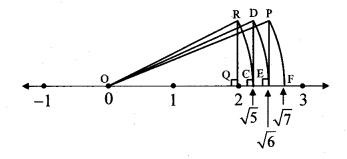
Question 3.
Show the number √7 on the number line.
Solution:
Draw a number line and take a point Q at 2 such that l(OQ) = 2 units.
Draw a line QR perpendicular to the number line through the point Q such that l(QR) = 1 unit.
Draw seg OR.
∆OQR formed is a right angled triangle.
By Pythagoras theorem,
[l(OR)]² = [l(OQ)]² + [l(QR)]²
= 2² + 1²
= 4 + 1
= 5
∴ l(OR) = √5 units
… [Taking square root of both sides]
Draw an arc with centre O and radius OR.
Mark the point of intersection of the number line and arc as C. The point C shows the number √5.
Similarly, draw a line CD perpendicular to the number line through the point C such that l(CD) = 1 unit.
By Pythagoras theorem,
l(OD) = √6 units
The point E shows the number √6 .
Similarly, draw a line EP perpendicular to the number line through the point E such that l(EP) = 1 unit.
By Pythagoras theorem,
l(OP) = √7 units
The point F shows the number √7.
Std 8 Maths Digest