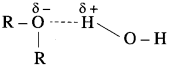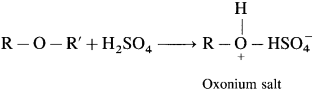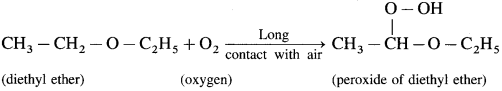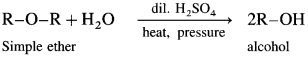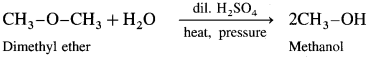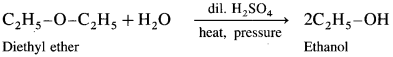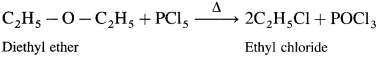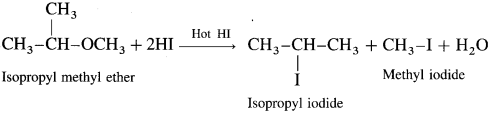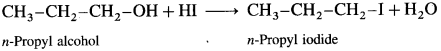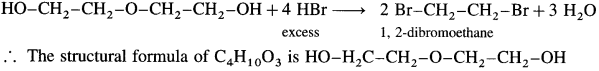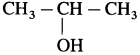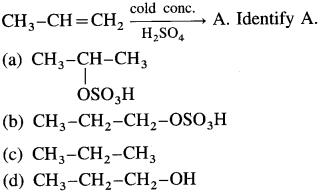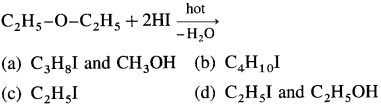Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Question 1.
What are alcohols? How are they classified?
Answer:
Alcohols are the hydroxy derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydroxyl group.
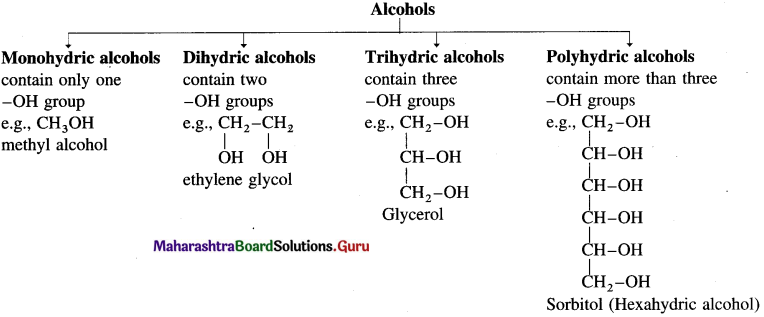
Examples : CH3 – OH methyl alcohol, CH3 – CH2 – OH ethyl alcohol. Depending on the basis of hydroxyl groups present in a molecule, alcohols are classified into monohydric, dihydric, trihydric and polyhydric alcohols.

Question 2.
What are monohydric alcohols? How are they classified?
Answer:
Alcohols having only one hydroxyl group in their molecules are called monohydric alcohols. Monohydric alcohols are classified according to the type of hybridization of the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached.
(1) Alcohols containing Csp3 – OH bond : In these alcohols -OH group is attached to a sp3 – hybridised carbon atom of alkyl group. These alcohols are represented as R-OH. They are further classified as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols in which – OH group is attached to primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms respectively.

(a) Allylic alcohols : In these alcohols -OH group is attached to a sp3 -hybridised carbon atom next to the carbon-carbon double bond i.e., to allylic carbon. Allylic alcohols may be primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
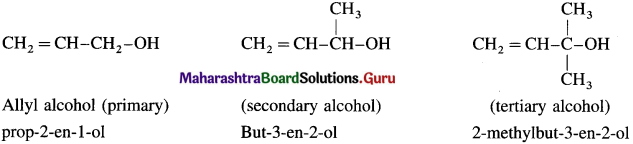
(b) Benzylic alcohols : In these alcohols -OH group is attached to a sp3 -hybridised carbon atom next to an aromatic ring. Benzylic alcohols may be primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
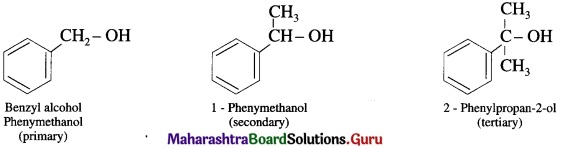
(2) Alcohols containing Csp3 – OH bond: In these alcohols -OH group is attached to a sp2 – hybridised carbon atom,
i.e., vinylic carbon. These alcohols are also called vinylic alcohols.
e.g., CH2 = CH – OH vinyl alcohol.
Question 3.
What are phenols (carbolic acids)?
Answer:
Hydroxy derivatives of aromatic hydrocarbons in which the hydroxyl group is directly attached to the aromatic ring are called phenols.
Examples:
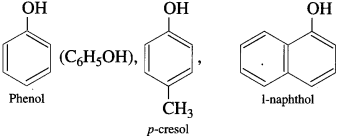
Question 4.
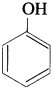
What is phenol? OR Define carbolic acid.
Answer:
The hydroxy derivative of benzene in which the OH group is directly attached to benzene ring is called phenol.
Question 5.
How are phenols classified? Give suitable examples.
Answer:
Phenols are classified on the basis of number of hydroxyl (- OH) groups present in a molecule of phenol.
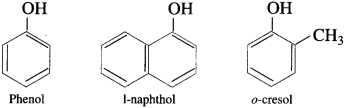
(1) Monohydric phenols : Phenols contain one hydroxyl group in their molecule.
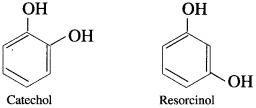
(2) Dihydric Phenols : Phenols contain two hydroxyl groups in their molecule.
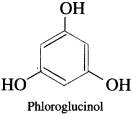
(3) Trihydric phenols : Phenols contain three hydroxyl groups in their molecule.

Question 6.
What are ethers? How are ethers classified?
Answer:
They are alkoxy derivatives of alkanes in which a hydrogen atom of alkane (R – H) is replaced by alkoxy group ( – O – R) and divalent oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl groups or two aryl groups or one alkyl and one aryl group. Ethers are organic oxides R – O – Ar, Ar – O – Ar.
E.g. R – O – R or C2H5 – O – C2H5.
Ethers are classified into two groups as follows :
(1) Simple or symmetrical ether : The ethers in which both alkyl (or aryl) groups attached to the oxygen atom are same are called simple ethers.
E.g. (R – O – R), CH3 – O – CH3, dimethyl ether; C6H5 – O -C6H5 diphenyl ether.
(2) Mixed or unsymmetrical ethers : The ethers in which the two alkyl (or aryl) groups attached to the oxygen atom are different are called mixed ethers.
E.g. (R – O – R), CH3 – O – C2H5 ethyl methyl ether; C2H5 – O – C6H5 ethyl phenyl ether.
Question 7.
What is the general formula of ethers?
Answer:
The general formula of ethers is CnH2n + 2 O. For example, dimethyl ether CH3 – O – CH3 has molecular formula C2H6O.
Common nomenclature system :
(1) In this system, monohydric alcohols (R — OH) are named as alkyl alcohols.
(2) According to the attachment of hydroxyl group to a carbon atom they are named with prefixes as n-(normal or primary) alcohol, sec-(secondary) alcohol, tert-(tertiary) alcohol.
(3) Alcohols with two hydroxyl groups are named as glycols.
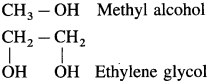
Carbinol system : In this system alcohols are considered as derivatives of methyl alcohol which is called carbinol. The alkyl group attached to the carbon carrying – OH group are named in alphabetical order. Then the suffix carbinol is added.
For example :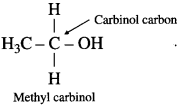
IUPAC system of nomenclature :
- In this system, alcohols are named as alkanols.
- A longest continuous chain of carbon atoms containing – OH group is chosen as a parent hydrocarbon and alcohol is considered as a hydroxy derivative of this alkane.
- The carbon atoms are numbered from a terminal carbon atom nearest to a carbon atom attached to – OH group so that the position of – OH group is indicated by the lowest locant.
- ‘e’ of an alkane is preplaced by ‘oT, giving alkanol. The number of OH groups is indicated by prefix, di, tri, etc. before ‘oT. The positions of -OH groups are indicated by appropriate locants.
- The different substituents are arranged in the alphabetical order, and their positions are indicated by proper numbers.
- Their names are hyphened on either sides except the last substituent.
- For cyclic alcohols are named by using prefix cyclo to the parent alkane considering – OH group attached to carbon atom C – 1.
Question 8.
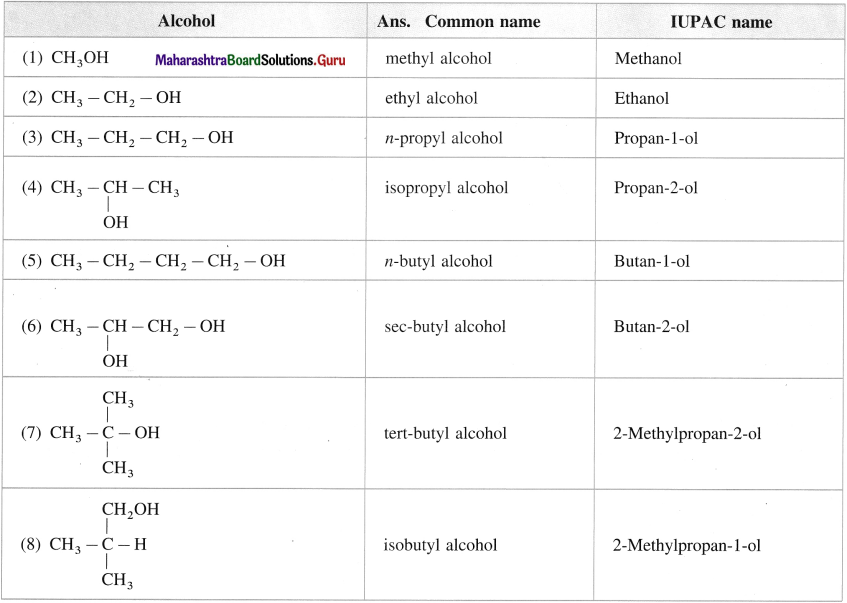
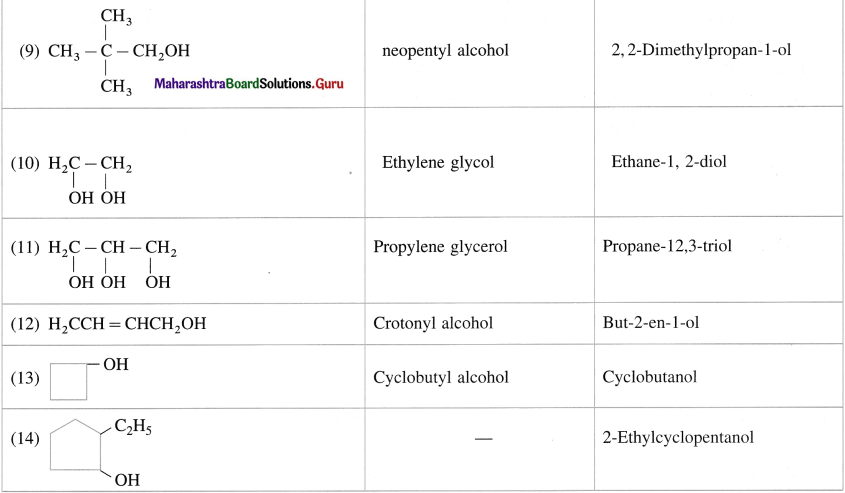
Give common and IUPAC names for the following :
Answer:

Question 9.
Classify the following alcohols as primary, secondary and tertiary and write their IUPAC names.
Answer:
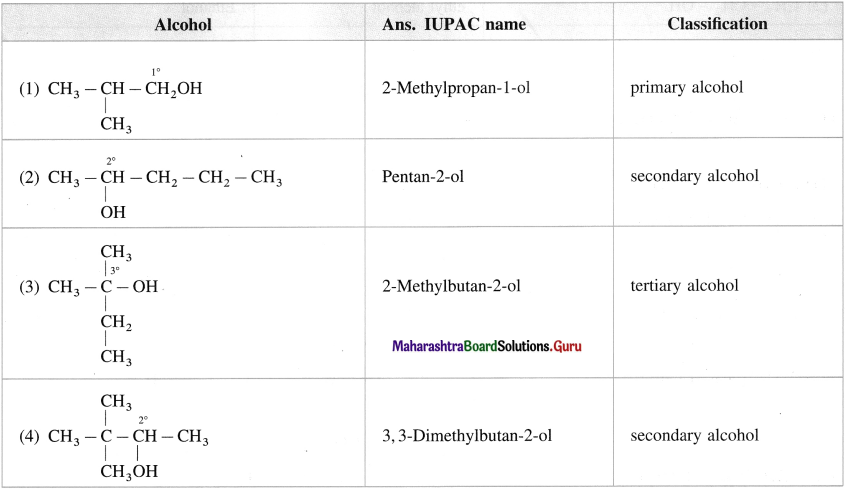
Question 10.
Give the structures of the following :
(1) Ethanol
(2) Propan-l-ol
(3) 2-Methylbutan-l-ol
(4) Pentan-3-ol
(5) Butan-2-ol
(6) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
(7) Hexan-l-ol
(8) 3-Methylpentan-3-ol
(9) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
(10) Butan-l-ol (H-Butyl alcohol)
(11) 2-Methylpropan-l-ol
(12) 2,3-Dimethylbutan-l-ol
(13) 2, 3-Dimethylbutan-2-oI
(14) 2-MethyIhexan-l-ol
(15) 2,2,3-Trimethylpentan-3-ol
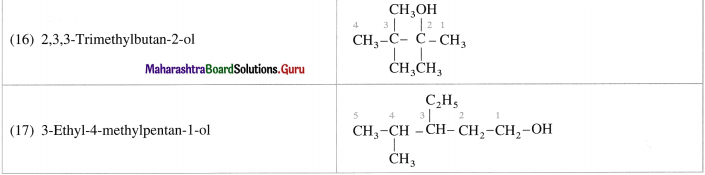
(16) 2,3,3-Trimethylbutan-2-ol
(17) 3-EthyI-4-methylpentan-l-ol.
Answer:


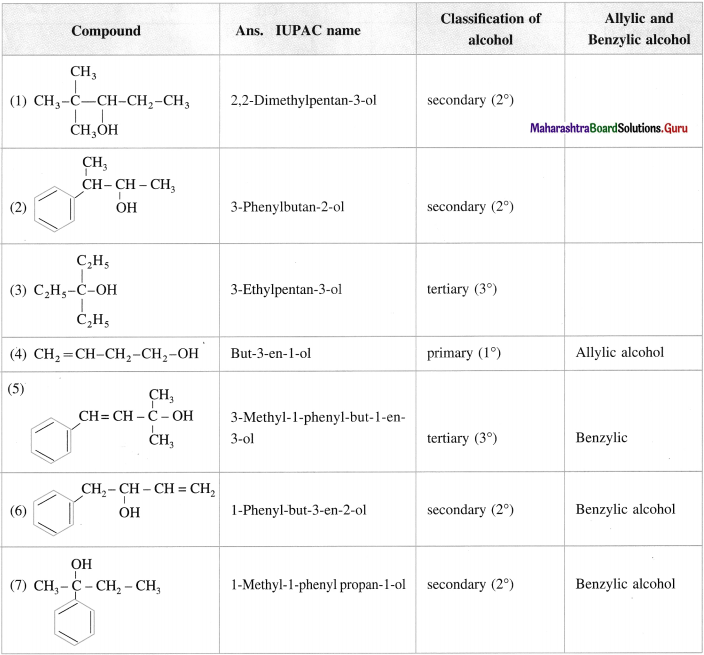
Question 11.
Give the IUPAC names of the following alcohols. Classify them as primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) alcohols. Identify allylic and benzylic alcohols amongst them.
Answer:

Question 12.
Write all the possible structural isomers of alcohol having molecular formula C6H140. Give their IUPAC names. Classify them as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. Identify optically active alcohols amongst them.
Answer:
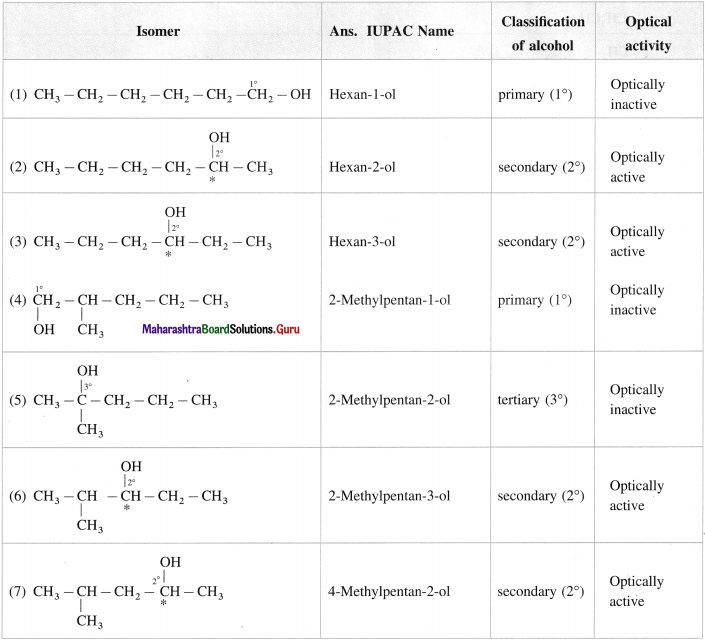
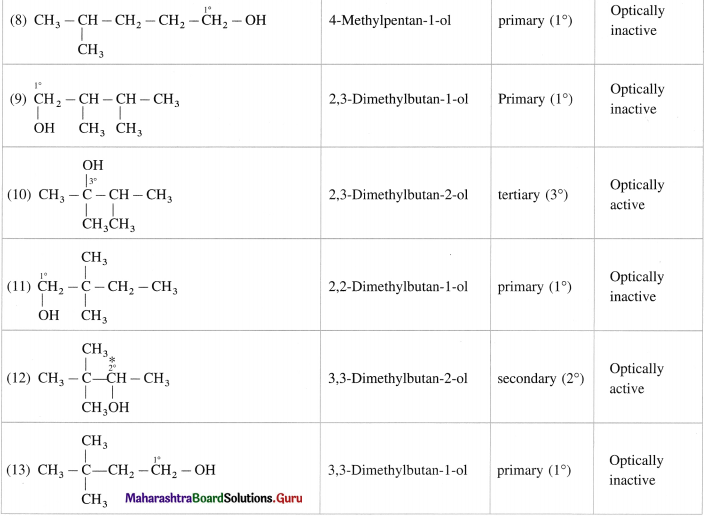
The optical isomers of C6H14O are (2), (3), (6), (7), (12).

Question 13.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
Answer:
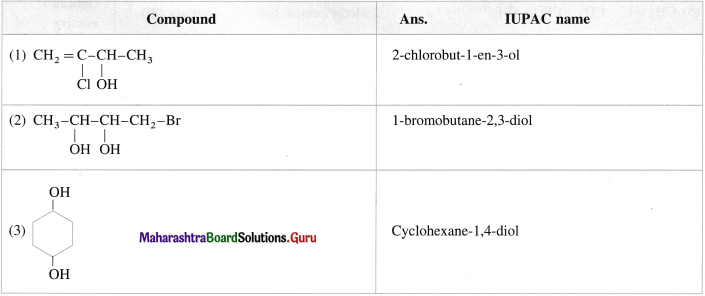
Question 14.
Write IUPAC names of following alcohols :
Answer:
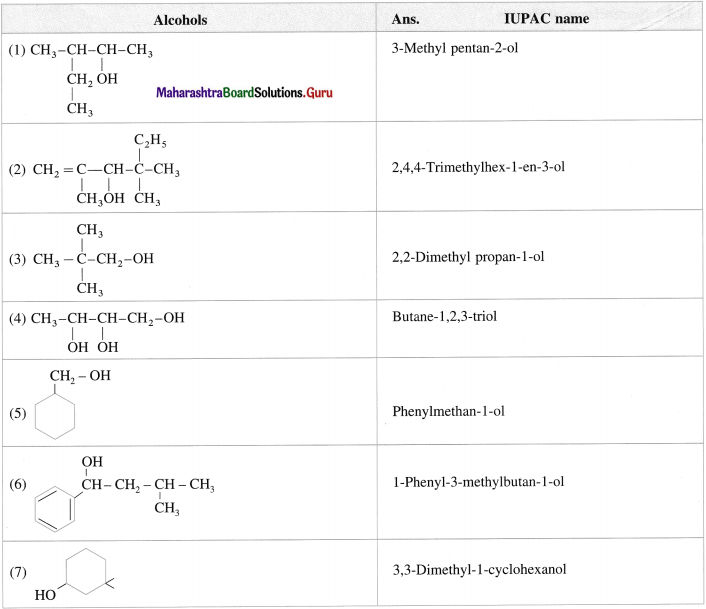
Question 15.
Write the structures of following alcohols : (1 mark each)
Answer:
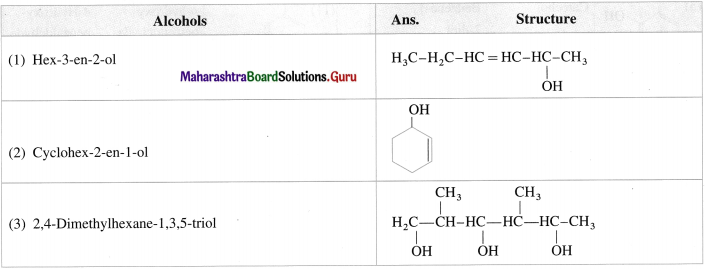
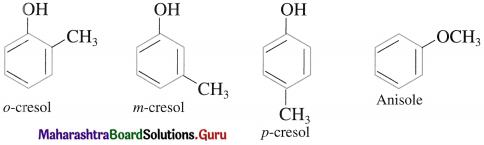
The IUPAC system name of phenol is benzenol. The common name phenol is also accepted by IUPAC. The common names have prefixes ortho, meta and para in substituted phenols. IUPAC system uses the locant 2-, 3-, 4-, etc. to indicate the positions of substituents.

Question 16.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds :
Answer:
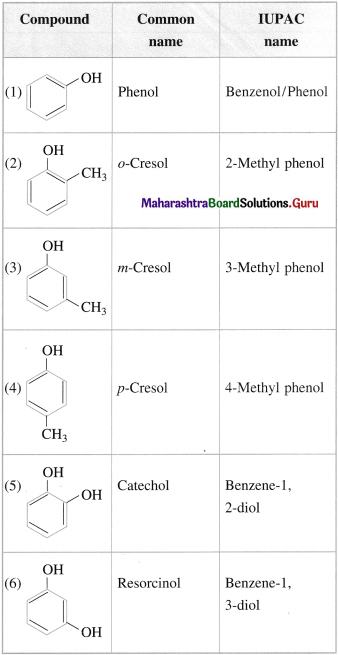
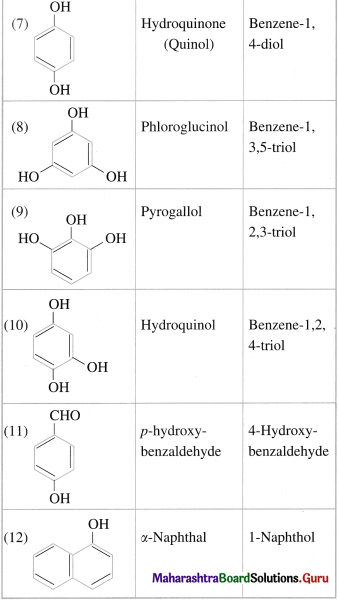
Question 17.
Write IUPAC name of the following compounds :
Answer:


Question 18.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of isomeric phenols represented by the molecular formula C8H10O.
Answer:
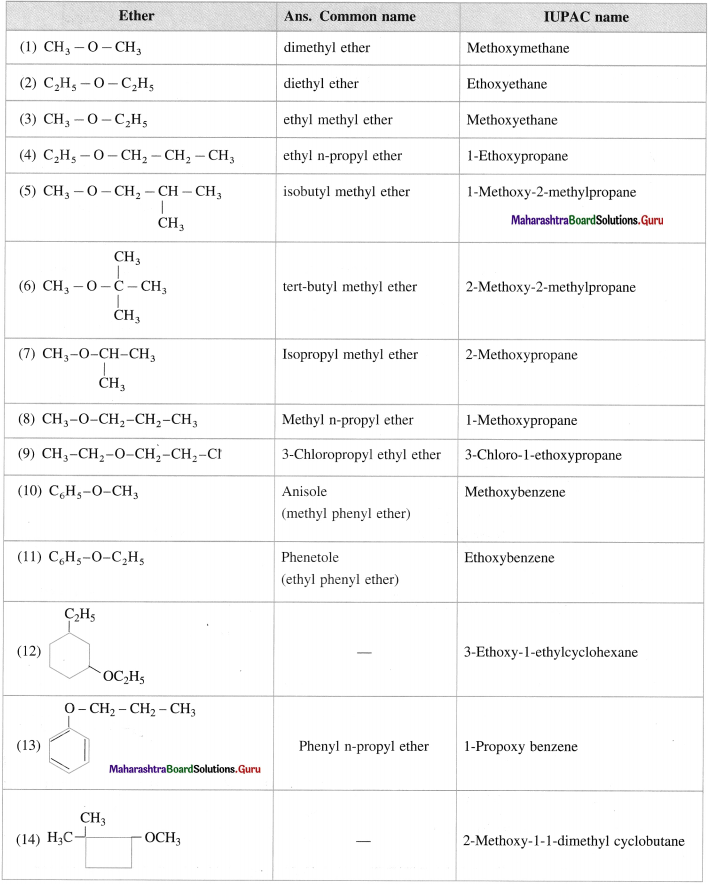
Common and IUPAC system of nomenclature of ethers
In the common system of nomenclature, the ethers are named by writing names of the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen atom in alphabetical order and word ether is added. If two alkyl groups are same, prefix di- is used. According too the IUPAC system of nomenclature, ethers are named as alkoxyalkanes. The larger alkyl group is considered to be parent alkane. The name of the smaller alkane is prefixed by the name of alkoxy group and its locant.
Question 19.
Give common name and JUPAC name for the I11owing ethers :
Answer:
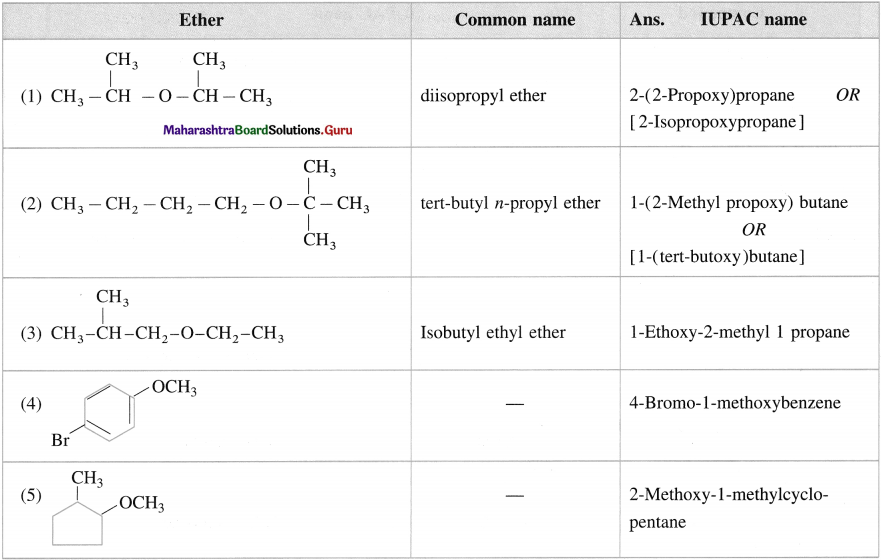
Question 20.
Give the IUPAC name of the following ethers.
Answer:
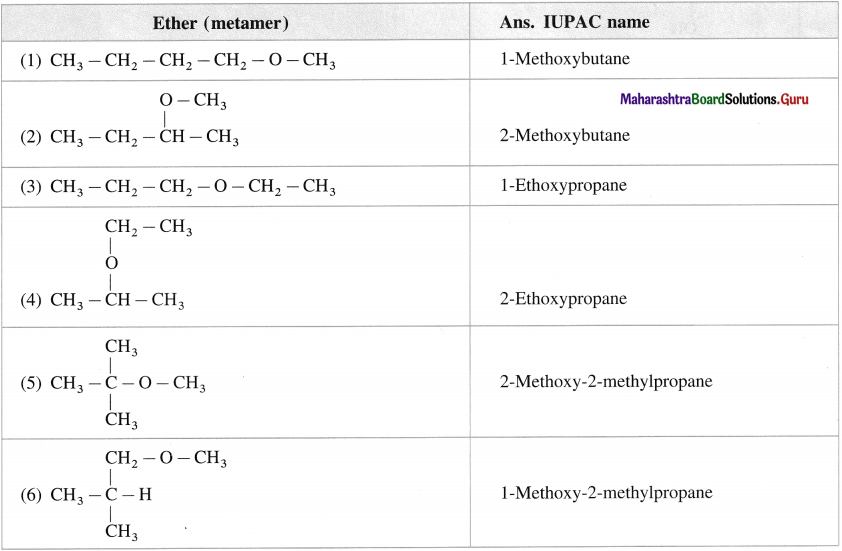
Question 23.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of all metameric ethers represented by formula C5H12O.
Answer:

Question 24.
How many isomeric compounds can be represented by formula C4H10O?
Answer:
A compound with the molecular formula C4H10O can show two functional isomers as a monohydric alcohol and ether.
Isomers of C4H10O as alcohol :

Isomers of C4H10O as ether :
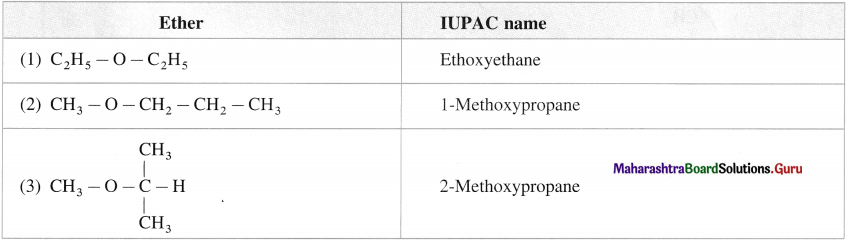
Hence, the total number of isomers of C4H10O are seven
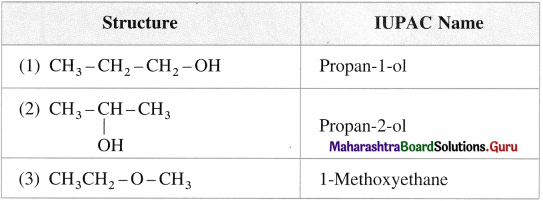
Question 25.
Write the structural formula and IUPAC names of all possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H8O.
Answer:
Possible isomers of C3H8O with structural formulae and IUPAC names :
Question 26.
Write structures of alcoholic and ether isomers of a compound having molecular formula C7H8O.
Answer:
Question 27.
How is alkyl halide converted into alcohol by using
(1) Aqueous NaOH (or KOH),
(2) Moist silver oxide?
Answer:
(1) When an alkyl halide (R – X), is boiled with aqueous NaOH (or KOH) an alcohol is obtained,
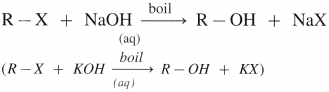
(2) Alkyl halide when heated with moist Ag2O, undergoes hydrolysis and forms an alcohol.

Question 28.
How are following compounds prepared by hydrolysis of alkyl halides
(1) Ethanol
(2) Isopropyl alcohol
(3) tert-butyl alcohol
(4) methyl alcohol
(5) butan-2-ol?
Answer:
(1) Ethanol When ethyl bromide (bromoethane) is refluxed with aqueous potassium hydroxide, ethyl alcohol is formed. The reaction is called a hydrolysis reaction.
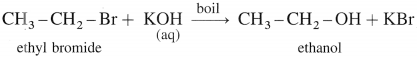
(2) Isopropyl alcohol : When isopropyl bromide (2-bromopropane) is boiled with aqueous potassium hydroxide, isopropyl alcohol is formed.
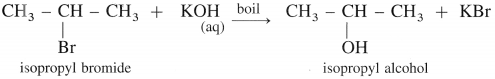
(3) Tert-butyl alcohol : When tert-butyl chloride is refluxed with aqueous potassium hydroxide, tert-butyl alcohol is formed.
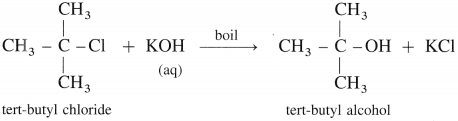
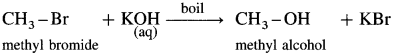
(4) Methyl alcohol : When methyl bromide (bromomethane) is heated with aq KOH, it is hydrolysed to methyl alcohol (methanol).
(5) Butan-2-ol : When 2-Chlorobutane is boiled with aqueous KOH, Butan-2-ol is obtained.
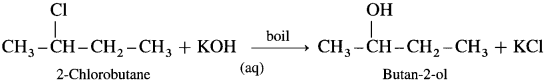

Question 29.
How are following compounds prepared from alkyl halides using moist silver oxide?
(1) Ethanol
(2) Propan-2-ol.
Answer: ‘
(1) Bromoethane (C2H5Br) when boiled with moist Ag2O undergoes hydrolysis and forms C2H5OH.
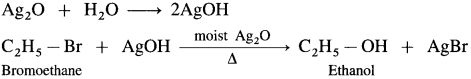
(2) When 2-chloropropane is boiled with moist Ag20, propan-2-ol is formed.

Question 30.
What is hydration of alkenes or olefins? How is it carried out? Explain with an example.
OR
How are alcohols prepared from alkenes?
Answer:
The addition of a water molecule across the double bond in an alkene is called hydration of alkenes or olefins.

Hydration does not take place directly. It is carried out by passing an alkene through cold and concentrated H2SO4 which forms deliquescent solid, alkyl hydrogen sulphate, which when boiled with water forms an alcohol.

Question 31.
How are the following compounds obtained by hydration of alkenes :
(1) Ethyl alcohol
(2) Isopropyl alcohol
(3) Tert-butyl alcohol?
Answer:
(1) When ethene is passed through cold 98 % H2SO4, ethyl hydrogen sulphate is formed, which on heating with water gives ethanol.
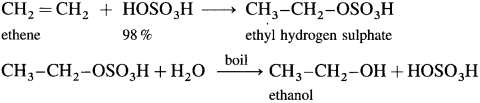
(2) Propene with cold 80% H2SO4 gives isopropyl hydrogen sulphate which further on boiling with water gives isopropyl alcohol.
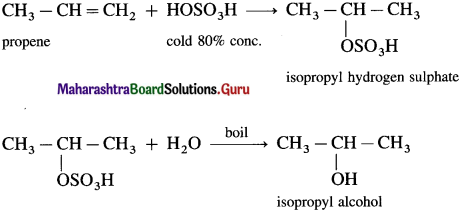
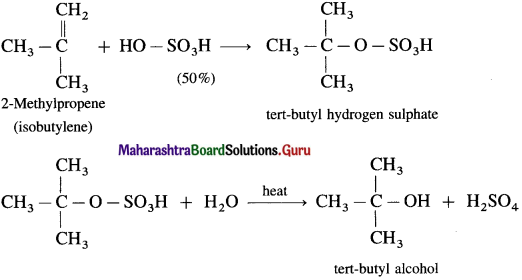
(3) 2-Methylpropene (isobutylene) directly reacts with 50 % H2SO4 giving tert-butyl hydrogen sulphate, which when heated with water gives tert-butyl alcohol.
Question 32.
Identify C in the following reaction.
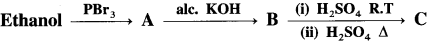
Answer:
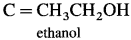

Question 33.
Explain hydroboration-oxidation of alkene.
Answer:
When diborane is treated with alkene in the presence of tetrahydrofuran (THF) solvent, an addition product trialkyl borane is formed. Trialkyl borane is then oxidised with alkaline peroxide forms primary alcohol.

The addition of diborane to the double bond takes place in such a way that the boron gots attached to the less substituted carbon. The overall reaction gives Anti-Markovnikov’s product from unsymmetrical alkenes.
Question 34.
How is propan-l-ol prepared using diborane?
Answer:
When diborane is treated with propene, in the presence of THF an addition product tripropyl borane is formed. Tripropyl borane is then oxidised to propan-l-ol using hydrogen peroxide in the presence of dil NaOH.
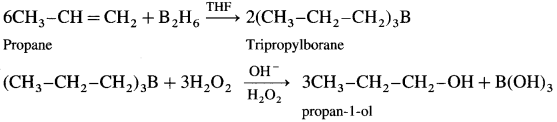
The addition of diborane to the double bond takes place in such a way that the boron gets attached to the less substituted carbon. The alcohol formed by the addition of water to the alkene in a way opposite to the Markovnikov’s rule.
Question 35.
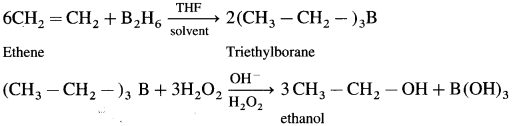
How is ethanol prepared using diborane?
Answer:
When diborane is treated with ethene in the presence of THF an addition product triethylborane is formed.Triethylborane is then oxidised with hydrogen peroxide to form ethyl alcohol.
Question 36.
Predict the major product when 2-methylbut-2-ene is converted into an alcohol in each of the following methods :
(1) acid catalysed hydration
(2) hydroboration by BH3 – THF complex.
Answer:
(1) Acid catalysed hydration :

(2) Hydroboration by BH3 – THF complex :
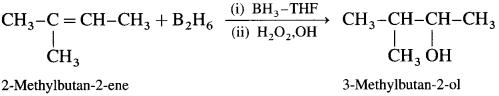
Question 37.
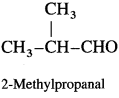
How are alcohols prepared from aldehydes and ketones?
OR
How are the following compounds obtained using Ni as catalyst and at high temperature
(1) Ethanol
(2) Propan-2-ol?
Answer:
Aldehyde and ketones are carbonyl compounds containing a carbonyl group C = O. The reduction of the carbonyl group gives an alcohol.
(1) Primary alcohols are prepared by the reduction of aldehydes.
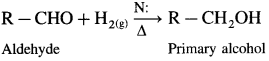
Example : When acetaldehyde is reduced with hydrogen in the presence of nickel as catalyst and at high temperature, ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is obtained.
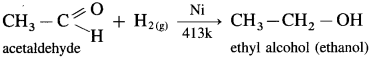
(2) Secondary alcohols are prepared by the reduction of ketones.
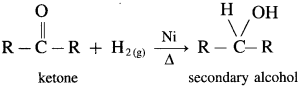
Example : When acetone is reduced with hydrogen in the presence of nickel as catalyst and at high temperature, isopropyl alcohol (propan-2-ol) is obtained.
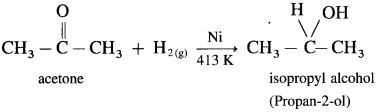

Question 38.
How will you convert carboxylic acids and esters to primary alcohols? Explain with suitable examples.
Answer:
Carboxylic acids and esters are not easily reduced by catalytic hydrogenation or by NaBH4. However, relatively more reactive and an expensive LiAlH4 is used to convert carboxylic acids and esters to primary alcohols. When acetic acid is reduced in the presence of LiAlH4 and followed by their acid hydrolysis, ethyl alcohol is obtained.
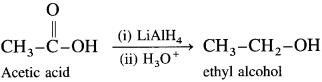
When ethyl acetate is reduced in the presence of LiA1H4 and followed by their acid hydrolysis. n-propyl alcohol and ethyl alcohol is obtained.
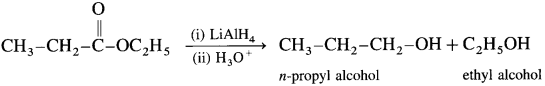
[Since LiA1H4 is an expensive reagent. commercially acids are reduced to alcohol by converting them to esters, followed by their reduction. (catalytic hydrogenation)
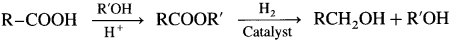
Question 39.
How is Crotoflyl alcohol obtained from crotonaldehyde?
Answer:
When crotonaldehyde is reduced in the presence of lithium aluminium hydride, the produc obtained is hydrolysed to give crotonyl alcohol. Here. LiA1H4 does not reduce carbon-carbon double bond.

Question 40.
WrIte the structure of aldehyde that yields
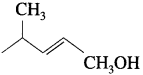
Answer:
The structure of aldehyde:
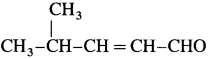
Question 41.
How are the following compounds prepared using Grignard reagent
(1) Ethanol
(2) Propan-l-ol
(3) Propan-2-ol
(4) 2-Methyl propan-2-ol?|
Answer:
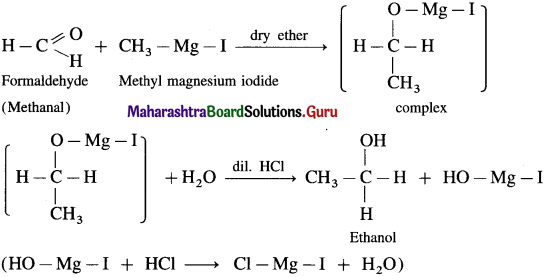
(1) Ethanol : Formaldehyde on reaction with Grignard reagent, CH3 – Mg – I in dry ether forms a complex which on further hydrolysis with dilute HCl forms ethanol.
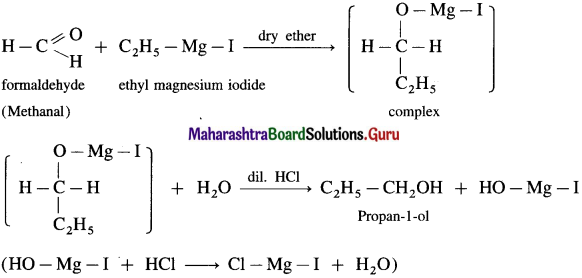
(2) Propanol-l-ol : Formaldehyde on reaction with Grignard reagent, C2H5 – Mg – I in dry ether forms a complex which on further hydrolysis with dilute HC1 forms Propan-l-ol.
(3) Propan-2-ol : An acetaldehyde on reaction with Grignard reagent in dry ether forms a complex which on further hydrolysis with dilute acid HC1, forms propan-2-ol.

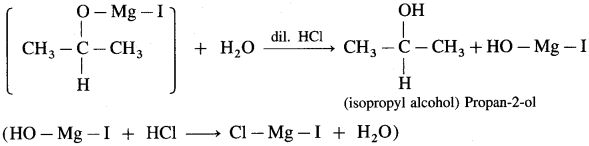
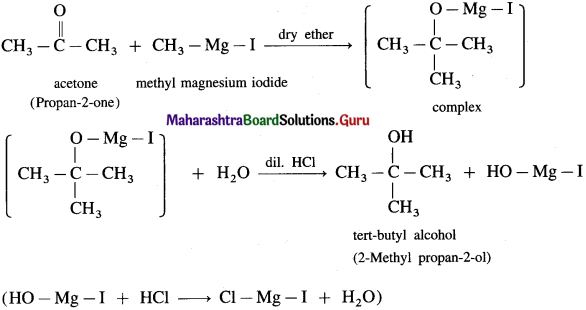
(4) 2-Methyl propan-2-ol : Acetone on reaction with Grignard reagent in dry ether forms a complex which on further hydrolysis with dilute acid HCl, forms a tertiary butyl alcohol.

Question 42.
Give a mechanism of following reaction.
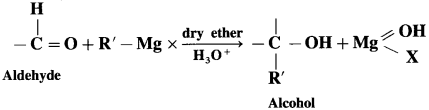
Answer:
Grignand reagent reacts with aldehyde or ketone to form an adduct which on hydrolysis with dil. acid gives the corresponding alcohol.
In the first step, the nucleophilic addition of Grigard reagent to the carbonyl group resulting in the formation of an adduct, which on hydrolysis yields an alcohol.

Question 43.
Write the structure of carbonyl compounds that can be converted by reduction methods into following alcohols :

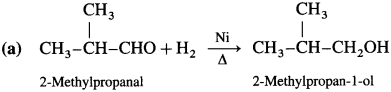
Answer:
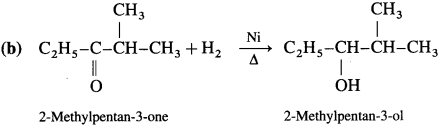
Answer:
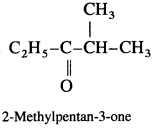
Question 44.
Using Grignard reagent, suggest synthesis of following alcohols from aldehydes or ketones. Wherever possible, suggest more than one combination.
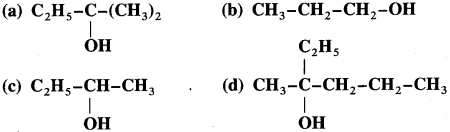
Answer:
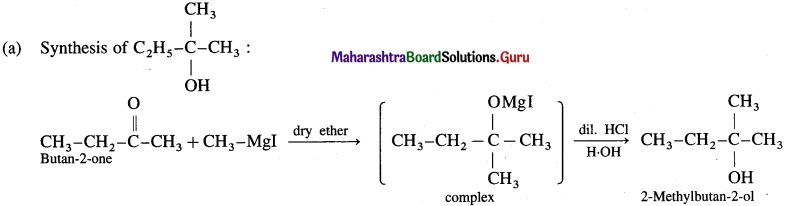
(b) Synthesis of propan- 1-01:
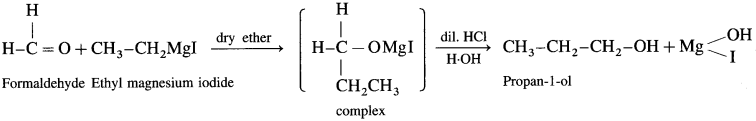
(c) Synthesis of butan-2-ol:
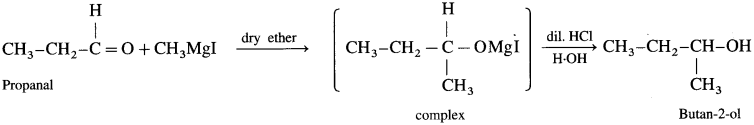
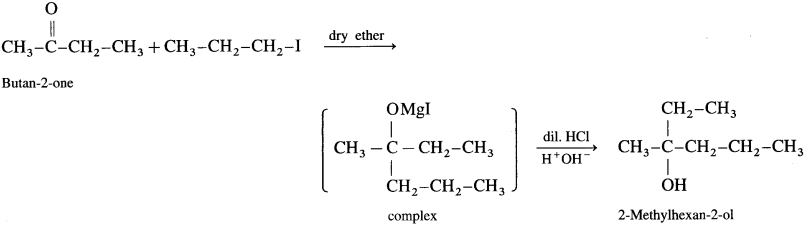
(d) Synthesis of 2-methylhexan-2-oI:

Question 45.
How will you obtain butan-2-ol from
(1) Propanal
(2) butan-2-one
(3) but-2-ene?
Answer:
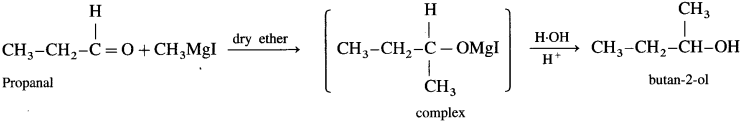
(1) Propanal : When propanal is treated with methyl magnesium iodide in the presence of dry ether, a complex is formed, which on acid hydrolysis butan 2-ol is obtained.
(2) Butan-2-one: When butan-2-one is hydrogenated at 413 K in the presence of catalyst finely divided nickel butan-2-ol is obtained.

(3) But-2-ene : When but-2-ene is passed through cold concentrated sulphuric acid, isobutyl hydrogen sulphate is formed. Isobutyl hydrogen sulphate on heating with water gives butan-2-ol.

Question 46.
Write the structure of aldehyde, carboxylic acid and ester that yield the following alcohol.
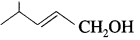
Answer:

Question 47.
How will you prepare?
(1) 2-Ntethylbutan-1-oI from an alkene.
Answer:
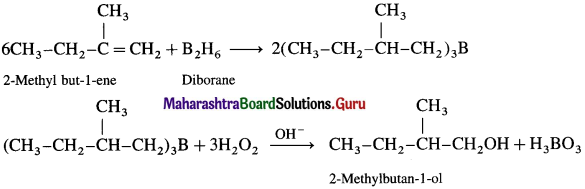
(2) CycIoheyImethanoI from a Grignard reagent.
Answer:
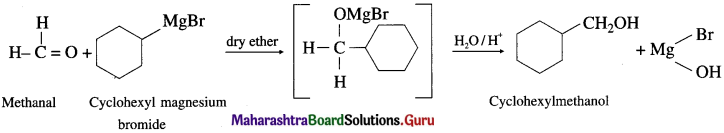
(3) 1-Phenyl ethanol from acelaldehyde.
Answer:


Question 48.
How are following conversions brought about?
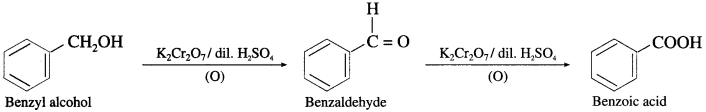
(1) Benzyl chloride to benzyl alcohol. (NCERT)
OR
How is benzyl alcohol prepared from benzyl chloride?
Answer:

(2) Benzyl alcohol to Benzoic acid.
Answer:
(3) 1-Ethyl cyclohexanol from cyclohexanone.
Answer:
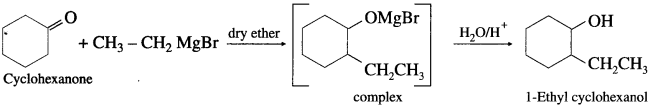
Question 49.
How is phenol (carbolic acid) prepared from chlorobenzene (Dow’s process)? OR
Write chemical reaction for the preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene.
Answer:
Preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene (Dow’s process) : Chlorobenzene is fused with NaOH at about 623 K under a pressure of about 150 atmospheres (1.5 x 107 Nm-2), when sodium phenoxide is formed. Sodium phenoxide is acidified with dil.HCl to obtain phenol.

Question 51.
How is phenol (carbolic acid) prepared from benzene sulphonic acid?
Answer:
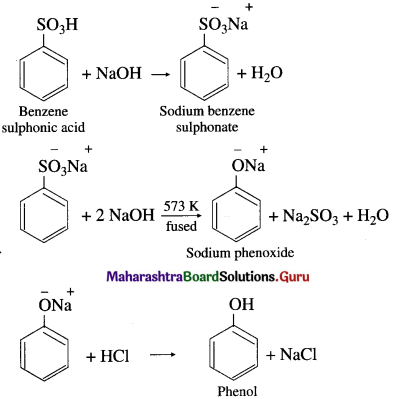
Preparation of phenol from benzene sulphonic acid : Benzene sulphonic acid is neutralized with the requisite quantity of soda ash (Na2CO3) or NaOH and the solution is evaporated to obtain sodium benzene sulphonate salt. Dry sodium benzene sulphonate is fused with an excess of caustic soda (NaOH) at about 573 K when sodium phenoxide is formed. The fused mass of sodium phenoxide on treatment with dilute HC1 gives phenol.

Question 52.
How is phenol (carbolic acid) prepared from aniline (diazotization)?
OR
How is carbolic acid prepared from amino benzene?
Answer:
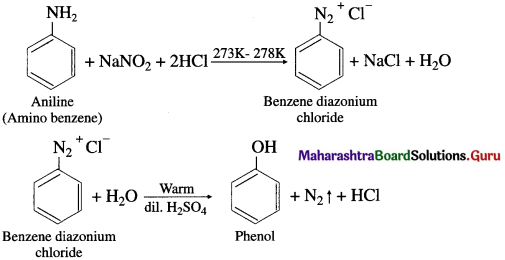
Preparation of phenol from aniline (diazotization) : When aniline is treated with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid (NaNO2 + HC1) at low temperature (0°C – 5°C), benzene diazonium chloride is formed. This reaction is called diazotization. An aqueous solution of benzene diazonium chloride on warming with water or dil. H2S04 gives phenol.
Question 54.
Describe the physical properties of alcohols and phenols.
Answer:
The properties of alcohols and phenols are mainly due to the hydroxyl group.
(1) Nature of intermolecular forces : Due to presence of – OH groups, alcohols and phenols are polar molecules. The polar – OH groups are held together by the strong intermolecular forces i.e. hydrogen bonding.

(2) Physical State : Lower alcohols are colourless, toxic liquids having characteristic alcoholic odour. Pure phenol is colourless, toxic, low melting solid having characteristic carbolic or phenolic odour.
(3) Boiling Points : The boiling points of alcohols and phenols increase with increase in their molecular mass.
Methyl alcohol – 65 °C
Phenol -182° C
n-Butyl alcohol-118 °C
o-nitrophenol-217 °C
(4) Solubility : Solubility of alcohols and phenols in water due to their ability to form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Question 55.
Arrange the following compounds in order of their increasing boiling points.
Butan-2-ol, ethanol, pentan-l-ol, butan -l-ol, propan-l-ol, methanol.
Answer:
Methanol, ethanol, propan:l-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1 -ol pentan-l-ol.
Question 56.
Explain the following :
(1) Ethanol has higher boiling point than ethane.
Answer:
(1) The hydroxyl group in alcohols is highly polar. The H-atom has partial positive charge and the oxygen atom has partial -ve charge. The hydroxyl group in ethanol is extensively hydrogen bonded.
(2) Large number of ethanol molecules associated together by intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The energy required to separate the molecules by breaking hydrogen bond into vapour state is higher. This results in increasing the boiling point of ethanol.
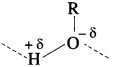
(3) On the other hand, in ethane (alkane) there is no hydrogen bonding between the molecules. The molecules of ethane are held together by weak van der Waals forces of attraction. Hence, these molecules can be easily separated. Thus, ethanol has higher boiling point than that of ethane.

(2) Methanol is more soluble in water than propan-l-ol.
Answer:
(1) Methanol being lower members of alcohols is more soluble in water, but as the size of an alkyl group or molecular weight of alcohol increases the solubility decreases.
(2) The solubility of methanol in water is due to polar characters of alcohols (R – O-δ -H+δ ) and water (H+δ – O-δ – H+δ).
(3) The solubility of methanol is due to the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonding between polar molecules of methyl alcohol and water. Hence, methyl alcohol is a associated liquid.
(4) In methyl alcohol, size of methyl group being very small, -OH group constitutes major part of the molecule giving more solubility. As size of alkyl group increases, the non-polar character increases the solubility decreases. Hence, methanol is more soluble in water than propan-l-ol.
Question 57.
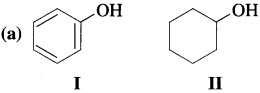
Which of the following pair is more acidic and why?
Answer:
Due to high electronegativity of sp2-hybridized carbon, electron density on oxygen in phenol (I) decreases. This increases the polarity of O – H bond and results in more ionization of phenol than that of cyclohexyl alcohol (II). Therefore, phenol is more acidic than cyclohexyl alcohol.
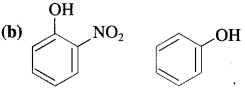
Answer:
In p-nitrophenol, nitro group (N02) is an electron-withdrawing group present at ortho position which enhances the acidic strength (- I effect). The O – H bond is under strain and release of proton (H+) becomes easily. Hence, o-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Question 58.
Draw intramolecular hydrogen bonding structures in the following compounds :
(a) o-nitrophenol
(b) o-hydroxy benzoic acid.
Answer:
(a) o-nitrophenol :
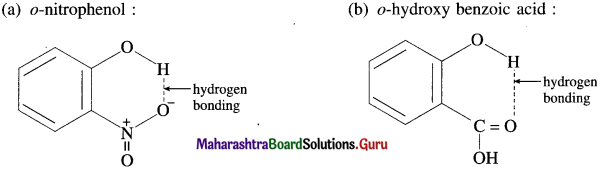
(b) o-hydroxy benzoic acid :
Question 59.
Explain laboratory test of alcohols and phenols.
Answer:
Laboratory test : Aqueous solution of alcohols and phenols can be tested with litmus paper. Aqueous solution of alcohols is neutral to litmus (neither blue nor red litmus change colour). Aqueous solutions of phenols turn blue litmus red. Thus, phenols have acidic character.
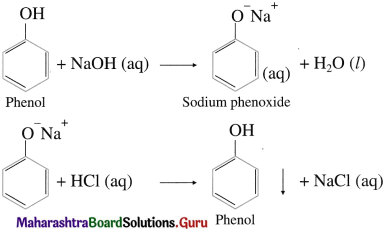
Question 62.
Write the action of aq NaOH on phenol and the product obtained is acidified.
Answer:
Phenols dissolve in aqueous NaOH by forming water soluble sodium phenoxide and are reprecipitated/ regenerated as phenols on acidification with HC1.
Question 63.
Explain the action of sodium on ethanol.
Answer:
When cthanol is treated with sodium metal, sodium ethoxide is formed and hydrogen gas is liberated.

Liberation of H2 gas is used to detect the presence of alcoholic -OH group of a molecule.

Question 64.
How are the following compounds obtained from alcohols using HCI:
(1) C2H5CI
(2) Isopropyl chloride
(3) tert-butyl chloride?
Answer:
(1) Ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH in the presence of Lucas reagent (ZnCl2 + HCI conc.) forms ethyl chloride.
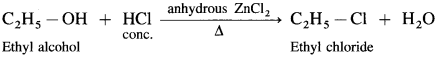
(2) Isopropyl alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent forms isopropyl chloride.
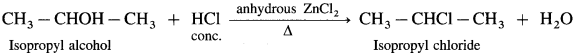
(3) Tert-butyl alcohol reacts with Lucas reagent forms tert-butyl chloride

Question 65.
What is Lucas reagent? What are its uses?
Answer:
Lucas reagent is composed of a mixture of concentrated HCl and Lewis acid. anhydrous ZnCI2.
It is used to prepare alkyl chlorides and distinguish between 10, 2° and 3° alcohols.

Question 66.
How can alcohols be distinguished with the help of Lucas reagent?
Answer:
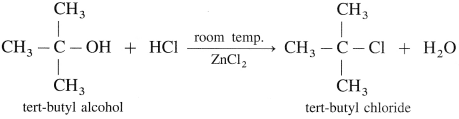
Lucas reagent is a mixture of concentrated HCI and anhydrous ZnCl2. It is used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Alcohol with Lucas reagent forms an alkyl chloride, R -Cl which is insoluble and gives cloudiness and forms separate layer.
The time required for cloudiness to appear is based on the type of the alcohol and its reactivity :
(1) Primary alcohol : It reacts with the Lucas reagent very slowly and on heating forms alkyl chloride. The cloudiness and separation of a layer takes place after a long time on heating.
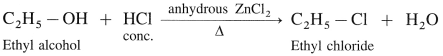
(2) Secondary alcohol : It reacts with the Lucas reagent much faster to form alkyl chloride. The cloudiness and separation of layer takes place slowly.

(3) Tertiary alcohol : It reacts immediately with the Lucas reagent at room temperature to form alkyl chloride. The cloudiness and separation of layer takes place instantaneously.
Question 67.
What is esterificatlon? how Is an ester obtained from alcohol or phenol?
Answer:
(1) When an alcohol or phenol is heated with a carboxylic acid in the presence of conc.sulphuric acid an ester is obtained. The reaction is called esterification. This is reversible reaction and the formation of an ester is favoured
using excess of alcohol in the presence of conc. H2SO4.
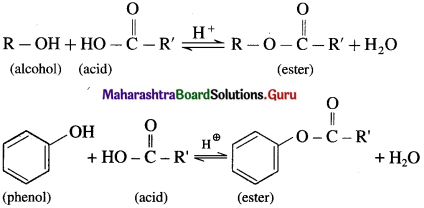
(2) Alcohols and phenols react with acid anhydrides in presence of acid catalyst to form eser.
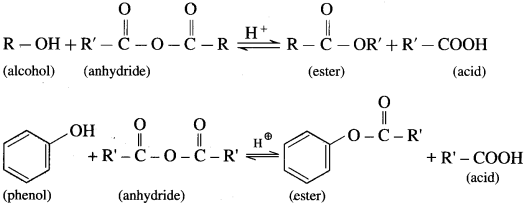
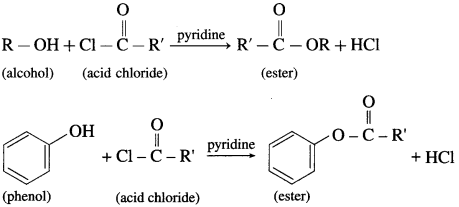
(3) The reaction of alcohol and phenols with acid chloride is carried out in the presence of pyridine (base), which neutralizes HCl.

Question 68.
Explain the action of the following on ethanol :
(1) Acetic acid
(2) Acetic anhydride
(3) Acetyl chloride.
Answer:
(1) Acetic acid : When ethanol is treated with acetic acid in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid, ethyl acetate (ester) is formed.

(2) Acetic anhydride : When ethanol is treated with acetic anhydride in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid, ethyl acetate (ester) is formed.
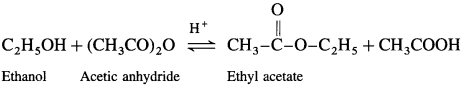
(3) Acetyl chloride : When ethanol is treated with acetyl chloride in the presence of pyridine, ethyl acetate (ester) is formed.
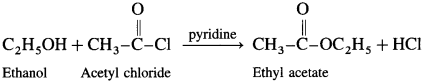
(Pyridine neutralises HC1 formed during reaction)
Question 69.
Explain the action of the following phenol :
(1) Acetic acid
(2) Acetic anhydride
(3) Acetyl chloride
Answer:
(1) Acetic acid : When phenol is treated with acetic acid in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid, (ester) is formed.
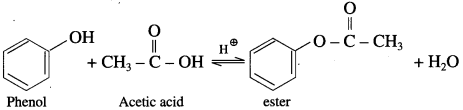
(2) Acetic anhydride : When phenol is treated with acetic anhydride in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid, (ester) is formed.
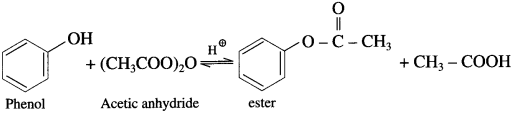
(3) Acetyl chloride : When phenol is treated with acetyl chloride in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid, (ester) is formed.
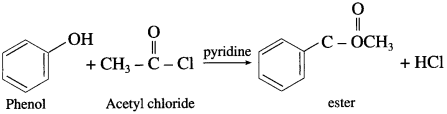
(Pyridine neutralizes HC1 formed during reaction.)
Question 70.
What is the action of acetic anhydride on salicyclic acid?
Answer:
When acetic anhydride is treated with salicyclic acid in presence of glacial acetic acid, acetyl salicyclic acid (aspirin) is obtained.
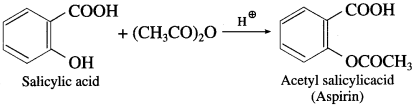
Aspirin is a common analgesic, antipyretic drug. Reactions involving breaking of C – O bond of alcohol :
Question 71.
How are the following compounds prepared by using HBr from corresponding alcohols :
(1) Ethyl bromide
(2) Isopropyl bromide
(3) Tert-butyl bromide (2-Methyl-propan-2-ol)?
Answer:
(1) When ethyl alcohol is heated with HBr, ethyl bromide is formed. (HBr is prepared in situ by adding NaBr to HCl or H2SO4)

(2) Isopropyl alcohol on heating with HBr forms isopropyl bromide.
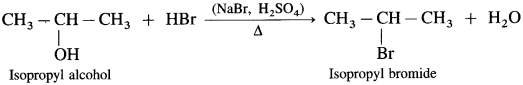
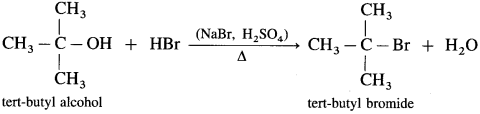
(3) Tert-butyl alcohol on heating with HBr forms tert-butyl bromide.

Question 72.
Explain the action of hydroiodic acid on the following :
(1) Propan-2-ol
(2) 3-Methyl butan-2-ol.
Answer:
(1) Propan-2-ol : When propan-2-ol is heated with hydroiodic acid, 2-iodopropane is formed.
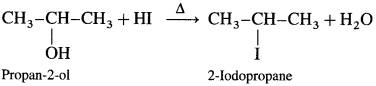
(2) 3-Methyl butan-2-ol : When 3-Methyl butan-2-ol is heated with hydroiodic acid, 2-Iodo-2-methyl butane is obtained. Here, secondary alcohol is converted into a tertiary alkyl halide.

Question 73.
Describe the action of PCl3 on
(1) ethanol
(2) Propan-l-ol
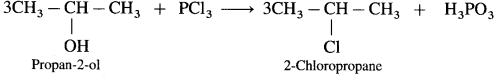
(3) Propan-2-ol.
Answer:
(1) Ethanol : When ethanol is treated with PCl3, ethyl chloride is obtained.
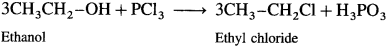
(2) Propan-l-ol : When propan-l-ol is treated with PCl3, n-propyl chloride is obtained.

(3) Propan-2-ol : When Propan-2-ol is treated with PCl3, 2-Chloropropane is obtained.
Question 74.
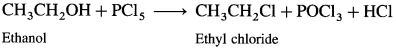
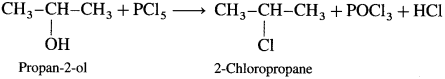
Describe the action of PCl5 on
(1) ethanol
(2) propan-2-ol.
Answer:
(1) Ethanol : When ethanol is treated with PCl5, ethyl chloride is obtained.
(2) Propan-2-ol : When propan-2-ol is treated with PCl5, 2-chloropropane is obtained.
Question 75.
Describe the action of SOCl2 on
(1) ethanol
(2) propan-l-ol.
Answer:
(1) Ethanol : When ethanol is treated with SOCl2 in the presence of pyridine, ethyl chloride is obtained.

(2) Propan-l-ol : When propan-l-ol is treated with SOCl2 in the presence of pyridine, w-propyl chloride is obtained.
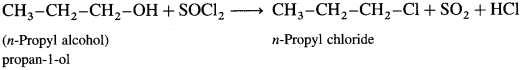
Question 76.
Explain dehydration of alcohols.
OR
What is dehydration of alcohols? Give the chemical reactions showing dehydration of primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) alcohols.
Answer:
Removal of water from an alcohol is called dehydration of alcohol. Alcohols having a /i-hydrogen is heated with dehydrating agents like concentrated H2SO4 (or H3PO4 or P2O5 or Al2O3). The ease of dehydration of alcohols is in the following order : tert-alcohol (3°) > secondary (2°) > primary (1°)
(1) Primary (1°) alcohol is dehydrated by heating it with 95% H2SO4 at 453 K.
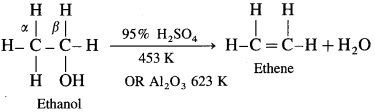
(2) Secondary alcohol (2°) is dehydrated by heating with 60% H2SO4 at 373 K.

(3) A ternary alcohol can be easily dehydrated by heating with 20% H2SO4 at 363 K.
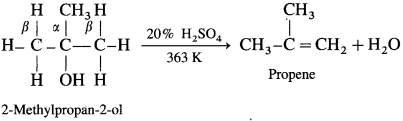
An alcohol can be dehydrated by passing vapours alcohols over heated alumina (Al2O3).
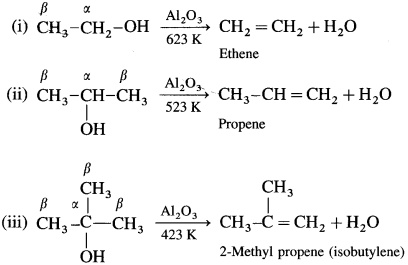

Question 77.
Explain oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols.
Answer:
(1) Primary alcohol on oxidation with CrO3 forms aldehyde. However, a better reagent to bring about this oxidation is PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate).
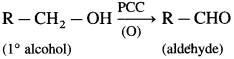
(2) Secondary alcohol on oxidation with chromic anhydride (CrO3) forms ketone.

Question 78.
What is the action of acidified K2Cr2O7 on the following :
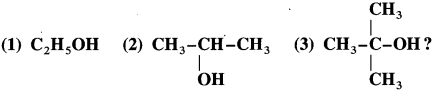
How are following alcohols distinguished :
(1) ethyl alcohol
(2) isopropyl alcohol
(3) tert-butyl alcohol?
OR
How will you distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols by oxidation process?
Answer:
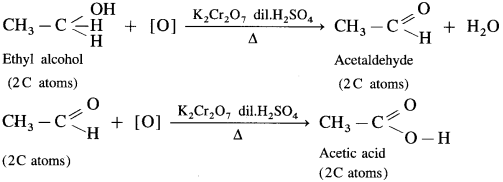
Primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are distinguished on the basis of their oxidation products, when their oxidation is carried out using K2Cr2O7 and dil. H2SO4. Acidified potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7 is an oxidising agent.

(1) Ethyl alcohol is a primary alcohol and on oxidation, it first forms acetaldehyde, which on further oxidation forms acetic acid. In this both, aldehyde and acid have same number of carbon atoms.
(2) Isopropyl alcohol is a secondary alcohol and on oxidation it gives a ketone, acetone with the same number of carbon atoms. Acetone resists further oxidation as it involves breaking of C-C bond.
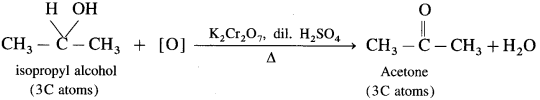
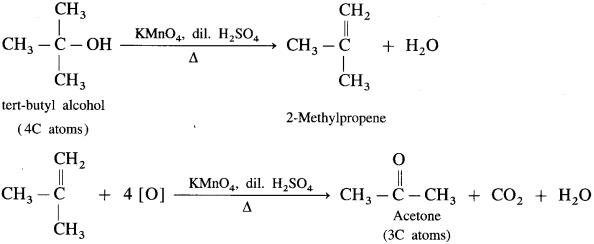
(3) The oxidation of tert-butyl alcohol is difficult, since it does not have a-hydrogen atom. It is oxidised by using acidic and stronger oxidising agents like KMn04, CrO3 at high temperature, which dehydrate tertiary alcohol to alkene and then oxidise it to a ketone, acetone with less number of carbon atoms.
Question 79.
What happens when vapours of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are passed over heated copper at 573 K?
Answer:
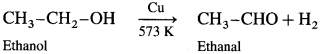
When vapours of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols are passed over heated copper at 573 K, dehydrogena¬tion of primary and secondary alcohol takes place while tertiary alcohols undergo dehydrogenation to given an alkene.
Primary alcohol :
Secondary alcohol :
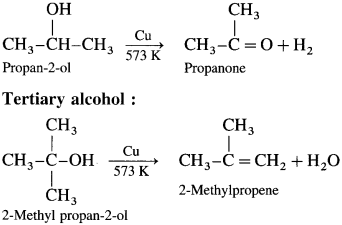

Reactions of phenols :
Question 80.
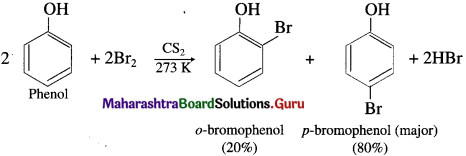
(1) Explain the action of bromine in carbon disulphide (CS2) on phenol (carbolic acid). OR Give equation of the reaction of bromine in CS2 with phenol.
Answer:
When phenol is stirred at a low temperature with bromine dissolved in a polar solvent such as carbon disulphide or CCl4 at (273 K), a mixture of o-bromophenol and p-bromophenol is formed, p-bromophenol is the major product.
Question 81.
Explain the action of bromine water on phenol (carbolic acid).
OR
Name the reagent used in the bromiriation of phenol to 2, 4, 6 tribromophenol.
Answer:
When phenol is treated with bromine water, a yellowish white precipitate of 2, 4, 6 – tribromophenol is formed.

Question 82.
Explain the action of dilute nitric acid on phenol (carbolic acid).
OR
Give equation of the reaction of dilute HNO3 with phenol.
Answer:
When phenol is treated with dilute nitric acid, a mixture of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol is formed. In this reaction, p-nitrophenol is formed as the major product.

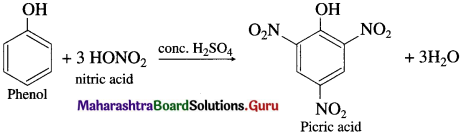
Question 83.
Explain the action of cone, nitric acid (nitrating mixture) on phenol (carbolic acid).
OR
How is phenol converted into picric acid?
Answer:
When phenol is warmed with a mixture of cone, nitric acid and cone, sulphuric acid (a nitrating mixture or the mixed acid), 2, 4, 6 – trinitrophenol, commonly called picric acid, is formed.
Question 84.
Explain the action of concentrated sulphuric acid on phenol at different temperatures.
Answer:
(a) At room temperature : When phenol is treated with cone. H2SO4 at room temperature (about 300 K), o-phenol sulphonic acid is formed.
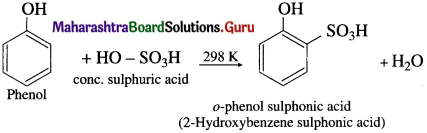
(b) At 373 K : When phenol is treated with cone. H2SO4 at about 373 K, p-phenol sulphonic acid is formed.

Question 85.
Explain (1) Kolbe’s reaction (2) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
Answer:
(1) Kolbe’s reaction : When phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium phenoxide is obtained. Phenoxide ion being more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitution. Phenoxide undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide at 398 K under pressure of 6 atm (a weak electrophile) forms salicylic acid as major product.

(2) Reimer-Tiemann reaction : Phenol is heated with chloroform along with aqueous NaOH, this is followed by acidification with dil. HC1 when salicyladehyde (2-hydroxy benzaldehyde) is formed as the major product, which can be separated from p-isomer by steam distillation. The stability of o-isomer is due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
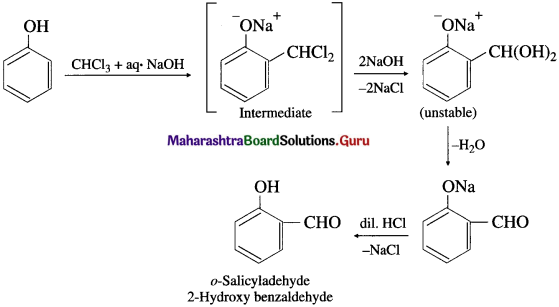

Question 86.
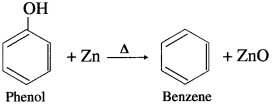
Explain the action of zinc dust on phenol.
OR
How is phenol converted into benzene?
Answer:
When phenol is heated with zinc dust, benzene is obtained.
Question 87.
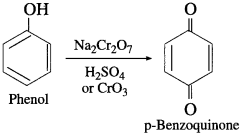
Explain the action of chromic acid on phenol.
OR
How is phenol converted into benzoquinone?
Answer:
When phenol is oxidised by chromic acid, a diketone, p-benzoquinone is formed. It is a conjugated diketone.
Question 88.
Explain catalytic hydrogenation of phenol.
Answer:
When a mixture of vapours of phenol and hydrogen is passed over nickel catalyst at 433 K., cyclohexanol is obtained.
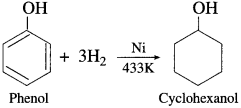
Question 89.
How is diethyl ether (ethoxyethane) obtained from alcohol?
Answer:
When excess of ethyl alcohol is distilled with concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) at 413 K, diethyl ether is formed.
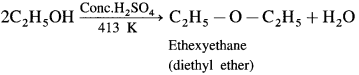
Question 91.
Write a note on Williamson’s synthesis.
OR
How are ethers prepared from Alkyl halides?
OR
How are simple ethers and mixed ethers prepared by Williamson’s synthesis?
Answer:
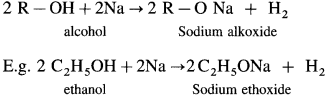
Williamson’s synthesis : When an alkyl halide (R – X) is heated with sodium alkoxide (R – O – Na), an ether is obtained, this reaction is known as Williamson’s synthesis. This method is used to prepare simple (or symmetrical) ethers and mixed (unsymmetrical) ethers.
Sodium alkoxide is obtained by a reaction of sodium with an alcohol.
(A) Simple (Symmetrical) ether : When an alkyl halide and sodium alkoxide having similar alkyl groups are heated, symmetrical ether is obtained.
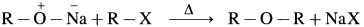
Sodium ethoxide on heating with ethyl bromide gives diethyl ether.

(B) Mixed (Unsymmetrical) ether : When an alkyl halide and sodium alkoxide or sodium phenoxide having different alkyl groups are heated, unsymmetrical ether (dialkyl ethers or alkyl aryl ether) is obtained.
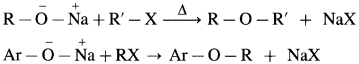
Sodium ethoxide on heating with methyl bromide gives ethyl methyl ether.
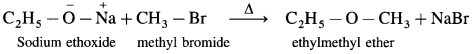
Sodium phenoxide on heating with ethyl bromide gives ethyl phenyl ether.
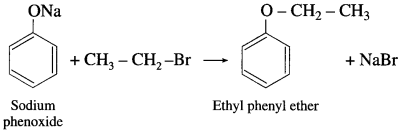

Question 92.
How is anisole obtained from phenol?
OR
How is methoxy benzene prepared from carbolic acid?
Answer:
Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide, sodium phenoxide is formed. When sodium phenoxide is heated with methyl iodide, anisole is obtained.

Question 93.
Explain the limitations for the preparation of unsymmetrical ethers.
OR
What care is to be taken in the preparation of unsymmetrical ethers by Williamson’s synthesis? Explain.
OR
Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson’s synthesis for the preparation of certain types of ethers.
Answer:
(1) In the preparation of unsymmetrical ethers by Williamson’s synthesis, the proper choice of the reactants namely alkyl halide and sodium alkoxide is necessary.
(2) The best yield of unsymmetrical ether is obtained when primary alkyl halide and tertiary alkoxide are heated, since primary alkyl halides are more susceptible to SN2 reaction.
(3) Secondary or tertiary alkyl halide undergo a and fi (halogen and hydrogen) elimination reaction giving an alkene instead of an ether since a carbon atom is sterically hindered by bulky alkyl groups.
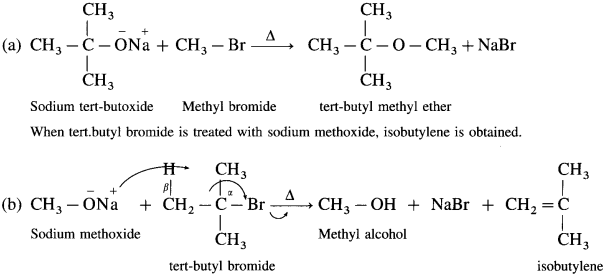
(4) For example : t-butyl methyl ether can be synthesised by reaction of methyl bromide with sodium t-butoxide.
Question 94.
State physical properties of ethers.
Answer:
(1) Dimethyl ether and ethyl methyl ether are gases. Other ethers are colourless liquids with pleasant odour.
(2) Lower ethers are highly volatile and highly inflammable substances.
(3) Boiling points of ethers show gradual increase with the increase in molecular mass.
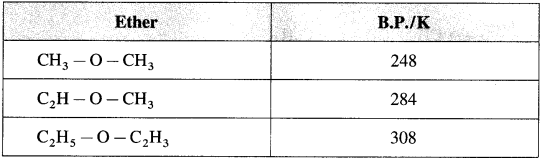
(4) The solubility/miscibility of ethers in water is similar to that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass.
Question 95.
Explain, ethers posses a small net dipole moment.
Answer:
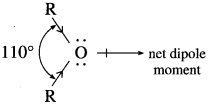
In ethers,  bond angle is 110° and not 180°, bond dipole moments of the two C – O bonds do not cancel each other, therefore, ethers possess a smal net dipole moment, (for example, dipole moment of diethyl ether is 1.18 D)
bond angle is 110° and not 180°, bond dipole moments of the two C – O bonds do not cancel each other, therefore, ethers possess a smal net dipole moment, (for example, dipole moment of diethyl ether is 1.18 D)
Question 96.
Explain, the solubility/miscibility of ethers in water is similar to that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass.
Answer:
The solubility/miscibility of ethers in water is similar to that of alcohols of comparable molecular mass. This is because ethers can form hydrogen bonds with water through ethereal oxygen.
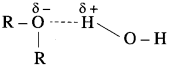
For example, diethyl ether and n-butyl alcohol have respective miscibilities of 7.5 and 9 g per 100 g of water.

Question 97.
Explain laboratory test for ethers.
Answer:
Ethers are neutral compounds in aqueous medium. Ethers do not react with bases, cold dilute acids, reducing agents, oxidizing agents and active metals. However, ethers dissolve in cold concentrated H2SO4 due to formation of oxonium salts.
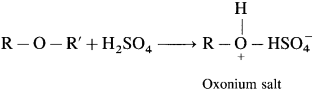
This property distinguishes ethers from hydrocarbons.
Question 98.
What is the action of atmospheric oxygen on diethyl ether?
Answer:
When atmospheric oxygen combines with diethyl ether, peroxide of diethyl ether is obtained.
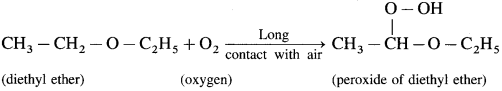
Question 99.
What is the action of dilute sulphuric acid on
(1) Dimethyl ether
(2) Diethyl ether
(3) Ethyl methyl ether?
(4) Anisole?
OR
Explain hydrolysis of ethers.
Answer:
Simple ethers on heating with dilute sulphuric acid under pressure undergoes hydrolysis to give alcohol.
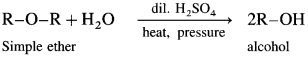
(1) Dimethyl hydrolysis on hydrolysis give methanol.
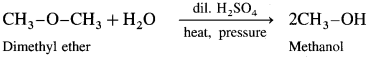
(2) Diethyl ether on hydrolysis give ethanol.
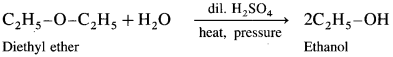
(3) A mixed ether on heating with dii. H2SO4 under pressure undergoes hydrolysis to give mixture of two different alcohols.
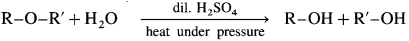
Ethyl methyl ether on hydrolysis give a mixture of ethanol and methanol.

(4) Anisole on hydrolysis give a mixture of phenol and methanol.
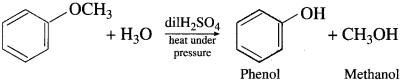
Question 100.
State the combustion products of diethyl ether.
Answer:
The combustion products of diethyl ether are CO2 and H2O.
Question 101.
What is the action of phosphorus pentachloride on
(1) Diethyl ether
(2) Ethyl methyl ether
(3) Methyl phenyl ether (anisole)?
Answer:
(1) Diethyl ether : When diethyl ether is heated with ethyl methyl ether, ethyl chloride is formed.
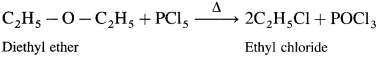
(2) Ethyl methyl ether : When ethyl methyl ether is heated with phosphorus pentachloride, a mixture of ethyl chloride and methyl chloride is formed.
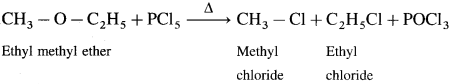
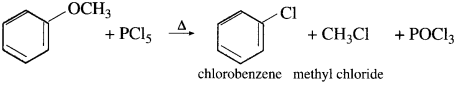
(3) Methyl phenyl ether (Anisole) : When methyl phenyl ether is heated with phosphorus pentachloride, a mixture of methyl chloride, chlorobenzene is formed.

Question 102.
Describe the action of hot concentrated HI on
(i) Dialkyl ether
(ii) Alkyl aryl ether.
Answer:
Ether reacts with excess of hot concentrated hydrogen halide to give two alkyl halide molecules.
R – O – R + HX → RX + R – OH
R – OH + HX → RX + H20
Alkyl aryl ether reacts with hot concentrated hydrogen halide to give phenol and alkyl halide.

Ethers with two different alkyl groups react with hot.conc. HI to give alkyl halides.
R – O – R’+ 2H – X → R – X + R’ – X + H2O
The order of reactivity of HX is HI > HBr > HC1
Question 103.
What is the action of hot HI on isopropyl methyl ether?
Answer:
When isopropyl methyl ether is treated with excess of hot hydroiodic acid, a mixture of isopropyl iodide and methyl iodide is formed.
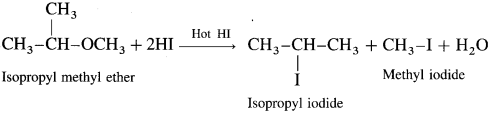
Question 104.
Describe the action of hydroiodic acid on the following :
(1) Diethyl ether.
Answer:
When diethyl ether (ethoxy ethane) is treated with hydroiodic acid, a mixture of ethanol and ethyl iodide is formed.
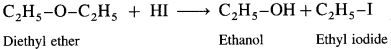
If excess of hydroiodic acid is available, then ethyl alcohol further reacts with hydroiodic acid at higher temperature to form ethyl iodide and water.

(2) Ethyl methyl ether.
Answer:
When ethyl methyl (methoxy ethane) is treated with hydroiodic acid, a mixture of ethyl alcohol and methyl iodide is formed.
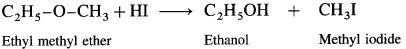
If excess of hydroiodic acid is available, then ethyl alcohol further reacts with hydroiodic acid at higher temperature to form ethyl iodide and water.

(3) Methyl n-propyl ether.
Answer:
When methyl n-propyl ether (1-Methoxy propane) is treated with hydroiodic acid, a mixture of n-propyl alcohol and methyl iodide is formed.
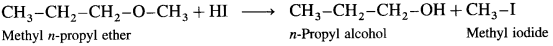
If excess of hydroiodic acid is available then n-propyl alcohol further reacts with hydroiodic acid at higher temperature to form n-propyl iodide and water.
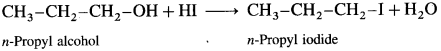
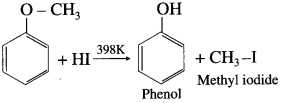
(4) Methyl phenyl ether (anisole).
Answer:
When methyl phenyl ether (anisole) is treated with hydroiodic acid, phenol and methyl iodide is formed. Here, phenol does not react further with HI because – OH group is attached to sp2-hybridised carbon atom and it cannot be replaced by iodide (nucleophile).

Question 105.
Draw the resonance structures of aromatic ethers.
Answer:
The alkoxy group in aromatic ether is a ring activating and ortho-, paradirecting group toward electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Resonance structures :
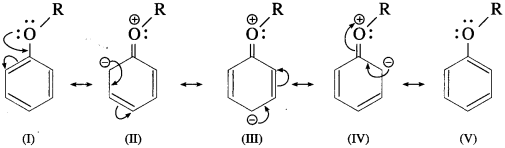
+ R Effect of – OR group results in increased electron density at the para- and two ortho-posotions (see resonance structures II, III and IV).
Question 106.
Describe the action of bromine in acetic acid on anisole.
OR
Write the equation of the reaction of bromination of anisole in ethanoic acid medium.
Answer:
When anisole is treated with bromine in acetic acid, /i-bromoanisole (major product) is obtained.

Question 107.
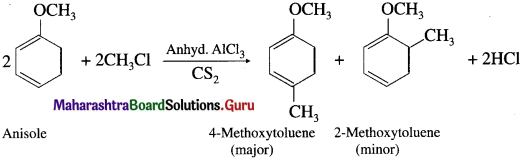
Describe the action of methyl chloride on anisole (Friedel-Crafts reaction).
OR
Write the equation of Friedel-Crafts reaction-alkylation of anisole.
Answer:
When anisole is treated with alkyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (a Lewis acid) as catalyst, 4-Methoxy toluene is formed as major product. The alkyl groups are introduced at -ortho and -para positions in anisole, the reaction is known as Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.
Question 108.
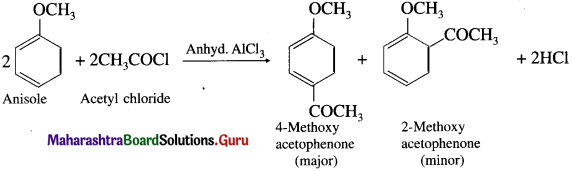
Describe the action of Acetyl chloride on anisole (Friedel-Crafts acylation).
OR
Write the equation of the reaction Friedel-Crafts acylation of anisole.
OR
Write a note on Friedel-Crafts acylation.
Answer:
When anisole is treated with acetyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride (a Lewis acid), 4-Methoxy acetophenone (major product) is obtained. The acetyl groups are introduced at -ortho and -para positions in anisole, the reaction is known as Friedel Craft’s acylation reaction.
Question 109.
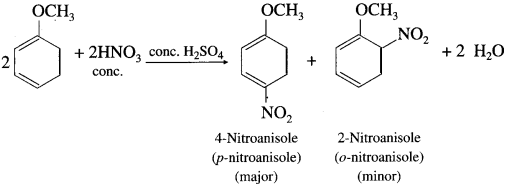
Describe the action of cone. HNO3 on anisole.
OR
Write the equation of nitration of anisole.
Answer:
When anisole is reacted with nitrating mixture (cone. HNO3 + cone. Fl2SO4), a mixture of p-nitroanisole and o-nitroanisole is obtained.

Question 110.
An organic compound with the formula C4H10O3 shows properties of ether and alcohol. When treated with an excess of HBr yields only one compound 1,2 dibromomethane. Write structural formula of ether and that of alcohol.
Answer:
When C4H10O3 is treated with excess of HBr, a single compound 1,2-dibromoethane is formed.
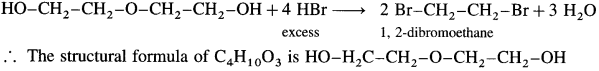
Question 111.
An organic compound ‘A’ having molecular formula C4H10O does not react with sodium metal. On hydrolysis with dilute H2SO4 it gives only one organic compound ‘B’ The compound B on heating with red phosphorus and iodine gives compound ‘C’. The compound C can also be obtained from compound ‘A’ on heating with excess HI. Identify the compounds A, B and C.
Answer:
(1) The organic compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H10O may be an alcohol or ether.
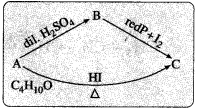
(2) Since ‘A’ does not react with sodium (Na), it is not an alcohol. Hence ‘A’ may be an ether.
(3) Since an ether ‘A’ on hydrolysis with dilute H2SO4 gives only one compound ‘B’, the compound ‘A’ must be a symmetrical (simple) ether. Hence compound ‘A’ may be, C2H5 – O – C2H5
Question 112.
How will you affect the following two-step conversions? Diethyl ether into n-butane :
Answer:

Question 114.
Answer in one sentence/word.
(1) Name the alcohol that is used to make propan-2-one.
Answer:
The alcohol used to make propan-2-one is iso-propyl alcohol.
(2) Which is the first oxidation product of secondary alcohol?
Answer:
The first oxidation product of secondary alcohol is ketone.
(3) Name the alcohol that is used to make acetic acid.
Answer:
The alcohol that is used to make acetic acid is ethyl alcohol.
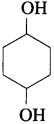
(4) Write the structure of cyclohexane-1, 4-diol.
Answer:

(9) Which of the following isomers is more volatile : o-nitrophenol or p-nitrophenol?
Answer:
The isomer o-nitrophenol with lower boiling point is more volatile.
(10) Identify the product of the following reaction.
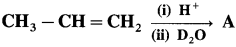
Answer:
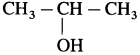
(11) Identify the product obtained by industrial synthesis of carboxylation of phenoxide ion followed by acidification.
Answer:
The product is phenol

(12) What is the product A obtained in the following reaction?
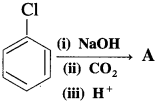
Answer:
The product is phenol
(13) Which positions are occupied by – NO2 group during nitration of carbolic acid?
Answer:
– o – (ortho) and – p – (para) positions are occupied by – NO2 group during nitration of carbolic acid.
(14) Write the name of reactants used for the preparation of ethyl-tert-butyl ether.
Answer:

are used for the preparation of ethyl-tert-butyl ether.
(15) The product formed in the reaction of reverse of dehydration of alcohol is
Answer:
The product formed in the reaction of reverse of dehydration of alcohol is alkene.
(16) Which rule is obeyed by hydroboration oxidation process?
Answer:
The rule obeyed by hydroboration oxidation process is opposite to the Markovnikov’s rule.
(17) Name the reagents for the complete hydroboration-oxidation reaction in step 1 and step 2.
Answer:
Step 1 : Diborane
Step 2 : Hydrogen peroxide and dil. NaOH.
(18) Write the name of the test by which methanol can be distinguished from ethanol.
Answer:
Iodoform test by which methanol can be distinguished from ethanol.
(19) Write the name of reactant used for preparation of phenol, which gives byproduct used as solvent.
Answer:
Reactant used in the preparation of phenol :

(20) Ether is a good solvent for Grignard reagent. Which property makes it a good solvent?
Answer:
Ether has a low polarity, this property makes it a good solvent.
(21) The C – O – C bond angle in dimethyl ether is
Answer:
The C – O – C bond angle in dimethyl ether is 110°.

Question 115.
State the uses of methyl alcohol.
Answer:
(1) Methyl alcohol is used as an industrial solvent for dissolving oils, fats, gums, etc.
(2) It is used for dry cleaning and preparation of perfumes and varnishes.
(3) It is used as antifreeze agent for automobile radiators at low temperature.
(4) It is used in the preparation of methyl chloride, dimethyl sulphate and formaldehyde.
(5) It is used to denature ethyl alcohol.
Question 116.
State the uses of ethyl alcohol. OR Write two uses of ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
(1) Ethyl alcohol is used as solvent for dyes, oils, perfumes, cosmetics and drugs.
(2) A mixture of 10-20% ethyl alcohol with petrol is used as motor fuel.
(3) A mixture of ethyl alcohol and calcium acetate in gel form is used as solid fuel.
(4) It is widely used in beverages.
(5) Since ethyl alcohol has low freezing point, it is used in thermometer.
(6) It is an effective tropical antiseptic therefore it is used in many mouth washes.
(7) It kills micro-organisms on wound surface and in the mouth but its low toxicity does not kill the cells of the skin or mouth tissues.
(8) It is used in the preparation of chloroform, iodoform, acetic acid and ethers.
(9) It is used as fuel.
Question 117.
Give the important uses of phenol.
OR
Write two uses of phenol.
Answer:
(1) Phenol is used in the preparation of phenol-formaldehyde polymer which is used in a plastic bakelite.
(2) It is used in the preparation of phenol-phthalein-an indicator and in certain dyes.
(3) It is used in the preparation of drugs such as salol, aspirin, etc.
(4) It is used in the preparation of dettol, which is an antiseptic.
(5) It is used in the preparation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid which is used as selective weed killer.
(6) It is used to prepare picric acid which is used as explosive.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 118.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each sub-question:
1. Which one of the following is a tertiary alcohol?
(a) Pentan-l-ol
(b) Pentan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylpentan-2-ol
(d) 3-Methylpentan-2-ol
Answer:
(c) 2-Methylpentan-2-ol
2. Which of the following is a primary alcohol?
(a) 3-ethyl-3-hexanol
(b) 2-butanol
(c) 3-methyl-l-butanol
(d) 1-hexanol
Answer:
(d) 1-hexanol
3. The molecular formula C4H10O represents
(a) aldehydes
(b) alcohols
(c) ethers
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (b) and (c)
4. The general formula of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols is
(a) CnH2nOH
(b) CnH2n-1OH
(c) CnH2n+1OH
(d) CnHn+1OH
Answer:
(c) CnH2n+1OH

5. Which of the following alcohols cannot be prepared by hydration of the corresponding alkene?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Propan- l-ol
(c) Propan-2-ol
(d) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
Answer:
(b) Propan- l-ol
6. Which of the following compounds when treated with CH3MgI in dry ether followed by the hydroly¬sis, will give Propan-2-ol?
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) CH3COCH3
Answer:
(b) CH3CHO
7. To prepare 3-Ethylpentan-3-ol, the reagents needed are
(a) CH3CH2MgBr + CH3COCH2CH3
(b) CH3MgBr + CH3CH2CH2COCH2CH3
(c) CH3CH2MgBr + CH3CH2COCH2CH3
(d) CH3CH2CH2MgBr + CH3COCH2CH3
Answer:
(c) CH3CH2MgBr + CH3CH2COCH2CH3
8. How is 1-propanol obtained?
(a) Using propanal
(b) Using propanone
(c) Using propene
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Using propanal
9.
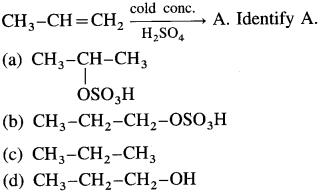
Answer:
(a)
10. Ketone on reduction gives
(a) 1° alcohol
(b) 2° alcohol
(c) 3° alcohol
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) 2° alcohol
11. Primary alcohols are prepared by catalytic hydro-genation of aldehydes in presence of ……………………………… as a catalyst
(a) aluminium bromide
(b) fluoroboric acid
(c) dry ether
(d) palladium
Answer:
(d) palladium
12. Lower member of alcohols are
(a) insoluble in water
(b) soluble in water
(c) insoluble in acetaldehyde
(d) insoluble in petrol
Answer:
(b) soluble in water
13. Which of the following compounds contain hydro¬gen bonds?
(a) Ethane
(b) Ethanol
(c) Methoxymethane
(d) Ethylene
Answer:
(b) Ethanol

14. Which of the following is a trihydric alcohol?
(a) n-propyl alcohol
(b) Glycerol
(c) Glycol
(d) Glycine
Answer:
(b) Glycerol
15. Aldehydes are first oxidation products of
(a) primary alcohols
(b) secondary alcohols
(c) tertiary alcohols
(d) carboxylic acids
Answer:
(a) primary alcohols
16. The oxidation product of alcohol depends on
(a) – OH group of an alcohol
(b) number of carbon atoms in alcohol
(c) number of hydrogen atoms attached to hydroxyl bearing carbon
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) number of hydrogen atoms attached to hydroxyl bearing carbon
17. The order of ease of oxidation is
(a) primary > secondary > tertiary
(b) primary < secondary < tertiary
(c) primary > tertiary > secondary
(d) secondary > tertiary > primary
Answer:
(b) primary < secondary < tertiary
18. Ethyl alcohol \(\frac{\text { conc. } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}}{443 \mathrm{~K}} \mathrm{~A} \stackrel{\mathrm{HBr}}{\longrightarrow}\) Ethyl bromide. Identify A.
(a) Ethyl hydrogen sulphate
(b) Ethylene
(c) Isopropyl hydrogen sulphate
(d) Acetic acid
Answer:
(b) Ethylene
19. One mole of PCl5 reacts with one mole of ethyl alcohol to give
(a) 1 mole Cl2
(b) 1/2 mole Cl2
(c) 1 mole HCl
(d) 1/2 mole HCl
Answer:
(c) 1 mole HCl
20. When ethyl alcohol is reacted with sodium metal and the compound so formed is treated with ethyl bromide, the product formed is
(a) an acid
(b) an alkane
(c) an ether
(d) an ester
Answer:
(c) an ether
21. Dehydration occurs at the lowest temperature and concentration for
(a) methyl alcohol
(b) n-propyl alcohol
(c) iso-propyl alcohol
(d) tert-butyl alcohol
Answer:
(d) tert-butyl alcohol
22. One mole of sodium when reacts with one mole of methyl alcohol, gives
(a) one mole of oxygen
(b) one mole of hydrogen
(c) half mole of hydrogen
(d) half mole of oxygen
Answer:
(c) half mole of hydrogen

23. A compound ‘X’(C3H8O) on oxidation gives com-pound ‘ Y’(C3H6O2), hence compound ‘X’ must be
(a) a ketone
(b) an aldehyde
(c) a primary alcohol
(d) a secondary alcohol
Answer:
(c) a primary alcohol
24. The toxicity of alcohols
(a) increases with an increase in their molecular weight
(b) decreases with an increase in their molecular weight
(c) increases with a decrease in their molecular weight
(d) does not depend on their molecular weight
Answer:
(a) increases with an increase in their molecular weight
25. The structural formula of 2-phenyl ethanol is
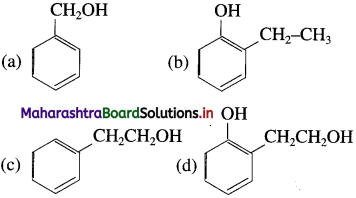
Answer:
(c)
26. Compound that fails to give effervescence with NaHCO3 is
(a) C6H5COO
(b) CH3COOH
(c) C6H5OH
(d) Picric acid
Answer:
(c)
27. Phenol is a bifunctional compound because
(a) it gives reactions of hydroxyl group (-OH) as well as aromatic ring
(b) it is a strong acid
(c) it is insoluble in NaOH
(d) it is readily soluble in water
Answer:
(a) it gives reactions of hydroxyl group (-OH) as well as aromatic ring
28. Phenol gives characteristic colour with
(a) iodine solution
(b) bromine water
(c) ammonium hydroxide
(d) aqueous ferric chloride solution
Answer:
(d) aqueous ferric chloride solution
29. Ethanol and phenol are distinguished from each other by the action of
(a) neutral ferrous chloride
(b) neutral ferric chloride
(c) ferric hydroxide
(d) ferrous hydroxide
Answer:
(b) neutral ferric chloride
30. Which of the following compounds is used to prepare bakelite resin?
(a) Acetaldehyde
(b) Ethanol
(c) Phenol
(d) Methyl amine
Answer:
(d) Methyl amine
31. Increasing order of acid strength among p-methoxy-phenol, p-methyl phenol and p-nitro- phenol is as
(a) p-nitrophenol > p-methoxyphenol > p-methylphenol
(b) p-methylphenol > p-methoxyphenol > p-nitrophenol
(c) p-nitrophenol > p-methylphenol > p-methoxyphenol
(d) p-methoxyphenol > p-methylphenol > p-nitrophenol
Answer:
(d) p-methoxyphenol > p-methylphenol > p-nitrophenol

32. The IUPAC name of the compound is 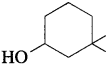
(a) 3,3-dimethyl-l-hydroxy cyclohexane
(b) l,l-dimethyl-3-cyclohexanol
(c) 3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexanol
(d) l,l-dimethyl-3-hydroxy cyclohexane
Answer:
(c) 3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexanol
33. Which of the following is the most reactive towards electrophilic attack?
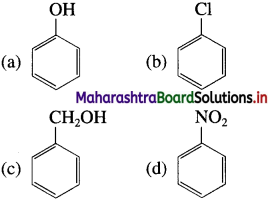
Answer:
(a)
34. In the following reaction, Ethanol \(\stackrel{\mathrm{PBr}_{3}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{A}\)\(\stackrel{\text { Alc-KOH }}{\longrightarrow} \text { B } \frac{\text { (i) } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \text {, room temp. }}{\text { (ii) } \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}, \text { heat }} \mathrm{C} \text {. }\). The product C is
(a) CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH3
(b) CH3 – CH2 – OSO3H
(c) CH3CH2OH
(d) CH2 = CH2
Answer:
(c) CH3CH2OH
35. What is the general formula of ethers?
(a) CnH2nO
(b) CnH2n+2O
(c) CnH2n-1O
(d) CnH2n-2O
Answer:
(b) CnH2n+2O
36. The 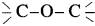 linkage is present in
linkage is present in
(a) proteins
(b) ketones
(c) ethers
(d) aldehydes
Answer:
(c) ethers
37. Methoxy ethane is the functional isomer of
(a) CH3CHOHCH3
(b) CH3CH2CH2OH
(c) CH3 – O – CH3
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (b)
38. An oxygen atom in ether is
(a) sp2-hybridized
(b) sp3-hybridized
(c) sp-hybridized
(d) sp2-d-hybridized
Answer:
(b) sp3-hybridized

39. C5H12O represents
(a) only an alcohol
(b) only an aldehyde
(c) only an ether
(d) an alcohol and an ether
Answer:
(d) an alcohol and an ether
40. Ether molecules are
(a) tetrahedral
(b) angular
(c) pyramidal
(d) diagonal
Answer:
(b) angular
41. Which one of the following compounds is not isomeric with Ethoxypropane?
(a) 1-Methoxypropane
(b) 2-Methoxypropane
(c) 2-Methylpropane-2-ol
(d) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Answer:
(d) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
42. The IUPAC name of C2H5 – O – CH2 – CH(CH3)2 is
(a) 1-Ethoxy-1-butane
(b) 2-Ethoxy-2-butane
(c) l-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
(d) 3-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
Answer:
(c) l-Ethoxy-2-methylpropane
43. The IUPAC name of CH3OC6H5 is
(a) methoxy phenyl ether
(b) phenoxy methane
(c) methoxy benzene
(d) methyl phenyl ether
Answer:
(c) methoxy benzene
44. In CH3(CH2)3 – O -CH3, the parent hydrocarbon of large alkyl group is
(a) n-butane
(b) butane
(c) pentane
(d) n-pentane
Answer:
(a) n-butane
45. Which one of the following alkyl halide gives best yield in Williamson’s synthesis?
(a) CH3 – Br
(b) CH3 – CH(Br) – CH3
(c) CH2 – CH(Br) – CH3 – CH3
(d) (CH3)3 C – Br
Answer:
(a) CH3 – Br
46. Which one of the following ethers cannot be pre¬pared by using diazomethane?
(a) Dimethyl ether
(b) Diethyl ether
(c) Ethyl methyl ether
(d) t-Butyl methyl ether
Answer:
(b) Diethyl ether

47. The continuous etherification is carried out at
(a) 473 K
(b) 413 K
(c) 498 K
(d) 403 K
Answer:
(b) 413 K
48. Williamson’s synthesis is used for the preparation of
(a) only unsymmetrical ethers
(b) only symmetrical ethers
(c) both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers
(d) only methyl ethers
Answer:
(c) both symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers
49. Which of the following ethers on hydrolysis gives two different products that are successive members of a homologous series?
(a) Methoxymethane
(b) Ethoxythane
(c) Methoxyethane
(d) 2-Methoxypropane
Answer:
(c) Methoxyethane
50. Which one of the following compounds dissolves in hot dilute sulphuric acid but does not react with sodium metal?
(a) Ethyl bromide
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Ethyl alcohol
(d) Diethyl ether
Answer:
(d) Diethyl ether
51. Identify ‘A’ in the following reaction :
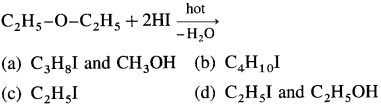
Answer:
(c)
52. The C-O-C bond angle in an ether is
(a) 180
(b) 90°
(c) 104.5°
(d) 109.5°
Answer:
(d) 109.5°
53. Ether free from moisture and alcohol is known as ,
(a) dry ether
(b) absolute ether
(c) pure ether
(d) spirit ether
Answer:
(b) absolute ether
54. The geometry of ether is similar to
(a) ammonia
(b) methane
(c) water
(d) ethyne
Answer:
(c) water
55. Sodium metal does not react with
Answer:
C2H5 – O – C2H3

56. Ethers have boiling points
(a) lower than those of alkanes of comparable molecular masses
(b) higher than those of isomeric alcohols
(c) lower than those of isomeric alcohols
(d) higher than those of alkanes of comparable molecular masses
Answer:
57. Ether on hydrolysis gives
(a) aldehyde
(b) alcohol
(c) acid
(d) ester
Answer:
(c) acid
58. Which of the following reactions represent Williamson’s reaction?
(a) R – O – R’ + HI →
\(\text { (b) } \mathrm{R}^{\prime}-\mathrm{OH}+\stackrel{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}}{\longrightarrow}\)
(d) R – O – Na + R’X →
Answer:
(c)
59. Which of the following reactions represent the continuous etherification process?
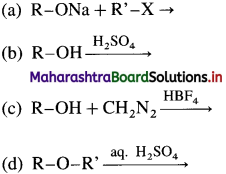
Answer:
(b)
60. Ethers on complete combustion produce
(a) an alcohol and water
(b) an alkene and water
(c) an alkane and an alkene
(d) carbon dioxide and water
Answer:
(d) carbon dioxide and water
61. Diethyl ether is used as a solvent in many organic reactions because it
(a) is liquid at room temperature
(b) has lower boiling point
(c) contains divalent oxygen atom
(d) is inert in nature
Answer:
(d) is inert in nature
62. Which of the following reagents can be prepared using ether as a solvent?
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Grignard’s reagent
(c) Schiff’s reagent
(d) Millon’s reagent
Answer:
(b) Grignard’s reagent
63. Diethyl ether is used as
(a) a hypnotic
(b) an antiseptic
(c) an anaesthetic
(d) an antipyretic
Answer:
(c) an anaesthetic
64. To obtain fuel, diethyl ether is mixed with
(a) ester
(b) ethanal
(c) ethanol
(d) 2-propanone
Answer:
(c) ethanol

65. Which of the following alcohols is prepared by acid catalyzed hydration of alkenes?
(a) Butan-l-ol
(b) Propan-l-ol
(c) Ethanol
(d) Methanol
Answer:
(c) Ethanol
66. Which of the following alcohols can be prepared by direct hydration of corresponding alkene in presence of 50 % sulphuric acid?
(a) Butan-l-ol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylpropan-1 -ol
(d) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
Answer:
(d) 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
67. Which of the following alcohols cannot be prepared by reduction of carbonyl compounds?
(a) Pentan-l-ol
(b) Pentan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylpentan-2-ol
(d) 3-Methylpentan-2-ol
Answer:
(c) 2-Methylpentan-2-ol
68. Which of the following conversions explains the acidic nature of alcohols?
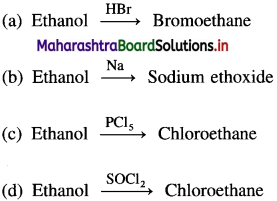
Answer:
(b)
69. Which of the following compounds gives 3-ethyl- pentan-3-ol by the action of ethyl magnesium iodide followed by acid hydrolysis?
(a) Propanone
(b) Butanone
(c) Pentan-2-one
(d) Pentan-3-one
Answer:
(d) Pentan-3-one
70. Benzyl phenyl ether reacts with hydrogen bromide to give
(a) benzyl bromide and phenol
(b) benzyl alcohol and bromobenzene
(c) benzyl bromide and bromobenzene
(d) benzyl alcohol and phenol
Answer:
(a) benzyl bromide and phenol
71. Ethers are considered as
(a) monoalkyl derivatives of water
(b) divalent oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl groups
(c) alkyl derivatives of fatty acids
(d) condensation products of acid and alcohol
Answer:
(b) divalent oxygen atom is attached to two alkyl groups
72. Which of the following compounds is not isomeric with ethoxyethane?
(a) 1-methoxypropane
(b) 2-methoxypropane
(c) 2-methylpropan-2-ol
(d) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
Answer:
(d) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
73. Which of the following compounds dissolves in hot dilute sulphuric acid but does not reacts with sodium metal?
(a) Ethyl bromide
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Ethyl alcohol
(d) Diethyl ether
Answer:
(d) Diethyl ether

74. Which of the following alcohol will have the fastest rate of dehydration?
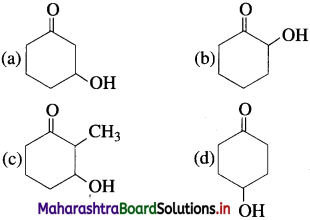
Answer:
(c)
75. The phenol having lowest acidity is
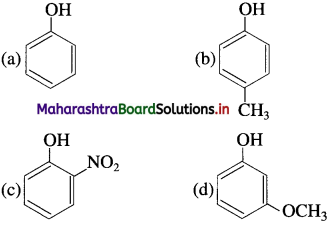
Answer:
(b)
76. Which of the following reagents is best for the following conversion?
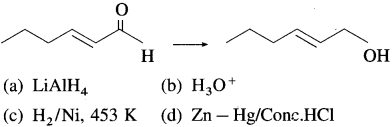
Answer:
(a)
77. 3-Methyl butane-2-ol on heating with HI gives
(a) 2 -iodo-3-methyl butane
(b) 2-iodo-2-methyl butane
(c) l-iodo-3-methyl butane
(d) l-iodo-2-methyl butane
Answer:
(b) 2-iodo-2-methyl butane
78. In phenol carbon atom attached to -OH group undergoes –
(a) sp3-hybridisation
(b) sp-hybridisation
(c) sp2-hybridisation
(d) No hybridisation
Answer:
(c) sp2-hybridisation
79. Which among the following reducing agents is ‘not’ used to reduce acetaldehyde to ethyl alcohol?
(a) Na-Hg and water
(b) Zn-Hg and cone. HCl
(c) H2-Raney Ni
(d) Li-A1H4/H+
Answer:
(b) Zn-Hg and cone. HCl
80. Identify the weakest acidic compound amongst the following :
(a) p-nitrophenol
(b) p-chlorophenol
(c) p-cresol
(d) p-aminophenol
Answer:
(d) p-aminophenol

81. Natalite is a mixture of
(a) diethyl ether and methanol
(b) diethyl ether and ethanol
(c) dimethyl ether and methanol
(d) dimethyl ether and ethanol
Answer:
(b) diethyl ether and ethanol
82. The alcohol used in thermometers is
(a) methanol
(b) ethanol
(c) propanol
(d) butanol
Answer:
(b) ethanol
83. Which of the following is the first oxidation product of secondary alcohol?
(a) Alkene
(b) Aldehyde
(c) Ketone
(d) Carboxylic acid
Answer:
(c) Ketone
84. When phenol is heated with cone. HNO3 in presence of cone. H2SO4 it yields
(a) o-nitrophenol
(b) p-nitrophenol
(c) 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol
(d) m-nitrophenol
Answer:
(c) 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()









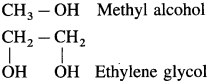
























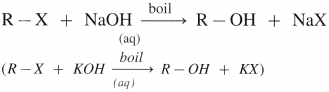

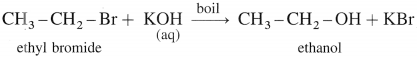
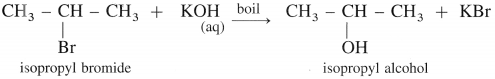


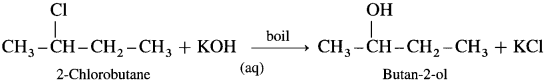




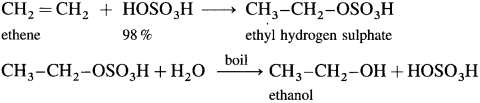






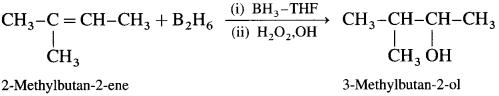
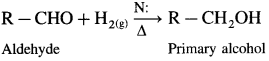
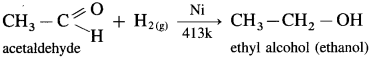
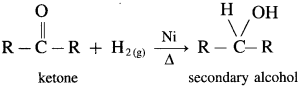
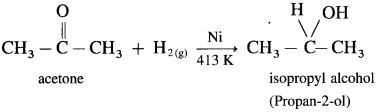
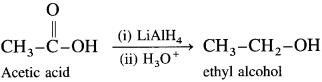



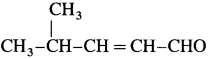



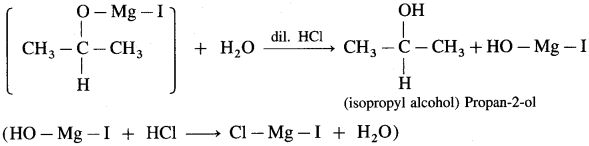

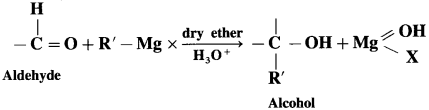


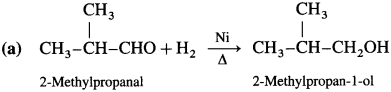

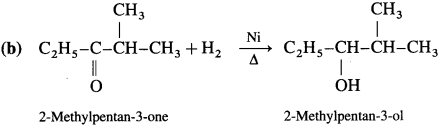
























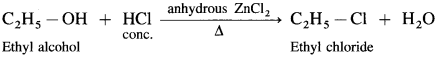
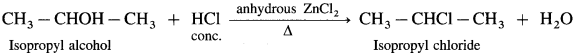


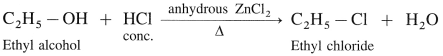











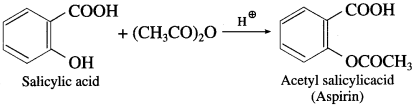

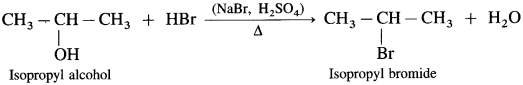

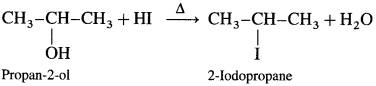




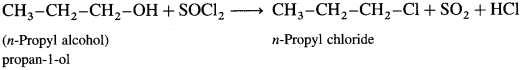




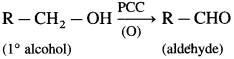

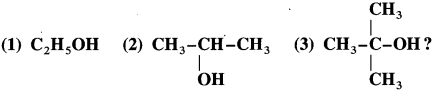

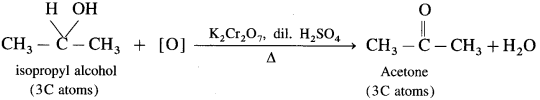














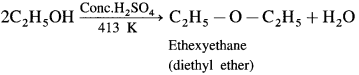


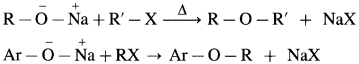
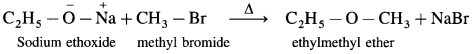




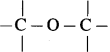 bond angle is 110° and not 180°, bond dipole moments of the two C – O bonds do not cancel each other, therefore, ethers possess a smal net dipole moment, (for example, dipole moment of diethyl ether is 1.18 D)
bond angle is 110° and not 180°, bond dipole moments of the two C – O bonds do not cancel each other, therefore, ethers possess a smal net dipole moment, (for example, dipole moment of diethyl ether is 1.18 D)