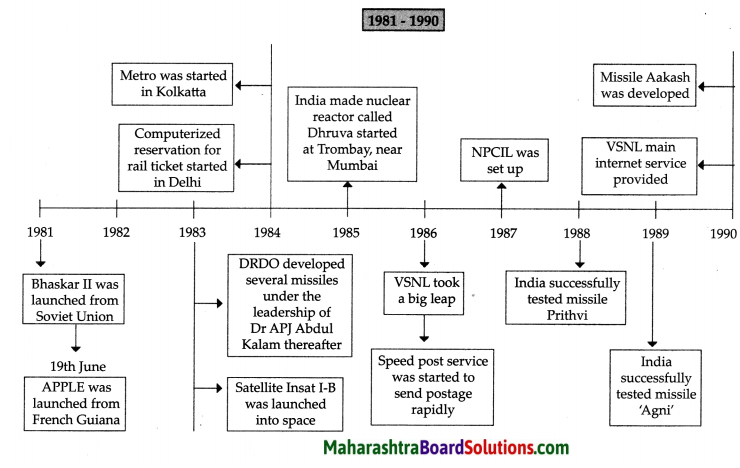
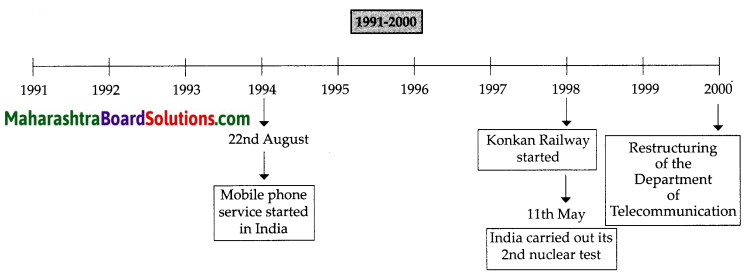
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Political Science Solutions Chapter 4 The United Nations Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
The United Nations Class 9 Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 4 The United Nations Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
Political Science Class 9 Chapter 4 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Choose the right option and rewrite the sentence:
Question 1.
This country is not a permanent member of United Nations Security Council _____.
(a) America
(b) Russia
(c) Germany
(d) China
Answer:
(c) Germany
![]()
Question 2.
The United Nations has _______ number of members.
(a) 190
(b) 193
(c) 198
(d) 199
Answer:
(b) 193
Question 3.
This international organisation conducts workshops in India on remedial measures to tackle the problem of malnutrition among children
(a) UNICEF
(b) UNESCO
(c) Trusteeship Council
(d) Red Cross
Answer:
(a) UNICEF
2. Explain with reasons whether the following statements are true or false:
Question 1.
The United Nations General Assembly is a platform to discuss global problems.
Answer:
True.
- Every year the General Assembly meets in its session. During the session, the General Assembly discusses important issues like environment, disarmament, etc.
- The significance of the General Assembly lies in it being a platform for representatives of member nations to come together and discuss and make policy decisions on issues of global importance.
![]()
Question 2.
The status of all the member nations of the United Nations is not equal.
Answer:
False.
- As mentioned in the principles of UN, all member nations have the same status.
- There is no discrimination among nations based on geographical size, economic or military power.
Question 3.
A resolution can be passed even if China exercises its veto power.
Answer:
False
- China is one of the five permanent members of the UN and the permanent members have veto power.
- If even one of the five permanent members uses it’s veto i.e. gives a negative vote, the decision cannot be taken.
Question 4.
India has played a major role in the work of the United Nations.
Answer:
True.
- India has always sent her troops to participate in the United Nations peacekeeping forces.
- India has participated in bringing issues like decolonisation, disarmament, racial segregation on the United Nations platform.
3. Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Veto
Answer:
(i) Security Council has 5 permanent members and 10 non-permanent members.
(ii) For any decision to be taken, the assent of all five permanent members and four non¬permanent members is necessary.
(iii) America, Russia, England, France and China are permanent members of the Security Council. They have the veto power.
(iv) If even one of the five permanent member uses its veto i.e. gives a negative vote, the decision cannot be taken
Question 2.
UNICEF
Answer:
(i) UNICEF is an affiliated organisation of the United Nations.
(ii) It works towards making nutritious food and health care available to children.
(iii) Several workshops were organised in India to find out measures to overcome malnutrition among babies and children.
4. Answer the following questions in brief:
Question 1.
Write the reasons for the establishment of the United Nations.
Answer:
The United Nations is the world’s largest international organisation. The reasons for the establishment of the United Nations are:
(i) Two World Wars were fought at the beginning of the twentieth century.
(ii) Life and property were destroyed on a large scale in these wars.
(iii) As a result, the League of Nations was established after the First World War and the United Nations was established after the Second World War out of a realisation that there has to be a mechanism to establish world peace.
(iv) The League of Nations did not succeed at all.
(v) But after the use of the nuclear weapons in the . Second World War, the idea took root that such destructive wars should be stopped and that it is the collective responsibility of all nations to do so.
(vi) The United Nations was established after the Second World War to instill this understanding among all nations.
(vii) Hence, the United Nations, an international organisation was established to ensure peace and security at the international level.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the objectives of the United Nations.
Answer:
The United Nations has its own definite objectives. They are as follows:
- To establish friendly relations among nations.
- To enhance international security by solving international disputes.
- To safeguard and foster human rights and freedom.
- Along with these, the United Nations also aim at enhancing economic cooperation at the international level.
Question 3.
What is the role of the Peacekeeping Forces of the United Nations?
Answer:
(i) The peacekeeping activity of the United Nations involves creating appropriate circumstances favourable for bringing about permanent peace in strife-tom areas.
(ii) The peacekeeping forces help these areas to progress towards peace.
(iii) In conflict ridden areas, security is provided and at the same time, help is extended for establishing peace.
(iv) The United Nations takes up peacekeeping as one of the tasks for safeguarding and fostering peace in the world.
5. Do as directed:
Question 1.
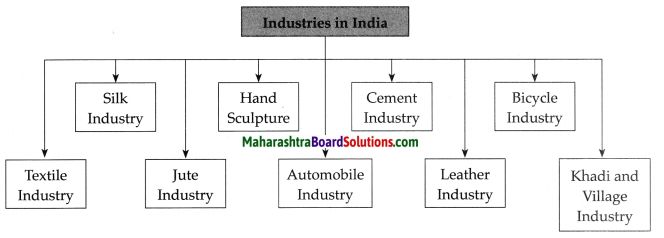
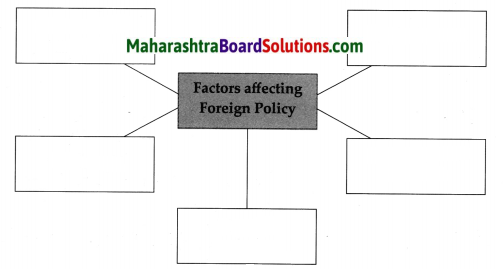
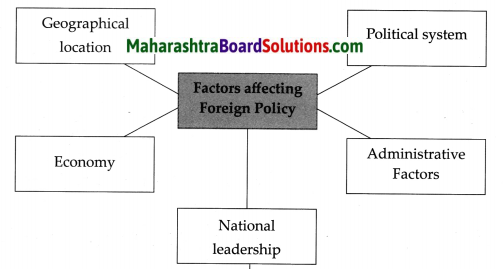
Complete the following chart giving information about the organs of the United Nations.
| S.No | Organ | Number of members | Functions |
| 1. | United Nations General Assembly | ………. | ……………. |
| 2. | United Nations Security Council | ………….. | ……………. |
| 3. | International Court of Justice | ………….. | ………………. |
| 4. | Economic and Social Council | ………….. | ……………….. |
Answer:
| S.No. | Organ | Number of members | Functions |
| (1) | United Nations General Assembly |
193 | (1) To elect the non-permanent members of the Security Council. (2) To choose the United Nations Secretary General and the judges of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in consultation with the Security Council. (3) To pass the annual budget of the United Nations. |
| (2) | United Nations Security Council | 15
(5 Permanent and 10 NonPermanent) |
(1) To maintain international peace and security. (2) To prepare policies for arms control. (3) To play a joint role along with the General Assembly in the appointments of the judges of the International Court of Justice and of the United Nations Secretary General. |
| (3) | International Court of Justice | 15 judges | (1) To settle the disputes between two or more member nations of the United Nations. (2) To interpret international law authentically. (3) To advise the various organs or subsidiary bodies of the United Nations about legal issues. |
| (4) | Economic and Social Council | 54 members | (1) Initiate discussions at the global level on issues like poverty, unemployment, economic and social inequality and suggest policies to tackle these problems. (2) Discuss issues like women’s questions, empowerment of women, human rights, fundamental freedoms, global trade, health related issues, etc., and make decisions. (3) Make efforts to establish cultural and educational cooperation at the international level. (4) Coordinate the functioning of the different organisations working in association with the United Nations. |
Question 2.
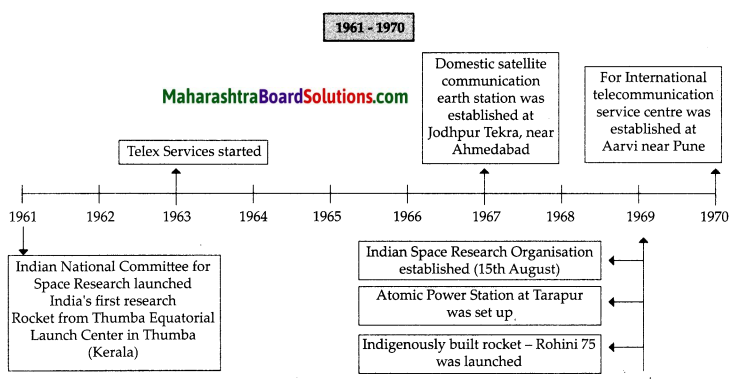
Show the chronology of the establishment of the United Nations.
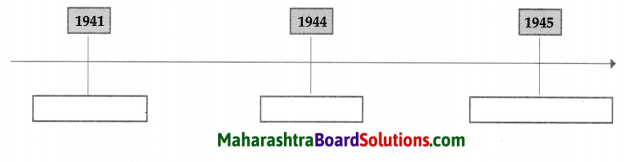
Answer:

![]()
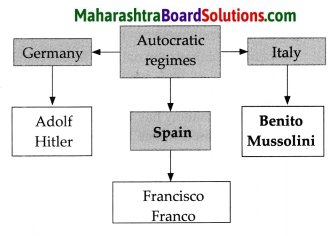
Question 3.
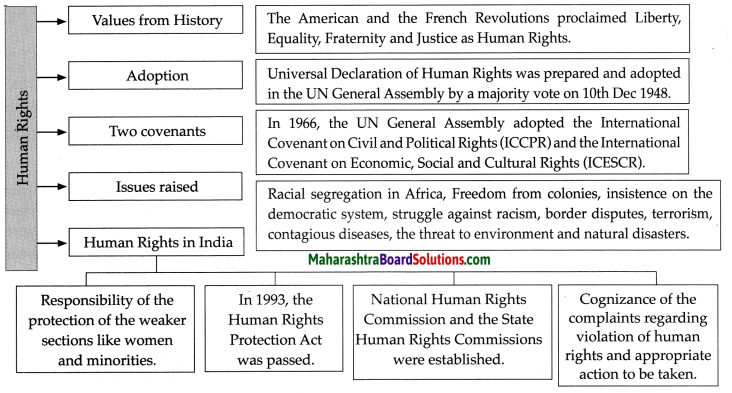
Complete the following tree diagram about the United Nations.
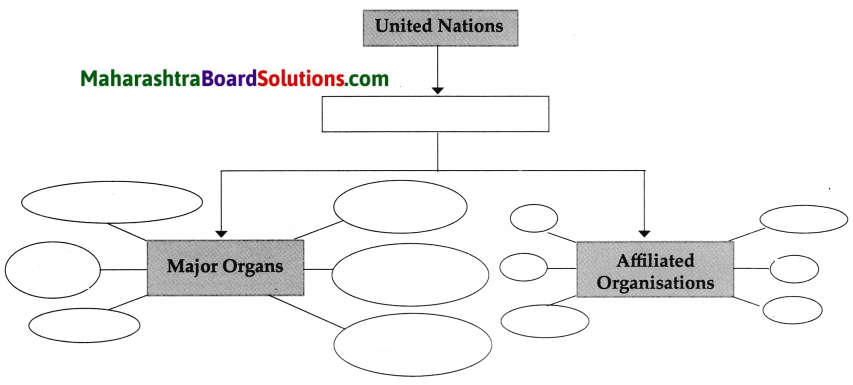
Answer:
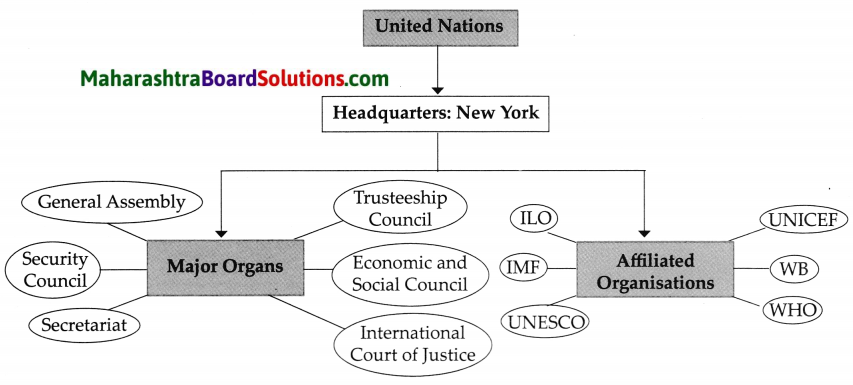
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 4 The United Nations Intext Questions and Answers
Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
Did India participate in the conferences during the Second World War?
Answer:
India was among the original members of the United Nations that signed the Declaration by United Nations at Washington, D.C. on 1st January, 1942 and also participated in the United Nations Conference on International Organization at San Francisco from 25th April to 26th June 1945.
Question 2.
Which day is celebrated as United Nations day?
Answer:
United Nations was established on 24th October 1945. The day is now celebrated each year . around the world as United Nations Day.
Question 3.
Can the United Nations intervene militarily if there is a serious threat to international peace?
Answer:
The United Nations can’t intervene militarily if there is a serious threat to international peace. The UN, after approval by the Security Council, sends peacekeepers to regions where armed conflict has recently ceased or stalled to enforce the terms of peace agreements and to discourage combatants from resuming hostilities.
Question 4.
What steps have the United Nations taken to foster human rights and freedom?
Answer:
One of the UN’s primary purposes is to promote and encourage respect for human rights and to ensure fundamental freedoms for all without distinction on the basis of race, sex, language, or religion. In 1948, the General Assembly adopted a Universal Declaration of Human Rights. In 1979, the General Assembly adopted the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women, followed by the Convention on the Rights of the Child, in 1989. United Nations Commission on Human Rights was formed in 1993 to oversee human rights issues for the UN.
![]()
Question 5.
Only one Indian has so far been the President of the UN General Assembly. Who is that person? When and at which session?
Answer:
Mrs. Vijayalakshmi Pandit is the only Indian so far who has been the President of the UN General Assembly, at the eighth session in 1953.
Activity:
Question 1.
Write the names of United Nations Secretary Generals until now.
Answer:
(i) Mr. Trygve Lie
(ii) Mr. Dag Hammarskjold
(iii) Mr. U. Thant
(iv) Mr. Kurt Waldheim
(v) Mr. Javier Perez de Cuellar
(vi) Mr. Boutros Boutros Ghali
(vii) Mr. Kofi Annan
(viii) Mr. Ban Ki Moon
(ix) Mr. Antonio Guterres
Question 2.
Is it necessary that the Secretary-General should be a citizen of the great powers/the big five?
Answer:
It is not necessary that the Secretary General should be a citizen of one of the great powers/ the big five. Here is the list of Secretary Generals with their countries: Mr. Trygve Lie (Norway) Mr. Dag Hammarskjold (Sweden)
- Mr. U. Thant (Mayanmar)
- Mr. Kurt Waldheim (Austria)
- Mr. Javier Perez de Cuellar (Peru)
- Mr. Boutros Boutros Ghali (Egypt)
- Mr. Kofi Annan (Ghana)
- Mr. Ban Ki Moon (South Korea)
- Mr. Antonio Guterres (Portugal)
Question 3.
Are citizens of a particular country given priority for being Secretary-General?
Answer:
The citizens of no particular country are given priority for being Secretary General.
Question 4.
Who is the current Secretary General and which country does he belong to?
Answer:
The current Secretary General is Antonio Guterres and he belongs to Portugal.
Class 9 Political Science Chapter 4 The United Nations Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option from the given options and rewrite the statements:
Question 1.
The United Nations Organisation was founded on _______.
(a) August 9,1944
(b) October 24,1944
(c) October 24,1945
(d) December 10,1945
Answer:
(c) October 24,1945
![]()
Question 2.
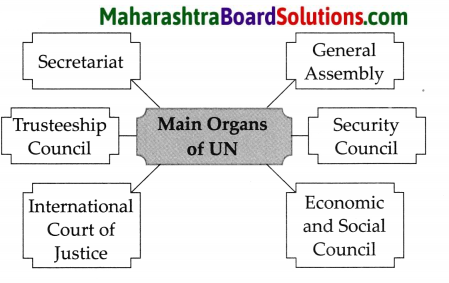
The United Nations has ____ main organs.
(a) four
(b) five
(c) six
(d) seven
Answer:
(c) six
Question 3.
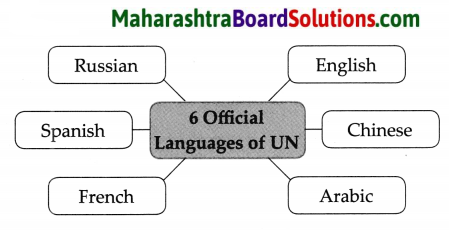
The United Nations has ______ official languages.
(a) four
(b) five
(c)six
(d) three
Answer:
(c)six
Question 4.
This language is not an official language of the United Nations
(a) French
(b) Spanish
(c) Arabic
(d) Italian
Answer:
(d) Italian
Question 5.
There are ______ permanent members in the Security Council.
(a) four
(b) five
(c)six
(d) seven
Answer:
(b) five
Question 6.
There are ________ non-permanent members in the Security Council.
(a) ten
(b) five
(c) fifteen
(d) seven
Answer:
(a) ten
Question 7.
The term of a non-permanent member of the Security Council is of ______.
(a) four years
(b) five years
(c) two years
(d) one year
Answer:
(c) two years
Question 8.
Which organ of the United Nations has suspended its operations since 1994?
(a) Trusteeship Council
(b) Economic and Social Council
(c) Secretariat
(d) International Court of Justice
Answer:
(a) Trusteeship Council
Question 9.
How many Judges are there in the International Court of Justice?
(a) 9
(b) 10
(c) 12
(d) 15
Answer:
(d) 15
Question 10.
What is the term of the United Nations Secretary General?
(a) 3 years
(b) 4 years
(c) 6 years
(d) 5 years
Answer:
(d) 5 years
![]()
Question 11.
UN Secretary General heads which principal organ of the United Nations Organisation?.
(a) General Assembly
(b) Security Council
(c) Economic and Social Council
(d) The Secretariat
Answer:
(d) The Secretariat
Question 12.
What is the term of a judge of the International Court of Justice?
(a) 9 years
(b) 4 years
(c) 6 years
(d) 5 years
Answer:
(a) 9 years
Question 13.
How many members does the Economic and Social Council have?
(a) 33
(b) 40
(c) 15
(d) 54
Answer:
(d) 54
Give the full forms of the following acronyms:
Question 1.
ILO:
Answer:
International Labour Organisation
Question 2.
FAO:
Answer:
Food and Agriculture Organisation
Question 3.
WHO:
Answer:
World Health Organisation
Question 4.
WB:
Answer:
World Bank
Question 5.
IMF:
Answer:
International Monetary Fund
Question 6.
UNICEF:
Answer:
United Nations Children’s Fund
Question 7.
UNESCO:
Answer:
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation
State whether the following statements are true or false with reasons:
Question 1.
UNICEF is the main organ of UN.
Answer:
False.
(i) The United Nations has six main organs:
- General Assembly
- Security Council
- Economic and Social Council
- International Court of Justice
- Trusteeship Council and
- Secretariat.
(ii) UNICEF is an affiliated organisation of the United Nations. It works towards making nutritious food and health care available to children.
![]()
Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Millennium Development Goals
Answer:
The United Nations member nations came together in 2000 and decided upon the development goals for the new millennium. Some of the important goals are as follows:
- To eliminate poverty and hunger.
- To make the facilities of primary education available.
- To bring about women’s empowerment, reduce infant mortality rate.
- To take special care of the health of pregnant women.
- To fight diseases like AIDS, malaria, etc.
- To protect the environment and increase the cooperation between developed and developing countries.
Question 2.
International Criminal Court
Answer:
(i) The International Criminal Court is an inter-governmental organisation and an international tribunal.
(ii) Its headquarters are at The Hague in the Netherlands.
(iii) The International Criminal Court has the jurisdiction to prosecute individuals for international crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity and war crimes that are of concern to the international community.
Question 3.
International Court of Justice.
Answer:
(i) International Court of Justice means the judicial branch of the United Nations. The International Court of Justice is located at The Hague in the Netherlands.
(ii) There are 15 judges in the International Court of Justice.
(iii) They are chosen by the General Assembly and the Security Council. Every judge has tenure of nine years.
(iv) Functions:
- To settle the disputes between two or more member nations of the United Nations.
- To interpret international law authentically.
- To advise the various organs or subsidiary bodies of the United Nations about legal issues.
Question 4.
The UN Security Council.
Answer:
Security Council is one of the 6 main organs of the UN:
(i) There are 15 members in the Security Council. Of them, five are permanent members, while ten are non-permanent members.
(ii) The non-permanent members are chosen every two years by the General Assembly. America, Russia, England, France and China are permanent members of the Security Council. They have the veto power.
(iii) For any decision to be taken, the assent of all five permanent members and four non permanent members is necessary. If even one of the five permanent member uses his veto i.e. gives a negative vote, the decision cannot be taken.
(iv) Functions of the Security Council:
(a) The main responsibility of the Security Council is to maintain international peace and security.
The Security Council may suggest one among the following alternatives in situations of international conflict:
- End/resolve conflict and make efforts to establish peace
- Impose economic sanctions or take a decision of military action against the aggressor nation.
(b) To prepare policies for arms control.
(c) To play a joint role along with the General Assembly in the appointments of the judges of the International Court of Justice and of the United Nations Secretary General.
Complete the following table:
Question 1.
| (1) | WHO | (a) | …………. |
| (2) | UNESCO | (b) | ………….. |
| (3) | UNICEF | (c) | ………… |
| (4) | ILO | (d) | ……………. |
Answer:
| (1) | WHO | (a) | World Health Organization |
| (2) | UNESCO | (b) | United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization |
| (3) | UNICEF | (c) | United Nations Children’s, Fund |
| (4) | ILO | (d) | International Labour Organization |
![]()
Question 2.
| (1) | New York | (a) | ………. |
| (2) | Hague, Netherlands | (b) | ………… |
| (3) | San Francisco | (c) | ……….. |
Answer:
| (1) | New York | (a) | Headquarters of UN |
| (2) | Hague, Netherlands | (b) | International Court of Justice |
| (3) | San Francisco | (c) | Drafting of UN Charter |
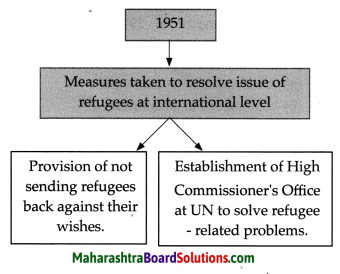
Complete the flow chart:
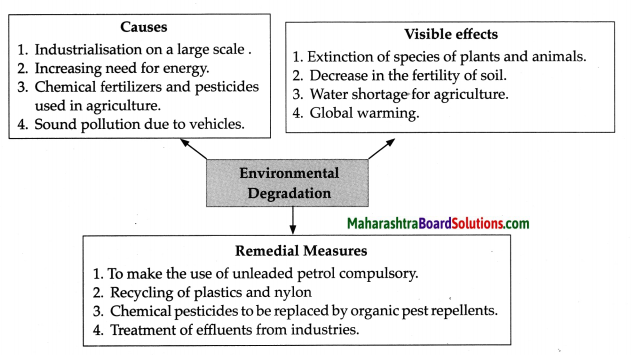
Question 1.
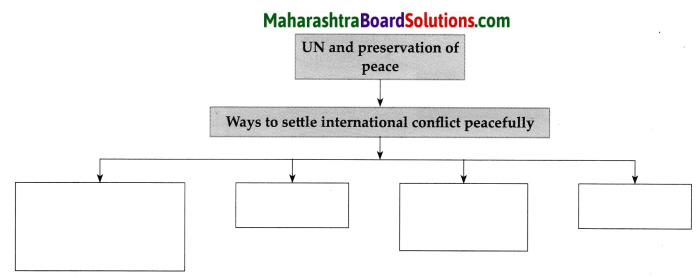
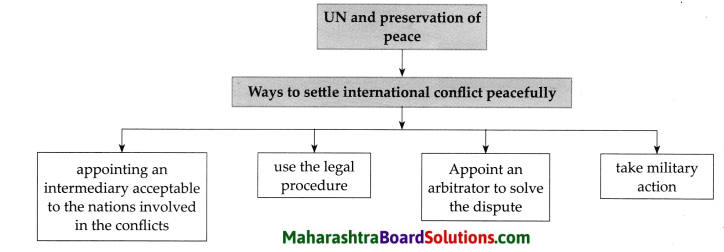
Answer:
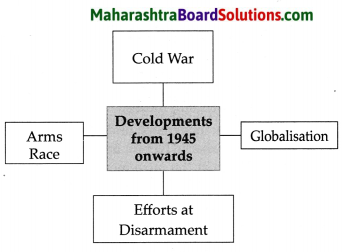
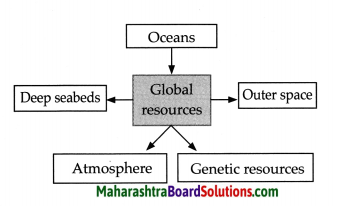
Complete the chart:
Question 1.

Answer:
Question 2.
Answer:
Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
State the role of UN General Assembly as platform to discuss global problems.
Answer:
The United Nations General Assembly is a platform to discuss global problems because:
- Every year the General Assembly meets in its session from September to December.
- During the session, the General Assembly discusses important issues like environment, disarmament, etc
- The decisions in the General Assembly are taken by the majority. These decisions are in the form of resolutions.
- The significance of the General Assembly lies in being a platform for representatives of member nations to come together and discuss and make policy decisions on issues of global importance.
Question 2.
United Nations plays an important role in preservation of peace. Explain the statement.
Answer:
(i) The objective of the United Nations is to settle international conflict peacefully.
(ii) The United Nations Charter lays down the ways and means to be employed to achieve this goal.
(iii) It includes appointing an intermediary acceptable to the nations involved in the conflict, use the legal procedure, appoint an arbitrator to solve the dispute and if needed, to take recourse to military means and ensure that conflict will not occur again.
(iv) In modem times, human security has been threatened by terrorism, racist and religious conflict. As a result, the function of securing peace of the United Nations has acquired a lot of importance.
(v) The United Nations makes efforts to ensure that violence does not erupt in strife-tom areas and normalcy is restored as soon as possible, by (for example), starting schools, creating awareness among the people about human rights, making social, economic, political facilities available, conducting elections, etc.
Question 3.
How had India helped to solve international conflicts peacefully?
Answer:
(i) India had participated in the different Conferences that were held before the establishment of the United Nations.
(ii) India has participated in bringing issues like decolonisation, disarmament and racial segregation on the United Nations platform.
(iii) In 1946, India was the first country to raise . the question of racism in the United Nations.India has always led the discussions about the problems of undeveloped and developing countries.
(iv) India has always sent her troops to participate in the United Nations peacekeeping forces. Not just that, India has sent an all-woman peacekeeping force as well.
(v) It is evident from the foregoing analysis that India makes serious efforts to solve international conflicts by peaceful means.
Question 4.
What is the role of UNESCO?
Answer:
UNESCO, is an affiliated organisation of the United Nations works towards peace and security in the world by promoting cooperation between member countries in the fields of education, science and culture.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the principles of the United Nations?
Answer:
The United Nations is an organisation created by the coming together of sovereign nations. Naturally, it is based on certain principles or rules. They are as follows:
- All member nations will have the same status. There is no discrimination among nations based on geographical size, economic or military power.
- All member nations of the United Nations should respect the freedom and geographical unity of other member nations.
- All member nations should solve their international disputes and mutual issues peacefully.
Question 6.
What are the functions of the General Assembly?
Answer:
The United Nations General Assembly is a platform to discuss global problems. Functions of General Assembly are:
- To elect the non-permanent members of the Security Council.
- To choose the United Nations Secretary General and the judges of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) in consultation with the Security Council.
- To pass the annual budget of the United Nations.
Question 7.
What are the specialised agencies of UN?
Answer:
(i) Apart from these six major organs, there are many affiliated organisations of the United Nations that help it in its functions. They are called specialised agencies.
(ii) Working in specific areas, they help different nations in those areas.
(iii) The following are some of these important agencies:
- International Labour Organisation (ILO)
- Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO)
- World Health Organisation (WHO)
- World Bank (WB)
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)
Question 8.
Why was the Trusteeship Council setup and why has it suspended its operations?
Answer:
(i) After the Second World War, the territories that were undeveloped were placed under the responsibility of the developed nations.
(ii) The latter were supposed to help bring about the development of the trust territories and once they attain independence from their colonies, help establish democracy.
(iii) The work of the Trusteeship Council is over as there are no trust territories left.
(iv) The work of the Trusteeship Council ended when Palau got independence on 1st November 1994.
Question 9.
Write about the phases in establishment of the United Nations.
Answer:
The United Nations is an international organisation of sovereign nations. It was established in the following manner:
(i) The Atlantic Treaty was signed between Prime Minister of England, Sir Winston Churchill and American, President Franklin D Roosevelt during the Second World War on 14th August 1941.
(ii) According to this treaty, a decision was taken to set up a permanent mechanism to establish international security after the Second World War was over.
(iii) Detailed discussions followed on this decision in two conferences among allied powers in 1944 and 1945.
(iv) A draft of the treaty to establish an international organisation was prepared.
(v) At San Francisco in America, representatives of fifty countries drafted the Charter of the United Nations after discussions.
(vi) As soon as the war was over, the Charter was signed on 24th October, 1945 and the United Nations was established.
Question 10.
Explain the characteristics of the Economic and Social Council.
Answer:
Economic and Social Council:
(i) The main objective of this organisation is to coordinate the economic and social policies of the United Nations.
(ii) The Council has 54 members. They are selected by the General Assembly.
(iii) Each member has a tenure of three years and each year, one-third of the members are newly chosen. Decisions are taken by majority vote.
(iv) Functions:
- Initiate discussions at the global level on issues like poverty, unemployment, economic and social inequality and suggest policies to tackle these problems.
- Discuss issues like women’s questions, empowerment of women, human rights, fundamental freedoms, global trade, health related issues, etc. and make decisions.
- Make efforts to establish cultural and educational cooperation at the international level.
- Coordinate the functioning of the different organisations working in association with the United Nations.
Activity:
Question 1.
Name the UN Secretary-General who later on became the President of his country.
Answer:
Mr. Kurt Waldheim of Austria.
![]()
Question 2.
Name the UN Secretary-General who died in an air-crash.
Answer:
Dag Hammarskjold of Sweden, died on September 18, 1961, during a Congo Mission.
9th Std Political Science Questions And Answers:
- Post World War Political Developments Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers
- India’s Foreign Policy Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers
- India’s Defence System Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers
- The United Nations Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers
- India and Other Countries Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers
- International Problems Class 9 Political Science Questions And Answers