Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Cell and Cell Organelles Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 8 Science Chapter 10 Cell and Cell Organelles Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Cell and Cell Organelles Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Who am I?
Question a.
I am ATP producing factory.
Answer:
Mitochondria
Question b.
I am single-layered but maintain cellular osmotic pressure.
Answer:
Vacuole
Question c.
I support the cell, but I am not cell wall. I have a body resembling net.
Answer:
Endoplasmic reticulum
![]()
Question d.
I am chemical factory of the cell.
Answer:
Chloroplasts in case of plant cells can be called chemical factory as they synthesise carbohydrates. Ribosomes also synthesise proteins, so those can also be called chemical factory. Golgi complex is secretory in function, hence it can be also called factory. Mitochondria though mainly referred to as powerhouse of the cell, it is also mentioned as chemical factory by some authors.
Question e.
Leaves are green because of me.
Answer:
Chloroplast.
2. What would have happened? If……….
Question a.
RBCs had mitochondria.
Answer:
Mitochondria continuously carry out oxidation and form energy inside the cell. They produce energy-rich compound, ATP. In this process, they utilize carbohydrates, fats and proteins present in the cell. If RBCs has mitochondria, they would have used oxygen for this purpose than carrying it to all the cells of the body. The cells would not have obtained oxygen.
![]()
Question b.
There had been no difference between mitochondria and plastids.
Answer:
Mitochondria carry out oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, etc. with the help of enzymes. Plastids are synthesising carbohydrates with the help of solar energy and chlorophyll. Both the cell organelles have their own sets of different enzymes as per their role. If there would have been no difference between mitochondria and plastids, the specific functions would not have been taken place.
Question c.
Genes had been absent on the chromosomes.
Answer:
Genes are functional segments on the chromosomes which are responsible for transmitting the hereditary information.
Question d.
Plasma membrane had not been selectively permeable.
Answer:
Selectively permeable membrane allows some substances to enter the cell, while prevents other unwanted or harmful substances. If plasma membrane would not have been selectively permeable, there would be no control over entry and exit of any substances. The process of osmosis would also be erroneous in such case.
Question e.
Plants lacked anthocyanin.
Answer:
If plants lacked anthocyanin, no part of the plant would display purple or blue colour. Anthocyanin attracts the insects for pollination and seed dispersal. These processes will be affected due to lack of anthocyanin. These pigments are also said to be protective in nature for the plant. This protection will not be given to the plant in absence of anthocyanin.
![]()
3. Who is odd man among us? Give reason.
Question a.
Nucleolus, mitochondria, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum
Answer:
Nucleolus. (All the others are cell organelles but nucleolus is not a cell organelle present in cytoplasm.)
Question b.
DNA, Ribosomes, Chlorophyll
Answer:
Chlorophyll. (DNA and Ribosomes are present in plant as well as in animal cells. Chlorophyll is present only in plant cells.)
4. Give functions.
Question a.
Plasma membrane.
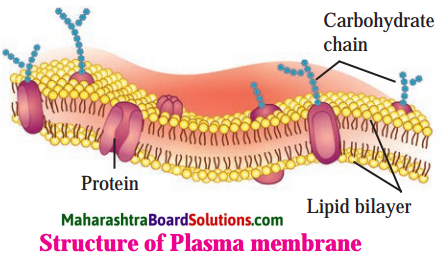
Answer:
- Plasma membrane acts as a selectively permeable membrane. It allows entry of those useful substances which are needed for the cell. It does not allow entry of the harmful and unwanted substances.
- Plasma membrane keeps the homeostasis in the cell. The cell is kept in steady state even if the external environment changes.
- Plasma membrane is responsible for processes of endocytosis and exocytosis.
- The processes of diffusion and osmosis are possible only due to plasma membrane.
- In animal cells, plasma membrane is the outermost protective covering of the cell.
![]()
Question b.
Cytoplasm.
Answer:
- All the cell organelles are spread in the cytoplasm of a cell.
- The cytoplasm is the medium for many cellular chemical reactions.
- The cytosol which is the part of cytoplasm other than cell organelles stores many vital substances like amino acids, glucose, vitamins, etc.
- Cytosol also helps in the cellular movements.
Question c.
Lysosome.
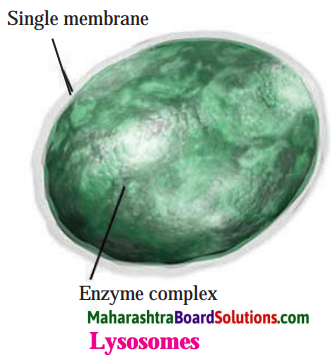
Answer:
- Lysosome helps in the destruction of attacking viruses and bacteria and thereby help in the immune response.
- Lysosomes act as demolition squads. They destroy worn-out cellular organelles and organic debris. This process is called autolysis which All Pagesmeans self-destruction.
- They are also called suicide bags as in a worn out, damaged or old cell, lysosomes automatically burst. The lytic enzymes present in the lysosome digest their own cells.
- Lysosomes can digest stored proteins, fats during starvation.
Question d.
Vacuole.
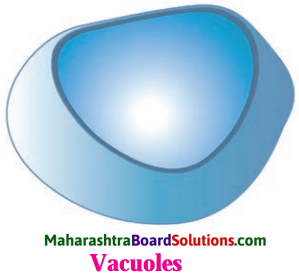
Answer:
- Vacuoles maintain the osmotic pressure of the cell.
- Various metabolic byproducts and end products such as glycogen, proteins, water, etc. are stored in the lysosome.
- In food vacuole of amoeba, the food is temporarily stored till digestion. In other animal cells, vacuoles can store waste products and food.
- Vacuoles of plant cells can provide turgidity and rigidity as it contains good amount of cell sap.
Question e.
Nucleus.
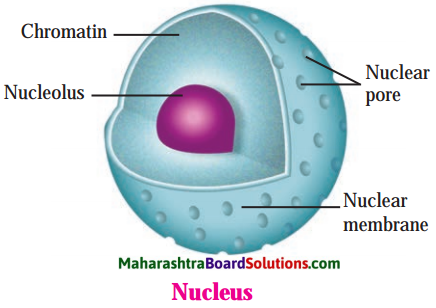
Answer:
- Nucleus is the controlling centre for the entire cell.
- It controls all metabolic activities of the cell.
- The cell division is possible due to the nucleus.
- The chromosomes present in the nucleus carry the genes. These genes are responsible for the transmission of hereditary characters from parental generation to the next generations.
![]()
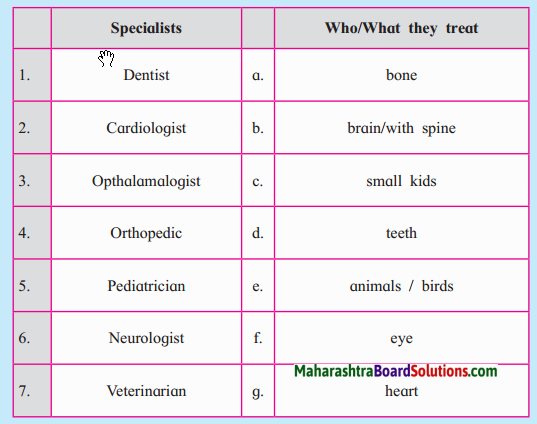
5. Who gives me the colour? (Select the correct option).
Question a.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Red tomato | a. Chlorophyll |
| 2. Green leaf | b. Carotene |
| 3. Carrot | c. Anthocyanin |
| 4. Violet | d. Lycopene |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Red tomato | d. Lycopene |
| 2. Green leaf | a. Chlorophyll |
| 3. Carrot | b. Carotene |
| 4. Violet | c. Anthocyanin |
![]()
Project:
Question 1.
Prepare model of a cell using different ecofriendly materials.
Question 2.
Study osmosis using parchment paper or a similar membrane.
Question 3.
Form a friends’ group in your class. Give each one role of a cell organelle. Present a skit accordingly.
Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Cell and Cell Organelles Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the sentences after filling the blanks:
Question 1.
Cell wall is mainly composed of carbohydrates like ……….. and …………. .
Answer:
Cell wall is mainly composed of carbohydrates like cellulose and pectin.
Question 2.
Plasma membrane is said to be a ……………. …………….. membrane as it allows some substances to enter the cell, while prevents other substances.
Answer:
Plasma membrane is said to be a selectively permeable membrane as it allows some substances to enter the cell, while prevents other substances.
Question 3.
Homeostasis is maintained in the cell by ………….. .
Answer:
Homeostasis is maintained in the cell by plasma membrane.
![]()
Question 4.
An …………… is a specialized subunit having specific function within the cell.
Answer:
An organelle is a specialized subunit having specific function within the cell.
Question 5.
……………. has ribosome granules on its outer surface.
Answer:
Rough ER has ribosome granules on its outer surface.
Question 6.
During starvation, ………………… digest stored proteins, fats.
Answer:
During starvation, lysosomes digest stored proteins, fats.
Question 7.
……………….. is the secretory organ of the cell.
Answer:
Golgi complex is the secretory organ of the cell.
![]()
Question 8.
……………. compound ATP is produced in the mitochondria.
Answer:
Energy-rich compound ATP is produced in the mitochondria.
Given below are incorrect statements. Rewrite them after correcting them:
Question 1.
In mitochondria, the inner membrane is porous and the outer membrane is deeply folded.
Answer:
In mitochondria, the outer membrane is porous and the inner membrane is deeply folded.
Question 2.
Vacuole is bound by double membrane.
Answer:
Vacuole is bound by single membrane.
Question 3.
If fruit pieces are kept in thick saturated sugar solution, the water from fruit pieces enter the sugar solution resulting into their swelling.
Answer:
If fruit pieces are kept in a thick saturated sugar solution, the water from fruit pieces enter the sugar solution resulting into their shrinking.
![]()
Question 4.
Raisins kept in water shrink after an hour.
Answer:
Raisins kept in water swell after an hour.
Question 5.
Lysosome produces vacuoles and secretory vesicles.
Answer:
Golgi complex produces vacuoles and secretory vesicles.
Who gives me the colour? (Select the correct option)
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Nucleus | a. Pipelines of the cell |
| 2. Endoplasmic reticulum | b. Powerhouse of the cell |
| 3. Golgi complex | c. Suicidal bags |
| 4. Mitochondria | d. Packing department |
| 5. Lysosomes | e. Controlling centre |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Nucleus | e. Controlling centre |
| 2. Endoplasmic reticulum | a. Pipelines of the cell |
| 3. Golgi complex | d. Packing department |
| 4. Mitochondria | b. Powerhouse of the cell |
| 5. Lysosomes | c. Suicidal bags |
![]()
Find the odd one out by giving suitable reasons:
Question 1.
Demolition squads, Suicide Bags, Immune system, Powerhouse of the cell.
Answer:
A powerhouse of the cell. (All the others are descriptions of the lysosomes.)
Question 2.
Lignin, Suberin, Cutin, Iodine
Answer:
Iodine. (All the others are polymers present in the cell wall.)
Question 3.
Nucleolus, Genes, Chromosomes, Ribosomes
Answer:
Ribosomes. (All the others are inclusions in the nucleus.)
Write definitions/Give meanings:
1. Homeostasis: The tendency of the cell to keep the cellular environment constant in spite of changes in the outer: environment is called homeostasis.
2. Endocytosis: To take in the food or any other substance from outer environment into the cell is called endocytosis.
3. Exocytosis: To give out the unwanted substances from the cell to the outer « environment is called exocytosis.
4. Diffusion: The movement of the molecules from region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration is called diffusion.
5. Osmosis: The movement of solute from low concentration to high concentration and the movement of solvent from high concentration to the region of low concentration across semipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
6. Plasmolysis: When the cell is kept ?! in hypertonic medium, the water exits through the process of exosmosis causing shrinkage of the cytoplasm, this is known as plasmolysis.
7. Isotonic solution: When the concentration of the cell and that of the medium in which the cell is kept is same, then such solution is called isotonic solution.
8. Hypotonic solution: When the concentration of the water in the cell is less than that of the concentration of the water in the surrounding medium in which the cell is kept, then such solution is called hypotonic solution.
9. Hypertonic solution: When the concentration of the water in the cell is more than that of the concentration of water in the surrounding medium then such solution is called hypertonic solution.
![]()
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell:
Answer:
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| 1. Nucleoid is present instead of a well-formed nucleus. | 1. Nucleus is well-formed with nuclear membrane, chromatin network and nucleolus. |
| 2. Chromosome number is always one. | 2. Chromosome number is more than one and is specific for every species. |
| 3. Membrane-bound cell organelles are absent. | 3. There are membrane-bound cell organelles. |
| 4. The size of the cell is 1 to 10 micrometre. Example: Bacteria | 4. The size of the cell is 5 to 100 micrometre. Example: All highly evolved unicellular and multicellular plants and animals. |
![]()
Question 2.
Plant cell and animal cell
Answer:
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| 1. The cell wall is the outermost covering on the cell. The plant cells have both cell wall and the cell membrane | 1. The cell membrane or plasma membrane is the outermost covering of the cell. The animal cells do not have cell wall |
| 2. The vacuoles are large and centrally placed. | 2. The vacuoles are small and uniformly distributed in the cytoplasm. |
| 3. There are plastids in the plant cells. The chloroplasts have chlorophyll. | 3. The plastids are absent in the animal cells. |
| 4. The lysosomes are absent in the plant cells. | 4. Lysosomes are present in the animal cells. They contain digestive enzymes. |
| 5. The cytoplasm is thin and pushed to the periphery due to central vacuole. | 5. The cytoplasm is dense and granular. It is uniformly spread throughout the cell. |
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What are the components of plasma membrane?
Answer:
In plasma membrane, protein molecules are embedded in two layers of phospholipids.
![]()
Question 2.
Which part of the cell maintains the homeostasis?
Answer:
Plasma membrane of the cell maintains the homeostasis.
Question 3.
What are genes?
Answer:
Genes are the functional segments on the chromosomes that carry hereditary i information from the parental generation to the offspring.
Question 4.
What is meant by rough ER?
Answer:
The endoplasmic reticulum that has ribosomes on its outer membrane is called rough ER.
Question 5.
Write the examples of plant pigments.
Answer:
Chlorophyll, Carotene, Xanthophyll, Anthocyanin, Betalains and Lycopene are some of the plant pigments.
Question 6.
What are the inclusions in the stroma of chloroplasts?
Answer:
Enzymes, DNA, ribosomes and carbohydrates that are necessary for photosynthesis are present in the stroma of the chloroplasts.
![]()
Question 7.
Which staining technique was developed by Camilio Golgi? Where was this technique used?
Answer:
Camilio Golgi developed the staining technique called ‘Black reaction’ which was used in the study of nervous system.
Question 8.
What type of work is done by National Centre for Cell Science?
Answer:
National Centre for Cell Science – NCCS is involved in research in cytology and research about cancer treatment and it also provides services for National Animal cell repository.
Question 9.
Ripe tomatoes appear red.
Answer:
When green tomatoes become ripe they lose chlorophyll and develop red pigment in them called lycopene. Therefore, ripe tomatoes appear red.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Raisins swell after keeping in plain water.
Answer:
When raisins are placed in plain water, there is action of endosmosis. The outer skin of raisins acts like selectively permeable membrane. Since the concentration of water inside the raisin is lesser than the concentration of water in the outer medium, water enters in the raisin. This causes raisins to swell after keeping them in plain water.
![]()
Question 2.
The fruit pieces kept in sugar syrup show shrinking.
Answer:
There is more concentration of water in the fruit pieces as compared to the concentration of water in the sugar syrup. Therefore, water is lost out by exosmosis. The membranes of the fruit pieces act as selectively permeable membranes. Thus the process of plasmolysis occurs resulting into shrinking of the fruit pieces.
Question 3.
The nucleus of the sieve tubes of the plant phloem is lost.
Answer:
The sieve tubes of the plant phloem conduct the food in plants. To make this transport easier, the nucleus of the sieve tubes of the plant phloem is lost,
Question 4.
Plant cells have less mitochondria than those of animal cells.
Answer:
Mitochondria are the cell organelles which are called powerhouse of the cell. They produce energy in the form of ATP. Animals are motile and need more energy for walking, running and moving. Plants are stationary. They do not need energy to greater extent. Therefore, they have lesser number of mitochondria.
Question 5.
Vacuoles do not have any typical size or shape.
Answer:
Vacuoles change their shape and size as per the need of the cell. Thus they do not have any fixed shape or size.
![]()
Question 6.
Ripe tomatoes appear red.
Answer:
When green tomatoes become ripe they lose chlorophyll and develop red pigment in them called lycopene. Therefore, ripe tomatoes appear red.
Give functions:
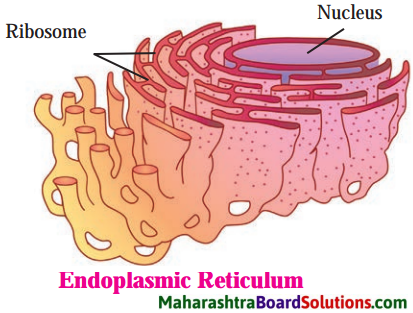
Question 1.
Endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer:
- Endoplasmic reticulum or ER is the supporting framework of the cell.
- The ribosomes attached to the membrane of the ER synthesize proteins. These proteins are conducted by ER.
- The detoxification process is done by ER. The toxins that enter the cell through food, air and water are removed out by making them water soluble.
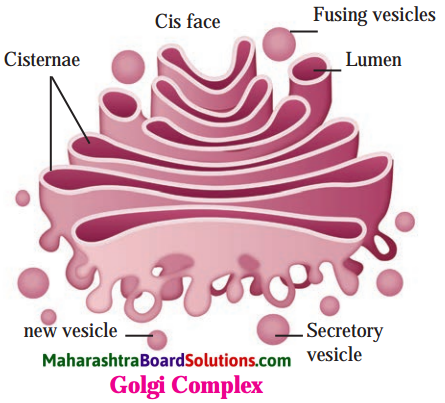
Question 2.
Golgi complex.
Answer:
- Different secretions are prepared in the Golgi complex. Hence it is called the secretory organ of the cell.
- The secretions are modified and sorted out as per their functions. They are further packed.
- The enzymes, mucus, proteins, pigments, etc. are sorted and then dispatched to various target regions like plasma membrane, lysosome, etc.
- Golgi complex also produces vacuoles and secretory vesicles.
- Formation of cell wall, plasma membrane and lysosomes is aided by Golgi complex.
![]()
Question 3.
Plastids.
Answer:
- Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll. They carry out the process of photosynthesis. They convert solar energy to chemical energy in the form of food.
- Chromoplasts with different pigments can impart different colours to flowers and fruits.
- Leucoplasts are responsible for the synthesis and storage of food like starch, oils and proteins.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
How does endosmosis and exosmosis occur in the cell?
Answer:
- When the water concentration inside the cell is less as compared to the medium in which it is present, then the endosmosis takes place. This makes the water to enter inside the cell.
- When water concentration inside the cell is more than the water concentration in the medium in which it is present, then the water comes out of the cell. This is called exosmosis.
- Since the cell membrane acts as a semipermeable membrane, the processes of endosmosis and exosmosis takes place in the cell.
Question 2.
What is cytoplasm? What are the constituents of cytoplasm?
Answer:
- The jelly like material present between the cell membrane and nucleus is called cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasm without cell organelles is called cytosol.
- All the cell organelles are spread in the cytoplasm.
- Cytosol stores many vital constituents such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, etc.
- The cytoplasm of animal cells is dense and granular while that of plant cells is thin and peripheral. It is pushed to sides due to large central vacuole.
Question 3.
Describe the structure of the nucleus in the cell.

Answer:
- Nucleus is the most important part of the eukaryotic cell.
- Inside the nucleus there is round darkly stained nucleolus.
- The nucleus is covered over by double membrane which is porous.
- The nuclear pores allow the transport of different substances in and out of the nucleus to cytoplasm.
- Inside the nucleus is the chromatin network which contains chromosomes. Chromatin fibres are thin which condense to form chromosomes. The chromosomes become clear and distinct at the time of cell division.
- In every cell there are specific number of chromosomes. Chromosomes contain genes which are bearers of hereditary characters.
![]()
Question 4.
Why is endoplasmic reticulum compared with the pipelines?
Answer:
- The endoplasmic reticulum works as pipelines to carry different substances in the cell.
- It is a net like structure consisting of interconnected small tubes and sheets filled with fluid.
- On the inner side the E.R. is connected to nucleus while at the outer side it is in contact with plasma membrane. Therefore, it works like a pipeline.
Question 5.
Write an account of the different structures seen in Golgi complex.
Answer:
- Golgi complex is made up of 5-8 hollow and flat sacs called cisternae.
- These are placed parallel to each other and are filled with different enzymes.
- Golgi complex has two faces called forming face and maturation face.
- The proteins packed in vesicles and coming from ER reach Golgi complex through cytoplasm.
- They fuse with the formation face of the Golgi membranes for emptying their contents in the cisternae.
- When these contents pass through the cisternae, they are chemically modified with the help of enzymes and are again packed in the vesicles.
- These vesicles come out of Golgi ‘ complex at the maturation face.
Question 6.
How is energy produced in the mitochondria? How the structures of mitochondria help in this process?
Answer:
- Around every mitochondrion there is a double membrane.
- The outer membrane of these is porous while the inner membrane is deeply folded.
- These folds or ‘cristae’ enclose the matrix filled with proteinaceous gel containing ribosomes, phosphate granules and DNA. Protein synthesis takes place in this matrix.
- Mitochondria carry out oxidation of carbohydrates and fats in the cell. This produces energy in the form of ATP, s i.e. Adenosine Tri Phosphate
![]()
Question 7.
What is the benefit of foldings of inner membrane in mitochondria?
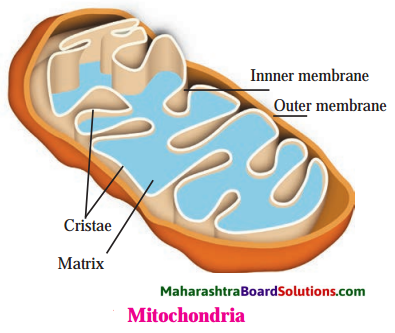
Answer:
The structure of the inner mitochondrial membrane is extensively folded and compartmentalized. The numerous imaginations of the membrane are called cristae. This folded inner membrane increases the area which is about 5 times more than that the outer membrane due to cristae. Cristae membranes have small round protein complexes known as Fx particles. In these particles the process of energy production goes on.
Research:
Question 1.
Keep 4 – 5 raisins in water and observe after an hour. Afterward, keep the same raisins in sugar solution and observe after an hour. Note down the observations and discuss in the classroom.
Answer:
When raisins are kept in water its outer skin acts as a semi-permeable membrane. The water content inside the raisin is lesser as compared to the water content in the outside medium. Therefore the water enters in the raisins due to process of endosmosis. Thus if raisins kept in plain water are observed after one hour, they are seen to be swollen.
On the other hand, if raisins are kept in sugar solution, they show plasmolysis and they shrink. The sugar solution acts as hypertonic medium. Water content in the raisin is higher than that present in the sugary solution. Thus water exists from raisins and its content thus shrinks.
![]()
Question 2.
Wooden doors fit very tightly in rainy season. Why does it happen?
Answer:
During rainy season there is more humidity in air. The doors get soaked in rain water. Though wood is non-living, it has the ability to absorb water. As the moisture is more in the surrounding area, it enters the wood. This is a type of endosmosis. It causes the doors to swell. The swollen doors then fit very tightly.
Diagram based questions:
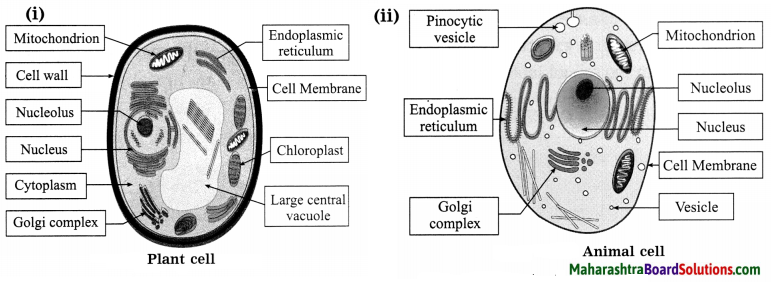
Question 1.
Structure of the cell:
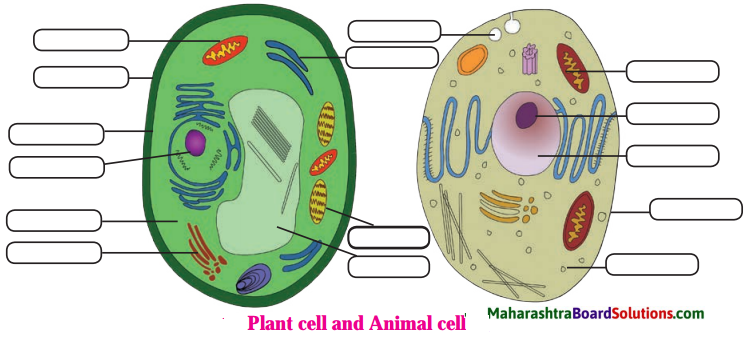
Answer:
(iii) Complete the chart:
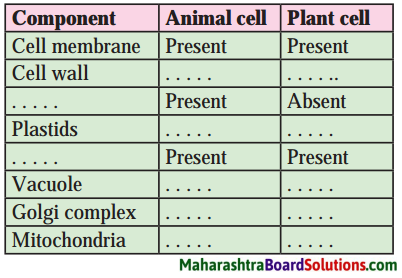
Answer:
| Component | Animal cell | Plant cell |
| Cell membrane | Present | Present |
| Cell wall | Absent | Present |
| Lysosomes | Present | Absent |
| Plastids | Absent | Present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Present | Present |
| Vocuole | Present | Present |
| Golgi complex | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Present | Present |
![]()
Question 2.
Sketch the diagrams to show how osmosis occurs in plant cell if kept separately in isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic medium.
Answer:
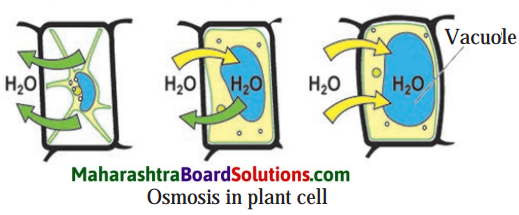
Question 3.
Sketch the diagrams to show how osmosis occurs in animal cell if kept separately in isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic medium
Answer:
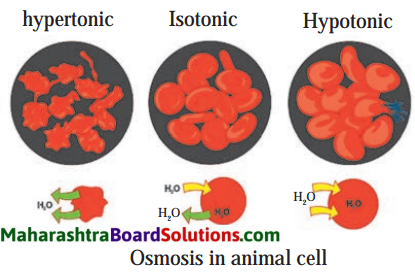
Activity-based questions:
Question 1.
Experiment Activity – Take a drop of water on a clean glass slide. Using an ice-cream spoon, gently scrap the inner surface of your cheek. With a needle, transfer a little material from spoon to the water drop on the slide and spread it evenly. Put a drop of methylene blue stain on the smear. Put a cover slip and observe under microscope. Did you observe the cells with blue nucleus?
Answer:
Students should do this activity at school laboratory. There are squamous epithelial cells in the inner side of the cheek. When stained with methylene blue the nucleus takes up dark stain and can be seen clearly.
![]()
Question 2.
Experiment Activity – Take out a thin peel of Rheo or Croton leaf and observe the chromoplasts under the compound microscope.
Answer:
Students are expected to do the observations in the school laboratory.
Question 3.
Can you recall? Observe the cells of onion peel under the microscope. Have you seen the fully turgid, rectangular cells of onion peelings?
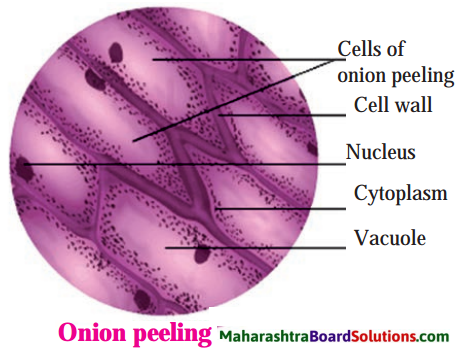
Answer:
Students are expected to do the observations in the school laboratory.
8th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- Living World and Classification of Microbes Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Health and Diseases Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Current Electricity and Magnetism Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Inside the Atom Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Composition of Matter Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Metals and Nonmetals Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Pollution Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Cell and Cell Organelles Class 8 Questions And Answers