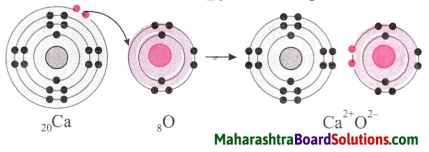
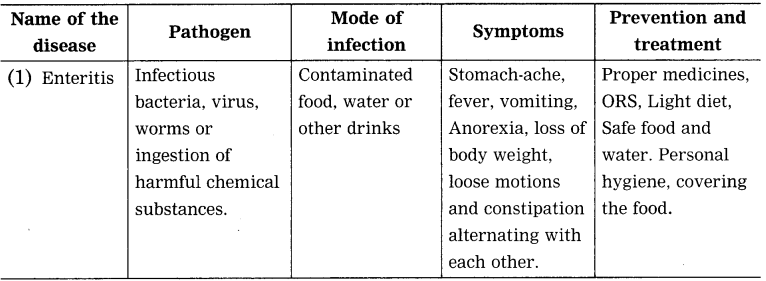
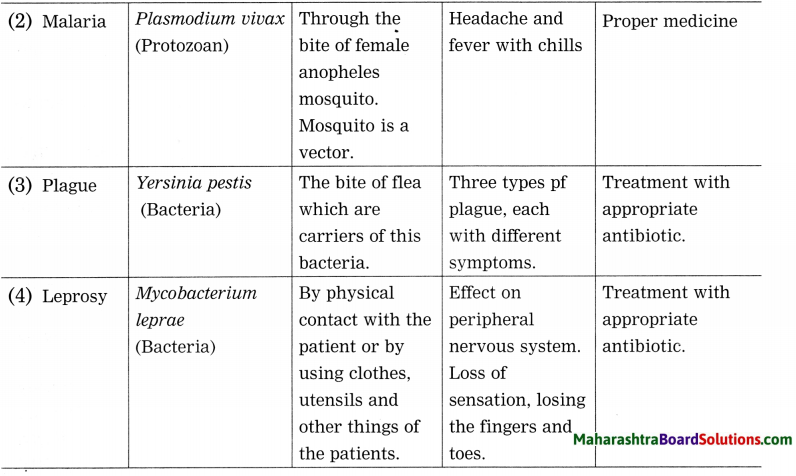
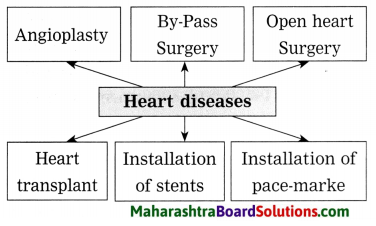
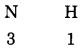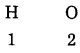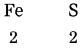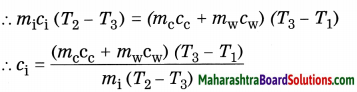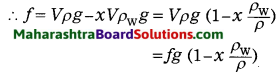Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 5 Inside the Atom Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 8 Science Chapter 5 Inside the Atom Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Inside the Atom Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Answer the following.
Question a.
What is the difference in the atomic models of Thomson and Rutherford?
Answer:
| Thomson’s atomic model | Rutherford’s atomic model |
| 1. According to Thomson’s atomic model, the negatively charged electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge. | 1. According to Rutherford’s atomic model the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus. |
| 2. Atom is homogenous sphere of positive charge. | 2. The positive charge is in the nucleus of the atom. |
Question b.
What is meant by valency of an element? What is the relationship between the number of valence electron and valency?
Answer:
Valency: The capacity of an ; element to combine with another element is known as valency.
Valence electrons: The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom of an element are called valence electrons.
Helium and neon, atoms of both these gaseous element do not combine with any other atom. These elements are chemically inert, i.e. their valency is zero.
Helium atom contains two electrons, indicates that the outermost shell of helium has an electron duplet. The valence shell of neon is completely filled, i.e. neon has an electron octet. Similarly argon contains eight electrons in the valence shell, i.e. argon has an electron octet. It is confirmed that the valency is zero when electron octet (or duplet) is complete.
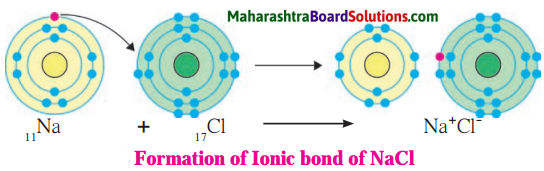
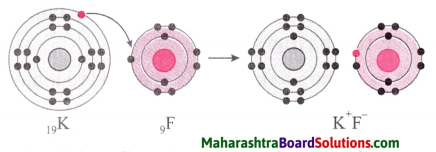
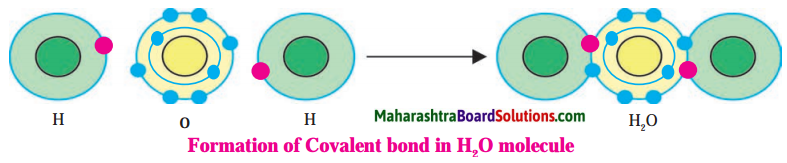
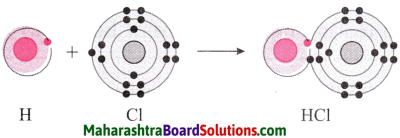
Atoms of all the elements except inert gases have tendency to combine with other atoms, i.e. they have a non zero valency. The molecules formed by combination with hydrogen (E.g. H2, HCl) that valency of hydrogen is one. The electronic configuration of hydrogen shows that there is one electron less than the complete duplet state. This number ‘one’ matches with the valency of hydrogen which is also one.
It means that there is relationship between the valency of an element and the number of electrons in its valence shell.
![]()
Question c.
What is meant by atomic mass i number? Explain how the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
Answer:
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. The atomic number, i.e. the proton number of carbon is 6 and the mass number is total number of protons and neutrons in the carbon, i.e. 6 protons + 6 neutrons = 12. Therefore, the atomic number and mass number of carbon are 6 and 12 respectively.
Question d.
What is meant by subatomic particle? Give brief information of three subatomic particles with reference to electrical charge, mass and location.
Answer:
A particle which is a constituent of an atom hence smaller than the atom is called subatomic particle.
An atom is formed from the nucleus and the extranuclear part. These contain three types of subatomic particles.
The nucleus contains two types of subatomic particles together called nucleons. Protons and neutrons are the two types of nucleons or subatomic particles and electrons are subatomic particles in the extra nuclear part.
1. Proton (p): Proton is a positively charged subatomic particle in the atomic nucleus. The positive charge on the nucleus is due to the proton in it. A proton is represented by the symbol ‘p’. Each proton carries a positive charge of +1e. (1e = 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb). When total positive charge on the nucleus is expressed in the unit ‘e’, its magnitude is equal to the number of proton in the nucleus.
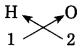
The mass of one proton is approximately lu (1 Dalton).
(1u = 1.66 × 10-27g) (The mass of one hydrogen atom is also approximately lu.)
2. Neutron (n): Neutron is an electrically neutral subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol ‘n’. The number of neutron in the nucleus is denoted by the symbol ‘N’ Atomic nuclei of all the elements except hydrogen with atomic mass lu, contain neutrons. The mass of a neutron is approximately lu, which is almost equal to that of a proton.
3. Electron (e–): Electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle and is denoted by the symbol ‘e-’. Each electron carries one unit of negative charge (-1e). Mass of an electron is 1800 times less than that of a hydrogen atom. Therefore the mass of an electron can be treated as negligible. Electron in the extranuclear part revolve in the discrete orbits around the nucleus. The energy of an electron is determined by the shell in which it is present.
![]()
2. Give scientific reasons:
Question a.
All the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Answer:
- The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
- The electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- The mass of an electron is negligible compared to that of a proton or a neutron.
- Hence, the mass of an atom depends mainly on the number of protons and neutrons. Therefore, practically all the mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
Question b.
Atom is electrically neutral.
Answer:
- An atom is made of two parts, viz. the nucleus and the extranuclear part.
- The nucleus is positively charged. The positive charge on the nucleus is due to protons.
- The extranuclear part of an atom is made of negatively charged electrons.
- In an atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of extranuclear electrons.
- The magnitude of the positive charge on the nucleus equals the magnitude of the negative charge on the electrons. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is electrically neutral.
Question c.
Atomic mass number is a whole number.
Answer:
- The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number (A).
- As protons and neutrons are whole numbers, the atomic mass number is also a whole number.
![]()
Question d.
Atoms are stable though negatively charged electron are revolving within it.
Answer:
- The entire mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus and the positively charged nucleus at centre of an atom.
- The negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- The total negative charge on all the electron is equal to positive charge on the nucleus. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is stable.
3. Define the following terms.
Question a.
Atom:
Answer:
An atom is the smallest particle of an element which retains its chemical identity in all physical and chemical changes.
Question b.
Isotope
Answer:
Atoms of the same element having the same atomic number, but different atomic mass numbers are called isotopes.
Question c.
Atomic number
Answer:
The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by Z.
Question d.
Atomic mass number
Answer:
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number. It is denoted by A.
![]()
Question e.
Moderator in nuclear reactor
Answer:
The substance which reduces the speed of fast-moving neutrons produced in a fission is called a moderator.
4. Draw a neal labelled diagram.
Question a.
Explain Rutherford’s scattering experiment.
Answer:
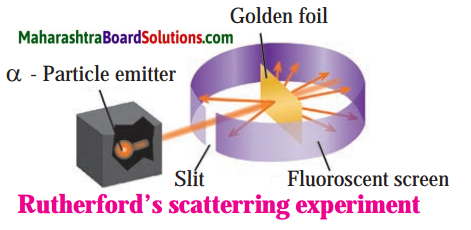
Alpha particles emitted by radioactive element bear a positive charge. Rutherford bombarded alpha particles through a very thin gold foil. He observed the path of α – particles by means of a fluorescent screen around the gold foil. It was expected that
- Most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil without any deviation.
- Some alpha particles were deflected from their path through small angles.
- A few alpha particles were scattered at large angles.
- A still smaller number of same sign particles get deflected through a larger angle and one a-particle out of 20000 bounced back in the direction opposite to the original path.
Question b.
Thomson’s atomic model.
Answer:
Thomson’s plum pudding model of atom:
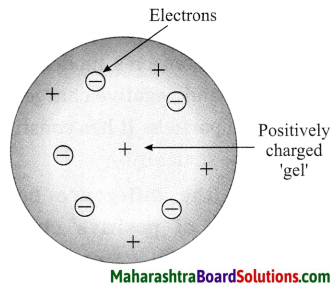
- According to Thomson’s model the positive charge is distributed throughout the atom and the negatively charged electron: are embedded in a gel of positive charge (a plum pudding model).
- The distributed positive charge is balanced by the negative charge on the electrons. Therefore the atom becomes electrically neutral.
Question c.
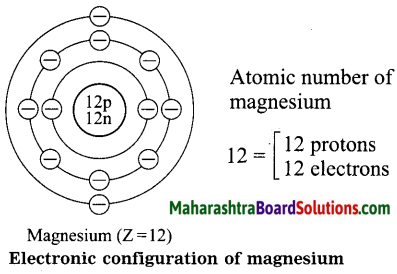
Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of magnesium (Atomic number 12).
Answer:
Question d.
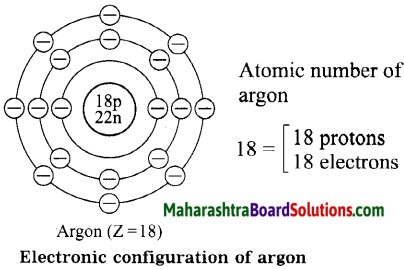
Diagrammatic sketch of electronic configuration of argon (Atomic number 18).
Answer:
5. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
Electron, proton, neutron are the types of ………… in an atom.
Answer:
Electron, proton, neutron are the types of subatomic particles in an atom.
![]()
Question 2.
An electron carries a ……………. charge.
Answer:
An electron carries a negative charge.
Question 3.
The electron shell ………….. is nearest to the nucleus.
Answer:
The electron shell K is nearest to the nucleus.
Question 4.
The electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of Magnesium is …………….. .
Answer:
The electronic configuration of magnesium is 2, 8, 2. From this it is understood that the valence shell of Magnesium is M.
Question 5.
The valency of hydrogen is one as per the molecular formula H2O. Therefore valency of ‘Fe’ turns out to be ………….. as per the formula Fe2O3.
Answer:
The valency of hydrogen is ‘one’ as per the molecular formula H2O. Therefore valency of ‘Fe’ turns out to be 3 as per the formula Fe2O3.
6. Match the pairs.
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Proton | a. Negatively charged |
| 2. Electron | b. Neutral |
| 3. Neutron | c. Positively charged |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Proton | c. Positively charged |
| 2. Electron | a. Negatively charged |
| 3. Neutron | b. Neutral |
![]()
7. Deduce from the datum provided.
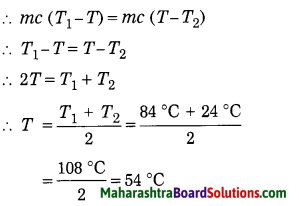
Question 1.
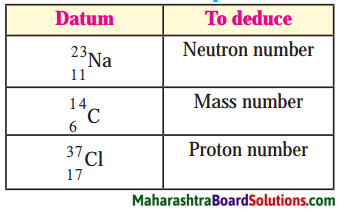
Answer:
1. There are 12 neutrons in the sodium \(\left({ }_{11}^{23} \mathrm{Na}\right)\).
(N = A – Z) 23 – 11 = 12
2. Atomic mass number of \({ }_{6}^{14} \mathrm{C}\) is 14.
3. There are 17 protons in chlorine \(\left({ }_{37}^{17} \mathrm{Cl}\right)\)
Project:
Explain the atomic models using the material such as old C.D., balloon, thread, marbles, etc.
Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Inside the Atom Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the sentences after filling the blanks:
Question 1.
An atom is electrically ……………. .
Answer:
An atom is electrically neutral.
Question 2.
Except hydrogen, the nuclei of all atoms contain ………….. .
Answer:
Except hydrogen, the nuclei of all atoms contain neutrons.
Question 3.
\({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\), …………… and …………. are isotopes of carbon.
Answer:
\({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\), \({ }_{6}^{13} \mathrm{C}\) and \({ }_{6}^{14} \mathrm{C}\) are isotopes of carbon.
Question 4.
An atom has 11 protons and …………. neutrons and hence its atomic mass number is 23.
Answer:
An atom has 11 protons and 12 neutrons and hence its atomic mass number is 23.
Question 5.
The element ………….. has two electrons in the K shell, but it is a noble gas.
Answer:
The element helium has two electrons in the K shell, but it is a noble gas.
Question 6.
Isotopes of the element have the same ……….. properties.
Answer:
Isotopes of the element have the same chemical properties.
![]()
Question 7.
Electrons must absorb …………….. to transit between orbits.
Answer:
Electrons must absorb energy to transit between orbits.
Question 8.
……….. discovered the electron.
Answer:
J. J. Thomson discovered the electron.
Question 9.
∝ – particles have ………….. charge.
Answer:
∝ – particles have positive charge.
Question 10.
Electrons revolve around the …………….. in certain discrete orbits.
Answer:
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in certain discrete orbits.
Question 11.
The shell-wise distribution of electrons is called the ………………… .
Answer:
The shell-wise distribution of electrons is called the electronic configuration.
Question 12.
Democritus termed the smallest particles of matter as …………… .
Answer:
Democritus termed the smallest particles of matter as atoms.
Question 13.
………………. discovered neutron.
Answer:
James Chadwick discovered neutron.
![]()
Question 14.
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in paths called ………….. .
Answer:
Electrons revolve around the nucleus in paths called orbits.
Question 15.
The second shell has the capacity of ……………… .
Answer:
The second shell has the capacity of 8 electrons.
Question 16.
Electrons in the ………….. shell have minimum energy.
Answer:
Electrons in the K or first shell have minimum energy.
Question 17.
Electrons in an atom occupy shells in increasing order of …………… .
Answer:
Electrons in an atom occupy shells in increasing order of energy.
Question 18.
Atomic masses are measured in a unit called …………… .
Answer:
Atomic masses are measured in a unit called dalton.
Question 19.
According to the atomic model of …………….., electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge.
Answer:
According to the atomic model of Thomson, electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge.
![]()
Question 20.
All atoms, except ………….. contain neutrons in their nuclei.
Answer:
All atoms, except normal hydrogen contain neutrons in their nuclei.
Question 21.
The maximum capacity of the M shell is ………………… electrons.
Answer:
The maximum capacity of the M shell is 18 electrons.
Question 22.
The atom of the element ……………. has eight electrons in the outermost shell.
Answer:
The atom of the element neon has eight electrons in the outermost shell.
Rewrite the following statements selecting the correct options:
Question 1.
The symbol A is used to denote the …………. .
(a) atomic number
(b) atomic radius
(c) atomic mass number
(d) atomic mass
Answer:
(c) atomic mass number
Question 2.
The existence of isotopes is due to the presence of different number of …………….. .
(a) electrons
(b) protons
(c) neutrons
(d) positrons
Answer:
(c) neutrons
![]()
Question 3.
In the nucleus of a sodium atom (\({ }_{11}^{23} \mathrm{Na}\)), there are ……………… neutrons.
(a) 11
(b) 12
(c) 10
(d) 9
Answer:
(b) 12
Question 4.
Isotopes of an element have the same number of …………….. .
(a) neutrons
(b) nucleons
(c) electrons
(d) atoms
Answer:
(c) electrons
Question 5.
The great Indian philosopher ………….. proposed that matter is made up of invisible tiny particles.
(a) Aryabhatta
(b) Kanad
(c) Bhaskaracharya
(d) Chanakya
Answer:
(b) Kanad
Question 6.
The maximum capacity of the M shell is …………… electrons.
(a) 2
(b) 8
(c) 18
(d) 32
Answer:
(c) 18
Question 7.
The mass of the electron is …………….. times less than that of a hydrogen atom.
(a) 1800
(b) 8100
(c) 1550
(d) 1600
Answer:
(a) 1800
![]()
Question 8.
The L shell is the valence shell in …………. .
(a) hydrogen
(b) chlorine
(c) oxygen
(d) sodium
Answer:
(c) oxygen
Question 9.
The M shell is the valence shell in ……………….. .
(a) fluorine
(b) neon
(c) carbon
(d) chlorine
Answer:
(d) chlorine
Question 10.
The N shell is the valence shell in ………….. .
(a) fluorine
(b) chlorine
(c) bromine
(d) helium
Answer:
(c) bromine
Question 11.
The maximum capacity of the N shell is ……………. electrons.
(a) 2
(b) 32
(c) 18
(d) 8
Answer:
(b) 32
Question 12.
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the third orbit is ………… .
(a) 3
(b) 8
(c) 32
(d) 18
Answer:
(d) 18
Question 13.
Rutherford alpha-particle scattering experiment was responsible for the discovery of the ………………. .
(a) atomic nucleus
(b) proton
(c) electron
(d) atomic mass
Answer:
(d) atomic mass
Question 14.
Isotopes of element have …………….. .
(a) different atomic numbers and different atomic mass
(b) different atomic numbers but the same atomic mass number
(c) the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers
(d) the same atomic number and the same atomic mass number
Answer:
(c) the same atomic number but different atomic mass numbers
![]()
Question 15.
The nucleus of an atom contains 19 protons and 21 neutrons. The atomic mass number of the element is ………….. .
(a) 19
(b) 21
(c) 40
(d) 39
Answer:
(c) 40
Question 16.
The nucleus of an atom contains 18 protons and 22 neutrons. The atomic number of the element is ……………… .
(a) 18
(b) 40
(c) 22
(d) 4
Answer:
(a) 18
Question 17.
When writing the symbol of its …………… and ………….. are written.
(a) atomic number, atomic mass number
(b) protons, electrons
(c) protons, neutrons
(d) atomic number, electrons
Answer:
(a) atomic number, atomic mass number
Question 18.
The particles in the atomic nucleus are …………….. .
(a) protons and electrons
(b) electrons
(c) electrons and neutrons
(d) protons and neutrons
Answer:
(d) protons and neutrons
State whether the following statements are True or False:
Question 1.
An atom as a whole is electrically neutral
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
The mass of an atom is distributed evenly within it.
Answer:
False. (The mass of atom is not distributed evenly, practically all the mass is concentrated in the nucleus.)
Question 3.
The electron has the same mass as that of the proton.
Answer:
False. (The mass of the electron is much less than that of the proton.)
Question 4.
The electron in the K shell has maximum energy.
Answer:
False. (The electrons in the K shell has minimum energy.)
![]()
Question 5.
Isotopes have same atomic number but different atomic mass number.
Answer:
True.
Question 6.
Matter is composed of molecules and molecules are made of atoms.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
In India, total 22 nuclear reactors in eight places are functioning.
Answer:
True.
Question 8.
The number of electrons in a given orbit is given by the formula n
Answer:
False. (The number of electrons in a given orbit is given by the formula 2n2)
Question 9.
Atomic masses are measured in a unit called the dalton (u).
Answer:
True.
Question 10.
The chemical properties of isotopes are different.
Answer:
False. (The chemical properties of isotopes are the same.)
Question 11.
The maximum capacity of the N shell is 18 electrons.
Answer:
False. (The maximum capacity of the N shell is 32 electrons.)
Question 12.
Deuterium is an isotope of hydrogen.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 13.
Isotopes are used in the treatment of cancer.
Answer:
True.
Question 14.
Atoms of all elements, except normal hydrogen contain neutrons.
Answer:
True.
Question 15.
Electrons moving in different orbits possess the same amount of energy.
Answer:
False. (Electrons moving in different orbits possess different amounts of energy.
Question 16.
Rutherford discovered the neutron.
Answer:
False. (Chadwick discovered the neutron.)
Question 17.
The nth orbit contains at the most 2n2 electrons.
Answer:
True.
Question 18.
Electrons have different energies according to their orbits.
Answer:
True.
Question 19.
The capacity of the second orbit is 18 electrons.
Answer:
False. (The capacity of the second orbit is 8 electrons.)
Question 20.
The radioactive isotope Sodium-24 is used in the medical treatment of cancer.
Answer:
False. (The radioactive isotope Sodium-24 is used for detection of cracks in the underground pipes.)
![]()
Question 21.
Uranium-235 is used in the production of electricity.
Answer:
True.
Consider the relation between I the items in the first pair and write the correlation for second pair:
Question 1.
K : 2 : M : …………. .
Answer:
18
Question 2.
Carbon : 2, 4 : : Fluorine : …………….. .
Answer:
2, 7
Question 3.
Nitrogen : Valency three : : Fluorine : …………….. .
Answer:
valency one
Question 4.
Atomic radius : pm : Atomic mass : ……………. .
Answer:
u
Question 5.
NaH : Valency of Na : 1 : : MgCl2 : Valency of Mg …………… .
Answer:
2
Question 6.
\(35 \mathrm{Cl}\) : number of neutrons 18 : : \({ }^{37} \mathrm{Cl}/latex] : …………….. .
Answer:
number of neutrons 20
![]()
Question 7.
Protons : Positive : : ……………. : Neutral.
Answer:
Neutrons.
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Thomson | a. Well defined orbits |
| 2. Rutherford | b. Neutron |
| 3. Chadwick | c. Scattering experiment |
| 4. Bohr | d. Electron |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Thomson | d. Electron |
| 2. Rutherford | c. Scattering experiment |
| 3. Chadwick | b. Neutron |
| 4. Bohr | a. Well defined orbits |
Question 2.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Atom | a. Treatment of goitre |
| 2. Isotopes of iodine | b. Protons + Neutrons |
| 3. Atomic mass number | c. Different number of neutrons |
| 4. Isotopes | d. Electrically neutral |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Atom | d. Electrically neutral |
| 2. Isotopes of iodine | a. Treatment of goitre |
| 3. Atomic mass number | b. Protons + Neutrons |
| 4. Isotopes | c. Different number of neutrons |
![]()
Question 3.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Alpha particles | a. Inert element |
| 2. Uranium-235 | b. Negatively charged particles |
| 3. Helium | c. Positively charged particles |
| 4. Isotopes | d. Krypton – 92, Barium 141 |
| e. U-233, Th-232 | |
| f. 12C, 13C, 14C |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Alpha particles | c. Positively charged particles |
| 2. Uranium-235 | d. Krypton – 92, Barium 141 |
| 3. Helium | a. Inert element |
| 4. Isotopes | f. 12C, 13C, 14C |
![]()
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Proton and Neutron:
Answer:
| Proton | Neutron |
| 1. The proton is positively charged particle | 1. The neutron does not have any charge. |
| 2. In an atom, the number of protons is always equal to the number of electrons. | 2. In general, in an atom, the number of neutrons is not equal to the number of electrons. |
Question 2.
Neutron and Electron:
Answer:
| Neutron | Electron |
| 1. The neutron is an electrically neutral particle. | 1. The electron is a negatively charged particle. |
| 2. Neutrons are present in the nucleus of an atom. | 2. Electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom in specific orbits. |
![]()
Question 3.
Proton and Electron:
Answer:
| Proton | Electron |
| 1. The proton is a positively charged particle | 1. The electron is a negatively charged particle. |
| 2 Protons are present in the nucleus of an atom. | 2. Electrons revolve around the nucleus of the atom in specific orbits. |
Question 4.
Atomic number and Atomic mass number:
Answer:
| Atomic number | Atomic mass number |
| 1. The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. | 1. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic mass number. |
| 2 All the isotopes of an element have the same atomic number. | 2. Different isotopes of the same element have different mass numbers. |
| 3. The atomic number is represented by the letter Z. | 3. The atomic mass number is represented by the letter A. |
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
Name the particles which are present in the nucleus of an atom.
Answer:
Protons and neutrons are present in the nucleus of an atom.
Question 2.
State the relation between the number of protons, the number of neutrons and the atomic mass number (A) of an element.
Answer:
Atomic mass = Number of + Number of number (A) protons (p) neutrons (n)
Question 3.
Chlorine contains 17 protons and 18 neutrons. What is its atomic mass number?
Answer:
The atomic mass number of chlorine is 35.
Question 4.
Carbon contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons. State its atomic number and atomic mass number.
Answer:
The atomic number of carbon is 6 and the atomic mass number is 12.
![]()
Question 5.
State one use of isotopes of cobalt.
Answer:
Isotopes of Cobalt-60 are used in the treatment of cancer.
Question 6.
State one use of isotopes of i uranium.
Answer:
Isotopes of uranium are used for production of electrical energy.
Question 7.
Write the electronic configuration of oxygen.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of oxygen is 2, 6.
Question 8.
Write the electronic configuration of chlorine.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of chlorine is 2, 8, 7.
Question 9.
State the number of electrons in the L shell of lithium.
Answer:
There is one electron in the L shell of lithium.
Question 10.
State the number of electrons in the M shell of argon.
Answer:
There are 8 electrons in the M shell of argon.
Question 11.
State the number of electrons in the K shell of helium.
Answer:
There are two electrons in the K shell of helium.
![]()
Question 12.
Name isotopes of hydrogen.
Answer:
Hydrogen, Deuterium and Tritium are the isotopes of hydrogen.
Question 13.
Name two isotopes of carbon.
Answer:
[latex]{ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\) and \({ }_{6}^{14} \mathrm{C}\) are the isotopes of carbon.
Question 14.
Name two elements in which the K and L shells of an atom are completely filled with electrons.
Answer:
The elements are neon and argon.
Question 15.
From the symbol \({ }_{8}^{16} \mathrm{O}\), state the electronic configuration of oxygen and the atomic mass number of isotope oxygen.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of oxygen : 2, 6. Atomic mass number of oxygen : 16.
Question 16.
The atomic mass number of an element is 18, and the element contains 8 electrons. What is the number of protons and neutrons in it?
Answer:
Number of protons : 8, Number of neutrons : 10.
Question 17.
An atom contains 2 protons, 2 electrons and 3 neutrons. State its atomic number and atomic mass number.
Answer:
Atomic number: 2, Atomic mass number: 5.
![]()
Question 18.
How many electrons could there be in the outermost orbit of an element whose valency is 3?
Answer:
If the valency of an element is 3 then there is a possibility of 3 or 5 electrons in the outermost orbit.
Question 19.
Which element is used as fuel in atomic reactors?
Answer:
Isotopes of uranium are used as fuel in atomic reactors.
Question 20.
Name the place and the first nuclear reactor in India.
Answer:
Apsara at Bhabha Atomic Research Centre in Mumbai is the first nuclear reactor in India.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Explain Dalton’s atomic theory.
OR
Write the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
Answer:
Dalton’s atomic theory:
- According to Dalton’s atomic theory matter is made up of atoms and atoms are indivisible and indestructible.
- All atoms of an element are alike while different element have different atom with different mass.
Try this:
Question a.
Take a solid ball and a Bundi Laddu. Press both these spheres with your palms. What did you find?
Answer:
Solid ball does not break and Bundi Laddu breaks into pieces if you press hard.
![]()
Question b.
Cut the solid ball with a sharp knife. What did you find?
Answer:
There is no cavity inside the ball.
Question 2.
How will you think about atomic mass distribution according to Thomson’s I model? Whether this distribution is uniform or non uniform as per Dalton’s atomic theory?
(Use your brainpower!
Answer:
In Thomson’s model the distribution of atomic mass is uniform. Dalton’s atomic theory does not say anything about atomic mass distribution.
Question 3.
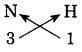
If the striker flicked by you misses the coin that you aimed at, where would the striker go?
Can you tell?
Answer:
The striker will continue to move practically with the same velocity till it strikes some other coin or the edge of the board or enter the pocket.
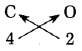
Question 4.
If the striker hits the coin, in which direction would it go? Straight forward to a side or in the reverse direction?
Answer:
Striker may go straight forward or it may be deflected depending upon the exact direction of the motion of the striker.
Question 5.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Thomson’s atomic model.
Answer:

Question 6.
What were the conclusions drawn from the alpha particle experiment performed hy Rutherford?
Answer:
On the basis of the alpha particle experiment the following conclusions were drawn by Rutherford:
- An atom has tiny, dense positively charged nucleus at centre of an atom.
- Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
- Negatively charged particles called electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- The total negative charge on all the ; electron is equal to the positive charge on ‘ the nucleus. As the opposite charges are balanced, the atom is electrically neutral.
- There is an empty space between the i revolving electron and the atomic nucleus.
![]()
Question 7.
Explain Rutherford’s atomic model.
Answer:
- An atom has tiny, dense, positively charged core called the nucleus.
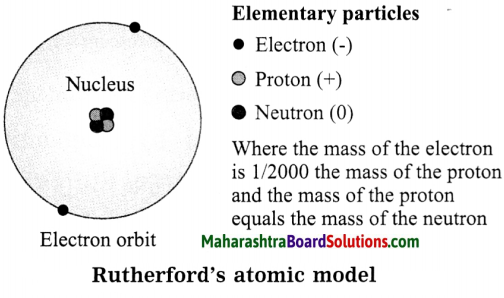
- Most of the mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
- Electrons bear negative charge. They revolve around the nucleus in orbits.
- The structure of an atom may be regarded as a miniature of the solar system, the nucleus as the sun and the electrons as the planets.
Question 8.
Which discovery did point out that an atom has internal structure?
(Use your brainpower!
Answer:
The discovery of radioactivity (1896) pointed out that an atom has internal structure.
Question 9.
What is the difference between the solid atom in Dalton’s atomic theory and Thomson’s atomic model?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
The solid atom in Dalton’s atomic theory is a single particle it does not have any structure and also does not have any constituents. In Thomson’s model, atom is made of positive and negative charges. Thus it is not a single particle. It has constituents and has internal structure.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the difference between the distribution of positive charge in Thomson’s atomic model and Rutherford’s atomic model.
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
According to Thomson’s atomic model, the atom is a homogeneous sphere of positive charge. According to Rutherford’s atomic model, the positive charge is concentrated in the nucleus.
Question 11.
What is the point difference between the place of electron in the atomic models of Thomson and Rutherford?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
According to Thomson’s atomic model, the negatively charged electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge and they are stationary. According to Rutherford’s atomic model, the negatively charged electrons revolve around the nucleus.
Question 12.
What is the thing which is present in Rutherford’s atomic model and not present in Dalton’s and Thomson’s atomic models?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
1. Dalton’s atomic model:
Dalton’s atomic theory does not tell anything about the structure of the atom. There is no mention of electron in Dalton’s atomic theory.
Rutherford’s atomic model:
Rutherford’s atomic model tells about the structure of the atom, i.e. the electron revolving around the nucleus.
2. Thomson’s atomic model:
The electrons are embedded in a gel of positive charge. Here the electrons are stationary and there is no concept of nucleus.
Rutherford’s atomic model:
In Rutherford’s atomic model, the electrons are not stationary, they revolve around the nucleus which is positively charged.
Question 13.
Explain Niels Rohr’s atomic model.
OR
Write the postulates of Bohr’s atomic model.
Answer:
The important postulates of Bohr’s atomic model are as follows:
- The electrons revolving around the atomic nucleus lie in the concentric circular orbits at certain distance from the nucleus.
- Energy of an electron is constant while it is in a particular orbit.
- When an electron jumps from an inner orbit to an outer orbit it absorbs specific amount of energy, and when it jumps from an outer orbit to an inner orbit it emits specific amount of energy.
- The energy emitted or absorbed during these transitions is equal to energy difference between the initial state and the final state of the electron.
![]()
Question 14.
How many types of subatomic particles are found in atom?
Use your brainpower!
Answer:
There are three types of subatomic particles found in atom, viz. the proton, neutron and electron.
Question 15.
Which subatomic particles are electrically charged?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The proton is a positively charged subatomic particle and the electron is a negatively charged particle.
Question 16.
Which subatomic particles are present in the nucleus?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The proton and neutron are present in the nucleus.
Question 17.
Where are electrons revolving around the nucleus placed?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
Electrons revolve in the discrete orbits around the nucleus.
Question 18.
State the characteristics of the neutron.
Answer:
- The neutron is electrically neutral and is denoted by the symbol ‘N’.
- It is present in the nucleus along with the proton.
- The mass of the neutron is almost equal to lu which is almost equal to that of the proton.
Question 19.
State the characteristics of protons.
Answer:
- Protons are positively charged particles and are denoted by the symbol ‘P’.
- They are present in the nucleus of an atom.
- The mass of the proton is very nearly equal to lu which is almost equal to that of the hydrogen atom.
- All the elements contain protons.
Question 20.
State the characteristics of electrons.
Answer:
- Electrons are negatively charged particles and are denoted by the symbol ‘e’.
- They have negligible mass.
- They revolve around the nucleus in certain discrete orbits.
- In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus (Z).
![]()
Question 21.
The symbol used for oxygen is ‘O’. There are 8 protons and 8 neutrons in its nucleus. From this determine the 1 atomic number (Z) and mass number (A) of oxygen and arrange these in a 1 conventional symbol.
Use your brain power!
Answer:
Atomic mass number
= Protons + Neutrons
= 8 + 8
Atomic mass number = 16
Atomic number, i.e. the proton number = 8
The conventional symbol = \(\mathrm{A} \mathrm{O}\)
Z = Atomic number
i.e. number of protons is 8.
A = Atomic mass number = 16.
The conventional symbol = \({ }_{8}^{16} \mathrm{O}\).
Question 22.
Atomic number of carbon is 6. How many electrons are there in a carbon atom?
Use your brainpower!
Answer:
The atomic number of carbon, i.e. the proton number of carbon is 6.
The number of electron in the extranuclear part is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus.
∴ The number of electrons in a carbon atom = 6.
Question 23.
A sodium atom contains 11 electrons. What is the atomic number of sodium?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The number of electron in the extranuclear part is equal to the number of protons, i.e. atomic number. The atomic number of sodium is 11.
Question 24.
The atomic number and mass number of magnesium are 12 and 24 respectively. How will you show this by the convention symbol?
Use your brainpower!
Answer:
The atomic number, atomic mass number and the symbol of an element are written as:
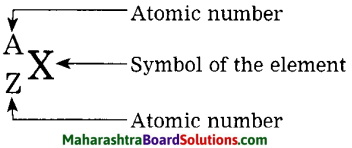
\({ }_{12}^{24} \mathrm{Mg}\) the conventional symbol for magnesium.
Question 25.
The atomic number and mass number of calcium are 20 and 40 respectively. Deduce the number of neutron present in the calcium nucleus.
Use your brain power!
Answer:
There are 20 neutrons in the nucleus of calcium.
[Note: The number of neutrons N = A – Z = 40 – 20 = 20]
![]()
Question 26.
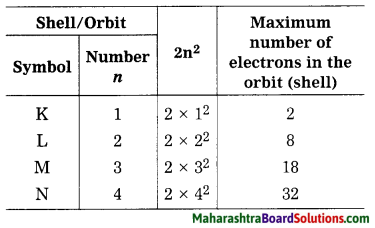
Write a note on distribution of electrons in orbits.
OR
What is the maximum number of ( electrons that can be accommodated in each of the orbits (shells) K, L, M, N, etc.?
Answer:
The number of maximum electrons in different orbits of the atom are fixed. The orbit (shell) closest to the nucleus is: given the number 1, the next orbit the ; number 2… etc. The orbits one are designated ; by letters K, L, M, N,… corresponding to the shell numbers n = 1, 2, 3, 4, … etc. The maximum number of electrons in a given orbit is 2n2, when n is the number of orbit (shell), thus the first shell has the capacity of 2 electrons, the second 8, the third 18, the fourth 32 and so on. The electrons in the K shell have minimum energy. The electrons in the subsequent shells possess higher energy.
Question 27
There is a similarity in atomic structure and solar system. The planets revolve around the sun due to the gravitational force. Which force might be acting in the atomic structure?
Can you tell?
Answer:
The electric force might be acting in the atomic structure. In the atomic structure, electric force is much stronger than gravitational force.
[Note: Here the gravitational force is very very small compared to the electric force, therefore, the gravitational force can be ignored.]
Question 28.
Positively charged proton are together in the nucleus. What might be, one of the function of the neutrons in the nucleus?
Can you tell?
Answer:
One of the function of the neutrons in the nucleus is to keep the protons and neutrons together by nuclear force.
Question 29.
What do you understand by electronic configuration?
Answer:
The shellwise distribution of the electron in an atom of an element is called the electronic configuration.?
![]()
Question 30.
Write the electronic configuration of the following elements:
(1) Hydrogen, (2) Magnesium. (3) Aluminium, (4) Phosphorus, (5) Sulphur.
Answer:
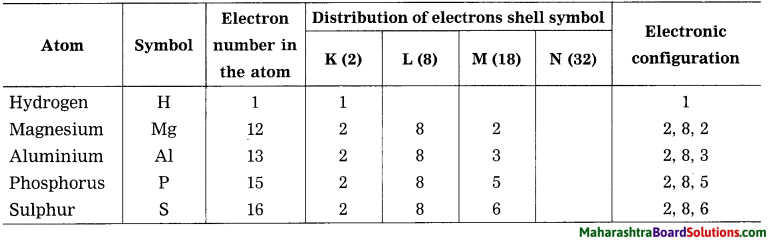
Question 31.
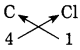
Use the following molecular formulae to determine the valencies of H, Cl, O, S, N, C, Br, I, Na.
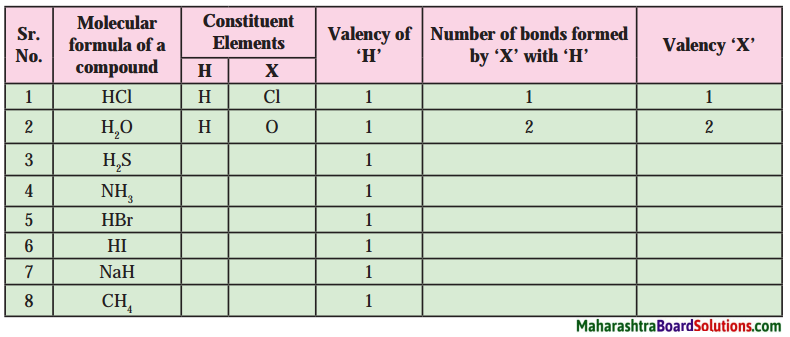
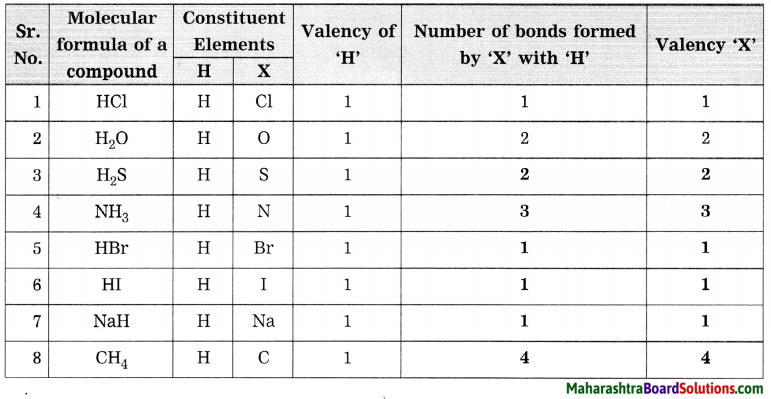
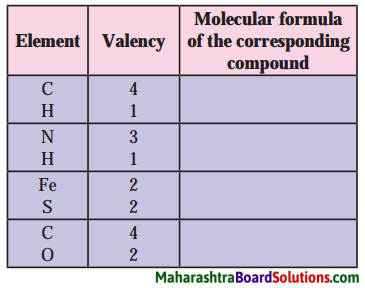
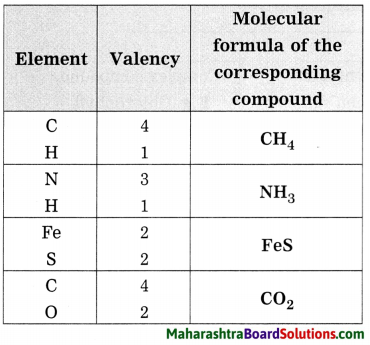
Molecular formulae – H2, HCl, H2O, H2S, NH3, CH4, HBr, HI, NaH.
Can you recall?
Answer:
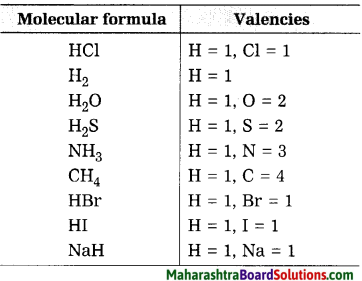
Question 32.
Draw suitable diagrams to show the electronic configuration of the atoms of the following elements: Hydrogen, helium, carbon, neon, sodium, chlorine.
Answer:
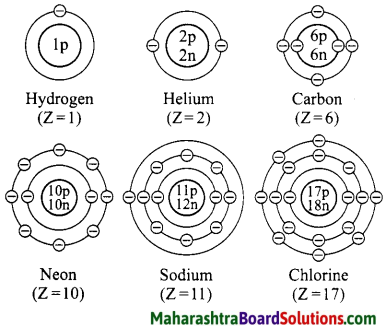
Question 33.
What are the symbols used for the shells which accommodate the electrons in various atoms?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The symbols used for the shells which accommodate the electrons are K, L, M, N, … respectively.
![]()
Question 34
What is the symbol and ordinal number of the innermost shell?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
The symbol of the innermost shell is K and ordinal number of the innermost shell is 1.
Question 35.
Write symbol of electron distribution in shell of fluorine atom?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
Symbol for fluorine atom = F,
Electronic configuration of fluorine \(\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{K} \\2\end{array}\), \(\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{L} \\7\end{array}\).
Question 36.
Which is the outermost shell of fluorine atom?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The outermost shell of fluorine atom is L.
Question 37.
Which is the outermost shell of sodium atom?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The outermost shell of sodium atom is M shell.
![]()
Question 38.
Which is the outermost shell of hydrogen atom?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The outermost shell of hydrogen is K shell.
Question 39.
What is meant by the atomic number (Z) of an element?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
Atomic number (Z): The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number. It is denoted by Z.
Question 40.
Atomic numbers (Z) of some elements are given here. Write down the number of electron present in the outermost shell of each of them.
Use your brain power!
Answer:
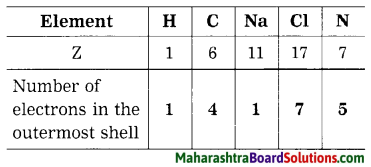
Question 41.
The number of electrons of some elements is given here. By using it write the electronic configuration, number of valence electron and valency of the respective elements.
Use your brain power!
Answer:
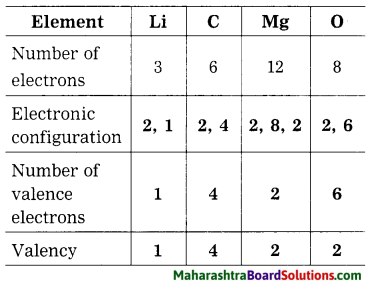
Question 42.
Why are the atomic numbers and atomic mass numbers always in whole numbers?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom is called the atomic mass number (A). The number of electrons or protons in an atom is called the atomic number (Z). Both protons and neutrons are whole numbers, therefore, atomic numbers and atomic mass numbers are always in whole numbers.
![]()
Question 43.
Sulphur contains 16 protons and 16 neutrons. What would be its atomic number and mass number?
Use your brain power.
Answer:
The atomic number of sulphur is 16 and the atomic mass number is 32.
Question 44.
State the uses of isotopes.
Answer:
Isotopes of some elements are radioactive. Isotopes are used in various fields such as industry, agriculture, medicine, research field.
- Isotopes of uranium is used for nuclear fission and production of electricity.
- Cobalt – 60 are used in the treatment of cancer.
- Iodine – 131 is used in the treatment of goitre.
- The radioactive isotopes, Sodium – 24 are used for detection of cracks (leakage) in the underground pipes.
- Radioactive isotopes are used for food preservation from microbes.
- The radioactive C – 14 is used for determining the age of archaeological objects.
Question 45.
Write a note on nuclear reactor.
Answer:
1. A machine that generates electricity on large scale by using atomic energy is called a nuclear reactor. In a nuclear reactor, the nuclear energy in atom is released by bringing about nuclear reactions on the nuclear fuel.
2. When uranium – 235 is bombarded with a slow speed neutron, it undergoes nuclear fission. Various elements are produced. For example: Krypton – 92 and Barium – 141 along with 2 to 3 neutrons are emitted on fission, these neutron have high speed. Their speed is reduced and they are used for bombarding more Uranium – 235 nuclei.
The process is repeated many times. In this way a chain reaction of nuclear fission takes place (See the figure). A large amount of nuclear energy is released during a chain reaction of fission. The chain reaction is controlled to prevent the probable explosion.
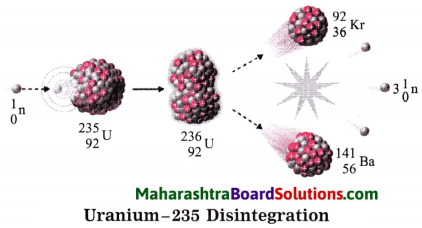
Neutrons are slowed down using graphite or heavy water as moderator. The chain reaction is controlled by absorbing neutron with the help of rods of boron, cadmium and beryllium. The heat produced in the fission is taken out by water as coolent. Water is converted into steam. The available heat is used to drive turbines to produce electricity.
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
In Rutherford’s experiment, some alpha particles colliding with the thin gold foil are turned back.
Answer:
1. All the positive charges in an atom is concentrated in a very small region at the centre of the atom. This region is called the nucleus. Electrons revolve around the nucleus, but most of the atom is empty. Alpha particles are positively charged.
2. When a thin sheet of gold is bombarded by alpha particles, most of the particles pass through it without deviation as the atom is almost empty. But some alpha particles move directly towards the positive nuclei, collide with them and due to the electric repulsion, turn back. Thus, in Rutherford’s experiment, some alpha particles colliding with the thin gold foil are turned back.
![]()
Question 2.
Two electrons in helium atom are placed in only one shell while three electrons in lithium atom occupy two shells.
Answer:
1. The electronic configuration of helium is (2). It indicates that helium atom has two electrons. Both the electrons are accommodated in the K shell. The maximum capacity of the K shell is two electrons and is maintained in all the elements. Hence, two electrons in helium are placed in only one shell.
2. The electronic configuration of lithium is (2, 1). It indicates that lithium atom has three electrons. The first shell K accommodates two electrons, i.e., the maximum capacity of the K shell. The remaining electron is accommodated in the next shell, i.e., the L shell. Thus, three electrons in lithium occupy two shells (K and L).
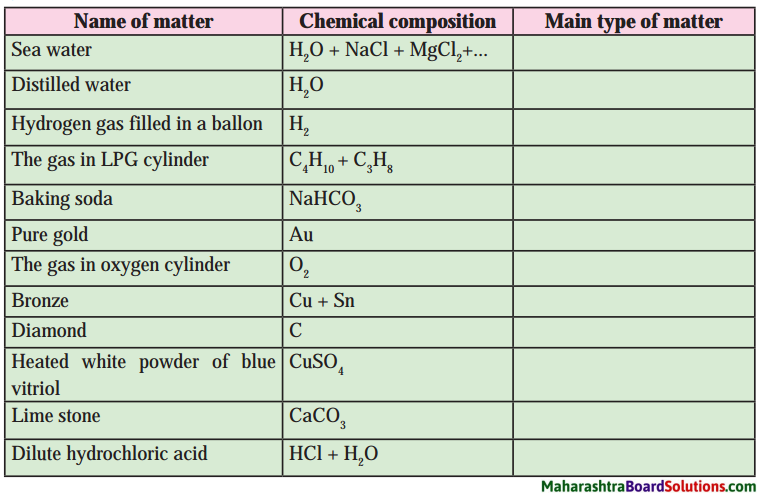
Complete the following:
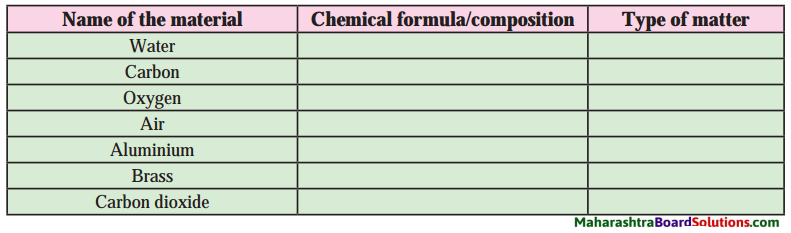
Question 1.
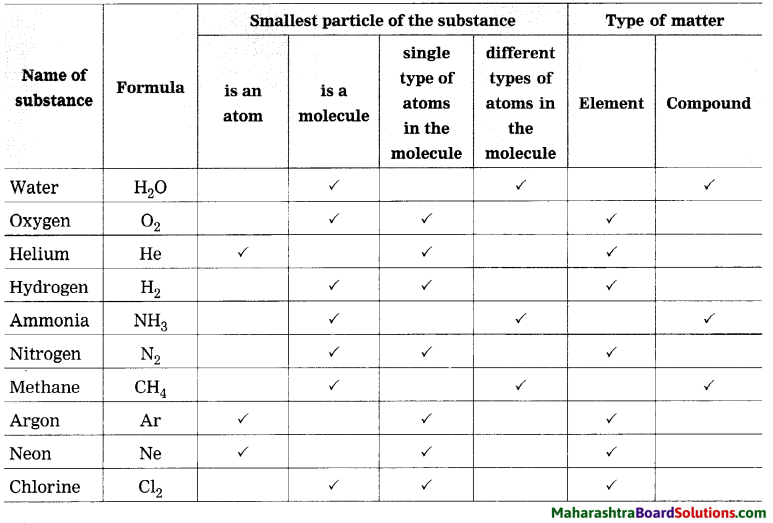
Complete the table by putting tick mark in appropriate box.
Answer:
Types of substances:
Question 2.
Complete the table:
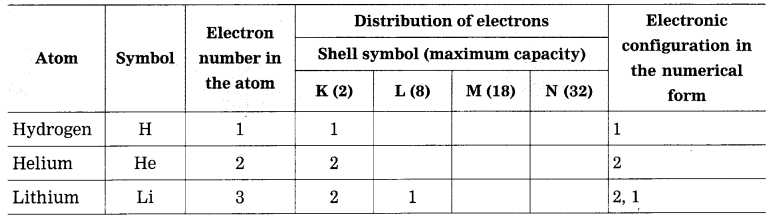
Answer:

Write the maximum number of electron in a shell using the above table. K Shell : 2, L Shell : 8, M Shell : 18, N Shell : 32.
![]()
Question 3.
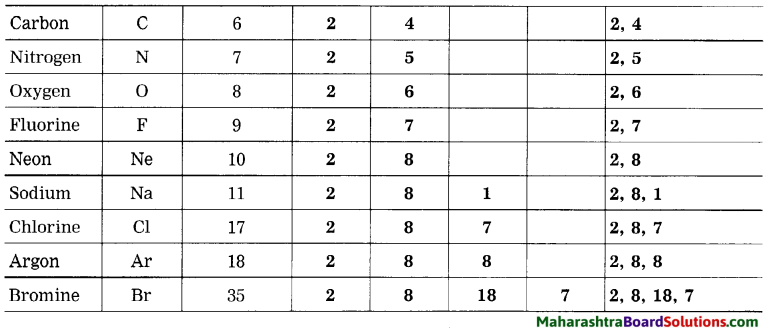
Complete the table:
Answer:
Electronic configuration of some elements:
Question 4.
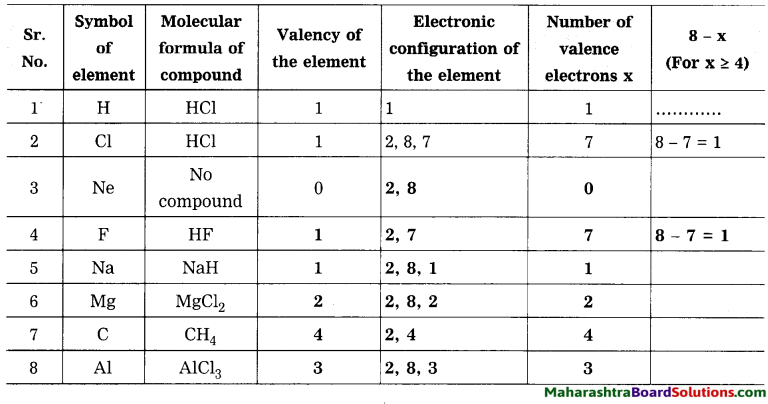
Complete the following table:
Answer:
Relationship between valency and electronic configuration:
Question 5.
In table 4 column you have written of that element? How many electrons identified valency from its molecular are used to complete the octet? formulae. When the number of the valency electrons in an element ‘x’ is 4 or less than 4, does ‘x’ match with the valency of that element?
Use your brain power!
Answer:
When the number of the valence electrons in an element x is 4 or less than 4, then x matches with the valency of that element.
![]()
Question 6.
When the number of the valence electrons in an element ‘x’ is 4 or more than 4, does’(8 – x)’ match with the valency of that element? How many electrons are used to complete the octet?
(Use your brain power!
Answer:
When the number of the valence electrons in an element x is 4 or more than 4, then (8-x) matches with the valency of that element. (8-x) electrons are used to complete the octet.
Question 7
Complete the table:
Answer:
| Isotopes | Proton number | Neutron number |
| \({ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}\) | 1 | – |
| \({ }_{1}^{2} \mathrm{H}\) | 1 | 1 |
| \({ }_{17}^{35} \mathrm{Cl}\) | 1 | 2 |
| \({ }_{17}^{35} \mathrm{Cl}\) | 17 | 18 |
| \({ }_{17}^{37} \mathrm{Cl}\) | 17 | 20 |
8th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- Living World and Classification of Microbes Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Health and Diseases Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Current Electricity and Magnetism Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Inside the Atom Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Composition of Matter Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Metals and Nonmetals Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Pollution Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 8 Questions And Answers
- Cell and Cell Organelles Class 8 Questions And Answers