Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 History Solutions Chapter 2 India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 History Chapter 2 Question Answer India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Maharashtra Board
Class 7 History Chapter 2 India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Question Answer Maharashtra Board
India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Class 7 Questions And Answers
1. Name the following:
Question 1.
The Queen of Gondvana –
Answer:
Rani Durgavati
Question 2.
The son of Udaysingh –
Answer:
Maharana Pratap
![]()
Question 3.
The founder of Mughal dynasty –
Answer:
Babur
Question 4.
The first Sultan of the Bahamani kingdom–
Answer:
Hasan Gangu
Question 5.
The fighting force established by Guru Gobindsingh –
Answer:
Khalsa Dal
2. Find the odd one out:
Question 1.
Sultan Mahmud, Qutubuddin Aibak, Muhammad Ghuri, Babur
Answer:
Sultan Mahmud
Question 2.
Adilshahi, Nizamshahi, Sultanate,Baridshahi
Answer:
Sultanate
Question 3.
Akbar, Humayun, Shershah, Aurangzeb
Answer:
Shershah
![]()
3. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
How did the kingdoms of Vijaynagar and Bahamani emerge?
Answer:
(i) During the reign of Sultan Muhammad Tughlaq of Delhi, there were many revolts in the South against the central power of Delhi.
(ii) From these revolts arose the formidable Vijaynagar and Bahamani kingdoms.
Question 2.
What reforms did Mahmud Gawan make?
Answer:
(i) Mahmud Gawan strengthened the Bahamani kingdom.
(ii) He started paying the soldiers their salary in cash instead of through land grants.
(iii) He brought discipline in the army.
(iv) He introduced many reforms in the land revenue system. He opened a Madarsa at Bidar for Arabic and Persian studies.
Question 3.
Why did it become impossible for the Mughals to strengthen their base in Assam?
Answer:
(i) While Aurangzeb ruled, the Ahoms had a prolonged struggle with the Mughals.
(ii) The Mughals attacked the Ahoms’ region.
(iii) The Ahoms united under the leadership of Gadadharsinha. Commander Lachit Borphukan gave an intense battle against the Mughals.
(iv) The Ahoms used the guerilla technique in the conflict against the Mughals.
(v) It became impossible for Mughals to create a strong base in Assam.
4. Write about them briefly in your own words.
Question 1.
Krishnadevaraya
Answer:
(a) Krishnadevaraya, ascended the throne of Vijaynagar in 1509 CE. He conquered Vijaywada, Rajmahendri and annexed the regions to his kingdom.
(b) He successfully took on the armies of the Sultans who had united under the leadership of the Bahamani Sultan Mahmud Shah.
(c) During his reign the Vijaynagar kingdom extended far and wide.
(d) He built the Hazar Ram temple and Vitthal temple in Vijaynagar.
(e) A scholar he wrote ‘Amuktamalyada’, a Telugu compendium on polity.
(f) Decline of the Vijaynagar kingdom began with his death in the year 1530 CE.
Question 2.
Chandbibi was murdered.
Answer:
(a) Chandbibi, the capable daughter of Husain Nizamshah of Ahmadnagar, bravely defended the fort displaying courage and valour.
(b) At this time, there was an internal strife among the factions of the Sardars in Nizamshahi’s kingdom resulting in the murder of Chandbibi.
Question 3.
Rani Durgavati
Answer:
(a) Rani Durgavati, bom in the dynasty Chandel Rajput became the queen of Gondvana after her marriage.
(b) She was an excellent administrator. Her struggle against the Mughals is important in Medieval history.
(c) After her husband’s death, Durgavati laid down her life but refused to surrender while fighting against Akbar.
5. Give reasons:
Question 1.
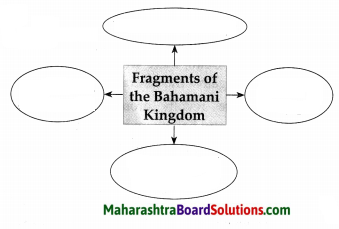
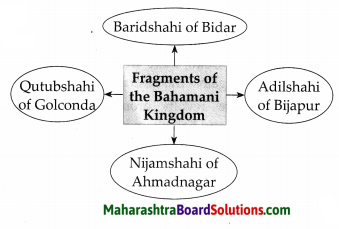
The Bahamani Kingdom disintegrated into five fragments.
Answer:
(a) After the death of Mahmud Gawan, factionsim increased among the Bahamani Sardars.
(b) The conflict with the Vijaynagar kingdom had an adverse effect on the Bahamani kingdom.
(c) The provincial Governors began to act more independently. This led to the disintegration of the Bahamani kingdom into five small power-Imadshahi of Varhad, Baridshahi of Bidar, Adilshahi of Bijapur, Nizamshahi of Ahmadnagar and Qutubshahi of Golconda.
![]()
Question 2.
Rana Sanga’s army was defeated.
Answer:
(a) After the battle of Panipat, Rana Sanga of Mewad brought all Rajput kings together.
(b) There was a battle between Babur and Rana Sanga at Khanua.
(c) Babur’s artillery and reserved force played a key role in this battle and Rana Sanga’s army was defeated.
Question 3.
Rana Pratap has become immortal in history.
Answer:
(a) After the death of Udaysingh, Maharana Pratap ascended the throne of Mewad.
(b) He continued the struggle for Mewad’s existence.
(c) Till the very end he struggled with Akbar to maintain his independence.
(d) He has become immortal in history due to his qualities of valour, courage, self-respect and sacrifice.
Question 4.
Aurangzeb imprisoned Guru Tegh Bahadur.
Answer:
(a) Guru Tegh Bahadur, protested strongly against Aurangzeb’s policy of religious intolerance.
(b) Aurangzeb imprisoned him and beheaded him in 1675.
Question 5.
The Rajputs fought against the Mughals.
Answer:
(a) Akbar had secured the cooperation of the Rajputs with his policy of amicable relations.
(b) Aurangzeb could not obtain the cooperation of Rajputs. After the death of Rana Jaswantsingh of Marwad, Aurangzeb annexed his kingdom to the Mughal empire.
(c) Durgadas Rathod crowned Jaswantsingh’s minor son of Ajitsingh of Marwad.
(d) Durgadas Rathod fought hard against the Mughals and continued his struggle against the Mughals for the existence of Marwad.
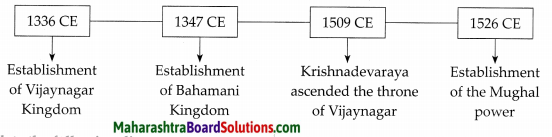
6. Complete the timeline.
Answer:
7. Using the internet, find out more about any one of the personalities you have studied here, and fill in the box below.
Activity
Obtain more information about the personalities mentioned in this chapter.Use reference books, the internet, newspapers, etc. Prepare a collage of the pictures information in your activity book and display it in the history cell.
Class 7 History Chapter 2 India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentences by choosing the appropriate words from the options given below:
Question 1.
‘Pal’ in the ______ was a famous dynasty in Bengal. (seventh century, eight century, ninth century)
Answer:
eight century
Question 2.
Prithviraj Chauhan belonged to _______ dynasty. (Rajput dynasty, Chauhan dynasty, Chola dynasty)
Answer:
Chauhan dynasty
![]()
Question 3.
The _____ period is considered to be the golden period of Marathi language. (Yadava, Rashtrakuta, Chola)
Answer:
Yadava
Question 4.
In the eleventh Century CE, the _____ began to invade India and reached the north-western frontier of India. (Afghans, Mughals, Turks)
Answer:
Turks
Question 5.
______ was the last Sultan and he was defeated by Babur, bringing the Sultanate to an end. (Muhammad Ghuri, Bulban, Ibrahim Lodi)
Answer:
Ibrahim Lodi
Question 6.
Hampi in today’s ______ was the capital of the kingdom of Vijaynagar. (Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu)
Answer:
Karnataka
Question 7.
Krishnadevaraya wrote ‘Amuktamalyada’, a Telugu Compendium on _______. (polity, economics, sociology)
Answer:
polity
Question 8.
______ was the first Sultan of the Bahamani kingdom. (Muhammad-bin-Tughlaq, Mahmud Gawan, Hasan Gangu)
Answer:
Hasan Gangu
Question 9.
In ______ the Sultanate of Delhi came to an end. (1526 CE, 1556 CE, 1605 CE)
Answer:
1526 CE
Question 10.
_______ was the Governor of Punjab under the Sultanate. (Babur, Ibrahim Lodi, Daulatkhan Lodi)
Answer:
Daulatkhan Lodi
Question 11.
_______ was the most powerful king of the Mughal dynasty. (Shahajahan, Akbar, Jahangir)
Answer:
Akbar
Question 12.
The struggle of Gondvana queen Durgavati against Mughals is important in ______ history. (modern, medieval, ancient)
Answer:
medieval
Question 13.
______ became the emperor in 1658 CE. (Shahajahan, Aurangzeb, Akbar)
Answer:
Aurangzeb
Question 14.
In the thirteenth century CE, the people of the Shaan community settled down in the valley of river ______. (Ganga, Brahmaputra, Yamuna)
Answer:
Brahmaputra
Question 15.
The ninth Guru of the Sikhs was ______.(Guru Gobind Singh, Guru Tegh Bahadur, Guru Nanak)
Answer:
Guru Tegh Bahadur
Question 16.
______ organised the Sikh youths into a fighting force called Khalsa Dal. (Guru Gobind Singh, Guru Tegh Bahadur, Guru Nanak)
Answer:
Guru Gobind Singh
![]()
Question 17.
Akbar had secured the co-operation of the ______ with his policy of amicable relations. (Rajputs, Marathas, Ahoms)
Answer:
Rajputs
Question 18.
In Maharashtra, the ______ Marathas offered stiff resistance to and defended their independence. (Babur, Humayun, Aurangzeb)
Answer:
Aurangzeb
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (1) Imadshahi | (a) Bidar |
| (2) Baridshahi | (b) Ahmadnagar |
| (3) Adilshahi | (c) Golconda |
| (4) Nizamshahi | (d) Varhad |
| (5) Qutubshahi | (e) Bijapur |
Answer:
1 – d
2 – a
3 – e
4 – b
5 – c
Name the following:
Question 1.
Two important dynasties among the Rajput dynasties in North India.
Answer:
(a) The Gahadwal dynasty
(b) Parmar dynasty
Question 2.
Eminent rulers belonging to the Chola dynasty in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
(a) Rajaraj I
(b) Rajendra I
Question 3.
The king belonging to the Hoysala dynasty.
Answer:
King Vishnuvardhan
Question 4.
The King who conquered the whole of Karnataka.
Answer:
King Vishnuvardhan
Question 5.
The Varkari movement emerged in
Answer:
The Yadava period
Question 6.
During his reign Rashtrakuta dynasty in Maharashtra the Rashtrakut power spread from Kanauj up to Rameshwar.
Answer:
Govind III
Question 7.
The last prosperous power before the period of Shivaji Maharaj.
Answer:
TheYadavas
Question 8.
The capital of Bhillam V of the Yadava dynasty which was near Aurangabad.
Answer:
Deogiri
Question 9.
The golden period of the Marathi Language.
Answer:
The Yadava period
![]()
Question 10.
The Arab General attacked the Sindh province in the eighth century.
Answer:
Muhammad-bin-Qasim
Question 11.
The power which began to invade India in eleventh century CE.
Answer:
The Turks
Question 12.
He invaded India many times and plundered the rich temples at Mathura, Vrindavan Kanauj and Somnath and carried away enormous wealth with him.
Answer:
Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni
Question 13.
In 1775 CE and 1178 CE, the Sultan of Ghur from Afghanistan who invaded India.
Answer:
Muhammad Ghuri
Question 14.
During his reign there were many revolts in the South against the central power of Delhi.
Answer:
Sultan Muhammad-bin-Tughluque
Question 15.
The brothers from South India who were Sardars in the service of Delhi Sultanate.
Answer:
(a) Harihar
(b) Bukka
Question 16.
The Hazar Ram temple and Vitthal temple were built in Vijaynagar during his reign.
Answer:
Krishnadevaraya
Question 17.
He defeated the army of the Sultan of Delhi.
Answer:
Hasan Gangu
Question 18.
The Chief Wazir of the Bahamani kingdom who started paying the soldiers their salaries in cash instead of giving land grants.
Answer:
Mahmud Gawan
Question 19.
The king of Farghana in Central Asia.
Answer:
Babur
Question 20.
After the battle of Panipat, he brought all Rajput kings together.
Answer:
Rana Sanga of Mewad
Question 21.
After ascending the throne of Mewad, he continued the struggle for Mewad’s existence.
Answer:
Maharana Pratap
Question 22.
The capable daughter of Husain Nizamshah of Ahmadn^gar who defended the fort of Ahmadnagar.
Answer:
Chandbibi
Question 23.
The Ahoms united under his leadership.
Answer:
Gadadharsinha
![]()
Question 24.
The commander who gave intense battle against the Mughals.
Answer:
Commander Lachit Borphukan
Question 25.
The ninth Guru of Sikhs who protested strongly against Aurangzeb’s policy of religious intolerance.
Answer:
Guru Tegh Bahadur
Question 26.
There was an attempt on the life of Guru Gobind Singh in 1708 CE at this place.
Answer:
Nanded
Question 27.
After his death Aurangzeb annexed his kingdom to the Mughal empire.
Answer:
Rana Jaswantsingh of Marwad.
Question 28.
In Maharashtra, Swaraj was established under his leadership.
Answer:
Shivaji Maharaj
Find out the odd man out:
Question 1.
Gadadharsinha, Rana Jaswantsingh, Durgadas Rathod, Ajit Singh.
Answer:
Gadadharsinha
Question 2.
Babur, Humayun, Krishnadevaraya, Jahangir
Answer:
Krishnadevaraya
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
Name the regions upto which the Gurjar- Pratihar power spread.
Answer:
The Gurjar-Pratihar power spread up to Andhra, Kalinga, Vidarbha, West Kathewad, Kanauj and Gujarat.
Question 2.
Which places did the Cholas conquer using their naval strength?
Answer:
The Cholas conquered the Maidive Islands and Sri Lanka using their naval strength.
Question 3.
In which period did the Mahanubhav Panth and the Varkari movement emerge?
Answer:
The Mahanubhav Panth and the Varkari movement emerged in the Yadava period.
![]()
Question 4.
Why did the Arab rulers turn towards India?
Answer:
The Arab rulers turned towards India to expand their empire.
Question 5.
Write the extent of the kingdom of Vij aynagar during Krishnadevaraya’s reign?
Answer:
During Krishnadevaraya’s reign, the kingdom of Vijaynagar extended from Cuttack in the east up to Goa in the West and from the Raichur Doab in the North up to the Indian Ocean in the South.
Question 6.
Who opposed Akbar when he tried to bring India under his central authority?
Answer:
When Akbar tried to bring India under his central authority he had to face the opposition of Maharana Pratap, Chandbibi and Rani Durgavati.
Question 7.
Which qualities of Maharana Pratap made him immortal in history?
Answer:
Maharana Pratap became immortal in history due to his qualities of valour, courage, self-respect and sacrifice.
Question 8.
Which regions together formed the Gondvana?
Answer:
Gondvana can be broadly said to comprise the eastern part of Vidarbha, part of Madhya Pradesh to its North, the Western part of today’s Chhattisgarh, Northern part of Andhra Pradesh and Western part of Odisha.
Question 9.
How did the Marathas defend their independence?
Answer:
Marathas offered stiff resistance to Aurangzeb and defended their independence.
Give reasons:
Question 1.
Babur invaded India.
Answer:
(a) The reigning Sultan of Delhi at that time was Ibrahim Lodi.
(b) Daulatkhan Lodi, was the governor of Punjab under the Sultanate.
(c) The relationship between Ibrahim Lodi and Daulatkhan Lodi was strained.
(d) Daulatkhan Lodi invited Babur to march to India. Taking this opportunity, Babur invaded India.
Write briefly in your own words:
Question 1.
The First Battle of Panipat
Answer:
(a) Ibrahim Lodi was the Sultan of Delhi and Daulat Khan Lodi was the Governor of Punjab.
(b) The relationship between Ibrahim Lodi and Daulatkhan Lodi became strained.
(c) Daulatkhan Lodi invited Babur to march on India.
(d) Taking advantage of this opportunity, Babur invaded India.
(e) To repel Babur’s invasion Ibrahim Lodi started with his army.
(f) There was a battle between Ibrahim Lodi and Babur on 21st April 1526 at Panipat.
(g) Babur defeated Ibrahim Lodi’s army. This is known as the First Battle of Panipat.
![]()
Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Write in brief about the conflict of the Mughals with the Marathas.
Answer:
(i) In Maharashtra, Sivaraj was established under the leadership of Shivaji Maharaj.
(ii) In his efforts to establish Swaraj, Shivaji Maharaj had to fight the Mughals too along with the other enemies.
(iii) Aurangzeb came down to the Deccan after the death of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj with the intention of conquering the whole of South India.
(iv) But the Marathas offered stiff resistance to Aurangzeb and defended their independence.
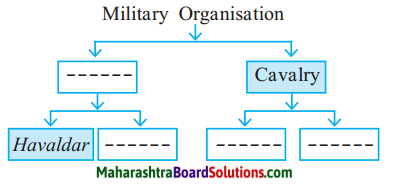
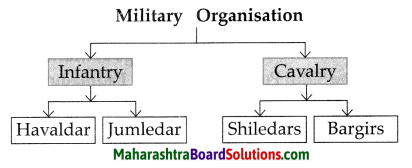
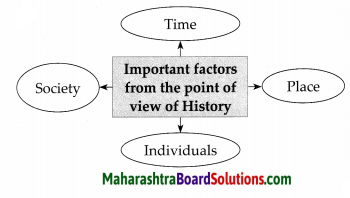
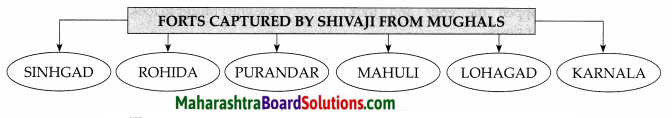
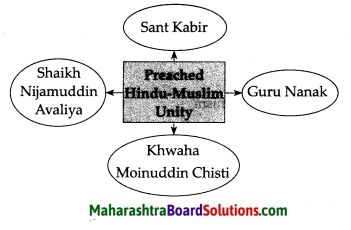
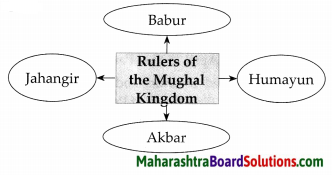
Complete the following diagrams:
Question 1.
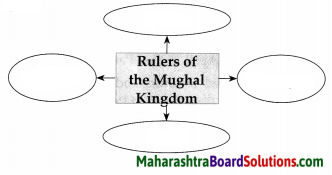
Answer:
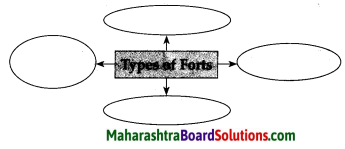
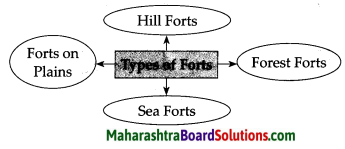
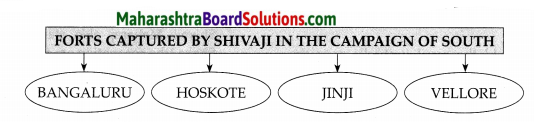
Question 2.
Answer:
![]()
Complete the following table:
Question 1.
| S.No | Political Power | Founders / Rulers | Capital |
Answer:
| S.No | Political Power | Founders / Rulers | Capital |
| (1) | Yadava | Bhillam V | Deogiri |
| (2) | Vijaynagar | Harihar & Bukka | Hampi |
| (3) | Bahamani | Hasan Gangu | Gulbarga |
| (4) | Mughal | Babur | Delhi |
7th Std History Questions And Answers:
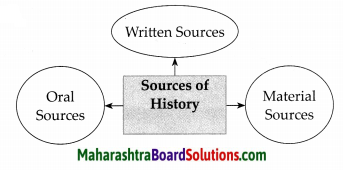
- Sources of History Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- India before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Religious Synthesis Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Maharashtra before the Times of Shivaji Maharaj Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- The Foundation of the Swaraj Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Conflict with the Mughals Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- The Administration of the Swaraj Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- An Ideal Ruler Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- The Maratha War of Independence Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- The Expansion of the Maratha Power Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Marathas – The Protectors of the Nation Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Progression of the Empire Class 7 History Questions And Answers
- Life of the People in Maharashtra Class 7 History Questions And Answers