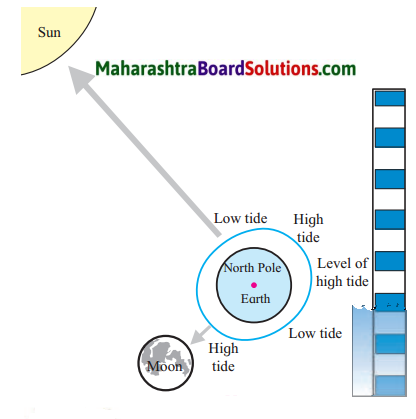
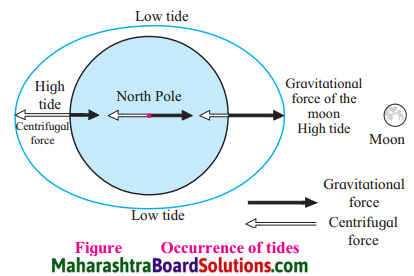
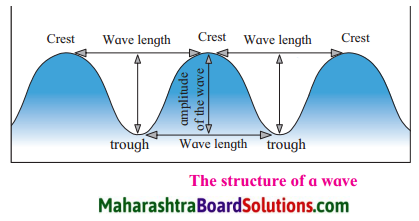
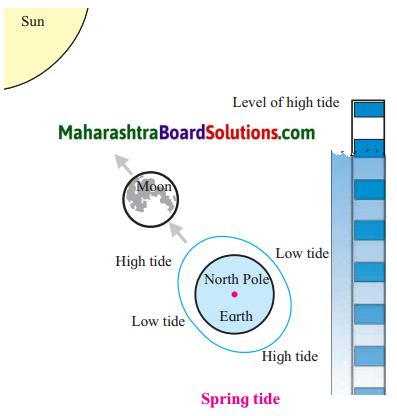
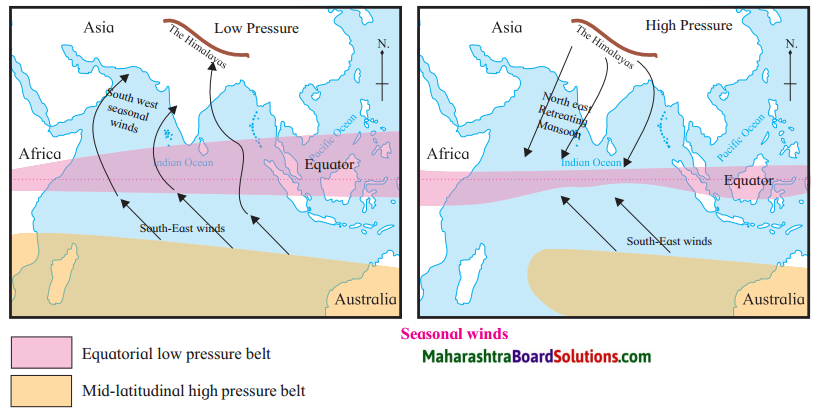
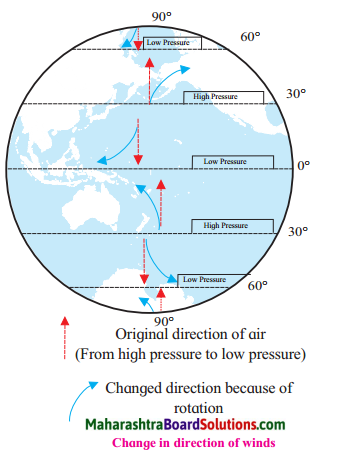
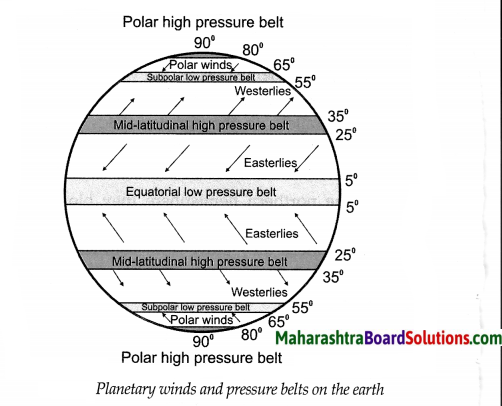
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Geography Solutions Chapter 7 Soils Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Geography Chapter 7 Question Answer Soils Maharashtra Board
Class 7 Geography Chapter 7 Soils Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Soils Class 7 Questions And Answers
1. Complete the following table.
| Factor/Process | Role in the formation of soil |
| (1) Parent rock | ……………. |
| (2) Regional climate | …………… |
| (3) Organic material | ………….. |
| (4) Microorganisms | …………….. |
Answer:
| Factor/Process | Role in the formation of soil |
| (1) Parent rock | The rock gets weathered depending on the hardness of the rock and the climate of the region. It turns into powdery material which further turns into soil. |
| (2) Regional climate | When the rock is exposed to a different climates, the same type of rock gives rise to different types of soil. |
| (3) Organic material | The organic material gets mixed into weathered powdery material and turn it into soil. |
| (4) Microorganisms | Microorganisms help in decomposing the dead remains of organic materials and get mixed into the soil to form humus. |
![]()
2. Why do the following occur?
Question 1.
To the west of Sahyadris, laterite soils are formed from the basalt rock.
Answer:
- Laterite soils are formed in regions of heavy rainfall.
- The climate of western Sahyadris is hot & humid.
- This leads to leaching of basalt rocks due to which there is formation of laterite soils.
Question 2.
Humus content in the soil increases.
Answer:
- Microorganisms and certain other organism help in decomposing the dead remains of organic materials.
- The biotic material thus produced is called humus.
- If organic manures, vermicompost compost are used regularly, the humus content in the soil increases.
Question 3.
Soil formation process is faster in the equatorial climate.
Answer:
- In the region of high rainfall and higher temperature the process of soil formation is faster.
- Equatorial climatic region have high temperature and receive high rainfall.
- Thus soil formation process is faster in the equatorial region.
Question 4.
The salinity of the soil increases.
Answer:
- Due to excessive irrigation, the salts from the soil are drawn upwards.
- This increases the salinity of the soil.
Question 5.
Rice is the staple diet of the people from Konkan.
Answer:
- Hot & humid climate, heavy rainfall & fertile alluvial soil are favourable for rice cultivation.
- This soil has good water holding capacity. Since these conditions are found in the konkan region, rice is grown on a large scale here.
- So rice is the staple diet of the people from Konkan.
![]()
3. Give information on:
Question 1.
Measures of soil conservation
Answer:
The following are the measures of soil conservation:
(i) Afforestation / Planting trees: Planting trees can control the velocity of wind. This helps reducing erosion by wind. The plant roots hold the soil and also reduces the erosion of soil.

(ii) Continuous contour trenches: Construction of continuous contour trenches at different height checks the velocity of water running along the slopes & hence reduces soil erosion. The water arrested in these trenches percolates into the ground.

(iii) Implementation of watershed Development program: The Government of Maharashtra has implemented the watershed development programme under which constructing embankment along slopes in rural areas, introducing CCTs along steep slopes etc. are undertaken. This led to the success of the scheme ‘Arrest water, let it percolate’. This has resulted in raising the ground water levels & reducing the erosion of soil.

(iv) Implementation of Jalayukt Shivar: Under the scheme of Jalayukt Shivar, works like construction of farm bunds, arresting waters of small streams, connecting the streams etc. are being carried out on a large scale.

Question 2.
Organic Manures.
Answer:
(i) Organic manures in farming, helps to maintain the pH balance.
(ii) It also increases the proportion of humus, and retain the fertility of soil.
![]()
Question 3.
Place where you will get the information about the suitability of a soil for a particular crop.
Answer:
(i) The information about the suitability of a soil can be obtained from Department of Agriculture of Government of Maharashtra, Natural Resource conservation services, soil testing laboratories in various states and at many agricultural universities.
(ii) The type of soil, soil fertility, pH status of the soil, etc. are determined in soil testing.
(iii) Based on the testing, an analysis of the soil is done & information about the suitability of a soil for a particular crop is provided.
Question 4.
Importance of soils for plant growth.
Answer:
(i) Soil is important for plant as it hold roots that provide support for plants and stores nutrient for the growth of plants.
(ii) Fertile soils favour plant growth.
4. Complete the following table with reference to soil.
| Action | Effect | Result (W.R.T. fertility) |
| Construction of embankments. | ||
| Wind speed decreased. | ||
| Farm land is kept fallow for some period. | Helps to maintain the pH balance and increase the proportion of humus. | Increases the fertility of soil. |
| Regular use of organic manures, vermicompost and compost. | ||
| Check the velocity of water running along the slopes. | ||
| Litter is burnt in the farm. | ||
| Decomposed vegetal litters, roots of plants and remains of animals. | ||
| Salt content in the soil increases. | ||
| Leads to the lowering of humus content in the soil. |
Answer:
| Action | Effect | Result (W.R.T. fertility) |
| Construction of embankments. | Protects soil from being washed away. | Protects fertility of soil. |
| Planting trees. | Wind speed decreased. | Protects fertility of soil |
| Farm land is kept fallow for some period. | Helps to maintain the pH balance and increase the proportion of humus. | Increases the fertility of soil. |
| Regular use of organic manures, vermicompost[1] and compost. | Humus content increased. | Increases the fertility of soil. |
| Trenches are dug across a slope. | Check the velocity of water running along the slopes. | Protects fertility of soil |
| Litter is burnt in the farm. | Decreases the amount of organic material in soil. | Decreases the fertility of soil. |
| Decomposed vegetal litters, roots of plants and remains of animals. | Proves favourable for micro organism. | Increases the fertility of soil. |
| Excessive Irrigation | Salt content in the soil increases. | Decreases the fertility of soil |
| Chemical fertilizers used excessively. | Leads to the lowering of humus content in the soil. | Decreases the fertility of soil |
Activity:
- Visit a soil testing centre/laboratory and note the work that is carried out in the centre.
- Prepare compost at home or in your housing society.
- Visit a place where ‘Arrest water, let it percolate’ is being implemented. Collect information about it and make a note of it.
![]()
Class 7 Geography Chapter 7 Soils InText Questions and Answers
Think about it:
Question 1.
Rohit and Prateeksha noted that their field had yielded a bumper crop. But they also noted that a part of their field had a stunted growth of plants. What investigation will you suggest to them?
Answer:
I would suggest that they should check whether organic manures, are used evenly on all the parts of the field. Also, they should check whether that part of the field is getting adequate supply of water or not.
Question 2.
Why do equatorial regions have fertile soils?
Answer:
The sun rays are perpendicular in equatorial
regions so the climate is very hot and humid. This region also receives very heavy rainfall. As the process of soil formation is faster in these regions, equatorial regions have fertile soil. Also vegetal litter roots of plants, remains of animals, etc.; get decomposed adding to soil fertility.
Question 3.
Why is the vegetation sparse in deserts?
Answer:
A desert is a barren area of land where a little precipitation occurs and consequently living conditions for plant and animal life are very hostile. It is an area where the soils are not fertile & hence vegetation is scanty.
Try this:
- Take three flower pots of the same size.
- Keep one pot empty. Fill the second pot. With water after closing the hole at the bottom and fill the third pot with soil.
- Put a few seeds in all of them. (You may use aserio, peas, gram, fenugreek, wheat, green gram, coriander seeds, etc.)
- Keep all the three pots in the sun. and water the empty pot and the soil-filled pot for 4-5 days. Observe and answer the following.
Question 1.
What happened to the seeds put in the empty pot and pot filled with water?
Answer:
Seeds in the empty pot and the pot filled with water did not germinate and did not show any sign of growth.
Question 2.
What happened to the seeds put in the pot (c) filled with soil?
Answer:
Seeds germinated and we could see some small twigs branching out.
Question 3.
What do you learn from this?
Answer:
We learn that plants need sunlight, water and soil to grow.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 7 Soils Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
_____ rock in a region is an important factor in soil. (Parent, Basalt, Granite)
Answer:
Parent
Question 2.
The process of weathering depends on the _____ of the region. (climate, weather, soil)
Answer:
climate
Question 3.
The _____ rock of the Deccan Plateau in Maharashtra turns into black soil after weathering. (granite, basalt, parent)
Answer:
basalt
Question 4.
______ soils along the river beds give higher yields. (Infertile, Fertile, Coarse)
Answer:
Fertile
Question 5.
The _____ material comes from the decomposition of the remains of the plants and animals in that region. (biotic1, abiotic, pH)
Answer:
biotic1
Question 6.
______ is a complete ecosystem.(Soil, Humus, weathered rocks)
Answer:
Soil
![]()
Question 7.
Food crops like jowar and bajra are produced in the _____ soils of Maharashtra Plateau. (regur, coarse, laterite)
Answer:
regur
Question 8.
The local agriculture produce determines the _______ diet of the people. (staple, supplementary, secondary)
Answer:
staple
Question 9.
The proportion of humus is negligible in _____ soil. (coarse, black, laterite)
Answer:
coarse
Question 10.
Planting trees can also control the _____ of the wind. (velocity, direction, temperature)
Answer:
velocity
Question 11.
Rocks like granite or gneiss in South India give rise to ____ soil. (black, red, regur)
Answer:
red
Question 12.
In the humid climate of western Sahyadris the leaching of basalt rocks leads to formation of ___ soil. (black, lateritic, red)
Answer:
lateritic
Question 13.
The excessive spraying of chemicals and use of chemical fertilizers lead to ______; (soil degradation soil fertility, soil powder)
Answer:
soil degradation
Complete the following sentences:
Question 1.
The biotic material comes from _____.
Answer:
the decomposition of the remains of the plants and animals in that region
Question 2
Microorganisms ajnd certain other organisms help decompose the dead remains of ______.
Answer:
organic materials
Question 3.
Production of compost needs sufficient period of time and ______.
Answer:
elements like organic waste, water, heat, etc.
Question 4.
In the region of high rainfall and higher temperatures, _____.
Answer:
the process of soil formation is faster
Question 5.
In regions of low temperatures and low rainfall the _____.
Answer:
soil formation takes more time
Question 6.
High use of chemical fertilizers, insecticides _____.
Answer:
leads to the degradation of soils
![]()
Question 7.
In the areas where the soil is not fertile, _______.
Answer:
egetation is scanty
Question 8.
When man realized that sowing of seeds in the soil leads to the growth of plants and yields crops, ______.
Answer:
he started using soil as a resource
Question 9.
Excessive irrigation draws the salts from the soil upwards and ______.
Answer:
makes the soil saline and then unproductive
Question 10.
Keeping the farmland fallow for some period and cultivating different crops alternatively is important ________.
Answer:
to help retain the fertility of soils.
Give one word for the following:
Question 1.
Soil formed due to weathering of basalt rock.
Answer:
Black soil
Question 2
Soil formed due to the leaching of the basalt rock.
Answer:
Lateritic soil
Question 3.
Biotic material mixed into the soils.
Answer:
Humus
Question 4.
The excessive spraying of chemicals and use of chemical fertilizers.
Answer:
Soil degradation
Question 5.
The govt, scheme, work like construction of farm bunds, arresting waters of small streams, etc.
Answer:
Jalayukt Shivar.
Who am I?
Question 1.
I am a very important rock factor in soil formation.
Answer:
Parent rock
Question 2
I form due to weathering of basalt rock. Jowar and Bajra mostly grow on this soil.
Answer:
Regur soil / Black soil
![]()
Question 3.
I am found in the hilltops of the western part of the Deccan plateau.
Answer:
Coarse soil
Question 4.
I am black in colour and have less organic components.
Answer:
Regur or Black soil
Question 5.
I am orange in colour and mostly found in the coastal belt of Konkan.
Laterite soil
Question 6.
I am found at the mouth of the river in the western coastal strip.
Answer:
Alluvial soil of the coastal strip
Question 7.
I am mainly found in areas of extreme rainfall but not very useful for agriculture.
Answer:
Yellow brown soil
Question 8.
I am a method of soil conservation which controls the velocity of wind.
Answer:
Afforestation / planting trees
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Coarse soil | (a) Alluvium deposition |
| (2) Regur soil | (b) Eastern part of Bhandara |
| (3) Laterite soil | (c) Ajanta, Balaghat, Mahaden hills |
| (4) Alluvial soil | (d) Coastal belt of konkan |
| (5) Yellow-brown soil | (e) Weathering of basalt rock |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – e
3 – d
4 – a
5 – b
Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
What do you mean by ‘Soil’?
Answer:
(i) The uppermost layer of the earth’s crust is called ‘Soil’.
(ii) It contains the organic as well as mineral matter necessary for the growth of plants.
![]()
Question 2
What are the factors necessary for the soil formation?
Answer:
Soil is formed by:
- Weathering of the parent rock material.
- Climatic conditions of the region.
- The decomposition of plant remains.
- Animal manures and dead animals.
- Very long period of time.
Question 3.
What is leaching ?
Answer:
(i) Leaching is a process is which the salts & other soluble material are washed out of the rock through percolation of water.
(ii) This process is dominant in the areas of high rainfall & humid climate.
Question 4.
What is Humus?
Answer:
(i) The decaying of organic material such as dead leaves, stems, root of the plant, vegetal litters, decomposed remains of animals get mixed into the soil.
(ii) This results in the formation of “Humus” thus retaining the fertility of soil.
(iii) If the proportion of humus in the soil is greater, the soil becomes fertile.
Question 5.
What leads to the degradation of soils?
Answer:
(i) For getting higher production, different types of chemical fertilizers, insecticides are used profusely.
(ii) This leads to the degradation of soils.
Question 6.
What led to record agricultural production?
Ans,
(i) To get richer harvests man made efforts to increase the fertility of soils.
(ii) In the process, use of different fertilizers became a practice which led to record agricultural production.
Question 7.
What is soil erosion?
Answer:
(i) When a layer of soil (top layer of soil) get removed due to wind or water it is called soil erosion.
(ii) Running water, climate and diversity in physiography are the reasons of soil erosion.
Question 8.
What helps to maintain the pH balance of the soil?
Answer:
(i) Organic manures, vermicompost, compost are used regularly.
(ii) It helps in maintaining the pH balance and retaining the fertility of the soil.
![]()
Why do the following occur:
Question 1.
Rice is the staple diet of the people from Konkan.
Answer:
(i) Hot & humid climate, heavy rainfall & fertile alluvial soil are favourable for rice cultivation.
(ii) This soil has good water holding capacity. Since these conditions are found in the konkan region, rice is grown on a large scale here.
(iii) So rice is the staple diet of the people from Konkan.
Question 2.
Soil Erosion.
(i) A layer of soil gets removed due to wind or water.
(ii) Running water, climate and diversity in physiography are the reasons of soil erosion.
Question 3.
Soil degradation.
Answer:
(i) To obtain a higher agricultural yield, chemical fertilizers, insecticides, weedicides, etc. are used.
(ii) The excessive spraying of chemicals and use of chemical fertilizers leads to soil degradation.
Give geographical reasons:
Question 1.
Planting trees is necessary to conserve the soil.
Answer:
(i) A layer of soil gets removed due to wind or water which leads to soil erosion.
(ii) Planting trees controls the velocity of the wind, thus reducing the erosion of soil by wind.
(iii) The roots of the plants hold the soil which also prevents soil erosion.
Question 2
Continuous contour trenches are constructed along the slopes.
Answer:
(i) Construction of continuous contour trenches (CCTs) at different heights checks the velocity of water running along the slopes.
(ii) This reduces soil erosion.
Question 3.
It is advisable to use organic manures, vermicompost and compost regularly.
Answer:
(i) Use of organic manures, vermicompost, compost helps maintain the pH balance.
(ii) It also increases the proportion of humus thus retaining the fertility of soil.
(iii) Hence, it is advisable to use organic manures, vermicompost & compost regularly.
Question 4.
There emerged competition among the people to discover fertile lands and settle there.
Answer:
(i) Man started producing greater amount of food crops for the growing population.
(ii) He realized that crop production and prosperity in agriculture depends on the fertility of soil and the optimum availability of water.
Hence, there emerged competition among the people to discover fertile lands & settle there.
Question 5.
There was a rise of Indus civilization.
Answer:
(i) When man realized that the fertile soils along the river beds give higher yields.
(ii) He settled in the valleys and started living there in groups.
(iii) This led to the rise of Indus civilization.
Question 6.
Countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman, etc., fulfil their requirements by importing food from other countries.
Answer:
(i) In countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman etc. the soils are not arable so there is need to fulfil their food requirement.
(ii) Hence, countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Oman import food from other countries.
![]()
Question 7.
Lets find the names of the soils we have learnt and which regions they are found?
Answer:
| Soils | Answers | Regions |
| (1) RUGER | Regur | (a) Western part of Deccan Plateau and eastern part of Vidarbha. |
| (2) LUILALVA | Alluvial | (b) Panvel, Uran Coast, Dharamtar creek. |
| (3) OARCSE | Coarse | (c) Ajanta, Balaghat and Mahadeo hills. |
| (4) AEILTRITE | Laterite | (d) Coastal belt of Konkan, West of Sahyadris and East of Vidarbha. |
Make Friends with maps!
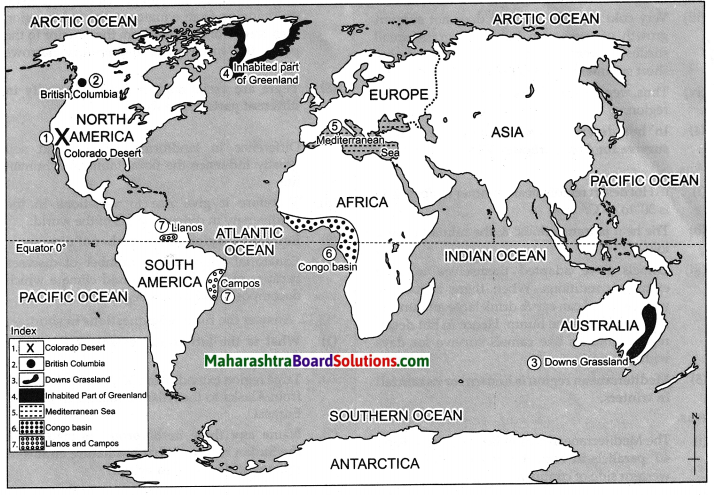
Observe the map given below and answer the following questions:
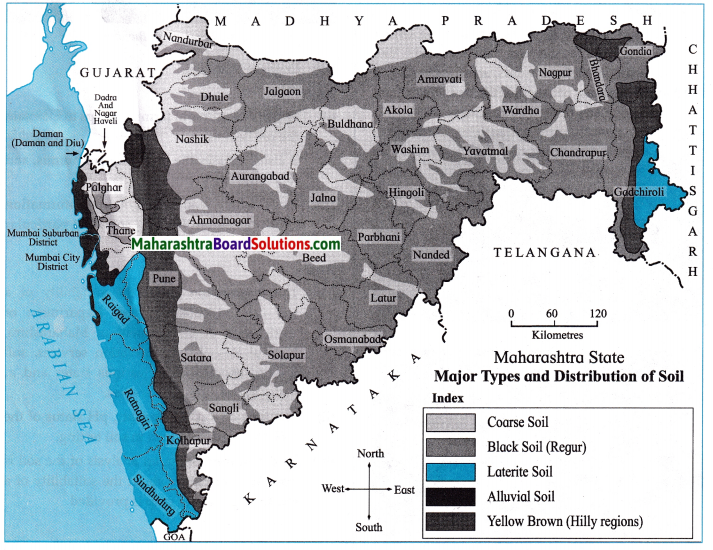
Question 1.
Which soil occupies most of the areas in Maharashtra?
Answer:
Black (Regur) soil occupies most of the areas in Maharashtra.
Question 2
In which areas are laterite soils found?
Answer:
Laterite soil is found in Raigad, Ratnagiri,Sindhudurg and some parts of Gadchiroli and Nashik.
Question 3.
Which soil is found in parts of the Sahyadri ranges?
Answer:
Yellow Brown soil is found in parts of the Sahyadri ranges.
Question 4.
In which region is alluvial soil found?
Answer:
Alluvial soil is found in Mumbai Suburban District, Mumbai city district some parts of Thane & Palghar district.
Question 5.
Which soil is found in the river valleys of Maharashtra?
Answer:
Fertile Alluvial Soil is found in the river valleys of Maharashtra.
7th Std Geography Questions And Answers:
- How Seasons Occur Part 1 Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- The Sun, the Moon and the Earth Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Tides Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Air Pressure Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Winds Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
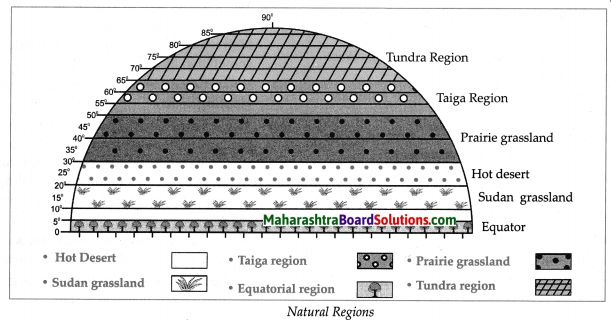
- Natural Regions Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Soils Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- How Seasons Occur Part 2 Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Agriculture Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Human Settlements Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers
- Contour Maps and Landforms Class 7 Geography Questions And Answers