Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 English Solutions Chapter 3.6 The Merchant of Venice Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 English Lesson 3.6 The Merchant of Venice Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 6 English Chapter 3.6 The Merchant of Venice Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Say whether the following statements are true or false.
Question a.
The merchant ships brought spices and other treasures from India and other countries to Italy.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question b.
Antonio had gone on a long voyage.
Answer:
False
Question c.
Bassanio was very rich.
Answer:
False
Question d.
Portia had many brothers and sisters.
Answer:
False
Question e.
Portia’s suitors chose the gold and silver caskets.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question f.
Bassanio borrowed money from Shylock in Antonio’s name.
Answer:
True
Question g.
Shylock was not at all generous.
Answer:
True
Question h.
Shy lock demanded a pound of Antonio’s flesh.
Answer:
True
Question i.
Portia saved Antonia in the court of law.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question j.
Antonio’s ships were lost at sea.
Answer:
False
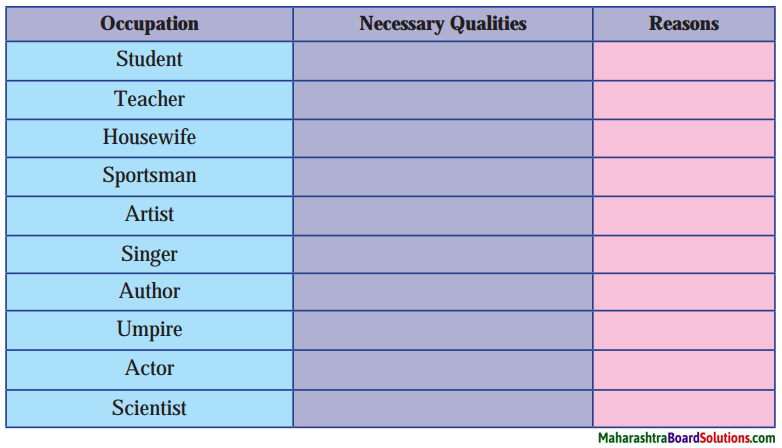
2. Write a few lines about each character.
Question 1.
Antonio:
Answer:
Antonio was a rich merchant who lived in the prosperous city of Venice in Italy. He sent his ships to faraway countries bringing back spices and other treasures, thus making a lot of profit. He was a kind man with many friends. His best friend was Bassanio, for whom he was even ready to stake his life.
Question 2.
Bassanio:
Answer:
Bassanio was a young and handsome nobleman with no money. He wanted to marry Portia. He had to go to Belmont to try his luck to marry Portia. He won Portia’s hand in marriage.
Question 3.
Portia:
Answer:
Portia was a beautiful and intelligent woman. She was the only daughter of a very wealthy man. Her father had died leaving her a large estate. Her father had written a will on how Portia’s husband had to be selected. Portia happily married Bassanio in accordance with her father’s will.
![]()
Question 4.
Shylock:
Answer:
Shylock was a Jewish moneylender. He had a lot of money. He was not a generous person. Money was all that he cared for. He did not like Antonio and wanted to harm him. He got a chance to do so when Antonio went to him to borrow money for Bassanio. He readily gave the money but with a strange condition which was very cruel and inhuman.
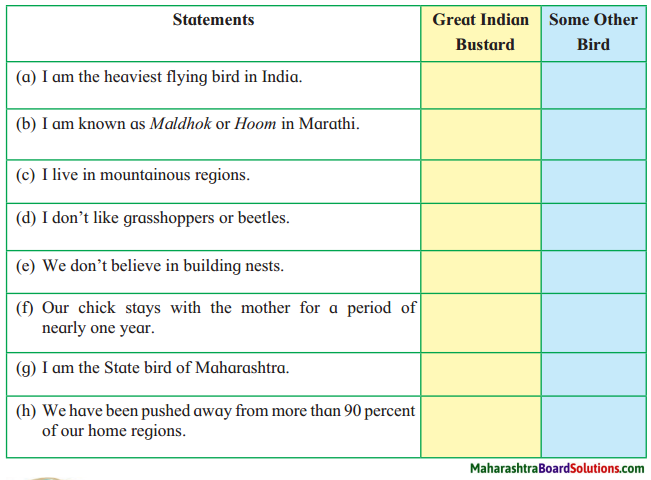
3. Write the following in short:
Question 1.
The story of the three caskets
Answer:
Portia’s father, a very wealthy man died leaving her a large estate. Her father had prepared a will in which he had written how her husband should be selected. He had to choose between three caskets – one of gold, one of silver and . one of lead. Each had something written on it and a message inside the box. The one who took the right casket which was the lead casket won Portia’s hand in marriage.
Question 2.
What the young lawyer pleaded?
Answer:
Antonio was taken to court by Shylock to demand and fulfill his strange and cruel condition. If the condition was fulfilled, Antonio would lose his life. A lawyer entered the court to fight Antonio’s case. The lawyer requested Shylock to show mercy though the law was on his side.
The lawyer pleaded that mercy is a quality of God. He further said that when a person shows mercy to someone, both are blessed. He said that mercy was more valuable than a king’s crown. All the pleadings of the young lawyer did not have any effect on Shylock who stuck to his inhuman condition of wanting a pound of Antonio’s flesh.
![]()
Question 3.
The events at the court
Answer:
When Antonio was taken to court by Shylock to get his inhuman demand fulfilled, the Duke who liked Antonio felt sorry for him. Portia asked Bassanio to pay Shylock double the amount which Shylock refused. Everyone in the court considered Shylock’s demand to be inhuman.
The Duke asked Shylock to show mercy but Shylock refused. A young lawyer entered the court to fight Antonio’s case. This was the turning point. The lawyer fought for Antonio very cleverly and helped him get out of the inhuman condition.
4. Write the conditions that Portia put down to warn Shylock.
Question 1.
Write the conditions that Portia put down to warn Shylock.
Answer:
The young lawyer fighting Antonio’s case asked Shylock to show mercy. Shylock was adamant and stuck to the bond saying that all he wanted was a pound of Antonio’s flesh. The lawyer then cleverly allowed Shylock to take Antonio’s pound of flesh. The lawyer warned the Jew that while doing so, he should not shed even one drop of Antonio’s blood. He also warned Shylock that he should cut exactly one pound of flesh – nothing less and nothing more, according to the bond.
5. Find four words ending with ‘-ous’ from the story. Can you add three more words ending with ‘-ous’ to this list?
Question 1.
Find four words ending with ‘-ous’ from the story. Can you add three more words ending with ‘-ous’ to this list?
Answer:
- prosperous
- generous
- monstrous
- jealous
![]()
6. Read the following words. Write the words that are combined to make these words. Add ten more to the list on your own.
Question 1.
Read the following words. Write the words that are combined to make these words.
- faraway
- nobleman
- whoever
- moneylender
- sometimes
Add ten more words to the list on your own. Each of the component words must be meaningful.
Answer:
- faraway – far, away
- nobleman – noble, man
- whoever – who, ever
- moneylender – money, lender
- sometimes – some, times
7. Read the following chains of words:
Question 1.
Read the following chains of words:
Answer:
- fortune – fortunate – fortunately – unfortunately
- know knowing – knowingly – unknowingly
- amaze – amazing – amazingly
- possible – impossible – impossibly
![]()
8. A letter or group of letters added to the front of a word to change its meaning and make a new word is called a prefix.
Examples: fortunately – unfortunately, agree – disagree, possible – impossible, human – inhuman, legal – illegal
Add proper prefixes to the following words to make new words:
- kind
- intelligent
- advantage
- happy
- allow
- safe
Answer:
- kind – unkind
- intelligent – unintelligent
- advantage – disadvantage
- happy – unhappy
- allow – disallow
- safe -unsafe
9. Find at least three sentences in the story which have modal verbs.
Question 1.
Portia’s husband should be selected.
Answer:
should-modal
Question 2.
Whoever chooses me, must give and hazard all he has.
Answer:
must-modal
![]()
Question 3.
Shylock would cut off a pound of Antonio’s flesh.
Answer:
would-modal
Question 3.
He was very happy that Antonio would not be able to pay the money.
Answer:
would – modal
Question 4.
But what could he do?
Answer:
could – modal
10. Visit a library. Read other tales by Shakespeare, for example, Julius Caesar, As You Like It, Macbeth and The Tempest.
11. Hold a mock trial for any one of the following offences. There should be a complainant, a defendant, and lawyers to argue that case on behalf of them. The whole class can vote to pass the judgement. On what occasions will you plead for justice? What punishment will you suggest? When will you plead for mercy?
a. A very poor and honest servant has broken a vase while cleaning it. The vase was valuable and the employer liked it very much.
b. A poor man stole some ornaments from a rich girl.
c. A young man was injured in a road accident due to another man’s careless driving.
![]()
Class 6 English Chapter 3.6 The Merchant of Venice Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
Where did Antonio live?
Answer:
Antonio lived in Venice, a prosperous city in Italy.
Question 2.
What did the ships of adventurous merchants bring back?
Answer:
The ships of adventurous merchants brought back spices and other treasures from India and other countries.
Question 3.
What made the merchants rich?
Answer:
The merchants sold the merchandise brought back from other countries in Europe and made a lot of profit, thus making them rich.
![]()
Question 4.
Who was Bassanio?
Answer:
Bassanio was a young and handsome nobleman, who had no money.
Question 5.
What had the suitors of Portia to choose between?
Answer:
Portia’s suitors had to choose between three caskets – one of gold, one of silver and one of lead.
Question 6.
What was written on the gold casket?
Answer:
‘Whoever chooses me shall gain what men desire’ was written on the gold casket.
Question 7.
What was written on the silver casket?
Answer:
‘Whoever chooses me shall get as much as he deserves’, was written on the silver casket.
![]()
Question 8.
What was written on the casket of lead?
Answer:
‘Whoever chooses me must give and hazard all he has’, was written on the casket of lead.
Question 9.
Who chose the gold casket?
Answer:
The Prince of Morocco chose the gold casket.
Question 10.
What was the message on the gold casket?
Answer:
The message on the gold casket was, ‘All that glitters is not gold’.
Question 11.
Who was Shylock?
Answer:
Shylock was a Jewish moneylender.
Question 12.
Why did Shylock dislike Antonio?
Answer:
Shylock disliked Antonio because he sometimes lent money to people without charging any interest on it.
![]()
Question 13.
What was the strange condition Shylock put to Antonio?
Answer:
The strange condition Shylock put to Antonio was that if Antonio failed to return the money he borrowed from Shylock within three months, he would cut a pound of Antonio’s flesh.
Question 14.
What news made Shylock happy? Why?
Answer:
The news that Antonio had lost his ships made Shylock happy. He was very happy because he was sure that Antonio would not be able to repay the money he had borrowed from Shylock.
Question 15.
Why was Antonio unable to avoid Shylock’s strange condition?
Answer:
Antonio was unable to avoid Shylock’s strange condition because Antonio had written a bond to that effect.
![]()
Question 16.
What did Portia tell Bassanio to do to save Antonio?
Answer:
Portia told Bassanio to pay Shylock twice the amount to save Antonio.
Question 17.
Why did Shylock want revenge?
Answer:
Shylock wanted revenge because he felt that Antonio and the others had treated him badly before.
Question 18.
What was mercy more valuable than?
Answer:
Mercy was more valuable than a king’s crown.
Question 19.
What did the lawyer warn Shylock while cutting off Antonio’s flesh?
Answer:
The lawyer warned Shylock that while cutting off the flesh, Shylock should not shed even one drop of Antonio’s blood. The lawyer also told Shylock that he should cut exactly one pound of flesh – nothing less and nothing more.
![]()
Question 20.
How was Antonio’s life saved?
Answer:
When Shylock realised that he could not do what the young lawyer had asked him to do, he accepted defeat and thus Antonio’s life was saved.
Question 21.
Why do you think Portia’s father prepared such a will?
Answer:
Portia was the only daughter of a wealthy man. Her father had died leaving Portia all his fortune and estate. He knew that Portia being alone could be cheated and would lose her wealth and property. So in order that Portia would get a good husband, Portia’s father made his will in this manner.
Reading Skills, Vocabulary and Grammar.
Question 1.
Write 3 sentences about Antonio.
Answer:
Antonia was a rich merchant of Venice, a prosperous city in Italy. He sent his ships to faraway countries bringing back spices and other treasures, thus making a lot of profit. He was a kind man with many friends. Bassanio was his best friend for whom he was ready even to stake his life.
![]()
Question 2.
When were sea voyages dangerous?
Answer:
Sea voyages were dangerous about five hundred years ago.
Question 3.
What was Antonio waiting for? Why?
Answer:
Antonio was waiting for his ships to return with merchandise. He was waiting for the ships because he had put almost all his money in the ships.
Question 4.
Antonio was a kind man. (Change into a negative sentence)
Answer:
Antonio was not an unkind man. OR Antonio was not a cruel man.
Question 5.
Give the antonyms of:
Answer:
a. dangerous × harmless, safe
b. kind × unkind
![]()
Question 6.
What are the qualities you would like in your best friend?
Answer:
A friend is one who is kind and good natured. He/She must be approachable so that I can tell him/ her my problems without being judgmental about me. I must feel free to confide all my happy as well as sad moments with him/ her. A best friend is one who makes you laugh a little louder, smile a little brighter and live a little better. These are the qualities I would like in my best friend.
Language Study.
Question 1.
Find four words ending with ‘-ous’ from the story. Add some more of your own words ending with ‘-ous’ to this list.
Answer:
- dangerous
- advantageous
- wondrous
- treacherous
- mountainous
Question 2.
Read the following words. Write the words that are combined to make these words. Add ten more to the list on your own.
Answer:
- cupboard – cup, board
- careless – care, less
- painless – pain, less
- comfortable – comfort, able
- handsome – hand, some
- forward – for, ward
- photograph – photo, graph
- strawberry – straw, berry
- pineapple – pine, apple
- anywhere – any, where
![]()
Question 3.
Read the following chains of words:
Answer:
1. taste – tasty – tasteful – tastefully
2. fashion – fashionable – unfashionable – fashionably – unfashionably
Do as directed:
Question 1.
Bassanio was a young and handsome nobleman. (Name the word class of the underlined word)
Answer:
young – adjective
Question 2.
He had no money. (Add a question tag)
Answer:
He had no money, hadn’t he?
![]()
Question 3.
They made a lot of profit. (Identify the kind of sentence)
Answer:
Assertive/Declarative – Affirmative
Question 4.
Antonio was waiting for his ships.
a. Pick out the verb and state its tense.
b. Pick out the auxiliary (helping) verb from the sentence
Answer:
a. was waiting – past continuous tense
b. was – auxiliary verb
The Merchant of Venice Summary in English
‘The Merchant of Venice’ written by William Shakespeare is a comical play. The story of the play revolves around Antonio, the rich merchant of Venice, his best friend Bassanio who wanted to marry Portia, the beautiful and intelligent daughter of a wealthy man but had no money to reach Belmont where Portia lived. Shylock, the Jewish moneylender who wanted a pound of Antonio’s flesh in exchange of the money he lent to Bassanio. In the court, Portia disguises as a man and fights Antonio’s case which ends on a happy note.
Introduction:
The play highlights the fact that love is more important than money and mercy is preferable to revenge and love lasts forever.
![]()
Glossary:
- prosperous (ad)) – to be successful
- adventurous (ad)) – willing to incur risks
- merchandise (n) – commodities offered for sale
- will (n) – a legal document stating one’s intent concerning the disposal of one’s property after death
- casket (n) – a little box, e.g., for jewelry
- hazard (v) – to risk something or put it in danger
- generous (adj) – willing to give and share
- adamant (adj) – firm, determined
- inhuman (adj) – something relating to cruelty, uncivilized
- tragic (adj) – causing great sadness or suffering
Std 6 English Digest Other Chapters:
- It Can Be Done Class 6 Question Answers
- Seven Sisters Class 6 Question Answers
- Stone Soup Class 6 Question Answers
- Sushruta (A Peep into the Past) Class 6 Question Answers
- The Donkey Class 6 Question Answers
- The Merchant of Venice Class 6 Question Answers
- At the Science Fair Class 6 Question Answers