Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Geography Solutions Chapter 1 The Earth and the Graticule Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answer The Earth and the Graticule Maharashtra Board
Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth and the Graticule Question Answer Maharashtra Board
The Earth and the Graticule Class 6 Questions And Answers
A. Place a tick mark (✓) against the correct option:
Question 1.
What term is used for the imaginary east-west horizontal lines on the earth?
(i) Meridians
(ii) International Date Line
(iii) Parallels
Answer:
Parallels
![]()
Question 2.
What is the shape of the meridians?
(i) Circular
(ii) Semicircular
(iii) Points
Answer:
Semicircular
Question 3.
What do the parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude together form on the globe?
(i) Angular distance
(ii) Hemisphere
(iii) Graticule
Answer:
Graticule
Question 4.
How many parallels are there in the northern hemisphere?
(i) 90
(ii) 89
(iii) 91
Answer:
90
Question 5.
Which circles form the eastern and western hemispheres?
(i) 0° parallel and 180° meridian
(ii) 0° Prime Meridian and 180° meridian
(iii) North and South Polar circles
Answer:
0° Prime Meridian and 180° meridian
Question 6.
Which circle appears as a point on the globe?
(i) Equator
(ii) North/South Pole
(iii) Prime Meridian
Answer:
North/South Pole
Question 7.
How many places on the earth may be located on 45° N parallel?
(i) One
(ii) Many
(iii) Two
Answer:
Many
![]()
B. Observe a globe and examine the following statements. Correct the wrong ones:
Question 1.
Parallels of latitude lie parallel to the Prime Meridian,
Answer:
Wrong: Parallels of latitude lie parallel to the equator.
Question 2.
All parallels of latitude converge at the equator.
Answer:
Wrong: All meridians of longitude converge at the poles.
Question 3.
Parallels and meridians are imaginary lines.
Answer:
Right.
Question 4.
8° 4′ 65″ N is a north meridian.
Answer:
Wrong: 8° 4′ 65″ N is a north parallel.
Question 5.
Meridians are parallel to each other.
Answer:
Wrong: Latitudes are parallel to each other.
C. Find the correct graticule out of the following and put a tick mark against it.
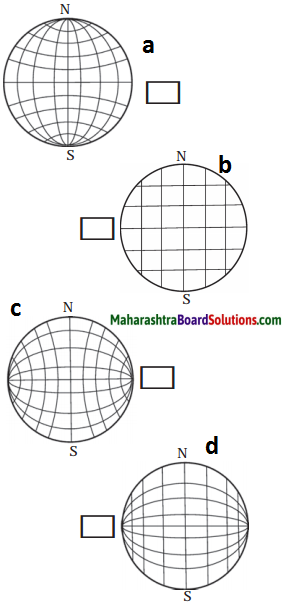
Answer:
Figure (a) is correct.
D. Answer the following:
Question 1.
How will you express the latitude and longitude of the North Pole?
Answer:
The latitude of the North Pole would be 90°N. All the meridians of longitudes pass through the North Pole. So the North pole would be 0° longitude.
Question 2.
How much is the angular distance between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn?
Answer:
The angular distance between the tropic of Cancer and tropic of Capricorn is 23°30′ + 23°30′ = 47°
![]()
Question 3.
Using a globe, write down the names of the countries through which the equator passes.
Answer:
The countries through which the equator passes are Ecuador, Colombia, Brazil, Sao tome and Principe, Gabon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Uganda, Kenya, Somalia, Maldives, Indonesia and Kiribati.
Question 4.
Write down the main uses of the graticule.
Answer:
Graticules help us to determine the locations on the earth. In the modern age, Geographical Information Systems, Global Positioning System, Google Maps, Wikimapia, Bhuvan of ISRO also make use of graticules.
E. Complete the following table:
| Characteristics | Parallels of latitude | Meridians of longitude |
| Shape | ||
| Size of each parallel is different | ||
| Distance | Distance between two meridians is larger on the equator and the same decreases towards the Poles. |
Answer:
| Characteristics | Parallels of latitude | Meridians of longitude |
| Shape | Circular | Semicircular |
| Size | Size of each parallel is different | Size of each meridian is same |
| Distance | Distance between two parallels is the same everywhere | Distance between two meridians is larger on the equator and the same decreases towards the Poles. |
Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth and the Graticule Textbook Questions and Answers
Think a little!
Question 1.
A game of reading the meridians on the world map is going on. Shaheen and Sanket are asking each other to locate places on specific meridians and are making notes of the same. Shaheen asks Sanket to locate Wrangel Island on 180° meridians. Sanket could locate the island in the map but both are confused while making a note of it. They are puzzled whether to write 180° E or 180° W? What would be the precise answer? Please help them. Can we use a similar logic with reference to 0° meridian as well?
Answer:
The 0° and the 180° meridians lie opposite to each other and form a circle around the earth. This circle divides the earth in the eastern and western hemisphere. Shaheen and Sanket can write the Wrangled island to be loacted on 180° meridian.
![]()
Do it yourself!
Use figure 1.4 of the geography textbook:
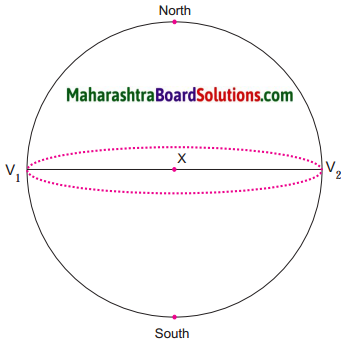
In the upper portion of the circle, at the centre X, draw angles of 30°, V1 X K1 and V2 X K2; K1 and K2 being the points on the circle. Draw an ellipse joining K1 and K2.
In the lower half of the circle, mark angles of 60° and name the points on the circle as P1 and P2.
Question 1.
Draw an ellipse joining P1 and P2.
Answer:
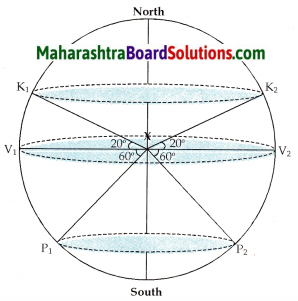
Can you tell?
Question 1.
Is the distance between K1 K2 and P1 P2 the same?
Answer:
No, the distance between K1 K2 and P1 P2 are not the same.
Question 2.
Compare the distances XK1 and XP2. Are these distances the same or are they different?
Answer:
Yes, the distances are the same.
Question 3.
Now compare the ellipses you have drawn. Which is the larger ellipse? Why?
Answer:
The ellipse through K1 and K2 is larger than the ellipse through P1 and P2 . This is because the distance between K1 K2 is greater than the distance between P1 P2.
![]()
Observe the picture (fig) on page 5 of the textbook and answer the following questions:
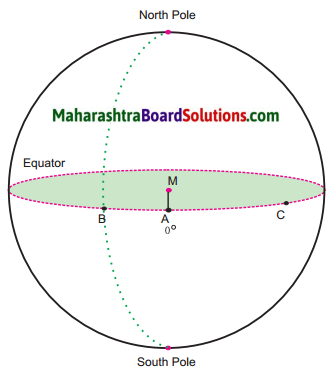
Let the line AM be 0°.
Draw the line MB. Measure the angle it makes with the line AM and write it near B. Note the semicircle that passes through B and joins the North and South Poles. Trace it.
Now join MC. Measure ∠AMC and write it next to C. Draw a semicircle that passes through ‘C’ and joins the North and South Poles.
Draw a line that passes through point A at 0°, and joins the North and South Poles.
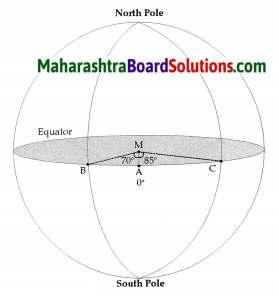
Answer:
∠AMB = 70°
∠AMC = 85°
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
How many parallels and meridians can be drawn on a globe at an interval of 10°?
Answer:
19 parallels and 36 meridians can be drawn on a globe at an interval of 10°.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth and the Graticule Textbook Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct options from the brackets:
Question 1.
A miniature model of the earth is called a _____.(ball, globe, sphere)
Answer:
globe
Question 2.
The location of any place on the earth is determined with reference to the ______ of the earth. (poles, circle, centre)
Answer:
centre
Question 3.
The _______ is considered as 0° parallel.(equator, poles, circles)
Answer:
equator
Question 4.
The ______ bisects the earth into north and south parts. (poles, equator, circles)
Answer:
equator
![]()
Question 5.
One can draw _____ parallels on the earth at the interval of 1°. (90,181,360)
Answer:
Question 6.
The 0° meridian is known as the _____. (Central meridian, Equator, Prime Meridian)
Answer:
Prime Meridian
Question 7.
Each degree is divided into 60 ______.(minutes, hours, seconds)
Answer:
minutes
Question 8.
One can draw _____ meridians each at a distance of 1°. (90,181, 360)
Answer:
360
Question 9.
All meridians are _______ in size.(unequal, equal, uneven)
Answer:
equal
Question 10.
Exact location of a place on the earth can be located using ______.(equator, latitude and longitude, Prime Meridian)
Answer:
latitude and longitude
Question 11.
The distance between any two adjacent parallels is _______ on the surface of the earth. (111 km, 102 km, 44 km)
Answer:
111 km
Question 12.
The parallels and meridians on the globe form a net that is called a ______.(latitude,graticule, longitude)
Answer:
graticule
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
| Different parallels | Distance between meridians |
| (1) Poles | (a) 111 km |
| (2) Tropic of Cancer | (b) 102 km |
| (3) Polar Circles | (c) 0 km |
| (4) Equator | (d) 44 km |
| (5) Meridians | (e) 360 |
| (f) 1° |
Answer:
1 – c
2 – b
3 – d
4 – a
5 – e
Place a tick mark (✓) against the correct option:
Question 1.
Which meridian is considered as the Prime Meridian?
(i) 0°
(ii) 80°
(iii) 90°
Answer:
0°
![]()
Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What are parallels of latitudes?
Answer:
Ellipses that are created at some angular distance from the centre of the earth and are parallel to one another are called parallels of latitudes.
Question 2.
How many parallels are there in the northern hemisphere?
Answer:
There are 90 parallels in the northern hemisphere.
Question 3.
Which circle divides the earth in the eastern and western hemisphere?
Answer:
The Prime Meridian divides the earth in the eastern and western hemisphere.
Question 4.
What is the distance between any two adjacent parallels on the surface of the earth?
Answer:
The distance between any two adjacent parallels on the surface of the earth is 111 km.
Question 5.
What is a graticule?
Answer:
The parallels and meridians on the globe form a net that is called a graticule.
Question 6.
What is used to determine the location on the earth?
Answer:
Latitude and longitude is used to determine the location on the earth.
Write the full forms of:
Question 1.
GIS
Answer:
Geographical Information System
Question 2.
GPS
Answer:
Global Positioning System
Question 3.
IRNSS
Answer:
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System
Question 4.
ISRO
Answer:
Indian Space Research Organisation
![]()
Give geographical reasons for the following statements:
Question 1.
Parallels and meridians are imaginary lines on the earth.
Answer:
Parallels and meridians can be drawn on a globe though not on the earth. That is why parallels and meridians are imaginary lines on the earth.
Question 2.
Geographers developed a miniature model of the earth in the form of a globe.
Answer:
Oceanic waters, uneven nature of the land, forest, innumerable islands of different sizes and buildings make it impossible to draw lines on the earth. In order to overcome this difficulty, geographers developed a miniature model of the earth in the form of a globe.
Question 3.
Latitude and longitudes are expressed into degree, minutes and seconds.
Answer:
To locate the places within the distance of 111 km exactly, the unit degree is divided into smaller units. Degrees are divided into minutes and seconds.
Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the term ‘equator’.
Answer:
- The equator is considered as 0° parallel.
- It is the largest parallel and great circle.
- It bisects the earth into two equal hemispheres viz, the northern and southern hemisphere.
Question 2.
What are Poles of the earth?
Answer:
On the globe and also on the earth, at the north and south ends of the earth’s axis, Poles appear as points. These are called the North Pole and the South Pole respectively.
Observe a globe and examine the following statements. Correct the wrong ones:
Question 1.
Parallels of latitude lie parallel to the Prime Meridian,
Answer:
Wrong: Parallels of latitude lie parallel to the equator.
Question 2.
All parallels of latitude converge at the equator.
Answer:
Wrong: All meridians of longitude converge at the poles.
Question 3.
Parallels and meridians are imaginary lines.
Answer:
Right.
Question 4.
80° 4′ 65″ N is a north meridian.
Answer:
Wrong: 80° 4′ 65″ N is a north parallel.
![]()
Question 5.
Meridians are parallel to each other.
Answer:
Wrong: Latitudes are parallel to each other..
6th Std Geography Questions And Answers:
- The Earth and the Graticule Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Let us Use the Graticule Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Comparing a Globe and a Map; Field Visits Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Weather and Climate Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
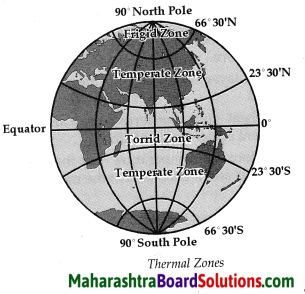
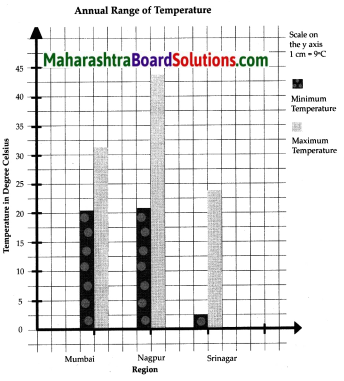
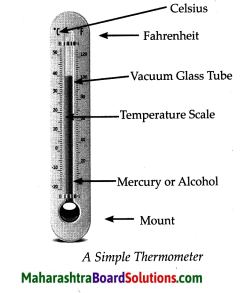
- Temperature Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
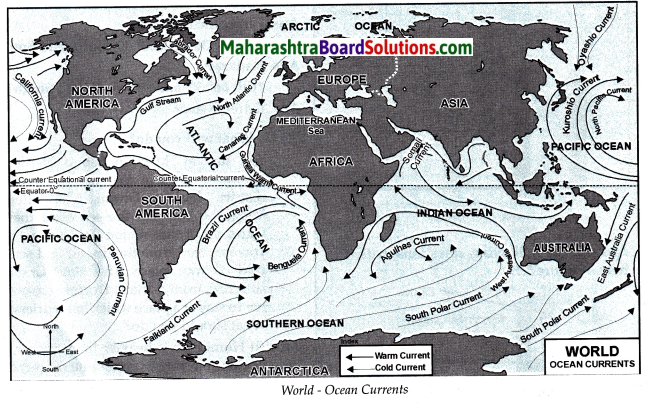
- Importance of Oceans Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Rocks and Rock Types Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Natural Resources Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
- Energy Resources Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers
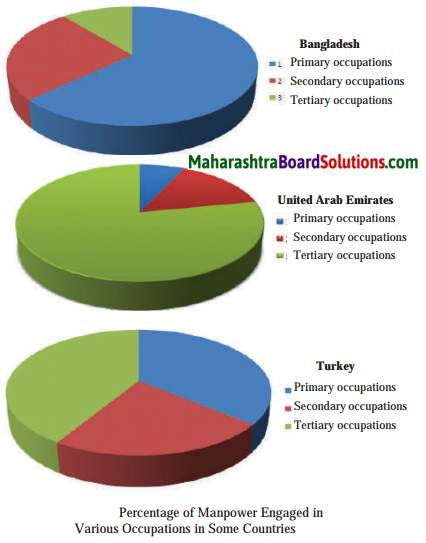
- Human Occupations Class 6 Geography Questions And Answers