Std 6 Civics Chapter 5 Question Answer District Administration Maharashtra Board
Class 6 Civics Chapter 5 District Administration Question Answer Maharashtra Board
District Administration Class 6 Questions And Answers
1. Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
Who heads the District Administration?
Answer:
The District Collector heads the District Administration.
Question 2.
What is the responsibility of the Tahsildar?
Answer:
As a judicial officer he gives judgements to resolve conflicts at the local level, he also has the responsibility of maintaining peace and order in Taluka.
![]()
Question 3.
Which court is at the apex of the judiciary?
Answer:
The Supreme Court of India is at the apex of the judiciary.
Question 4.
Which disaster can we be forewarned about?
Answer:
We can be forewarned about floods and storms.
2. Match the following:
Question 1.
| Group A | Group B |
| (a) District Collector | (1) Taluka Magistrate |
| (b) District court | (2) Maintaining law and order |
| (c) Tahsildar | (3) Resolving disputers |
| Disaster management | (4) Scientific and organized manner |
Answer:
a – 2
b – 3
c – 1
d – 4
![]()
3. Discuss the following issues:
Question 1.
Disaster Management
Answer:
(a) Sometimes, we may have to face a calamity. It could be a natural disaster like floods, fire, a cloudburst, cyclone, earthquake, landslide or problems like riots, bomb blasts, breaking of a dam, epidemics, etc.
(b) These disasters lead to loss of human lives and displacement of people beside tremendous financial losses.
(c) Therefore, the issues of rehabilitation becomes important.
(d) Disaster management is a process which enables one to face a disaster in a scientific and organized manner. The entire machinery of a district is involved in the process.
Question 2.
Functions of the District Collector.
Answer:
(a) The District Collector is the head of the district administration.
(b) He has to perform many functions from collecting agricultural tax to maintaining law and order in the district. To ensure smooth conduct of elections and disaster management.
4. Which of the following positions would you like to be in, and why?
Question 1.
District Collector, Chief of the District Police, Judge.
Answer:
I would like to be the chief of the District Police. Joining the Police Department is my childhood dream. I would like to maintain law and order in the society and provide people a sense of security. I have the qualities of patriotism and determination which are vital to join the police service. I will work for my fitness too and serve my country with total commitment.
![]()
Activities:
- Visit the police station nearest to you and obtain information about the work that is done there.
- Make a chart of the different disasters showing what precautions are to be taken and important phone numbers. Display the chart in your class.
- Send New Year greetings to the District Collector, Chief of the District Police and the District Judge.
Class 6 Civics Chapter 5 District Administration Additional Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks by choosing the correct option from the brackets:
Question 1.
The _______ is a part of the rural local government system.
(a) District Collector
(b) District Police
(c) Zilla Parishad
Answer:
Zilla Parishad
Question 2.
District Collector is appointed by the _______ government.
(a) Central
(b) State
(c) Union
Answer:
State
Question 3.
The ______ has the responsibility of maintaining peace and order in the taluka.
(a) District Collector
(b) Tahsildar
(c) Police Inspector
Answer:
Tahsildar
![]()
Question 4.
The Constitution of India has established an _______ judiciary.
(a) independent
(b) dependent
(c) system
Answer:
independent
Question 5.
______ is the process which enables one to face a disaster in a scientific and organised manner.
(a) Event management
(b) Disaster management
(c) Management
Answer:
Disaster management.
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
Name the lower courts in the Indian judiciary.
Answer:
District courts, Taluka courts, Revenue courts.
Question 2.
What are the effects of disasters?
Answer:
Disasters leads to loss of lives and displacement of people besides tremendous financial losses.
Question 3.
Explain the term: Disaster management.
Answer:
Disaster management is a process which enables one to face a disaster in a scientific and organised manner.
![]()
Which of the following positions would you like to be in, and why?
Question 1.
District Collector, Chief of the District Police, Judge.
Answer:
I would like to be the chief of the District Police. Joining the Police Department is my childhood dream. I would like to maintain law and order in the society and provide people a sense of security. I have the qualities of patriotism and determination which are vital to join the police service. I will work for my fitness too and serve my country with total commitment.
Question 2.
Complete the tree diagram and write a short note on the District Court.
Answer:
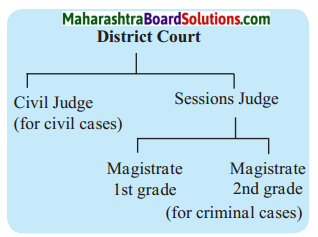
- The court at the district level is known as the District court.
- The district court has a Chief District Judge and some other judges.
- Their main function is to hear the various cases in the district and deliver the final judgement.
- One can appeal against the judgement of the Taluka Court in the District Court.
Question 3.
Complete the table to enlist different functions of the District Collector.
Answer:
District Collector
| Agriculture | Law and Order | Election Officer | Disaster Management |
| To collect agricultural tax. | Establish peace in the district. | To ensure smooth conduct of elections. | To take quick decisions during time of disaster and prevent or minimise the damage. |
| To implement laws relating to agriculture. | To maintain social harmony. | To take necessary decisions related to the electoral process. | To give orders to the disaster management units/cells. |
| To provide relief in case of drought and scarcity of fodder. | To restrict unlawful assembly, impose curfew if required. | To update the voters’ lists | To rehabiliate/those affected by a disaster. |
![]()
Complete the analogy:
Question 1.
Superintendent of Police : District :: Police Commissioner : ________.
Answer:
City
Question 2.
______ : natural :: Bomb blast : man made calamity
Answer:
Floods
Question 3.
Civil Judge : Civil cases :: Magistrate 2nd grade : ______.
Answer:
Criminal cases
Name the following:
Question 1.
The rural local government system of which the Zilla Parishad is a part:
Answer:
Panchayati Raj system.
Question 2.
It appoints Head of the district administration:
Answer:
State Government.
Question 3.
Any one function of the courts at the district level:
Answer:
Resloving disputes.
Question 4.
The court below the Supreme Court of India:
Answer:
High Court.
![]()
State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons:
Question 1.
In Maharashtra the sole responsibility of the administration of the district is on Zilla Parishad:
Answer:
False.
In Maharashtra, the administration of the district is shared by both the Zilla Parishad and District Collector. The Union Goverment and State Government both participate in the administration.
Question 2.
The Court at the district level play an important role in resolving conflicts.
Answer:
True.
The Courts at the district level have to perform the function of resolving disputes, delivering judgements and ensuring that conflicts are resolved at the earliest.
So the courts at the district level play an important role in resolving conflicts.
Question 3.
There is a hierarchy in the Indian Judiciary
Answer:
True.
The Constitution of India has established an independent judiciary. At the apex of the system is the Supreme Court of India. Below this are the High Court, and below them, the lower courts. These include District Courts, Taluka Courts and Revenue Courts.
6th Std Civics Questions And Answers:
- Our Life in Society Class 6 Civics Questions And Answers
- Diversity in Society Class 6 Civics Questions And Answers
- Rural Local Government Bodies Class 6 Civics Questions And Answers
- Urban Local Government Bodies Class 6 Civics Questions And Answers
- District Administration Class 6 Civics Questions And Answers