Class 6 Hindi Chapter 4 Sona Aur Loha Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Hindi Solutions Sulabhbharati Chapter 4 साेना और लोहा Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 6 Hindi Chapter 4 Sona Aur Loha Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 4 साेना और लोहा Textbook Questions and Answers
अध्ययन कौशल:
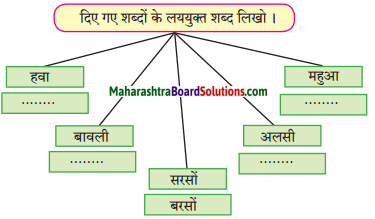
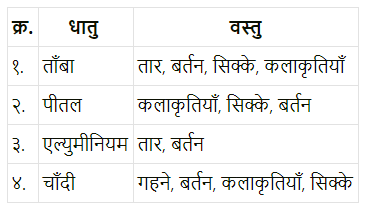
विभिन्न धातुओं के नाम और उनसे बनने वाली वस्तुएँ लिखो।
Answer:
![]()
विचार मंथन:
आराम हराम है
Answer:
‘आराम हराम है।’ यह नारा देश के पहले प्रधानमंत्री पं. जवाहरलाल नेहरू ने दिया था। नेहरू जी ने यह नारा उस समय दिया था, जब देश स्वतंत्र हुआ था। आलस करना या अत्यधिक आराम करना हमारे लिए नुकसानदेह हो सकता है। परीक्षा का समय हो, तो डटकर पढ़ाई करनी चाहिए। किसी प्रकार की प्रतियोगिता हो, तो उसकी तैयारी करनी चाहिए। सोचो यदि हम परीक्षा की तैयारी करने के बजाय आराम करते हैं, तो परीक्षा में असफल भी हो सकते हैं। हम छोटे से जीव चींटी से भी परिश्रम की सीख ले सकते हैं। वह दिन-रात मेहनत कर अपना भोजन इकट्ठा करती है और बरसात के वक्त आराम से अपनी मेहनत का लाभ उठाती है।
भाषा की ओर:
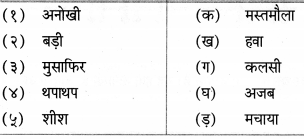
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में प्रत्यय लगाकर लिखो।
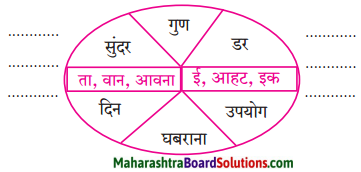
Answer:
- सुंदरता
- गुणवान
- डरावना
- उपयोगी
- घबराहट
- दैनिक
![]()
सुनो तो जरा |
बस/रेल स्थानक की सूचनाएँ ध्यानपूर्वक सुनकर सुनाओ।
Answer:
१. बस स्थानक की सूचना:
स्थान: माथेरान एस टी बस स्टैंड।
यात्रीगण कृपया ध्यान दें। माथेरान से मुंबई जाने वाली दो बसों के समय में परिवर्तन किया गया है। सुबह ९ बजकर ३० मिनट पर रवाना होने वाली बस अब १० बजकर ११ मिनट पर रवाना होगी तथा सुबह ११ बजे रवाना होने वाली बस दोपहर १२ बजे रवाना होगी। यात्रियों को होने वाली | असुविधा के लिए हमें खेद है। धन्यवाद!
२. रेल स्थानक की सूचना:
स्थान: दादर रेलवे कार्यालय।
नमस्कार! हम दादर के केंद्रीय कार्यालय से बोल रहे हैं। ट्रैक नंबर दो पर मरम्मत-कार्य चालू होने के कारण आज दोपहर चार बजे तक सी. एस. टी. से माटुंगा की दिशा में जाने वाली सभी डाउन गिाड़याँ ट्रैक नंबर एक से चलाई जाएँगी। यात्रियों को होने वाली असुविधा के लिए हमें खेद है। धन्यवाद!
बताओ तो सही।
थर्मामीटर में किस धातु का प्रयोग होता है, बताओ।
Answer:
पारा
![]()
मेरी कलम से
अंकुरित अनाजों की सूची बनाओ और उपयोग लिखो।
Answer:

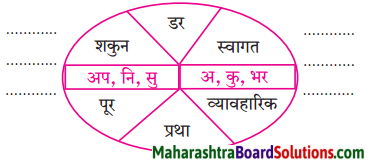
सदैव ध्यान में रखो।
प्रत्येक का अपना-अपना महत्त्व होता है।
Answer:
प्रत्येक वस्तु का अपना-अपना महत्त्व होता है। कोई भी छोटा अथवा बड़ा नहीं होता। बड़ी चीज जितनी उपयोगी है, छोटी चीज भी उतने ही काम की है। बड़ी-बड़ी मशीनों के कल-पूजों को जोड़नेवाले नट-बोल्ट छोटे-छोटे ही होते हैं। सोना अगर कीमती धातु है, तो लोहा मजबूत और रोजाना काम आने वाली धातु है।
जरा सोचो ….. चर्चा करो
यदि खनिज तेल का खजाना समाप्त हो जाए तो…
Answer:
यदि खनिज तेल का खजाना समाप्त हो जाए, तो यातायात व्यवस्था ठप हो जाएगी। खनिज तेल से पेट्रोल, डीजल, मिट्टी का तेल, कुकिंग गैस, वैसलीन आदि बनते हैं। खनिज तेल के समाप्त होने से सड़कों पर गिाड़याँ नहीं दौड़ पाएँगी। हम यात्रा नहीं कर पाएँगे। रोज-रोज पैदल चलना कठिन काम होगा। ट्रक न चलने से घरों, दूकानों, बाजारों तक सामान नहीं पहुँच पाएगा। हम भूखे-प्यासे रह जाएँगे। एलपीजी गैस जिससे खाना बनाया जाता है, उसके बिना घरों में खाना नहीं बन पाएगा। खनिज तेल कई दवाइयों के निर्माण में काम आते हैं। इनके बिना दवाइयाँ भी नहीं बन पाएँगी। इस तरह खनिज तेल समाप्त हो जाने पर पूरी दुनिया का काम-काज रुक जाएगा।
![]()
अध्याय
सही या गलत बताओ।
सोना और लोहा प्रश्न उत्तर Question 1.
युद्ध में लोहे के अस्त्र – शस्त्र काम देते हैं।
Answer:
सही
Sona Aur Loha Question Answer Question 2.
रोटियाँ भी सोने के तवे पर सेंकी जाती हैं। ङ्के
Answer:
गलत
Class 6th Hindi Sona Aur Loha Question 3.
श्रम में ही जीवन की सफलता है।
Answer:
सही
Sona Aur Loha 6 Standard Question 4.
जो काम करेंगे, उन्हीं का अब सम्मान नहीं होगा।
Answer:
गलत
![]()
Sona Aur Loha Hindi Question 5.
आराम हराम है।
Answer:
सही
सोना और लोहा हिंदी पाठ Question 6.
हमें घमंड करना चाहिए।
Answer:
गलत
खोजबीन:
रुपयों (नोट) पर लिखी कीमत कितनी और किन भाषाओं में अंकित है, बताओ।
Answer:

स्वयं अध्ययन:
सदगुणों को आत्मसात करने के लिए क्या करोगे, इसपर आपस में चर्चा करो।
Answer:

![]()
व्याकरण
निम्नलिखित शब्दों का रोमन लिपि में लिप्यंतरण करो।
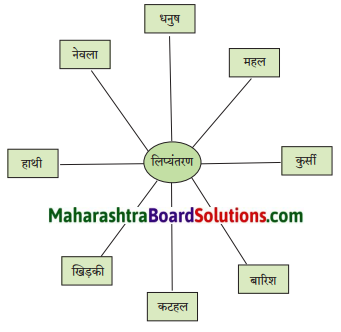
Answer:
i. Dhanush
ii. Mahal
iii. Kursi
iv. Barish
v. Katahal
vi. Khidki
vii. Hathi
viii. Nevala
![]()
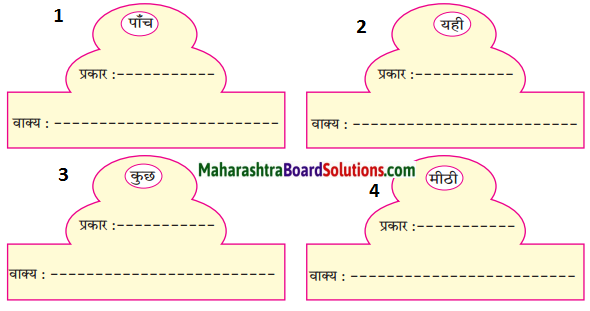
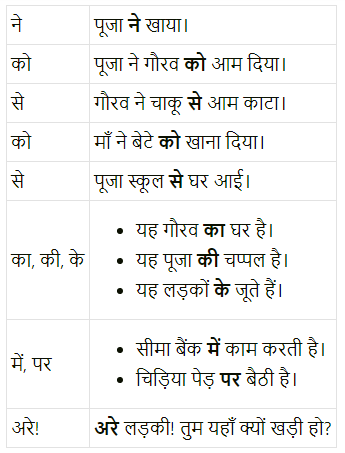
निम्नलिखित कारकों का अपने वाक्यों में प्रयोग करो।
Answer:
![]()
Hindi Sulabhbharti Class 6 Solutions Chapter 4 साेना और लोहा Additional Important Questions and Answers
निम्नलिखित शब्दों में से सही शब्द चुनकर रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए:
(रक्षा, मूल्य, सेवा, आराम, लद)
6th Standard Hindi Lesson Sona Aur Loha Question 1.
राजाओं के दिन ……………… गए।
Answer:
लद
Sona Or Loha 6 Standard Question 2.
तेरी ……………… का भार मुझ पर है।
Answer:
रक्षा
Question 3.
मैं तो ……………… से रहना चाहता हूँ।
Answer:
आराम
Question 4.
रुपयों में किसी वस्तु का ……………… लगाना व्यर्थ
Answer:
मूल्य
Question 5.
गरीबों की ……………… करने में मुझे सुख मिलता है।
Answer:
सेवा
![]()
निम्नलिखित बाक्य सही हैं या गलत लिखिए:
Question 1.
युद्ध में लोहे के अस्त्र – शस्त्र काम देते हैं।
Answer:
सही
Question 2.
रोटियाँ भी सोने के तवे पर सेंकी जाती हैं।
Answer:
गलत
Question 3.
श्रम में ही जीवन की सफलता है।
Answer:
सही
Question 4.
जो काम करेंगे, उन्हीं का अब सम्मान नहीं होगा।
Answer:
गलत
Question 5.
आराम हराम है।
Answer:
सही
Question 6.
हमें घमंड करना चाहिए।
Answer:
गलत
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-एक शब्द में लिखिए:
Question 1.
सोना किन लोगों का लाड़ला है?
Answer:
राजाओं और धनिकों का।
Question 2.
अब किन लोगों के दिन आए हैं?
Answer:
श्रमिकों के।
Question 3.
लोहा किन लोगों का प्यारा है?
Answer:
किसानों और मजदूरों का।
Question 4.
लोहा किसकी रक्षा करता है?
Answer:
सोने की।
Question 5.
सोने का रंग कैसा है?
Answer:
पीला।
![]()
निम्नलिखित वाक्य किसने, किससे कहे?
Question 1.
संसार में मैं सबसे सुंदर हूँ।
Answer:
सोने ने लोहे से कहा।
Question 2.
अच्छा, तू राजा और मैं नौकर?
Answer:
लोहे ने सोने से कहा।
Question 3.
अरे, लोहे से कैसे पेट भरता है।
Answer:
सोने ने लोहे से कहा।
Question 4.
मुझसे तो मेहनत नहीं होती।
Answer:
सोने ने लोहे से का।
Question 5.
छोड़ दूँगा भैया, मगर मेरी रक्षा करना।
Answer:
सोने ने लोहे से कहा।
![]()
निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक-एक वाक्य में लिखिए:
Question 1.
सबको किसकी चाह होती है।
Answer:
सबको सोने की चाह होती है।
Question 2.
राजा की रक्षा कौन करते हैं?
Answer:
राजा की रक्षा उसके नौकर – चाकर करते हैं
Question 3.
रोटियाँ किस पर सेकी जाती है।
Answer:
रोटियाँ लोहे के तवे पर सेंकी जाती है।
Question 4.
जीवन की सफलता किसमें होती है?
Answer:
जीवन की सफलता श्रम करने में होती है।
Question 5.
लोहे ने सोने को कौन-सा वचन दिया?
Answer:
लोहे ने सोने को उसकी रक्षा करने का वचन दिया।
![]()
व्याकरण और भाषाभ्यास
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के दो-दो पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए:
- राजा
- रात
- श्रम
- नौकर
- मकान
Answer:
- नृप, नरेश
- रात्रि, निशा
- कष्ट, मेहनत
- सेवक, चाकर
- घर, गृह
![]()
निम्नलिखित शब्दों के विरुद्धार्थी लिखिए:
- राजा
- दिन
- भीतर
- गुण
- भला
Answer:
- रंक
- रात
- बाहर
- दोष
- बुरा
![]()
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में कारक को रेखांकित करके उनके भेद लिखिए:
Question 1.
मेरे एक चाँटे से तेरा रूप बदल जाएगा।
Answer:
से – करण कारक
Question 2.
राजा की रक्षा उसके नौकर – चाकर करते हैं।
Answer:
की – संबंध कारक
Question 3.
तू तिजोरी से बाहर क्यों आया?
Answer:
से – अपादान कारक
Question 4.
कोई बड़ा काम करना हो, लोहे के बिना हो ही नहीं सकता।
Answer:
के – संबंध कारक
Question 5.
श्रम में ही जीवन की सफलता है।
Answer:
Answer:
में – अधिकरण
Hindi Sulabhbharati 6th Standard Digest Guide दूसरी इकाई