Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Marathi Solutions Kumarbharti Chapter 18 निर्णय Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions, and Answers.
Class 10th Marathi Kumarbharti Chapter 18 निर्णय Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Std 10 Marathi Chapter 18 Question Answer
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Digest Chapter 18 निर्णय Textbook Questions and Answers
कृति
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न १ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी…
प्रश्न 1.
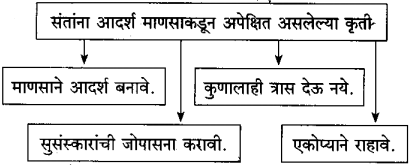
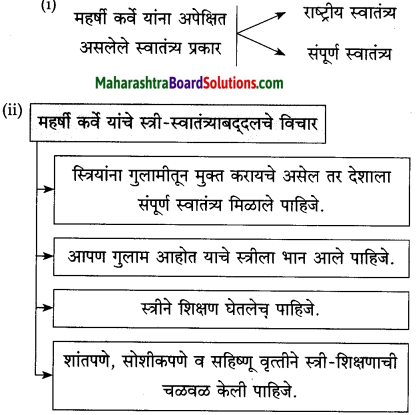
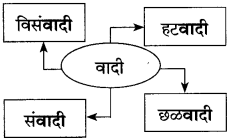
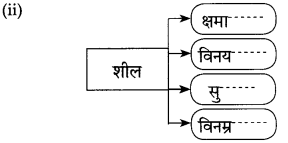
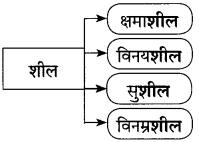
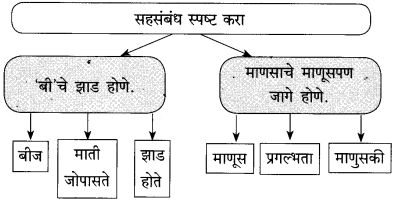
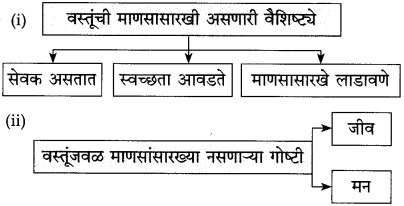
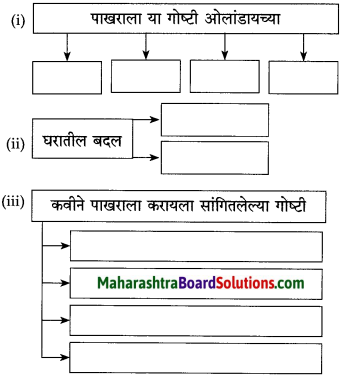
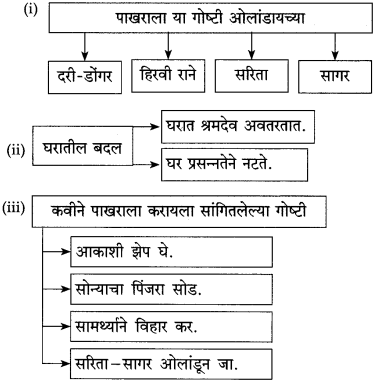
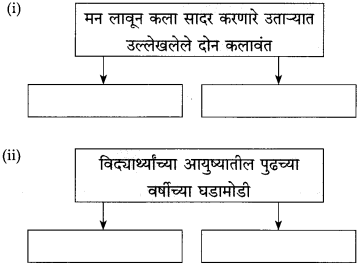
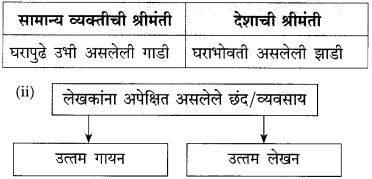
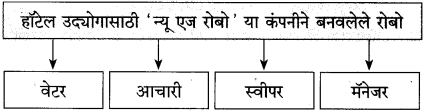
खालील आकृती पूर्ण करा.
(i) 
उत्तर:
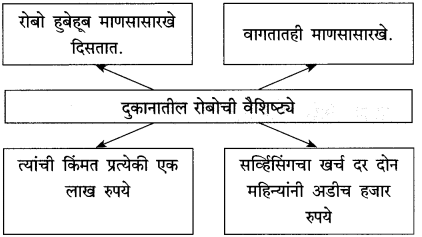
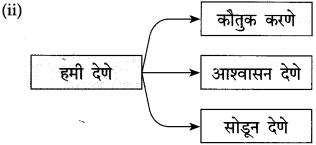
(ii) 
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 2.
कारणे लिहा.
(अ) हॉटेल मालकाने चार रोबो खरेदी केले, कारण ……………………………”
(आ) हॉटेल मालकाची द्विधा मन:स्थिती संपली, कारण ……………………………
उत्तर:
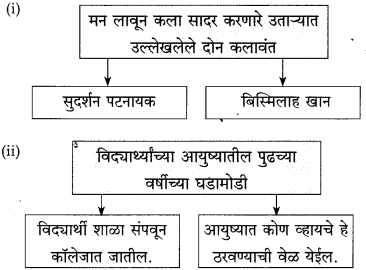
(अ) हॉटेलच्या मालकाने चार रोबो खरेदी केले; कारण त्याला वेटरचा प्रश्न कायमचा निकालात काढायचा होता.
(आ) हॉटेल मालकांची द्विधा मन:स्थिती संपली, कारण रोबो वेटरपेक्षा मानवी वेटर ठेवणेच श्रेयस्कर आहे, हे मालकांना पटले.
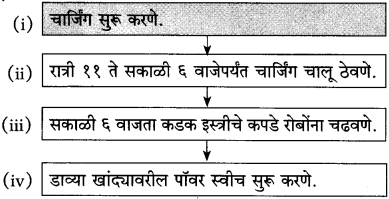
प्रश्न 3.
रोबर्बोना कामे करण्यासाठी सज्ज करण्याच्या कृतींच्या घटनाक्रमाचा ओघतक्ता तयार करा.
(अ) चार्जिंग सुरू करणे.
(आ) ↓
________________
(इ) ↓
________________
(ई) ↓
________________
उत्तर:

प्रश्न 4.
खालील शब्दसमूहांचा अर्थ तुमच्या शब्दांत लिहा.
(अ) वाळवंटातील हिरवळ ________________
(आ) कासवगती ________________
(इ) अचंबित नजर ________________
(ई) द्विधा मन:स्थिती ________________
उत्तर:
प्रश्न 5.
खालील वाक्प्रचारांचा योग्य अर्थ शोधा व लिहा.
(अ) आनंद गगनात न मावणे
(१) आनंद हद्दपार होणे.
(२) आकाश हातात न मावणे.
(३) खूप आनंद होणे.
(४) आकाशाशी नाते जडणे.
उत्तर:
आनंद गगनात न मावणे – खूप आनंद होणे.
(आ) काडीचाही त्रास न होणे
(१) प्रचंड त्रास होणे.
(२) काडीमोड होणे.
(३) अजिबात त्रास न होणे.
(४) खूप त्रास न होणे.
उत्तर:
काडीचाही त्रास न होणे – अजिबात त्रास न होणे.
प्रश्न 6.
शब्दसमूहाबद्दल एक शब्द लिहा.
(अ) अपेक्षा नसताना [ ]
(आ) ज्याचे आकलन होत नाही असे [ ]
(इ) कुठलीही अपेक्षा न ठेवता [ ]
उत्तर:
(अ) अपेक्षा नसताना – अनपेक्षित
(आ) ज्याचे आकलन होत नाही असा – अनाकलनीय
(इ) कुठलीही अपेक्षा न ठेवता – निरपेक्षतेने

प्रश्न 7.
स्वमत.
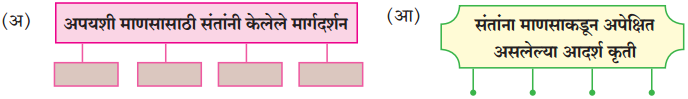
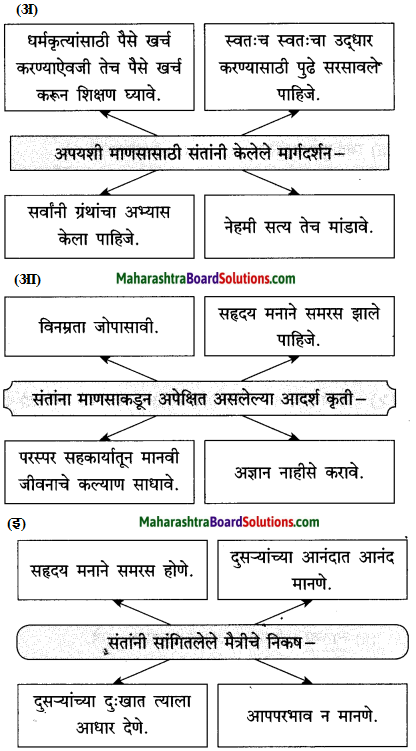
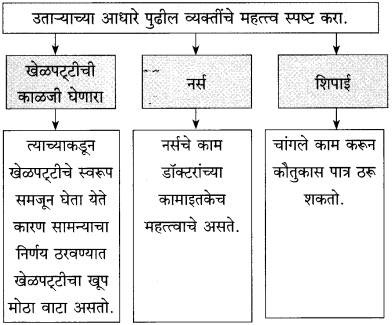
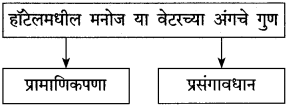
(अ) रोबो व माणूस यांच्या वागण्यातील ठळक फरक पाठाच्या आधारे स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
हॉटेल हेरिटेजमध्ये काम करणारे चार रोबो वेटर हे यंत्र होते. अचानक एके दिवशी त्यांच्यात बिघाड झाला आणि विचित्र पद्घतीने वागून त्यांनी मोठा गोंधळ उडवून दिला. तिथे माणसे असती तर वेगळे चित्र दिसले असते. मानवी वेटरांनी परिस्थिती बघून स्वत:हून कामात योग्य ते बदल केले असते. रोबोंसारखी विचित्र कृती नक्कीच केली नसती. दुसऱ्या प्रसंगी तर झोपलेली बाई आणि बेशुद्ध पडलेली बाई यांच्यातला फरक रोबोंना कळलाच नाही. ती बाई बेशुद्ध पडलेली आहे, हे मनोजला कळले. म्हणून योग्य ती उपाययोजना तातडीने केली गेली आणि त्या बाईचा प्राण वाचला. रोबोला स्वत:ची बुद्धी नसल्यामुळे तो स्वतंत्रपणे विचार करू शकला नाही. जिथे जिथे यंत्रमानव आहेत तिथे तिथे हेच घडणार.
(आ) तंत्रज्ञान हे माणसाला पूरक आहे, पर्याय नाही’, या विधानाबाबत तुमचे विचार लिहा.
उत्तर :
आपण करीत असलेले काम योग्य की अयोग्य, चांगले की वाईट, हे यंत्राला ठरवता येत नाही. ते माणूसच ठरवू शकतो. कारण माणसाकडे मन, बुद्धी व भावना या गोष्टी असतात. यंत्राकडे मात्र या गोष्टी नसतात, माणूस स्वत:च्या बुद्धीने, स्वत:च्या अंत:करणाने काम करतो. यंत्र हे.सांगकाम्या नोकर असते. त्याला सज्जन-दुर्जन, पापीपुण्यवान हे काहीही कळत नाही. म्हणून यंत्र कधीच मानवाची जागा घेऊ शकत नाही. कामे त्वरेने, अचूक व सफाईदारपणे करण्यासाठी यंत्र मदत करते; म्हणजे ते माणसाला पूरक आहे. ते माणसाला पर्याय ठरू शकत नाही.
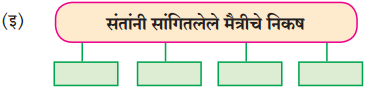
(इ) ‘माणसुकीमुळेच माणूस श्रेष्ठ ठरतो’, या विधानाचा अर्थ स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर :
हॉटेल हेरिटेजमध्ये घडलेल्या प्रसंगातून आपल्याला खूप मोलाचा संदेश मिळतो. या हॉटेलमध्ये रोबो वेटर ठेवल्यामुळे खूप फायदा झाला, वेटरसंबंधातल्या समस्या दूर करता आल्या, यात शंका नाही, पण कोणत्याही मानवी व्यवहारांमध्ये एवढे पुरेसे नसते. माणसांशी माणसासारखे वागण्याला खूप महत्त्व असते. असे वागता येण्यासाठी प्रथम आपल्या मनात माणुसकी असावी लागते. रोबो यांत्रिकपणे निर्णय घेतात. एक गोष्ट येथे लक्षात घेतली पाहिजे की, कोणत्याही घटनेने माणसांच्या जीवनात भावनिक व वैचारिक वादळे निर्माण होतात. हा परिणाम प्रत्येकाला ओळखता आला पाहिजे. हे फक्त मानवी मनालाच शक्य आहे. माणसाकडेच माणुसकी असते. सर्व प्राण्यांमध्ये माणूस श्रेष्ठ ठरला, याचे कारण माणसाकडे असलेली माणुसकी होय.

उपक्रम : ‘यंत्रमानवाचा रिमोट माणसाच्या हातात’, या विधानाबाबत वर्गात चर्चा करा व चर्चेतील मुद्द्यांचा अहवाल लिहा.
भाषाभ्यास
खालील कृती सोडवा.
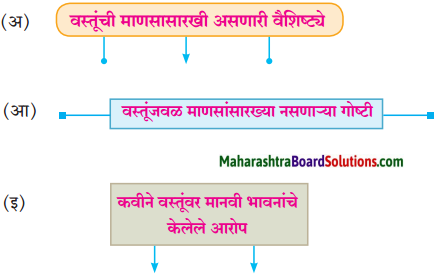
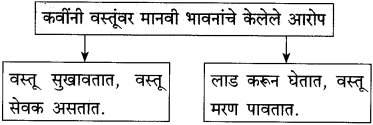
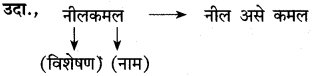
(अ) आला हा दारि उभा वसंत फेरीवाला पोते खांदयावरि सौदयाचे, देईल ज्याचे त्याला
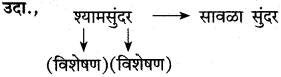
(१) वरील उदाहरणातील अलंकार-
(२) त्या अलंकाराची वैशिष्ट्ये- (i) [ ]
(ii) [ ]
उत्तर:
(१) निर्जीव वस्तूवर सजीव मानवी भावनांचे आरोपण करणे.
(२) वसंत ऋतूला फेरीवाला असे संबोधिले आहे.
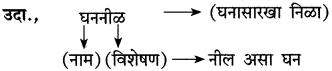
(आ) लहानपण देगा देवा। मुंगी साखरेचा रवा।
ऐरावत रत्न थोर। त्यासि अंकुशाचा मार।
(१) संत तुकाराम महाराजांनी वरील अभंगात ज्या दोन गोष्टींची तुलना केली आहे त्या गोष्टी
उत्तर:
[मुंगी]
(२) वरील उदाहरणातील अलंकार
उत्तर:
अलंकार – हा दृष्टान्त अलंकार आहे.
(३) या अलंकाराची वैशिष्ट्ये- (i) ………………………………
(ii) ………………………………
उत्तर:
(१) नम्रता या गुणाची महती सांगितली आहे.
(२) एखादा विचार पटवून देताना त्याच अर्थाची समर्पक उदाहरणे दिली आहेत.
(इ) संसार सागरी विहरे जीवन नौका
(१) वरील उदाहरणातील उपमेये – [ ] [ ]
(२) वरील उदाहरणातील उपमाने – [ ] [ ]
(३) वरील उदाहरणातील अलंकार – [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) उपमेय → (१) [संसार] [जीवन]
(i) उपमाने → (२) [सागर नौका]
(iii) अलंकार → [रूपक]

(ई) खालील ओळी वाचून रिकाम्या जागा भरा.
सावळा ग रामचंद्र। रत्नमंचकी झोपतो।
त्याला पाहता लाजून। चंद्र आभाळी लोपतो।।
| उपमेय |
उपमान |
अलंकाराचे नाव |
अलंकाराची वैशिष्ट्ये |
|
|
|
|
उत्तर:

मैत्री तंत्रज्ञानाशी
आई : तुषार, अरे तुषार आवर लवकर. आपल्याला किराणा सामान खरेदी करायला जायचं आहे. थोडे कपडेही खरेदी करायचे आहेत, चल आवर लवकर.

तुषार : आई, आज नको गं. मला खूपच कंटाळा आला आहे. आज मला सुट्टी आहे. खरेदीला गेलो, तर मला खेळायलाही मिळणार नाही.
आई : अरे, असं काय करतोस. आपण लवकर परत येऊ.
वडील : (तुषारच्या आईस) अगं, तुझा आणि तुषारचा वेळ खरेदीसाठी कशाला घालवतेस. आजकाल सर्व वस्तूंची खरेदी घरबसल्या करता येते. ऑनलाइन खरेदी करशील, तर तूही नक्कीच शिकशील. कशी करायची ते मी तुला शिकवतो. यामुळे तुझा वेळ आणि श्रमही वाचतील. प्रयत्न
आई : अहो, तुमचेही बरोबर आहे. घरबसल्या ऑनलाइन खरेदी केल्याने कितीतरी कामे सोपी होत आहेत. मला माझ्या कामाच्या पद्धतीत बदल केलाच पाहिजे. आजपासून मीही ऑनलाइन खरेदी करण्याचा नक्कीच प्रयत्न करणार आहे.

वडील : बरोबर आहे. काळानुरूप प्रत्येकानेच नवनवीन बदल स्वीकारले पाहिजेत.
Marathi Kumarbharti Class 10 Textbook Solutions Chapter 18 निर्णय Additional Important Questions and Answers
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १ : (आकलन)
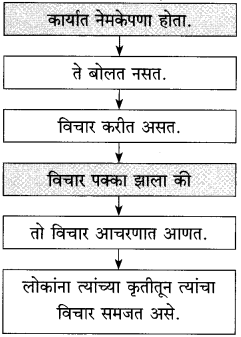
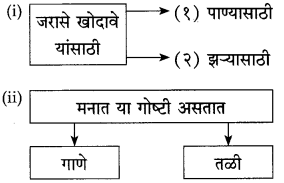
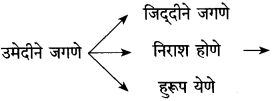
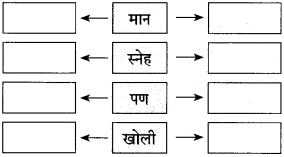
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा :
(i) 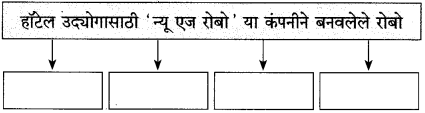
उत्तर:
(ii) 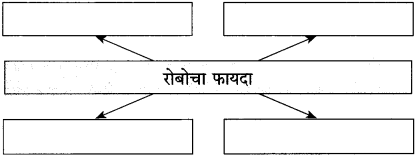
उत्तर:
(iii) 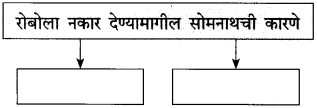
उत्तर:

कृती २ : (आकलन)
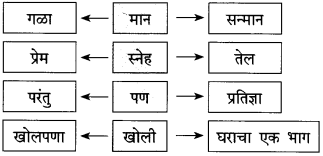
प्रश्न 1.
आकृत्या पूर्ण करा :
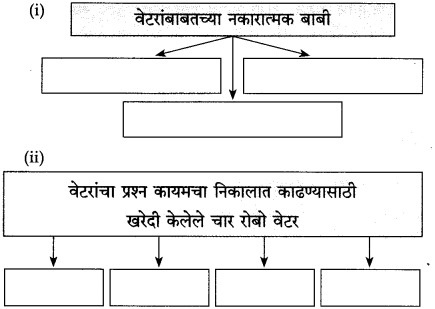
उत्तर:
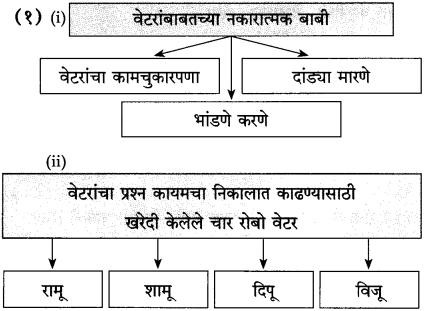

प्रश्न 2.
कारणे लिहा :
(i) रोबोंमुळे कमाई दुप्पट होण्याची शक्यता होती; कारण –
उत्तर:
रोबोंमुळे कमाई दुप्पट होण्याची शक्यता होती; कारण रोबो वेटर हे मानवी वेटरच्या दुप्पट काम करतात,
प्रश्न 3.
दोन-तीन महिन्यांत परिणाम घडवून आणणाऱ्या बाबी :
(i) ……………………………………
(ii) ……………………………………
(iii) ……………………………………
उत्तर:
(i) स्वच्छता
(ii) टापटीप
(iii) विनम्र व तत्पर सेवा.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
पुढील वाक्यातील एकवचनी शब्दांचे अनेकवचनी रूप योजून वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा :
शहराच्या बाजारपेठेत असणारे आमचे हॉटेल चांगले प्रशस्त आहे.
उत्तर:
शहरांच्या बाजारपेठांमध्ये असणारी आमची हॉटेले चांगली प्रशस्त आहेत.
प्रश्न 2.
‘खाणेपिणे’ यासारखे आणखी चार जोडशब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) येणेजाणे
(ii) उठणेबसणे
(ii) करणेसवरणे
(iv) रडणेभेकणे.

प्रश्न 3.
पुढील शब्दांना मराठी प्रतिशब्द लिहा :
(i) एजंट
(ii) स्वीपर
(iii) रोबो
(iv) वेटर
(v) हेरिटेज
(vi) सर्व्हिस
(vii) सर्व्हिसिंग
(viii) मेमरी कार्ड
(ix) पॉवर स्वीच,
उत्तर:
(i) एजंट – दलाल, प्रतिनिधी.
(ii) स्वीपर – सफाई कामगार.
(iii) रोबो – यंत्रमानव.
(iv) वेटर – वाढपी.
(v) हेरिटेज – वारसा.
(vi) सर्व्हिस – सेवा.
(vii) सर्व्हिसिंग – सुस्थितीकरण.
(viii) मेमरी कार्ड – स्मरणकोश.
(ix) पॉवर स्वीच – वीजबटण.
उतारा क्र. २
प्रश्न. पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
कारणे लिहा :
(i) वीस हजार रुपये वाचवल्याचा मला आनंद झाला होता; कारण –
(ii) पण वीस हजार वाचवल्याचा आनंद फार काळ टिकला नाही; कारण –
उत्तर:
(i) वीस हजार रुपये वाचवल्याचा मला आनंद झाला होता, कारण हॉटेलच्या मालकांनी स्वत:च चारही रोबोंचे सर्व्हिसिंग केल्याने सर्व्हिसिंगचा वीस हजार रुपये हा खर्च वाचला होता.
(ii) पण वीस हजार वाचवल्याचा आनंद फार काळ टिकला नाही, कारण मालकांनी स्वत:च सर्व्हिसिंग केलेले रोबो विचित्र वागू लागले आणि हॉटेलची अब्रू जायची वेळ आली.

प्रश्न 2.
शामूच्या विचित्रपणाच्या कृती लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) कोणालाही विपरीत वाटावे इतक्या सावकाशीने शामू हालचाली करीत होता.
(ii) मध्येच भराभर ताटे उचलू लागला आणि ती मांडू लागला. ही कृती पुन्हा पुन्हा करू लागला. त्याच्या अनाकलनीय हालचालींमुळे सर्व ग्राहक आश्चर्याने थक्क होऊन एकमेकांकडे, तर कधी शामूकडे पाहत होते.
प्रश्न 3.
सर्व्हिसिंगचे शुल्क दुप्पट झाल्याचा परिणाम लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) दुप्पट शुल्कवाढ हॉटेल मालकांना पटलीच नाही.
(ii) सर्व्हिसिंगचे काम त्या कंपनीला देण्याऐवजी आपणच करावे; सर्व्हिस इंजिनियर जे जे करतो ते ते आपण करावे, असे मालकांना वाटले.
(iii) शहरात रोबो मेकॅनिक खूप झाले असल्याने दुरुस्तीसंबंधात फार अडचण होणार नाही, असेही मालकांना वाटले.
(iv) मालकांनी त्या रोबो कंपनीशी सर्व्हिसिंगचा करार केला नाही.
प्रश्न 4.
ग्राहकांनी केलेल्या तक्रारी सांगा,
उत्तर:
(i) शामू कासवाप्रमाणे खूपच सावकाश काम करतो.
(ii) राजू पंधरा मिनिटांपूर्वी विलक्षण त्वरेने कामे करीत होता. आता अवसान गळल्याप्रमाणे मंदगतीने काम करीत होता.
(iii) एका बाईने स्वत:च्या लहानग्या बाळासाठी एक कप दूध आणायला सांगितले. पण तास उलटून गेला तरी अजून दूध आणलेले नाही. पोरगे झोपले म्हणून बरे झाले.
(iv) शामू तर भराभर ताटे उचलत होता आणि मांडत होता. हीच कृती तो पुन्हा पुन्हा करीत होता.
कृती २ : (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
ग्राहकांच्या तक्रारींचे निवारण करताना मालकांनी केलेल्या कृती लिहा.
उत्तर:
(i) मालकांनी ताबडतोब मनोजला लंच विभागाकडे लक्ष दयायला सांगितले.
(ii) शामूला घेऊन ते स्वयंपाकघराकडे गेले.
(iii) शामूच्या बॅटरीतला विदयुतसाठा कमी झाल्यामुळे तो मंद गतीने काम करीत असावा अशी शंका त्यांना आली. म्हणून बॅटरीमध्ये अधिक दयुतसाठा भरण्यासाठी त्यांनी शामूच्या पोटावरील ‘एनर्जी’ हे बटण चारपाच वेळा दाबले.
(iv) शामू पूर्वीसारखा त्वरेने, तत्परतेने काम करू लागल्याने मालकांना खूप आनंद झाला.

प्रश्न 2.
मालकांनी शामूच्या पोटावरील ‘एनर्जी’ हे बटण दाबल्याने घडून आलेले परिणाम सांगा,
उत्तर:
(i) शामू पूर्वीसारखा नीट काम करू लागला.
(ii) शामूमध्ये झालेला बदल पाहून मालक आनंदित झाले.
(iii) पण थोड्याच अवधीत शामू अचानक अधिक चपळ झाला. त्याच्या कामाचा वेग प्रचंड वाढला.
(iv) तो अचानक भराभर ताटे उचलू लागला आणि लागलीच मांडू लागला. हीच गोष्ट तो पुन्हा पुन्हा करू लागला.
प्रश्न 3.
पुढील तक्ता पूर्ण करा :
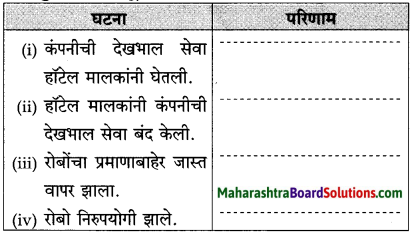
उत्तर:
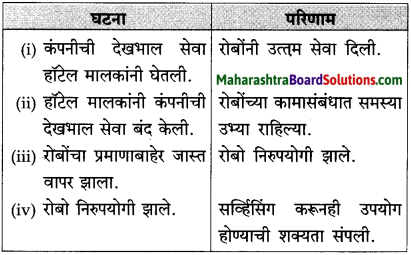
प्रश्न 4.
रोबो कंपनीने तयार केलेल्या नवीन रोबोंची माहिती लिहा.
उत्तर:
रोबो कंपनीच्या नवीन रोबो वेटरांचा दर्जा खूपच चांगला आहे. रिमोट सिस्टिममुळे लांबूनही त्यांच्यावर नियंत्रण ठेवणे शक्य आहे. कंपनीची देखभाल सेवा स्वीकारल्यावर तर काडीचाही त्रास होणार नाही, अशी रोबो कंपनीचे प्रतिनिधी हॉटेलच्या मालकांना खात्री देत होते.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
रिकाम्या चौकटी भरा :
अनाकलनीय : प्रत्यय – [ ]
हा प्रत्यय असलेले अन्य शब्द – [ ]
उत्तर:
अनाकलनीय : प्रत्यय – [ईय]
हा प्रत्यय असलेले अन्य दोन शब्द – {भारतीय कुटुंबीय]

प्रश्न 2.
पुढील शब्दांना प्रमाण मराठीतील प्रतिशब्द द्या :
(i) मेकॅनिक
(ii) लंच सेक्शन
(ii) चार्जिग
(iv) एनर्जी
(v) किचन
(vi) क्वालिटी
(vii) रिमोट कंट्रोल सिस्टिम,
उत्तर:
(i) मेकॅनिक – यंत्रज्ञ
(ii) लंच सेक्शन – भोजनकक्ष, भोजनघर
(iii) चार्जिंग – वीज साठवण
(iv) एनर्जी – ऊर्जा
(v) किचन – स्वयंपाकघर
(vi) क्वालिटी – गुणवत्ता
(vii) रिमोट कंट्रोल सिस्टिम – दूरनियंत्रण व्यवस्था,
प्रश्न 3.
‘हालचाल’ यासारखे अन्य चार शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर:
कपडालत्ता, कागदपत्र, अक्कलहुशारी, बाजारहाट,
उतारा क्र. ३
प्रश्न, पुढील उतारा वाचा आणि दिलेल्या सूचनांनुसार कृती करा :
कृती १: (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
कारणे लिहा :
(i) हॉटेल मालक द्विधा मन:स्थितीत होते; कारण –
(ii) हॉटेलमध्ये गि-हाईक जेमतेम येत होतं; कारण –
उत्तर :
(i) हॉटेल मालक द्विधा मन:स्थितीत होते, कारण इंजिनियरचे बोलणे आठवले की रोबो वेटर घेण्याची इच्छा होई आणि रोबो वेटरांमुळे झालेली फजिती आठवली की रोबो वेटर न घेतलेले बरे, असे वाटू लागे.
(ii) हॉटेलमध्ये गिहाईक जेमतेम येत होतं, कारण रोबो वेटरांनी घातलेल्या गोंधळामुळे हॉटेलची बरीच बदनामी झाली होती.

प्रश्न 2.
शनिवारी हॉटेलात आलेल्या स्त्री-ग्राहकासंबंधीचा प्रसंग लिहा.
उत्तर :
एक साधारणपणे पस्तीस वर्षांची स्त्री स्वत:च्या कारमधून उतरली. तिच्यासोबत तिची दोन मुले होती. ती मुलांसोबत एसी रूममध्ये गेली. त्या खोलीची जबाबदारी रोबो रामूकडे होती. तो तत्परतेने आत गेला. एसी चालू केला. खादयपदार्थांची मागणी नोंदवून घेतली. ते पदार्थ त्यांना आणून दिले आणि मग तो दुसऱ्या कामाला लागला.
प्रश्न 3.
एसी रूममधील काळजी वाटायला लावणारी घटना लिहा.
उत्तर :
सुमारे दहाएक मिनिटांनंतर एसी खोलीतून लहान मुलाचा रडण्याचा आवाज ऐकू येऊ लागला. काही वेळातच तो आवाज वाढला. थोड्याच वेळात दोन मुलांच्या रडण्याचा आवाज ऐकू आला. ही मालकांना काळजी करायला लावणारी घटना होती.
प्रश्न 4.
एसी रूममधील मुले रडण्याच्या घटनेचे –
(i) रोबो वेटरने केलेले निरीक्षण :
(ii) मनोजने केलेले निरीक्षण :
उत्तर :
एसी खोलीतल्या मुलांच्या रडण्याच्या घटनेचे –
(i) रोबो वेटरने केलेले निरीक्षण : रोबो वेटरला वाटले की, ती बाई झोपली आहे आणि आई झोपली म्हणून मुले रडत आहेत.
(ii) मनोजने केलेले निरीक्षण : दृश्य पाहून मनोज घाबरला. ती बाई चक्कर आल्यामुळे बेशुद्ध होऊन खाली पडली. या अनपेक्षित प्रसंगाने मुले घाबरली आणि रडू लागली.
कृती २ : (आकलन)
प्रश्न 1.
डॉक्टरांनी बाईच्या आजारपणाबाबतचे केलेले निदान व त्यांनी दिलेला सल्ला सांगा.
उत्तर :
डॉक्टरांचे निदान असे होते : त्या बाईचा रक्तदाब अचानक कमी झाला, रक्तदाब कमी झाला की माणूस बेशुद्ध होऊन खाली कोसळतो. त्या बाईच्या बाबतीत तसेच झाले. अशा वेळी ताबडतोब वैदयकीय उपचार सुरू केले पाहिजेत. हॉटेल मालकांनी त्वरित हालचाली करून तिला हॉस्पिटलमध्ये नेले. ही त्वरा झाली नसती, तर त्या बाईच्या जिवाला धोका निर्माण झाला असता. आता तसा धोका नव्हता. डॉक्टरांनी तिला विश्रांती घ्यायला सांगितले.

प्रश्न 2.
स्त्री-ग्राहक बेशुद्ध होऊन पडण्याच्या प्रसंगानंतर मालकांच्या मनात आलेला विचार लिहा.
उत्तर :
रात्री झोपताना मालकांच्या मनात विचार आला की, मनोजला त्या एसी खोलीत निरीक्षण करण्यासाठी पाठवले म्हणून बरे झाले. ते रोबो वेटरवर विसंबून राहिले असते तर त्या स्त्रीचा मृत्यू ओढवला असता. हॉटेलमध्ये मृत्यूघडल्यामुळे मालकांवर निष्काळजीपणाचा ठपका आला असता. प्रचंड गहजब झाला असता, नाचक्की झाली असती आणि हॉटेल बंद करावे लागले असते. मालकांना केवळ कल्पनेनेच हादरवून टाकणारा हा प्रसंग होता.
प्रश्न 3.
फरक लिहा :
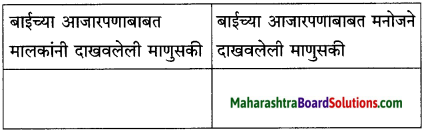
उत्तर :

प्रश्न 4.
हॉटेलमध्ये एक बाई आजारी पडण्याच्या प्रसंगानंतर मालकांना झालेली जाणीव स्पष्ट करा.
उत्तर:
मालकांना तीव्रपणे एका वस्तुस्थितीची जाणीव झाली. रोबो हा अत्यंत यांत्रिकपणे, कोरडेपणाने निरीक्षण करतो. त्याला मन, बुद्धी व भावना नसल्याने तो यांत्रिकपणे घटनेकडे पाहतो. मनोजचे तसे नाही. ती स्त्री झोपलेली नसून बेशुद्ध पडली आहे, हे त्याला तत्काळ जाणवले. त्याच्या या निरीक्षणामुळे पुढील हालचाली होऊन तिचा जीव वाचला. हॉटेल व्यवसायाचा माणसाच्या जिवाशी निकटचा संबंध असतो. त्यामुळे तिथे मानवी जाण असणे, माणुसकी असणे अत्यंत गरजेचे असते. ही माणुसकी रोबोमध्ये असणे शक्य नाही. त्यामुळे मालक आपोआपच रोबो वेटर न नेमण्याच्या निर्णयाला आले.
कृती ३ : (व्याकरण)
प्रश्न 1.
कंसांतील सूचनांनुसार उत्तरे लिहा :
(i) शनिवारी दुपारी साडेबाराची वेळ होती. (भविष्यकाळ करा.)
(ii) एका कृतीने बदनामीचा कलंक धुतला गेला. (भविष्यकाळ करा.)
(iii) तिच्या सर्वांगाला घाम सुटला होता. (वर्तमानकाळ करा.)
उत्तर:
(i) शनिवारी दुपारी साडेबाराची वेळ असेल.
(ii) एका कृतीने बदनामीचा कलंक धुतला जाईल.
(iii) तिच्या सर्वांगाला घाम सुटला आहे.

प्रश्न 2.
पुढील नामांचे अनेकवचन लिहा :
(i) अंथरूण
(ii) पाठ
(iii) धोका
(iv) रीत.
उत्तर:
(i) अंथरूण – अंधरुणे
(ii) पाठ – पाठी
(iii) धोका – धोके
(iv) रीत – रिती,
प्रश्न 3.
अधोरेखित शब्दांच्या जागी अनेकवचनी रूपे योजून वाक्य पुन्हा लिहा :
रात्री अंथरुणावर पाठ टेकल्यावर माझ्या मनात सहज विचार आला.
उत्तर:
रात्री अंथरुणांवर पाठी टेकल्यावर आमच्या मनांत सहज विचार आले.
व्याकरण व भाषाभ्यास
कृतिपत्रिकेतील प्रश्न ४ (अ) आणि (आ) यांसाठी….)
(व्याकरण घटकांवर आधारित कृती:
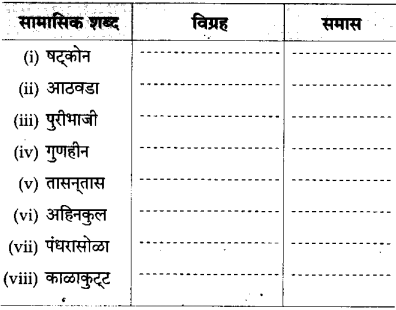
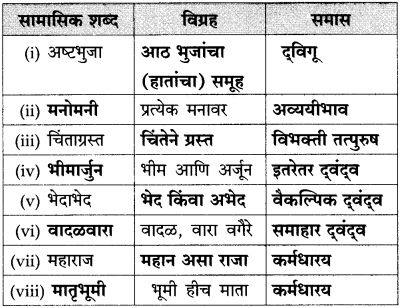
१. समास :
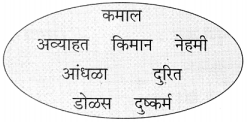
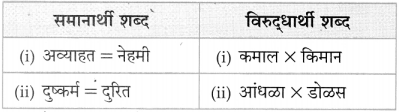
(१) तक्ता पूर्ण करा : (ठळक अक्षरांत उत्तरे दिली आहेत.)
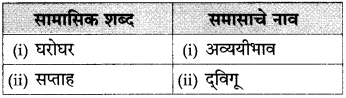
(२) पुढील वाक्यांतील सामासिक शब्द ओळखा व त्या शब्दाच्या समासाचेनावलिहा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
(i) राजू स्वत:च्या मालाची जाहिरात करण्यास घरोघर फिरला.
(ii) या सप्ताहात शरदरावांची फारच घावपळ झाली.
उत्तर:
२. अलंकार :
पुढील कृती सोडवा :
उत्तर:
[चेतनगुणोक्ती]

३. वृत्त :
पुढील ओळींचे गण पाडून वृत्त ओळखा :
‘दे दान गुप्त उपकार, करी न बोले
मानी प्रमोद जरि मान्य घरासी आले.’
उत्तर:

वृत्त : हे वसंततिलका अक्षरगण वृत्त आहे.
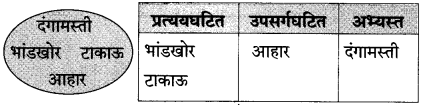
४. शब्दसिद्धी :
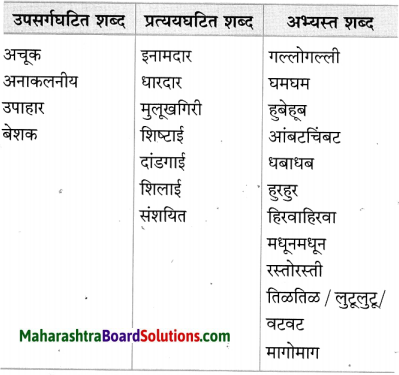
(१) बाजूच्या आकृतीतील शब्दांचे वर्गीकरण करा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
उत्तर:
(२) ‘आड’ हा उपसर्ग लावून चार शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर :
(i) आडवाट
(ii) आडनाव
(iii) आडकाठी
(iv) आडवळण,
(३) ‘आळू’ हा प्रत्यय लावून चार शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर :
(i) लाजाळू
(ii) झोपाळू
(iii) मायाळू
(iv) विसराळू,
(४) ‘खळखळ सारखे चार अभ्यस्त शब्द लिहा.
उत्तर :
(i) हळहळ
(ii) कळकळ
(iii) मळमळ
(iv) सळसळ,

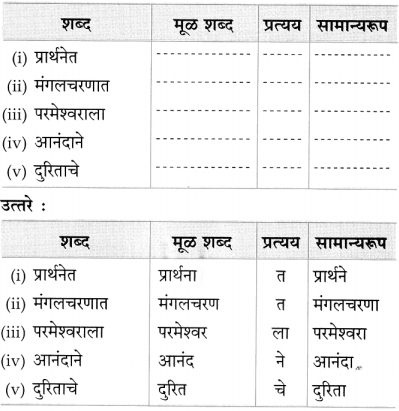
५. सामान्यरूप.
पुढील शब्दांचे सामान्यरूप ओळखा :
(i) आम्हांला – …………………………………..
(ii) कामांचा – …………………………………..
(iii) रामूला – …………………………………..
(iv) आवाजात – …………………………………..
उत्तर:
(i) आम्हां
(ii) कामां
(iii) रामू
(iv) आवाजा.
भाषिक घटकांवर आधारित कृती:
१. शब्दसंपत्ती :
(१) शब्दसमूहांबद्दल एक शब्द लिहा :
(i) अपेक्षा नसताना
(ii) ज्याचे आकलन होत नाही असे
(iii) कुठलीही अपेक्षा न ठेवता
(iv) एक आठवड्यातून प्रसिद्ध होणारे – (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
(v) दोन आठवड्यातून एकदा प्रसिद्ध होणारे –
उत्तर:
(i) अनपेक्षित
(ii) अनाकलनीय
(iii) निरपेक्ष
(iv) साप्ताहिक
(v) पाक्षिक.
(२) विरुद्धार्थी शब्द लिहा :
(i) कडक x ……………………………
(ii) स्वच्छता x ……………………………
(iii) विनम्र x ……………………………
(iv) सावकाश x ……………………………
उत्तर:
(i) कडक x नरम
(ii) स्वच्छता x अस्वच्छता
(iii) विनम्र x उद्घट
(iv) सावकाश x जलद

(३) पुढील शब्दांचे भिन्न अर्थ लिहा :
(i) [ ] ← [कळ] → [ ]
(ii) [ ] ← [तट] → [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) [ वेदना ] ← [कळ] → [ बटन ]
(ii) [ काठ ] ← [तट] → [ कडा ]
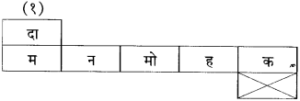
(४) पुढील शब्दांतील अक्षरांपासून चार अर्थपूर्ण शब्द लिहा
(i) सोमनाथ → [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
(ii) हाताबाहेर → [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ]
उत्तर:
(i) सोमनाथ → [सोम] [नाम] [नाथ] [मना]
(ii) हाताबाहेर → [हात] [हार] [हेर] [बाहेर]
(५) ‘आकलनकृती’ या शब्दातील आकलन व कृती हे दोन शब्द सोडून इतर दोन शब्द लिहा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
उत्तर:
[कल] – [आकृती]
२. लेखननियम :
(१) अचूक शब्द निवडा:
(i) तत्त्वज्ञान/तत्वज्ञान/तत्त्वन्यान/तात्त्वज्ञान,
(ii) पुनरर्चना/पुनर्रचना/पूनर्रचना/पूनरर्चना.
(iii) अभीव्यक्ती/अभिवक्ति/अभिव्यक्ती/अभीव्यक्ति.
(iv) पुर्नविचार/पुनरविचार/पूनर्विचार/पुनर्विचार. (सराव कृतिपत्रिका २)
उत्तर:
(i) तत्त्वज्ञान
(ii) पुनर्रचना
(iii) अभिव्यक्ती
(iv) पुनर्विचार.
(२) पुढील वाक्ये लेखननियमांनुसार लिहा :
(i) तूम्हांला काडिचाही त्रास होणार नाही.
(ii) पतीनिधनाचे असीम दुःख बाजुला ठेवले. (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
उत्तर:
(i) तुम्हांला काडीचाही त्रास होणार नाही.
(ii) पतिनिधनाचे असीम दुःख बाजूला ठेवले.

३. विरामचिन्हे :
(१) पुढील वाक्यांतील विरामचिन्हे ओळखून लिहा :
(i) काय आश्चर्य! शामू पूर्वीसारखा काम करू लागला, हे पाहून मला खूप आनंद झाला.
(ii) कंपनीने आम्हांला सांगितलं, “यापुढे एका वेटरच्या सर्व्हिसिंगला अडीचऐवजी पाच हजार रुपये पडतील.”
उत्तर:
(i) [ ! ] उद्गारचिन्ह [ , ] स्वल्पविराम [ . ] पूर्णविराम.
(ii) [ , ] स्वल्पविराम [ ” ” ] दुहेरी अवतरणचिन्ह [ . ] पूर्णविराम.
(२) उदया कोकिळेचं ‘कुह’ ऐकू येईल का? बघू है। वरील वाक्यातील विरामचिन्हे खाली लिहून नावे लिहा : (सराव कृतिपत्रिका-२)
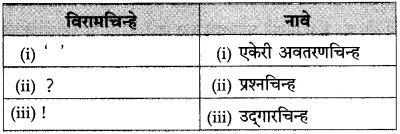
.
४. पारिभाषिक शब्द :
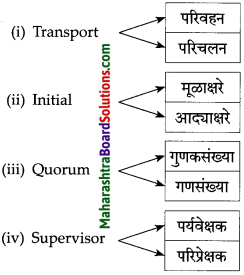
पुढील इंग्रजी पारिभाषिक शब्दांना मराठी प्रतिशब्द लिहा :
उत्तर:
(i) Therapy – उपचारपद्धती
(ii) Reservation – आरक्षण
(iii) Refreshment – अल्पोपाहार
(iv) workshop – कार्यशाळा

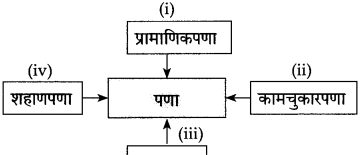
५. अकारविल्हे/भाषिक खेळ :
कृती करा :
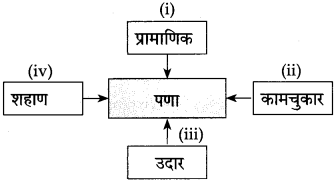
उत्तर:
निर्णय Summary in Marathi
निर्णय कथेचा गोषवारा
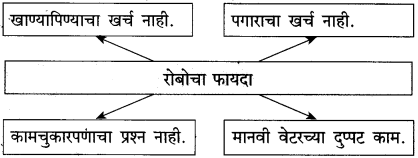
न्यू एज रोबो कंपनी हॉटेल व्यवसायासाठी रोबो तयार करते. त्या कंपनीचा प्रतिनिधी हॉटेल हेरिटेजच्या मालकांना रोबो वेटरची माहिती देत होता. रोबो वेटर मानवी वेटरपेक्षा कुशलतेने काम करतात. त्यांच्यासाठी अन्य कोणताही खर्च येत नाही. माणसांप्रमाणे त्यांचा त्रास होत नाही. हे सर्व तो प्रतिनिधी हॉटेलच्या मालकांना समजावून सांगत होता.
हॉटेलचे मालक वेटरच्या समस्यांनी त्रासलेले होतेच. ते चार रोबो वेटरची खरेदी करतात. वर्षभर रोबोंनी छान काम केले. कमाई दुप्पट झाली. एका वर्षानंतर रोबो बिघडले. नवीन रोबो खरेदी करण्याची वेळ आली.
दरम्यान, एक भयंकर प्रसंग घडला. एक बाई रक्तदाब कमी झाल्यामुळे बेशुद्ध होऊन पडली. परंतु रोबोला ती झोपली आहे, असे वाटले. त्यांनी दुर्लक्ष केले. त्याच स्थितीत आणखी वेळ गेला असता तर ती बाई मरण पावली असती. परंतु मनोज या मानवी वेटरने खरी परिस्थिती ओळखली. त्या बाईवर वैदयकीय उपचार करता आले. तिचे प्राण वाचले.
यावरून हे लक्षात येते की, यंत्रमानव यांत्रिक बुद्धीने काम करतात. त्यांना स्वतंत्र बुद्धिमत्ता नसते. माणसांचे व्यवहार, त्यांच्या भावभावना यंत्रमानवाला ओळखता येत नाहीत. फक्त माणूसच त्या जाणू शकतो. म्हणून यंत्रमानव कधीही माणसाची जागा घेऊ शकत नाही.
निर्णय शब्दार्थ
- हुबेहूब – तंतोतंत,
- मेकॅनिक – यंत्रज्ञ, यंत्रांची दुरुस्ती-देखभाल करणारा.
- अवसान – शक्ती.
- बेणं – बियाणे (येथे एखादया कुटुंबातील व्यक्ती),
- द्विधा – गोंधळलेली स्थिती.
- सर्व्हिसिंग इंजिनियर – देखभाल अभियंता.
- काडीचाही – अत्यल्पसुद्धा.
- निकामी – निरुपयोगी.
निर्णय वाक्प्रचार व त्यांचे अर्थ
- निकालात काढणे : निर्णय करून टाकणे.
- आनंद गगनात न मावणे : खूप आनंद होणे.
- नाचक्की होणे : बदनामी होणे.
- दैव बलवत्तर असणे : केवळ दैवामुळेच वाचणे.
- प्रसंगाला तोंड देणे : प्रसंगात धीराने वागणे.
- द्विधा मन:स्थितीत असणे : गोंधळलेल्या मन:स्थितीत असणे.
Marathi Kumarbharti Std 10 Guide Pdf भाग-४
![]()
![]()