Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 States of Matter Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 10 States of Matter
Question 1.
What are the three distinct physical forms of a substance?
Answer:
The three distinct physical forms of a substance are solid, liquid and gas.
Question 2.
What are the different forms (physical states) in which water exists?
Answer:
Water exists in the three different forms solid ice, liquid water and gaseous vapours.
Question 3.
Give the differences between the three states of matter.
OR
State the properties of three states of matter.
Answer:
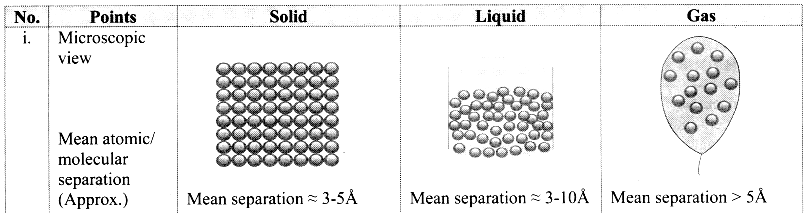
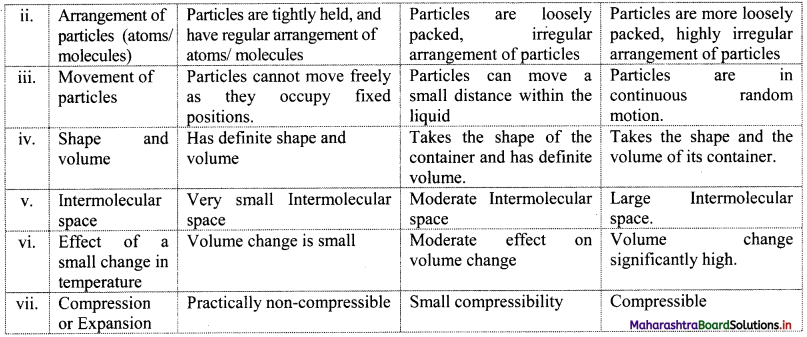
Question 4.
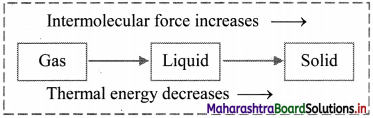
With suitable diagram, explain how three states of matter are interconvertible by exchange of heat.
Answer:
- On heating, solid changes to liquid, which on further heating changes to gas.
- On cooling, gas condenses to liquid, which on further cooling change to solid.
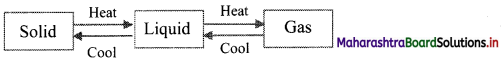
Question 5.
What are intermolecular forces? Explain the role of these forces in different states of matter.
Answer:
- Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces as well as repulsive forces present between the neighbouring molecules.
- The attractive force decreases with the increase in distance between the molecules.
- The intermolecular forces are strong in solids, less strong in liquids and very weak in gases. Thus, the three physical states of matter can be determined as per the strength of intermolecular forces.
- The physical properties of matter such as melting point, boiling point, vapor pressure, viscosity, evaporation, surface tension and solubility can be studied with respect to the strength of attractive intermolecular forces between the molecules.
- During the melting process, intermolecular forces are partially overcome, whereas they are overcome completely during the vapourization process.
![]()
Question 6.
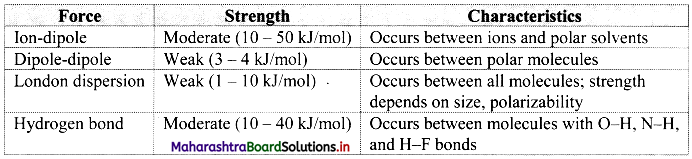
Name the different types of intermolecular forces.
Answer:
The types of intermolecular forces are as follows:
- Dipole-dipole interactions
- Ion-dipole interactions
- Dipole-induced dipole interactions
- Hydrogen bonding
- London dispersion forces
Question 7.
Write a short note on dipole moment.
Answer:
Dipole moment:
i. Dipole moment (µ) is the product of the magnitude of the charge (Q) and the distance between the centres of positive and negative charge (r).
ii. It is designated by a Greek letter (µ) (mu) and its unit is Debye (D).
iii. Dipole moment is a vector quantity and is depicted by a small arrow with tail in the positive centre and head pointing towards the negative centre.
iv. For example, HCl is a polar molecule.
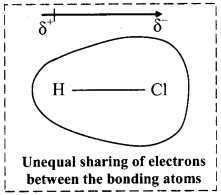
The crossed arrow ![]() above the structure represents an electron density shift. Thus, polar molecules have permanent dipole moments.
above the structure represents an electron density shift. Thus, polar molecules have permanent dipole moments.
Question 8.
Explain dipole-dipole interactions.
Answer:
Dipole-dipole interactions:
i. When a polar molecule encounters another polar molecule, the positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another polar molecule. Interaction between such molecules is termed as dipole-dipole interaction.
ii. These forces are generally weak, with energies of the order of 3-4 kJ mol-1 and are significant only when molecules are in close contact, i.e., in a solid or a liquid state.
iii. For example, C4H9Cl, (butyl chloride), CH3 – O – CH3 (dimethyl ether), ICl (iodine chloride, B.P. 27 °C), are dipolar liquids.
iv. The molecular orientations due to dipole-dipole interaction in ICl liquid is shown in the following figure:
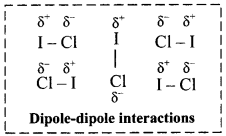
v. More polar the substance, greater the strength of its dipole-dipole interactions.
Question 9.
Explain the effect of dipole moment on boiling point with an example.
Answer:
Higher the dipole moment, stronger are the intermolecular forces. Thus, higher is the boiling point.
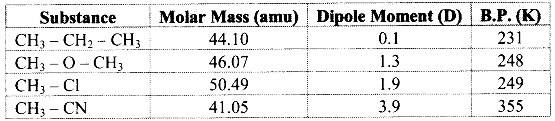
e.g. Dipole moment of dimethyl ether (CH3 – O – CH3) is 1.3 D while that of ethane (CH3 – CH2 – CH3) is 0.1 D. Since, dipole moment of dimethyl ether is higher than that of ethane, the boiling point of dimethyl ether is higher than that of ethane.
Note: Dipole moments and boiling points of some compounds:
Question 10.
Explain ion-dipole interactions.
Answer:
Ion-dipole interactions:
i. An ion-dipole force is the result of electrostatic interactions between an ion (cation or anion) and the partial charges on a polar molecule.
ii. The strength of this interaction depends on the charge and size of an ion. It also depends on the magnitude of dipole moment and size of the molecule.
iii. Ion-dipole forces are particularly important in aqueous solutions of ionic substances. When an ionic compound is dissolved in water, the ions get separated and surrounded by water molecules. This process is called hydration of ions.
iv. For example, Na+ ion (cation) – H2O interaction is shown in the following figure:
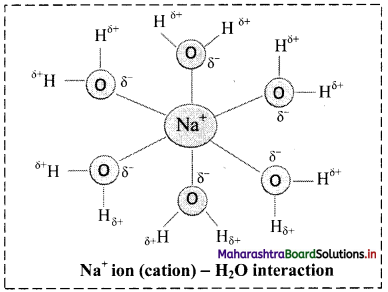
v. The charge density on Na+ is more concentrated than the charge density on Cl– because Na+ is smaller in size than Cl–. This makes the interaction between (Na+) and negative end of the polar H2O molecule stronger than the corresponding interaction between (Cl–) and positive end of the polar H2O molecule.
vi. More the charge on cation, stronger is the ion-dipole interaction. For example, Mg2+ ion has higher charge and smaller ionic radius (78 pm) than Na+ ion (98 pm), hence Mg2+ ion is surrounded (hydrated) more strongly with water molecules and exerts strong ion-dipole interaction.
Thus, the strength of interaction increases with increase in charge on cation and with decrease in ionic size or radius.
Therefore, ion-dipole forces increase in the order: Na+ < Mg2+ < Al3+.
![]()
Question 11.
Write a short note on dipole-induced dipole interactions.
Answer:
Dipole-induced dipole interactions:
i. When polar molecules (like H2O, NH3) and nonpolar molecules (like benzene) approach each other, the polar molecules induce dipole in the nonpolar molecules. Hence, ‘Temporary dipoles’ are formed by shifting of electron clouds in nonpolar molecules.
ii. For example, ammonia (NH3) is polar and has permanent dipole moment while Benzene (C6H6) is nonpolar and has zero dipole moment. The force of attraction developed between the polar and nonpolar molecules is of the type dipole-induced dipole interaction. This is shown in the following figure:
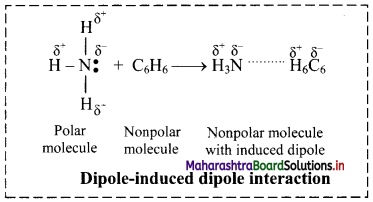
Question 12.
Explain briefly London dispersion forces.
Answer:
London dispersion forces:
- In nonpolar molecules and inert gases, only dispersion forces exist.
- Dispersion forces are also called as London forces or van der Waals forces.
- It is the weakest intermolecular force that develops due to interaction between two nonpolar molecules.
- In general, all atoms and molecules experience London dispersion forces, which result from the motion of electrons.
- At any given instant of time, the electron distribution in an atom may be asymmetrical, giving the atom a short-lived dipole moment. This momentary dipole on one atom can affect the electron distribution in the neighbouring atoms and induce momentary dipoles in them. As a result, weak attractive force develops.
- For example, substances composed of molecules such as O2, CO2, N2, halogens, methane gas, helium and other noble gases show van der Waals force of attraction.
- The strength of London forces increases with increase in molecular size, molecular mass and number of electrons present in an atom or molecule.
Question 13.
Give reason: Benzene has zero dipole moment and has no dipole-dipole forces yet it exists in liquid state.
Answer:
- Benzene (C6H6) is nonpolar molecule and has zero dipole moment.
- In benzene, only London forces exist due to momentary dipoles.
- The strength of London forces increases with increase in molecular size, molecular mass and number of electrons present in an atom or molecule.
- Hence, due to the presence of London forces, benzene exists in liquid state.
Question 14.
Explain the term polarizability.
Answer:
Polarizability:
- When two nonpolar molecules approach each other, attractive and repulsive forces between their electrons and the nuclei will lead to distortions in the size of electron cloud, a property referred to as polarizability.
- Polarizability is a measure of how easily an electron cloud of an atom is distorted by an applied electric field.
- It is the property of atom.
- The ability to form momentary dipoles, that means, the ability of the molecule to become polar by redistributing its electrons is known as polarizability of the atom or molecule.
![]()
Question 15.
Describe how London dispersion forces affect the boiling points of isomeric compounds like n-pentane and neopentane.
Answer:
- More the spread out of shapes, higher the dispersion forces present between the molecules.
- London dispersion forces are stronger in a long chain of atoms where molecules are not compact.
- For example, n-Pentane boils at 309.4 K, whereas neopentane boils at 282.7 K.
- Both the substances have the same molecular formula, C5H12, but n-pentane is longer and somewhat spread out, whereas neopentane is more spherical and compact.
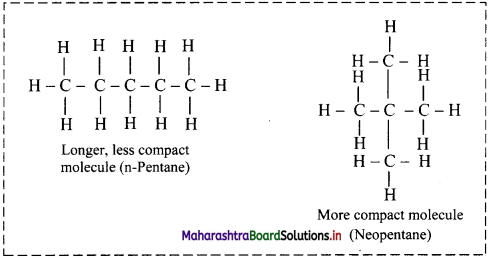
Question 16.
Write a short note on hydrogen bonding.
Answer:
Hydrogen bonding:
- The electrostatic force of attraction between positively polarised hydrogen atom of one molecule and a highly electronegative atom (which may be negatively charged) of other molecule is called as hydrogen bond.
- Strong electronegative atoms that form hydrogen bonds are nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine.
- A hydrogen bond is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction.
- Hydrogen bonds are generally stronger than usual dipole-dipole and dispersion forces, and weaker than true covalent or ionic bonds.
- Hydrogen bond is denoted by (….) dotted line.
e.g. Water (H2O) and ammonia (NH3) show hydrogen bonding.
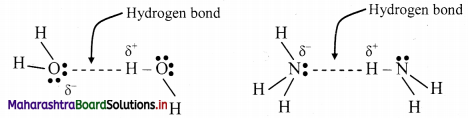
Question 17.
Explain intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bond with suitable examples.
Answer:
i. Hydrogen bond which occurs within one single molecule represents intramolecular hydrogen bond.
e.g. H-bonding in ethylene glycol:

ii. A hydrogen bond present between two like or unlike molecules represents intermolecular hydrogen bond.
e.g. H-bonding in H-F:
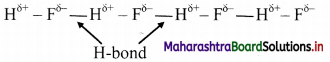
Question 18.
How does hydrogen bonding influence boiling points of compounds?
Answer:
- Due to the presence of hydrogen bonding in the compounds, more energy is required to break the bonds.
- Therefore, boiling point is more in case of liquid molecules containing hydrogen bond.
- Hydrogen bonds can be quite strong with energies up to 40 kJ/mol.
- The boiling point generally increases with increase in molecular mass, but the hydrides of nitrogen (NH3), oxygen (H2O) and fluorine (HF) have abnormally high boiling points due to the presence of hydrogen bonding between the molecules.
[Note: Due to presence of H-bond, viscosity’ of liquid increases. Hydrogen bonds play vital role in determining structure and properties of proteins and nucleic acids present in all living organisms.]
Question 19.
Observe the following figure and answer the questions:
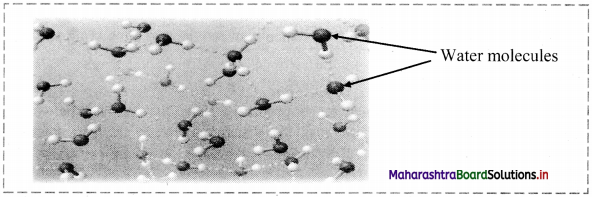
i. What do the dotted lines represent?
ii. A water molecule can form how many H-bonds?
iii. Is this an example of intramolecular H-bonding?
Answer:
i. The dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds.
ii. A water molecule can form four H-bonds.
iii. No, it is an example of intermolecular H-bonding.
![]()
Question 20.
Explain the relation between intermolecular forces and thermal energy.
Answer:
- Thermal energy is the measure of kinetic energy of the particles of matter that arises due to movement of particles.
- It is directly proportional to the temperature; that means, thermal energy increases with increase in temperature and vice versa.
- Three states of matter are the consequence of a balance between the intermolecular forces of attraction and the thermal energy of the molecules.
- If the intermolecular forces are very weak, molecules do not come together to make liquid or solid unless thermal energy is decreased by lowering the temperature.
- When a substance is to be converted from its gaseous state to solid state, its thermal energy (or temperature) has to be reduced. At this stage, the intermolecular forces become more important than thermal energy of the particles.
Note: Comparison of intermolecular forces:
Question 21.
State true or false. Correct the false statement.
i. London dispersion force is the weakest intermolecular force that develops due to interaction between two nonpolar molecules.
ii. More the charge on cation, stronger is the ion-dipole interaction.
iii. A hydrogen bond is a special type of dipole-induced dipole attraction.
iv. Thermal energy is directly proportional to the temperature.
Answer:
i. True
ii. True
iii. False,
A hydrogen bond is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction.
iv. True
Question 22.
Name the major intermolecular forces between:
i. Cl2 and CBr4
ii. SiH4 molecules
iii.He atoms in liquid He
iv. HCl molecules in liquid HCl
v. He and a polar molecule
vi. Water molecules
Answer:
i. London dispersion forces
ii. London dispersion forces
iii. London dispersion forces
iv. Dipole-dipole interactions
v. Dipole-induced dipole
vi. Hydrogen bonding
Question 23.
Why is the chemistry of atmospheric gases an important subject of study?
Answer:
The chemistry of atmospheric gases is an important subject of study as it involves air pollution. O2 in air is essential for survival of aerobic life.
Question 24.
What are the measurable properties of gases?
OR
Explain the following measurable properties of gases in detail: Mass, volume, pressure, temperature and diffusion.
Answer:
Measurable properties of gases are as follows:
i. Mass:
- The mass (m) of a gas sample is measure of the quantity of matter it contains.
- It can be measured experimentally.
- The SI unit of mass is kilogram (kg).
1 kg = 103 g. - The mass of a gas is related to the number of moles (n) by the expression:
n = \(\frac{\text { mass in grams }}{\text { molar mass in grams }}=\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
ii. Volume:
- Volume (V) of a sample of gas is the amount of space it occupies.
- It is expressed in terms of different units like Litres (L), millilitres (mL), cubic centimetre (cm3), cubic metre (m3) or decimetre cube (dm3).
- The SI Unit of volume is cubic metre (m3).
- Most commonly used unit to measure the volume of the gas is decimetre cube or litre.
iii. Pressure:
- Pressure (P) is defined as force per unit area.
Pressure = \(\frac{\text { Force }}{\text { Area }}=\frac{\mathrm{f}}{\mathrm{a}}\) - Pressure of gas is measured with ‘manometer’ and atmospheric pressure is measured by ‘barometer’.
- The SI unit of pressure is pascal (Pa) or Newton per metre square (N m-2).
iv. Temperature:
- It is the property of an object that determines direction in which energy will flow when that object is in contact with another object.
- In scientific measurements, temperature (T) is measured either on the Celsius scale (°C) or the Kelvin scale (K).
- The SI unit of temperature of a gas is Kelvin (K).
- The Celsius and Kelvin scales are related by the expression: T(K) = t °C + 273.15
v. Density: Density (d) of a substance is the mass per unit volume.
d = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{V}}\)
∴ The SI unit of density is kg m-3.
In the case of gases, relative density is measured with respect to hydrogen gas and is called vapour density.
∴ Vapour density = \(\frac{\text { Molar mass }}{2}\)
vi. Diffusion:
a. Diffusion is the process of mixing two or more gases to form a homogeneous mixture.
b. The volume of gas diffused per unit time is the rate of diffusion of that gas.
![]()
c. SI Unit for rate of diffusion is dm3 s-1 or cm3 s-1.
![]()
Question 25.
Convert:
i. 3.5 atm to mm Hg
ii. 1520 torr to atm
iii. 5 m3 to dm3
iv. 580 °c to Kelvin
Answer:
I. 3.5 atm to mm Hg:
1 atm = 760 mm Hg
∴ 3.5 atm = 3.5 × 760
= 2660 mm Hg
ii. 1520 torr to aim:
1 atm = 760 torr
∴ 1 torr = \(\frac {1}{760}\) atrn
∴ 1520 torr = \(\frac {1520}{760}\) = atm
iii. 5 m3 to dm3:
1 m3 = 103 dm3
∴ 5m3 = 5 × dm3 = 5000 dm3
iv. 580 °C to Kelvin:
T(K) = t °C + 273.15
∴ T(K)= (580 °C) + 273.15 = 853.15 K
Question 26.
Name four measurable properties that are essential to study behaviour of gases.
Answer:
- Pressure
- Volume
- Temperature
- Number of moles
Question 27.
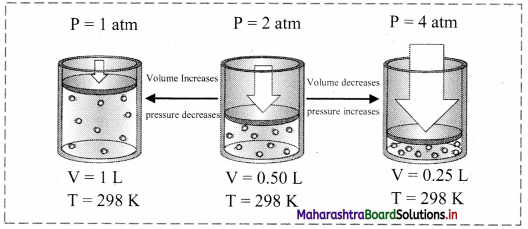
Explain Boyle’s law with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Boyle’s law (Pressure-Volume relationship):
i. Statement: For a fixed mass (number of moles ‘n’) of a gas at constant temperature, the pressure (P) of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume (V) of the gas.
ii. Explanation:
The mathematical expression of Boyle’s law is:
P ∝ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~V}}\) (at constant T and n) k1
∴ P = \(\frac{\mathrm{k}_{1}}{\mathrm{~V}}\) (where, k1 is the proportionality constant)
On rearranging the above equation,
∴ PV = k1 = constant
This implies that at constant temperature, product of pressure and volume of the fixed amount of a gas is constant.
Thus, when a fixed amount of a gas at constant temperature (T) occupying volume V1 initially at pressure (P1) undergoes expansion or compression, volume of the gas changes to V2 and pressure to P2.
According to Boyle’s law,
P1V1 = P2V2 = constant
iii. Schematic illustration of Boyle’s law:
Question 28.
Give the different graphical representations of Boyle’s law.
Answer:
i. Graph of pressure (P) versus volume (V) of a gas at constant temperature:
If the pressure (P) is plotted against volume (V) at constant temperature, a curve is obtained.
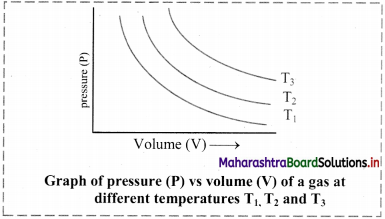
As the pressure increases, the volume decreases exponentially. The product of pressure and volume is always constant (PV = k). For a given mass of a gas, the value of k varies only with temperature.
[Note: Each curve is an isotherm as it is plotted at constant temperature, (iso = constant, therm = temperature).]
ii. Graph of PV versus pressure (P) of a gas constant temperature:
If the product of pressure and volume (PV) is plotted against pressure (P), a straight line is obtained parallel to x-axis (pressure axis).
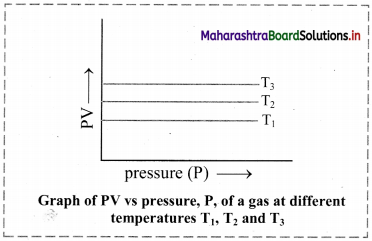
iii. Graph of pressure (P) of a gas versus reciprocal of volume (1/V) at constant temperature:
If the pressure (P) of the gas is plotted against (1/V), a straight line is obtained passing through the origin.
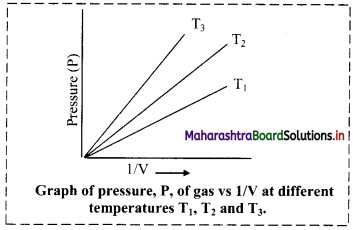
[Note: At high pressure, deviation from Boyle’s law is observed in the behaviour of gases.]
Question 29.
Derive the relationship between density and pressure.
Answer:
Relationship between density and pressure:
With increase in pressure, gas molecules get closer and the density (d) of the gas increases. Hence, at constant temperature, pressure is directly proportional to the density of a fixed mass of gas.
From Boyle’s law,
PV = k1 …….(1)
∴ V = \(\frac{\mathrm{k}_{1}}{\mathrm{P}}\)
But, d = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{V}}\)
On substituting, V from equation (2),
d = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{K}_{1}}\) × P
∴ d = k P …….(3)
where k = New constant
∴ d ∝ P
Above equation shows that at constant temperature, the pressure is directly proportional to the density of a fixed mass of the gas.
![]()
Question 30.
Write a short note on absolute temperature scale.
Answer:
Absolute temperature scale:
- Absolute temperature scale is related to Celsius temperature scale by the equation:
T K = t °C + 273.15 - This also called thermodynamic scale of temperature.
- The units of this absolute temperature scale is called (K) in the honour of Lord Kelvin who determined the accurate value of absolute zero as -273.15 °C in the year 1854.
Question 31.
Explain Charles’ law with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Charles’ law (Temperature-Volume relationship):
i. Statement: At constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin.
ii. Explanation:
For an increase of every degree of temperature, volume of the gas increases by \(\frac{1}{273.15}\) of its original value at 0 °C. This is expressed mathematically as follows:
Vt = V0 + \(\frac{t}{273.15} V_{0}\) ………….(1)
Where Vt and V0 are the volumes of the given mass of gas at the temperatures t °C and 0 °C. Rearranging the Eq. (1) gives

The equation (3) on rearrangement takes the following form:
\(\frac{\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{t}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{t}}}=\frac{\mathrm{V}_{0}}{\mathrm{~T}_{0}}\)
From this, a general equation can be written as follows:
\(\frac{\mathrm{V}_{1}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{V}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{2}}\) …………(4)
\(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{T}}\) = K2 = constant (at constant P and n)
∴ V = k2T OR V ∝ T ……(5)
The equation (4) is the mathematical expression of Charles’ law.
iii. Schematic illustration of Charles’ law:
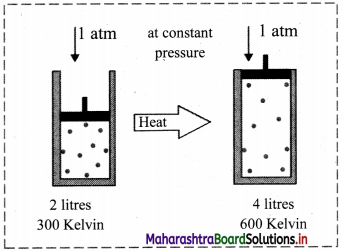
This shows that at constant pressure, gases expand on heating and contract on cooling.
Question 32.
Give the different graphical representation of Charles’ law.
Answer:
Graph of volume versus temperature at constant pressure:
- According to Charles’ law, the graph of volume of a gas (at given constant pressure, say P1) versus its temperature in Celsius, is a straight line with a positive slope.
- On extending the line to zero volume, the line intercepts the temperature axis at -273.15 °C.
- At any other value of pressure, say P2, a different straight line for the volume temperature plot is obtained, but we get the same zero-volume temperature intercept at -273.15 °C.
- The straight line of the volume versus temperature graph at constant pressure is called isobar.
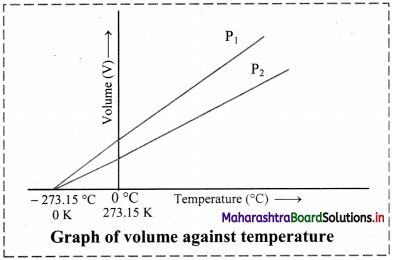
[Note: Zero volume for a gas sample is a hypothetical state. In practice, all the gases get liquified at a temperature higher than -273.15 °C. This temperature is the lowest temperature that can be imagined but practically cannot be attained. It is the absolute zero temperature on the Kelvin scale (0 K).]
Question 33.
Write the statement for Gay-Lussac’s law.
Answer:
Statement for Gay-Lussac’s law:
At constant volume, pressure (P) of a fixed amount of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (T).
![]()
Question 34.
Give the mathematical expression for Gay-Lussac’s law.
Answer:
Gay-Lussac’s law (Pressure-Temperature relationship):
i. Statement: At constant volume, pressure (P) of a fixed amount of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature (T).
ii. Explanation:
Gay-Lussac’s law can be mathematically expressed as:
P ∝ T
∴ P = k3T
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{T}}\) = Constant (at constant V and n)
Thus, according to Gay-Lussac’s law,
\(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{1}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{2}}\) = constant
Question 35.
Give the graphical representation of Gay-Lussac’s law.
Answer:
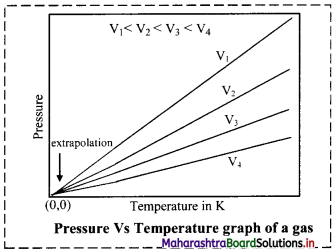
Graph of pressure versus temperature of a gas at constant volume:
When a graph is plotted between pressure (P) in atm and temperature (T) in kelvin, a straight line is obtained It is known as isochore.
Question 36.
Define the following terms:
i. Isotherm
ii. Isobar
iii. Isochore
Answer:
i. A graph of pressure (P) versus volume (V) at a constant temperature is known as isotherm.
ii. A graph of volume (V) versus absolute temperature (T) at a constant pressure is known as isobar.
iii. A graph of pressure (P) versus absolute temperature (T) at a constant volume is known as isochore.
Question 37.
State and explain Avogadro law.
Answer:
Avogadro law (Volume-Amount relationship):
i. Statement: Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
ii. Explanation:
V is directly proportional to n (number of moles) at constant ‘P’ and ‘T’.
V ∝ n
V = k4 × n (where, k4 is proportionality constant)
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{n}}\) = constant (at constant T and P)
Note: Representation of Avogadro law
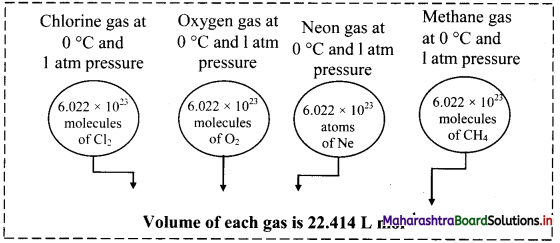
Question 38.
What is molar volume?
Answer:
The volume occupied by one mole of an ideal gas at STP is 22.414 L. This volume is known as molar volume.
![]()
Question 39.
Derive the relation between density of a gas and its molar mass.
Answer:
Relation between density of a gas and its molar mass:
According to Avogadro’s law, V ∝ n
Now, n = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\) (where, m is the mass of the gas and M is the molar mass of the gas)
∴ V ∝ \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
M ∝ \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{V}}\)
But, \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{V}}\) = d (where, d is the density of the gas)
∴ d ∝ M
Thus, density of a gas is directly proportional to its molar mass.
Question 40.
The volume occupied by a given mass of a gas at 298 K is 25 mL at 1 atmosphere pressure.
Calculate the volume of the gas if pressure is increased to 1.25 atmosphere at constant temperature.
Solution:
Given: P1 = Initial pressure = 1 atm, V1 = Initial volume = 25 mL
P2 = Final pressure = 1.25 atm
To find: V2 = Final volume of the gas
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
Calculation: According to Boyle’s law, P1V1 = P2V2
Substituting the values of P1, V1 and P2 in the above expression, we get
V2 = \(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{P_{2}}=\frac{1 \times 25}{1.25}\) = 20 mL
Ans: The volume occupied by the gas is 20 mL.
Question 41.
The volume of a given mass of a gas is 0.6 dm3 at a pressure of 2 atm. Calculate the volume of the gas if its pressure is increased to 2.4 at the same temperature.
Solution:
Given: P1 = Initial pressure = 2 atm
V1 = Initial volume of given mass of the gas = 0.6 dm3
P2 = Final pressure = 2.4 atm
To find: V2 = Final volume of the gas
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
Calculation: According to Boyle’s law,
P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
V2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{1} \mathrm{~V}_{1}}{\mathrm{P}_{2}}=\frac{2 \times 0.6}{2.4}=0.5 \mathrm{dm}^{3}\)
Ans: The volume of the given gas is 0.5 dm3.
Question 42.
What will be the minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 5 bar to 200 dm3 at 25 °C.
Solution:
Given: P1 = Initial pressure = 5 bar
V1 = Initial volume = 500 dm3; V2 = Final volume = 200 dm3
To find: P2 = Final pressure
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
Calculation: According to Boyle’s law,
P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
∴ P2 = \(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{1} \mathrm{~V}_{1}}{\mathrm{~V}_{2}}=\frac{5 \times 500}{200}\) = 12.5 bar
Ans: The minimum pressure required to compress 500 dm3 of air at 5 bar to 200 dm3 at 25 °C is 12.5 bar.
Question 43.
A balloon has certain volume at sea level. At what pressure (in kPa) will its volume be increased by 40% if the temperature is kept constant?
Solution:
Given: P1 = Initial pressure = 101.325 kPa (∵ The pressure at sea level = 101.325 kPa)
V1 = Initial volume at sea level = 100 dm3 (assumption)
V2 = Final volume = (100 + 40) = 140 dm3
To find: P2 = Final pressure
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
Calculation: According to Boyle’s law,
P1V1 = P2V2 (at constant n and T)
P2 = \(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}}{V_{2}}\)
∴ P2 = \(\frac{101.325 \times 100}{140}\) = 72.375 kPa
Ans: The pressure at which volume of the given balloon will be increased by 40% at a given temperature is 72.375 kPa.
![]()
Question 44.
At 300 K, a certain mass of a gas occupies 1 × 10-4 dm3 volume. Calculate its volume at 450 K and at the same pressure.
Solution:
Given: T1 = Initial temperature = 300 K, V1 = Initial volume = 1 × 10-4 dm3,
T2 = Final temperature = 450 K
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: \(\frac{V_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{V_{2}}{T_{2}}\) (at constant n and P)
Calculation: According to Charles’ law, at constant pressure.

Ans: The volume of given gas becomes 1.5 × 10-4 dm3 at the temperature of 450 K and same pressure.
Question 45.
A certain mass of a gas occupies a volume of 0.2 dm3 at the temperature, x K. Calculate the volume of the gas if its absolute temperature is doubled at same pressure.
Solution:
Given: V1 = Initial volume = 0.2 dm3, T1 = Initial temperature = x K
T2 = Final temperature = 2 × x = 2x K
To find: V2 = Final volume of the gas
\(\frac{V_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{V_{2}}{T_{2}}\) (at constant n and P)
Calculation: According to Charles’ law,
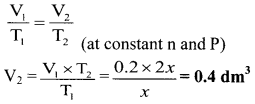
Ans: The volume of given gas becomes 0.4 dm3 when the temperature is doubled.
Question 46.
The volume of a given mass of a gas at 0 °C is 0.2 dm3. Calculate its volume at 100 °C, if the pressure remains the same.
Solution:
Given: V1 = Initial volume = 0.2 dm3, T1 = Initial temperature = 0 °C = 273.15 K,
T2 = Final temperature = 100 °C = 100 + 273.15 K = 373.15 K
To find: V2 = Volume at 100 °C
Formula: \(\frac{V_{1}}{T_{1}}=\frac{V_{2}}{T_{2}}\) (at constant n and P)
Calculation: According to Charles’ law,
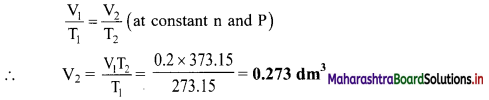
Ans: The volume of gas at 100 °C is 0.273 dm3.
Question 47.
A glass container is sealed with a gas at 0.8 atm pressure and at 25 °C. The glass container sustains a pressure of 2 atm. Calculate the temperature to which the gas can be heated before bursting the container.
Solution:
Given: P1 = Initial pressure = 0.8 atm, P2 = Final pressure = 2 atm
T1 = Initial temperature = 25 °C = 25 + 273.15 K = 298.15 K
To find: T2= Final temperature
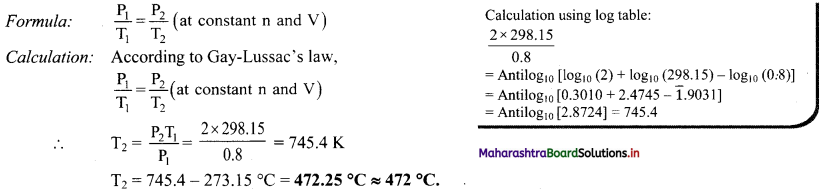
Ans: The temperature to which the gas can be heated before bursting the container is 472 °C.
Question 48.
An 8.0 L of sample at 0 °C and 5.6 atm of pressure contains 2.0 moles of a gas. If more 1.0 mole of gas at the same temperature and pressure is added, calculate the final volume.
Solution:
Given: V1 = Initial volume = 8.0 L
n1 = Initial mol = 2.0 mol
n2 = Final mol = (2.0 + 1.0) = 0.3 mol
To find: V2 = Final volume

Ans: The final volume is 12 L.
![]()
Question 49.
What is an ideal gas equation?
Answer:
Ideal gas equation is obtained by combining three gas laws, namely, Boyle’s law, Charles’ law and Avogadro law. Mathematically, it is given as:
PV = nRT
where,
P = Pressure of gas, V = Volume of gas, n = number of moles of gas,
R = Gas constant, T = Absolute temperature of gas
Question 50.
Derive the ideal gas equation.
Answer:
According to Boyle’s law,
V ∝ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{P}}\) (at constant T and n) ………..(1)
According to Charles’ law,
V ∝ T (at constant P and n) …….(2)
According to Avogadro’s law,
V ∝ n (at constant P and T) …….(3)
Combining relations (1), (2) and (3), we get
V ∝ \(\frac{\mathrm{nT}}{\mathrm{P}}\)
Converting this proportionality into an equation by introducing a constant of proportionality (‘R’ known as gas constant), we get
∴ V = \(\frac{\mathrm{nRT}}{\mathrm{P}}\)
On rearranging the above equation, we get
PV = nRT
where,
P = Pressure of gas,
V = Volume of gas,
n = number of moles of gas,
R = Gas constant,
T = Absolute temperature of gas.
This is the ideal gas equation or equation of state.
[Note: In the ideal gas equation, R is called gas constant or universal gas constant, whose value is same for all the gases. In this equation, if three variables are known, fourth can be calculated. The equation describes the state of an ideal gas. Hence, it is also called as equation of state.]
Question 51.
Deduce values of gas constant ‘R’ in different units.
Answer:
i. R in SI Unit (in Joules): Value of R can be calculated by using the SI units of P, V and T. Pressure P is measured in N m-2 or Pa, volume V in meter cube (m3) and temperature T in Kelvin (K).

ii. R in litre atmosphere: If pressure (P) is expressed in atmosphere (atm) and volume in litre (L) or decimeter cube (dm3) and Temperature in kelvin (K), (that is, old STP conditions), then value of R is,
R = \(\frac{1 \mathrm{~atm} \times 22.414 \mathrm{~L}}{1 \mathrm{~mol} \times 273.15 \mathrm{~K}}\)
∴ R = 0.0821 L atm K-1 mol-1
OR
R = 0.0821 dm3 atm K-1 mol-1
iii. R in calories: We know, 1 calorie = 4.184 Joules
∴ R= \(\frac{8.314}{4.184}\) = 1.987 ≅ 2 cal K-1 mol-1
Question 52.
Derive the following expression:
M = \(\frac{\text { mRT }}{\text { PV }}\)
Answer:
According to ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
n = \(\frac{\mathrm{PV}}{\mathrm{RT}}\)
Now, for a known mass ‘m’ of gas having molar mass ‘M’, number of moles ‘n’ is given as:
n = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
Therefore, \(\frac{m}{M}=\frac{P V}{R T}\)
On rearranging the equation, we get
M = \(\frac{\text { mRT }}{\text { PV }}\)
Question 53.
Derive the expression for combined gas law.
Answer:
The ideal gas equation is written as
PV = nRT …….(1)
On rearranging equation (1), we get,
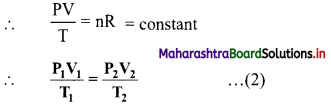
The ideal gas equation used in this form is called combined gas law.
![]()
Question 54.
Derive the relation between density, molar mass and pressure.
Answer:
Relation between density, molar mass and pressure:
According to ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT …..(1)
On rearranging equation (1), we get
\(\frac{\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{V}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{RT}}\) ……….(2)
Now, n = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
On substituting the value of n, equation (2) becomes
\(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{MV}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{RT}}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{M}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{RT}}\) ……….(3)
where d = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{V}}\) = density of the gas
On rearranging the equation, we get
M = \(\frac{\mathrm{dRT}}{\mathrm{P}}\) ……(4)
This equation can be used to calculate molar mass of a gas in terms of its density.
Question 55.
State Boyle’s law in terms of density.
Answer:
Boyle’s law in terms of density is stated as ‘At constant temperature, pressure of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to its density’.
Question 56.
Derive the expression that relates partial pressure with mole fraction of a gas.
Answer:
The partial pressures of individual gases can be written in terms of ideal gas equation as follows:

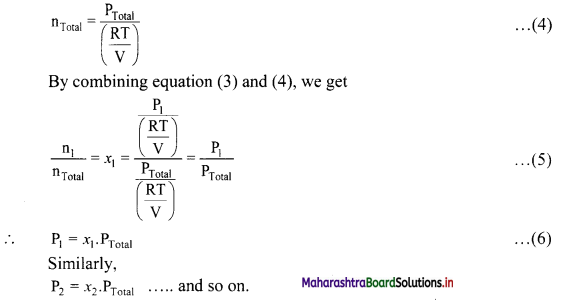
Thus, partial pressure of a gas is obtained by multiplying the total pressure of mixture by mole fraction of that gas.
Question 57.
What is water vapour?
Answer:
The ‘gas’ above the surface of liquid water is described as water vapour.
![]()
Question 58.
Write a short note on aqueous tension.
Answer:
Aqueous tension:
i. When the liquid water is placed into a container and air above is pumped away and the container is sealed, then the liquid water evaporates and only water vapour remains in the above space. After sealing, the vapour pressure increases initially, then slows down as some water molecules condense back to form liquid water. After a few minutes, the vapour pressure reaches a maximum value, which is called the saturated vapour pressure. The pressure exerted by saturated water vapour is called aqueous tension (Paq).
ii. Aqueous tension increases with increase in temperature.
Question 59.
Explain how pressure of a dry gas can be calculated using aqueous tension.
Answer:
i. When a gas is collected over water in a closed container, it gets mixed with the saturated water vapour in that space. Therefore, the measured pressure corresponds to the pressure of the mixture of that gas and the saturated water vapour in that space.
ii. Pressure of pure and dry gas can be calculated by using the aqueous tension. It is obtained by subtracting the aqueous tension from the total pressure of the moist gas.
∴ PDry gas = PTotal – Paq
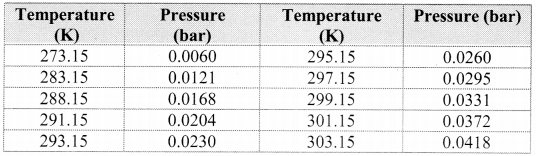
i.e., PDry gas = PTotal – Aqueous Tension
Note: Aqueous tension of water (vapour pressure) as a function of temperature.
Question 60.
A sample of N2 gas was placed in a flexible 9.0 L container at 300 K at a pressure of 1.5 atm. The gas was compressed to a volume of 3.0 L and heat was added until the temperature reached 600 K. What is the new pressure inside the container?
Solution:
Given: V1 = Initial volume = 9.0 L, V2 = Final volume = 3.0 L,
P1 = Initial pressure = 1.5 atm
T1 = Initial temperature = 300 K, T2 = Final temperature = 600 K
To find: P2 = Final pressure
Formula: \(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{1} \mathrm{~V}_{1}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}_{2} \mathrm{~V}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{2}}\)
Calculation: According to combined gas law,
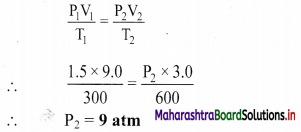
Ans: The new pressure inside the container is 9 atm.
Question 61.
A gas at 772 mm Hg and at 35 °C occupies a volume of 6.851 L. Calculate its volume at STP.
Solution:
Given: V1 = Initial volume = 6.851 L
P1 = Initial pressure = 772 mm Hg, P2 = Final pressure = 760 mm Hg
T1 = Initial temperature = 35 °C = 35 + 273.15 K = 308.15 K
T2 = Final temperature = 273.15 K
To find: V2 = Final volume
Formula: \(\frac{\mathrm{P}_{1} \mathrm{~V}_{1}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{P}_{2} \mathrm{~V}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{2}}\)
Calculation: According to combined gas law,
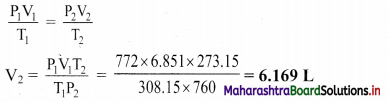
Ans: The volume of gas at STP is 6.169 L.
Question 62.
Find the temperature in °C at which volume and pressure of 1 mol of nitrogen gas becomes 10 dm3 and 2.46 atmosphere respectively.
Solution.
P = 2.46 atm, V = 10 dm3, n = 1 mol, R = 0.0821 dm3-atm K-1 mol-1
To find: Temperature (T)
Formula: PV = nRT
According to ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
∴ T = \(\frac{\mathrm{PV}}{\mathrm{nR}}=\frac{2.46 \times 10}{1 \times 0.0821}\)
T = 299.63 K
Temp, in °C = 299.63 – 273.15 = 26.48 °C
Ans: The temperature of the nitrogen gas under the given conditions is 26.48 °C.
![]()
Question 63.
Calculate the temperature of 5.0 mol of a gas occupying 5 dm3 at 3.32 bar.
(R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1)
Solution:
Given: n = number of moles = 5.0 mol, V = volume = 5 dm3
P = pressure = 3.32 bar, R = 0.083 bar dm3 K-1 mol-1
To find: Temperature (T)
Formula: PV = nRT
Calculation: According to ideal gas equation,
PV = nRT
∴ T = \(\frac{\mathrm{PV}}{\mathrm{nR}}=\frac{3.32 \times 5}{5.0 \times 0.083}\) = 40 K
Ans: The temperature of the gas is 40 K.
Question 64.
Calculate the number of moles of hydrogen gas present in a 0.5 dm3 sample of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 101.325 kPa at 27 °C.
Solution:
Given: V = 0.5 dm3 = 0.5 × 10-3 m3, P = 101.325 kPa = 101.325 × 103 Pa = 101.325 × 103 Nm-2
T = 27 °C = 27 + 273.15 K = 300.15 K, R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1
To find: n = number of moles of gas
Formula: PV = nRT
Calculation: According to ideal gas equation,
![]()
Ans: The number of moles of hydrogen gas present in the given volume is 0.020 moles.
Question 65.
A mixture of 28 g N2, 8 g He and 40 g Ne has 20 bar pressure. What is the partial pressure of each of these gases?
Solution:
Given: mN2 = 28 g, mHe = 8 g, mNe = 40 g,
PTotal = 20 bar
To find: Partial pressure of each gas
Formula: P1 = x1 × PTotal
Calculation: Determine the number of moles (n) of each gas using the formula: n = \(\frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{M}}\)
Determine the mole fraction of each gas using the formula:
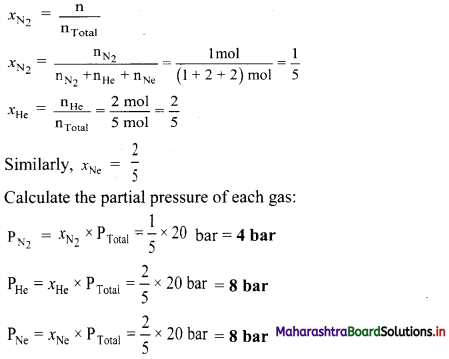
Ans: The partial pressure of nitrogen, helium and neon are 4 bar, 8 bar and 8 bar respectively.
Question 66.
What is an ideal gas?
Answer:
Ideal gas:
- The gases which obey’ ideal gas equation over a complete range of temperature and pressure are called ideal gases.
- For an ideal gas, the ratio of PV/RT = 1.
- In an ideal gas, there are no interactive forces between the molecules and the molecular volume is negligibly small compared to the volume occupied by the gas. The gas particles are considered as point particles.
Question 67.
What are real gases?
Answer:
Real gases:
- Gases, which do not obey ideal gas equation under all the conditions of temperature and pressure are called real gases.
- For real gases, the ratio of PV/RT will be either greater than 1 or less than 1.
- Real gases show deviation from ideal gas behaviour at higher pressures and lower temperatures.
- The intermolecular attractive forces are not negligible in real gases.
- In real gases, the actual volume of the molecules cannot be neglected as compared to the total volume of the container.
![]()
Question 68.
Explain the reason for deviations of gases from ideal behaviour.
Answer:
A deviation from the ideal behaviour is observed at high pressure and low temperature. It is due to two reasons.
- The intermolecular attractive forces are not negligible in real gases. These do not allow the molecules to collide the container wall with full impact. This results in decrease in the pressure.
- At high pressure, the molecules are very close to each other. The short range repulsive forces start operating and the molecules behave as small but hard spherical particles. The volume of the molecule is not negligible.
Therefore, very less volume is available for molecular motion. - At very low temperature, the molecular motion becomes slow and the molecules are attracted to each other due to the attractive force. Hence, the behaviour of the real gas deviates from the ideal gas behaviour.
- Deviation with respect to pressure can be studied by plotting pressure (P) vs volume (V) curve at a given temperature.
- From the graph, it is clear that at very high pressure, the measured volume is more than theoretically calculated volume assuming ideal behaviour. However, at low pressure, measured and theoretically calculated volumes approach each other.
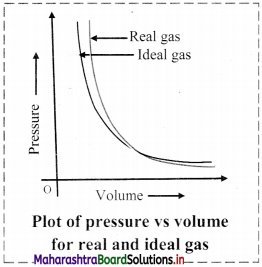
Question 69.
What is compressibility factor (Z)?
Answer:
Compressibility factor (Z):
i. It is defined as the ratio of product PV and nRT.
Z = \(\frac{\mathrm{PV}}{\mathrm{nRT}}\)
ii. Deviation from ideal behaviour is measured in terms of compressibility factor.
iii. For ideal gases, Z = 1 under all conditions of temperature and pressure. Therefore, the graph of Z versus P will be a straight line parallel to pressure axis.
iv. For gases that deviate from ideal behaviour, value of Z deviates from unity.
Note: Variation of compressibility factor for some gases
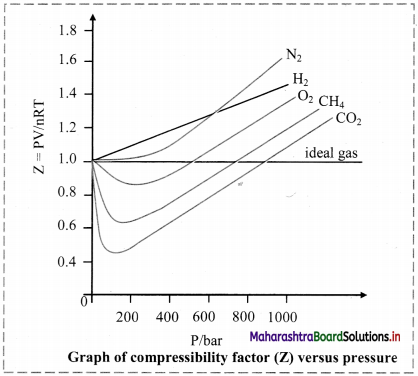
Question 70.
Show that the compressibility factor can be represented as Z = \(\frac{V_{\text {real }}}{V_{\text {ideal }}}\)
Answer:
For real gas,
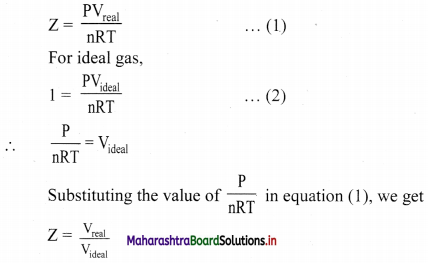
Thus, the compressibility factor (Z) is the ratio of actual molar volume of a gas to its molar volume if it behaved ideally, at that temperature and pressure.
Question 71.
Explain: Liquefaction of CO2 with the help of pressure vs volume isotherm.
Answer:
Most gases behave like ideal gases at high temperature. For example, the PV curve of CO2 gas at 50 °C is like the ideal Boyle’s law curve. As the temperature is lowered, the PV curve shows a deviation from the ideal Boyle’s law curve. At a particular value of low temperature, the gas gets liquified at certain increased value of pressure. For example, CO2 gas liquifies at 38.98 °C and 73 atmosphere pressure. This is the highest temperature at which liquid CO2 can exist. Above this temperature, liquid CO2 cannot form even if very high pressure is applied. Other gases also show similar behaviour.
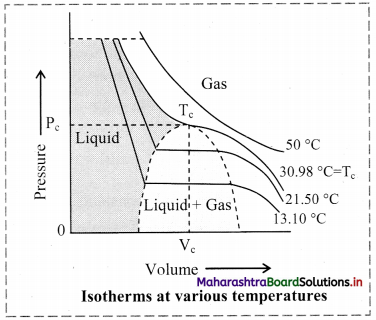
Question 72.
Define: Critical temperature, critical volume and critical pressure.
Answer:
i. The temperature above which a substance cannot be liquified by increasing pressure is called its critical temperature (Tc).
ii. The molar volume at critical temperature is called the critical volume (Vc).
iii. The pressure at the critical temperature is called the critical pressure (Pc).
Note: Critical constants for common gases
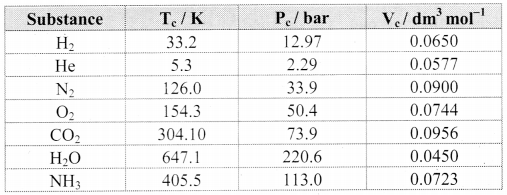
i. N2 and O2, have Tc values much below 0 °C and their Pc values are high. Consequently, liquefaction of O2 and N2 (and air) requires compression and cooling.
ii. The Tc value of CO2 nearly equals the room temperature; however, its Pc value is very high. Therefore, CO2 exists as gas under ordinary condition.
Question 73.
Water has Tc = 647.1 K and Pc = 220.6 bar. What do these values imply about the state of water under ordinary conditions?
Answer:
The Tc and Pc values of water are very high compared to the room temperature and common atmospheric pressure. As a result, water exists in liquid state under ordinary condition of temperature and pressure.
![]()
Question 74.
Gases possess characteristic critical temperature which depends upon the magnitude of intermolecular forces between the gas particles. Critical temperatures of ammonia and carbon dioxide are 405.5 K and 304.10 K respectively. Which of these gases will liquefy first when you start cooling from 500 K to their critical temperature?
Answer:
When cooling of ammonia and carbon dioxide gas is started from 500 K, then ammonia reaches its critical temperature first (i.e., 405.5 K.) and hence, it is also the first to get liquefied.
When the cooling is continued further, carbon dioxide gas is liquefied as it reaches its critical temperature (i.e., 304.10 K).
Question 75.
CO2 has Tc = 38.98 °C and Pc = 73 atm. How many phases of CO2 coexist at
i. 50 °C and 73 atm
ii. 20 °C and 50 atm.
Answer:
i. 50 °C and 73 atm represent a condition for CO2 above its Tc. Therefore, under this condition CO2 exists only as single phase.
ii. 20° C and 50 atm represent a condition for CO2 below its Tc. Therefore, under this condition two phases of CO2, namely, liquid and gas can coexist.
Question 76.
In which of the following cases, water will have the highest and the lowest boiling point?
i. Water is boiled in an open vessel.
ii. Water is boiled in a pressure cooker.
iii. Water is boiled in an evacuated vessel.
Answer:
Higher the pressure to which a liquid is exposed, higher will be its boiling point. The pressure to which water is exposed is maximum in the pressure cooker and minimum in the evacuated vessel. Therefore, boiling point of water is highest in a pressure cooker and lowest in an evacuated vessel.
Question 77.
Define: Liquid state
Answer:
Liquid state is the intermediate state between solid state and gaseous state.
Question 78.
Give reason: Liquid possesses properties such as fluidity, definite volume and ability to take shape of the bottom of the container in which it is placed.
Answer:
Molecules of liquid are held together by moderately strong intermolecular forces and can move about within the boundary of the liquid. As a result, liquid possesses properties such as fluidity, definite volume and ability to take shape of the bottom of the container in which it is placed.
![]()
Question 79.
Name some measurable properties of liquid.
Answer:
- Density
- Boiling point
- Freezing point
- Vapour pressure
- Surface tension
- Viscosity.
Question 80.
What are the factors affecting vapour pressure?
Answer:
Factors affecting vapour pressure:
- Nature of liquid: Liquids having relatively weak intermolecular forces possess high vapour pressure. Such liquids are called volatile liquids.
e. g. Petrol evaporates quickly than motor oil. Hence, petrol has higher vapour pressure than motor oil. - Temperature: When the liquid is gradually heated, its temperature rises and its vapour pressure increases.
Question 81.
Explain how temperature affects surface tension.
Answer:
Surface tension is a temperature dependent property. When attractive forces are large, surface tension is large. Surface tension decreases as the temperature increases. With increase in temperature, kinetic energy of molecules increases. So, intermolecular forces of attraction decrease, and thereby surface tension decreases.
Question 82.
Mention some applications of surface tension.
Answer:
Applications of surface tension:
- Cleaning action of soap and detergent is due to the lowering of interfacial tension between water and oily substances. Due to lower surface tension, the soap solution penetrates into the fibre, surrounds the oily substance and washes it away.
- Efficacy of toothpastes, mouthwashes and nasal drops is partly due to presence of substances having lower surface tension. This increases the efficiency of their penetrating action.
Question 83.
Give reason: Liquid droplets acquire spherical shape.
Answer:
For a given volume of a liquid, spherical shape always imparts minimum surface area thereby reducing the surface tension. Hence, liquid droplets acquire spherical shape.
Question 84.
Define: Coefficient of viscosity
Answer:
Coefficient of viscosity is defined as the degree to which a fluid resists flow under an applied force, measured by the tangential frictional force per unit area per unit velocity gradient when the flow is laminar.
![]()
Question 85.
Describe various factors affecting viscosity of a liquid.
Answer:
Factors affecting viscosity of a liquid:
i. Temperature: Viscosity is a temperature dependent property.
Viscosity ∝ \(\frac{1}{\text { Temperature }}\)
ii. Nature of liquid: Viscosity also depends on molecular size and shape. Larger molecules have more viscosity and spherical molecules offer the least resistance to flow and therefore are less viscous. Greater the viscosity, slower is the liquid flow.
Question 86.
Describe three daily life instances where viscosity plays an important role.
Answer:
- Lubricating oils are viscous liquids. Gradation of lubricating oils is done on the basis of viscosity. A good quality lubricating oil does not change its viscosity with increase or decrease in temperature.
- Increase blood viscosity than the normal value is taken as an indication of cardiovascular disease.
- Glass panes of old buildings are found to become thicker with time near the bottom. This indicates that glass is not a solid but a supercooled viscous liquid.
Question 87.
For an experiment, a scientist fills different gases in four flasks as shown below:
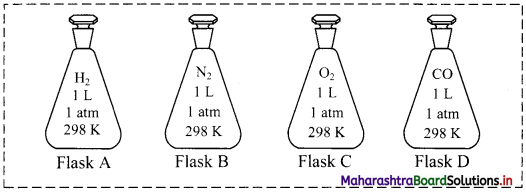
i. What is the ratio of the number of molecules of the gases in flask A to flask B?
ii. Calculate the pressure exerted by nitrogen gas in flask B if the temperature is doubled.
iii. If the scientist transfers the gas in flask D to another flask of 2.5 L at 1 atm pressure, what will be the temperature of the gas in the new flask?
Answer:
i. 1:1
ii. P ∝ T (when V and n are constants)
∴ If temperature is doubled, pressure also doubles.
∴ P = 2 atm
iii. \(\frac{\mathrm{V}_{1}}{\mathrm{~T}_{1}}=\frac{\mathrm{V}_{2}}{\mathrm{~T}_{2}}\) (when P and n are constants)
∴ \(\frac{1}{298}=\frac{2.5}{T_{2}}\)
∴ T2 = 745 K
Question 88.
A balloon containing 0.6 mol of helium gas has a volume of 1.5 L.
i. Assuming that the temperature and pressure remains constant, what happens to the volume of the balloon if an additional 0.6 mol of helium is added?
ii. Assuming that the temperature and pressure remains constant, what happens to the volume of the balloon if 0.3 mol of helium is removed?
Answer:
i. The volume of the balloon increases.
ii. The volume of the balloon decreases.
Question 89.
In an experiment conducted to study the diffusion of gases using same experimental conditions, following data were recorded.
Gas A: 50 cm3 of gas A takes 7 minutes to diffuse from one container to the adjacent container.
Gas B: 50 cm3 of gas B takes 10 minutes to diffuse from one container to the adjacent container.
i. What is the rate of diffusion of gas A?
ii. What is the rate of diffusion of gas B?
iii. Which gas has higher molecular mass?
Answer:
i. Volume of gas A diffused = 50 cm3
Time required for diffusion = 7 minutes = 7 × 60 seconds
![]()
∴ The rate of diffusion of gas A is 0.12 cm3 s-1.
ii. The rate of diffusion of gas B is 0.083 cm3 s-1.
iii. Gas B has higher molecular mass.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is CORRECT for both gases and liquids?
(A) Indefinite volume
(B) Definite shape
(C) Indefinite shape
(D) Definite volume
Answer:
(D) Definite volume
2. The composition of …………. in air is about 78% by volume.
(A) CO2
(B) O2
(C) N2
(D) Ar
Answer:
(C) N2
3. Which of the following expression at constant pressure represents Charles’s law?
(A) V ∝ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~T}}\)
(B) V ∝ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{~T}^{2}}\)
(C) V ∝ T
(D) V ∝ d
Answer:
(C) V ∝ T
4. The pressure of 2 mole of ideal gas at 546 K having volume 44.8 L is …………….
(A) 2 atm
(B) 3 atm
(C) 7 atm
(D) 1 atm 1023
Answer:
(A) 2 atm
5. At 300 K, the density of a certain gaseous molecule at 2 bar is double to that of dinitrogen at 4 bar. The molar mass of gaseous molecule is …………….
(A) 28 g mol-1
(B) 56 g mol-1
(C) 112 g mol-1
(D) 224 g mol-1
Answer:
(C) 112 g mol-1
![]()
6. As the temperature increases, average kinetic energy of molecules increases. What would be the effect of increase of temperature on pressure provided the volume is constant?
(A) Increases
(B) Decreases
(C) Remains same
(D) Becomes half
Answer:
(A) Increases
7. Assuming ideal gas behaviour, the ratio of density of ammonia to that of hydrogen chloride at same temperature and pressure is ………….. (Atomic wt. of Cl = 35.5 u)
(A) 1.46
(B) 0.46
(C) 1.64
(D) 0.64
Answer:
(B) 0.46
8. The number of moles of H2 in 0.224 L of hydrogen gas at STP (273 K, 1 atm) assuming ideal gas behaviour is …………..
(A) 1
(B) 0.1
(C) 0.01
(D) 0.001
Answer:
(C) 0.01
9. The volume occupied by 11.5 g of carbon dioxide at STP is approximately equal to:
(A) 5.9 L
(B) 22.5 L
(C) 86 L
(D) 259 L
Answer:
(A) 5.9 L
10. Which of the following is CORRECT regarding a fixed amount of ideal gas?
(A) Doubling the temperature, doubles the volume, provided the pressure remains the same.
(B) Doubling the temperature, halves the volume, provided the pressure remains the same.
(C) Doubling the pressure, doubles the volume, provided the temperature remains the same.
(D) Doubling the volume, doubles the pressure, provided the temperature remains the same.
Answer:
(A) Doubling the temperature, doubles the volume, provided the pressure remains the same.
![]()
11. When one mole of an ideal gas is heated from 300 K to 360 K at constant pressure of 1 atm, its volume …………….
(A) increases from V to 6.0V
(B) increases from V to 3.6V
(C) increases from V to 1.2V
(D) increases from V to 1.6V
Answer:
(C) increases from V to 1.2V
12. The partial pressure of a gas is obtained by multiplying the total pressure of mixture by …………… of that gas.
(A) molar mass
(B) moles
(C) mass
(D) mole fraction
Answer:
(D) mole fraction
13. The highest temperature at which liquid CO2 can exist is ……………..
(A) 18.98 °C
(B) 38.98 °C
(C) 50.0 °C
(D) 73.9 °C
Answer:
(B) 38.98 °C
14. The SI unit of surface tension is ……………..
(A) Pascal
(B) N s m-2
(C) km-2 s
(D) N m-1
Answer:
(D) N m-1
























