Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions Kumarbharati Chapter 2.4 The Fall of Troy Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 9 English Chapter 2.4 Question Answer Maharashtra Board
The Fall of Troy Poem 9th Std Question Answer
Warming up:
Building a Story :
Form groups of eight. The group leader prepares slips of paper for each of the seven points given below and distributes them among the others. The group sits in a circle, taking their seats according to the number on the slip they have. Then each one completes the sentence on his/her slip without sharing it with the others. The group leader collects the slips and reads all the sentences aloud as one continuous passage. Does the story make sense? The group then works on the story to make it more meaningful and interesting.
This game may be played again, changing the groups, to form new stories.
1. Once there was a ……………………….
2. Who lived in a ……………………….
3. He/She ate ……………………….
4. She/He went ……………………….
5. There she/he saw ……………………….
6. She/He was …………………………
7. That is why ……………………….
Question 1.
- Once there was a ……………………….
- Who lived in a ……………………….
- He/She ate ……………………….
- She/He went ……………………….
- There she/he saw ……………………….
- She/He was …………………………
- That is why ……………………….
Answer:
- Once there was a beautiful princess.
- Who lived in a dirty old shoe in a park.
- He/She ate nails and screws and paper.
- She/He went on a plane to the Arctic Circle.
- There she/he saw green mountains, lush forests and thundering waterfalls.
- She/He was very happy to go to Mars in the spaceship.
- That is why the doctor gave me the bitter medicine.
![]()
The sentences as one continuous passage :
Once there was a beautiful princess who lived in a dirty old shoe in a park. She/He ate nails and screws and paper. She went on a plane to the Arctic Circle. There she saw green mountains, lush forests and thundering waterfalls. She was very happy to go to Mars in the spaceship. That is why the doctor gave me the bitter medicine.
The sentences read as one continuous passage do not make sense. However, if we make changes in the story, the passage will make sense.
- Once there was a beautiful princess.
- Who lived in a beautiful palace in a large forest.
- She ate only fresh fruits, vegetables and salads for every meal.
- She went on a voyage to the Arctic Circle.
- There she saw frozen seas, ice bergs and a variety of sea animals.
- She was thrilled to see so many different things, which she had never seen before.
- That is why she decided to visit a new place every year.
When we put these sentences given above as a continuous passage, they form a small and sensible story.
(Students can play the game again, changing the groups, to form new stories.)
![]()
Interviews:
(a) Why? : Form groups of five. Choose a familiar character from any one of the epics you know. One person from the group plays the role of that character. Others in the group frame questions related to that character’s life. The condition is that all the questions should begin with ‘Why …?‘. They interview the character using these ‘Why -?‘ questions. Practise and present the interview in the classroom.
(b) How? : Follow the above procedure. Now all questions should begin with ‘How -?‘
(c) Prepare a short script of your interviews.
Question a.
Why?
Answer:
Form groups of five. Choose a familiar character from any one of the epics you know. One person from the group plays the role of that character. Others in the group frame questions related to that character’s life. The condition is that all the questions should begin with a ‘Why…’? They interview the character using these ‘Why?’ questions. Practice and present the interview in the classroom.
Example: Questions for Lord Rama. Epic: Ram ay an
- Why did you marry Sita?
- Why did your father ask you to leave the kingdom?
- Why did your stepmother want you to leave the kingdom?
- Why did Lakshman accompany you to the forest?
- Why did Lakshman leave Sita alone in the hut?
Question b.
How? : Follow the above procedure. Now all questions should begin with ‘How -?‘
Answer:
Example :
- How did you marry Sita?
- How many brothers did you have?
- How did your stepmother make you leave the kingdom?
- How did Ravana trick Sita?
- How did Hanuman help you?
Question c.
A short script of the interviews:
Answer:
Example :
Question 1.
Why did your father ask you to leave the kingdom?
Answer:
My father fulfilled my stepmother Kaikeyi’s wish and banished me from Ayodhya.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did your stepmother want you to leave the kingdom?
Answer:
My stepmother Kaikeyi wanted her son Bharat to become the king. This would not have been possible if I had been in Ayodhya. Hence she wanted me to leave the kingdom.
Question 3.
Why did Lakshman accompany you to the forest?
Answer:
Lakshman loved me and wanted to ensure my safety in the forest. Hence he accompanied me to the forest.
Part – I
English Workshop:
1. Read the passage and name the following.
(a) He composed the Illiad and Odyssey: ……………….
(b) He persuaded Helen to elope wjth him: ……………….
(c) She was wife of the King Menelaus: ……………….
(d) He led the defence of Troy for nthe years: ……………….
(e) He was killed by a poisoned arrow that entered his heel: ……………….
Question 1.
(a) He composed the Illiad and Odyssey: ……………….
(b) He persuaded Helen to elope with him: ……………….
(c) She was wife of the King Menelaus: ……………….
(d) He led the defense of Troy for nine years: ……………….
(e) He was killed by a poisoned arrow that entered his heel: ……………….
Answer:
(a) He composed The Iliad and – The Odyssey Homer
(b) He persuaded Helen to elope with him. Paris
(c) She was the wife of King Menelaus. Helen
(d) He led the defense of Troy for nine years Hector
(e) He was killed by a poisoned arrow that entered his heel. Achilles
![]()
2. Find antonyms of the following from the passage.
(a) barren × ……………..
(b) offended × ……………..
(c) cowardly × ……………..
(d) peace × ……………..
(e) surrender × ……………..
(f) exposed × ……………..
(g) defenceless × ……………..
Question 1.
Find antonyms of the following from the passage.
(a) barren × ……………..
(b) offended × ……………..
(c) cowardly × ……………..
(d) peace × ……………..
(e) surrender × ……………..
(f) exposed × ……………..
(g) defenceless × ……………..
Answer:
(a) barren × fertile
(b) offended × pleased
(c) cowardly × brave
(d) peace × war
(e) surrender × attack
(f) exposed × protected.
(g) defenceless × safe.
![]()
3. From other sources find synonyms of the following words used in the story.
(a) great (hero)
(b) beautiful (woman)
(c) fight (verb)
(d) rich (city)
(e) safe
(f) strong (city)
(g) brave
Question 1.
From other sources find synonyms of the following words used in the story.
(a) great (hero)
(b) beautiful (woman)
(c) fight (verb)
(d) rich (city)
(e) safe
(f) strong (city)
(g) brave
Answer:
(a) great – gallant (hero)
(b) beautiful – entrancing (woman).
(c) fight – attack (verb)
(d) rich – prosperous (city)
(e) safe – sheltered.
(f) strong – well-protected (city)
(g) brave – courageous.
![]()
4. Correct the following sentences using facts from the passage.
(a) Troy traded in cattle and grass, with other cities.
(b) During war, Trojans jumped over the fort gates to fight die enemy.
(c) Helen eloped with Menelaus.
(d) Troy was attacked because it was a strong. rich city.
(e) The Greek armies and heroes always defeated the Trojans.
(f) Both the enemies were eager to continue fighting.
(g) The great heroes avoided one another.
(h) Achilles was killed by an arrow that pierced his heart.
Question a.
Correct the following sentences using facts from the passage.
(a) Troy traded in cattle and grass, with other cities.
(b) During war, Trojans jumped over the fort gates to fight die enemy.
(c) Helen eloped with Menelaus.
(d) Troy was attacked because it was a strong. rich city.
(e) The Greek armies and heroes always defeated the Trojans.
(f) Both the enemies were eager to continue fighting.
(g) The great heroes avoided one another.
(h) Achilles was killed by an arrow that pierced his heart.
Answer:
(a) Troy traded in goods and grain with other cities.
(b) During the war, Trojans came out of the open fort gates to fight the enemy.
(c) Helen eloped with Paris.
(d) Troy was attacked because its Prince Paris had! persuaded Helen, the wife of a Greek king Menelaus, to elope with him.
(e) Sometimes the Trojans seemed to have the better of the fight and sometimes the Greeks.
(f) The Trojans were tired of being shut up in their city and the Greeks were longing to see their homes again.
(g) Sometimes there were single fights, between two great heroes.
(h) Achilles was killed by an arrow that pierced his heel.
![]()
5. State the counter-action for the following actions.
Question 1.
State the counter-action for the following actions.

Answer:
| Action | Counter-action |
| 1. Helen eloped with Paris. | Greece declared war against the Troy. |
| 2. The Greeks sailed to Troy and attacked it. | The Trojans fought hard and the siege continued for ten years. |
| 3. Hector was killed by Achilles. | Achilles himself was killed later by a poisoned arrow. |
| 4. The siege continued for ten long years. | The Trojans fought hard and the fighting went on daily. |
6. From either of our two Indian epics, find out which battle/war lasted the longest? Write down about its cause, the enemy armies, its heroes, its duration and the final outcome.

7. Complete the following sentences with reference to the passage.
(a) Epics are long poems that ………………… .
(b) They may be composed and sung or recited for many years before …………….. .
(c) Nobody knows for certain who ………………………….. .
(d) It is believed that ……………. Homer, who ………….. and who ……………… to all who ……………. .
(e) At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida, from which ………….. .
Question 1.
Complete the following sentences with reference to the passage.
(a) Epics are long poems that ………………… .
(b) They may be composed and sung or recited for many years before …………….. .
(c) Nobody knows for certain who ………………………….. .
(d) It is believed that ……………. Homer, who ………….. and who ……………… to all who ……………. .
(e) At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida, from which ………….. .
Answer:
(a) Epics are long poems that relate the deeds of a great national hero or a great national war.
(b) They may be composed and sung or recited for many years before they are actually written down.
(c) Nobody knows for certain who the author of these early epics is.
(d) It is believed that The Iliad and The Odyssey were composed and recited by a blind poet named Homer, who lived about 900 BCE and who wandered from one Greek city or village to another, singing his poems to all who would receive him in their homes.
(e) At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida, from which flowed many rivers and streams.
Underline the clauses in the above sentences and also the words that link or connect the clauses.
Question 1.
Epics are long poems that relate the deed of a great national hero or a great national war.
Answer:
Epics are long poems – Clause
that relate the deed of a great national hero or a great national war – Clause
![]()
Question 2.
They may be composed and sung or recited for many years before they are actually written down.
Answer:
They may be composed – Clause (they may be)
sung – Clause (they may be)
recited for many years – Clause
before they are actually written down – Clause
Question 3.
Nobody knows for certain who the author of these early epics is.
Answer:
Nobody knows for certain – Clause
who the author of these early epics is – Clause
Question 4.
It is believed that The Iliad and The Odyssey were composed and recited by a blind poet named Homer, who lived about 900 BCE and who wandered from one Greek city or village to another, singing his poems to all who would receive him in their homes.
Answer:
It is believed – Clause
that The Iliad and The Odyssey were composed – Clause
(that The Iliad and The Odyssey were)
recited by a blind poet named Homer – Clause
who lived about 900 BCE – Clause
![]()
Question 5.
At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida, from which flowed many rivers and streams.
Answer:
At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida – Clause
from which flowed many rivers and streams – Clause
Part – II
1. Find and write the Greek and Trojan names used in the story (Part I and II).
Question 1.
Find and write the Greek and Trojan names used in the story (Part I and II).
2. List all the words related to ‘war’ from both parts of the story.
Question 1.
List all the words related to ‘war’ from both parts of the story.
3. Note the following constructions carefully and then use them to express your ideas:
Question 1.
Note the following constructions carefully and then use them to express your ideas:

4. Put the following events in the order in which they took place. Number them accordingly.
Question 1.
(a) The Trojans found a Greek man under the big wooden horse. [ ]
(b) They broke down part of the wall and brought the horse in. [ ]
(c) The cunning Odysseus thought of a plan. [ ]
(d) The Greeks burnt their tents and sailed away. [ ]
(e) Troy was burnt down. [ ]
(f) The Greeks built a big wooden horse. [ ]
(g) The great heroes hid inside the horse. [ ]
(h) The priest warned the Trojans not to break the wall. [ ]
(i) The Trojans were happy to see the Greek ships go. [ ]
(j) The Trojans slept soundly. [ ]
(k) The Greeks came out of the horse and opened the gates. [ ]
(l) The Greek army entered the city. [ ]
Answer:
(a) The Trojans found a Greek man under the big wooden horse. [f]
(b) They broke down part of the wall and brought the horse in. [h]
(c) The cunning Odysseus thought of a plan. [a]
(d) The Greeks burnt their tents and sailed away. [d]
(e) Troy was burnt down. [i]
(f) The Greeks built a big wooden horse. [b]
(g) The great heroes hid inside the horse. [c]
(h) The priest warned the Trojans not to break the wall. [g]
(i) The Trojans were happy to see the Greek ships go. [e]
(j) The Trojans slept soundly. [i]
(k) The Greeks came out of the horse and opened the gates. [j]
(l) The Greek army entered the city. [k]
![]()
5. Form pairs. Imagine you are a pair of Trojans and you have come to know about Odysseus’s plan. Make a counter plan to defeat the Greeks. Write down your plan as you would explain it to your fellow Trojans.
Question 1.
Form pairs. Imagine you are a pair of Trojans and you have come to know about Odysseus’s plan. Make a counter plan to defeat the Greeks. Write down your plan as you would explain it to your fellow Trojans.
6. Identify one example of a main clause and one example of a dependent clause from page 46. (Read the entry regarding clause in the Language Study pages.)
Question 1.
Identify one example of a main clause and one example of a dependent clause from page 46. (Read the entry regarding clause in the Language Study pages.)
Answer:
Many of the Trojans were killed before they could put on their armour.
Many of the Trojans were killed – Main Clause before they could put on their armour – Dependent Clause
![]()
7. Be a writer.
(a) Now read the beginning and end of a sci-fi story given below and complete the story using your imagination.
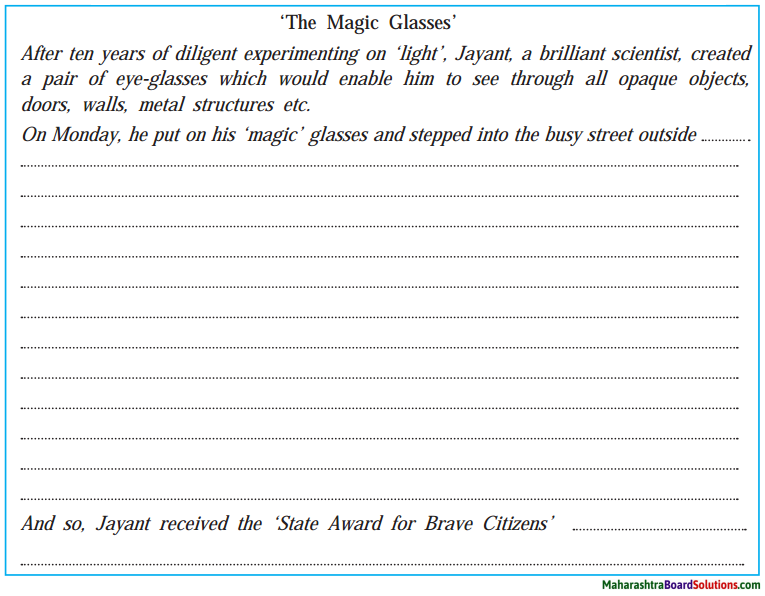
Question a.
Now read the beginning and end of a sci-fi story given below and complete the story using your imagination.
Answer:
‘The Magic Glasses’
After ten years of diligent experimenting on ‘light’, Jayant, a brilliant scientist, created a pair of eye-glasses that would enable him to see through all opaque objects, doors, walls, metal structures, etc. .
On Monday, he put on his ‘magic’ glasses and stepped into the busy street outside …
Everything seemed normal – the traffic, the crowds, etc. Suddenly, Jayant tripped over something and he looked down. It was the metal covering of a manhole. As he looked, he saw a strange sight. There were three little children below, deep under the footpath! How was that possible? Why was no one helping them? They were crying and wailing, sitting in the mess inside the drain. He looked up, and then realized that he had seen them because of his magic eye-glasses.
“Come on, help!” he shouted. “There are children trapped under this footpath, inside this drain!”
Several people stopped. “How do you know?” asked a non-believer.
“What is going on here?” asked an officious- looking policeman.
“Don’t talk – just help!” snapped Jayant, trying to prise open the manhole cover. It was heavy, and several good Samaritans stepped forward to help. Within a few moments, the heavy lid was in their hands.
Everyone peered into the dark, gloomy and smelly drain. They could hear the faint sounds of crying. “I’m going down,” said Jayant. “Those little ones will not be able to bear the poisonous gases much longer.”
With the help of the cooperative by-standers, Jayant went down into the manhole and rescued the little kids – all of whom were below the age of five. Everyone clapped when he came out, dirty and smelly, with the three half-conscious kids.
And so, Jayant received the ‘State Award for Brave Citizens’. ………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. .
![]()
Question b.
Read the following and observe the use of tenses.
‘Last week I witnessed a strange accident. Let ¡ne tell you about it. The signal flashes green. Vehicles start from the opposite direction. They ¡nove fast. Suddenly a speeding motorcyclist tries to cut across, from the wrong side. He is about to collide with a loaded truck. He applies the brakes. He falls and slides out with his bike from under the truck. He comes out unscathed on the other side.’ When an event, which has occured in the past, is narrated in the Present Tense to create a dramatic effect its Tense is called the ‘Dramatic Present Tense’ Now try to relate Jayant s sci-fI story, in brief, in the dramatic past tense.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer:
Jayant wears his magic glasses and steps into the street. He trips over a manhole and looks down. What! Are there three little kids trapped inside the drain under the footpath? Jayant looks around for help, but there are non – believers around him. He tries to prise open the manhole cover. Suddenly, willing hands help him.
The cover is open, and they hear the sounds of children crying. Jayant bravely lowers himself down the dirty drain. He soon rescues the three kids trapped inside. As he hands over the kids to the policeman, the people around clap for him. He is a hero. Jayant later receives the ‘State Award for Brave Citizens’.
![]()
English Kumarbharati 9th Digest Chapter 2.4 The Fall of Troy Additional Important Questions and Answers
Read the following passages carefully and complete the activities :
Simple Factual Activity :
1. Name the following :
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
- The language of The Iliad and The Odyssey : Ancient Greek
- The language of The Mahabharata : Sanskrit
- The most beautiful woman in the world : Helen of Troy.
2. Complete the following sentences :
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
- Odysseus thought of a plan to obtain victory.
- Troy was taken, not by force but by a trick.
- Two great heroes, Menelaus and Odysseus, entered the horse.
- Only one man was left behind to persuade the Trojans to drag the horse into their city.
![]()
3. Write the correct number against the sentences in the order in which it happened :
- They found a Greek with his hands tied together. ]2]
- Let us make a hole in the wall and drag the horse in. [4]
- They saw the huge, wooden horse. [1]
- The Greek told them his tale. [3]
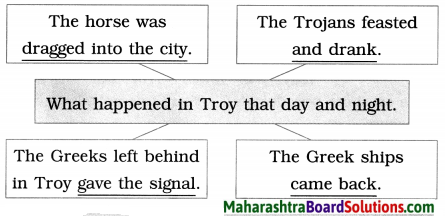
4. Complete the web:
(The answers are given directly and underlined.)
Complex Factual Activity :
Question 1.
How were epics transmitted from generation to generation?
Answer:
Epics were transmitted from generation to generation through songs and recitals for many years before they were actually written down.
![]()
Question 2.
Why is Homer honoured with the title ‘Father of European Poetry?’
Answer:
It is believed that the two great epics of European literature, The Iliad and The Odyssey, were composed and recited by Homer. Hence he has been honoured with the title ‘Father of European Poetry’.
Question 3.
How did Odysseus plan to defeat the Trojans ?
Answer:
Odysseus advised the Greeks to build a great wooden horse, big enough to hold men inside it. Some of their best fighters would hide inside the horse. Then they would burn their tents and pretend to sail away in their ships. But instead of sailing away, they would return at midnight. One man would be left behind with the horse to persuade the Trojans to drag the horse into their city.
After the horse with the soldiers had entered the city, at the appropriate time, the door in the horse would be opened and the soldiers hiding inside would attack Troy. The gates would be opened to allow the remaining Greek soldiers from the ships into the city. The combined force of the Greeks would defeat the Trojans and they would destroy the city of Troy.
Question 4.
What was the reason for Troy to rejoice and celebrate?
Answer:
The Trojans rejoiced and celebrated because after ten long years, the siege was finally over. The tents of the Greeks had been burnt. The shore was deserted. The Greek ships had all gone. The Trojans could go out on the plain and move around as they pleased.
![]()
Activities based on Vocabulary :
Question 1.
Find the synonyms of the following words used in the story :
famous
Answer:
famous – well-known
Question 2.
Write the adjective forms of the following words :
- hospitality
- hero
- history
- poem
Answer:
- hospitality – hospitable
- hero – heroic
- history – historical
- poem – poetic.
![]()
Question 3.
Write from the passage words that sound the same (homophones) as the following :
- grate
- sale
- would
- site
Answer:
- great
- sail
- wood
- sight.
Question 4.
Use the phrase ‘enough to’ in your own sentence :
Answer:
Our school auditorium was big enough to hold a grand function.
Question 5.
Give one word from the passage for :
- great surprise
- pulled out forcibly
Answer:
- great surprise – astonishment
- pulled out forcibly – dragged
![]()
Question 6.
Use these phrases in your own sentences :
(Please refer to textbook page 47 for examples.)
- tired of
- afraid of
- too … to …
Answer:
- We were tired of the long wait for the bus.
- The children were afraid of the commotion.
- The bed was too big to be kept in the room.
Question 7.
Use the phrases in your own sentences :
- so … that
- as soon as
- all that day
- in order to
Answer:
- The teenagers were so excited that it was difficult to control them.
- I opened my umbrella as soon as it began to rain.
- Though their mother shouted at them, the girls lazed about all that day.
- We have to work hard in order to do well in life.
![]()
Activity-based on Contextual Grammar :
Question 1.
Change the voice of the following sentences :
- It is believed that The Iliad and The Odyssey were composed by Homer.
- Nobody knows who the author of these epics is.
Answer:
- People believe that Homer composed The Iliad and The Odyssey.
- It is not known who the author of these epics is.
Question 2.
When the Trojans are asleep, we will attack the city. (Pick out and name the clauses.)
Answer:
we will attack the city – Main Clause.
When the Trojans are asleep – Subordinate Adverb Clause of Time.
Question 3.
The Greek leaders decided to follow the advice of the wise Odysseus. (Frame a Wh-question to get the underlined part as the answer.)
Answer:
Whose advice did the Greek leaders decide to follow?
![]()
Question 4.
Rewrite the sentence using ‘no sooner than’ :
As soon as they were hidden by an island, they had lowered their sails.
Answer:
No sooner were they hidden by an island, than they had lowered their sails.
Question 5.
Rewrite the sentence using ‘too … to’ :
They were so excited that they paid no attention to his words.
Answer:
They were too excited to pay any attention to his words.
Personal Response :
Question 1.
Have you seen any of the stories mentioned in the passage in TV serials or movies?
Answer:
Yes, I have seen both the Ramayana and the Mahabharata as TV serials.
Question 2.
Who are considered to be the authors of the epics ‘Ramayana’ and ‘Mahabharata’ respectively?
Answer:
Sage Valmiki is considered to be the author of ‘The Ramayana’ and Ved Vyasa is considered to be the author of ‘The Mahabharata’.
![]()
Question 3.
What do you think about Odysseus?
Answer:
I think that Odysseus was cunning and used underhand methods to win the war. The war should have been fought and won honestly, not by the use of a trick. Odysseus should not have given such advice and the Greeks should not have taken it.
Question 4.
What, do you think, is needed for a city to be prosperous?
Answer:
To be prosperous, a city must be well situated and have good natural resources, like water and fertile land. It should be safe from enemies. The people and the rulers should be intelligent, sensible and honest. They should also be hard-working. If all these factors are present, then a city will become prosperous.
![]()
Question 5.
Do you think that wars can solve problems?
Answer:
No, they cannot. Problems can be solved only by sitting around a table and sorting out the disputes. The practice of ‘an eye for an eye’ will only end up making the whole world blind. Wars kill people and destroy civilizations.
Question 6.
Do you think the Greeks and Trojans were superstitious? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
There is nothing to indicate that the Greeks were superstitious. But the Trojans were superstitious and believed that the wooden horse would bring them luck if they dragged it into their city.
Question 7.
How could the fall of Troy been avoided?
Answer:
The fall of Troy could have been avoided if the Trojans had been wise enough to detect the ‘wooden horse plot’ hatched by the Greeks. They should also not have been stupid enough to believe the silly story told by the lone Greek. They should at least, have listened to their wise priest who had warned them that the horse could be a trick to destroy Troy.
![]()
Question 8.
What do you think the Trojans should have done when they found the horse?
Answer:
The Trojans should not have believed the Greeks. They should have been cautious and examined the horse minutely. They should also not have been superstitious enough to bring the horse into the city, expecting good luck. They should have heeded the words of the wise priest.
Complex Factual Activities :
Question 1.
How did the location of Troy help it to grow into a very rich, prosperous city?
Answer:
Troy was well situated. In front of it was the sea over which sailed the ships of Troy, carrying goods and grain. At the back rose the high peak of Mount Ida, from which flowed many rivers and streams. The valleys were well-watered and fertile. Cattle fed on the rich grass of the meadows while sheep fed on the slopes of the hills. Thus, it was well situated, both for commerce and agriculture, and grew into a rich, prosperous city.
Question 2.
How were the Trojans protected during wartime?
Answer:
The Trojans had built a strong wall around the city so that no enemy should attack them from the sea. There were huge gates in the wall. In times of war, the gates would be closed, and then the city was like a strong fortress, quite safe from all attack.
It was thus protected by the walls around it as well as by the hills behind.
![]()
Question 3.
Was it enough to use the wooden horse to hide? What was done to make the Trojans take it inside the city?
Answer:
It was not enough to use the wooden horse to hide. It had to be taken inside the city. To achieve this, a Greek, who had been left behind for this very purpose, said that the horse had been left behind as an offering to the god of the sea. It had been made very big so that the Trojans could not take it inside their city. If they did so, the luck would go to the Trojans and not to the Greeks. When they heard this, the Trojans wanted to take the wooden horse inside the city, and they broke their walls to do so.
Question 4.
How did the cunning Greek explain the presence of such a large wooden horse?
Answer:
The cunning Greek said that the Greeks who had left were afraid of the long voyage home. They had made the horse and left it behind as an offering to the god of the sea. It had been made very big so that the Trojans could not take it inside their city. If they did so, the luck would go to the Trojans and not to the Greeks.
![]()
Question 5.
What was the cause of the ten-year-old war between the Greeks and the Trojans?
Answer:
Paris, a prince of Troy, had persuaded Helen, wife of a Greek King called Menelaus, to elope j with him. He had brought her to Troy. The Greeks wanted to take revenge on Troy for the wrong done to Menelaus. This was the cause of the ten-year-old war between the Greeks and the Trojans.
Question 6.
What reckless, thoughtless step did the Trojans take?
Answer:
The reckless/thoughtless step that the Trojans took was to break down part of their wall and drag the wooden horse into the city. They also celebrated and slept soundly.
Question 7.
How did the Greeks enter the city of Troy?
Answer:
When the cunning Greek who had been left behind saw the Greek fleet returning to the shores of Troy, he crept to the wooden horse and gave the signal. The side of the horse opened, and the Greeks who were inside climbed out and opened the gates. * The whole Greek army entered the city.
![]()
Question 8.
How did the Greek ships remain hidden from Troy?
Answer:
As soon as the Greek ships were hidden : by an island, they lowered their sails and dropped anchor. Thus they remained hidden from Troy.
Activities based on Contextual Grammar :
Question 1.
Round their city the Trojans had built a strong wall. (Pick out the verb and state its tense.)
Answer:
had built – past perfect tense.
Question 2.
The wall was so broad that people could stand on it. (Pick out the modal auxiliary and state what it indicates.)
Answer:
could – indicates ability.
![]()
Question 3.
Pick out the clauses from the following sentence and state their type :
He spoke and told them this false tale.
Answer:
He spoke – Main Clause.
(He) told them this false tale – Main Clause.
Question 4.
Rewrite the sentence using ‘which’ :
They saw on the sands the huge, wooden horse.
Answer:
They saw on the sands a huge horse which
was made of wood.
Question 5.
He had brought her to Troy.
(Rewrite beginning ‘She …’)
Answer:
She had been brought to Troy (by him).
Question 6.
The fighting went on daily, but the siege did not end. (Rewrite replacing the underlined word with its verb form.)
Answer:
They fought daily, but the siege did not end.
![]()
Question 7.
Write two present participles from the passage, used as adjectives. Also, write the nouns they modify:
Answer:
| Present Participles used as Adjectives | Nouns they modify |
| 1. leaping | flames |
| 2. weeping | women |
| 3. sleeping | Trojans |
Simple Activities :
Question 1.
Write two compound words of your own.
Answer:
walking stick, fire engine
Question 2.
Make a meaningful sentence using the phrase : ‘among the hills’
Answer:
The tribal communities living among the hills are very poor.
![]()
Question 3.
Spot the error and correct the sentence :
It is believe that The Iliad and The Odyssey were compose by Homer.
Answer:
It is believed that The Iliad and The Odyssey were composed by Homer.
Question 4.
Pick out a present participle from the given sentence :
The valleys were fertile, with corn growing in the fields.
Answer:
present participle – growing.
Question 5.
Identify the type of sentence :
But all the kings and heroes had declared war against the Trojans.
Answer:
Assertive sentence
Question 6.
Find out two hidden words from the word ‘hospitality
Answer:
hospitality – hospital, soapy, (spoil, host)
Question 7.
Form a present participle in which the last letter is doubled.
Answer:
hit-hitting
![]()
Question 8.
Write the following words in alphabetical order.
great, grain, final, fight
Answer:
fight, final, grain, great.
Question 9.
Make a word chain of four more abstract nouns:
revenge →
Answer:
revenge → empathy → youth → health → humility
![]()
Question 10.
Write two compound words of your own.
Answer:
policeman, washing machine
Question 11.
Make a meaningful sentence using the phrase : ‘to follow the advice’
Answer:
Our parents told us to follow the advice of the counseller.
Question 12.
Spot the error and correct the sentence :
Paris himself were killed, also by a poisoned arrow.
Answer:
Paris himself was killed, also by a poisoned arrow.
Question 13.
Use the word ‘sleeping’ as a gerund in your own sentence :
Answer:
I love sleeping.
![]()
Question 14.
Identify the type of sentence, and state ; whether it is affirmative or negative :
The Greeks have gone and the walls are no longer necessary.
Answer:
Assertive sentence (negative)
Question 15.
Find out two hidden words from the word :
celebration
Answer:
celebration – liberate, berate, (clear, brain).
Question 16.
Pick out the verb from the following that forms its past participle by doubling the last letter :
mail, cut, hit, rot
Answer:
rot (rotted)
![]()
Question 17.
Arrange these words in alphabetical order :
wooden, walls, terror, tower
Answer:
terror, tower, walls, wooden
Medium-Level Activities :
Question 1.
Use the word ‘peak’ and its homophone in two separate sentences :
Answer:
(a) Mt. Everest is one peak I wish to climb.
(b) I might take a peek at the proposed site.
Question 2.
The Trojans fought hard. (Use the past perfect progressive tense of the verb.)
Answer:
The Trojans had been fighting hard.
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare a word register for all the words related to ‘war’ from the lesson.
Answer:
war-enemy, attack, fortress, soldiers, siege, battles, armies, heroes, fought, fighting, killed, taken, victory, fighters, terror, death, weapons, armour, conquerors.
Question 4.
Use the word ‘sail’ and its homophone in two separate sentences :
Answer:
(a) The sea gull sat on the sail of the boat.
(b) There is a wonderful sale at the mall this week.
Question 5.
The Greeks burned their tents.
(Use the present perfect tense of the verb.)
Answer:
The Greeks have burned their tents.
![]()
Question 6.
“ But why did the Greeks make such a huge horse?” some of the Trojans asked.
(Rewrite using reported speech.)
Answer:
Some of the Trojans asked why the Greeks had made such a huge horse.
Question 7.
Prepare a word register of all the Greek and Trojan names in the story.
Answer:
Greek and Trojan names – Odysseus, Menelaus, Agamemnon, Troy, King Priam, Hector, Helen, Aphrodite, Iliad, Odyssey, Achilles, Homer, Ilium, Aegean Sea, Mount Ida, Greece, Paris.
Challenging Activities :
Question 1.
Use the word ‘force’ as a noun and a verb in two separate sentences.
Answer:
(a) The policeman had to use a lot of force ; to open the door, (noun)
(b) Parents should not force children into careers j that the children do not like, (verb)
![]()
Question 2.
The Trojans too fought hard and the siege j continued for ten long years. (Pick out the clauses j and write the type of sentence.)
Answer:
The Trojans too fought hard – Coordinate Clause the siege continued for ten long years – Coordinate Clause ; Compound Sentence
Question 3.
Use the words ‘rejoicing’ and ‘voyage’ in a single sentence.
Answer:
There was a lot of rejoicing by the seamen on the voyage home.
Question 4.
It may be a trick that will ruin us. (Pick out the modal and state its function.)
Answer:
may-possibility
Maharashtra State Board Class 9 English Solutions
9th Std English Questions And Answers:
- Invictus Class 9 English Questions And Answers
- A True Story of Sea Turtles Class 9 English Questions And Answers
- Somebody’s Mother Class 9 English Questions And Answers
- The Fall of Troy Class 9 English Questions And Answers
- Autumn Class 9 English Questions And Answers
- The Past in the Present Class 9 English Questions And Answers