Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Plants: Structure and Function Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 Science Chapter 2 Plants: Structure and Function Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Plants: Structure and Function Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Give examples of 3 plants that have:
Question a.
Spiny fruits
Answer:
Jack fruit, Pineapple, Lychee (litchi), Datura
Question b.
Spiny stem
Answer:
Cactus, Wild rose, Catclaw acacia, Silk, Cotton
Question c.
Red flowers
Answer:
Rose, Dahlia, Hibiscus, Tulips,
![]()
Question d.
Yellow flowers
Answer:
Marigold, Daffodil, Sunflower, Daisy
Question e.
Leaves which close at night
Answer:
Mimosa plant, Tallwood, Prayer plant, Gulmohar
Question f.
Single seeded fruits
Answer:
Mango, Lychee, Jamun
Question g.
Many seeded fruits
Answer:
Custard apple, Papaya, Watermelon.
2. Observe any one flower and its various parts and describe it in your own words.
Question a.
Answer:
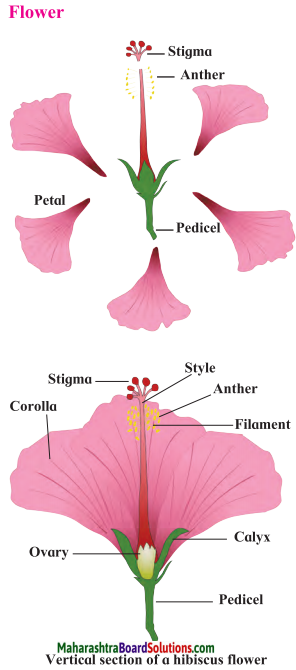
A flower has following parts:
1. Pedicel: (a) Flower may have a long or a short stalk called pedicel, (b) One end of the pedicel is attached to the stem, (c) The other end of the pedicel is expanded and swollen. It is called the receptacle, (d) Petals and other parts of the flower are supported on the receptacle.
2. Calyx: In the bud condition, the petals are covered by leaf like parts called sepals which are green in colour. They form the calyx.
3. Corolla: This is made up of colourful parts called petals.
4. Androecium: (a) This is the male reproductive part of the flower, (b) It consists of stamens, (c) Each stamen is made up of anther and filament.
5. Gynoecium: (a) This is the female reproductive part of the flower, (b) This is made up of carpels, (c) A carpel consists of stigma, style and ovary.
![]()
3. What are the similarities and differences between?
Question a.
Jowar and Moong
Differences:
| Jowar | Moong |
| i. It has fibrous root. | i. It has tap root. |
| ii. It is a monocotyledonous seed. | ii. It is a dicotyledonous seed. |
| iii. It is a rabi crop. | iii. It is a kharif crop |
Similarities:
Jowar and Moong both are angiosperms.
![]()
Question b.
Onion and Coriander
Differences:
| Onion | Coriander |
| i. It is a biennial plant. | i. It is an annual plant. |
| ii. It has monocotyledonous seed. | ii. It has dicotyledonous seeds. |
| iii. It has fibrous root. | iii. It has tap root but later on changes to fibrous root system. |
Similarities:
- Both are used in cooking.
- Both are edible.
- Both belongs to kingdom plantae.
Question c.
Leaves of banana and Leaves of mango
Answer:
| Leaves of banana | Leaves of mango |
| i. It has parallel venation. | i. It has reticulate venation. |
| ii. It is very large in size. | ii. It is small in size. |
| iii. It is a monocotyledonous plant. | iii. It is a dicotyledonous plant. |
![]()
Question d.
Coconut tree and Jowar stalk plant
Answer:
Differences:
| Coconut tree | Jowar stalk plant |
| i. It is tall and has a thick stem | i. It is small and has a thin stem. |
| ii. It has strong root system. | ii. It has weak root system. |
| iii. Each and every part of tree is useful. | iii. Only seeds are useful. |
Similarities:
- Both are from same kingdom plantae.
- Both are autotrophic.
- Both are monocotyledonous plants.
4. Explain the following images in your own words.
Question a.

Answer:
- Diagram A is of maize seed. It is a monocotyledonous seed and does not divide into two equal parts. The plant has fibrous root system.
- Diagram B is of bean seed. It is a dicotyledonous seed and it divides into two equal parts. The plant has tap root system.
![]()
5. Describe the functions of various parts of a plant.
Question a.
Describe the functions of various parts of a plant.
Answer:
The functions of various parts of a plant are as below.
1. Root: (a) Fixation: It anchors the plant body to the soil, so helps in fixation, (b) Absorption: It absorbs water and nutrients from the soil, so helps in absorption, (c) Conduction: The root translocates water and mineral salts into the stem. (d) Storage: A certain amount of food is stored in the root which is utilized as it grows.
(e) Preventing soil erosion: It helps to bind the soil particles and prevent them from being blown away by wind or water.
2. Stem: (a) It supports and holds leaves, flower and fruits, (b) The stem conducts the water and minerals from roots to leaves and fruits, (c) It stores the food.
3. Leaves: (a) It synthesizes food for the plant, (b) Stomata, the tiny openings in the leaf help in gaseous exchange and are responsible for the process of transpiration.
4. Flower: It helps in pollination.
5. Fruit: (a) It protects the seed, (b) It helps in seed dispersal.
6. Seed: A new plant develops from it.
6. Certain properties are mentioned below. Find a leaf corresponding to each property and describe those plants.
Question a.
Certain properties are mentioned below. Find a leaf corresponding to each property and describe those plants.
leaves with smooth surface, leaves with rough surface, fleshy leaf, spines on leaf.
Answer:
- Leaves with smooth surface: e.g. Banana leaf. It is large in size. It is closely rolled up one over the other. Together they look like a trunk but they form only an apparent trunk. It has parallel venation.
- Leaves with rough surface: e.g. Hibiscus leaf. It has reticulate venation. Leaf margin is toothed.
- Fleshy leaf: e.g. Jade plant, water hyacinth. It has fleshy, glossy and smooth leaves. They are coloured jade green and having a slightly red tinge towards the edge of leaves when exposed to higher level of light.
- Spines on leaf: e.g. Opuntia, Ci/cas, kevda. Opuntia is a desert plant. Leaf is thick, fleshy and having spines on it.
![]()
7. Find the plant parts.
Question a.
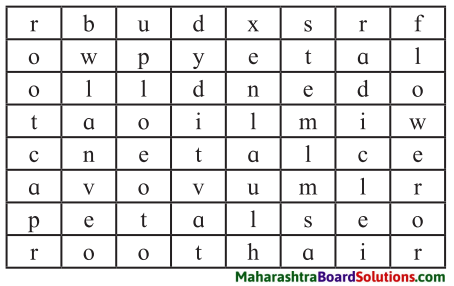
Answer:
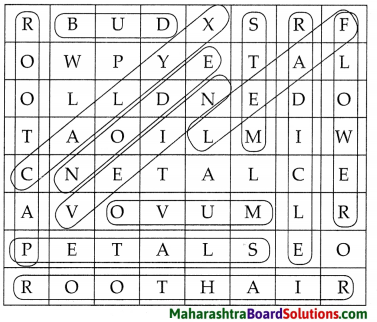
ROOT, ROOT CAP, ROOT HAIR, BUD, PETALS, STEM, RADICLE, FLOWER, LEAF, VEIN, CALYX, NODE, OVUM.
Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Plants Structure And Function Question Answer Activity:
Sketch various types of leaves in Paintbrush on the computer and save the sketches in a folder of your own name.
Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Plants: Structure and Function Important Questions and Answers
Plants Structure And Function Exercise Fill in the blanks:
Plants Structure And Function Class 7 Questions And Answers Question 1.
The part that grows from inside the seed towards the soil is called the …………….. .
Answer:
radicle
![]()
Plants Structure And Function Class 7 Question 2.
The part that grows above the soil from the seed is called the …………….. .
Answer:
plumule
Plants Structure And Function Question And Answer Question 3.
The part of the plant growing below the soil from radicle for support is called …………….. .
Answer:
root
Plants Structure And Function Class 7 Exercise Question 4.
The …………….. protects the root-tip from injuries.
Answer:
root cap
Plants Structure And Function Exercise Question 5.
Roots bearing hair like processes near the root tips are called …………….. .
Answer:
root hairs
Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Plants Structure And Function Question Answer Question 6.
Thread-like or fibre like roots arising from the stem are called ……………. .
fibrous roots
Question 7.
The stem grows above the soil from the …………….. of the sprouting seed.
Answer:
plumule
Question 8.
Leaves come out at the …………….. .
Answer:
nodes
![]()
Question 9.
The part of the stem between two nodes is called …………….. .
Answer:
inter node
Question 10.
The tip or the apical end of the stem is called a …………….. .
Answer:
bud
Question 11.
The broad, spread out part of the leaf is called the …………….. or …………….. .
Answer:
leaf blade, lamina
Question 12.
The tip of the leaf is called the …………….. .
Answer:
leaf apex
Question 13.
Leaves of some plants have a stalk called a …………….. .
Answer:
petiole
Question 14.
The portion of the leaf attached to the stem is called the …………….. .
Answer:
leaf base
Question 15.
Small leaf like structures near the leaf base is called …………….. .
Answer:
stipides
![]()
Question 16.
Flowers may have a long or a short stalk called …………….. .
Answer:
pedicel
Question 17.
One end of the pedicel is attached to the …………….. .
Answer:
stem
Question 18.
…………….. is a male reproductive organ of the flower.
Answer:
Androecium
Question 19.
…………….. is a female reproductive organ of the
Answer:
gynoecium
Question 20.
Androecium consists of …………….. .
Answer:
stamens
Question 21.
Gynoecium consists of …………….. .
Answer:
carpels
Question 22.
Seeds which get divided into two equal parts are called …………….. seeds.
Answer:
dicotyledonous
![]()
Question 23.
Seeds which do not divide into two equal parts are …………….. called seeds.
Answer:
monocotyledonous
Question 24.
Petals and other parts of the flower are supported on the …………….. .
Answer:
receptacle
Question 25.
Sepals are …………….. in colour.
Answer:
green.
Match the columns:
Question 1.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Peepal | a. carpels |
| 2. Maize | b. stamen |
| 3. Androecium | c. parallel venation |
| 4. Gynoecium | d. reticulate venation |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Peepal | d. reticulate venation |
| 2. Maize | c. parallel venation |
| 3. Androecium | b. stamen |
| 4. Gynoecium | a. carpels |
![]()
Question 2.
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Tap roots | a. stem |
| 2. Fibrous roots | b. root |
| 3. Radicle | c. monocotyledonous plants |
| 4. Plumule | d. dicotyledonous plants |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Tap roots | d. dicotyledonous plants |
| 2. Fibrous roots | c. monocotyledonous plants |
| 3. Radicle | b. root |
| 4. Plumule | a. stem |
![]()
Question 3.
| Column A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Leaf-tip | a. petiole |
| 2. Edge of leaf blade | b. leaf margin |
| 3. Portion of leaf attached to stem | c. lamina |
| 4. Stalk of leaf | d. leaf apex |
| e. leaf base |
Answer:
| Column A’ | Column B’ |
| 1. Leaf-tip | d. leaf apex |
| 2. Edge of leaf blade | b. leaf margin |
| 3. Portion of leaf attached to stem | e. leaf base |
| 4. Stalk of leaf | a. petiole |
![]()
Say whether True or False Correct and rewrite the false statements:
Question 1.
Stem grows from radicle.
Answer:
False. Stem grows from the Plumule
Question 2.
Leaf margins may be entire, dentate or lobed.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The leaf blade of leaves in some plants is divided into many small parts called leaflets.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Maize plant has reticulate venation.
Answer:
False. Maize plant has parallel venation
Question 5.
A carpel consists of stigma, style and ovary.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 6.
A stamen is made up of nodes and internodes.
Answer:
False. A stamen is made up of anther filament
Question 7.
The ovary develops into a fruit.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
Fertilized ovules form the seeds.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
A mango fruit contains many seeds.
Answer:
False. A mango fruit contains only one seed
Question 10.
A fruit like cashew have seed outside the fruit.
Answer:
True.
Question 11.
Leaves of some plants do not have a petiole.
Answer:
True
![]()
Question 12.
The peepal leaf has parallel venation.
Answer:
False. It has reticulate venation.
Find the odd one out:
Question 1.
Pea, Moong, maize, groundnut
Answer:
Maize – Its seed is monocotyledonous, while others have dicotyledonous seeds.
Question 2.
Cashew, apple, mango, chikoo
Answer:
Cashew – Its seed is outside the fruit, others have internal seeds.
Question 3.
Stigma, anther, style, ovary
Answer:
Anther – It is a part of androecium, while others are a part of gynoecium.
![]()
Question 4.
Petiole, vein, calyx, apex
Answer:
Calyx – It is a part of flower, whereas others are parts of leaf.
Question 5.
Aerial, stilt, runner, lobed
Answer:
Lobed – It is a type of leaf margin, while others are types of modified roots.
Answer the following in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
Which types of roots do the fenugreek, spinach and onion plants have?
Answer:
- Fenugreek and spinach have tap roots with a few secondary roots whereas onion has fibrous root.
- Fenugreek roots also have some nodules which contain nitrogen fixing bacteria.
Question 2.
What are called prop roots?
Answer:
Roots emerging from the trunk and branches of a banyan tree grow towards the soil. These roots are called prop roots.
![]()
Question 3.
What is called reticulate venation?
Answer:
- A leaf is divided into two equal parts by a single mid-vein which lies along the midline of the leaf blade.
- Secondary veins arise from the mid-vein. They are branched and form a network or reticulum. Such a type of venation is called reticulate venation.
Question 4.
What is called parallel venation?
Answer:
In a leaf all the veins are parallel, running from the leaf base to the leaf apex. Such a venation is called parallel venation.
Question 5.
What is pollination?
Answer:
After maturity, anthers burst and the pollen grains which are released fall on the stigma. This process is called pollination.
Question 6.
Why are the underground parts of plants like radish, carrot, beet and sweet potato thick, fleshy and swollen? Which parts of the plant are they?
Answer:
The underground parts of plants like radish, carrot, beet and sweet potato are thick, fleshy and swollen because they store food in the form of starch. These are the root part of the plant.
![]()
Distinguish between:
Question 1.
Tap roots and fibrous roots.
Answer:
| Tap roots | Fibrous roots |
| 1. Roots of some plants produce secondary roots that grow obliquely and spread far and wide in the soil. This type of root is called a tap root. | 1. Thread like or fibre roots arising from the stem are called fibrous roots. |
| 2. It is found in dicotyledonous plant. | 2. It is found in monocotyle-donous plant. |
Question 2.
Dicotyledonous seeds and monocotyledonous seeds.
Answer:
| Dicotyledonous seeds | Monocotyledonous seeds |
| 1. Seeds which get divided into two equal parts are called dicotyledonous seeds. | 1. Seeds which do not divide into two equal parts are called monocotyledonous seeds. |
| 2. Dicotyledonous seeded plants have tap root system. | 2. Monocotyledonous seeded plants have fibrous root system. |
![]()
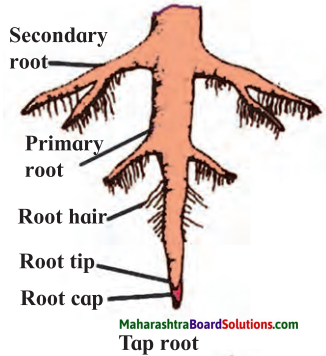
Draw neat and labelled diagram for the following:
Question 1.
Tap root
Answer:
Question 2.
Parts of a leaf.
Answer:
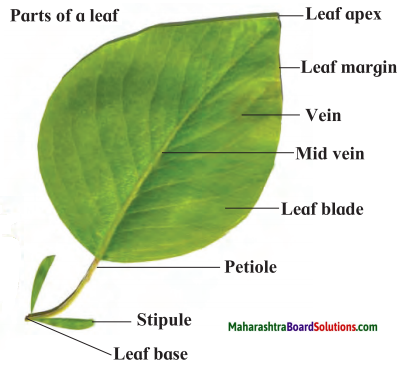
Question 3.
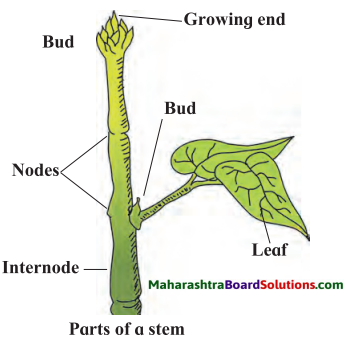
Parts of stem
Answer:
![]()
Do as directed:
Question 1.
Certain properties are mentioned below. Find a leaf corresponding to each property and describe those plants.
Answer:
- Leaves with smooth surface: e.g. Banana leaf. It is large in size. It is closely rolled up one over the other. Together they look like a trunk but they form only an apparent trunk. It has parallel venation.
- Leaves with rough surface: e.g. Hibiscus leaf. It has reticulate venation. Leaf margin is toothed.
- Fleshy leaf: e.g. Jade plant, water hyacinth. It has fleshy, glossy and smooth leaves. They are coloured jade green and having a slightly red tinge towards the edge of leaves when exposed to higher level of light.
- Spines on leaf: e.g. Opuntia, Cycas, kevda. Opuntia is a desert plant. Leaf is thick, fleshy and having spines on it.
Use your brainpower!
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What would have happened if plants like tamarind, banyan and mango had fibrous roots?
Answer:
If plants like banyan, mango, tamarind had fibrous roots they would get uprooted and fall even with a little strong wind as the roots would not be able to support and anchor the trees firmly.
Question 2.
What will happen if the root-tip is injured?
Answer:
- Root cap helps the root to grow downward It protects the sensitive part of the root and eases the movement of the root through the soil.
- Injury of the root tip causes the root to grow randomly and it also may lead to injury of the sensitive part of the root.
![]()
Question 3.
Which types of roots do the fenugreek, spinach and onion plants have?
Answer:
- Fenugreek and spinach have tap roots with a few secondary roots whereas onion has fibrous root.
- Fenugreek roots also have some nodules which contain nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Question 4.
Of what use to a plant are the insects flitting about around its flowers?
Answer:
- The insects try to suck the nectar from the flowers and in that process the pollen grains stick to their legs.
- When they sit on another flower the pollen grain stick to the stigma and the pollination takes place. Thus, these insects help in the pollination.
Observe the figure and answer the questions given.
1.
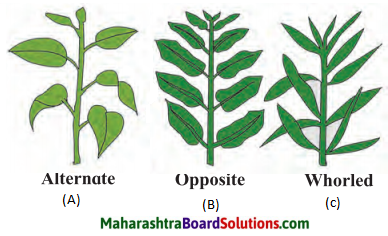
Question a.
What is shown in the picture?
Answer:
The picture shows the arrangement of leaves on the stem.
![]()
Question b.
What arrangement is shown in (A), (B), and (C)?
Answer:
(A) Alternate (B) Opposite (C) Whorled
2.
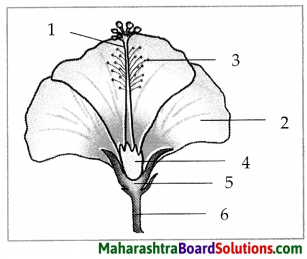
Question a.
Lable parts 1 to 6.
Answer:
- Gynoecium or carpel
- Corolla
- Androecium (Stamen)
- Ovary
- Corolla
- Pedicel
Question b.
Name the female reproductive part.
Answer:
Gynoecium
![]()
Question c.
Name the colourful part of the flower.
Answer:
Corolla
Question d.
Which part develops into fruit?
Answer:
Ovary
Question e.
Which pa pollination?
Answer:
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of flower is called pollination.
7th Std Science Questions And Answers:
- The Living World: Adaptations and Classification Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Plants: Structure and Function Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Properties of Natural Resources Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Nutrition in Living Organisms Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Food Safety Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Measurement of Physical Quantities Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Motion, Force and Work Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Static Electricity Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Heat Class 7 Questions And Answers
- Disaster Management Class 7 Questions And Answers
