Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Civics Solutions Chapter 5 The State Government Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 The State Government Questions And Answers Maharashtra Board
The State Government Class 8 Questions And Answers Chapter 5 Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 The State Government Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Choose the correct option and complete the statements:
Question 1.
The winter session of Maharashtra Legislature takes place at ……………… .
(a) Mumbai
(b) Nagpur
(c) Pune
(d) Aurangabad
Answer:
(b) Nagpur
Question 2.
The ……………. appoints the Governor.
(a) Chief Minister
(b) Prime Minister
(c) President
(d) Chief Justice
Answer:
(c) President
![]()
Question 3.
The right to summon the state legislature lies with the …………… .
(a) Chief Minister
(b) Governor
(c) President
(d) Speaker
Answer:
(b) Governor
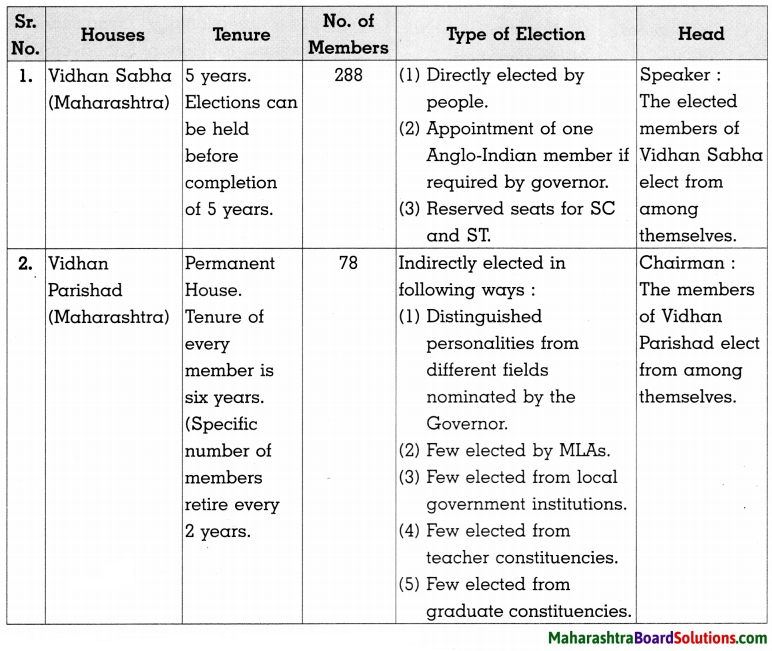
2. Complete the table:
Question 1.
Answer:
3. Write short notes on:
Question 1.
The Governor:
Answer:
- The Governor is the titular/ nominal head of the state.
- The government of the state is run in the name of the Governor.
- He is appointed by the President and holds the office during the pleasure of the President.
- He appoints the Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers.
- As the head of the state, he enjoys certain important Legislative and Executive powers.
- He has a right to summon the session of the state legislature.
- In case the need arises, he can issue ordinance to make the law.
![]()
Question 2.
Functions of the Chief Minister:
Answer:
The functions of the Chief Minister, as an Executive head of the state, are as follows:
- To form an able Council of Ministers giving maximum representation to various regions and social groups.
- To distribute portfolios considering the political experience, administrative skills, public awareness, leadership, etc. of the ministers.
- To develop proper cooperation and coordination between Departments, resolve their conflicts and make them work effectively.
- To lead the state, frame proper policies and implement them effectively, intervene in issues of the state and solve them for the comfort of the people.
4. Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
Enumerate the functions of the Speaker of the Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly).
Answer:
The Speaker is elected by the members of Vidhan Sabha. His functions are as follows:
- To prepare the order of daily proceedings in the House.
- To carry out the proceedings of the House in a disciplined manner.
- To suspend the members for misbehaviour or misconduct.
- To control and guide the proceedings of the House during sessions.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did the Constitution adopt a federal system for India?
Answer:
- India is a country having large geographic expanse.
- It has a multicultural population.
- There is a great diversity in language, religion, ways of life and regional characteristics.
- It would not have been possible to govern such a huge country from a centralised place. Hence, the Constitution adopted a federal system of India.
Question 3.
What are the considerations of the Chief Minister while allocation of portfolios?
OR
Formation of Council of Ministers is a challenging task for the Chief Minister.
Answer:
After the formation of the Council of Ministers, the Chief Minister has to distribute portfolios among the ministers. He has to consider following aspects:
- Some portfolios are of prime importance while others are of secondary importance. He has to select appropriate people for each portfolio.
- He has to consider the experience i and the efficiency of the ministers he has selected.
- The political experience and administrative skills of the concerned ministers is also taken into consideration by him.
- Other factors like the awareness of public issues, effective leadership, etc. are also considered by him.
- If the government is in a coalition, he has to distribute portfolios appropriately among the constituent parties in the alliance.
Do you know?

- At present, India has 29 Constituent States and 7 Union Territories.
- All Constituent States have Legislative Assemblies.
- Out of the 7 Union Territories, only Delhi and Puducherry have Legislative Assemblies (Vidhan Sabha).
- Jammu and Kashmir, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh have Bicameral Legislatures (both the Houses).
![]()
Project:
Visit official website of the Maharashtra Government and collect information of various ministers and the working of their respective departments.
Class 8 Civics Chapter 5 The State Government Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct option and complete the statements:
Question 1.
The Indian Union has totally …………….. constituent states.
(a) 22
(b) 25
(c) 29
(d) 32
Answer:
(c) 29
Question 2.
In India, only ……………… states have Bicameral legislatures.
(a) three
(b) five
(c) six
(d) seven
Answer:
(d) seven
![]()
Question 3.
Maharashtra’s legislature conducts minimum ………………. sessions in a year.
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(b) three
Question 4.
Distinguished personalities from various fields are nominated by the ……………. to the Vidhan Parishad.
(a) Chief Minister
(b) Speaker
(c) Governor
(d) Chairman
Answer:
(c) Governor
Question 5.
When the legislature is not in session and need arises to make law, the Governor can issue ……………….. .
(a) a Bill
(b) a Proposal
(c) an Ordinance
(d) an Order
Answer:
(c) an Ordinance
State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the False statements and rewrite:
Question 1.
States in India have been formed on the basis of population.
Answer:
False. States in India have been formed on the basis of language.
Question 2.
In exceptional circumstances, elections to Vidhan Sabha can be held before the completion of 5 years.
Answer:
True.
![]()
Question 3.
Absence of cooperation and coordination between Departments can affect the working of the government.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
The people look at the Governor as a ‘Problem Solver’.
Answer:
False. The people look at the Chief Minister as a ‘Problem Solver’.
Question 5.
Every constituent state has a Vidhan Parishad.
Answer:
False. Every constituent state has a Vidhan Sabha.
Find and write:
Question 1.
The State having a government machinery different than other states
Answer:
Jammu and Kashmir
Question 2.
The Vidhan Bhavan of Maharashtrais located in:
Answer:
Mumbai
Question 3.
The member of Vidhan Sabha are called:
Answer:
MLA
![]()
Question 4.
Major challenges faced by Maharashtra:
Answer:
Terrorism and Naxalite movements
Question 5.
The place where the winter session of Maharashtra’s legislature is conducted:
Answer:
Nagpur.
Complete the following concept maps:
Question 1.
Answer:
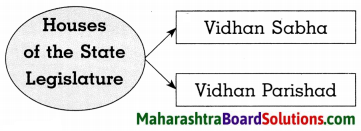
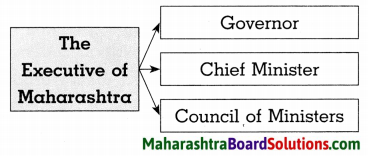
Question 2.
Answer:
Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Session:
Answer:
- A session is a meeting where members of both the Houses meet.
- Maharashtra’s legislature conducts minimum three sessions in a year.
- The budget session and monsoon session of Maharashtra is held in Mumbai while the winter session is held at Nagpur.
- The Governor has the right to summon and conclude the session.
- During the session, new laws are passed, existing laws are amended and out-dated laws are repealed.
- The sessions are conducted under the leadership and guidance of the Speaker and the Chairman.
![]()
Question 2.
Council of Ministers:
Answer:
- The Council of Ministers consists of the Chief Minister and other ministers.
- The leader of the majority party in Legislative Assembly is appointed as the Chief Minister by the Governor.
- The Governor also appoints the other ministers chosen by the Chief Minister to form Council of Ministers.
- Framing appropriate laws, working for the welfare of the people, governing the state efficiently are some of the functions of the Council of Ministers.
- The Chief Minister along with his Council of Ministers is collectively responsible to the Legislative Assembly.
Write short notes on:
Question 1.
Powers of the Governor:
Answer:
The Governor enjoys certain important Legislative and Executive powers as the head of the state.
- The Bills passed by Vidhan Sabha and Vidhan Parishad are converted into laws only after receiving his assent.
- He has the right to summon the session of the state legislature and to conclude it.
- He can issue an ordinance to make law, on important subject if required, when the Legislature is not in session.
- He appoints the Chief Minister and the other Council of Ministers.
Explain the following statements with reasons:
Question 1.
The Governor is the titular/nominal head of the state.
Answer:
- The Constitution has granted Executive powers to the Governor as the head of the state.
- The government of the state is run in the name of the Governor.
- But in reality, the administration is carried out by the Chief Minister. Hence, the Governor is the titular/ nominal head of the state.
![]()
Question 2.
Vidhan Parishad (Legislative Council) is a permanent House.
Answer:
- All members of the Vidhan Parishad (MLCs) do not retire at the same time.
- A specific number (1/3rd) of the members retire every 2 years.
- These vacant seats are filled again by conducting fresh elections for those seats.
- The tenure of each member is 6 years.
- Since the Vidhan Parishad is never fully dissolved, it is a permanent House.
Question 3.
India has 29 constituent states, but 31 Vidhan Sabha.
Answer:
- According to the Constitution, every constituent state must have a Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly).
- India has 29 constituent states and each state has its Vidhan Sabha.
- Out of the 7 Union Territories in India, Delhi and Puducherry have Vidhan Sabha. Hence, India has 29 constituent states, but 31 Vidhan Sabha.
Question 4.
The Chief Minister’s post is most important in the state.
Answer:
- The Chief Minister can select his Council of Ministers according to his choice.
- He can ask any of his ministers to resign.
- Framing policies of public welfare and developing the state in a progressive manner entirely depends upon the Chief Minister.
- The Chief Minister leads the state and people look at him as a problem solver.
- His intervention in solving the problems of the state comforts the people.
Hence, all these executive powers makes the Chief Minister’s post most important in the State.
Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
Mention the eligibility conditions for contesting Vidhan Sabha elections.
Answer:
Following are the eligibility conditions for candidates contesting for Vidhan Sabha elections:
- He/She should be a citizen of India.
- He/She should have completed 25 years of age.
- He/She should be a resident of Maharashtra.
![]()
Question 2.
Do you consider Maharashtra to be progressive state?
Answer:
- Industrial development has taken place in Maharashtra on a large scale. It has many industries based on modern technology.
- Maharashtra’s literacy rate is higher than many other states.
- It has a rich tradition of saints and social reformers who have nurtured progressive thinking among people.
- Maharashtra is leading in many fields like education, health, agriculture, sports, tourism, etc.
- Maharashtra has been a land of Movements. Many important movements like the Labour movement, Farmer’s movement have been initiated here.
- Similarly, many progressive laws have been passed in Maharashtra.
- Maharashtra is facing many challenges like terrorism, poverty, crime, Naxalite movements, etc. Even then, I feel that Maharashtra is a progressive state.
8th Std Civics Questions And Answers:
- Introduction to the Parliamentary System Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Indian Parliament Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Union Executive Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The Indian Judicial System Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- The State Government Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers
- Bureaucracy Class 8 Civics Questions And Answers