Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Sociology Important Questions Chapter 4 Processes of Social Change in India Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Sociology Important Questions Chapter 4 Processes of Social Change in India
1A. Complete the following statements by choosing the correct alternative given in the brackets and rewrite it.
Question 1.
___________ is the process of the use of unbiotic power for the mass production of goods. (digitalisation, urbanisation, industrialisation)
Answer:
industrialization
Question 2.
Process of industrialization spread from ___________ to other regions of the world. (Asia, Europe, Australia)
Answer:
Europe
![]()
Question 3.
In the process of ___________ human society is transformed from a state pre-industrial to an industrial. (urbanisation, modernisation, industrialisation)
Answer:
industrialization
Question 4.
The development of industries led to the of workplaces. (urbanisation, digitalisation, mechanisation)
Answer:
mechanization
Question 5.
The use of precision techniques and accuracy in production is required in ___________ (mechanization, computerisation, capital)
Answer:
mechanization
Question 6.
In the process of mechanization workers led to feel ___________ from the process of production. (alienated, integrated, neutral)
Answer:
alienated
Question 7.
The high mechanization and automation of industrial processes naturally depend on ___________ resources available. (social, financial, natural)
Answer:
financial
![]()
Question 8.
Industries required skilled workforce and ___________ of apprentices at the workplace. (specific training, unskill, eatables)
Answer:
specific training
Question 9.
Early industries required skilled and unskilled ___________ workforce to complete various tasks at all levels. (animal, human, machines)
Answer:
human
Question 10.
Special institutes like ___________ are established to impart technical education and also for professional education. (management training, urbanisation, modernisation)
Answer:
management training
Question 11.
Industrialisation led to ___________ on the basis of specialisation and expertise. (capital, labour, division of labour)
Answer:
division of labour
Question 12.
Modern ___________ was a result of industrialisation. (education, facilities, urbanisation)
Answer:
urbanisation
Question 13.
___________ is a typical feature of urban living. (urbanism, rural, tribal)
Answer:
urbanism
Question 14.
Urbanisation is a ___________ way process. (two, three, four)
Answer:
two
![]()
Question 15.
Urbanisation consists of large ___________ number of people from rural to urban areas. (outward flow, overflow, inward flow)
Answer:
inward flow
Question 16.
The gradual emergence of factories led to the ___________ of people from rural and tribal areas, to the factory locations. (communication, migration, specialisation)
Answer:
migration
Question 17.
The flux of people for the purpose of employment has resulted in cities getting ___________ (overpopulated, less dense, shut down)
Answer:
overpopulated
Question 18.
Overpopulated cities are expanding and turning into ___________ such as Mumbai, Pune. (rural, metropolises, tribal)
Answer:
metropolises
Question 19.
The place of residence and one’s place of which work drift apart with the passage of time which means ___________ (a division of labour, spatial segregation, capital intensive)
Answer:
spatial segregation
![]()
Question 20.
Urbanisation led to a ___________ gathering of people of different gender, sexuality, caste, creed, class, language and so forth. (homogeneous, barriers, heterogeneous)
Answer:
heterogeneous
Question 21.
Urbanism as a ___________ of life. (solution, way, tradition)
Answer:
way
Question 22.
Secondary modes of security control in urban areas are ___________ (law, belief, morals)
Answer:
law
Question 23.
Division of labour is based on one’s ___________ and ___________ (skills and expertise, knowledge and experience, limitations and unskilled)
Answer:
skills and expertise
Question 24.
The term modernisation was coined by ___________ (Anderson, Daniel Lerner, Giddens)
Answer:
Daniel Lerner
Question 25.
___________ is the application of modern science to human affairs. (Globalisation, Digitalisation, Modernisation)
Answer:
Modernisation
Question 26.
Self-criticism, willingness to introspect critically, is also an aspect of ___________ thinking. (logical, critical, analytical)
Answer:
critical
Question 27.
___________ means the approach and ability to provide logical explanations for any phenomenon. (rationalism, science, art)
Answer:
rationalism
![]()
Question 28.
Scientific reasoning explains ___________ relationships between factors. (mortal, casual, immortal)
Answer:
Causal
Question 29.
Being ‘modern’ cannot be limited to only using modern devices or gadgets but there should be a willingness to receive ___________ ideas. (new, old, superstitious)
Answer:
new
Question 30.
The new economic policy means ___________ policy. (PNG, LPG, CNG)
Answer:
LPG
Question 31.
LPG stands for Liberalisation, Privatisation and ___________ (Googlisation, Globalisation, Geometrisation)
Answer:
Globalisation
Question 32.
Process of ___________ opened up the skies for Indian economy. (modernisation, digitalisation, globalisation)
Answer:
globalisation
Question 33.
This new economic policy brought in much ___________ and criticism. (superstitions, beliefs, skepticism)
Answer:
skepticism
Question 34.
The principle of ___________ is an integral part of globalisation as a process of change. (laissez faire, loss, profit)
Answer:
laissezfaire
Question 35.
___________ is a process where government control services are opened up for private service providers. (privatisation, marketisation, globalisation)
Answer:
privatisation
![]()
Question 36.
Privatisation has encouraged many service providers to indulge in ___________ (donation, profiteering, social service)
Answer:
profiteering
Question 37.
Privatisation is mainly oriented to ___________ (production, marketing, profits)
Answer:
profits
Question 38.
Globalisation led to increase in production, this in turn has led to large-scale ___________ (marketisation, privatisation, liberalisation)
Answer:
marketisation
Question 39.
The term ___________ was coined by Capgemini and MIT. (bhakti movement, digital transformation, laissez-faire)
Answer:
digital transformation
Question 40.
___________ has led to frequent changes in business models. (consumerism, digitalisation, materialistic)
Answer:
digitalisation
Question 41.
Now a days we use ___________ for various purposes such as production, surgery, robotics etc. (artificial intelligence (AI), machines, capital)
Answer:
artificial intelligence (AI)
Question 42.
___________ has escalated the speed of the processes with a far greater extent of accuracy. (industrialisation, modernisation, digitalisation)
Answer:
digitalisation
![]()
Question 43.
___________ is based on technology, innovation, research and development. (modernisation, urbanisation, digitalisation)
Answer:
digitalisation
Question 44.
In the field of education, we are working towards ___________ technology for the purpose of education in the 21st century. (integrating, managing, old)
Answer:
integrating
Question 45.
Industrialization with the growth of cities has caused the breakdown of the ___________ (nuclear families, joint families, marriage)
Answer:
joint families
Question 46.
India is now an integral part of the ___________ economy. (personal, social, global,)
Answer:
global
Question 47.
___________ and ___________ has opened up a range of options to the user with a click of button. (computerisation and digitalisation, modernisation and urbanisation, transportation and communication)
Answer:
computerisation and digitalisation
Question 48.
Digitization has increased ___________ networking. (cultural, economic, social)
Answer:
social
1B. Correct the incorrect pair and rewrite it.
Question 1.
(a) Growth Of industries – Industrialisation
(b) Alienated from the process of production – Mechanisation
(c) Extent of mechanization and automation depend on – Finances
(d) Skilled workforce – Capital
Answer:
(d) Skilled workforce – Specific Training
![]()
Question 2.
(a) Formation of economic classes – Industrialisation
(b) Industrial expansion – Modernisation
(c) Tasks assigned on the basis of – Division of labour
(d) Emergence of metropolis – Urbanisation
Answer:
(b) Industrial expansion – Spatial Segregation
Question 3.
(a) Metropolises – Mumbai, Pune
(b) Heterogenous gathering of people – Urbanisation
(c) Secondary modes of security control – Family
(d) A way of life – Urbanism
Answer:
(c) Secondary modes of security control – Law, city traffic signal, police, etc
Question 4.
(a) Based on one’s skills of expertise – Division of labour
(b) Modernisation – Daniel Lerner
(c) Scientific reasoning – Causal Relationships
(d) Shift to secular and rational values from spiritual values – Nationalism
Answer:
(d) Shift to secular and rational values from spiritual values – Rationalism
Question 5.
(a) Scepticism and criticism – Self-criticism
(b) Technological advancement – Industrialisation
(c) Ability to explain the constructive and destructive aspect – Critical thinking
(d) New economic policy – LPG
Answer:
(a) Scepticism and criticism – New economic policy
Question 6.
(a) Free trade and free competition – Laissez Faire
(b) Private service provider – Insurance, radio, etc.
(c) Increase production need – Distribution
(d) To make max profit – Privatisation
Answer:
(c) Increase production need – Marketisation
Question 7.
(a) Increased consumerism – Large production
(b) Sharing of resources – Nationalist movement
(c) Materialistic – Globalisation
(d) All nations interdependent – Global economy
Answer:
(b) Sharing of resources – Technological outsourcing
![]()
Question 8.
(a) Use of digital technology – Digitalisation
(b) Digital transformation – Capgemini and MIT
(c) Use of computers – Computerisation
(d) Technology-driven – Rural
Answer:
(d) Technology-driven – Digitalisation
Question 9.
(a) Migration of people from rural to urban – Westernisation
(b) Developed scientific temperament – Modernisation
(c) India is part of the global economy – Globalisation
(d) Impact of computers on various aspects of life – Digitalisation
Answer:
(a) Migration of people from rural to urban – Urbanisation
1C. Identify the appropriate term from the given options in the box and rewrite it against the given statement.
Rational Outlook, Factory System, Division of Labour, Technological Advancement, Digitalisation, Mechanisation, Labour Intensive System, Global Economy, Marketisation, Industrialisation, Capital Intensive, Industrial Growth, Law and City Police, etc., Liberal Principle, Urbanisation, Modernisation, Scientific Temperament, Critical Thinking, Laissez-Faire, Profiteering, Interdependence, Outsourcing, Capgemini of MIT, Digitalisation, Computerisation.
Question 1.
Establishment of large factories for the purpose of production.
Answer:
Factory System
Question 2.
Use of heavy machines and techniques for the production of goods and services.
Answer:
Mechanisation
Question 3.
In industrialisation extent of automation and mechanisation.
Answer:
Capital Intensive
Question 4.
The need for skilled force at the workplace.
Answer:
Labour Intensive System
Question 5.
Individuals’ qualities, skills, efficiency, education, and training are the determinants.
Answer:
Division of Labour
Question 6.
A process of migration of rural population to urban areas.
Answer:
Urbanisation
![]()
Question 7.
Advanced means of commutation are the pre-requisites.
Answer:
Industrial Growth
Question 8.
Means of secondary control.
Answer:
Law and City Police etc.
Question 9.
Daniel Lerner coined the term.
Answer:
Modernisation
Question 10.
The development of a scientific way of understanding and explaining any phenomenon.
Answer:
Scientific Temperament
Question 11.
The approach and ability to provide logical explanations for any phenomenon.
Answer:
Rational Outlook
Question 12.
Use of advanced technology in industries.
Answer:
Technological Advancement
Question 13.
Ability to explain the constructive and destructive aspects of a phenomenon.
Answer:
Critical Thinking
![]()
Question 14.
Opening up of the economy to private players.
Answer:
Liberal Principle
Question 15.
Free trade and free competition.
Answer:
Laissez-Faire
Question 16.
Privatisation has encouraged many service providers to indulge in it.
Answer:
Profiteering
Question 17.
Increase in production results in large scale of.
Answer:
Marketization
Question 18.
Parts of a product being manufactured in one country and assembled in faraway places is an example of.
Answer:
Interdependence
Question 19.
It has made all people and nations interdependent.
Answer:
Global Economy
Question 20.
People go beyond geographical borders, to perform specific tasks without moving out from their location.
Answer:
Outsourcing
Question 21.
The integration of digital technologies into everyday life.
Answer:
Digitalisation
Question 22.
The term ‘digital transformation’ was coined by.
Answer:
Capgemini of MIT
![]()
Question 23.
Expansion of the use of computers in all walks of life.
Answer:
Computerisation
1D. Correct the underlined words and complete the statement.
Question 1.
Social change means a change in social life.
Answer:
Social change means a change in social structure.
Question 2.
The domestic production system is replaced by traders.
Answer:
The domestic production system is replaced by a factory system.
Question 3.
The process of industrialisation was started in India.
Answer:
The process of industrialisation was started in Europe.
Question 4.
Industrialisation leads to agrarianism.
Answer:
Industrialisation leads to urbanisation.
Question 5.
Urbanisation is a process of migration of rural populations to tribal areas.
Answer:
Urbanisation is a process of migration of rural population to urban areas.
Question 6.
Daniel Lerner coined the term industrialisation.
Answer:
Daniel Lerner coined the term modernisation.
Question 7.
Urbanism is a way of society.
Answer:
Urbanism is a way of life.
![]()
Question 8.
Urbanisation implies controls and obligations by traditional bodies.
Answer:
Urbanisation implied controls and obligations by civil administrations.
Question 9.
Industrialisation leads to unity.
Answer:
Industrialisation leads to urbanisation.
Question 10.
Urbanisation leads to homogeneity.
Answer:
Urbanisation leads to heterogeneity.
Question 11.
Industrialisation is a process whereby human energy to produce was replaced by the social process for higher production.
Answer:
Industrialisation is a process whereby human energy to produce was replaced by mechanical processes for higher production.
Question 12.
This is the era of computerisation and modernisation.
Answer:
This is the era of computerisation and digitalisation.
Question 13.
Digitalisation is based on belief.
Answer:
Digitalisation is based on technology.
Question 14.
The main aim of digitalisation is the importance of the material.
Answer:
The main aim of digitalisation is important to customers.
![]()
Question 15.
The principle of‘Laissez-Faire’ is an integral aspect of medicines.
Answer:
The principle of ‘Laissez-Faire’ is an integral aspect of globalisation.
Question 16.
The principle of ‘Laissez-Faire’ is originally a Greek term.
Answer:
The principle of ‘Laissez-Faire’ is originally a French term.
Question 17.
Being ‘modern’ means openness to traditional ideas.
Answer:
Being ‘modern’ means openness to new ideas.
Question 18.
Self- criticism, willingness to introspect critically is also an aspect of spiritual thinking.
Answer:
Self-criticism, willingness to introspect critically is also an aspect of critical thinking.
Question 19.
Globalisation involves two processes like liberalisation and generalisation.
Answer:
Globalisation involves two processes like liberalisation and privatisation.
Question 20.
Globalisation is the process of the creation of a global city.
Answer:
Globalisation is the process of the creation of a global economy.
Question 21.
Globalisation is a process that ‘opened up the skies’ for the Japanese economy.
Answer:
Globalisation is a process that ‘opened up the skies’ for the Indian economy.
Question 22.
The flux of people from all over the country to urban areas has resulted in cities getting popular.
Answer:
The flux of people from all over the country to urban areas has resulted in cities getting overpopulated.
Question 23.
Industrialisation is the way by which people go beyond geographical borders, without moving out from their location.
Answer:
Outsourcing is the way by which people go beyond geographical borders without moving out from their location.
![]()
Question 24.
Digital transformation means radically improving knowledge.
Answer:
Digital transformation means radically improving performance.
Question 25.
Maintain individual privacy in the web world is a great challenge in urbanisation.
Answer:
Maintaining individual privacy in the web world is a great challenge in digitalisation.
Question 26.
Due to growth in newer technologies business modules get frequent repetitions.
Answer:
Due to growth in newer technologies business modules get frequent changes.
Question 27.
Cap Gemini is a Spanish data processing company.
Answer:
Cap Gemini is a French data processing company.
2. Write short notes.
Question 1.
Privatisation/Private enterprise
Answer:
- Privatisation signifies the process wherein, the government transfers ownership, management, and control of the public sector enterprises to the private sector entities.
- Allows the private sector to set up industries in the field earlier reserved for the public sector.
- Privatisation has substantially reduced the role of the government in economic activities.
- Privatisation is an allied process that accompanies globalisation.
- Under the process of privatisation, reducing the involvement of the state in economic activities and increasing the involvement of the private sector are expected.
- The government has been thereby trying to mobilise resources for improving the efficiency of the remaining public sector units.
- Under the policy of globalisation, various countries have adopted the process of privatisation.
Question 2.
Liberalisation/Liberal Principle
Answer:
- Liberalisation implies the withdrawal of restrictions on industry and business.
- It also means opening up the economy to private players.
- It has more reliance on ‘Laissez-Faire’ means free trade and free competition.
- It encourages foreign trade by a reduction in the tariff rates.
- Adopting uniform exchange rate.
- Removal of import/export duties.
- Duty-free access to foreign goods and services.
![]()
Question 3.
Negative Impact of globalisation
Answer:
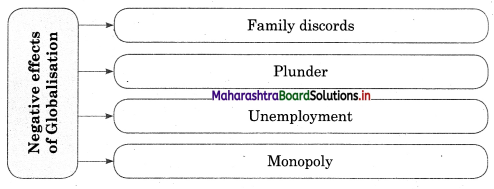
- There is a considerable increase in the immigration of the young technocrats to the developed countries, leaving behind aging parents.
- There is an increase in the family arguments and break up of more and more marriages and families.
- The role of the state has been greatly curtailed in economic activities.
- The role of the state-owned, managed, and controlled public sector has also been curtailed by privatisation and disinvestment.
- The state also withdrawing from essential social services like health insurance and education by means of privatisation.
- There is the cultural invasion of western culture. The traditional value and norms of behaviour have slackened up.
- Consumerism and the pursuit of materialist culture are increasing.
- The conflict of traditional and modern values has threatened the traditional culture of India.
Question 4.
Modernisation
Answer:
- It is a process of social transformation.
- It develops new attitudes, new values, and social relationships. There is a shift to secular and rational values from spiritual-religious values.
- It has paved a way for developing a scientific temperament. Emphasis has been set on the need for empirical evidence in support of given arguments.
- It encompasses social, economic, political, religious, and intellectual changes. There is a willingness to receive new ideas, to examine daily events, literature, culture, art, customs, beliefs from a critical point of view.
- Modernisation is a current term of an old process of social change.
3. Write differences.
Question 1.
Liberalisation and Globalisation
Answer:
| Liberalisation | Globalisation |
| (i) Meaning: Liberalisation refers to the removal of undue restrictions and eliminations of bureaucratic controls on productive activities and paves the way for economic development. | (i) Meaning: Globalisation refers to the integration of the domestic economy with the world economy. |
| (ii) Liberalisation is a means to achieve globalisation.
e.g. reduction in tariff is a liberal measure. |
(ii) Globalisation can be realised through external liberalisation. e.g. if the tariff is reduced, transfer of resources, goods, etc., can be made easier. |
| (iii) Effect: Liberalisation has given a boost to foreign trades. | (iii) Effect: Globalisation has led to the increase in foreign direct investment and technical collaboration. |
| (iv) Manifestations: Abolishing industrial licenses, scrapping the MRTP limit, etc., are the measures adopted to liberate the Indian economy. | (iv) Manifestations: Relaxing the FEAR/FEMA regulations, eliminating the trade barriers, providing tax concessions and other incentives to the foreign investors. |
Question 2.
Globalisation and Privatisation
Answer:
| Globalisation | Privatisation |
| (i) Globalisation refers to “all those processes by which the people of the world are incorporated, into a single world society.” | (i) Privatisation means “transferring of ownership rights from public sector to the private sector”. |
| (ii) Eliminating the trade barriers, relaxing the FERA/FEMA regulations, and other incentives to the foreign investors. | (ii) The policy of disinvestment is adopted to privatise the public sector enterprises. |
| (iii) Globalisation leads to sharing of resources, goods, and capital across the country. | (iii) The public sector enterprises are taken over by the private sector. It enables the country to improve the efficiency of these enterprises. |
| (iv) It has adversely affected agriculture and is a cause of misery in the rural area. | (iv) Their policies lead to an increase in unemployment. |
Question 3.
Privatisation and Liberalisation
Answer:
| Privatisation | Liberalisation |
| (i) Privatisation means reducing the involvement of the public sector and increasing the involvement of the private sector in the country’s economic activities. | (i) Liberalisation means reducing or relaxing unnecessary restrictions over economic activities. |
| (ii) The policy of reduction investment is adopted to privatise the public sector. | (ii) Automatic approval to the foreign technology, providing tax concessions and other incentives to the foreign investors, etc. |
| (iii) The public sector enterprises are taken over by the private sector. It enables the country to improve the efficiency of these enterprises. | (iii) Liberalisation has given a boost to the industries in the private sector and given momentum to the industrial development of India. |
| (iv) Their policies lead to an increase in unemployment. | (iv) It has encouraged the culture of consumerism. |
4. Explain the following concepts with examples.
Question 1.
Industrialisation
Answer:
- The process of industrialisation was started in England in the 17th and 18th Centuries.
- Industrialisation means the process whereby human energy to produce was replaced by mechanical processes and machines to enable higher production.
- The village population migrated to the industrial centres in the search of employment.
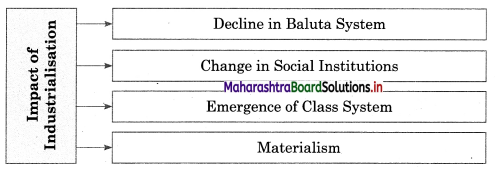
- Industrialisation signifies the mechanisation of the production process, growth of industries, division of labour and specialisation, capital and labour intensive, etc.
- Due to industrialisation decline in the Baluta system, the emergence of industry-oriented economy, the emergence of the class system, etc.
- Examples:
- Industrial hubs like Mumbai, Pune, Bangalore.
- The transformation of an urban area into an IT hub is an example of industrialisation.
![]()
Question 2.
Modernisation
Answer:
- The term modernisation was coined by Daniel Lerner.
- Modernisation is the process where there is the use of scientific and rational thinking that is deep-seated.
- Modernisation has led to changes in values, beliefs, and norms.
- Modernisation is a process of transformation from traditional society to technological modern society.
- It is a notion of rationalism and the ability to provide scientific and logical explanations for any phenomenon.
- Being ‘Modern’ means not only using modern devices or gadgets but also openness to receive new ideas, examine alternatives, find new pathways, use creative ways to solve problems, do critical thinking, etc.
- Examples:
- Acceptance of rational scientific outlook
- Individualism
- Secularism.
Question 3.
Globalisation
Answer:
- The process of globalisation in the Indian context received an impetus in 1991.
- In India, New Economic Policy was declared in 1991 by Finance Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh.
- Globalisation is basically an economic process. It proposes to integrate the national economy with the global economy.
- There is free flow not only of capital, goods, and technology but also of skilled human resources and ideas across the globe.
- It proposes to remove barriers in the free movement of human beings and broaden their mental horizons.
- Due to globalisation, the impact of the western culture and decline of the traditional values as well as changes in the social institutions like family, marriage, etc.
- We are beset with the positive and negative impacts of globalisation.
- Examples: International companies such as Pepsi, Coca-Cola, McDonald’s.
Question 4.
Rational outlook
Answer:
Rational outlook refers to an approach that is based on reasoning, and the ability to provide logical explanations for any phenomenon.
Explanation:
A rational outlook is based on the idea of rationalism or reasoning. This means Here, one seeks to establish laws that link facts and which govern social life. To have a rational outlook means that one’s view of a situation or a problem or an event is understood on the basis of reason. This refers to the development of a scientific way of understanding and explaining any phenomenon. Scientific reasoning explains causal relationships between factors. There is a shift to secular and rational values from spiritual-religious values.
For example, non-rational explanation of all-natural calamities are the expressions of God’s anger.
Rational explanation: Scientific explanation for natural calamities.
![]()
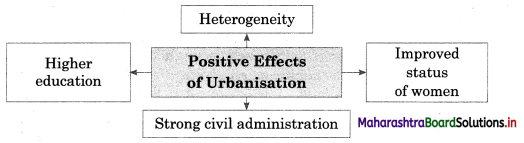
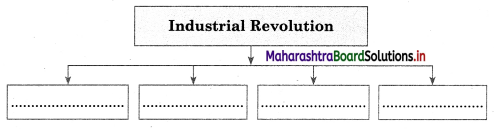
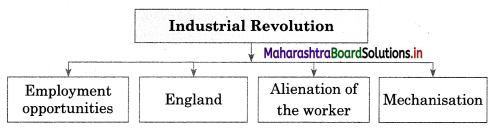
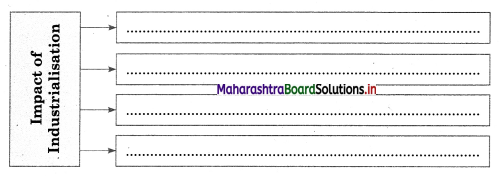
5A. Complete the concept map.
Question 1.

Answer:
Question 2.
Answer:
Question 3.
Answer:
Question 4.

Answer:

![]()
Question 5.

Answer:

Question 6.

Answer:
Question 7.
Answer:
Question 8.
Answer:
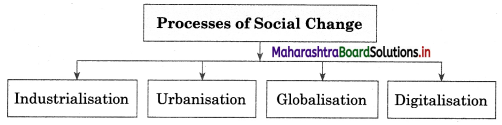
Question 9.

Answer:

5B. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
Question 1.
In industrialisation workers feel alienated from the process of production.
Answer:
This statement is True.
- In industries for large-scale production, purpose capitalists started automation and mechanisation of workplaces.
- It led to mass production due to which machine-made goods were much cheaper than hand-made goods.
- The use of machines gives more precision, techniques, and accuracy in production.
- This leads to workers feeling less important in the work of production and they get alienated from the process of production.
![]()
Question 2.
Industrialisation leads to Urbanisation.
Answer:
This statement is True.
The process of industrial growth led to the large-scale emergence of factories. This in turn resulted in migration to places nearer the factory sites, leading to the growth of towns, which soon became cities and then metropolitan cities.
Since cities become the centres of trade, commerce, industry, education, etc, People from rural areas migrate towards urban areas for getting employment.
The process of urbanisation is the consequence of industrialisation as urbanisation is characteristic of industrialisation.
Question 3.
Urbanisation implies primary means of social control.
Answer:
This statement is False.
- Urbanisation means a flux of people migrated from all over the country to urban areas.
- Due to that urban centres are overpopulated. The hold of customs, traditions, religion on people’s behavior, has diminished.
- The urban environment and way of life are more materialist, radical, commercial, individualist, and non-conforming.
- Urbanisation implies controls and obligations that are not administered by traditional bodies such as panchayats There are secondary modes of security control, e.g., law enforcement systems such as traffic signals, city police, etc.
- So, in urban areas, secondary means of social control are useful such as law, city police, etc.
Question 4.
Raj stays in Mumbai and has never faced any problems with commutation.
Answer:
This statement is False.
- As per the above statement, Raj stays in Mumbai i.e., a Metropolitan city.
- Which is overpopulated and has a shortage of means of transportation.
- In metropolises, it is not uncommon to find people spending 3-4 hours commuting to and from the workplace.
- So, Raj stays in Mumbai means every day he must face problems in commutation.
Question 5.
Modernisation is rational and scientific change.
Answer:
This statement is True.
- Modernisation is the application of modern science to human affairs.
- It is linked to the notion of rationalism; the approach and ability to provide logical explanations for any phenomenon.
- Scientific reasoning explains causal relationships between factors. There N is a shift to secular and rational values from spiritual-religious values.
- Persons who claim to be modern are willing to examine daily events, literature, culture, art, customs, beliefs from a critical point of view and be able to explain the constructive and destructive aspects of a phenomenon.
- The ultimate aim of this rational and scientific perspective in modernisation is to make human life better and satisfactory.
Question 6.
In digitalisation, with one click of a button, one can open up a web world.
Answer:
This statement is True.
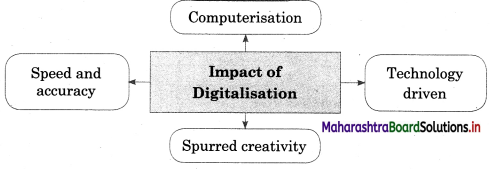
- The impact of changes resulting from computerisation and digitisation. Processes have had far-reaching changes in
- Indian society in terms of access to knowledge artificial intelligence, e-governance, e-commerce, e-learning, e-trade, e-shopping, etc., the list is endless.
- Digitalisation has sped up the processes of data mining and data management and has made this world a global village.
- The click of a button can open up a range of options to the user through a very simple procedure.
Question 7.
Digitisation is the use of digital technologies for handling data of various nature
Answer:
This statement is True.
- Programming, information technology, and computer science have aided the process of computerisation, which in turn has digitised processes for several sectors, e.g., education, banking, revenue, taxation, marketing, etc.
- Digitisation is based on technology, innovation, research, and development.
- Digitisation had led to frequent changes in business models due to growth in newer technologies, e.g., Artificial
- Intelligence is used for various purposes such as production, manufacturing, surgery, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
Globalisation is an eco-friendly process.
Answer:
This statement is False.
- Due to globalisation, the environmental problem has become more serious.
- To gain more and more profit, industrialists and multinational companies are excessively using natural resources.
- Because of this, the intensity of environmental problems such as deforestation, pollution, rise in atmospheric temperature, etc.
6. Give your personal response.
Question 1.
Do you think, during the pandemic situation of COVID-19, people in India will accept digitalised ways for work from home? Why?
Answer:
Being a student of HSC, I feel yes most Indians will accept digitalised ways for work. Because being Indian this pandemic situation is such an eyewash situation for all. As our nation is a developing nation and if we want economic survival then most Indians will start to learn E-Content, even though this will be our first step towards standing in the market, but most Indians will accept digitalized way as this is need of the hour.
Question 2.
Being vigilant student how you will do an online awareness campaign on COVID-19.
Answer:
As COVID-19 is a pandemic and a contagious disease. I will create an online group of my friends and we will remain connected online while staying at home. United through social media groups we will jointly put posters and graffiti on social media to make the general public aware of the deadly disease.
Question 3.
Do you think in the 21st Century people prefer living in a nuclear family? Why?
Answer:
As we are in 2020, in the modern era, so I think yes people will prefer living in a nuclear family. Since the nuclear family provides them with extra space, quality of life and mainly in the nuclear family status of women are high, gender equality, the standard of living is high as the couple is working, less impact of traditional beliefs and superstitions. So, one will prefer individuality i.e. nuclear family.
7. Answer the following question in detail. (About 150-200 words)
Question 1.
You belong to a generation that has been by and large part of digital India. Discuss how digitalisation has brought about positive and negative effects.
Answer:
(i) Positive effects of digitalisation
- Due to digitalisation, closer cross-border ties.
- It makes our lives better and easy. It is a most essential technology.
- It makes people become more efficient and this leads to increased productivity.
- Digitalisation saves time, cost and gives quick and precise service,
- Digitalisation boosts the country to do cashless transactions.
- For example, for filing Income Tax returns, obtaining Birth and Death Certificates from the Municipal Corporation, for online admission, for declaration of election results, etc. Nowadays all these processes make use of digitalisation and it has radically transformed the processes, compared to those used just a few decades ago.
![]()
(ii) Negative effects of digitalisation
- The excessive use of digital technology has health hazards like affecting sleep.
- Preventing children from engaging in physical activity that resulting in cases of obesity among children.
- In extreme cases, there can be mental illnesses like social isolation, aggression, etc.
- In short, it affects social, physical, and mental health.
- Due to the acceptance of digitalisation big industries take over the smaller ones.
- One of the major problems is individual privacy in the web world. This is always under threat.