Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 History Important Questions Chapter 5 India: Social and Religious Reforms Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th History Important Questions Chapter 5 India: Social and Religious Reforms
1A. Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the statement.
Question 1.
The practice of Sati was abolished by a law passed in the year __________
(a) 1829
(b) 1830
(c) 1831
(d) 1832
Answer:
(a) 1829
Question 2.
Raja Ram Mohan Roy started a philosophical discussion circle named ‘ __________’.
(a) Prarthana Samaj
(b) Arya Samaj
(c) Satyashodhak Samaj
(d) Atmiya Sabha
Answer:
(d) Atmiya Sabha
![]()
Question 3.
The Brahmo Samaj was founded in the year __________
(a) 1826
(b) 1827
(c) 1828
(d) 1829
Answer:
(c) 1828
Question 4.
The Mughal emperor of India conferred the title of ‘____________’ on Ram Mohan Roy.
(a) Pandit
(b) Raja
(c) Alamgir
(d) Badshah
Answer:
(b) Raja
Question 5.
__________ has its origins in Paramhamsa Sabha.
(a) Prarthana Samaj
(b) Arya Samaj
(c) Brahmo Samaj
(d) Satyashodhak Samaj
Answer:
(a) Prarthana Samaj
Question 6.
__________ established ‘Scientific Society’ for Muslims.
(a) Mahatma Phule
(b) Sir Sayyad Ahmad
(c) Swami Dayanand
(d) Tarabai Shinde
Answer:
(b) Sir Sayyad Ahmad
Question 7.
__________ participated in the Vykom Satyagraha in Travancore against untouchability.
(a) Ramaswamy Naikar
(b) Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay
(c) Dr. Ambedkar
(d) Swami Vivekananda
Answer:
(a) Ramaswamy Naikar
![]()
Question 8.
Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj was strongly opposed to __________
(a) Bajubandi
(b) Setubandi
(c) Rajbandi
(d) Rotibandi
Answer:
(d) Rotibandi
1B. Find the incorrect pair from group ‘B’ and write the corrected one.
Question 1.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (a) Sati Act | 1829 |
| (b) Restriction of Press | 1830 |
| (c) Arya Samaj | 1875 |
| (d) Ramkrishna Mission | 1897 |
Answer:
Restriction of Press – 1824
2A. Write the names of historical places/persons/events.
Question 1.
Governor-General who abolished Sati in 1829 –
Answer:
Lord William Bentinck
Question 2.
The company that put restrictions on the freedom of the press –
Answer:
The British East India Company
Question 3.
The social reformer who severely criticized untouchability in his book ‘Vital Vidhwamsan’ –
Answer:
Gopalbaba Walangkar
![]()
Question 4.
Editor of ‘Ain-i-Akbari’ written by Abul Fazl –
Answer:
Sir Sayyad Ahmad Khan
Question 5.
The movement led by Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar at Mahad –
Answer:
Satyagraha of Chavadar Tank
Question 6.
Founder of ‘Independent Labour Party –
Answer:
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar
Question 7.
The ruler who organised‘Sahabhoj for all castes –
Answer:
Maharaja Sayajirao Gaikwad
Question 8.
The ruler who opposed ‘Vyavasaybandi’ –
Answer:
Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj
2B. Choose the correct reason from those given below and complete the sentence.
Question 1.
The progress of Indian society was stunted because of __________
(a) superstitions
(b) the orthodox way of life
(c) caste discriminations
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
![]()
Question 2.
Sati was abolished in 1829 because __________
(a) a law was passed by Lord William Bentinck abolishing this inhuman practice
(b) the people of India wanted this custom to be abolished
(c) the Brahmin class wanted Sati to be abolished
(d) women wanted to put an end to this custom
Answer:
(a) a law was passed by Lord William Bentinck abolishing this inhuman practice
Question 3.
The Mughal emperor conferred the title of‘Raja’ on Ram Mohan Roy because __________
(a) Ram Mohan Roy was the emperor’s favourite
(b) Ram Mohan Roy had gone to England to plead the case of the Mughal emperor
(c) Ram Mohan Roy was an efficient lawyer
(d) Ram Mohan Roy visited England
Answer:
(b) Ram Mohan Roy had gone to England to plead the case of the Mughal emperor
Question 4.
Swami Vivekanand established the Ramkrishna Mission because __________
(a) he was asked by his Guru to do so
(b) he wanted to compete with other organisations
(c) he wanted to serve the needy people
(d) so that many people join his Mission
Answer:
(c) he wanted to serve the needy people
3. Complete the following concept map.
Question 1.
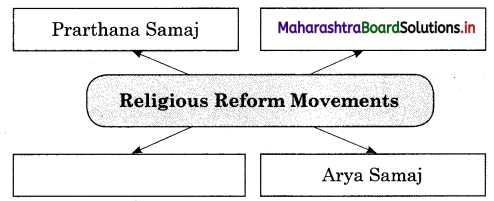
Answer:
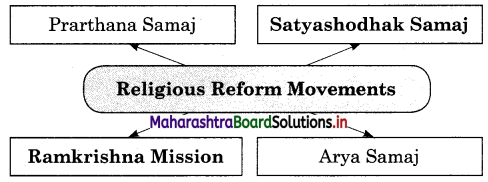
Question 2.
| Social Reformers | Participated in Movements |
| 1. Maharshi V.R.Shinde | ……………………………….. |
| 2. ………………………………… | Kala Ram Temple, Nasik |
| 3. Ramaswamy Naikar | ……………………………….. |
| 4. Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay | ……………………………….. |
| 5. ……………………………….. | Non-Brahmanical Movement, Kolhapur |
Answer:
| Social Reformers | Participated in Movements |
| 1. Maharshi V. R. Shinde | Parvati Temple, Pune |
| 2. Dr. B. R. Ambedkar | Kala Ram Temple, Nasik |
| 3. Ramaswamy Naikar | Vykom Satyagraha, Travancore |
| 4. Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay | Quit India Movement |
| 5. Rajarshi Shahu Maharaj | Non-Brahminical Movement, Kolhapur |
4A. Write short notes.
Question 1.
Arya Samaj.
Answer:
Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Swami Dayanand Saraswati in 1875.
- Regarded Vedas as holy.
- Rejected discrimination based on caste differences.
- Encouraged education of women, widow remarriage, and inter-caste marriage.
![]()
Question 2.
Tarabai Shinde.
Answer:
Tarabai Shinde:
- Born in 1839.
- She demanded gender equality.
- She was the first woman to challenge the patriarchal system.
- She was of the opinion that religious systems suppress women because religions are created by men.
4B. Explain the following statements with reasons.
Question 1.
The British wanted to bring progress to Indian society.
Answer:
The progress of Indian society was stunted because of superstitions, an orthodox way of life, caste discriminations, false social notions, lack of curiosity, and rationality that prevailed on a large scale. The British felt the need to create a new society that was based on the values of ‘Freedom, Equality, Fraternity, and Humanism’.
Question 2.
Raja Ram Mohan Roy was the first Indian to oppose the custom of Sati.
Answer:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy witnessed his brother’s wife commit Sati and this disturbed him deeply. He pointed out that none of the religious texts mentioned the practice of Sati as a prescribed religious obligation. It is because of his efforts that a law was passed by Governor-General Lord William Bentinck abolishing the practice of Sati in 1829.
Question 3.
Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar used print media to create public awareness.
Answer:
Dr. B. R. Ambedkar knew the importance of print media. For him, it was the best instrument to create awareness and to build the movement for social equality. Therefore, he began to publish his own newspapers namely ‘Mooknayak’, ‘Bahishkrut Bharat’, ‘Janata’ and ‘Samata’.
5. State your opinion.
Question 1.
Tarabai Shinde was the first Indian woman to challenge the patriarchal system.
Answer:
Tarabai Shinde was of the opinion that religious systems suppress women because religious systems are created by men. Therefore, she took a brave step in expressing her thoughts in a brave manner in her essay on women’s rights. In this essay, she not only discussed reforms like widow remarriage, women’s education, abolition of Sati but demanded greater gender equality.
![]()
Question 2.
Arya Samaj was founded by Swami Dayanand Saraswati in 1875.
Answer:
Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Swami Dayanand Saraswati in 1875.
- Regarded Vedas as holy.
- Rejected discrimination based on caste differences.
- Encouraged education of women, widow remarriage, and inter-caste marriage.
6. Answer the following question with the help of the given points.
Question 1.
Discuss the role played by Religious Reform Organisations in the field of religious awakening.
(a) Prarthana Samaj
(b) Satyashodhak Samaj
(c) Arya Samaj
(d) Ramkrishna Mission
Answer:
(a) Prarthana Samaj:
- Had its origins in Paramhamsa Sabha.
- Founded by Dadoba Pandurang Tarkhadkar.
- Founding members like Dr. Atmaram Pandurang, Justice M. G. Ranade, Dr. R. G. Bhandarkar opposed idol worship and emphasized monotheism.
- Opened schools for girls, orphanages, and night schools for workers.
- Focussed on gender equality, wiping outcaste discriminations, and appreciating the values of mundane life.
(b) Satyashodhak Samaj:
- Founded in 1873 by Mahatma Jotirao Phule in Pune.
- Cracked a whip on the social customs and practices which pushed the Indian masses into a miserable state.
- Showed a new path to artisans, workers, and other downtrodden people.
- Characteristics of Satyashodhak Samaj included monotheism, rejection of the authority of Vedas and Puranas, acceptance of rationality, opposition to the dominance of priests and idol worship, etc.
- Mahatma Phule and his wife Savitribai Phule started a school for girls.
- His work was continued by Gopalbaba Walangkar who criticized untouchability in his book ‘Vital Vidhwamsan’.
- Shivram Janba drew attention to the problems of deprived women like Murali, Jagatini, and Devdasi.
(c) Arya Samaj:
- Founded by Swami Dayanand Saraswati in 1875.
- Regarded Vedas as holy.
- Rejected discrimination based on caste differences.
- Encouraged education of women, widow remarriage, and inter-caste marriage.
(d) Ramkrishna Mission:
- Swami Vivekananda founded the Ramkrishna Mission in 1897.
- Focussed on serving needy people, working for people affected by famine, health care for the sick people, education for women, etc.
- It also gave a message to the Indian youth to get up to awaken and keep moving until the goal is achieved.
![]()
Question 2.
What role did the following social reformers play in bringing about social change?
(a) Sir Sayyad Ahmad Khan
(b) Tarabai Shinde
(c) Maharshi Vitthal Ramji Shinde
(d) Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay.
(e) Ramaswamy Naikar
Answer:
(a) Sir Sayyad Ahmad Khan:
- Was born in 1817 in Delhi.
- Fluent in Urdu, Persian, Arabic, and English.
- Established ‘Scientific Society’ for Muslims.
- After returning from England he founded the Mohammadan Anglo-Oriental College in 1875 which later developed into ‘Aligarh Muslim University.
- Started a periodical entitled ‘Mohammadan Social Reformer’.
- Worked for the propagation of modern education, science, and technology.
(b) Tarabai Shinde:
- Born in 1839.
- She demanded gender equality.
- She was the first woman to challenge the patriarchal system.
- She was of the opinion that religious systems suppress women because religions are created by men.
(c) Maharshi Vitthal Ramji Shinde:
- Opened Marathi schools and schools for technical training in Parel, Deonar in Mumbai under the umbrella of ‘Depressed Classes Mission’ that was established by him.
- Worked to create public awareness about the issues affecting the depressed classes like entry into temples (for example, protestations for the right of entry in Parvati temple in Pune), agricultural conference, and joint electorate system of depressed classes.
(d) Kamaladevi Chattopadhyay:
- Was an active volunteer of Congress.
- She convinced Mahatma Gandhi to let women participate in salt satyagraha, and she participated in the satyagraha.
- She worked for women’s rights.
- Organized demonstrations to draw attention to the problems of workers and farmers.
- Emphasized justice to female agricultural labourers.
- Insisted that women working in factories should have the necessary facilities.
- Followed up the issue of maternity leave to women.
- Imprisoned by the British for one year for participating in the Quit India Movement.
![]()
(e) Ramaswamy Naikar:
- Born in ‘Erode’ in Tamil Nadu in 1879.
- He became a follower of Mahatma Gandhi’s philosophy and worked for propagating the use of ‘Swadeshi’.
- He participated in the Vykom Satyagraha in Travancore against untouchability.
- Started the ‘Swabhiman Andolan’ in Tamil Nadu.
- Fought against the varna system and child marriage.
- He was addressed as ‘Periyar’ or Great Soul because of his magnanimous work.
- Was a great speaker and author.
- Took a radical position on issues like women’s rights and family planning.