Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Important Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro and Macro Economics
1. A. Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
The term ‘Micro’ is derived from the Greek word.
(a) Makros
(b) Maikros
(c) Mikros
(d) Mikrosoft
Options:
(1) a
(2) b
(3) c
(4) d
Answer:
(3) c
Question 2.
The term ‘micro’ and ‘macro’ economics were first coined and used by Norwegian Economist.
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Ragnar Frisch
(c) Dr. Marshall
(d) Prof. Ricardo
Options :
(1) a
(2) b
(3) d
(4) c
Answer:
(2) b
![]()
Question 3.
Statements related to features of Micro economics.
(a) The study of individual unit
(b) It deals with income theory
(c) It splits the whole economy
(d) It suggests suitable economic policies to promote economic growth
Options :
(1) a, b, c and d
(2) a and b
(3) a, c and d
(4) b and d
Answer:
(3) a, c and d
Question 4.
Scope of Micro economics.
(a) Theory of factor pricing
(b) Theory of general price level
(c) Theory of product pricing
(d) Theory of economic welfare
Options :
(1) a, b, c and d
(2) a and b
(3) a, c and d
(4) b and d
Answer:
(3) a, c and d
Question 5.
Theory of Economic Welfare.
(a) Efficiency in production
(b) Efficiency in consumption
(c) Overall economic efficiency
(d) Efficiency in social activities
Options :
(1) c and d
(2) a, b and d
(3) a, b and c
(4) b, c and d
Answer:
(3) a, b and c
Question 6.
Main features of macro economics.
(a) Income theory
(b) Lumping method
(c) Price theory
(d) Study of aggregates
Options :
(1) a, b and c
(2) b, c and d
(3) a, b and d
(4) Only b
Answer:
(3) a, b and d
Question 7.
Importance of Micro Economics.
(a) Free market economy
(b) Functioning of an economy
(c) Basis of welfare economy
(d) Foreign Trade
Options :
(1) a, b, c and d
(2) a, b and c
(3) a, b and d
(4) a, c and d
Answer:
(4) a, c and d
![]()
Question 8.
Micro Economic is based on certain assumption.
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Pure capitalism
(c) Full employment
(d) Fluctuations in the national income
Options :
(1) b, c and d
(2) c and d
(3) a, b and c
(4) a, c and d
Answer:
(3) a, b and c
Question 9.
Importance of Macro-economics.
(a) National Income
(b) Economic development
(c) Price determination
(d) General level of employment
Options :
(1) b, c and d
(2) a, b and d
(3) a, b, c and d
(4) None of these
Answer:
(2) a, b and d
Question 10.
Scope of Macro economics.
(a) Theory of Income and employment
(b) Theory of General Price level and inflation
(c) Theory of Economic growth and development
(d) Theory of Factor Pricing
Options :
(1) a and b
(2) a, b and c
(3) a, c and d
(4) a, b, c and d
Answer:
(2) a, b and c
Question 11.
Factors of Production which make contribution in production process.
(a) Land
(b) Profit
(c) Labour
(d) Transport
Options :
(1) a, b and c
(2) a and c
(3) b, c and d
(4) All of above
Answer:
(2) a and c
B. Complete the correlation:
1. Macro economic theory : Income and employment:: Micro economics : ………………
2. General equilibrium : Macro economics :: ……………… : Micro economic
3. Macro Economics : Large :: Micro Economics : ………………
4. Classical Economist: ……………… :: Neo-classical Economist: Prof. Alfred Marshall J
5. Prof. Alfred Marshall : Principles of Economics :: ……………… : General theory of Employment, Interest and Money
6. Study of Individual unit: ……………… :: Study of aggregates : Macro economics
7. Theory of Economic welfare : Scope of Micro economics :: ……………… : Scope of Macro economics
8. Land: Rent:: ……………… : Wages
9. Capital: ……………… :: Entrepreneur : Profit
10. ……………… : Demand and Supply Analysis :: Theory of Income and employment : Consumption and Investment function
11. Macro economics : Entire economy :: Micro economics: ………………
12. Study of the whole economy : Lumping ’ method :: Study of small individual unit : ………………
Answers:
- Price theory
- Partial equilibrium
- Small
- Adam Smith
- Maynard Keynes
- Micro economics
- Theory of Economic growth and development
- Labour
- Interest
- Theory of Product Pricing
- Small part of economy
- Slicing method
(C) Give economic terms.
(1) Micro economics derived from the Greek word.
(2) Macro economics derived from the Greek word.
(3) Study of large economic unit.
(4) Study of small or millionth part of economic unit.
(5) Price determination of individual commodity by forces of demand and supply.
(6) Price determination of factor of production for contributing to the production process.
(7) Maximum satisfaction of people due to efficiency in the allocation of resources.
(8) Determination of the prices of goods and services as well as factors of production.
(9) Equal distribution of produce goods and services to the society for consumption.
(10) Production of most desired goods and services.
(11) Equilibrium position of an individual economic unit.
(12) Assumption of Micro economics i.e. other things remaining constant.
(13) Micro economics does not deal with macro problems.
(14) Economic decisions are taken at individual levels without intervention of government.
(15) Explanation of effects of tariffs, exchange rate, etc.
(16) Micro economics explain various complex economic situation with the help of economic models.
(17) Equilibrium position of whole economy.
Answer:
(1) Mikros
(2) Makros
(3) Macro economics
(4) Micro economics
(5) Theory of Product Pricing
(6) Theory of Factor Pricing
(7) Theory of Economic Welfare
(8) Price Theory
(9) Efficiency in Consumption
(10) Overall Economic Efficiency
(11) Partial equilibrium
(12) Ceteris Paribus
(13) Limited scope
(14) Free Market economy
(15) Foreign Trade
(16) Economic Model building
(17) General Equilibrium Analysis
![]()
(D) Find the odd word out:
(1) Prof. Pigou, Prof. Samuelson, Adam Smith, J. R. Hicks.
(2) Individual consumer, Individual producer, Particular commodity, Total savings.
(3) Product pricing, Investment function, Factor pricing, Economic welfare.
(4) Efficiency in social activities, Efficiency in production, Efficiency in consumption, Overall economic efficiency.
(5) Price theory, Slicing method, Limited scope, Lumping method.
(6) Aggregate demand, Aggregate supply, Personal income, National income.
(7) National income, National output, National employment, National anthem.
(8) Keynes, Malthus, Fisher, Marshall.
(9) Theory of Economic welfare, Theory of income and employment, Theory of General price level, Theory of Economic growth.
(10) National Income, National Product, Per Capita Income, Gross Salary.
(11) Big, Large, Vast, Tiny.
(12) Microscopic, Massive, Small, Minimum.
(13) Rent, Wages, Capital, Profit.
(14) Land, Labour, Interest, Entrepreneur.
(15) Railways, Reliance, K.E.M. Hospital,
Answer:
(1) Adam Smith
(2) Total savings
(3) Investment
(4) Efficiency in
function social activities
(5) Lumping
(6) Personal income method
(7) National
(8) Marshall anthem
(9) Theory of Economic Income
Welfare
(10) Per Capita
(11) Tiny
(12) Massive
(13) Capital
(14) Interest
(15) Reliance
(E) Complete the following statements.
(1) The term Macro Economics is derived from the Greek word ‘Makros’ which means …………….
(2) The terms ‘Micro economics’ and ‘Macro economics’ were coined by Norwegian Economist …………….
(3) According to Maurice Dobb, Micro economics is in fact a ……………..
(4) The price of all commodity is determined by the forces of …………….
(5) Four main factors contributing to the production process, are …………….
(6) Micro economics deals with the study of behaviour of …………….
(7) Micro economics is based on ‘Ceteris Paribus’ assumptions which means …………….
(8) Micro economics is useful to government in framing …………….
(9) According to Keynes, macro economics is a …………….
(10) Macro economics is known as theory of Income …………….
(11) Macro economics examines the forest …………….
Answer:
(i) study of large unit
(2) Ragnar Frisch
(3) microscopic study of the economy
(4) demand and supply
(5) land, labour, capital and entrepreneur
(6) small individual unit
(7) other things remaining constant
(8) economic policies
(9) policy oriented science
(10) and employment
(11) not a single tree
[F] Choose the wrong pair :
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1)Macro | Individual unit |
| (2) Factor pricing | Rent, wages, interest and profit |
| (3) Ceteris paribus | Other things being constant |
| (4) Micro | Price theory |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Macro – Individual unit
II.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Slicing method | Micro economics |
| (2) Economic welfare | Overall economic efficiency |
| (3)Macro economics | Income theory |
| (4) Maynard Keynes | Microscopic study of economy |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Maynard Keynes Microscopic study of economy
III.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Lumping method | Macro economics |
| (2) Product Pricing | Forces of demand and supply |
| (3) Micro economics | General equilibrium |
| (4) National income | Study of aggregate |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Micro economics – General equilibrium
IV.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Maynard Keynes | Macro economic approach |
| (2) Micro | Mikros |
| (3) Adam Smith | Classical economist |
| (4) Census | Limited scope |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Census – Limited scope
V.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Macro | (a) Makros |
| (2) Prof. Alfred Marshall | (b) Neo-classical economist |
| (3) Lumping method | (c) Splits the whole economy |
| (4) Partial equilibrium | (d) Micro economics |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Lumping method – Splits the whole economy
![]()
(G) Assertion and Reasoning
Question 1.
Assertion (A) – Micro of a small part of the national economy.
Reasoning (R) – Micro economics divides the economy into small units.
(1) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 2.
Assertion (A) – Micro economics is known as Price theory.
Reasoning (R) – Macro economics is known as Income theory.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 3.
Assertion (A) – Macro economics studies overall conditions in the economy.
Reasoning (R) – Micro economics deals with National income and employment.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Question 4.
Assertion (A) – General equilibrium deals with the behaviour of individual price of commodity.
Reasoning (R) – Lumping method is the study of aggregates.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 5.
Assertion (A) – Macro economic analyses shows how the general price level is determined.
Reasoning (R) – The study of general price level is important on account of the problems created by inflation and deflation.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A) – In Micro economics decision regarding production of goods can be taken by individual.
Reasoning (R) – Study of macro economics help to understand the problems of developing countries and suggest important steps to achieve economic development.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 7.
Assertion (A) – Micro economics is based on assumption of ‘Ceteris paribus’.
Reasoning (R) – Macro economics consists of the story of economic growth and development.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Question 8.
Assertion (A) – Micro economics help to analyse the general level of employment of out put in an economy.
Reasoning (R) – Macro economics helps us to analyse the performance of an economy.
(i) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(iii) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(iv) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Answer:
(ii) (A) is false but (R) is true.
(H) Choose the correct pair :
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1)Macro | (a) Slicing method |
| (2) Micro | (b) Classical economist |
| (3) Adam Smith | (c) Neo-classical economist |
| (4) Prof. Marshall | (d) Inflation |
| (e)Lumping method |
Answer:
(1)-(e), (2)-(a), (3)-(b), (4) – (c).
II.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Factor of Production | (a) Other things being equal |
| (2) Ceteris Paribus | (b) Land |
| (3) Price theory | (c) Micro economics |
| (4) Lumping method | (d) Profit |
| (e)Whole economy |
Answer:
(1)-(b), (2) – (a), (3) -(c), (4) -(e).
III.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) National Income | (a) Rent, wages, interest, etc. |
| (2) Factor Pricing | (b) Mikros |
| (3) Micro | (c) Study of aggregate |
| (4) Slicing method | (d) Makros |
| (e)Splits the whole economy |
Answer:
(1)-(c), (2)-(a), (3)-(b), (4)-(e).
IV.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Micro economics | (a) Theory of investment |
| (2) Macro economics | (b) Key tool of micro economics |
| (3) Marginalism | (c) Price theory |
| (4) Aggregate study | (d) Forest |
| Income and employment theory |
Answer:
(1) – (c), (2) – (e). (3) – (b). (4) – (d).
V.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| (1) Maurice Dobb | (a) Principles of Economics |
| (2) Ragnar Frisch | (b) Policy oriented science |
| (3) Alfred Marshall | (c) Microscopic study |
| (4) Adam Smith | (d) Oslo University |
| (e) Classical economist |
Answer:
(1)-(c), (2)-(d), (3)-(a), (4)-(e).
![]()
2.[A] Identify and explain the concept from given illustrations.
Question 1.
Through public distribution system rationing shops distribute goods to poor people.
Answer:
Concept: Efficiency in consumption.
Explanation : Efficiency in consumption means distribution of produced goods and services to the people for consumption for having maximum satisfaction.
Public distribution system is developed specially to help economically weaker section of society to satisfy their consumption.
Rationing shops provide subsidized food and non food items to below poverty line people.
Question 2.
Mukesh divided his departmental J store into two separate divisions i.e. S food grains and garments to find actual profitability separately.
Answer:
Concept: Slicing method.
Explanation : Micro economics splits or divides the whole economy into small individual units and then studies each unit separately in detail.
Mukesh has divided its business into two separate divisions to understand thedetail cost of operations and profitability separately for food business as well as garment business.
Government collect whole information about population through census.
Concept : Lumping method / Macro economics.
Explanation : Macro economics use lumping method to study the whole economy rather than its part.
Question 6.
Government collect whole information about population through census.
Answer:
Concept : Lumping method / Macro economics.
Explanation : Macro economics use lumping method to study the whole economy rather than its part.
Govern ment collects data through census which gives them details about population such as sex ratio, literacy rate, unemployment rate, age composition, etc.
Question 7.
Reliance industries has created more employment opportunities through its biggest oil refinery in Jamnagar and improved the standard of living of its employee.
Answer:
Concept: Economic development. Explanation : Macro economics help to understand the problems of developing countries and suggest important steps to achieve economic development.
Economic development is a growth of the standard of living of people from low income to high income.
Through developing oil refinery Reliance has created numbers of job opportunities and hence improved the standard of living. Amul has fixed price of ₹ 44 per litre of milk after considering the cost such as machinery cost, labour cost, transportation cost, etc.
Concept: Price determination.
Explanation : Micro economics is known as price theory because it deals with determination of the prices of goods and services as well as factors of production. After considering cost of operations such as machinery cost, raw material cost, labour cost, transportation cost, etc. Amul has fixed price of its product (milk).
B. Distinhbish between
Question 1.
Micro Economics and Macro Economics.
Answer:
| Micro Economics | Macro Economics |
| (a) Micro economics deals with the economic behaviour of small units like particular firm, particular household, individual prices, wages, etc. | (a) Macro economics deals with the economic behaviour of large units or entire economy such as National Income, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, etc. |
| (b) It studies each unit in depth by using slicing method. | (b) It studies the economy as a whole using lumping method. |
| (c) It is based on partial equilibrium analysis based on assumptions. | (c) It is based on a general equilibrium analysis. |
| (d) Micro economic analysis is also called as ‘Price theory.’ | (d) Macro economic analysis is also called as ‘Income theory.’ |
| (e) Most of the theories are given by Dr. Alfred Marshall. | (e) Theories are profounded by Lord J. M. Keynes. |
![]()
Question 2.
Micro Variables and Macro Variables.
Answer:
| Micro Variables | Macro Variables |
| (a) Micro variables refer to individual demand, market demand, individual supply, price of a commodity, etc. | (a) Macro variables refer to inflation rate, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, employment. |
| (b) Micro variables are mostly independent. It does not affect the whole economy, as they are based on assumptions. | (b) Macro Variables are inter related and inter dependent. It affects the working of the economy as a whole. |
| (c) E.g., Price and Quantity demanded are universally related. This will hold true only if the income of the consumer, taste, fashion, etc., remain constant. | (c) Change in aggregate demand, aggregate supply will affect income, employment, etc. in the economy. |
Question 3.
Partial Equilibrium and General Equilibrium.
Answer:
| Partial Equilibrium | General Equilibrium |
| (a) Micro economics uses Partial Equilibrium analysis based on the assumption, other things remaining constant. | (a) Macro economics uses general equilibrium. It is not based on assumption. |
| (b) Partial Equilibrium studies the equilibrium of a consumer, a firm, an industry or a market. | (b) It deals with the Equilibrium position of the economy as a whole. |
| (c) It deals with one or two variables at a time. So it is a simple method. It is independent. | (c) It deals with all the variables of the Economic System simultaneously. So it is sophisticated. There is inter dependence. |
| (d) Partial Equilibrium is regarded as a worm’s eye-view. | (d) General Equilibrium is a bird’s eye-view. |
Question 4.
Micro Theory of Distribution and Macro Theory of Distribution.
Answer:
| Micro Theory of Distribution | Macro Theory of Distribution. |
| (a) Micro Theory of distribution refers to distribution of Factor Income to individual factor owners for their contribution to the production of a commodity or service. | (a) Macro theory of distribution refers to distribution of National Income to factors like wages to the labourers, rent to landlords and interest to capitalist. |
| (b) It is determined by the market forces of demand and supply. | (b) It is determined by the Aggregate demand and Aggregate supply and Employment level in the country. |
Question 5.
Slicing Method and Lumping Method.
Answer:
| Slicing Method | Lumping Method |
| (a) In slicing method the entire economy is cut into individual slices and each unit is studied in depth. | (a) In lumping method, we study the economy as a whole without slicing it. |
| (b) Micro Economics uses the slicing method. | (b) Macro Economics uses the Lumping Method. |
| (c) In slicing method, in depth study of the behaviour of an individual unit like a household, a firm, a product, a factor is done. | (c) In lumping method, it deals with the behaviour of large aggregates like National Income, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, employment and their functional relationship is studied. |
| (d) It relates to the in-depth study of a tree and not the study of forest as a whole. | (d) It relates to the study of the forest as a whole and not a particular tree. |
| (e) Here we achieve a worm’s eye view. | (e) It gives a bird’s eye view of the whole economy. |
3. State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements:
Question 1.
Micro economics is the study of aggregate.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement.
OR Micro economics studies individual economic units.
Yes, I agree with this statement.
- Micro economics is the microscopic study of individual economic units in great detail.
- It deals with individual firms, individual demand and supply, prices of individual, firms, etc.
- But macro-economics deals with economic behaviour of the whole economy with respect to national income, aggregate demand and supply, general price level, etc.
- Hence, micro economics is the study of individual economic units whereas macro economics is the study of aggregates.
Question 2.
Macro economics is a partial equilibrium analysis.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement.
OR
Macro Economics deals with the whole s economy.
Yes, I agree with this statement.
- Macro economics deals with entire economy.
- Macro economics follow general equilibrium analysis. On the other hand, micro economics follow partial equilibrium analysis.
- Macro economics studies the behaviour of number of aggregate economic variables.
- Macro economics follows general equilibrium. It assumes “everything depends on every thing else.”
- General equilibrium deals with the behaviour of demand, supply and prices in the whole economy.
- Therefore, macro economics is not a partial equilibrium analysis but it is a general equilibrium analysis.
Question 8.
Micro economics is useful to the Government.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
Useful to Government : It is useful in formulating and evaluating economic policies including pricing and distribution policies that promote economic welfare. It is useful in determining tax policy, public, expenditure policy, etc.
Question 9.
The scope of macro economics is wide.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
(A) Theory of Income and Employment : It ?
explains which factors determine the level of National Income and employment and what causes fluctuations in the level of income, output and employment.
To understand how the level of employment is determined, we have to study the consumption function. It includes theory of business cycles.
(B) Theory of General Price Level and Inflation: Macro economics analyses shows how the general price level is determined and the causes for fluctuations in it. This study is important for understanding the problems created by inflation and deflation.
(C) Theory of Economic Growth and Development : Macro economics studies the causes of under development and poverty in poor countries and suggests strategies for accelerating growth and development in the country.
(D) Macro theory of Distribution : Macro theory of distribution deals with the relative share of rent, wages, interest and profit in the total national income of various classes.
Question 10.
Theories of micro economics are based on certain assumptions.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
Based on certain ssumption : Micro economics is based on ‘ceteris paribus’ assumption i.e., other things remaining constant like full employment, laissez faire policy, perfect competition, pure capitalism, etc.
Question 11.
Macro economics is also known as income and employment theory.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
Theory of Income and Employment : It ?
explains which factors determine the level of National Income and employment and what causes fluctuations in the level of income, output and employment.
To understand how the level of employment is determined, we have to study the consumption function. It includes theory of business cycles.
![]()
4. Study the following table / figures / passages and answer :
Question 1.
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
The census of 1991 was the fifth census of independent India and conducted as usual from 9th to 28th February, 2001 to present census data as on sunrise of 1st March 2001, the reference date. The two phases were continued in the same way like previous two censuses.
In the first phase a house list was canvassed to collect the information on housing data and also amenities available to the households. The scope of house list was enlarged and for the first time a question regarding type of fuel used for cooking was canvassed. In 1981 the question on availability of toilet facility was canvassed for urban areas only. However, in 1991, it was canvassed for rural area also.
During 2nd phase following two schedules were canvassed, (a) Household schedule and (b) Individual slip
1. Between which dates the census for 2001 was conducted.
Answer:
The census for 2001 was conducted between 9th to 28th February 2001.
2. What information was collected in the first phase of census?
Answer:
In the first phase of census a house list was canvassed for collecting information about housing data and amenities available.
3. Which question was canvassed in 1991?
Answer:
In 1991 question on availability of toilet were canvassed – (a) household schedule and facility was canvassed for rural area. I 03) Individual slip.
4. Which two schedule were canvassed in IInd phase?
Answer:
During IInd phase below two schedules were canvassed –
(a) household schedule and
(b) Individual slip.
Question 2.
Go through the following chart and answer the questions.
Answer:
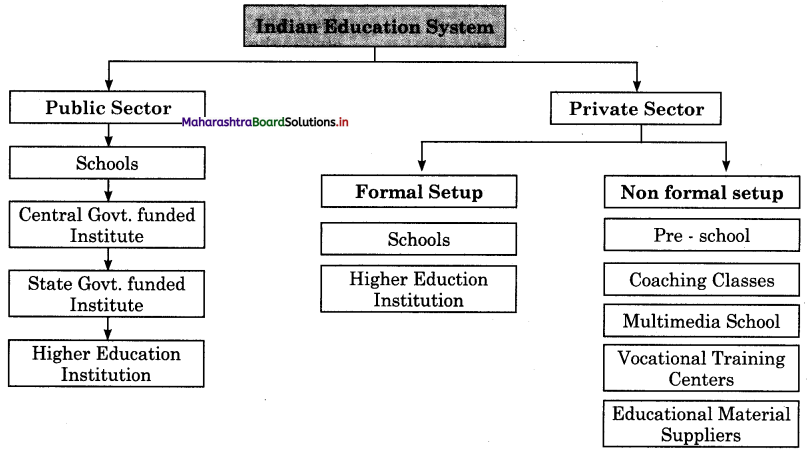
1. Which are the two main sectors in Indian education system?
Answer:
The two main sectors in Indian education system are (a) Public sector (b) Private sector.
2. What does public sector education system includes?
Answer:
Public sector education system includes public schools, central government funded institutions, state government funded institutions and higher education institutions.
3. Where are multimedia schools positioned in Indian education system?
Answer:
Multimedia school comes under non-formal setup of private sector in Indian education system.
4. What are the setups in private sector educational system?
Answer:
There are two setups in private sector educational system i.e. formal setup and non-formal setup.
Question 3.
Study the below table and answer the given questions.
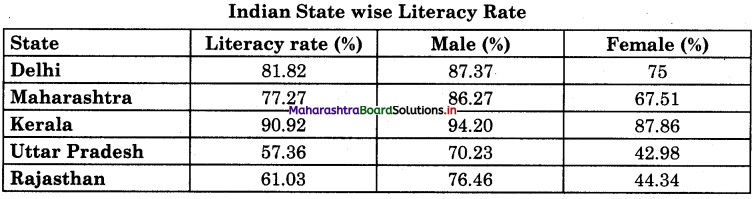
(1) Which state has the highest literacy [ rate?
Answer:
Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 90.92%.
(2) What is the male literacy rate for1 Maharashtra?
Answer:
For Maharashtra the male literacy rate is 86.27%.
(3) What is difference of female literacy rate between Delhi and Rajasthan?
Answer:
There is a difference of 30-66% as a whole in female literacy rate between Delhi and Rajasthan.
(4) Which states has highest male literacy and lowest female literacy rate?
Answer:
Kerala has the highest male literacy rate of 94.20% and Uttar Pradesh has the lowest female literacy rate of 42.98%.
![]()
5. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain the scope of Micro economics.
OR
Explain the subject matter of micro economics.
Answer:
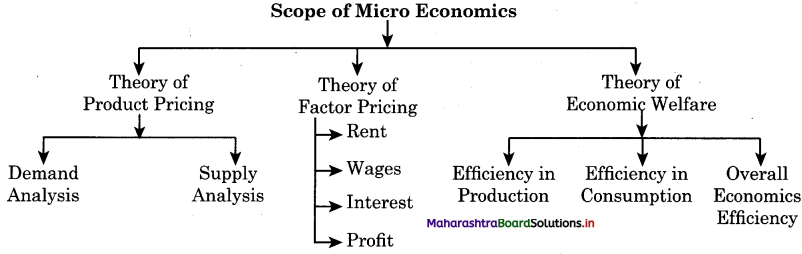
(a) Theory of Product Pricing : The price of each commodity is determined by the forces of demand and supply. Micro economics is a study of demand analysis i.e. individual consumer behaviour and supply analysis i.e. individual producer behaviour.
(b) Theory of Factor Pricing : There are four main factors contributing to the production process which are land, labour, capital and entrepreneur. Micro economics helps in determining the factor rewards like land gets rent, labour gets wages, capital gets interest and entrepreneur gets profit.
(c) Theory of Economic Welfare : This theory deals with efficiency in allocation of resources which aim at maximum satisfaction of people. Three economic efficiencies are as follows :
- Efficiency in production: It mean producing the maximum amount of goods and services from a given amount of goods and j services from a given amount of resources.
- Efficiency in consumption: It means distribution of produce goods and services to the society for consumption in such a way to have maximum total satisfaction of people.
- Overall economics efficiency: It means to produce those goods and services which are most desired by the people.