Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Question 1.
What is a carbonyl group?
Answer:
Carbonyl group : A functional group in which a carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom by a double bond and remaining two valencies of carbon atom are free is called a carbonyl group and represented as ![]() . Carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones.
. Carbonyl group is present in aldehydes and ketones.
![]()
Question 2.
What are carbonyl compounds?
Answer:
The organic compounds containing a carbonyl group ![]() are called carbonyl compounds. For example, acetaldehyde,
are called carbonyl compounds. For example, acetaldehyde, 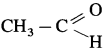 , acetone,
, acetone,  . As carbonyl group is common in aldehydes and ketones, their methods of preparation and properties show similarities.
. As carbonyl group is common in aldehydes and ketones, their methods of preparation and properties show similarities.
Question 3.
What are carboxylic compounds?
Answer:
The compounds in which the functional group is – COOH are known as carboxylic compounds. Due to the – OH group bonded to ![]() group, carboxylic acids are distinct from aldehydes and ketones.
group, carboxylic acids are distinct from aldehydes and ketones.
Question 4.
How are carbonyl compounds classified ?
OR
Name the compounds containing carbonyl group.
Answer:
The carbonyl compounds contain a group ![]() . They are classified as follows :
. They are classified as follows :

Question 5.
What are aliphatic aldehydes?
Answer:
The compounds in which the – CHO group (formyl group or aldehyde group) is attached directly to sp3 hybridized carbon atom that is saturated carbon atom are called aliphatic aldehydes. (Exception : Formaldehyde, H – CHO is also classified as aliphatic aldehyde though – CHO group is not attached to any carbon).
For example :
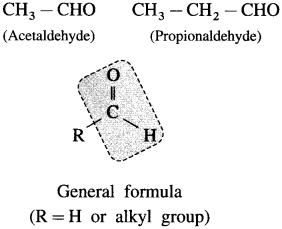
![]()
Question 6.
What are aromatic aldehydes ?
Answer:
The compounds in which – CHO group is attached directly to an aromatic ring are called aromatic aldehydes.
For example :
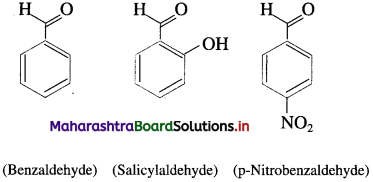
Question 7.
Explain the structure of carbonyl functional group.
Answer:
- In the carbonyl functional group, carbon atom is attached to an oxygen atom by a double bond and remaining two valencies of carbon atom are free, and it is represented as
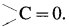 .
.
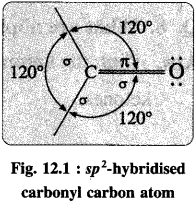
- The carbonyl carbon atom is sp2-hybridised forming coplanar three sigma (σ) bonds with the bond angle 120°.
- One sigma bond is formed with oxygen atom while other two sigma (σ) bonds are formed with hydrogen or carbon atoms.
- The remaining unhybridised 2pz orbital of carbon atom overlaps with p orbital of oxygen atom colaterally forming a pi (π) bond. Hence, carbon atom is joined to oxygen atom by a double bond of which one is sigma and another is n.
- The oxygen atom in the carbonyl group has two lone pairs of electrons.
- The carbonyl bond is strong, short and polarized.
- The polarity of the carbonyl group is explained on the basis of resonance involving neutral and dipolar structures as shown below :

Question 8.
What are aliphatic ketones? How are they classified?
Answer:
Aliphatic ketones : The compounds in which ![]() group is attached to two alkyl groups are called aliphatic ketones.
group is attached to two alkyl groups are called aliphatic ketones.

Ketones are classified into two types :
- Simple or symmetrical ketones and
- mixed or unsymmetrical ketones.
1. Simple or symmetrical ketone : The ketone in which the carbonyl carbon is attached to two identical alkyl groups is called a simple or symmetrical ketone.

2. Mixed or unsymmetrical ketone : The ketone in which the carbonyl carbon is attached to two different alkyl groups is called a mixed or unsymmetrical ketone.

Question 9.
What are aliphatic carboxylic acids? Give their general formula.
Answer:
The organic compounds in which carboxyl (- COOH) group is bonded to an alkyl group are called aliphatic carboxylic acids or fatty acids. (Exception : Formic acid, H-COOH is also classified as aliphatic carboxylic acid though-COOH group is not attached to any carbon).
For example :
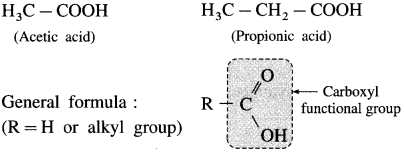
![]()
Question 10.
How are carboxylic acids classified ? Give examples. (3 marks)
Answer:
Carboxylic acids are classified according to the presence of number of carboxyl groups into mono-, di-, tri- and polycarboxylic acids.
- Monocarboxylic acids : These carboxylic acids contain one carboxyl group.
Example :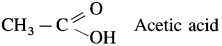
- Dicarboxylic acids : These contain two carboxyl groups
Example :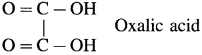
- Tricarboxylic acid : These contain three carboxyl groups
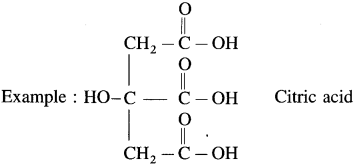
Question 11.
What are aromatic carboxylic acids ? Give examples.
Answer:
Aromatic carboxylic acids : These are the compounds in which one or more carboxyl groups (- COOH) are attached directly to the aromatic ring.
For example :
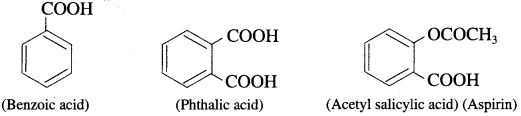
Question 12.
Give examples of common carboxylic acids which are used in daily life.
Answer:
Common carboxylic acids are widely distributed in nature, they are found in both the plants and animals.
- Acetic acid is main constituent of vinegar.
- Butyric acid of butter which is responsible for odour of rancid butter.
- L-lactic acid is present in curd.
- Citric acid is found in citrus fruits.
- Higher carboxylic acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid and oleic acid are the components of animal fats and vegetable oils.
Nomenclature of Aldehydes :
(A) Common System :
- The names of aldehydes are derived from the common names of acids.
- The suffix ‘-ic acid’ of an acid is replaced by ‘aldehyde’.
- The positions of the substituents in the molecule are indicated by Greek letters α, β, γ, etc.
- starting from the carbon atom attached to the carbonyl group. E.g.

(B) I UP AC System :
- The longest carbon atoms chain containing aldehyde carbon atom is selected as a parent hydrocarbon.
- ‘e’ of the alkane is replaced by ‘al’. Alkane → Alkanal
- The position (locant) of aldehyde group need not be mentioned since it is always at the end position.
- The substituents in the alkyl group are prefixed in an alphabetical order by appropriate locants.
- When two – CHO groups are present at the two ends of the chain the ending ‘e’ of alkane is retained and the suffix ‘-dial’ is added to the name of parent aldehyde.
- In IUPAC nomenclature an alicyclic compound -in which – CHO group is attached directly to the ring is named as a carbaldeliyde. The suffix ‘carbaldehyde’ is added after the full name of parent cycloalkane structure.
![]()
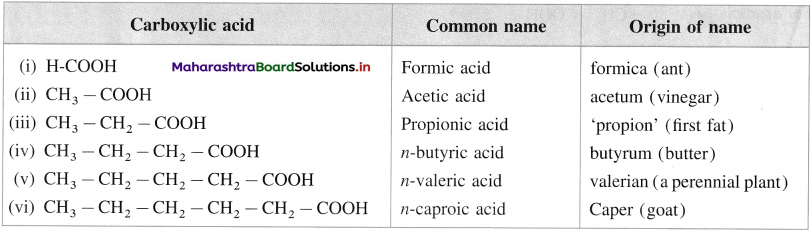
(C) Common or trivial names :
(1) The common name of a carboxylic acid is derived from the source from which it was first isolated.
The following table gives common names and the source or origin of name.
(2) In branched carboxylic acids, the position of substituents are indicated by Greek alphabet.
For example : ![]()
(D) IUPAC system of nomenclature :
- The longest continuous cha in of carbon atoms including the carbon atom of – COOH group ¡s selected.
- The carboxvlic acid is conside red (IS a derivative of the corresponding parent a/kane.
- The carbon atom of the – COOH group is always at terminal position, hence need not to be indicated while writing IUPAC name.
- The position of the other substitutents are indicated by the appropriate locants in alphabetical order.
- In case of dicarboxylic acids, ‘dioic acid’ is added to parent alkane.
- In an alicyclic compound having a carboxyl group directly attached to alicyclic ring is named as cycloalkane carboxylic acid.
Trivial and IUPAC names of carboxylic acids and aldhydes
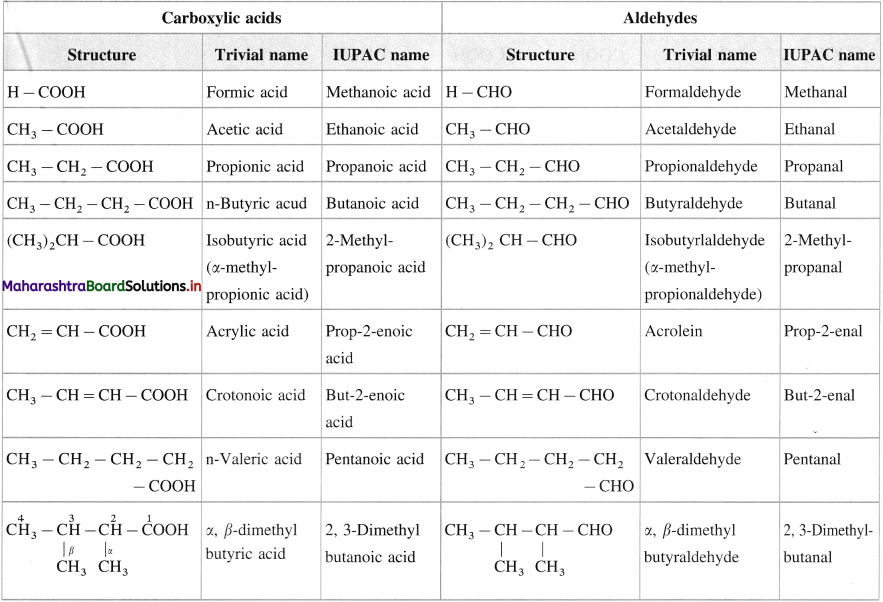

![]()
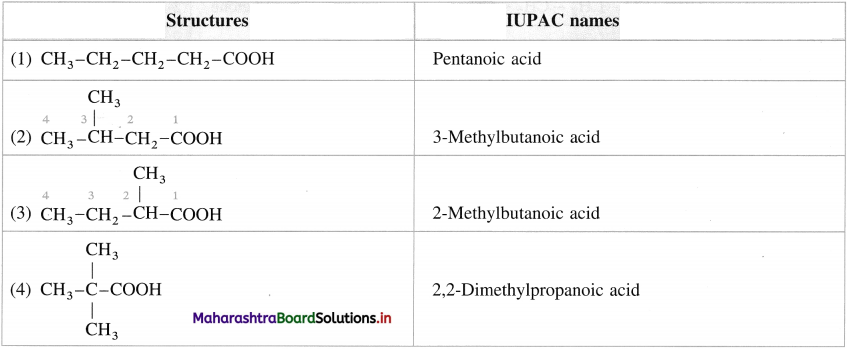
Question 13.
Give the common names and IUPAC names of the Miowing aldehydes :
Answer:

Question 14.
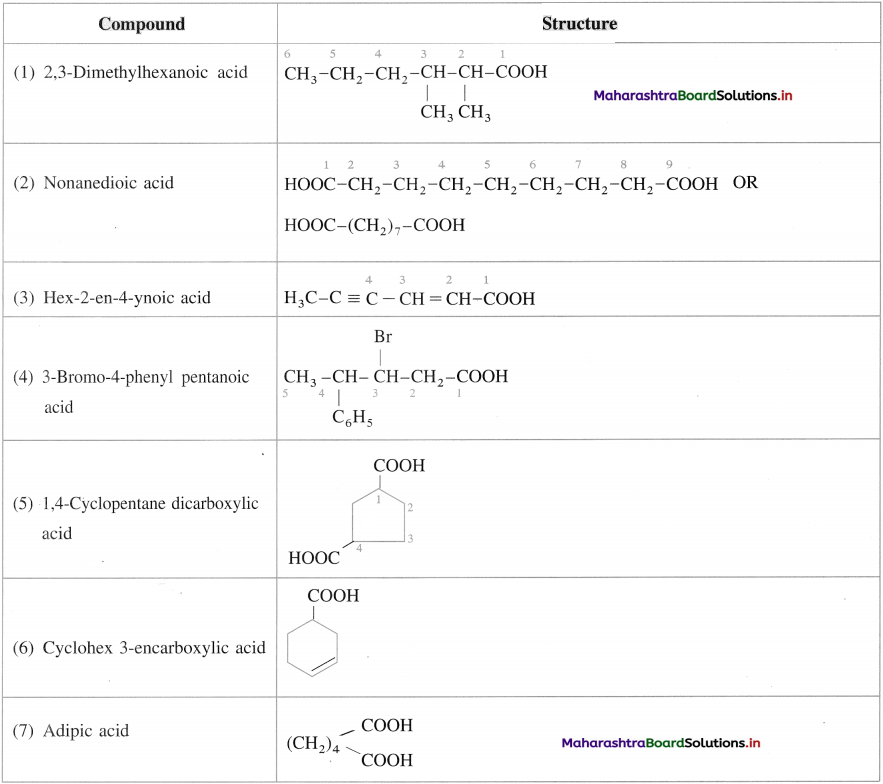
Write the structures of the following compounds :
Answer:

![]()
Question 15.
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?

Answer:
IUPAC name : 2-Amino butanoic acid
Question 16.
Write IUPAC name of
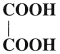
Answer:
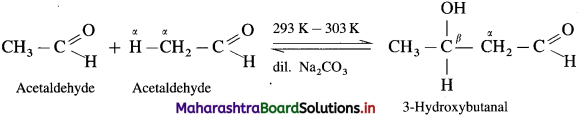
IUPAC name : Ethanedioic acid
Question 17.
Write the structure and give IUPAC names of following carboxylic acid.
![]()
Answer:

Question 18.
Draw the structures of the following compounds :
Answer:
Question 19.
Give IUPAC names of the following carboxylic acids.
Answer:

![]()
Question 20.
Write the structures and IUPAC names of all isomers of carboxylic acids having molecular formula C5H10O2. HOW many of them are chiral?
Answer:
Nomenclature of ketones :
(A) Common System :
- Ketones are named according to the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon atom followed by the word ketone.
- The substituents in the alkyl groups are indicated by Greek letters a, f, y, etc. starting from the carbon atom attached to the carbonyl group.
(B) IUPAC System :
- The longest continuous chain containing carbonyl carbon atom is selected as a parent hydrocarbon.
- ‘e’ of the alkane is replaced by ‘one’. Alkane → Alkanone
- The position of carbonyl group is represented by the lowest locant.
- The substituents in the alkyl groups are prefixed in the alphabetical order along with their positions by appropriate locants.
- When two C = O groups are present, then ending ‘e ’ of alkane is retained and the suffix – ‘dione ’ is added to the name of parent ketone indicating the locants of ketonic carbonyl groups.
- In case of polyfunctional ketones, higher priority group is given lower number.
- When ketonic carbonyl is a lower priority group it is named as ‘oxo’, preceded by the locant. In alicyclic ketones, carbonyl carbon is numbered as 1.
Question 21.
Give the common and IUPAC names of the following ketones :
Answer:
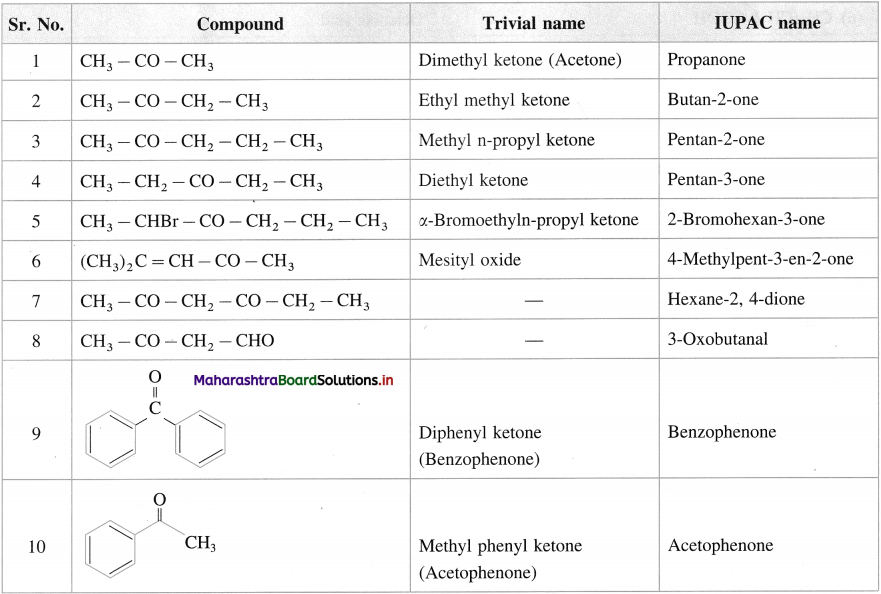

![]()
Question 22.
Give the structures of the following compounds :
Answer:


Question 23.
Give IUPAC names of the following compounds :
Answer:

![]()
Question 24.
Write the structures and give common names and IUPAC names of the carbonyl compounds represented by formula C5H10O.
Answer:
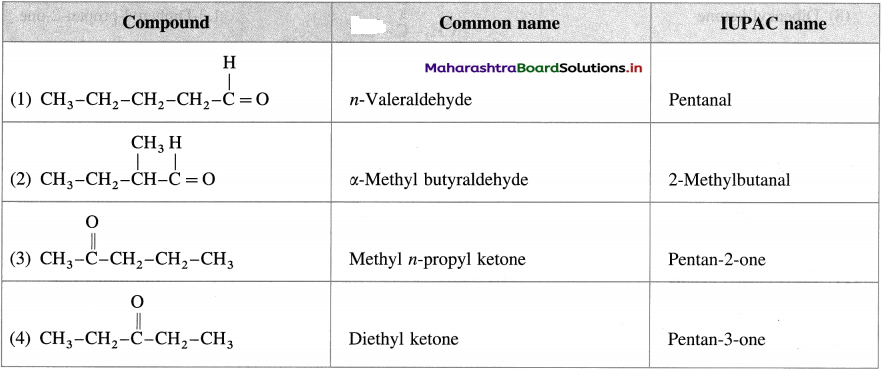
Question 25.
Write the structure and give IUPAC names of the following compounds :
Answer:
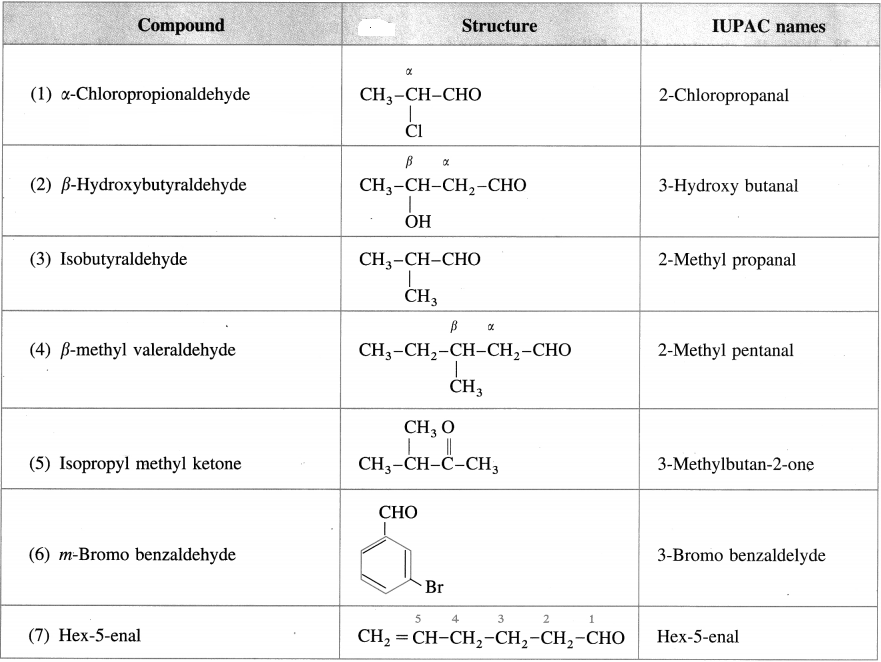

![]()
Question 26.
Write the structure of the following compounds :
Answer:

Question 27.
How is an aldehyde obtained from an alcohol ?
Answer:
When a primary alcohol is oxidized with potassium dichromate and dil. H2SO4 under controlled conditions, an aldehyde is obtained.
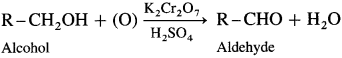
For example, when ethanol is oxidized with potassium dichromate and dil. H2SO4 under controlled conditions, acetaldehyde (ethanal) is obtained.
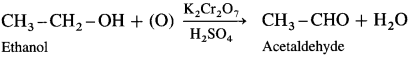
Question 28.
How is ketone obtained from an alcohol?
Answer:
When a secondary alcohol is oxidized with potassium dichromate and dii. H2SO4 under controlled conditions, a ketone is obtained.

For example. when 2-propanol is oxidized with potassium dichromate and dii, H2SO4 under controlled conditions, accIone (propanone) is obtained.

![]()
Question 29.
How are the following compounds obtained from alcohol:
(1) Methanal
(2) Propanal
(3) BuLanal
(4) 3-Methylpentanal?
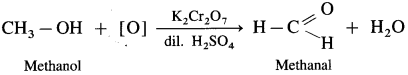
Answer:
- Mehanol on controlled oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and dilute H2SO4 forms methanal.
- Propan-1-ol on controlled oxidation with K,Cr20 and dilute H2SO4 forms propanal.
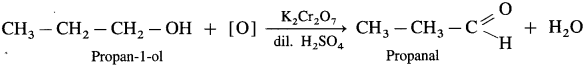
- Butan..l-ol on controlled oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and dilute H2SO4 forms butanal.

- 3-Mcthylpcntan.1-ol on controlled oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and dilute H2SO4 gives 3-Methylpentanal.
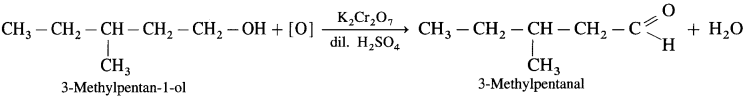
Question 30.
How are the following compounds prepared from alcohol :
(1) Butanone
(2) Pentan-3-one
(3) 2,2-Dimethylpropanal?
Answer:
- Butan-2-ol on controlled oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and dilute H2SO4 forms butanone.
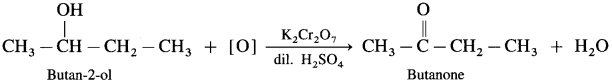
- Pentan-3-ol on oxidation with K2Cr2O7 and dilute H2SO4 forms Pentan-3-one.
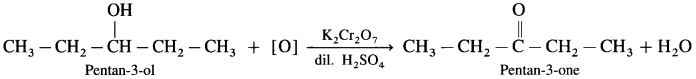
- 2,2-Dimethylpropan- I -ol on oxidation with K2Cr2O7 or KMnO4 and dilute H2SO4 forms 2,2-Dimethyipropanal.
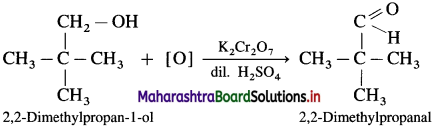
Question 31.
How is an aldehyde obtained from primary alcohol ?
Answer:
When vapours of primary alcohol is passed over heated copper at 573 K, dehydrogenation takes place, an aldehyde is formed.
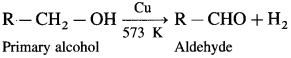
For example : When vapours of isopropyl alcohol is passed over heated copper at 573 K, acetone (propanone) is obtained.
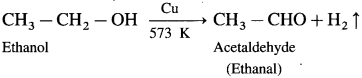
![]()
Question 32.
How is ketone obtained from secondary alcohol?
Answer:
When vapours of secondary alcohol is passed over heated copper at 573 K. dehydrogenation takes place, a ketone is obtained.
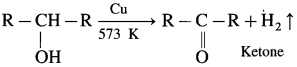
For example : When vapours of isopropyl alcohol is passed over heated copper at 573 K. acetone (propanone) is obtained.

Question 33.
How are the following compounds obtained from alkene :
(1) Formaldehyde
(2) Acetaldehyde and
(3) Acetone ?
Answer:
When a stream of ozonised oxygen is passed through a solution of an alkene, in organic solvent, an unstable addition cyclocompound, ozonide is formed which on reduction with zinc dust and water forms an aldehyde or a ketone or a mixture of both.
- Formaldehyde : Under these conditions ethylene gives formaldehyde.
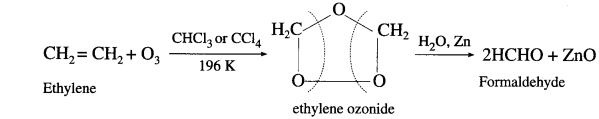
- AcetuIdeh&: Symmetrically disubstituted alkene like but-2-ene gives acetaldehyde.

- scctnne: Tetrasubshtwed alkene like 2,3-dimethyl but-2-ene gives acetone.
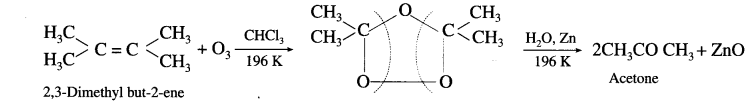
Question 34.
Write ozonolysis reaction for
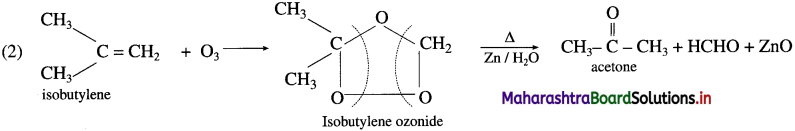
(1) Propylene and
(2) Isobutylene.
Answer:
(1) Propylene on reaction with ozonised oxygen in the organic solvent forms propylene ozonide which on reduction with zinc dust and water forms acetaldehyde and formaldehyde.
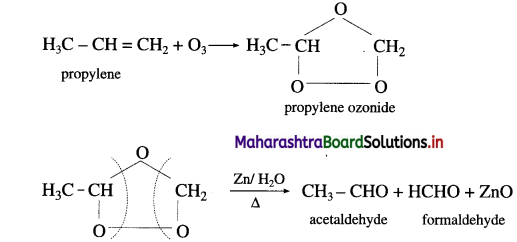
Question 35.
How are the following compounds obtained from alkynes :
(1) Acetaldehyde
(2) Acetone?
Answer:
- Acetaldehyde : On passing acetylene through warm 40% H2SO4 in the presence of 1 % HgSO4, vinyl alcohol is obtained which tautomerises and forms acetaldehyde. It is a hydration reaction.

- Acetone : On passing propyne through warm 40 % H2SO4 in the presence of 1 % HgSO4, alkenol is obtained which on tautomerisation form acetone.

![]()
Question 36.
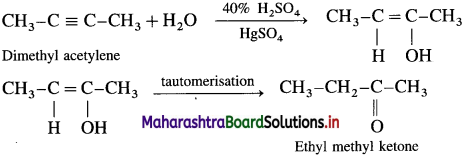
Predict the products when
(1) dimethyl acetylene
(2) ethyl acetylene and
(3) diethyl acetylene are treated with mercuric sulphate in dilute sulphuric acid.
Answer:
(1) Dimethyl acetylene with 40% H2SO4 in the presence of mercuric sulphate (HgSO4) forms ethyl methyl ketone by tautomerisation.
(2) Ethyl acetylene with 40% H2SO4 in the presence of mercuric sulphate (HgSO4) forms Butan-2-one by tautomerisation.

(3) Diethyl acetylene with 40% H2SO4 in the presence of mercuric sulphate (HgSO4) forms hexan-3-one.


Question 37.
Write the structures of aldehydes and ketones obtained by ozonolysis.

Answer:
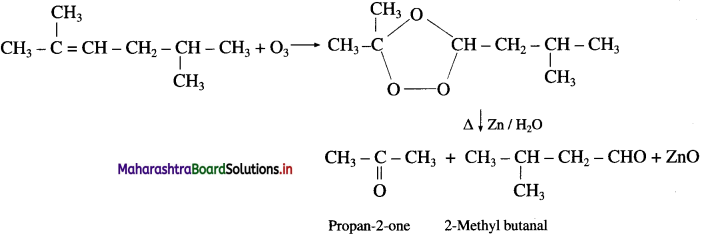

Answer:
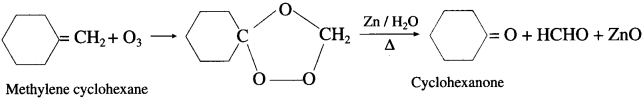
Question 38.
Predict the structures of ketones produced by hydration of but-l-yne and but-2-yne.
Answer:

![]()
Question 39.
How is acetaldehyde prepared from acetyl chloride?
Answer:
Acetyl chloride is reduced to acetaldehyde by hydrogen in presence of Pd catalyst poisoned with BaSO4. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
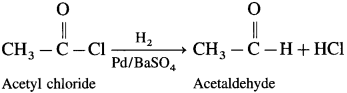
Question 40.
How is benzaldehyde obtained from benzoyl chloride?
OR
Write chemical equation for Rosenmund reduction.
Answer:
When benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in the presence palladium on barium sulphate (Pd/BaSO4), benzaldehyde is obtained. This reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
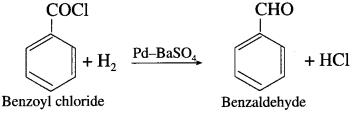
Question 41.
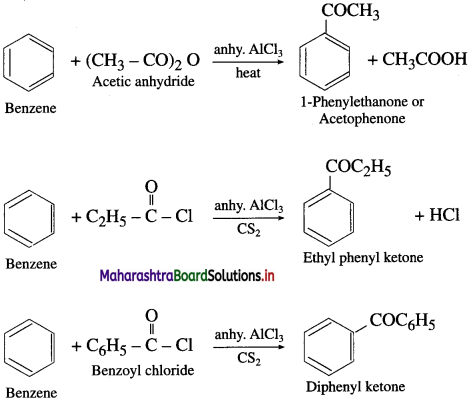
How will you prepare acetophenone from benzene? (Friedel – Crafts acylation).
Answer:
When benzene is treated with acetyl chloride in the prcscncc of anhydrous aluminium chloride, acetophenonc is obtained. This reaction is known as Friedel – Crafts acylation.
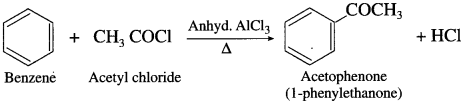
Question 42.
How will you convert benzene into 1-phenylethanone?
Answer:

Question 43.
How will you obtain 4-Nitrobenzaldehyde from 4-Nitrotoluene ? (Friedel- Crafts reaction).
Answer:
When 4-nitrotoluene is treated with chromium oxide in acetic anhydride, a diacetate derivative is obtained which on acid hydrolysis produces 4-nitrobenzaldehyde.
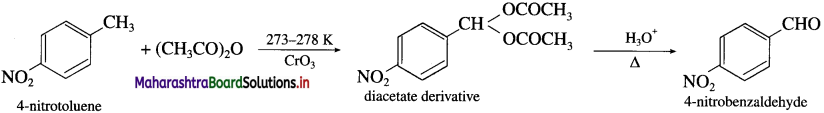
Question 44.
How will you prepare Propanone (acetone) from Grignard reagent?
Answer:
Grignard reagent (methyl magnesium iodide) reacts with cadmium chloride to give dimethyl cadmium. When acetyl chloride reacts with dimethyl cadmium, propanone (acetone) is obtained.
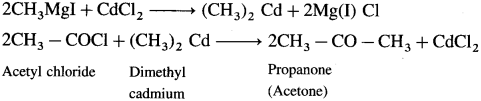
Question 45.
How is acetophenone obtained from Grignard reagent ?
Answer:
Grignard reagent (methyl magnesium iodide) reacts with cadmium chloride to give dimethyl cadmium. When benzoyl chloride reacts with dimethyl cadmium, acetophenone is obtained.
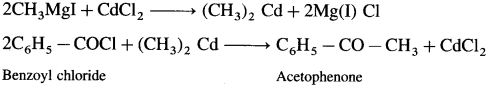
![]()
Question 46.
How is benzyl methyl ketone obtained from Grignard reagent ?
OR
Convert: Acetyl chloride to benzyl methyl ketone.
Answer:
Grignard reagent (Benzyl magnesium chloride) reacts with cadmium chloride to give diphenyl cadmium. When acetyl chloride reacts with dibenzyl cadmium, benzyl methyl ketone is obtained.
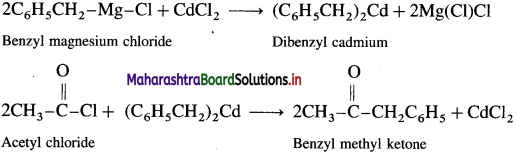
Question 47.
How is an aldehyde obtained from alkyl nitrile ?
OR
What is Stephen reaction ?
OR
Write a note on Stephen reaction.
Answer:
(1) An ethereal solution of a nitrile is reduced to imine hydrochloride by SnCl2 in the presence of HCl gas. Further, imine hydrochloride on acid hydrolysis gives aldehyde. This reaction is called Stephen reaction.

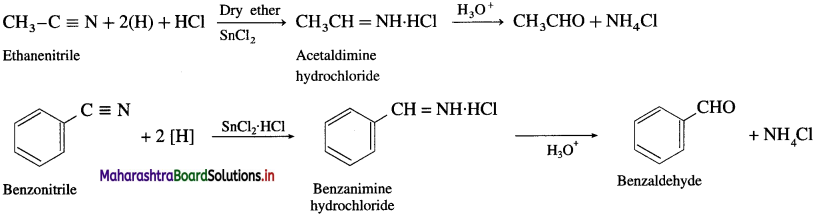
(2) Alternatively, nitriles are selectively reduced by diisobi.ityl aluminium hydride (DIBAI-H) lo imines which on acid hydrolysis to aldehydes.

Question 48.
How are following compounds prepared using Gngnard reagent
(1) Acetone
(2) Benzophenone?
Answer:
(1) Acetone: Acetoniti-ile (ethanenitrile) reacts with methyl magnesium iodide in presence of dry ether to give imine complex which on hydrolysis gives acctonc. During reaction acetonitrile and methyl magnesium iodide should be
taken in equimolecular proportion.

(2) Benzophenone: Benzonitrile reacts with phenyl magnesium bromide in presence of dry ether to give an imine complex which on acid hydrolysis gives a benzophenone. During reaction bcnzonitrile and phenyl magnesium bromide should be aken in equimolecular proportion.
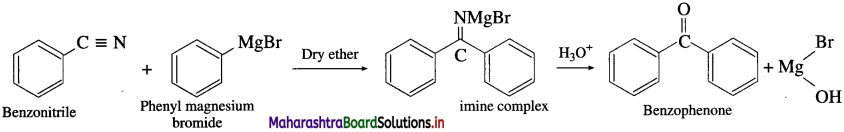
![]()
Question 49.
Write the structures and IUPAC names of ketones produced by Friedel-Crafts acylation of benzene with
(i) C2H5COCl
(ii) C6H5COCl.
Answer:

Question 50.
Predict the products of the following conversions.
Answer:
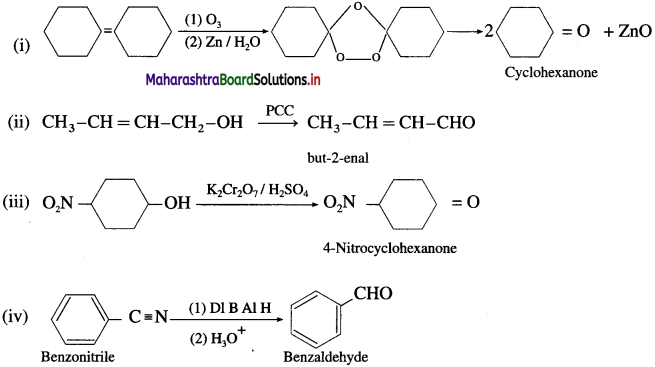
Question 51.
How are the following preparations carried out ?
(1) Benzaldehyde from toluene. (Etard oxidation)
Answer:
When toluene is treated with solution of chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) in Cs2, brown chromium complex is obtained, which on acid hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde. This reaction is called Etard reaction.

(2) Benzaldehyde from methyl arene.
Answer:
Methylarene is converted into a benzyllidene diacetate on treatment with chromium oxide in acetic anhydride at 273-278 K. The diacetate derivative on acid hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.

(3) Benzaldehyde from toluene (commerical method).
Answer:
Side chain chlorination of toluene gives benzal chloride which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde.
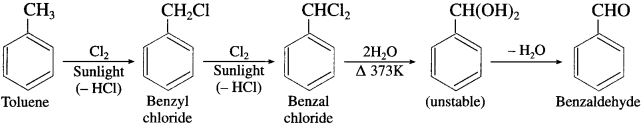
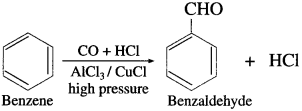
(4) Benzaldehyde from benzene (Gattermann-Koch synthesis).
OR
Write chemical equation for Gatter- mann-Koch formylation.
Answer:
When benzene is treated with vapours of carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride in the presence of a catalyst mixture of A1Cl3 and CuCl under high pressure, benzaldehyde is obtained. This reaction is called Gattermann- Koch synthesis.
Preparation of aromatic ketones from hydrocarbons
![]()
Question 52.
Explain Friedel-Craft’s acylation reaction.
Answer:
The reaction in which hydrogen atom of benzene is replaced by an acyl group 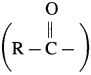 I in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is called Friedel-Craft’s acylation. When benzene is heated with an acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, forms acetophenone (1-Phenyl ethanone).
I in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is called Friedel-Craft’s acylation. When benzene is heated with an acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, forms acetophenone (1-Phenyl ethanone).
Electrophile : R – C + = O acylium ion Formation of the electrophile :

Question 53.
Give the preparation of acetophenone from benzene using
(i) acetyl chloride
(ii) acetic anhydride.
Answer:
The reaction in which hydrogen atom of benzene is replaced by an acyl group 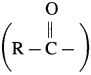 I in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is called Friedel-Craft’s acylation. When benzene is heated with an acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, forms acetophenone (1-Phenyl ethanone).
I in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is called Friedel-Craft’s acylation. When benzene is heated with an acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, forms acetophenone (1-Phenyl ethanone).
Electrophile : R – C + = O acylium ion Formation of the electrophile :


![]()
Question 54.
How will you prepare propionaldehyde from ethyl propionate?
Answer:
When ethyl propionate is reduced in presence of diisobutyl aluminium hydride (DIBAI-H), propionaldehyde is obtained.
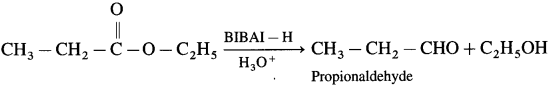
Question 55.
Explain the structure of carboxyl group.
Answer:
In carboxyl group, the carboxyl carbon is sp2-hybridised and the bonds to the carboxyl carbon lie in one plane. The C-C = O and O = C-O bond angles are 120°. The carboxylic carbon is less electrophilic than carbonyl carbon because of the resonance structures shown below :

Question 56.
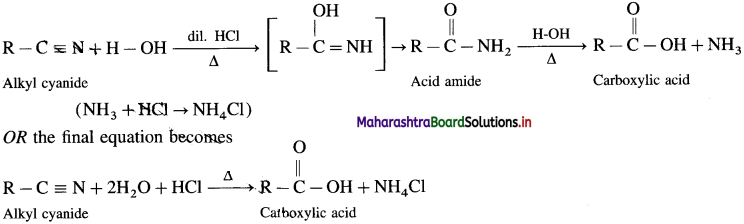
How is carboxylic acid obtained by the acid hydrolysis of an alkyl cyanide ?
Answer:
Alkyl cyanides or alkyl nitriles on acid or alkaline hydrolysis give corresponding carboxylic acids.
Acid Hydrolysis of Alkyl ankle: When alkyl cyanide is boiled wiLh dilute mineral acid, it gives corresponding carboxylic acid. In this, acid amide is obtained as the intermediate product.
Question 57.
How is ethanoic add obtained from methyl cyanide by acid hydrolysis?
Answer:
When methyl cyanide is heated with dilutc hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid. ethanoic acid is obtained.

Question 58.
How Is proplonlc acid obtained from an alkyl nitrile?
Answer:
When ethyl cyanide (propionitrile) is boiled with dilute HCI or dilute H2SO4, propionic acid is obtained.

Question 59.
How Is benzoic acid obtained from bcnzamide?
Answer:
When benzarnide is heated with dil. HCl. benzoic acid is obtained.

Question 60.
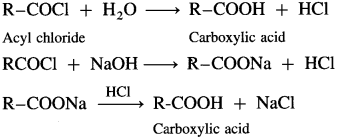
How is carboxylic acid obtained from acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides?
Answer:
When acyl chloride is hydrolysed with water, carboxylic acid is obtained. The reaction is carried out in presence of a base pyridine or NaOH to remove HCl generated.
Acetyl chloride reacts with water almost explosively while benzoyl chloride very slowly.

Acid anhydrides react with water to give carboxylic acid.

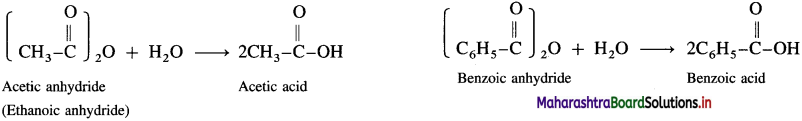
![]()
Question 61.
How is benzoic acid obtained from
(i) ethyl benzoate
(ii) styrene?
Answer:
(i) Benzoic acid from ethyl benzoate : When an ethyl benzoate is heated with dil. H2SO4, undergoes hydrolysis to form benzoic acid and ethyl alcohol.

(ii) Benzoic acid from styrene:
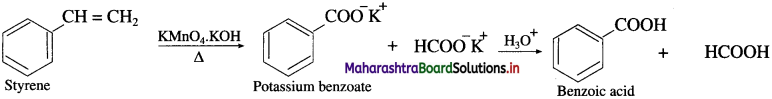
Question 62.
How is propanoic acid obtained from phenyl propanoate?
Answer:
When phenyl propanoate is heated with dil. NaOH, sodium salt is obtained, which on hydrolysis gives propanoic- acid.
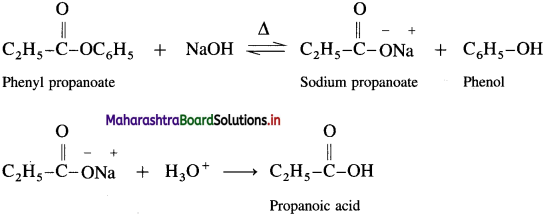
Question 63.
How is propanoic acid obtained from methyl propanoate ?
OR
When methyl propanoate is heated with dil. NaOH, sodium, salt is obtained, which on hydrolysis gives propanoic acid.
Answer:
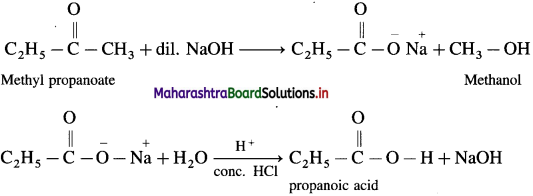
Question 64.
How is benzoic acid obtained from phenyl ethene?
Answer:
When phenyl ethene is heated with strong oxidising agents like acidic KMnO4 or acidic K2Cr2O7, benzoic acid is obtained.
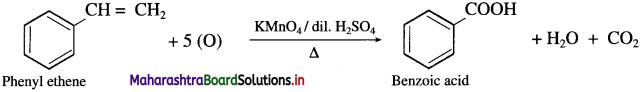
Question 65.
How is adipic acid obtained from cyclohexene?
Answer:
When cyclohexene is heated with acidified KMnO4, adipic acid (Hexane-1, 6-dioic acid) is obtained.
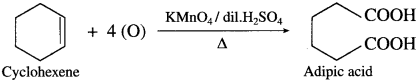
![]()
Question 66.
What is carbonation of Grignard reagent ? How is acetic acid prepared by this reaction ? How is ethanoic acid pepared from dry ice?
Answer:
Addition reaction of carbon dioxide (0 = C = 0) to Grignard reagent, forming a complex and further formation of carboxylic acid is called carbonation of Grignard reagent.
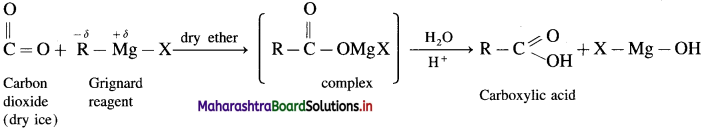
Example : When methyl magnesium iodide is added to solid carbon dioxide, a complex is formed which on acid hydrolysis forms acetic acid.

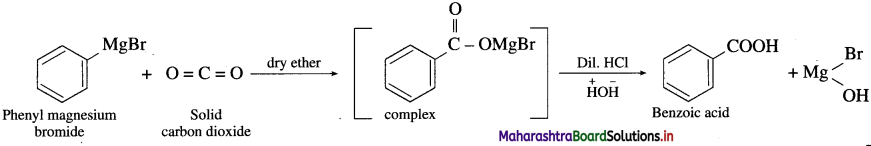
Question 67.
How is benzoic acid prepared from Grignard reagent?
OR
Write the preparation of benzoic acid from dry ice.
Answer:
When phenyl magnesium bromide is treated with dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) in the presence dry ether, complex is obtained which on acidification gives benzoic acid.
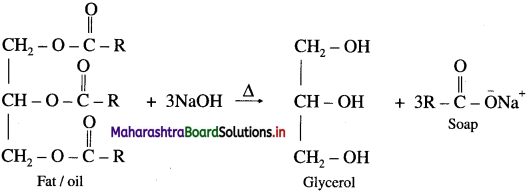
Question 68.
What are soaps ? How are they prepared ?
Answer:
The sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids are known as soaps. Soaps contain more than twelve carbon atoms.
When fat or oil is hydrolysed using sodium or potassium hydroxide solution, soap obtained remains in colloidal form. Soap and glycerol are separated by adding sodium chloride. Soap precipitates out due to common ion effect, and glycerol remains in the solution can be recovered by fractional distillation.
Question 69.
How is benzoic acid prepared from alkyl benzenes ?
OR
How will you convert the following :
(1) n-butyl benzene to benzoic acid.
(2) Toluene to benzoic acid.
(3) Cumene to benzoic acid ?
Answer:
When an alkyl benzene is heated with strong oxidizing agents like acidic or alkaline KMnO4 or acidified K2Cr2O7 etc. gives aromatic carboxylic acid. The alkyl side chain gets oxidised to -COOH group irrespective of the size of the chain.
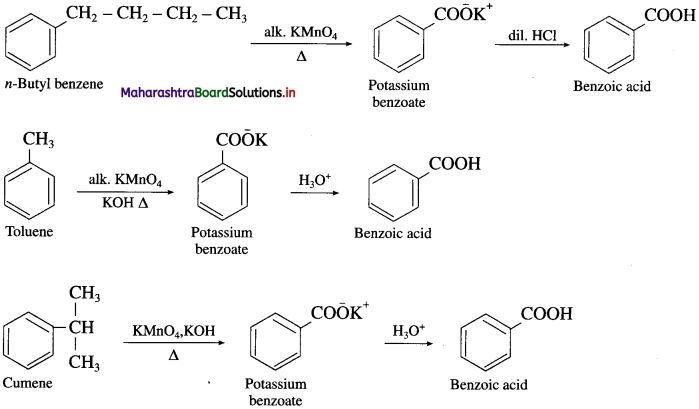
![]()
Question 70.
Lower aldehydes and ketones are water soluble whereas higher homologues are insoluble. Explain, why.
Answer:
(1) The oxygen atom of ![]() shows hydrogen bonding with water molecule.
shows hydrogen bonding with water molecule.
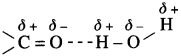
(2) As a result of this, the lower aldehydes and ketones are water soluble (example – acetaldehyde, acetone). As the molecular mass increases, the proportion of hydrocarbon part of the molecule increases which cannot form hydrogen bonding with water and the solubility of higher homologues in water decreases.
Question 71.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than those of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, ethers, hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain, why.
Answer:
(1) Carboxylic group (-COOH) in acids is highly polar. in liquid state, pair of carboxylic acid molecules is held together by two intermolecular hydrogen bonds, have higher aggregations and in the vapour.
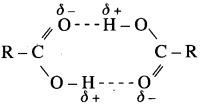
(2) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding in carboxylic acids state most of the carboxylic acid.s exist as dimmers in which two molecules are held by two hydrogen R – R bonds. Acidic hydrogen of one molecule forms hydrogen bond with carbonyl oxygen of the other molecule. This doubles the size of the molecule resulting in increase in o – intermolecular van der Waals forces, which in turn results in high boiling points. Therefore, carboxylic acids possess higher boiling points than those of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones. ether, hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Question 72.
Lower aliphatic carboxylic acids are miscible with water while higher carboxylic acids are immiscible.
Answer:
(1) Lower aliphatic carboxylic acids are miscible with water due to the formation of hydrogen bonding with water molecules.

(2) Hydrogen bonding between acid and water. As the molecular mass increases (he solubility of carboxylic acids in water decreases. The insolubility of carboxylic acids is due to increased hydrophobic interaction of hydrocarbon parts with water.
Question 73.
Explain why carboxylic acids are much weaker acids than mineral acids.
Answer:
Carboxylic acids are the organic compounds which are acidic in nature. However, compared to mineral acids like HCI or H2SO4. the carboxylic acids are weaker acids.
The strength of acidity depends upon their ability to release H+ ions. Greater the ease with which they release H+ ions, stronger is the acid.
Carboxylic acids when dissolved in water, pcoduce H+ due to its dissociation. (it does not dissociate completely.)

The mineral acid-s like HCI, H2SO4 release H+ ion to a larger extent as they dissociatc almost complctcly in aqueous solution for e.g. HCl → H+ Cl– thus carboxylic acids are weaker than mineral acids. The equilibrium exists in aqueous solution of carboxylic acid as
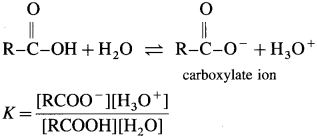
Since concentration of water practically remains constant
![]()
where Ka is acidity constant
Larger the value Ka greater is the extent of ionization and stronger is the acid. But strength of acids is expressed in ternis of their pKa values. Smaller the value of pKa. the stronger is the carboxylic acid. Here pKa value of carboxylic acids is higher than mineral acids. Hence, carboxylic acids arc weaker than mineral acids.
![]()
Question 74.
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols and alcohols. Explain. Why?
Answer:
(1) Carboxylic acid loses a proton as compared to phenol. Consider the ionization of carboxylic acid and phenol

Due to delocalization the negative charge over the ortho and para positions of aromatic ring, phenoxide anion is more stable than phenol. Thus phenol easily undergoes ionization

However, alcohol and alkoxide ion are single structures. In an alkoxide anion the negative charge is localized on a single oxygen atom. Hence, phenols are more acidic than alcohols.
(2) Carboxylic acid has two resonance hybride non equivalent structures (I & II) while carboxylate anion has two resonance hybrid equivalent structures (III & IV). The carboxylate ion is more stable than carboxylic acid and equilibrium is shifted towards the direction of increased ionization.
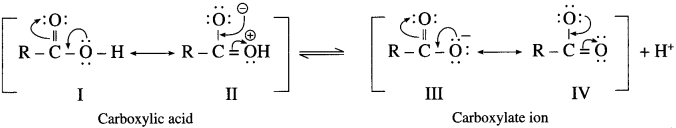
(3) Carboxylate ion has two equivalent resonance structures with nejative charge is delocalized over two electro negative oxygen atoms. Phenoxide anion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which negative charge is
delocalized over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atom. As a result carboxylate anion is more stable than phenoxide ion. Hence carboxylic acids ionize to the greater extent than phenol furnishing higher concentration of H+ ions. Therefore, carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols and alcohols.
Question 75.
Trichloro acetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. ExplaIn.
Answer:
(1) The acidic nature of carboxylic acid is due to the ability to release H ions. Greater the ease with which they release H+ ions, stronger is the acid. Any factor that stabilizes the carboxylate ion would help the release of H+
ions and thus increase the strength of the acid. The electron-withdrawing group attached to -carbon atom increases the strength of the acid. In trichloroacetic acid, three chloro substituents on s-carbon atom of acetic acid makes the electrons withdrawing effect more pronounced and the negative charge of carboxylate ion formed gets dispersed.
Thus, increases the stability of carboxylate ion.
![]()
(2) The acetate ion formed gets destabilised due to the electron releasing effect of a methyl group (+ I effect). As a result, acetic acid dissociates to a lesser extent.
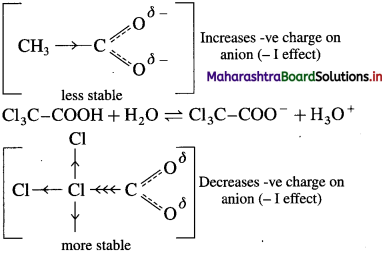
(3) The trichloro acetate ion formed gels stabilised due to electron-withdrawing effect of three 3Cl atoms (- I effect). As a result. trichloro acetic acid dissociates to a greater extent. Trichioro acetic acid having lower pKa value than acetic acid. Hence. trichloro acetic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
![]()
Question 76.
Which is the stronger acid in each of the following pairs ?
(1) CH3-COOH and CH2 = CH-COOH
Answer:
CH2 = CH-COOH is the stronger acid than CH3-COOH
(2) C6H5-COOH and C6H5-CH2-COOH
Answer:
C6H5-COOH is the stronger acid than C6H5-CH2-COOH

Answer:

(4) CH3-CH2-COOH and NC-CH2-COOH
Answer:
NC-CH2-COOH is the stronger acid than CH3-CH2-COOH
(5) (CH2)2CH-CH2-COOH and (CH3)2NH-CH2-COOH
Answer:
(CH3)2NH-CH2-COOH is the stronger acid than (CH3)2CH-CH2-COOH
(6) O2N-CH2-C00H and Cl-CH2-COOH
Answer:
NO2-CH2-COOH is the stronger acid than Cl-CH2-COOH.
Question 77.
Arrange the following acids in their increasing order of acidic strength.
(1) Acetic acid, chloroacetic acid, propionic acid, formic acid.
Answer:
Propionic acid < acetic acid < formic acid < chloroacetic acid
(2) Bromoacetic acid, chloroacetic acid, fluoroacetic acid, iodoacetic acid.
Answer:
Iodoacetic acid < bromoacetic acid < chloroacetic acid < fluoroacetic acid.
(3) Acetic acid, chloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid.
Answer:
Acetic acid < chloroacetic acid < dichloroacetic acid < trichloroacetic acid.
(4) n-butyric acid, 3-chlorobutyric acid, 2-chlorobutyric acid, 3-chlorobutyric acid.
Answer:
n-Butyric acid < 3-chlorobutyric acid < 2-chlorobutyric acid < 1-chlorobutyric acid.
(5) Acetic acid, benzoic acid, p-methoxy benzoic acid, p-nitrobenzoic acid.
Answer:
Acetic acid < benzoic acid < p-methoxy benzoic acid < p-nitrobenzoic acid.
(6) Acetic acid, phenyl acetic acid, p-nitro phenyl acetic acid.
Answer:
Acetic acid < phenyl acetic acid < p-nitro phenyl acetic acid.
(7) Benzoic acid, p-toluic acid, p-chlorobenzoic acid.
Answer:
p-toluic acid < benzoic acid < p-chlorobenzoic acid.

Question 78.
Arrange the following carboxylic acids in order of increasing acidity : m-Nitrobenzoic acid, Trichloroacetic acid, benzoic acid, a-Chlorobutyric acid.
Answer:
Acidity in the increasing order : Benzoic acid, m-nitrobenzoic acid, a-chlorobutyric acid, trichloroacetic acid.
![]()
Question 79.
Arrange the following carboxylic acids with increasing order of their acidic strength and justify your answer.
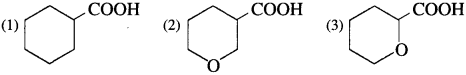
Question 80.
Explain polarity of carbonyl group.
Answer:
The polarity of a carbonyl group is duc to higher electronegativity of oxygen compared to carbon. It is explained on the basis of resonance involving neutral and dipolar structures.
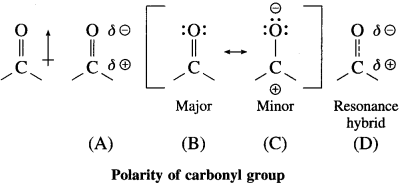
The carbonyl carbon has positive polarity (see structures (A) and (D)). Therefore, it is electron deficient. As a result, this carbon atom is electrophilic (electron loving) and is susceptible to attack by a nucleophile (Nu : –).
Question 81.
Explain SchifPs reagent test.
OR
What is a SchifPs reagent ? How is it used to detect aldehydes ?
Answer:
- Schiff’s reagent is prepared by dissolving pink p-rosaniline hydrochloride (dye Fuchsin) in water and passing SO2 gas till the pink solution is decolourised.
- Schiff s reagent is an oxidising agent.
- When an aldehyde is added to Schiff s reagent, the colourless solution turns pink or in magenta colour and aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
- This test is not given by ketones, hence, used to distinguish between aldehyde and ketone.
Question 82.
Which colour is obtained when SchifFs reagent is treated with acetaldehyde?
Answer:
When Schiff s reagent is treated with acetaldehyde, pink colour is obtained.
Question 83.
What is Tollen’s reagent?
Answer:
- Tollen’s reagent is an ammoniacal silver nitrate, [Ag(NH3)2]+ OH–.
- It is prepared by adding NH4OH solution to silver nitrate solution.

- It is a stronger oxidising agent than Fehling solution. Aldehyde when heated with Tollen’s reagent, silver mirror is deposited.
Question 84.
Explain Tollen’s reagent test.
OR
Explain silver mirror test.
Answer:
- Tollen’s reagent is an (ammoniacal silver nitrate) [Ag(NH3)2]+ OH–.
- When an aldehyde, like acetaldehyde is heated with Tollen’s reagent, it is oxidised to acetic acid and silver ions Ag+ in Tollen’s reagent complex are reduced to silver Ag giving greyish black precipitate or deposition of silver on inner surface of the test tube which shines like a mirror. Hence this test is also called silver mirror test.

- This test is not given by ketones.
- Hence Tollen’s reagent is used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
![]()
Question 85.
What is Fehling’s solution? How is it prepared?
Answer:
- Fehling’s solution is a complex of cupric ions with tartaric acid.
- It is a mild oxidising agent.
- It is prepared by mixing equal amount of Fehling’s solution ‘A’ containing CuSO4 solution and Fehling’s solution ‘B’ containing sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle salt) in caustic soda (NaOH) solution.
- It is used to detect aldehydes that decolourise deep blue colour of the solution and give red precipitate of Cu2O.
Question 86.
Explain Fehling’s solution test.
Answer:
- Fehling’s solution is a mixture of Fehling’s solution ‘A’ containing CuSO4 solution and Fehling’s solution ‘B’ containing sodium potassium tartrate (Rochella salt) in caustic soda (NaOH) solution.
- When an aldehyde is heated with Fehling’s solution, the deep blue colour of the solution disappears and Cu+2 (cupric ion) is reduced to Cu+ ion a red precipitate of cuprous oxide, Cu2O is obtained while aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylate ion.
- For example,
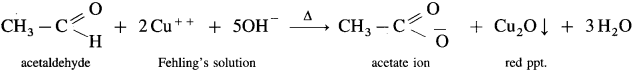
- This test is not given by ketones, since they cannot be oxidised by Fehling solution.
- Aromatic aldehydes are not oxidised by Fehling solution.
- Hence this test is used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones.
Question 87.
What is the action of the following reagents on ethanal :
(1) Fehling’s solution,
(2) Tollen’s reagent or Ammonical silver nitrate ?
Answer:
- When ethanal is heated with Fehling’s solution, the deep blue colour of the solution disappears and a red precipitate of Cu2O is obtained.
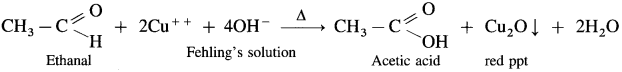
- When ethanal is heated with Tollen’s reagent a greyish black precipitate or deposition of silver is obtained.

Question 88.
Why is benzaldehyde NOT oxidized by Fehling solution ?
Answer:
When benzaldehyde is treated with Fehling solution, it does not reduce cupric ion (Cu+2). Fehling solution does not oxidise benzaldehyde. Thus, Fehling test cannot be used for aromatic aldehyde.
Question 89.
Explain laboratory test for ketonic group or sodium nitroprusside test.
Answer:
Laboratory test for ketonic group : Sodium nitroprusside test : When a freshly prepared sodium nitroprusside solution is added to a ketone, mixture is shaken well and basified by adding sodium hydroxide solution drop by drop, red colour appears in the solution, which indicates the presence of ketonic (> C = O) group.

The anion of ketone formed by alkali reacts with nitroprusside ion to form a red coloured complex which indicates the presence of the ketonic group.
Question 90.
What is the action of hydrogen cyanide on the following :
(1) Acetaldehyde
(2) Acetone
(3) Benzaldehyde?
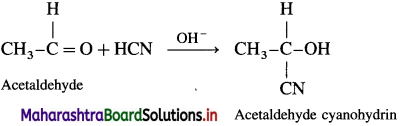
Answer:
(1) Action of HCN on acetaldehyde : When acetaldehyde is treated with hydrogen cyanide, acetaldehyde cyanohydrin is formed.
(2) Action of HCN on acetone : When acetone is treated with hydrogen cyanide, acetone cyanohydrin is formed.

(3) Action of HCN on benzaldehyde : When benzaldehyde is treated with hydrogen cyanide, benzaldehyde cyanohydrin is formed.

![]()
Question 91.
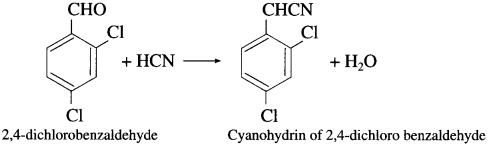
What is the action of hydrogen cyanide in basic medium on (1) butanone (2) 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde?
Answer:
(1) Action of hydrogen cyanide on butanone : When butanone is treated with hydrogen cyanide, butanone cyanohydrin is obtained.

(2) Action of hydrogen cyanide on 2,4-dichlorobenzaldehyde : When 2, 4-dichloro benzaldehyde is treated with hydrogen cyanide, cyanohydrin of 2,4-dichloro benzaldehyde is obtained.
Question 92.
What is the action of sodium bisulphite on :
(1) Acetaldehyde
(2) Acetone (propanone)?
Answer:
(1) Acetaldehyde reacts with saturated aqueous solution of sodium bisulphite (NaHSO3) and forms crystalline acetaldehyde sodium bisulphite. It is water soluble crystalline solid.

(2) Acetone reacts with saturated aqueous solution of sodium bisuiphite (NaHSO3) and forms crystalline acetone sodium bisuiphite. It is water soluble crystalline solid.

Question 93.
A carbonyl compound ‘A’ having molecular formula C5H10O forms crystalline precipitate with sodium bisulphite and gives positive iodoform test but does not reduce Fehling solution. Write the structure of carbonyl compound.
Answer:
A carbonyl compound C5H10O has two structures.

Pentan-2-one forms crystalline precipitate with sodium bisulphite and gives positive iodoform test. But does not reduce Fehling solution.
Pentan-3-one does not react with iodine and NaOH because it does not contain  group.
group.
![]()
Question 94.
How does alcohols react with aldehydes and ketones?
Answer:
Aldehyde reacts with one molecule of anhydrous monohydric alcohol in presence of dry hydrogen chloride to give alkoxyalcohol known as hemiacetal, which further reacts with one more molecule of anhydrous monohydric alcohol to give a geminaldialkoxy compound known as acetal as shown in the reaction.

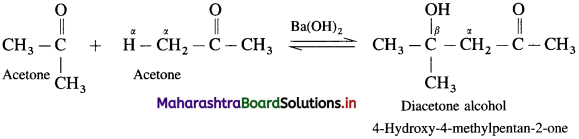
Ketones react with 1, 2 – or 1, 3 – diols in presence of dry hydrogen chloride to give five or six-membered cyclic ketals.
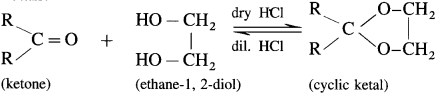
Question 95.
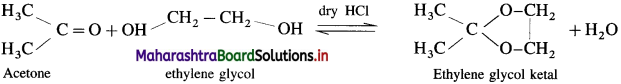
What is the action of ethanol on acetaldehyde ? What is the action of ethylene glycol on acetone ?
Answer:
Acetaldehyde reacts with one equivalent of monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry hydrogen chloride to form an intermediate known as hemiacetal, which further adds another molecule of alcohol to form a gem-dialkoxy compound known as acetal. Acetone reacts with ethylene glycol under similar conditions to form cyclic products known as ethylene glycol ketals.

Question 96.
Write the structure of product in the following reactions:
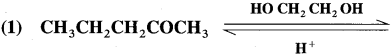
Answer:

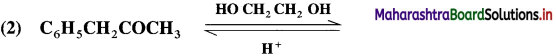
Answer:
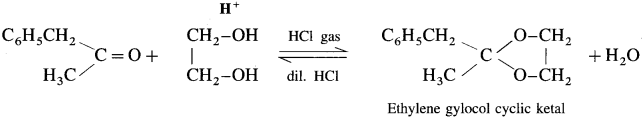
Question 97.
How does Grignard reagent react with the carbonyl compounds (or aldehydes and ketones)?
Answer:
The carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones react with Grignard reagent (R – Mg – X) in dry ether and form a complex which on further hydrolysis with acid forms the corresponding alcohol.

![]()
Question 98.
What is the action of Grignard reagent, CH3 – Mg – I on : (1) formaldehyde (2) acetone?
Answer:
(1) Grignard reagent with formaldehyde gives a primary alcohol.
Formaldehyde on reaction with Grignard reagent, CH3 – Mg – I in dry ether forms a complex which on hydrolysis with dilute HCl forms ethyl alcohol.

(2) Acetone on reaction with Grignard reagent, CH3 – Mg – I in dry ether forms a complex which on hydrolysis with dilute HC1 forms tert-butyl alcohol.
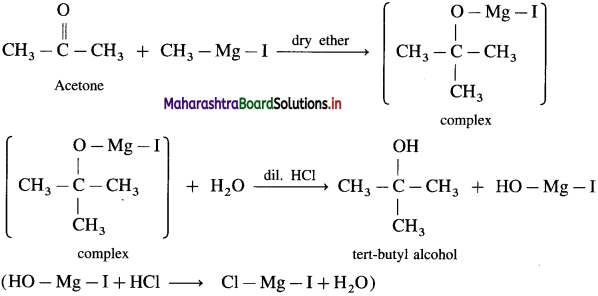
Question 99.
Explain the mechanism of addition reactions of ammonia derivatives H2N-Z with carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones).
Answer:
Derivatives of ammonia H2N-Z reacts with carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones) in weakly acidic medium to give addition products, which loses a water molecule to give a final product imine derivatives. A substituted imine is called a Schiff base. Schiff bases are solids and have sharp melting points.
General reaction :

Question 100.
What Is the action of ethylamine on :
(1) acetaldehyde
(2) acetone ?
Answer:
(1) Acetaldehyde on reaction with ethyl amine forms imine (Schiff base).
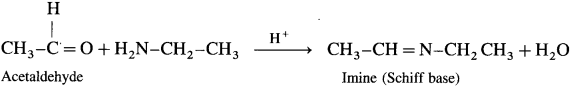
(2) Acetone on reaction with ethyl amine forms imine (Schiff base).

![]()
Question 101.
What are oximes? Which functional group do they contain?
Answer:
Oximes : These are the compounds obtained by the reactions of carbonyl compounds namely aldehydes and ketones with hydroxyl amine NH2OH.

Question 102.
What is the action of hydroxyl amine (NH2OH) on (1) acetaldehyde (2) acetone?
Answer:
(1) Acetaldehyde on reaction with hydroxyl amine (in weakly acidic medium) forms crystalline acetaldoxime.

(2) Acetone on reaction with hydroxyl amine (in weakly acidic medium) forms crystalline acetoxime.

Question 103.
What are hydrazones?
Answer:
Carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones react with hydrazine forming compounds like hydrazones. For example, acetaldehyde on reaction with hydrazine gives acetaldehyde hydrazone.
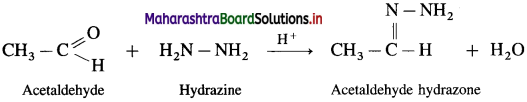
Question 104.
Which compound can convert ![]()
Answer:
The compound which can convert![]() .
.
Question 105.
What is the action of hydrazine on (1) formaldehyde (2) acetone ?
Answer:
(1) Formaldehyde on reaction with hydrazine forms formaldehyde hydrazone.

(2) Acetone with hydrazine forms acetone hydrazone.

Question 106.
What are phenylhydrazones?
Answer:
The carbonyl compounds like aldehydes and ketones on reaction with phenylhydrazine form hydrazones. For example, acetaldehyde on reaction with phenylhydrazine forms acetaldehydephenylhydrazone.

Question 107.
What is the action of phenylhydrazine on (1) formaldehyde (2) acetone (propanone) ?
Answer:
(1) Formaldehyde on reaction with phenylhydrazine forms formaldehydephenylhydrazone.

(2) Acetone on reaction with phenylhydrazine forms acetone phenylhydrazone.

![]()
Question 108.
What is the action of 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine on
(1) Acetaldehyde
(2) Acetone
(3) Butanone
(4) Benzaldehyde ?
OR
Complete and rewrite the balanced chemical equation : Butanone + 2, 4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine.
Answer:
(1) Acetaldehyde on reaction with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine forms 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone.

(2) Acetone on reaction with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine forms 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone.
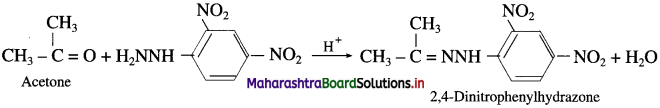
(3) Butanone on reaction with 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine forms 2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazone.

Question 109.
What is the action of semi carbazide on (1) Acetaldehyde (2) Acetone?
Ans.
(1) Acetaldehyde on reaction with semicarbazide forms scrnicarbazone derivative.
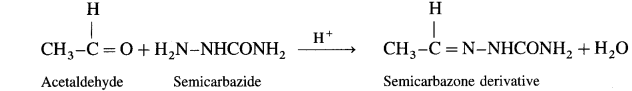
(2) Acetone on reaction with sernicarbazide forms semicarbazone derivative.

Question 120.
Write the structures of carbonyl compounds and ammonia derivatives that combine to give following imines.
Answer:
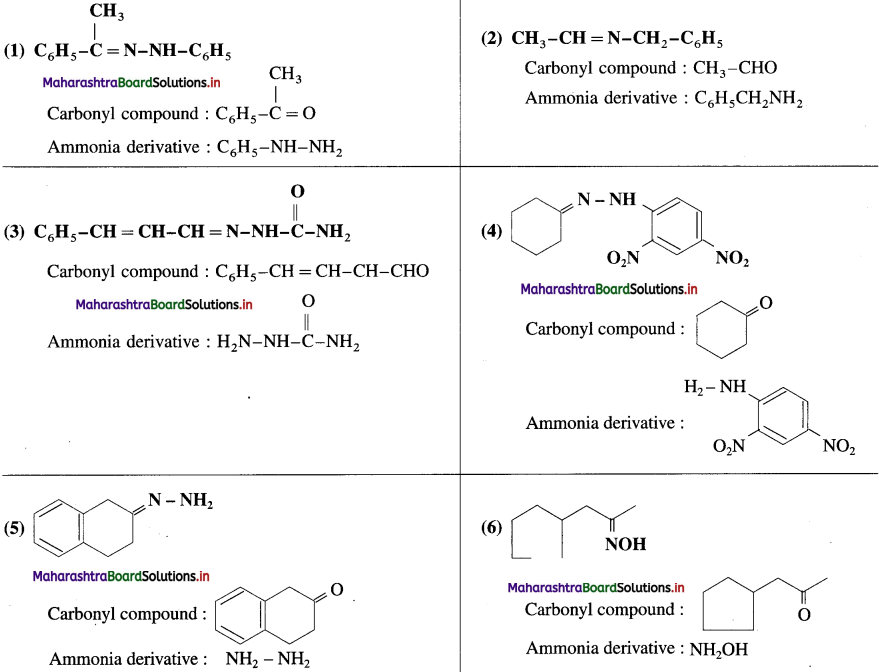
![]()
Question 121.
Write the structure of the products obtained from the following ketones by action of hydrazine in presence of (1) slightly acidic medium (2) strong base KOH.
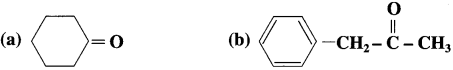
Answer:
(1) In slightly acidic medium
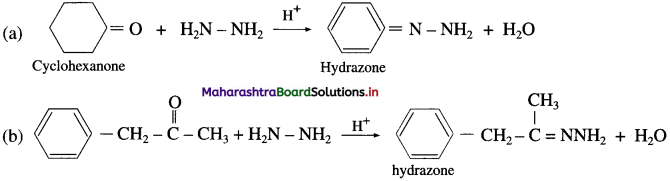
(2) In the presence of a strong base KOH
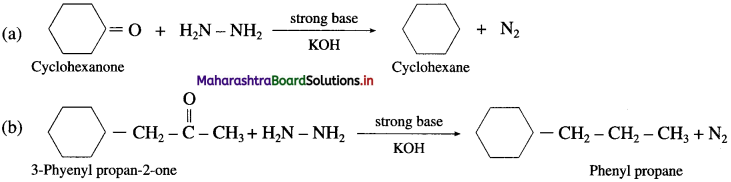
Question 122.
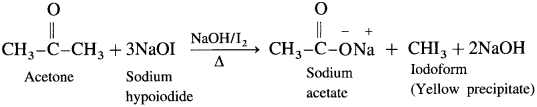
Explain haloform reaction.
Answer:
A ketone containing -COCH3 group is oxidised by sodium hypohalite a mixture of (sodium hydroxide and halogen) results in the formation of sodium salt of carboxylic acid having one carbon atom less than that of ketone and methyl group is converted to haloform.

Acetaldehyde is the only aldehyde which gives haloform reaction. In this reaction, R may be hydrogen, methyl group or aryl group and X may be Cl, Br or I. The reaction is given by all methyl ketones (CH3 – CO – R) and all alcohols containing CH3 – (CHOH) group.
When a methyl ketone is warmed with iodine and sodium hydroxide, a yellow precipitate of iodoform is obtained. The iodoform reaction is used as a qualitative test for detection of CH3CO-group in a organic compound.
Question 128.
Identify the compounds, amongst the following, that give positive iodoform test.
(CH3)2CHOH, (CH3)3COH, CH3COCH2CH2CH3, CH3CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH(OH)CH2CH3, CH3CH2OH, C6H5COCH2CH3, CH3CHO, C6H5CH2CH2OH and CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3.
Answer:
For an iodoform test, the carbonyl compound must have 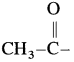 group.
group.
The compounds that give positive iodoform test :
![]()
Question 129.
Explain cross aldol condensation.
Answer:
(1) An aldol condensation between two different carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and or ketones) takes place even though one of the two carbonyl compounds molecules does not contain a-hydrogen atom e.g. HCHO and C6H5CHO.
(2) If both aldehydes or ketones contain two a-hydrogen atoms each, then a mixture of four products, is formed. For example, a mixture of ethanal and propanal on reaction with dilute alkali followed by heating gives a mixture of four products.
Self aldol condensation:

Cross aldol condensation:
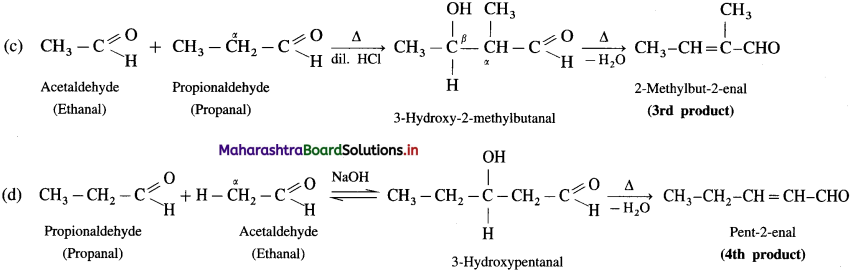
Question 130.
Write the structure of the major product of the following crossed aldol condensation.
Answer:
(1) Formaldehyde and propionaldehyde :

(2) Benzaldehyde with acetone:
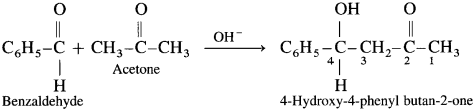
Question 131.
Explain aldol condensation reaction of propionaldehyde.
Answer:
Since propionaldehyde has an a-hydrogen atom it undergoes aldol condensation with alkali Ba(OH)2, forming 3-Hydroxy-2-methylpentanal.
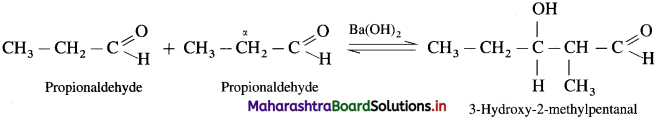
3-Hydroxy-2-methylpentanal on heating undergoes dehydration and forms 2-Methylpent-2-enal.

![]()
Question 132.
If a mixture of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde is subjected to aldol condensation, predict the products formed and draw their structures.
Answer:
Since formaldehyde, ![]() does not have α-hydrogen atom it will not undergo self aldol condensation. Since acetaldehyde
does not have α-hydrogen atom it will not undergo self aldol condensation. Since acetaldehyde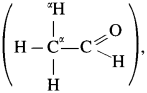 has a-hydrogen atom, it will undergo self aldol condensation.
has a-hydrogen atom, it will undergo self aldol condensation.
Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde undergo cross aldol condensation.

Hence two aldol condensation products will be obtained.
Question 133.
Indicate by equations, what happens when a mixture of acetaldehyde and acetone are treated with alkali.
Answer:
When a mixture of acetaldehyde and acetone is treated with alkali, Ba(OH)2, they undergo self aldol condensation and cross aldol condensation.
(1) Self aldol condensation acetaldehyde :

(2) Self aldol condensation of acetone:
(3) Cro5s aldol condensation:

Question 134.
Explain Cannizzaro reaction.
OR
Write a note on Cannizzaro reaction.
OR
Write a note on self oxidation-reduction reaction of aldehyde with suitable example.
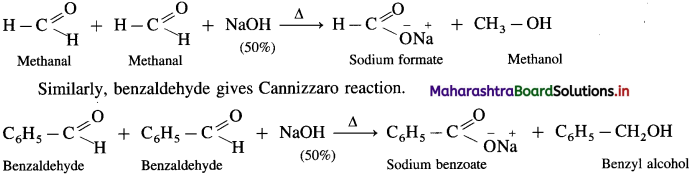
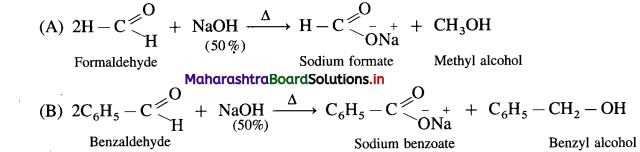
Answer:
- Aldehydes which do not have a-hydrogen atom, on heating with concentrated alkali (50% aqueous or ethanolic solution of NaOH or KOH) undergo self oxidation and reduction reaction or redox reaction.
- This self redox reaction or disproportionation reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction.
- In this reaction one molecule of the aldehyde is oxidised to carboxylic acid while the second molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to alcohol (carboxylic acid formed, reacts with alkali, NaOH and forms a salt R – COONa).
- When formaldehyde (methanal) is heated with 50% NaOH solution, methanol (reduction product) and sodium formate (oxidation product) are formed.
- Ketones and aldehydes like acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, etc. having a – H atom do not give Cannizzaro reaction.
![]()
Question 135.
Explain cross Cannizzaro reaction with example.
OR
Write the reaction for the action of 50 % NaOH on a mixture of formaldehyde and benzaldehyde.
Answer:
The reaction between two different aldehydes, not having a-hydrogen atoms is called cross Cannizzaro reaction. These two aldehydes undergo disproportionation in presence of concentrated alkali to give four products. However, if one of the aldehydes is formaldehyde, the reaction yields exclusively formate and alcohol to corresponding aldehyde.
Formaldehyde and benzaldehyde since do not have a-hydrogen atom, will undergo Cannizzaro (redox) reactions.
(1) Self Cannizzaro (redox) reaction :
(2) Cmss Cannizzaro (redox) reaction:
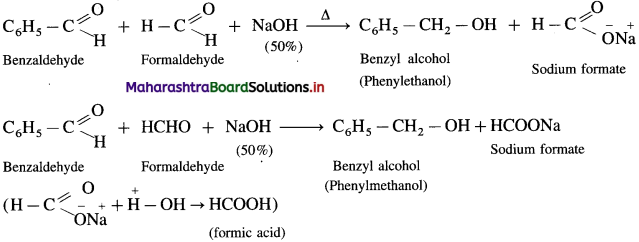
Question 136.
What is the action of cone, potassium hydroxide on benzaldehyde?
Answer:
When benzaldehyde is heated with concentrated potassium hydroxide in presence of methanol, a mixture of potassium benzoate and phenyl methanol (benzyl alcohol) is obtained.

Question 137.
Differentiate between Cannizzaro reaction and Aldol reaction.
Answer:
| Cannizzaro reaction | Aldol reaction |
| 1. It is given by aldehydes not having alpha hydrogen atom. 2. In this reaction an aldehyde is converted to the corresponding acid and an alcohol. 3. It is a disproportionate ion reaction. 4. It requires concentrated alkali as a catalyst. |
1. It is given by aldehydes and ketones possessing alpha hydrogen atom. 2. In this reaction aldehydes and ketones are converted into aldol and ketols, respectively. 3. It is an addition reaction. 4. It requires dilute alkali as a catalyst. |
Question 138.
Write the chemical equations for aldol condensation or Cannizzaro reaction that the following compounds undergo :
(1) Propanal
(2) 2-Methyl propanal (isobutyraldehyde)
(3) Pentanal
(4) 3-Methylbutanal
(5) Acetophenone
(6) p-Methoxybenzaldehyde
(7) 2-Methyl cyclohexanone
(8) Chloral
(9) Cyclopentanone
(10) Phenyl acetaldehyde
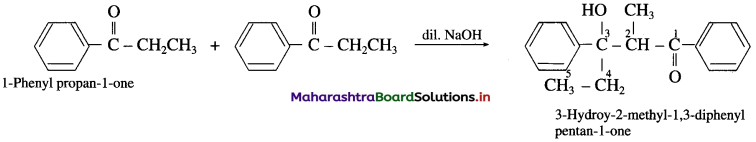
(11) 1-Phenyl propan-l-one.
Answer:
(1) Propanal (Aldol condensation) : Propanal contains α-H atom. Two molecules of propanal undergo self condensation in presence of dil. alkali to form 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl pentanal.
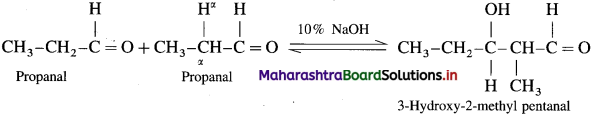
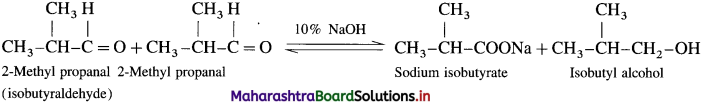
(2) 2-NIethvl propanal (Canniuaro reaction) : Two molecules of them undergo cannizzaro reaction in the presence of 50% alkali to form sodium isobutyrate and isohutyl alcohol.
(3) Pentanal (Aldol condensation) : Pentanal contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self condensation in the presence of dil. alkali to form 3-Hydroxy-2-propyl heptanal.

(4) 3-Methyl butanal (Aldol condensation) : 3-Methyl butanal contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self condensation in the presence of dil. alkali to form 3-Hydroxy-2-isopropyl-5-methyl hexanol.

(5) Acetophenone (Aldol condensation) : Acetophenone contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self condensation in the presence of base to form 3-Hydroxy-1, 3-diphenyl but-l-one.

(6) p-Methoxybenzaldehyde (Cannizzaro reaction) :

(7) 2-Methyl cyclohexanone
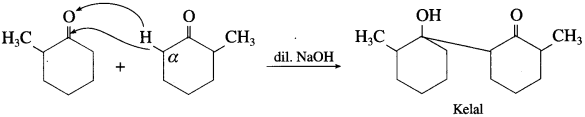
(8) Chloral (Cannizzaro’s reaction) : There is no α-H atom CCl3CHO, therefore it undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction.

(9) Cyclopentanone (Aldol condensation) : Cyclopentanone contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self-condensation in the presence of base to form 2-(l-Hydroxy-1 cyclopentyl) cyclo pentane-l-one.

(10) Phenyl acetaldehyde (Aldol condensation) : Phenyl acetaldehyde contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self-condensation in the presence of base to form 3-Hydroxy-2, 4-diphenylbutanal.
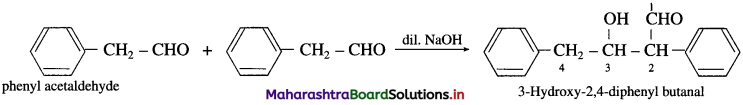
(11) 1-phenyl propan-l-one (Aldol condensation) : 1-phenyl propan-l-one contains a-H atom. Two molecules of them undergo self-condensation in the presence of base to form 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-l, 3-diphenyl pentan-l-one
3-Hydroy-2-methyl-1, 3-diphenyl pentan-l-one
![]()
Question 139.
Write a note on Clemmensen reduction.
OR
Explain Clemmeusen’s reduction.
OR
Explain the reduction of carbonyl group into methylene group.
Answer:
- The carbonyl group
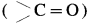 on reduciion with zinc amalgam (Zn – Hg) in concentrated hydrochloric acid is converted into methylene group ( – CH2 -).
on reduciion with zinc amalgam (Zn – Hg) in concentrated hydrochloric acid is converted into methylene group ( – CH2 -).

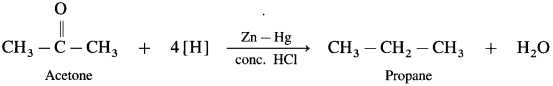
- Aldehydes and kctoncs on reaction with Zn – Hg in concentrated HCl forms corresponding alkanes. ibis reduction is called Clemmensen reduction.

- Acetaldehyde on reduction with Zn – Hg in concentrated HCl forms ethane.

- Acetone on reduction with Zn – Hg in concentrated HCl forms propane.
Question 140.
Explain Wolff-Kishner reduction.
Answer:
Hydrazine (NH2-NH2) reduces carbonyl group![]() of aldehydes or ketones to metylene group
of aldehydes or ketones to metylene group ![]() When aldehyde or ketone is heated with hydrazine in the presence of base such as potassium hydroxide and ethylene glycol, an alkane is obtained due to reduction of carbonyl compound.
When aldehyde or ketone is heated with hydrazine in the presence of base such as potassium hydroxide and ethylene glycol, an alkane is obtained due to reduction of carbonyl compound.
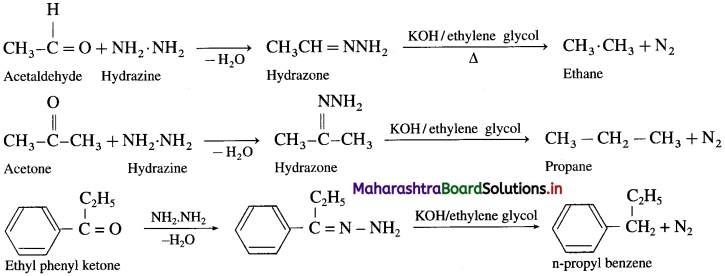
Question 141.
Compound A (C5H10O) form a phenyl hydrazone and gives a negative Tollen’s reagent test and iodoform test. On reduction with Zn-Hg/HCl, compound A gives n-pentane. Write the structure of ‘A’.
Answer:
Since A (C5H10O) forms a phenyl hydrozone, it is a carbonyl compound. Since it gives negative Tollen’s reagent test, it is not an aldehyde but it must be a ketone.
Since it doesn’t give iodoform test, it doesn’t have  group.
group.
Hence the structure of ‘A’ will be,
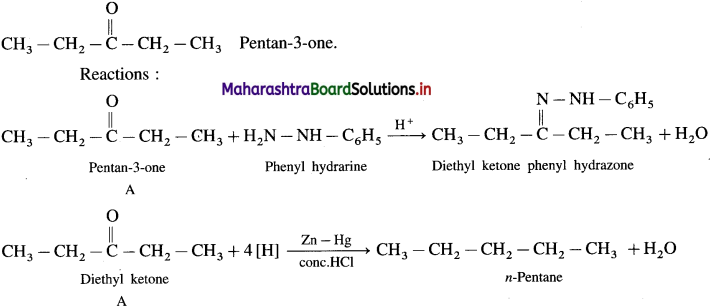
![]()
Question 142.
Identify A and B in the following reactions :
![]()
Answer:

![]()
Answer:
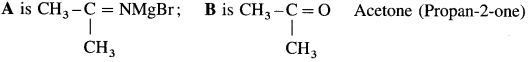
![]()
Answer:
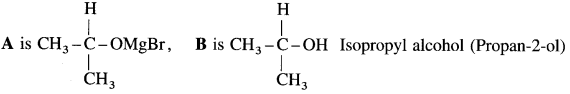
![]()
Answer:

Question 143.
What is the action of concentrated nitric acid on (1) Benzaldehyde (2) Benzophenone?
Answer:
- Benzaldehyde on reaction with concentrated nitric acid in presence of cone. H2SO4 forms m-nitrobenzaldehyde

- Benzophenone on reaction with concentrated nitric acid in presence of cone. H2SO4 forms m-nitrobenzophenone
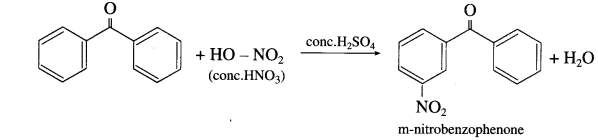
Question 144.
Explain laboratory tests for carboxyl (- COOH) group.
Answer:
The presence of – COOH group in carboxylic acids is identified by the following tests :
(1) Litmus test : (valid for water soluble substances)
Aqueous solution of Organic compound containing – COOH group turns blue litmus red which indicates the presence of acidic functional group.
(2) Sodium bicarbonate test : When sodium bicarbonate is added to an organic compound containing – COOH group, a brisk effervescence of carbon dioxide gas is evolved. Water insoluble acid goes in solution and gives precipitate an acidification with cone. HCl. This indicates the presence of -COOH group.
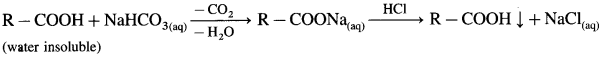
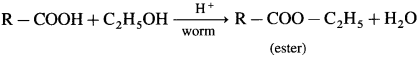
(3) Ester test : One drop of concentrated sulfuric acid is added to a mixture of given organic compound containing – COOH group and one mL of ethanol, the reaction mixture is heated for 5 minutes in hot water bath. After this, hot solution is poured in a beaker containing water, fruity smell of ester confirms the presence of carboxylic acid.
![]()
Question 145.
How is acid chloride obtained from carboxylic acid?
Answer:
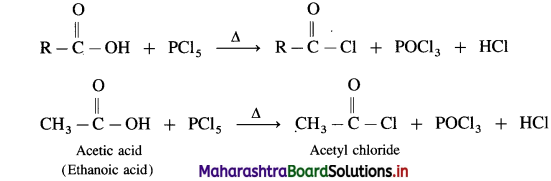
Carboxylic acid on heating with thionyl chloride (SOCl2), phosphorus trichloride (PCl3) or phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) give corresponding acid chlorides. In this reaction – OH of carboxyl group is replaced by -Cl.
The reactions are :
(1) Action on SOCl2 on carboxylic acid :
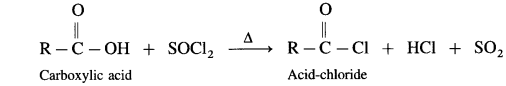
Example : Acetic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to give acetyl chloride.

(2) Action of PCl3 on carboxylic acid (ethanoic acid) :

Example : Action of phosphorus trichloride on acetic acid gives acetyl chloride.
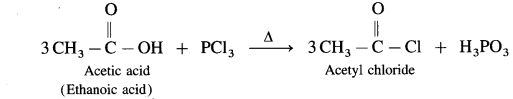
(3) Action of PCI5 on carboxIic acid :
Question 146.
How will you convert 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid to 3,5-Dinitrobenzoyl chloride?
Answer:
When 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid is heated with phosphorus pentachloride, 3,5-Dinitrobenzoyl chloride is obtained.

Question 147.
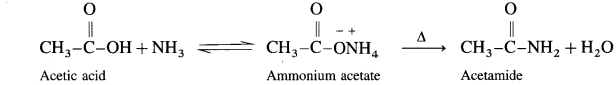
How is acid amide obtained from carboxylic acid?
Answer:
Carboxylic acid or acid chloride with ammonia salts, which on further strong heating at high temperature decompose to give amides.
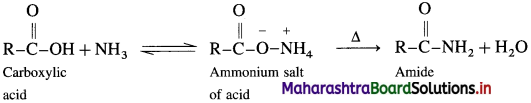
When acetic acid is treated with ammonia, ammonium acetate is obtained. Ammonium acetate on strong heating decomposes to form acetamide.
When acetyl chloride is treated with ammonia, acetamide is obtained

![]()
Question 148.
How is acid anhydride obtained from carboxylic acid?
Answer:
When carboxylic acid is heated with strong dehydrating agent like phosphorus pentoxide or concentrated sulphuric acid, an acid anhydride is obtained,
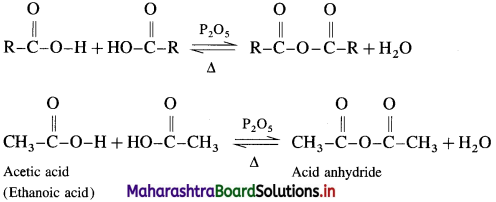
The reaction is reversible and anhydride is hydrolysed back to acid.
Alternatively, when sodium acetate is heated with acetyl chloride, acetic anhydride is obtained. This reaction is irreversible.

Question 149.
What is decarboxylation of an acid ? How is it done?
OR
What happens when sodium acetate is heated with soda lime ?
Answer:
Removal of a carboxylic group from acid is called decarboxylation. Decarboxylation of an acid is carried out by heating anhydrous sodium salts of carboxylic acids with soda lime (NaOH + CaO). The product hydrocarbons obtained contain one carbon atom less than the carboxylic acid.
![]()
When sodium acetate is heated with soda lime, methane is obtained.
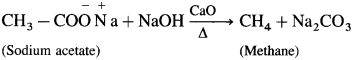
Question 150.
How is alcohol obtained from carboxylic acid ?
OR
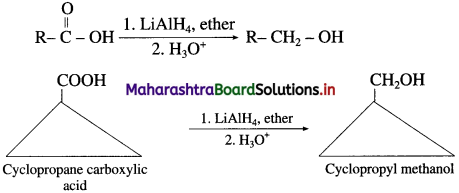
What is the action of LiAlH4/H3O+on ethanoic acid? Write balanced equation for the conversion :
Cyclopropane carboxylic acid to Cyclopropylmethanol.
Answer:
Carboxylic acids are reduced to primary alcohols using powerful reducing agent lithium aluminium hydride.
(i) When ethanoic acid is reduced in the presence of LiAlH4 in dry ether, forms ethanol.
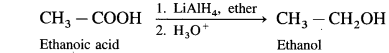
(ii) When cyclopropane carboxylic acid is reduced in the presence of lithium aluminium hydride in dry ether, forms cyclopropyl methanol.
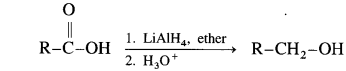
![]()
Question 151.
What is the action 9f following compounds on cyclohexanone in presence of dry hydrogen chloride?
(1) Ethyl alcohol
(2) Ethylene glycol
Answer:
(1) With Ethyl alcohol : Cyclohcxanonc reacts with one equivalent of monohydric ethyl alcohol lo form hemi ketal, which further adds another molecule of alcohol to form a gem-dialkox compound known as ketal.
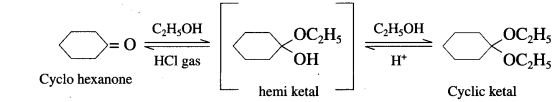
(2) With Ethylene glycol : cyclohexanone reaCts with ethylene glycol to form cyclic ketal.

Question 152.
Answer the following in one sentence.
1. Name the compound which reacts with formaldehyde to produce ethyl alcohol.
Answer:
The compound which reacts with formaldehyde to produce ethyl alcohol is methyl magnesium iodide.
2. What are imines ?
Answer:
These are the compounds obtained by the reactions of carbonyl compounds namely aldehydes and ketones with primary amine.

3. Why does skin have burning sensation, when an ant bites ?
Answer:
When an ant bites, formic acid is released from an ant which gives burning sensation as the acid comes in contact with the skin.
4. What is the percentage of acetic acid in vinegar?
Answer:
The percentage of acetic acid in vinegar is 6 to 8%.
5. Which reagent is used to distinguish formic acid and acetic acid?
Answer:
The reagent used to distinguish formic acid and acetic acid is ammoniacal silver nitrate.
6. What happens when acetyl chloride is treated with dibenzyl cadmium ? Give reaction.
Answer:
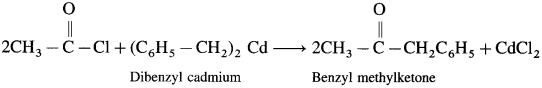
7. Complete the following reaction :
Answer:
8. Give reason : Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Answer:
Aromatic carboxylic acids do not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction because the catalyst aluminium chloride (Lewis acid) gets bonded to carboxyl group.
9. Write the name of two compounds which do not contain carbonyl group but show iodoform test.
Answer:
The name of two compounds which do not contain carbonyl group but show iodoform test are ethanol
10. Give reason : In semicarbazide, – NH2 group bonded to carbonyl group is not involved in the formation of semicarbazone.
Answer:
NH2 group attached to – NH group in semicarbonide is more active than NH2 group attached to carbonyl group due to electron density difference.
![]()
11. Fehling solution does not oxidise benzaldehyde but Tollen’s reagent oxidises benzaldehyde. Give reason.
Answer:
When benzaldehyde is heated with Fehling solution, there is no change in colour of the solution, Cu2+ ion is not reduced, hence Fehling solution does not oxidise benzaldehyde. However, Tollen’s reagent oxidises benzaldehyde to give silver mirror test.
12. Give reason : Direct attachment of vinyl group to carboxylic group increases the acidity of corresponding acids.
Answer:
Direct attachment of vinyl group to carboxylic group increases the acidity of corresponding acids due to greater electronegativity of sp2-hybridised carbon to which carboxyl carbon is attached.

Multiple Choice Questions
Question 153.
Select and write the most appropriate answer from the given alternatives for each sub-question :
1. IUPAC name of
(a) l-Phenylhexan-2-one
(b) 6-Phenylhexan-5-one
(c) l-Benzylhexan-2-one
(d) Dodecan-5-one
Answer:
(a) l-Phenylhexan-2-one
2. The general formula of carbonyl compounds is
(a) CnH2n+1OH
(b) CnH2nO
(c) CnH2nO2
(d) CnH2n+1O
Answer:
(b) CnH2nO
3. Aldehydes and ketones are
(a) chain isomers
(b) functional isomers
(c) geometrical isomers
(d) position isomers
Answer:
(b) functional isomers
4. Identify ‘C’ in the following reaction,
\(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{Br} \stackrel{\mathrm{KCN}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{A} \stackrel{\mathrm{H}^{+} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{B} \stackrel{\mathrm{LiAlH}_{4}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{C}\)
(a) Propan – 1 – ol
(b) Propanone
(c) 2-Ethyl-3-pentanone
(d) Propanal
Answer:
(d) Propanal
5. Grignard reagent when reacted with alkyl cyanide followed by hydrolysis gives
(a) an aldehyde
(b) a ketone
(c) a primary alcohol
(d) a secondary alcohol
Answer:
(b) a ketone
![]()
6. Identify ‘ B ’ in the following reaction :
\(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{N} \stackrel{\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{MgI}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{A} \underset{\mathrm{HCl}}{\stackrel{2 \mathrm{HOH}}{\longrightarrow}} \mathrm{B}+\mathrm{NH}_{3}+\mathrm{MgIOH}\)
(a) Magnesium intermediate
(b) Ethanol
(c) Propanal
(d) Propanone
Answer:
(d) Propanone
7. \(\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B} \stackrel{\text { dry ether }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Col}\) Complex \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} / \mathrm{H}^{+}\) Ethyl Methyl Ketone. In the above reaction, A and B are
(a) Formonitrile, Propyl magnesium bromide
(b) Ethyl cyanide, Ethyl magnesium bromide
(c) Hydrogen cyanide, Ethyl magnesium bromide
(d) Acetonitrile, Ethyl magnesium bromide
Answer:
(d) Acetonitrile, Ethyl magnesium bromide
8. A dilute solution of p-rosaniline hydrochloride in water whose pink colour has been discharged by passing sulphur dioxide, does not restore its colour by
(a) HCHO
(b) CH2CHO
(c) (CH3)2COCH3
(d) CCl3CHO
Answer:
(c) (CH3)2COCH3
9. The reagent with which both acetaldehyde and acetone reacts easily is –
(a) Fehling’s solution
(b) Tollen’s reagent
(c) Grignard reagent
(d) Schiff s reagent
Answer:
(c) Grignard reagent
10. Isopropyl methyl ketone when treated with Zn-Hg and concentrated hydrochloric acid give
(a) iso-butane
(b) iso-pentane
(c) n-pentane
(d) neo-pentane
Answer:
(b) iso-pentane
11. The formation of acetone cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of
(a) Nucleophilic addition
(b) Nucleophilic substitution
(c) Electrophilic addition
(d) Electrophilic substitution
Answer:
(a) Nucleophilic addition
12. Which of the following is Fehling solution ‘A’?
(a) CuSO4 solution
(b) CaSO4 solution
(c) NaOH solution
(d) Sodium potassium tartarate solution
Answer:
(a) CuSO4 solution
13. The compound ‘X’ upon alkaline hydrolysis gives a product which reacts with phenylhydrazine but does not reduce ammoniacal silver nitrate solution. A possible structure for ‘X’ is
(a) CH3CHCl CH2Cl
(b) CH3CCl2CH3
(c) CH3CH2CH2Cl
(d) CH3CH2CHCl2
Answer:
(b) CH3CCl2CH3
![]()
14. Which of the following is the correct statement with respect to aldehyde and ketones ?
(a) Ketones are reducing agents
(b) Aldehydes are good reducing agents
(c) Cannizzaro reaction is an addition reaction
(d) Ketones do not react with Grignard reagent
Answer:
(b) Aldehydes are good reducing agents
15. Acetaldehyde acts as
(a) a catalyst
(b) a reducing agent
(c) an oxidizing agent
(d) a mordant
Answer:
(b) a reducing agent
16. An organic compound (A) C3H80 on oxidation gives (B) C3H6O2. The compound A may be
(a) an ester
(b) an alcohol
(c) an aldehyde
(d) a ketone
Answer:
(b) an alcohol
17. Identify ‘B’ from the following reaction :
\(\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CHO}+\mathrm{NH}_{2} \mathrm{OH} \rightarrow \mathrm{A} \stackrel{\mathrm{Na} / \mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{OH}}{\Delta} \mathrm{B}\)
(a) Propan-1-amine
(b) Propan-2-amine
(c) Isopropylamine
(d) Dimethylamine
Answer:
(a) Propan-1-amine
18. Sodium borohydride does not reduce
(a) – COOH group
(b) – NO2 group
(c) – X atom
(d) – CHO group
Answer:
(a) – COOH group
19. An aldehyde when warmed with Zn/Hg and cone. HCl gives
(a) alcohol
(b) hydrocarbon
(c) carboxylic acid
(d) ketone
Answer:
(b) hydrocarbon
20. Acetaldol is
(a) 3-hydroxy butanol
(b) 3-hydroxy butanal
(c) 2-hydroxy propanal
(d) 3-hydroxy pentanal
Answer:
(b) 3-hydroxy butanal
21. Acetone can be reduced to propane, the reduction is called
(a) Clemmensen’s reduction
(b) catalytic reduction
(c) Rosenmund’s reduction
(d) partial reduction
Answer:
(a) Clemmensen’s reduction
![]()
22. Which of the following reagents can react with acetaldehyde to give water soluble white crystal-line solid?
(a) NaHSO4
(b) NaHSO3
(c) Na2SO3
(d) Na2SO4
Answer:
(b) NaHSO3
23. Which of the following compounds does NOT undergo aldol condensation?

Answer:
(a)
24. Formalin is 40% aqueous solution of :
(a) Methanal
(b) Methanoic acid
(c) Methanol
(d) Methanamine
Answer:
(a) Methanal
25. Which of the following compounds do not produce pink colour with Schiff s reagent?
(a) Formaldehyde
(b) 2-propanone
(c) 3-pentanone
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
26. Both aldehydes and ketones can react with
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) the Grignard reagent
(c) Fehling’s solution
(d) Schiffs reagent
Answer:
(b) the Grignard reagent
27. Aldol reaction is.
(a) an addition reaction
(b) an elimination reaction
(c) a self-reduction reaction
(d) a disproportionate ion reaction
Answer:
(a) an addition reaction
28. The reaction in which two molecules combine to form a new molecule with the elimination of a small molecule like water is called
(a) an oxidation reaction
(b) a condensation reaction
(c) a hydrolysis reaction
(d) a redox reaction
Answer:
(b) a condensation reaction
29. Benzaldehyde undergoes Cannizzaro’s reaction to give
(a) sodium benzoate and methyl alcohol
(b) sodium benzoate and benzyl alcohol
(c) benzyllic acid and benzyl alcohol
(d) phenol and benzoic acid
Answer:
(b) sodium benzoate and benzyl alcohol
![]()
30. Identify ‘X’ in the following reaction :
CH3-CHO + X → CH3-CH = N-NH-C6H5 + H2O
(a) C6H5-NH2
(b) C6H5-NH-NH2
(c) C6H5-N = NH
(d) C6H5-NH-NH-CH3
Answer:
(b) C6H5-NH-NH2
31. What happens when propanal is treated with zinc amalgam and conc.HCl ?
(a) Propan-l-ol
(b) Propan-2-ol
(c) Propane
(d) Propanone
Answer:
(c) Propane
32. Identify ‘ B ’ in the following reaction :
\(2 \mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CHO} \frac{\text { dil. base or acid }}{300 \mathrm{~K}} \mathrm{~A} \underset{\text { dehydration }}{\text { dehy }} \mathrm{B}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(a) CH3-CH(OH)-CH2-CHO
(b) CH3-CH2-CH(OH)-CHO
(c) CH3-CH = CH-CHO
(d) CH3-CO-CH3
Answer:
(c) CH3-CH = CH-CHO
33. The blue colour of Fehling’s solution is due to
(a) Cu2O
(b) CuCO3
(c) CuO
(d) Cu++ ions
Answer:
(d) Cu++ ions
34. How is Schiff s reagent prepared?
(a) By passing CO2 through p-rosaniline solution
(b) By passing NO2 through p-rosaniline solution
(c) By passing SO2 through p-rosaniline solution
(d) By passing NH3 through silver nitrate solution
Answer:
(c) By passing SO2 through p-rosaniline solution
35. Benzaldehyde when treated with cone. HNO3 gives
(a) o-nitrobenzaldehyde
(b) p-nitrobenzaldehyde
(c) m-nitrobenzaldehyde
(d) a mixture of -o and -p-nitrobenzaldehyde
Answer:
(c) m-nitrobenzaldehyde
36. Which of the following carbonyl compounds undergoes aldol condensation ?
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Benzophenone
(c) Acetophenone
(d) tert-Butyl phenyl ketone
Answer:
(c) Acetophenone
37. Which of the following carbonyl compounds undergoes self redox reaction in presence of concentrated base ?
(a) 3-Methylpentanal
(b) 2-Chlorobutanal
(c) 2,2-Dimethylpropanal
(d) tert-Butyl methyl ketone
Answer:
(c) 2,2-Dimethylpropanal
![]()
38. The smell of bitter almond is given by the compound.
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Vanillin
(d) Cinnamaldehyde
Answer:
(b) Benzaldehyde
39. Which of the following will not give yellow precipitate when treated with NaOH and H?
(a) 3-Methylbutan-2-one
(b) 2-methylpentan-3-one
(c) Propanone
(d) Hexan-2-one
Answer:
(b) 2-methylpentan-3-one
40. A β-hydroxyl carbonyl compound is obtained by the action of NaOH on
(a) HCHO
(b) C6H5CHO
(c) CR3CHO
(d) CH3CHO
Answer:
(d) CH3CHO
41. Decarboxylation of sodium propionate gives
(a) methane
(b) ethane
(c) propane
(d) ethene
Answer:
(b) ethane
42. Ester on hydrolysis with dil HCl gives
(a) RCOOH + ROH
(b) RCOR + ROH
(c) ROH + ROH
(d) RCOR + RCOOH
Answer:
(a) RCOOH + ROH
43. \(\mathrm{CH}_{3}-\mathrm{CO}-\mathrm{CH}_{3} \stackrel{\mathrm{CrO}_{3}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{A}\) The compound A is
(a) acetic acid
(b) propionic acid
(c) formic acid
(d) benzoic acid
Answer:
(a) acetic acid
44. The reaction of C6H5CH = CHCHO with LiAlH4 gives
(a) C6H5CH2CH2CH2OH
(b) C6H5CH2CH2CHO
(c) C6H5CH = CHCH2OH
(d) C6H5CH2CHOHCH3
Answer:
(a) C6H5CH2CH2CH2OH
45. A mixture of sodium benzoate and sodalime on heating yields
(a) methane
(b) benzene
(c) sodium benzoate
(d) calcium benzoate
Answer:
(b) benzene
46. Which is the strongest acid?
(a) CH3COOH
(b) CH3CH2COOH
(c) (CH3)3CCOOH
(d) CICH2COOH
Answer:
(d) CICH2COOH
![]()
47. Benzaldehyde when treated with alkaline KMnO4 yields
(a) Benzyl alcohol
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) CO2 and H2O
(d) Salicylic acid
Answer:
(a) Benzyl alcohol
48. Acetonitrile on acidic hydrolysis gives
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3NC
(c) CH3COONa
(d) CH3COOH
Answer:
(d) CH3COOH
49. The organic compounds A and B reacts with sodium metal and liberates hydrogen gas. A and B reacts together to give ethyl acetate. The A and B are
(a) CH3COOH & C2H5OH
(b) HCOOH & C2H5OH
(c) CH3COOH & HCOOH
(d) CH3COOH & CH3OH
Answer:
(a) CH3COOH & C2H5OH
50. Which one of the following undergoes reaction with 50% NaOH to give to corresponding alcohol and acid?
(a) Phenol
(b) Benzoic acid
(c) Benzaldehyde
(d) Butanal
Answer:
(c) Benzaldehyde
51. Identify the reactant in the following reaction.
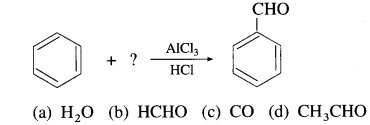
Answer:
(c) CO
52. The strongest acid is

Answer:
(c)
53. Predict the product in the following reaction
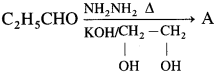
The compound A is
(a) butane
(b) propane
(c) ethane
(d) propene
Answer:
(b) propane
![]()
54. Ethyl benzoate when heated with dil H2SO4 gives
(a) acetic acid
(b) benzoic acid
(c) ethanoic acid
(d) phenyl methanol
Answer:
(b) benzoic acid
55. Margarine contains
(a) acetaldehyde
(b) propionaldehyde
(c) butyraldehyde
(d) formaldehyde
Answer:
(c) butyraldehyde
56. Monocarboxylic acids have the general formula
(a) CnH2n+1O2
(b) CnH2nO2
(c) CnH2nO
(d) CnH2n-1O2
Answer:
(b) CnH2nO2
57. Formic acid is obtained from
(a) vinegar
(b) red ants
(c) butter
(d) oil
Answer:
(b) red ants
58. Butter contains
(a) lactic acid
(b) butyric acid
(c) citric acid
(d) acetic acid
Answer:
(b) butyric acid
59. Glacial acetic acid is
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) CH3CH2COOH
(d) C3H7COOH
Answer:
(b) CH3COOH
60. Which of the following acids is optically active?
(a) Oxalic acid
(b) Salicylic acid
(c) Acetic acid
(d) Lactic acid
Answer:
(d) Lactic acid
![]()
61. Lactic acid is
(a) propionic acid
(b) α-hydroxy propionic acid
(c) p-hydroxy benzoic acid
(d) butyric acid
Answer:
(b) α-hydroxy propionic acid
62. The carbon atom of the carboxylic group is
(a) sp3-hybridized
(b) sp2-hybridized
(c) sp-hybridized
(d) unhybridized
Answer:
(b) sp2-hybridized
63. The common name of carboxylic fatty acids is derived from
(a) the name of parent alkanes
(b) the name of corresponding aldehydes
(c) from their original sources
(d) the name of alkyl group present in them
Answer:
(c) from their original sources
64. The IUPAC name of a-methylpropionic acid is
(a) Propanoic acid
(b) Butanoic acid
(c) 2-Methylpropanoic acid
(d) 2-Methylbutanoic acid
Answer:
(c) 2-Methylpropanoic acid
65. For the nomenclature of carboxylic acids, the suffix used is
(a) -ane
(b) -oic
(c) -al
(d) -ol
Answer:
(b) -oic
66. Propionic acid can be prepared by the
(a) action of propyl magnesium chloride on dry ice
(b) alkaline hydrolysis of propyl cyanide
(c) acid hydrolysis of ethyl cyanide
(d) oxidation of Propanone
Answer:
(c) acid hydrolysis of ethyl cyanide
67. The intermediate compound formed during hy-drolysis of acetonitrile to acetic acid is
(a) acetone
(b) acetamide
(c) ammonium acetate
(d) ethyl ammonium chloride
Answer:
(b) acetamide
68. Carbonation of CH3MgI gives organic compound. The same compound can also be obtained by
(a) oxidation of Methanol
(b) oxidation of Methanal
(c) acid hydrolysis of acetonitrile
(d) alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl cyanide
Answer:
(c) acid hydrolysis of acetonitrile
69. The acid that cannot be prepared by the action of Grignard reagent on dry ice is
(a) methanoic acid
(b) ethanoic acid
(c) propanoic acid
(d) butanoic acid
Answer:
(a) methanoic acid
70. The compound which on acid hydrolysis followed by oxidation gives acetic acid is
(a) CH3I
(b) CH2Cl2
(c) ClCH2CH2C1
(d) CH3CHCl2
Answer:
(d) CH3CHCl2
![]()
71. The hydrolysis product of alkyl cyanide is
(a) primary amine
(b) amides
(c) aldehyde
(d) carboxylic acid
Answer:
(d) carboxylic acid
72. To prepare acetic acid,
(a) methyl alcohol is oxidized with KMnO4
(b) calcium acetate is distilled with calcium for-mate under dry conditions
(c) acetaldehyde is oxidized in the presence of K2Cr2O7 and dil. H2SO4
(d) glycerol is heated with H2SO4
Answer:
(c) acetaldehyde is oxidized in the presence of K2Cr2O7 and dil. H2SO4
73. Solid carbon dioxide when treated with etheral solution of C2H5MgBr followed by acid hydrolyzis gives
(a) propanoic acid
(b) ethanoic acid
(c) propionic acid
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (a) and (c)
74. Which of the following compound does not give acetic acid on oxidation ?
(a) Ethanol
(b) Propan-l-ol
(c) Propan-2-ol
(d) 2-Methyl propan-2-ol
Answer:
(b) Propan-l-ol
75. A carboxylic acid resembles an alcohol with respect to its reaction with
(a) acidified K2Cr2O7
(b) washing soda
(c) caustic soda
(d) sodium metal
Answer:
(d) sodium metal
76. Acetic acid can be converted into acetic anhydride on heating with
(a) POCl3
(b) PCl3
(c) PCI5
(d) P2O5
Answer:
(d) P2O5
![]()
77. Acetyl chloride reacts with ammonia to give
(a) ammonium acetate
(b) ethylammonium chloride
(c) ethylamine
(d) acetamide
Answer:
(d) acetamide
78. The reagent that reacts with acetic acid to give sodium acetate with liberation of carbon dioxide gas is
(a) sodium metal
(b) caustic soda
(c) caustic potash
(d) baking soda
Answer:
(d) baking soda
79. An alkene on hydration gives a compound, which reacts with propionic acid to produce isopropyl propionate. The alkene is
(a) CH2 = CH2
(b) CH3-CH = CH2
(c) CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2
(d) CH3 – CH = CH – CH3
Answer:
(b) CH3-CH = CH2
80. Both the compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ react with sodium metal to liberate hydrogen gas and react with each other to give Methylethanoate. The compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ are
(a) C2H5 – COOH and CH3 – OH
(b) C2H5 – COOH and C2H5 – OH
(c) CH3 – COOH and C2H5 – OH
(d) CH3 – COOH and CH3 – OH
Answer:
(d) CH3 – COOH and CH3 – OH
81. Identify the product ‘D’ in the following series of reactions.
(a) CH3COOCH3
(b) CH3COOC2H5
(c) C2H5COOCH3
(d) C2H5COOC2H5
Answer:
(b) CH3COOC2H5
82. Acetyl chloride on heating with sodium acetate gives
(a) ethyl acetate
(b) acetamide
(c) acetic anhydride
(d) acetaldehyde
Answer:
(c) acetic anhydride
83. Carboxylic acids are acidic in nature because
(a) it dissociates to give H+ ions
(b) it donates proton
(c) it reacts with active metal and liberates hydro-gen gas
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
84. Carboxylic acids on heating with P2O5 give
(a) acid chlorides
(b) alkyl halides
(c) acid amides
(d) acid anhydrides
Answer:
(d) acid anhydrides
![]()
85.

Answer:
(c)
86. The compound having general formula is called
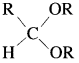
(a) diester
(b) acid anhydride
(c) hemiacetal
(d) acetal
Answer:
(d) acetal
87. Identify the strongest acid amongst the following :
(a) Chloroacetic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Trichloroacetic acid
(d) Dichloroacetic acid
Answer:
(c) Trichloroacetic acid
88. Acetaldehyde, when treated with which among the following reagents does ‘not’ undergo addition reaction?
(a) ammonia
(b) hydroxyl amine
(c) ammoniacal silver nitrate
(d) semicarbazide
Answer:
(c) ammoniacal silver nitrate
89. Popcorn has butter flavour which contains
(a) butan-l-one
(b) butane-2, 3-dione
(c) butan-2-one
(d) butyric acid
Answer:
(b) butane-2, 3-dione
![]()
90. On acid hydrolysis, propane nitrile gives
(a) propanal
(b) acetic acid
(c) propionamide
(d) propanoic acid
Answer:
(d) propanoic acid