Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Kingdom Plantae Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Kingdom Plantae
Question 1.
What is the basis of classification of kingdom Plantae?
Answer:
Kingdom plantae is classified on the basis of characteristics like absence or presence of seeds, vascular tissues, differentiation of plant body, etc.
![]()
Question 2.
What are Phanerogams and Cryptogams?
Answer:
1. Phanerogams are seed producing plants. These plants produce special reproductive structures that are visible.
2. Cryptogams are spore producing plants. These plants do not produce seed and flowers. They reproduce sexually by gametes, however their sex organs are concealed.
Question 3.
Write a short note on Chlorophyceae.
Answer:
- Chlorophyceae includes green algae.
- These are mostly fresh water (few brackish water and marine).
- Plant body is unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
- Cell wall contains cellulose.
- Chloroplasts are of various shapes like discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, ribbon-shaped or spiral with chlorophyll a and b.
- Reserved food is in the form of starch.
- Pyrenoids are located in the chloroplast.
- Green algae like Chlorella are rich in protein, hence used as food even by space travelers, e.g. Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Chara, Volvox, Ulothrix, etc.
Question 4.
Observe the given figure of Chara and identify the parts labelledas.
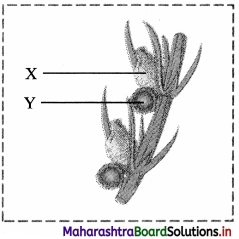
Answer:
X: Oogonium (contains egg)
Y: Antheridium (contains sperms)
![]()
Question 5.
Internet my friend (Textbook page no. 20)
Make a list of green algae with their characteristic shape of chloroplast.
Answer:
Green algae with their characteristic shapes of chloroplast:
- Chlamydomonas – Cup-shaped
- Spirogyra – Spiral or ribbon-shaped
- Oedogonium – Reticulate
- Zygnema – Stellate or Star-shaped
[Students are expected to search for more information regarding green algae with their characteristic shape of chloroplast from internet.]
Question 6.
Write the characteristics of Phaeophyceae.
Answer:
Characteristics of Phaeophyceae (Brown algae):
- These algae are mostly marine, rarely fresh water.
- Plant body is simple branched, filamentous (e.g. Ectocarpus) or profusely branched (e.g. Petalonia).
- Cell wall has cellulose, fucans and algin.
- Photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-c and fucoxanthin are present.
- Mannitol, laminarin are stored food materials. Body is usually differentiated into holdfast, stalk called stipe and leaf-like photosynthetic organ called frond.
- Many species of marine algae are used as food. e.g. Laminaria, Sargassum.
- Some species are used for the production of hydrocolloids (water holding substances), e.g. Ectocarpus, Fucus, etc.
Question 7.
Identify the given figure of a algae and explain the characteristics of its class with the help of following points:
Habitat, Plant body, photosynthetic pigments, cell wall, stored food

Answer:
The given figure is of Gracillaria. It belongs to class Rhodophyceae (Red algae).
Characteristics of Rhodophyceae:
- Habitat: These are found in marine as well as fresh water on the surface, deep sea and brackish water.
- Plant body: Plant body is thalloid.
- Photosynthetic pigments: Cells contain chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-d and phycoerythrin.
- Cell wall: Cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectin glued with other carbohydrates.
- Stored food: Stored food is in the form of Floridean starch.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the commercial use of red algae?
Answer:
Red algae like Gelidium and Gracilaria are used to obtain agar-agar which is used as solidifying agent in tissue culture medium.
Question 9.
Differentiate between red algae and brown algae.
Answer:
1. Photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-d and phycoerythrin. Photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll – a, chlorophyll-c and fucoxanthin.
2. Reserve food is Floridean starch. Reserve food is mannitol and laminarin.
e.g. Porphyra, Gracilaria, Gelidium, Polysiphonia, etc. Ectocarpus, Sargassum, Fucus, Laminaria, etc.
Question 10.
How rhizoids in liverworts differ from that of mosses?
Answer:
Rhizoids are unicellular in liverworts while they are multicellular in mosses.
Question 11.
Explain the thallus structure in lower members of Bryophyta. Give its two examples.
Answer:
1. Liverworts (Hepaticeae) are known as lower members of Bryophyta.
2. Gametophyte possesses flat plant body called thallus.
The thallus is green, dorsiventral, prostrate with unicellular rhizoids.
Examples: Riccia, Marchantia.
Question 12.
What are Hornworts? Give one example.
Answer:
Hornworts (Anthocerotae) are bryophytes which have flattened thallus that produces hornlike structures called as sporophytes. e.g. Anthoceros. In liverworts, asexual reproduction occurs by fragmentation of thalli or with the help of specialized structures called as gemmae. These are green, multicellular, asexual buds which grow in receptacles called gemma cup located on thalli. These gemmae detach from the thallus and germinate to form new individual.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain alternation of generation in life cycle of Bryophyta.
Answer:
- Life cycle of Bryophytes shows sporophytic and gametophytic stages.
- They alternate with each other to complete their life cycle.
- Gametophyte is haploid, thalloid or leafy and dominant, (photosynthetic, independent thalloid or erect phase)
- Sporophyte is short lived, multicellular and depends totally or partially on gametophyte for nutrition and anchorage.
Question 14.
Explain in detail the two stages of gametophytic phase in life cycle of Mosses.
Answer:
- Gametophytic phase of the life cycle of Mosses (Musci) includes two stages namely; protonema stage and leafy stage.
- The protonema is prostrate green, branched and filamentous (it is also called juvenile gametophyte). It bears many buds.
- Leafy stage is produced from each bud.
- Vegetative reproduction takes place by fragmentation and budding in secondary protonema.
- The leafy stage has erected, slender stem like (Cauloid) main axis bearing spiral leaf like structures (Phylloid).
- It is fixed in soil by multicellular branched rhizoids.
- Leafy stage bears sex organs.
Question 15.
1. Name the two groups of Bryophytes.
2. Give the role of rhizoids in Bryophytes.
Answer:
1. Liverworts and mosses
2. Rhizoids absorb water and minerals and also help in fixation of thallus to the substratum.
Question 16.
Write economic importance of Bryophytes.
Answer:
Economic importance of Bryophytes:
- Some mosses provide food for herbivorous mammals, birds, etc.
- Species of Sphagnum, a moss; provides peat used as fuel.
- Mosses are also used as packing material for transport of living materials because they have significant water holding capacity.
- Mosses along with lichens are the first living beings to grow on rocks. They decompose rocks to form soil and make them suitable for growth of higher plants.
- Dense layers of mosses help in prevention of soil erosion, thus act as soil binders.
![]()
Question 17.
Which group of plant is known as first vascular and true land plants? Write their characteristics in detail.
Answer:
- Pteridophytes are known as first vascular and true land plants.
- Habitat: Pteridophytes grow in moist and shady places, e.g. Ferns, Horsetail. Some are aquatic (Azolla, Marsilea), xerophytic (Equisetum) and epiphytic (Lycopodium).
- Plant body: It is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- Primary root: The primary root is short lived and is soon replaced by adventitious roots.
- Stem: The stem may be aerial or underground.
- Leaves: This group contains plants with pinnate (feather – like) leaves. Leaves may be scaly (e.g. Equisetum), simple and sessile (e.g. Lycopodium), small (microphylls e.g. Selaginella) or large (macrophylls) and pinnately compound (e.g. Nephrolepis l Ferns).
- Vascular tissues: In these members xylem consists of only tracheids and phloem consists of only sieve cells.
- Secondary growth: Secondary growth is not seen in pteridophytes due to absence of cambium.
- Alternation of generations: Pteriodphytes show heteromorphic alternation of generations in which the sporophyte is diploid, dominant, autotrophic and independent. Gametophyte is haploid multicellular, generally autotrophic and short lived.
Question 18.
Match the columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Psilopsida | (a) Selaginella |
| 2. Lycopsida | (b) Equisetum |
| 3. Sphenopsida | (c) Adiantum |
| (d) Psilotum |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Psilopsida | (d) Psilotum |
| 2. Lycopsida | (a) Selaginella |
| 3.Sphenopsida | (b) Equisetum |
Question 19.
Write economic importance of Pteridophytes.
Answer:
1. Pteridophytes are used for medicinal purpose and as soil binders.
2. Many varieties are grown as ornamental plants.
![]()
Question 20.
Compare the gametophyte and sporophyte of Bryophytes with that of Pteridophytes.
Answer:
| Bryophytes | Pteridophytes | |
| Gametophyte | It is haploid, dominant, photosynthetic, independent, thalloid or erect. | It is haploid, multicellular, generally autotrophic and short lived. |
| Sporophyte | It is short lived, multicellular and depends totally or partially on gametophyte for nutrition and anchorage. | It is dominant, independent and | vascular plant body. i |
Question 21.
Explain the given figure.

Answer:
1. The given figure represents megasporophyll of Cycas.
2. Megasporophyll of Cycas:
Megasporophylls are usually arranged in compact structures called female cones or female strobili. Megasporophyll contains megasporangia (ovule) which produce megaspores.
[Students are expected to collect more information about coralloid roots, scale leaf and megasporophyll of Cycas.]
Question 22.
Give the economic importance of Cycas and Pinus.
Answer:
1. Cycas is grown as an ornamental plant.
2. Pinus is used as source of pine wood, turpentine oil and pine resin.
![]()
Question 23.
Name the following:
Question 1.
Smallest gymnosperm
Answer:
Zamiapygmaea
Question 2.
The plant known as the ‘Coast red wood of California’.
Answer:
Sequoia sempervirens
Question 24.
Ginlcgo biloba is called as living fossil. Why?
Answer:
Ginkgo biloba is called as living fossil, because this plant is found in living as well as fossil form and the number of fossil forms is much more than the living forms.
Question 25.
Which of the following nuts will not be enclosed in fruits?
Betel nut/ Areca nut, pine nut, walnut, almond, cashew nut, nutmeg.
Answer:
1. Pine nuts are edible seeds of pines which are not enclosed in a fruit. It belongs to class gymnospermae thus, seeds are not enclosed within the fruit.
2. Nuts like betel nut/ areca nut, walnut, almond, cashew nut, nutmeg will be enclosed in fruits. It is because these plants belong to class angiospermae in which seeds are enclosed within the fruit.
Question 26.
Name various groups of vascular plants. Give one characteristic feature of each group.
Answer:
There are 3 groups of vascular plants:
1. Pteridophytes
2. Gymnosperms
3. Angiosperms
Characteristics of Pteridophytes: Pteridophytes are the only cryptogams with vascular tissue. Characteristics of Gymnosperms: Gymnosperms are the plants which possess naked seeds and also known as phanerogams without ovary.
Characteristics of Angiosperms: Angiosperms are the flowering plants in which the seeds remain enclosed within the fruits. Double fertilization is the unique feature of angiosperms. [Any one feature]
![]()
Question 27.
Classify the given plants into their respective groups and complete the given table.
Equisetum, Chara, Marchantia, Ginkgo biloba, Riccia, Spirogyra, Adiantum, Sorghum
Answer:
| Chlorophyceae | Liverworts | Pteridophyta | Gymnosperms | Monocotyledonae |
| Chara, Spirogyra | Riccia, Marchantia | Equisetum, Adiantum | Ginkgo biloba | Sorghum |
Question 28.
Match the columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Bryophyta | (a) 70 genera and 1000 living species |
| 2. Pteridophyta | (b) 32 genera and 80 species |
| 3. Gymnospermae | (c) 960 genera and 25000 species |
| (d) 400 genera and 11000 species |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Bryophyta | (c) 960 genera and 25000 species |
| 2. Pteridophyta | (d) 400 genera and 11000 species |
| 3. Gymnospermae | (a) 70 genera and 1000 living species |
[Source: Textbook of Biology, standard XI, First Edition; 2019, page no. 21,22,23.]
![]()
Question 29.
Identify the plants in the given figure and match the columns.
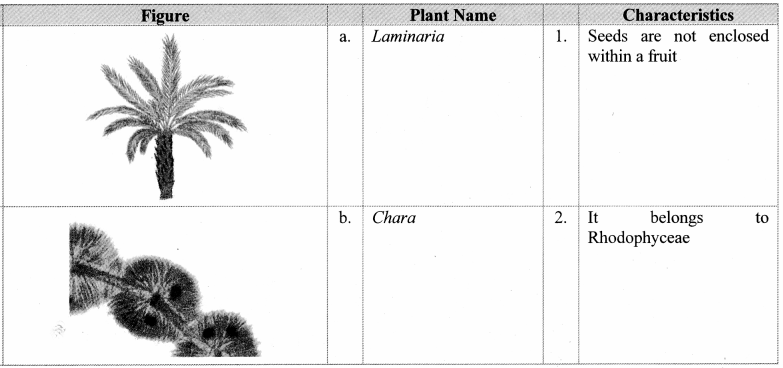
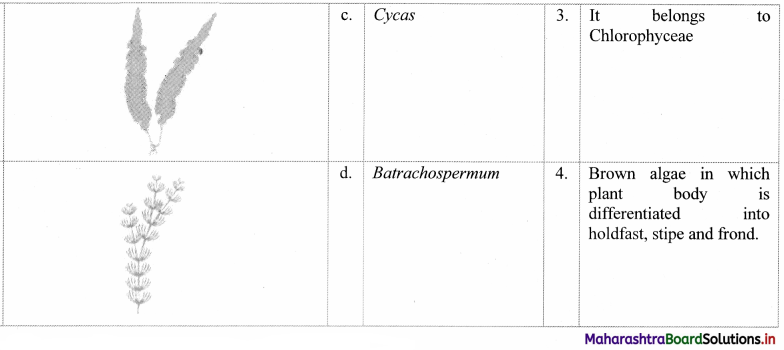
Answer:
1. c – 1
2. d – 2
3. a – 4
4. b – 3
Question 30.
Write a short note on Haplontic life cycle.
Answer:
1. In haplontic life cycle mitosis occurs in haploid cells.
2. It results in the formation of a single celled haploid or a multicellular haploid organism.
3. These forms produce the gametes through mitosis.
4. Zygote is formed after fertilization. This cell is the only diploid cell in the entire life cycle of the organism.
5. Thus, the same zygotic cell later undergoes meiosis.
6. This type of life cycle observed in some algae and fungi.
[Note: Haplontic life cycle is observed in many algae]
![]()
Question 31.
Observe the given figure and explain in detail.
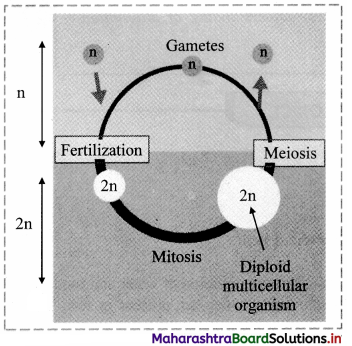
Answer:
- The given figure indicates diplontic life cycle.
- Here, mitotic division occurs only in diploid cells.
- Gametes formed through meiosis are haploid in nature.
- The diploid zygote formed after fertilization divides mitotically.
- In this process, production of multicellular diploid organism or the production of many diploid single cells takes place.
- Animals show diplontic life cycle.
[Note: Diplontic type of life cycle is commonly observed in animals and all seed-bearing plants i.e. gymnosperms and angiosperms.]
Question 32.
Explain the term: Haplo-diplontic life cycle.
Answer:
1. In haplo-diplontic life cycle, mitosis occur in both diploid and haploid cells.
2. These organisms undergo through a phase in which they are multicellular and haploid (the gametophyte), and a phase in which they are multicellular and diploid (the sporophyte).
3. It is observed in land plants and in many algae.
[Note: It is commonly observed in bryophytes and pteridophytes.]
Question 33.
Fill in the blanks.
1. In haplo-diplontic life cycle, mitosis occurs in cells.
2. In diplontic life cycle, mitosis occurs in cells.
3. In haplontic life cycle, mitosis occurs in cells.
Answer:
1. diploid and haploid cells
2. diploid cells
3. haploid cells
![]()
Question 34.
Practical/Project:
Question 1.
Visit any nursery or botanical garden. Observe some older leaves of fern plant. You can observe some brown spots on back side of the leaflets as shown in the picture given below. Collect more information about it.
Answer:
1. The brown spots on the back side of older leaves of fern are sori.
2. They reproduce asexually by spores produced within sporangia, which are present in sori. These sori are located along the posterior surface of leaflets.
Question 35.
Read the given points.
1. A plant shows thalloid body.
2. A plant shows presence of rhizoids instead of true roots.
3. A plant needs external water for fertilization.
4. Vascular tissues are absent.
Identify the division of the plant described above.
Answer:
The plant belongs to division Bryophyta.
Question 36.
If a person wants to obtain agar for tissue culture, which plant group he should search?
Answer:
A person should search Rhodophyceae. It is because, ‘agar’ which is used as solidifying agent in tissue culture is obtained from red algae-Gelidium and Gracilaria.
Question 37.
Vinaya while playing in garden observed a pond with a green coloured covering which was floating on the surface of water? Next day she asked her teacher about the same. What her teacher must have told her?
Answer:
Vinaya’s teacher must have told her that the green coloured covering floating on the surface of pond water can be green algae like Spirogyra, Chlorella, Chlamydomonas, etc.
Question 38.
Identify the following:
- These plants belong to thallophyta and grow upto 100 meters in height.
- Plants used to obtain a product which is used a solidifying agent in preparation of ice-creams and jellies.
- Gymnosperm which has girth of about 125 feet.
- Xerophytic fern which belongs to sphenopsida.
- Unicellular motile alga which belongs to Chlorophyceae and shows cup-shaped chloroplast.
Answer:
- Kelps
- Gelidium, Gracilaria
- Taxodium mucronatum
- Equisetum
- Chlamydomonas
![]()
Question 39.
Quick Review:
Question 40.
Exercise:
Question 1.
Name the group of spores producing plants in
which sex organs are concealed.
Answer:
Cryptogams are spore producing plants. These plants do not produce seed and flowers. They reproduce sexually by gametes, however their sex organs are concealed.
Question 2.
Name the two divisions of phanerogams.
Answer:
v – phanerogamae
Question 3.
Complete the given flow chart.
Answer:
Quick Review
![]()
Question 4.
Define phanerogams.
Answer:
Phanerogams are seed producing plants. These plants produce special reproductive structures that are visible.
Question 5.
Write any two examples of phaeophyceae.
Answer:
Examples of phaeophyceae
Question 6.
Enlist the accessory pigments of algae.
Answer:
Various types of photosynthetic pigments are found in algae.
1. The accessory pigments are chlorophyll-b, chlorophyll-c, chlorophyll-d, carotenes, xanthophylls and phycobilins. Phycobilins are of two types, i.e. phycocyanin and phycoerythrin.
[Students are expected to collect more information about pigments found in algae from internet.]
Question 7.
Bryophytes are the amphibians of the plant kingdom. Justify
Answer:
Members of Bryophyta are mostly terrestrial plants which depend on water for fertilization and completion of their life cycle. Hence, they are called ‘amphibians of Plant Kingdom’.
Question 8.
Distinguish between Rhodophyceae and phaeophyceae with respect to photosynthetic pigments and reserve food.
Answer:
1. Photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-d and phycoerythrin. Photosynthetic pigments are chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-c and fucoxanthin.
2. Reserve food is Floridean starch. Reserve food is mannitol and laminarin.
e.g. Porphyra, Gracilaria, Gelidium, Polysiphonia, etc. Ectocarpus, Sargassum, Fucus, Laminaria, etc.
Question 9.
Write the characteristics of division that includes members like Chlamydomonas, Fucus, Gelidium, etc.
Answer:
Algae belongs to division Thallophyta.
Salient features of algae:
- Habitat: Algae are mostly aquatic, few grow on other plants as epiphytes and some grow symbiotically. Some algae are epizoic i.e. growing or living non-parasitically on the exterior of living organisms.
Aquatic algae grow in marine or fresh water. Most of them are free-living while some are symbiotic. - Structure: Plant body is thalloid i.e. undifferentiated into root, stem and leaves. They may be small, unicellular, microscopic like Cblorella (non-motile), Chlamydomonas (motile). They can be multicellular, unbranched, filamentous like Spirogyra or branched and filamentous like Chara. Sargassum is a huge macroscopic sea weed which measures more than 60 meters in length.
- Cell wall: The algal cell wall contains either polysaccharides like cellulose / glucose or a variety of proteins or both. Reserve food material: Reserve food is in the form of starch and its other forms.
- Photosynthetic pigments: Photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll – a, chlorophyll – b, chlorophyll – c, chlorophyll – d, carotenes, xanthophylls, phycobilins are found in algae.
- Reproduction: Reproduction takes place by vegetative, asexual and sexual method.
- Life cycle: The life cycle shows phenomenon of alternation of generation, dominant haploid and reduced diploid phases.
![]()
Question 10.
Name the two algae from which agar is obtained.
Answer:
Red algae like Gelidium and Gracilaria are used to obtain agar-agar which is used as solidifying agent in tissue culture medium.
Question 11.
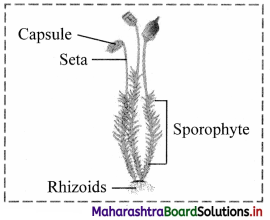
Identify the incorrectly labelled part in the figure of Funaria.
Answer:
Question 12.
Which are the first terrestrial plants to possess xylem and phloem?
Answer:
Pteridophytes are known as first vascular and true land plants.
Question 13.
Explain in detail three classes of algae.
Answer:
- Chlorophyceae includes green algae.
- These are mostly fresh water (few brackish water and marine).
- Plant body is unicellular, colonial or filamentous.
- Cell wall contains cellulose.
- Chloroplasts are of various shapes like discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, ribbon-shaped or spiral with chlorophyll a and b.
- Reserved food is in the form of starch.
- Pyrenoids are located in the chloroplast.
- Green algae like Chlorella are rich in protein, hence used as food even by space travelers, e.g. Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Chara, Volvox, Ulothrix, etc.
Characteristics of Phaeophyceae (Brown algae):
- These algae are mostly marine, rarely fresh water.
- Plant body is simple branched, filamentous (e.g. Ectocarpus) or profusely branched (e.g. Petalonia).
- Cell wall has cellulose, fucans and algin.
- Photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll-a, chlorophyll-c and fucoxanthin are present.
- Mannitol, laminarin are stored food materials. Body is usually differentiated into holdfast, stalk called stipe and leaf-like photosynthetic organ called frond.
- Many species of marine algae are used as food. e.g. Laminaria, Sargassum.
- Some species are used for the production of hydrocolloids (water holding substances), e.g. Ectocarpus, Fucus, etc.
![]()
Question 14.
Write ecological importance of Bryophytes.
Answer:
Economic importance of Bryophytes:
1. Some mosses provide food for herbivorous mammals, birds, etc.
2. Mosses along with lichens are the first living beings to grow on rocks. They decompose rocks to form soil and make them suitable for growth of higher plants.
3. Dense layers of mosses help in prevention of soil erosion, thus act as soil binders.
Question 15.
Mention one example each of aquatic and xerophytic pteridophytes.
Answer:
Habitat: Pteridophytes grow in moist and shady places, e.g. Ferns, Horsetail. Some are aquatic (Azolla, Marsilea), xerophytic (Equisetum) and epiphytic (Lycopodium).
Question 16.
State the uses of algae.
Answer:
(a) Many species of algae are used as food. For e.g. Chlorella (rich in cell proteins hence used as food supplement, even by space travelers), Sargassum, Laminaria, Porphyra, etc.
(b) Alginic acid is produced commercially from Kelps.
(c) Hydrocolloids like algin and carrageen are obtained from brown algae and red algae respectively.
(d) ‘Agar’ which is used as solidifying agent in tissue culture is obtained from red algae like Gelidium and Gracilaria.
(e) Brown algae like sea weeds are used a fodder for sheep, goat, etc.
[Students are expected to collect more information about the economic importance of algae.]
(f) Role of algae in environment.
Answer:
(a) Being photosynthetic, algae help in increasing the level of dissolved oxygen in their immediate environment.
(b) Algae are primary producers of energy rich compounds which forms the basis of food cycles in aquatic animals.
[Students are expected to find out more information about the role of algae in environment on internet.]
Question 17.
Mosses are used as packing material during transport of living material. Give reason.
Answer:
Mosses are also used as packing material for transport of living materials because they have significant water holding capacity.
![]()
Question 18.
Write the important characteristics of gymnosperms with respect to following points:
1. Vascular tissues
2. Roots
3. Spores
4. Leaves
Answer:
(b) Vascular tissues: They are vascular plants having xylem with tracheids and phloem with sieve cells.
(e) Roots: The root system is tap root type. In some gymnosperms, the roots form symbiotic association with other life forms. Coralloid roots of Cycas show association with blue green algae and roots of Pinus show association with endophytic fungi called mycorrhizae.
(g) Leaves: The leaves are dimorphic. The foliage leaves are green, simple needle like or pinnately compound, whereas scale leaves are small, membranous and brown.
(h) Spores: Spores are produced by microsporophyll (Male) and megasporophyll (Female).
Question 19.
What are the essential and accessory whorls in flower?
Answer:
Flower: Besides the essential whorls of microsporophylls (androecium) and megasporophylls (gynoecium), there are accessory whorls namely, calyx (sepals) and corolla (petals) arranged together to form flowers.
Question 20.
Write the characteristics of the class which includes Helianthus annuus.
Answer:
Habitat: Angiosperms is a group of highly evolved plants, primarily adapted to terrestrial habitat.
![]()
Question 21.
Secondary growth is absent in monocotyledonous plants. Justify.
Answer:
(a) In dicots, vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and open type. Cambium is present between xylem and phloem for secondary growth.
(b) Whereas in monocots, vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed type. Thus, due to absence of cambium, secondary growth does not occur in majority of monocots.
Question 22.
State characteristic of class monocotyledonae.
Answer:
b. Monocotyledonae:
- These plants have single cotyledon in their embryo.
- They have adventitious root system and stem is rarely branched.
- Leaves generally have sheathing leaf base and parallel venation.
- Flowers show trimerous symmetry.
- The vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed type.
- Cambium is absent between xylem and phloem.
- In Monocots, except few plants secondary growth is absent, e.g. Zea mays (Maize)
Question 23.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of:
1. Helianthus annuus (sunflower) plant.
2. Maize Plant.
Answer:
Two classes of Angiosperms are Dicotyledonae and Monocotyledonae.
а. Dicotyledonae:
- These plants have two cotyledons in their embryo.
- They have a tap root system and the stem is branched.
- Leaves show reticulate venation.
- Flowers show tetramerous or pentamerous symmetry.
- Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and open type.
- Cambium is present between xylem and phloem for secondary growth.
- In dicots, secondary growth is commonly found.
e. g. Helianthus annuus (Sunflower)
b. Monocotyledonae:
- These plants have single cotyledon in their embryo.
- They have adventitious root system and stem is rarely branched.
- Leaves generally have sheathing leaf base and parallel venation.
- Flowers show trimerous symmetry.
- The vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral and closed type.
- Cambium is absent between xylem and phloem.
- In Monocots, except few plants secondary growth is absent, e.g. Zea mays (Maize)
Question 24.
Which is the diploid phase in life cycle of a plant?
Answer:
The life cycle of a plant includes two generations, sporophytic (diploid = 2n) and gametophytic (haploid = n)
![]()
Question 25.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Which of the following is not included in sub-kingdom Cryptogamae?
(A) Thallophyta
(B) Dicotyledonae
(C) Pteridophyta
(D) Bryophyta
Answer:
(B) Dicotyledonae
Question 2.
Unicellular, non-motile alga is
(A) Chara
(B) Chlorella
(C) Funaria
(D) Chlamydomonas
Answer:
(B) Chlorella
Question 3.
Which of the following is a brown algae?
(A) Laminaria
(B) Pteris
(C) Ulothrix
(D) Gelidium
Answer:
(A) Laminaria
Question 4.
Agar is obtained from group of algae.
(A) Rhodophyceae
(B) Chlorophyceae
(C) Phaeophyceae
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Rhodophyceae
Question 5.
In Chlamydomonas, pyrenoid is located in
(A) nucleus
(B) mitochondria
(C) chloroplast
(D) flagella
Answer:
(C) chloroplast
Question 6.
In bryophytes, represents sporophytic
generation.
(A) rhizoids
(B) thalloid
(C) capsule
(D) leafy plant body
Answer:
(C) capsule
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is an example of liverwort?
(A) Funaria
(B) Marchantia
(C) Polytrichum
(D) Sphagnum
Answer:
(B) Marchantia
Question 8.
The late Paleozoic era is regarded as the age of ______ .
(A) Thallophytes
(B) Gymnosperms
(C) Pteridophytes
(D) Angiosperms
Answer:
(C) Pteridophytes
Question 9.
Which of the following is an epiphytic pteridophyte?
(A) Azolla
(B) Equisetum
(C) Marsilea
(D) Lycopodium
Answer:
(D) Lycopodium
Question 10.
Complete the given analogy:
Lycopsida: _______:: Pteropsida: Pteris
(A) Adiantum
(B) Selaginella
(C) Equisetum
(D) Psilotum
Answer:
(B) Selaginella
Question 11.
Bryophytes differ from Pteridophytes in being
(A) vascular
(B) seeded
(C) non-vascular
(D) sporophytic
Answer:
(C) non-vascular
![]()
Question 12.
Endophytic fungi or mycorrhizae are found in the roots of
(A) Cycas
(B) Pinus
(C) Equisetum
(D) Hibiscus
Answer:
(B) Pinus
Question 13.
Gymnosperms are characterized by the absence of
(A) tracheids in xylem
(B) sieve cells in phloem
(C) heterosporous condition
(D) fruit formation
Answer:
(D) fruit formation
Question 14.
Complete the given analogy:
Tallest angiosperm : Eucalyptus :: Smallest angiosperm : _________ .
(A) Zanta pygmaea
(B) Sequoia sempervirens
(C) Taxodium mucronatum
(D) Wolffia
Answer:
(D) Wolffia
![]()
Question 15.
Select the INCORRECT statement with respect to angiosperms.
(A) Seeds are enclosed within a fruit.
(B) These plants show heteromorphic alternation of generation.
(C) Megaspores are borne on highly specialized microsporophyll.
(D) They are most advanced group of flowering plants.
Answer:
(C) Megaspores are borne on highly specialized microsporophyll.
Question 16.
Parallel venation is a characteristic feature of
(A) Monocotyledons
(B) Dicotyledons
(C) Pteridophytes
(D) Bryophytes
Answer:
(A) Monocotyledons
Question 17.
In gymnosperms and angiosperms _______ is much reduced.
(A) gametophyte
(B) root
(C) sporophyte
(D) vascular bundle
Answer:
(A) gametophyte
Question 18.
Presence of rhizoids in place of true roots is a characteristic of
(A) Gymnosperms
(B) Bryophyta
(C) Pteridophyta
(D) Angiosperms
Answer:
(B) Bryophyta
Question 19.
Competitive Corner:
Question 1.
Which one of the following statements is wrong?
(A) Laminaria and Sargassum are used as food.
(B) Algae increase the level of dissolved oxygen in the immediate environment.
(C) Algin is obtained from red algae, and carrageen from brown algae.
(D) Agar-agar is obtained from Gelidium and Gracilaria.
Hint: Algin is obtained from brown algae and carrageenan from red algae.
Answer:
(C) Algin is obtained from red algae, and carrageen from brown algae.
Question 2.
Select the CORRECT statement.
(A) Sequoia is one of the tallest trees.
(B) The leaves of gymnosperms are not well adapted to extremes of climate.
(C) Gymnosperms are both homosporous and heterosporous.
(D) Salvinia, Ginkgo and Pinus all are gymnosperms.
Hint: The leaves of gymnosperms are well adapted to withstand extremes of climate. Gymnosperms are heterosporous. Salvinia is a Pteridophyte.
Answer:
(A) Sequoia is one of the tallest trees.
![]()
Question 3.
In bryophytes and pteridophytes, transport of male gametes requires
(A) Birds
(B) Water
(C) Wind
(D) Insects
Answer:
(B) Water