Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Study of Animal Type: Cockroach Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Study of Animal Type: Cockroach
Question 1.
Why are cockroaches said to be omnipresent?
Answer:
Cockroaches are said to be omnipresent as they are present everywhere, all over the world. They are usually seen in damp and moist places, crevices.
![]()
Question 2.
Cockroaches are nocturnal and cursorial. Give reason.
Answer:
1. Cockroaches are active at night hence, they are termed as nocturnal.
2. They are cursorial insects as they show terrestrial adaptations for running.
Question 3.
Name the common species of cockroach found in India.
Answer:
Periplaneta americana, Blatta orientalis and Blatta germanica.
Question 4.
Describe in detail the external morphology of cockroach.
Answer:
External morphology of cockroach:
1. Shape and size: Cockroach has elongated, bilaterally symmetrical, dorso-ventrally flattened and truly segmented body.They are triploblastic and eucoelomate. The body cavity called haemocoel is filled with the fluid haemolymph.
2. Coloration: Their colour is glistening brown or reddish brown.
3. Exoskeleton: Tough, waxy, non-living chitinous exoskeleton protects the body of the cockroach. It is made up of nitrogenous polysaccharide – chitin that provides strength, elasticity and surface area for attachment of muscles. Each body segment of cockroach is covered by four chitinous plates called sclerites namely, dorsal tergum, ventral sternum and two lateral pleurons.
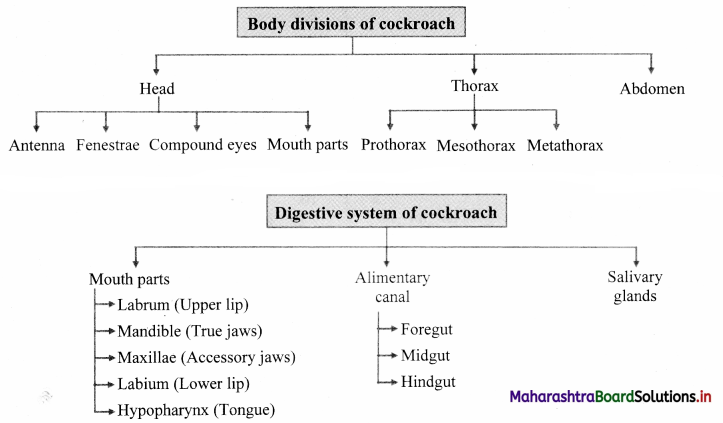
4. Body division: The body is divided into three regions viz. head, thorax and abdomen.
5. Head: It is formed by the fusion of six segments. It is triangular or ovate in shape. The head is highly mobile due to flexible neck. It bears a pair of long antennae, a pair of compound eyes and mouthparts adapted for biting and chewing of food.
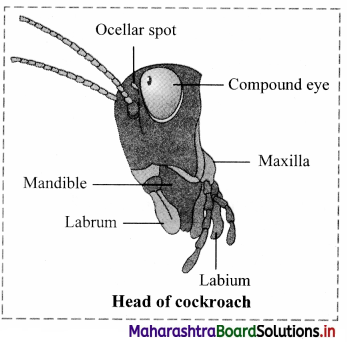
Head of cockroach bears following structures:
(a) Antennae: They are also called as feelers.These are long, filamentous, segmented structures that can move in all directions.They are lodged in membranous pits known as antennal sockets.They are tactile (touch) as well as olfactory (smell) organs.
Function: They are useful in locating the food material in the vicinity.
(b) Fenestrae: Fenestrae also called as ocellar spots.
They are situated at the base of each antenna and appear as white spots.
(c) Compound eyes: Compound eyes are paired, dark, kidney – shaped structures placed on the dorsolateral sides of the head. They are made up of large number of hexagonal ommatidia i.e. around 2000 ommatidia (sing, ommatidium).
These ommatidia are the structural and functional unit of compound eye, each forming an image of very small part of visual field. Collectively, the compound eye produces a mosaic image. Even though the compound eye gives a mosaic or hazy vision yet the animal can detect the slightest movement of the object. Compound eyes provide low resolution and more sensitive vision.
d. Mouthparts: Cockroach has a pre-oral cavity in front of the mouth in which food is received. It is bounded by mouthparts which are of chewing and biting type. This includes: labrum, labium, a pair of mandibles, a pair of maxillae and tongue like hypopharynx (present at the centre of mouth). Salivary duct opens at the base of hypopharynx and the mouth opens into foregut.
6. Thorax: Thorax is made up of three distinct segments – prothorax (anterior segment), mesothorax and metathorax (posterior segment). Ventrally, the thorax bears three pairs of walking legs, one at each segment. Dorsally, the thorax bears two pairs of wings attached to mesothoracic and metathoracic segment of the body.
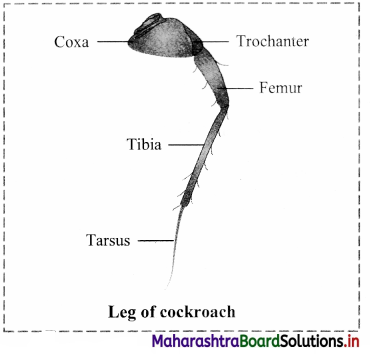
(a) Legs: Three pairs of walking legs are present on the ventral side. Each leg is formed of five podomeres namely coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus.Tarsus is the last segment and it is made up of five movable segments or tarsomeres. The last tarsomere bears a pair of claws and cushion-like arolium helpful in clinging.
(b) Wings: Forewings and hindwings form the two pair of wings present on the dorsal side. Forewings are the first pair of dark, opaque, thick, leathery wings. Hindwings are thin, broad, membranous delicate and transparent.They are attached to tergum of metathorax.
Functions: Forewings are protective in function and hindwings are helpful in flight, thus are called true wings.
7. Abdomen:
a. The abdomen is elongated and made up of ten segments. Each segment has a dorsal tergum and ventral sternum.
b. Tergum is jointed to the sternum laterally by a soft cuticle called pleura.
c. The posterior segments are telescoped in. Due to this, the eighth and ninth terga get overlapped by the seventh. The tenth tergum projects backward and is deeply notched. It bears a pair of small, many jointed anal cerci.
d. The abdomen is narrow and tapering in males as compared to females.The ninth sternum of males also bears a pair of short, unjointed anal style.
![]()
Question 5.
Write about the compound eyes of cockroach.
Answer:
Compound eyes: Compound eyes are paired, dark, kidney — shaped structures placed on the dorsolateral sides of the head. They are made up of large number of hexagonal ommatidia i.e. around 2000 ommatidia (sing, ommatidium). These ommatidia are the structural and functional unit of compound eye, each forming an image of very small part of visual field. Collectively, the compound eye produces a mosaic image. Even though the compound eye gives a mosaic or hazy vision yet the animal can detect the slightest movement of the object. Compound eyes provide low resolution and more sensitive vision.
Question 6.
Explain the structure of legs in cockroach.
Answer:
Legs: Three pairs of walking legs are present on the ventral side. Each leg is formed of five podomeres namely coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus.Tarsus is the last segment and it is made up of five movable segments or tarsomeres. The last tarsomere bears a pair of claws and cushion-like arolium helpful in clinging.
Question 7.
Sketch a neat and labelled diagram of dorsal and ventral view of cockroach.
Answer:
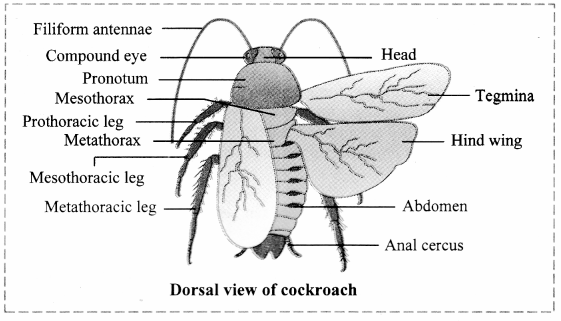
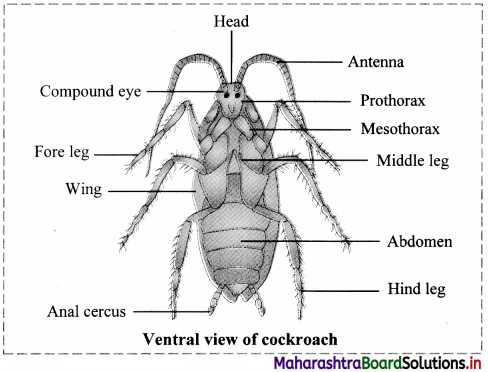
Question 8.
Write a short on body cavity of cockroach.
Answer:
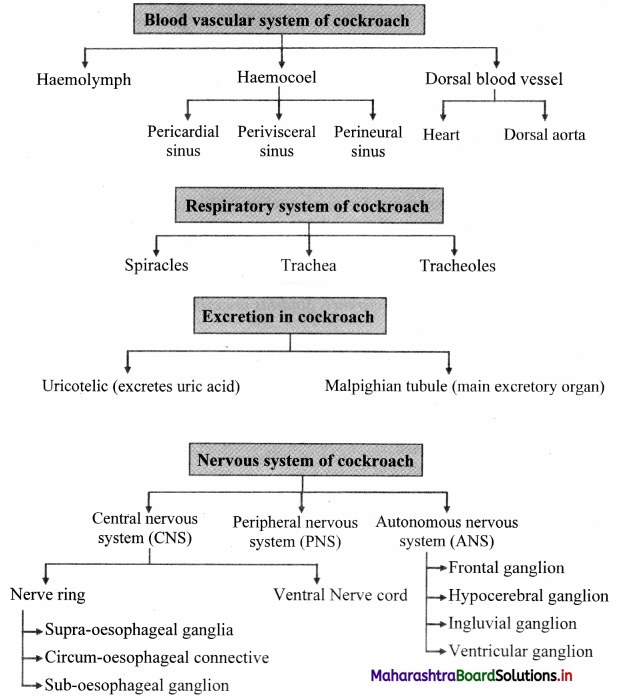
1. Cockroach has a body cavity or true coelom present around the viscera.
2. The body cavity of cockroach is known as haemocoel as it is filled with haemolymph (blood). Cockroaches have open type of circulation thus; the body cavity is filled with haemolymph.
3. The body cavity contains fat bodies. These are in the form of loose, whitish mass of tissue. They are made up of large, polygonal cells which contain fat globules, proteins and sometimes glycogen.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the role of hypopharynx?
Answer:
Hypopharynx: Hypopharynx is also known as lingua. It is a somewhat cylindrical single structure, located in front of the labium and between first maxillae. The salivary duct opens at the base of hypopharynx. Hypopharynx bears comb-like plates called super-lingua on either side. Hypopharynx is present at the centre of the mouth.
Function: It is useful in the process of feeding and mixing saliva with food,
Question 10.
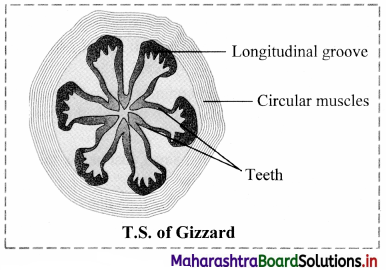
Sketch a neat and labelled diagram of gizzard of cockroach.
Answer:
Question 11.
Describe the heart in cockroach.
Answer:
Heart: It is about 2.5 cm long, narrow, muscular tube that is open anteriorly and closed posteriorly. It starts from 9th abdominal segment and extends anteriorly upto 1st thoracic segment. Heart of cockroach is 13 chambered, out of which 10 chambers are in abdominal region and 3 chambers are in thoracic region. Each chamber has a pair of vertical slit-like incurrent aperture or opening called ostium (plural: ostia). Ostia are present along lateral side in the posterior region of first 12 chambers. Each ostium has lip-like valves that allow the flow of blood from sinus to heart only.
Question 12.
What are alary muscles?
Answer:
Dorsal diaphragm: It has 12 pairs (10 abdominal and 2 thoracic) of fan-like alary muscles. Alary muscles are triangular with pointed end attached to terga at lateral side and broad end lies between the heart and dorsal diaphragm.
Question 13.
Explain the mechanism of blood circulation in cockroach.
Answer:
Mechanism of blood circulation:
- Blood (haemolymph) circulates between sinuses and heart due to contraction and relaxation of heart and alary muscles.
- The heart contracts (systole) and relaxes (diastole) alternatively. After diastole, there is a third phase in the heart cycle known as diastasis. During diastasis, heart remains in expanded state.
- During diastole, heart expands and the alary muscles contract, making the dorsal diaphragm flat. As a result, blood passes from perivisceral sinus to pericardial sinus through fenestrae and finally to the heart through ostia.
- During systole, contraction starts at the posterior end and the wave of contraction passes anteriorly. Due to this, blood is pushed towards the dorsal aorta.
- Ostia remain closed with the help of valves, during systole. As a result, blood flushes into head region from where it goes to perivisceral and perineural sinuses.
- During systole, alary muscles are relaxed and due to this, the dorsal diaphragm becomes convex.
- The volume of pericardial sinus is now reduced. This makes the blood to move from pericardial sinus to perivisceral sinus through fenestrae.
Question 14.
Which muscles are involved in renewal of air in tracheal system?
Answer:
The rhythmic movements of thoracic and abdominal muscles are involved in the renewal of air in tracheal system.
![]()
Question 15.
Give the role of chitin in trachea of cockroach.
Answer:
The inner lining of chitin in trachea prevents the trachea from collapsing.
Question 16.
Write in short about the spiracles in cockroach.
Answer:
Spiracles: They are paired respiratory openings. Spiracles are present on the ventro-lateral side of the body, in pleural membrane. Cockroaches have two pairs of thoracic and eight pairs of abdominal spiracles.The spiracles open into a series of air sacs from which arise the tubes called The spiracles let the air into and out of trachea.
Question 17.
Describe the excretory system in cockroach.
Answer:
- Malpighian tubules are the main excretory organs of cockroach.
- They are thin, yellow coloured, ectodermal thread-like structures that lie in the haemocoel.
- These tubules are 150 in number. Malpighian tubules are attached to the alimentary canal between the midgut and hindgut.
- Each Malpighian tubule is lined with a single layer of glandular epithelial cells having microvilli. The distal portion of Malpighian tubule is secretory and the proximal part is absorptive in function.
- They extract water and nitrogenous wastes from the haemocoel and convert them into uric acid and pass them into ileum. As the cockroach excretes uric acid, it is said to be uricotelic.
- Also, fat bodies, nephrocytes and uricose glands (only in males) help in excretion.
- In cockroach, nephrocytes (urate cells) associated with fat bodies and cuticle are also believed to be excretory in function. The nephrocytes are cells present along with the fat bodies or present along the heart and store nitrogenous wastes.
- The excretory products later are removed in the haemocoel. Some nitrogenous wastes are deposited on the cuticle and eliminated during moulting.
Question 18.
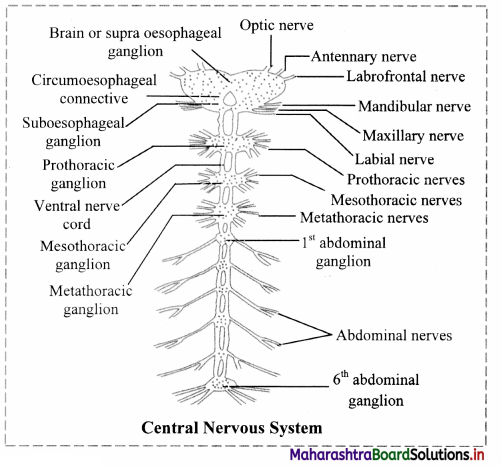
Sketch and label the central nervous system of cockroach.
Answer:
![]()
Question 19.
Sense organs: Collect the information and complete the chart.
Answer:
| Sense organ | Location | Function |
| 1. Antenna | Head | Detect touch, smell and locate the food in vicinity |
| 2. Eyes | Head | Provides mosaic vision, detect slightest movement of object, provide more sensitive vision but less resolution |
| 3. Maxillary palp | Mouth | Detects smell and taste. |
| 4. Labial palp | Mouth | Detects smell and taste. |
| 5. Anal cerci | Abdomen | Detect touch and sound (respond to air or vibrations) |
Question 20.
Describe the male reproductive system of cockroach.
Answer:
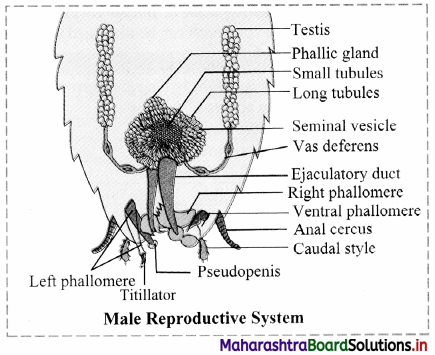
- Male reproductive system includes primary and secondary reproductive organs.
- Primary sex organs (male gonads) are called testes. They are paired and located in the 4th and 6th abdominal segments. Sperms produced in testis are carried by vasa deferentia.
- Vasa deferentia is a pair of thin tubular structure that arise from the testes and open into ejaculatory duct through seminal vesicle. They carry sperms to ejaculatory duct.
- Ejaculatory duct opens into male gonopore situated ventral to anus.
- Sperms produced by testis are stored in seminal vesicles in the form of bundles called spermatophores. These spermatophores are deposited in female reproductive tract during copulation.
- Mushroom shaped gland or utricular gland is an accessory reproductive gland. It is present in the 6th – 7th abdominal segments.
- Male gonapophyses or phallomere form the external genitalia of male. These are three asymmetrical chitinous structures surrounding the male gonophore.
Question 21.
Name the following:
Question 1.
The other term for gizzard in cockroach.
Answer:
Proventriculus
![]()
Question 2.
After sufficient growth, nymph undergoes moulting and enters into this stage:
Answer:
Instar
Question 3.
Paired accessory sex glands present in female cockroach that open in genital chamber.
Answer:
Collaterial glands.
Question 4.
The structural and functional unit of eye of cockroach.
Answer:
Ommatidia
Question 5.
Body segment of cockroach is covered by these four chitinous plates.
Answer:
Dorsal tergum, ventral sternum and two lateral pleurons.
Question 22.
Explain the process of fertilization in cockroach.
Answer:
- The process of fertilization in cockroach is internal.
- Male and female cockroaches come together by their posterior phallomeres.
- The spermatophores are transferred to the genital chamber of female cockroach.
- Sperms released from the spermatophore reach the spermatheca.
- The eggs are discharged from both the ovaries alternately into the common oviduct and pass into the genital chamber.
- Sperms coming from the spermatheca fertilize the eggs in the genital chamber.
Question 23.
Name the gland whose secretions form ootheca or egg case.
Answer:
The secretion of collaterial glands forms a capsule around them is called as ootheca or egg case.
Question 24.
Describe the stages of development in cockroach.
Answer:
- The development in cockroach (Periplaneta americana) is paurametabolous as the development occurs through nymphal stage.
Fertilized egg → Nymph → Adult - The nymph looks like adult but it is smaller and sexually immature.
- After sufficient growth, nymph undergoes moulting and enters into a stage between two successive moults known as instar.
- Cockroaches may undergo moulting for around 13 times before reaching the adult stage.
- The nymphal stages have wing pads but only adult cockroaches have wings.
- The embryonic period in cockroach varies as per temperature and humidity. At 24°C, the duration is about 58 days and at 30° C, the duration is about 32 days.
![]()
Question 25.
Fill in the blanks.
- The head of cockroach is formed by fusion of ________ segments.
- Hindwings are attached to the tergum of ________.
- _________ pairs of walking legs are present on ventral side of cockroach.
- Laterally, the tergum in cockroach is jointed to sternum by soft cuticle called ________.
- Tongue-like single structure present in front of the labium between first maxillae is called as ______.
Answer:
- 6
- Metathorax
- 3
- Pleura
- Hypopharynx /lingua
Question 26.
Why are cockroaches considered as pests?
Answer:
Cockroaches are considered pests due to following reasons:
1. Cockroaches damage household materials like clothes, shoes, paper, etc.
2. Cockroaches eat and destroy the foodstuff. They contaminate food, which gives a typical smell to food and make it unpalatable.
3. They cany pathogens of diseases like cholera, diarrhoea, tuberculosis, typhoid, etc.
Question 27.
Cockroaches are considered as a part of food chain. Justify.
Answer:
Many amphibians, birds, lizards and rodents prey upon cockroaches and this makes them a part of food chain. They are also eaten by certain groups of people in South America, China and Myanmar.
Question 28.
Lata was surprised to see cockroaches used as specimen in her college laboratory. She asked her teacher the reason for cockroach being used as experimental animal in laboratory. What would be the probable reason given by her teacher?
Answer:
Cockroach are used in laboratories as experimental animal for biological research as they can be obtained easily without causing damage to ecological balance. Cockroaches are commonly used as experimental animal in laboratory because of their large size, omnivorous food habit, hardiness (chitinous exoskeleton), rapid growth and reproduction. Also they are available almost any season, at any locality.
![]()
Question 29.
Give the measures to control the population of cockroach.
Answer:
Cockroaches are economically harmful organism. They must be controlled in an efficient way.
Following are the measures to control the population of cockroach:
1. Maintain good sanitation: Dark and humid places of kitchen, cupboards, trolleys must be cleaned regularly. Cracks and crevices and other such areas must be filled. Accumulation of garbage at home should be avoided.
2. Keeping water in drainage trap: If the drain trap is dry, cockroaches frequently enter home by migrating up from sewer connections. So, we should always keep the drain trap filled with water.
3. Chemical control: Organophosphates, carbamates, pyrethroids and boric acid are efficient poisons of cockroaches. Various types of their formulations are available in market under various brand names.
Question 30.
Depending upon nature of food and feeding habits, different insects have different types of mouthparts. Collect images of different mouthparts and paste in appropriate boxes.
Answer:
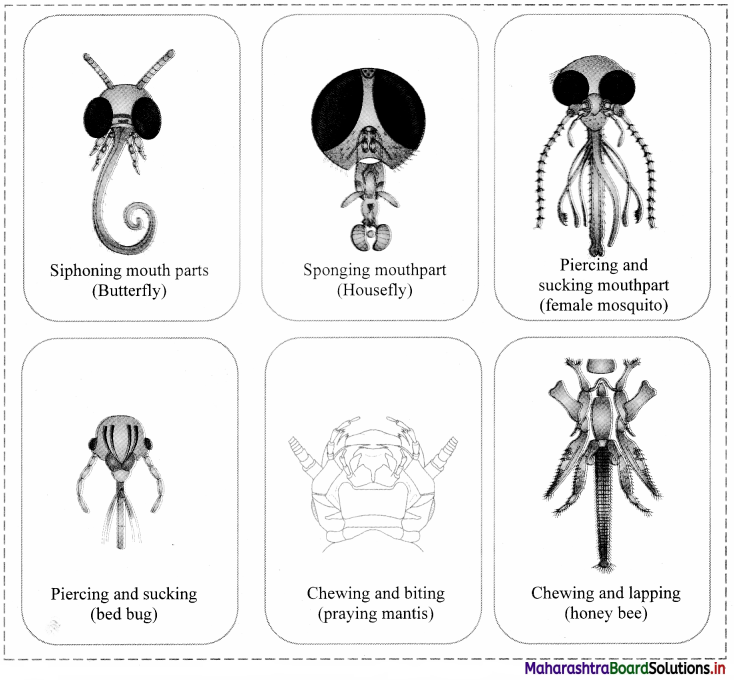
Question 31.
Apply Your Knowledge
Question 1.
The cockroach was dissected so as to expose the digestive system. Student found tubules at two places in the digestive system:
1. Around the anterior part of stomach
2. At the junction of mid-gut and hind-gut Identify the tubules and give their functions.
Answer:
1. Hepatic caeca
2. Malpighian tubules
For functions: Hepatic caeca: These are thin, transparent, short, blind (closed) and hollow tubules.
Function: They secrete digestive enzymes.
For functions:
- Malpighian tubules are the main excretory organs of cockroach.
- They are thin, yellow coloured, ectodermal thread-like structures that lie in the
- These tubules are 150 in number. Malpighian tubules are attached to the alimentary canal between the midgut and hindgut.
- Each Malpighian tubule is lined with a single layer of glandular epithelial cells having microvilli. The distal portion of Malpighian tubule is secretory and the proximal part is absorptive in function.
- They extract water and nitrogenous wastes from the haemocoel and convert them into uric acid and pass them into ileum. As the cockroach excretes uric acid, it is said to be uricotelic.
- Also, fat bodies, nephrocytes and uricose glands (only in males) help in excretion.
- In cockroach, nephrocytes (urate cells) associated with fat bodies and cuticle are also believed to be excretory in function. The nephrocytes are cells present along with the fat bodies or present along the heart and store nitrogenous wastes.
- The excretory products later are removed in the haemocoel. Some nitrogenous wastes are deposited on the cuticle and eliminated during moulting.
![]()
Question 2.
Rita’s mother while cleaning the house spotted a darkish reddish to blackish brown coloured capsule glued on the crack. Her mother showed it to Rita and asked her about it. Rita recollected that it resembles to a picture shown by her teacher in classroom while teaching about cockroach. What it must be?
Answer:
- The darkish reddish to blackish brown coloured capsule may be ootheca.
- The secretion of collaterial glands forms a capsule around them is called as ootheca or egg case.
- It is about 8 mm long and ranges from dark reddish to blackish brown.
- Ootheca contains 14 to 16 fertilized eggs in two rows.
- They are dropped or glued to a suitable surface, like a crack or crevice with good humidity near a food source.
- A female cockroach on an average, produces 9 to 10 oothecae during its lifespan.
Question 32.
Quick Review
Question 33.
Exercise
Question 1.
Which species of cockroach are found in India?
Answer:
Periplaneta americana, Blatta orientalis and Blatta germanica.
![]()
Question 2.
Cockroaches are said to be omnipresent. Justify
Answer:
Cockroaches are said to be omnipresent as they are present everywhere, all over the world. They are usually seen in damp and moist places, crevices.
Question 3.
Classify cockroach giving reasons for its systematic position.
Answer:
| Classification | Reasons | |
| Kingdom | Animalia | Cell wall absent, heterotrophic nutrition. |
| Phylum | Arthropoda | They have jointed appendages. Body is chitinous and segmented. |
| Class | Insecta | They possess two pairs of wings and three pairs of walking legs. |
| Genus | Periplaneta | Straight wings and nocturnal. |
| Species | americana | Originated in the continent of America. |
Question 4.
Describe in detail the body division of cockroach.
Answer:
Body division: The body is divided into three regions viz. head, thorax and abdomen.
Abdomen:
- The abdomen is elongated and made up of ten segments. Each segment has a dorsal tergum and ventral sternum.
- Tergum is jointed to the sternum laterally by a soft cuticle called pleura.
- The posterior segments are telescoped in. Due to this, the eighth and ninth terga get overlapped by the seventh. The tenth tergum projects backward and is deeply notched. It bears a pair of small, many jointed anal cerci.
- The abdomen is narrow and tapering in males as compared to females.The ninth sternum of males also bears a pair of short, unjointed anal style.
Question 5.
Name the last segment in the leg of cockroach.
Answer:
Legs: Three pairs of walking legs are present on the ventral side. Each leg is formed of five podomeres namely coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus.Tarsus is the last segment and it is made up of five movable segments or tarsomeres. The last tarsomere bears a pair of claws and cushion-like arolium helpful in clinging.
![]()
Question 6.
What is arolium in cockroach?
Answer:
Legs: Three pairs of walking legs are present on the ventral side. Each leg is formed of five podomeres namely coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus.Tarsus is the last segment and it is made up of five movable segments or tarsomeres. The last tarsomere bears a pair of claws and cushion-like arolium helpful in clinging.
Question 7.
What are ommatidia?
Answer:
Compound eyes: Compound eyes are paired, dark, kidney — shaped structures placed on the dorsolateral sides of the head. They are made up of large number of hexagonal ommatidia i.e. around 2000 ommatidia (sing, ommatidium). These ommatidia are the structural and functional unit of compound eye, each forming an image of very small part of visual field. Collectively, the compound eye produces a mosaic image. Even though the compound eye gives a mosaic or hazy vision yet the animal can detect the slightest movement of the object. Compound eyes provide low resolution and more sensitive vision.
Question 8.
What is the function of labium?
Answer:
Each gland has a salivary duct. Both the ducts unite to form a common salivary duct.
Question 9.
What are the antennae of cockroach also known as?
Answer:
Antennae: They are also called as feelers.These are long, filamentous, segmented structures that can move in all directions.They are lodged in membranous pits known as antennal sockets.They are tactile (touch) as well as olfactory (smell) organs.
Function: They are useful in locating the food material in the vicinity.
Question 10.
Write a short note on exoskeleton of cockroach.
Answer:
Exoskeleton: Tough, waxy, non-living chitinous exoskeleton protects the body of the cockroach. It is made up of nitrogenous polysaccharide – chitin that provides strength, elasticity and surface area for attachment of muscles. Each body segment of cockroach is covered by four chitinous plates called sclerites namely, dorsal tergum, ventral sternum and two lateral pleurons.
![]()
Question 11.
Describe the mouthparts of cockroach briefly.
Answer:
- Hepatic caeca: These are thin, transparent, short, blind (closed) and hollow tubules.
- Function: They secrete digestive enzymes.
- Hindgut or proctodaeum: It consists of ileum, colon and rectum.
- Ileum: It is short and narrow part of hindgut. Malpighian tubules open in the anterior lumen of ileum, near the junction of midgut and hindgut. Posterior region of ileum contains sphincter. Ileum directs the nitrogenous wastes and undigested food towards colon.
- Colon: It is a longer and wider part of the hindgut. It directs waste material towards the rectum. It reabsorbs water from wastes as per the need.
- Rectum: It is oval or spindle-shaped, terminal part of the hindgut. It contains six rectal pads along the internal surface for absorption of water. Rectum opens into anus. Anus is present on the ventral side of the 10th segment. It is the last or posterior opening of the digestive system. The undigested food is released out of the body through anus.
Question 12.
Give another name for upper lip and lower lip of cockroach.
Answer:
- Cockroach has a pair of salivary glands which secrete saliva.
- Each gland has a salivary duct.
- Both the ducts unite to form a common salivary duct.
Question 13.
Mention the three segments of thorax.
Answer:
Thorax: Thorax is made up of three distinct segments – prothorax (anterior segment), mesothorax and metathorax (posterior segment). Ventrally, the thorax bears three pairs of walking legs, one at each segment. Dorsally, the thorax bears two pairs of wings attached to mesothoracic and metathoracic segment of the body, a. Legs: Three pairs of walking legs are present on the ventral side. Each leg is formed of five podomeres namely coxa, trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus.Tarsus is the last segment and it is made up of five movable segments or tarsomeres. The last tarsomere bears a pair of claws and cushion-like arolium helpful in clinging.
Question 14.
Which wings are known as true wings? Why?
Answer:
Wings: Forewings and hindwings form the two pair of wings present on the dorsal side. Forewings are the first pair of dark, opaque, thick, leathery wings. Hindwings are thin, broad, membranous delicate and transparent.They are attached to tergum of metathorax.
Functions: Forewings are protective in function and hindwings are helpful in flight, thus are called true wings.
![]()
Question 15.
Write a short note on haemocoel.
Answer:
- Cockroach has a body cavity or true coelom present around the viscera.
- The body cavity of cockroach is known as haemocoel as it is filled with haemolymph (blood). Cockroaches have open type of circulation thus; the body cavity is filled with haemolymph.
- The body cavity contains fat bodies. These are in the form of loose, whitish mass of tissue. They are made up of large, polygonal cells which contain fat globules, proteins and sometimes glycogen.
Question 17.
Which region of the alimentary canal is also known as stomodaeum?
Answer:
- Foregut or stomodaeum: It consists of pharynx, oesophagus, crop and gizzard.
- Pharynx: It is very short, narrow but muscular tube that opens into oesophagus.
- Function: Conduction of food into the oesophagus.
- Oesophagus: It is slightly long and narrow tube which opens into crop.
- Crop: Crop is a large, pear shaped and sac- like organ.
- Function: It temporarily stores the food and then sends it to gizzard.
- Gizzard: Gizzard or proventricuius is a small spherical organ. It is provided internally with a circlet of six chitinous teeth and backwardly directed bristles.The foregut ends with gizzard.
Function: The chitinous teeth present in gizzard are responsible for crushing the food and the bristles help to filter the food.
Question 18.
Explain in detail the hindgut of cockroach.
Answer:
Hindgut or proctodaeum: It consists of ileum, colon and rectum.
Question 19.
Write a short note on mesentron.
Answer:
- Midgut or mesenteron: It consists of stomach and hepatic caeca.
- Ventriculus or stomach: It is straight, short and narrow. Stomach is lined by glandular epithelium which secretes digestive enzymes.
- Function: It is mainly responsible for digestion and absorption.
Question 20.
Explain the three parts of alimentary canal.
Answer:
1. Digestive system of cockroach consists of mouthparts, alimentary canal and salivary glands.
2. Mouthparts: Pre-oral cavity present in front of the mouth receives food. It is bounded by chewing and biting type of mouth parts.
3. These are movable, segmented appendages that help in ingestion of food. The mouthparts of cockroach comprises of:
a. Labrum: It forms the upper lip. It is a single flap-like movable part which covers the mouth from upper side. It forms an anterior wall of pre¬oral cavity.
Function: It is useful in holding the food during feeding.
b. Mandibles: These are two dark, hard, chitinous structures with serrated median margins.They are true jaws present on either side, behind the labrum.
Function: They perform co-ordinated side-wise movements with the help of adductor and abductor muscles to cut and crush the food.
c. Maxillae: These are the accesssory jaws. They are also called as first pair of maxillae. These are situated on the either side of mouth behind the mandibles. Each maxilla consists of sclerites like cardo, stipes, galea, lacinia and maxillary palps.
Functions: Maxillae hold food, help mandibles for mastication. They are also used for cleaning the antennae and front legs. Maxillary palps act as tactile organs.
d. Labium: It forms the lower lip. Labium is also known as second maxilla which covers the pre-oral cavity from the ventral side. It is firmly attached to the posterior part of head. It has three jointed labial palps which are sensory in function.
Function: It is useful in pushing the chewed food in the pre-oral cavity. It prevents the loss of food falling from the mandibles, while chewing.
e. Hypopharynx: Hypopharynx is also known as lingua. It is a somewhat cylindrical single structure, located in front of the labium and between first maxillae. The salivary duct opens at the base of hypopharynx. Hypopharynx bears comb-like plates called super-lingua on either side. Hypopharynx is present at the centre of the mouth.
Function: It is useful in the process of feeding and mixing saliva with food, iii. Alimentary canal: It is long a (6 – 7cm) tube of different diameters with two openings.
![]()
Question 21.
Explain the three sinuses in the coelom cockroach.
Answer:
Sinuses: The coelom of cockroach is divided into three sinuses – pericardial sinus, perivisceral sinus and perineural sinus.
- Pericardial sinus: It is dorsal, very small and contains dorsal vessel.
- Perivisceral sinus: It is middle and largest sinus. It contains fat bodies and almost all major visceral organs of alimentary canal and reproductive system.
- Perineural sinus: It is ventral, small and contains ventral nerve cord. It is continuous into legs. All the three sinuses communicate with each other through the pores present between two successive points of attachments of diaphragms.
Question 22.
Define: alary muscles.
Answer:
Dorsal diaphragm: It has 12 pairs (10 abdominal and 2 thoracic) of fan-like alary muscles. Alary muscles are triangular with pointed end attached to terga at lateral side and broad end lies between the heart and dorsal diaphragm.
Question 24.
Write a short note on haemolymph.
Answer:
Haemolymph: Haemolymph is colourless as it is without any pigment. It consists of plasma and seven types of blood cells/haemocytes. Plasma consists of water with some dissolved organic and inorganic solutes. It is rich in nutrients and nitrogenous wastes like uric acid.
Question 26.
What are spiracles?
Answer:
Spiracles: They are paired respiratory openings. Spiracles are present on the ventro-lateral side of the body, in pleural membrane. Cockroaches have two pairs of thoracic and eight pairs of abdominal spiracles.The spiracles open into a series of air sacs from which arise the tubes called trachea. The spiracles let the air into and out of trachea.
Question 27.
With the help of neat and labelled diagram, explain the tracheal system of cockroach.
Answer:
1. Cockroach has an internal respiratory system of air tubes called tracheal system by which the air is brought into the body and is in contact with every part of the body. It allows the exchange of gases directly between the air and tissues without the need of blood.
These air tubes of internal respiratory system begin at the opening on body surface called spiracles.
2. Spiracles: They are paired respiratory openings. Spiracles are present on the ventro-lateral side of the body, in pleural membrane. Cockroaches have two pairs of thoracic and eight pairs of abdominal spiracles.The spiracles open into a series of air sacs from which arise the tubes called trachea. The spiracles let the air into and out of trachea.
3. Trachea: The trachea form a definite pattern of branching tubes arranged transversely as well as longitudinally. They are about 1mm thick and have spiral or annular thickening of chitin. The inner lining of chitin prevents the trachea from collapsing. Each trachea further branches into smaller tubes called tracheoles.
4. Tracheoles: These are fine intracellular tubes that penetrate deep into tissues. They are thin and not lined by chitin. They end blindly in the cells. Each tracheole at the blind end is filled with a watery fluid through which exchange of gases takes place. The content of this fluid keeps changing. At high muscular activity, part of fluid part is drawn into the tissues to enable more and rapid oxygen intake.
![]()
Question 28.
Write a short note on Malpighian tubules.
Answer:
- Malpighian tubules are the main excretory organs of cockroach.
- They are thin, yellow coloured, ectodermal thread-like structures that lie in the
- These tubules are 150 in number. Malpighian tubules are attached to the alimentary canal between the midgut and hindgut.
- Each Malpighian tubule is lined with a single layer of glandular epithelial cells having microvilli. The distal portion of Malpighian tubule is secretory and the proximal part is absorptive in function.
- They extract water and nitrogenous wastes from the haemocoel and convert them into uric acid and pass them into ileum. As the cockroach excretes uric acid, it is said to be uricotelic.
- Also, fat bodies, nephrocytes and uricose glands (only in males) help in excretion.
- In cockroach, nephrocytes (urate cells) associated with fat bodies and cuticle are also believed to be excretory in function. The nephrocytes are cells present along with the fat bodies or present along the heart and store nitrogenous wastes.
- The excretory products later are removed in the haemocoel. Some nitrogenous wastes are deposited on the cuticle and eliminated during moulting.
Question 29.
Write a short note on peripheral nervous system of cockroach.
Answer:
Peripheral nervous system (PNS):
- The peripheral nervous system comprises of nerves that arise from various ganglia of CNS.
- Six pairs of nerves arise from the supra-oesophageal ganglia.They supply to the eyes, antenna and labrum.
- Nerves arising from the sub-oesophageal ganglion supply to the mandibles, maxillae and labium.
- Nerves arising from the thoracic ganglia supply to the wings, legs and internal thoracic organs.
- Nerves from abdominal ganglia go to the abdominal organs of respective abdominal segments.
Question 30.
Explain in detail the central nervous system of cockroach.
Answer:
Central nervous system (CNS): Central nervous system consists of nerve ring and ventral nerve cord.
Nerve ring consists of:
- a pair of supra-oesophageal ganglia
- a pair of circum-oesophageal connectives
- a pair of sub-oesophageal ganglia
- Supra-oesophageal ganglia or cerebral ganglia: A pair of supra-oesophageal ganglia is collectively known as the brain. Brain is present in head, above the oesophagus and between antennal bases. Each supra-oesophageal ganglion is formed by the fusion of three small ganglia – protocerebram, deutocerebrum and tritocerebrum.
- Circum-oesophageal connectives: Supra-oesophageal ganglia are connected to sub-oesophageal ganglion by a pair of lateral nerves called as circum-oesophageal connectives. Connectives arise from supra-oesophagial ganglia.
- Sub-oesophageal ganglia: It is a bilobed and present below the oesophagus, in head. It is also formed by the fusion of three pairs of ganglia.
- Ventral nerve cord:
- It arises from the sub-oesophageal ganglion. It is present along mid-ventral position, in perineural sinus.
- It is double ventral nerve cord and consists of nine segmental, paired ganglia.
- First three pairs of segmental ganglia are large and known as thoracic ganglia. The other six pairs of segmental ganglia are in abdomen (abdominal ganglia).
- 6th abdominal ganglion is the largest and it is present in 7th abdominal segment.
![]()
Question 31.
Enlist the four ganglia of autonomous nervous system of cockroach.
Answer:
Autonomic nervous system (ANS): It consists of four ganglia and a retrocerebral complex.
The ganglia are as follows:
- Frontal ganglion: It is present above the pharynx and in front of brain.
- Hypocerebral ganglion: It is present on the anterior region of oesophagus.
- Ingluvial ganglion: It is present on crop. It is also called as visceral ganglion.
- Ventricular ganglion: It is present on gizzard.
Question 32.
Explain the structures and functions of different parts involved in female reproductive system of cockroach.
Answer:
- Female reproductive system of cockroach consists a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, vagina, spermatheca and accessory glands.
- Ovaries are primary reproductive organs. They are paired and lie lateral in position in 2nd – 6lh abdominal segments. Each ovary is formed of a group of 8 ovarian tubules or ovarioles, containing a chain of developing ova. All ovarioles of an ovary open in lateral oviduct of respective side.
- The lateral oviducts unite to form a common oviduct or vagina. Common oviduct or vagina opens into the Bursa copulatrix (genital chamber), the female organ of copulation.
- Spermatheca, is a sperm storing structure present in the 6th segment opens into genital chamber. It receives the sperms during copulation and store them for fertilization.
- Collaterial glands are accessory paired glands that open in genital chamber.
- Female gonapophyses consists of six chitinous plates surrounding the genital pore. In males, genital pouch or genital chamber lies at the hind end of abdomen which is bounded dorsally by 9th and 10th terga and ventrally b; male genital pore and gonapophysis.
Question 33.
Explain in detail male reproductive system of cockroach.
Answer:
- Male reproductive system includes primary and secondary reproductive organs.
- Primary sex organs (male gonads) are called testes. They are paired and located in the 4th and 6th abdominal segments. Sperms produced in testis are carried by vasa deferentia.
- Vasa deferentia is a pair of thin tubular structure that arise from the testes and open into ejaculatory duct through seminal vesicle. They carry sperms to ejaculatory duct.
- Ejaculatory duct opens into male gonopore situated ventral to anus.
- Sperms produced by testis are stored in seminal vesicles in the form of bundles called spermatophores. These spermatophores are deposited in female reproductive tract during copulation.
- Mushroom shaped gland or utricular gland is an accessory reproductive gland. It is present in the 6th – 7th abdominal segments.
- Male gonapophyses or phallomere form the external genitalia of male. These are three asymmetrical chitinous structures surrounding the male gonophore.
Question 34.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Cockroach shows ________ adaptations.
(A) Cursorial
(B) Arboreal
(C) Fossorial
(D) Aquatic
Answer:
(A) Cursorial
Question 2.
Cockroach is a/an animal.
(A) omnivorous
(B) nocturnal
(C) cursorial
(D) all of these
Answer:
(D) all of these
![]()
Question 3.
Ocellar spots situated at the base of each antenna of cockroach is called as __________
(A) ommatidia
(B) lingua
(C) fenestrae
(D) proventrieulus
Answer:
(C) fenestrae
Question 4.
Foregut of cockroach is also known as ________ .
(A) stomodaeum
(B) mesenteron
(C) proctodaeum
(D) tergum
Answer:
(A) stomodaeum
Question 5.
Circlet of six chitinous teeth and backwardly directed bristles are present in _____ .
(A) fenestrae
(B) mesenteron
(C) rectum
(D) gizzard
Answer:
(D) gizzard
Question 6.
Blood filled cavity in cockroach is called ________
(A) haemocoel
(B) paracoel
(C) spongocoel
(D) metacoel
Answer:
(A) haemocoel
Question 7.
In cockroach, ventral nerve cord is present in the
(A) pericardial sinus
(B) perineural sinus
(C) head sinus
(D) perivisceral sinus
Answer:
(B) perineural sinus
Question 8.
In cockroach, malpighian tubules are present at junction of
(A) foregut and midgut
(B) midgut and hindgut
(C) hindgut and foregut
(D) foregut and hindgut
Answer:
(B) midgut and hindgut
![]()
Question 9.
The main excretory organ of cockroach is
(A) gizzard
(B) malpighian tubules
(C) utricular gland
(D) mushroom shaped gland
Answer:
(B) malpighian tubules
Question 10.
Central nervous system consists of
(A) nerve ring
(B) ingluvial ganglion
(C) ventral nerve cord
(D) both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(D) both (A) and (C)
Question 11.
Common oviduct opens into
(A) phallomere
(B) bursa copulatrix
(C) utricular gland
(D) vagina
Answer:
(B) bursa copulatrix
Question 12.
________ are external genitalia of male cockroach.
(A) Phallomeres
(B) Utricular gland
(C) Seminal vesicles
(D) Spermatheca
Answer:
(A) Phallomeres
Question 13.
The total number of ovarian tubules in a female cockroach is
(A) 8
(B) 2
(C) 16
(D) 26
Answer:
(C) 16
Question 14.
The secretion of collaterial glands forms a capsule around them is called
(A) spermatophore
(B) nymph
(C) ootheca
(D) gonophore
Answer:
(C) ootheca
![]()
Question 15.
Select the INCORRECT statement from the following.
(A) Head of cockroach is formed by the fusion of six segments.
(B) In cockroach, anus is present on ventral side of 10th segment.
(C) In cockroach, heart has 22 chambers.
(D) Cockroach has open type of circulatory system.
Answer:
(C) In cockroach, heart has 22 chambers.
Question 35.
Competitive Corner
Question 1.
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
(A) Female cockroach possesses sixteen ovarioles in the ovaries.
(B) Cockroaches exhibit mosaic vision with less sensitivity and more resolution.
(C) A mushroom-shaped gland is present in the 6th – 7th abdominal segments of male cockroach.
(D) A pair of spermatheca is present in the 6th segment of female cockroach.
Hint: Cockroaches exhibit mosaic vision with more sensitivity but less resolution.
Answer:
(B) Cockroaches exhibit mosaic vision with less sensitivity and more resolution.
Question 2.
Select the CORRECT sequence of organs in the alimentary canal of cockroach starting from mouth:
(A) Pharynx → Oesophagus → Gizzard → Ileum → Crop → Colon → Rectum
(B) Pharynx → Oesophagus → Ileum → Crop → Gizzard → Colon → Rectum
(C) Pharynx → Oesophagus → Crop Gizzard → Ileum → Colon → Rectum
(D) Pharynx → Oesophagus → Gizzard → Crop → Ileum → Colon → Rectum
Answer:
(C) Pharynx → Oesophagus → Crop Gizzard → Ileum → Colon → Rectum
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following features is used to identify a male cockroach from a female cockroach?
(A) Forewings with darker tegmina
(B) Presence of caudal styles
(C) Presence of a boat shaped sternum on the 9th abdominal segment
(D) Presence of anal cerci
Answer:
(B) Presence of caudal styles