Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Commerce BK Important Questions Chapter 2 Accounts of ‘Not for Profit’ Concerns
1. Objective Type Questions:
A. Select the most appropriate alternatives from those given below.
Question 1.
Purchases of stationery is a ______________ expenditure.
(a) capital
(b) revenue
(c) long-term
(d) deferred revenue
Answer:
(b) revenue
Question 2.
Usually ______________ is a major source of revenue income for ‘Not for Profit’ concerns.
(a) subscription
(b) donations
(c) legacies
(d) entrance fees
Answer:
(a) subscription
![]()
Question 3.
An Income and Expenditure Account and a Balance Sheet are prepared as final accounts by a ______________
(a) ‘Not for Profit’ concern
(b) Trading concern
(c) commercial organisation
(d) Public Limited Company
Answer:
(a) ‘Not for Profit’ concern
Question 4.
Non-cash items are not recorded in ______________
(a) Income and Expenditure Account
(b) Receipts and Payments Account
(c) Balance Sheet
(d) Profit and Loss Account
Answer:
(b) Receipts and Payments Account
Question 5.
The excess of assets over liabilities is termed as ______________
(a) surplus
(b) deficit
(c) capital fund
(d) loan
Answer:
(c) capital fund
Question 6.
For a library, expenditure on the purchase of books is a ______________ Expenditure.
(a) Capital
(b) Revenue
(c) General
(d) Recurring
Answer:
(a) Capital
![]()
Question 7.
______________ Account starts with the opening Cash Balance.
(a) Income and Expenditure
(b) Receipts and Payments
(c) Capital Fund
(d) Subscriptions
Answer:
(b) Receipts and Payments
Question 8.
Only ______________ incomes and expenses are shown in the Income and Expenditure Account.
(a) revenue
(b) capital
(c) business
(d) non-recurring
Answer:
(a) revenue
Question 9.
A debit balance on the Income and Expenditure Account denotes ______________
(a) deficit
(b) surplus
(c) profit
(d) excess of income over expenditure
Answer:
(a) deficit
Question 10.
Non-trading organisation writes summary of all cash transactions in the ______________ Account.
(a) Cash
(b) Receipts and Payments
(c) Income and Expenditure
(d) Profit and Loss
Answer:
(b) Receipts and Payments
Question 11.
Both capitalised receipts and capital expenditure are shown in the ______________
(a) Profit and Loss A/c
(b) Balance Sheet
(c) Trading A/c
(d) Income and Expenditure A/c
Answer:
(b) Balance Sheet
![]()
Question 12.
‘Not for Profit’ organisation prepares ______________ to find out its financial position.
(a) Receipts and Payments A/c
(b) Balance Sheet
(c) Trading A/c
(d) Income and Expenditure A/c
Answer:
(b) Balance Sheet
Question 13.
Subscriptions received from the members is considered as ______________ receipts.
(a) capital
(b) revenue
(c) non-recurring
(d) commercial
Answer:
(b) revenue
Question 14.
Fund which provides permanent source of income to non-trading organisation is called ______________ fund.
(a) endowment
(b) general
(c) specific
(d) capital
Answer:
(a) endowment
Question 15.
For a public hospital, expenditure on the purchase of medicines is a ______________ Expenditure.
(a) General
(b) Non-recurring
(c) Capital
(d) Revenue
Answer:
(d) Revenue
Question 16.
Which of the following items will not appear in the Balance Sheet of a club?
(a) Subscriptions received in advance
(b) Special donation received during the year
(c) Subscriptions due for the year
(d) Entrance fees paid by new members
Answer:
(d) Entrance fees paid by new members
![]()
Question 17.
The main purpose of incurring a ______________ expenditure is to earn an income or to increase the earning capacity of the business.
(a) recurring
(b) capital
(c) revenue
(d) business
Answer:
(b) capital
Question 18.
Excess of Expenditure over Income is termed as ______________
(a) Surplus
(b) Deficit
(c) Capital Fund
(d) Profit
Answer:
(b) Deficit
Question 19.
Receipts and Payments Account is a ______________
(a) Personal Account
(b) Real Account
(c) Nominal Account
(d) Profit and Loss Account
Answer:
(b) Real Account
B. Write the Word/Term/Phrase which can substitute each of the following statements.
Question 1.
Such concerns, which are formed for rendering some useful services to its members without having profit motive.
Answer:
‘Not for Profit’ concern
Question 2.
Excess of expenditure over income of ‘Not for Profit’ concerns.
Answer:
Deficit
Question 3.
A statement showing the financial position of a concern on a particular date.
Answer:
Balance Sheet
![]()
Question 4.
The debit balance of an Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
Deficit
Question 5.
Fees received from the member only once at the time of his entry into the ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Answer:
Life membership fees
Question 6.
Specific amount paid by the members annually to non-trading organisation to get certain services or benefits.
Answer:
Subscription
Question 7.
Donation or gift received from the members or outsiders for specific purpose.
Answer:
Specific donation
Question 8.
Donation received for general purpose like welfare of the members or society.
Answer:
General donation
Question 9.
The gifts received from legal representatives as per the will of a deceased person.
Answer:
Legacies
![]()
Question 10.
An expenditure which is incurred for carrying the day-to-day business activities.
Answer:
Revenue Expenditure
Question 11.
Capital resources which are owned and possessed by the ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Answer:
Capital Fund
Question 12.
An account which is prepared by the ‘ Not for Profit’ concern to record summary of all types of receipts and payments.
Answer:
Receipts and Payments Account
Question 13.
Closing debit balance of Receipts and Payments Account.
Answer:
Cash in Hand and or Cash at Bank
Question 14.
A payment made by the non-trading organisation periodically for consecutive issue of magazines, newspapers, etc.
Answer:
Subscriptions paid
Question 15.
The major source of revenue to a ‘Not for Profit’ concern, from its members.
Answer:
Subscriptions
Question 16.
Fees paid by persons to become members of a ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Answer:
Entrance Fees or Admission Fees
![]()
Question 17.
The concerns which prepare Income and Expenditure Account instead of Profit and Loss Account.
Answer:
‘Not for Profit’ concern
Question 18.
The expenditure which is recurring in nature.
Answer:
Revenue Expenditure
Question 19.
The expenditure which is non-recurring in nature.
Answer:
Capital Expenditure
Question 20.
An account opened by non-trading concerns, to find out surplus/deficit during the particular financial year.
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account
C. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons.
Question 1.
All receipts are the items of revenue income.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In ‘Not for Profit’ concern receipts includes revenue receipts as well as capital receipts of current year or of previous year or of next year, so we can say that all receipts are not the items of revenue income.
Question 2.
In the Income and Expenditure Account, all incomes received during the year irrespective of the year for which they are received, are to be recorded.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the Income and Expenditure Account, all revenue incomes, received during the current year, are to be recorded only.
![]()
Question 3.
Receipts and Payments Account shows the amount of profit earned or loss suffered during a year.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Receipts and Payments Account shows the amount of receipts and payments (in cash or through bank) of any year in the current year and do not shows any profit earned or loss suffered during a year.
Question 4.
Every year ‘Not for Profit’ concerns, prepares Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
This statement is True.
To get the idea of sufficient income, other expenditure, for smooth run of concern, every year ‘Not for Profit’ concern prepares Income and Expenditure Account.
Question 5.
‘Deficit’ means excess of income over expenditure in the Income and Expenditure Account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
In the Income and Expenditure Account ‘Deficit’ means excess of expenditure over incomes.
Question 6.
‘Revenue receipts’ means receipts which are not recurring in nature.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Revenue Receipts means receipts which frequently takes place and which are recurring in nature.
D. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
An Income and Expenditure Account and a Balance Sheet are prepared as final account by a ______________
Answer:
‘Not for Profit’ concern
Question 2.
______________ is a major source of revenue income for ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Answer:
Subscription
![]()
Question 3.
Non-cash items are not recorded in ______________
Answer:
Receipts and Payments Account
Question 4.
______________ concerns have profit motive.
Answer:
Trading
Question 5.
In a Trading concerns ______________ is prepared to know the financial position of the business.
Answer:
Balance Sheet
Question 6.
Excess of Receipts over Payments means ______________
Answer:
Cash or Bank balance
Question 7.
Legacy is received by ‘Not for Profit’ concerns on a ______________ basis.
Answer:
permanent
![]()
Question 8.
Incomes which are to be capitalised are to be added to ______________
Answer:
Capital Fund
Question 9.
Subscription received in advance, in current year, is to be ______________ from subscription amount.
Answer:
subtracted
Question 10.
Subscription received in advance, in previous year is to be ______________ to subscription amount.
Answer:
added
Question 11.
Locker’s rent is ______________ for ‘Not for Profit’ concern.
Answer:
revenue income
Question 12.
Life membership fees, Legacy, Surplus, etc. are to be ______________ to Capital Fund.
Answer:
added
Question 13.
All revenue incomes and revenue expenses are to be recorded in ______________
Answer:
Income and Expenditure Account
Question 14.
All Receipts and Payments are recorded in the Receipts and Payment Account ______________ of the year.
Answer:
irrespective
![]()
Question 15.
Incomes or Expenses having recurring nature are known as ______________ incomes or expenses.
Answer:
revenue
E. Answer in one sentence only.
Question 1.
What is deferred revenue expenditure?
Answer:
Expenditure which is basically revenue expenditure but benefits of which accured to the organisation for more than one year is called deferred revenue expenditure.
Question 2.
What is Entrance Fees?
Answer:
The fees which is paid by the persons who wish to become a member of the organisation are called Entrance Fees.
Question 3.
What is Deficit?
Answer:
Excess of expenditure over income shown by Income and Expenditure Account is called Deficit for the financial year.
Question 4.
State the meaning of Revenue Expenditure.
Answer:
An expenditure which is incurred for carrying day-to-day business activities and maintaining fixed assets in working condition is called Revenue Expenditure.
Question 5.
What do you mean by Capital Expenditure?
Answer:
An expenditure which is non recurring is nature and incurred to purchase new fixed assets, to increase earning capacity, efficiency and working life of the existing fixed assets and to achieve economy of operation an existing fixed assets is called Capital Expenditure.
![]()
Question 6.
Which final accounts do the ‘Not for Profit’ concern prepare?
Answer:
‘Not for Profit’ concern prepare Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet as their final accounts.
Question 7.
Give the examples for ‘Not for Profit’ concerns.
Answer:
Examples of ‘Not for Profit’ concerns are: sports club, charitable hospitals, schools, colleges, universities, welfare association, chamber of commerce, etc.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Recurring Expenses?
Answer:
Recurring expenses are those expenses, benefit of which lasts for a maximum period of one year and is increased on purchase of goods or services, in order to carry out the main activity of the business.
Question 9.
Why Receipts and Payments Account is prepared?
Answer:
To record all cash and Bank transactions taken place in the organisation, Receipt and Payment Account is prepared.
Question 10.
In Income and Expenditure Account, which kind of incomes and expenses are to be recorded?
Answer:
In Income and Expenditure Account, ‘Revenue’ incomes and expenses are to be recorded.
Solved Problems
Question 1.
With the information given below regarding ‘Subscription’ give accounting effects of it in the Final Accounts of a ‘Not for Profit’ concern:

Additional Information:
1. Subscriptions received during the year includes:
Subscriptions received for 2018-2019 ₹ 8,750 and for 2020-21 ₹ 7,500.
2. There are 500 members of the concern and each member pays ₹ 500 as annual subscription.
3. During the year 2018-19 subscription received for the year 2019-20 was ₹ 12,500.
Solution:
In the books of _____________________
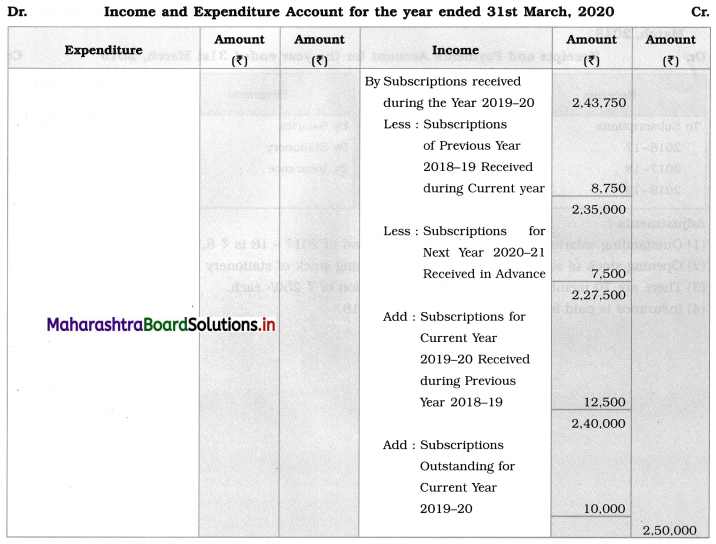
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2020
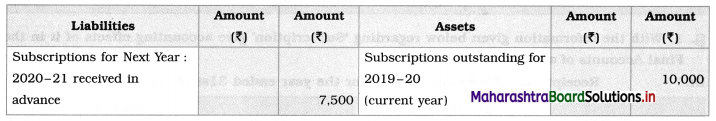
Working Notes:
Amount of subscriptions outstanding for current year 2019-20 is calculated as follows:
Subscriptions outstanding (receivable) = (Subscriptions due from all members) – (Subscriptions received)
= (500 members × ₹ 500 per member) – (Subscriptions received during current year + Subscription received during previous year)
= (500 × 500) – (2,27,500 + 12,500)
= 2,50,000 – 2,40,000
= ₹ 10,000.
![]()
Question 2.
Show the following items in the Income and Expenditure Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018:
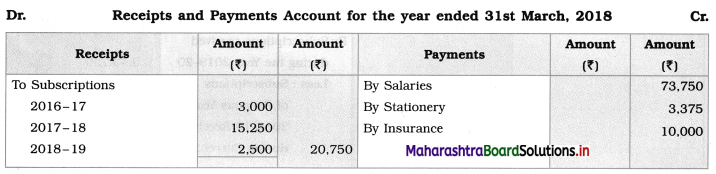
Adjustments:
1. Outstanding salaries for 2016-17 is ₹ 11,250 and of 2017 – 18 is ₹ 8,125.
2. Opening stock of stationery is ₹ 5,000 and Closing stock of stationery is ₹ 2,500.
3. There are 70 members paying annual subscription of ₹ 250/- each.
4. Insurance is paid for year ended 30th June, 2018.
Solution:
In the books of _____________________
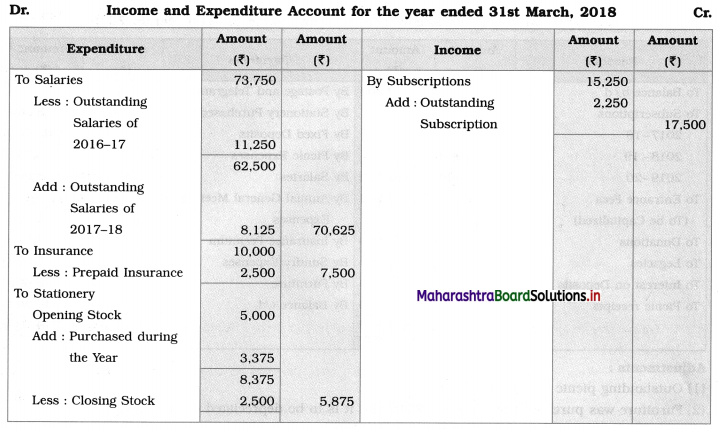
Working Notes:
1. Outstanding subscriptions for the current year 2017-18 are calculated as follows:
Outstanding subscriptions = Subscriptions due or receivable – Subscriptions received
= 70 × 250 – 15,250
= 17,500 – 15,250
= ₹ 2,250.
Subscriptions for 2016 – 17 and 2018 – 19 will not appear in the Income and Expenditure Account prepared for 2017 – 18.
2. Prepaid insurance is calculated as follows:
Insurance is paid in advance for 3 months i.e. from 1st April, 2018 to 30th June, 2018.
Prepaid insurance = \(\frac{3}{12}\) × Insurance premium paid
= \(\frac{3}{12}\) × 10,000
= ₹ 2,500.
Prepaid insurance deducted from Insurance on the Debit side of Income and Expenditure Account.
Question 3.
The following is the Receipts and Payments Account for the year ended on 31st March, 2019:
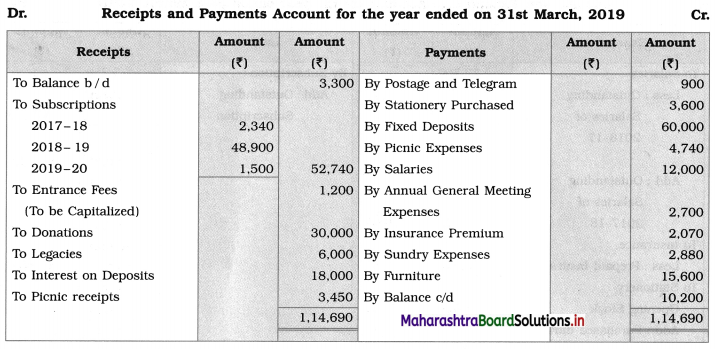
Adjustments:
1. Outstanding picnic receipts ₹ 2,550.
2. Furniture was purchased on 01 – 10 – 2018 and it is to be depreciated @ 10% p.a.
3. Outstanding subscriptions for current year ₹ 4,920.
4. Stock of Stationery on 1st April 2018 was ₹ 390 and on 31st March 2019 was ₹ 690.
5. Entire amount of legacies and 50 % of donations are to be capitalized.
With the above information, you are required to prepare Income and Expenditure Account for the year ending on 31st March 2019.
Solution:
In the books of _____________________
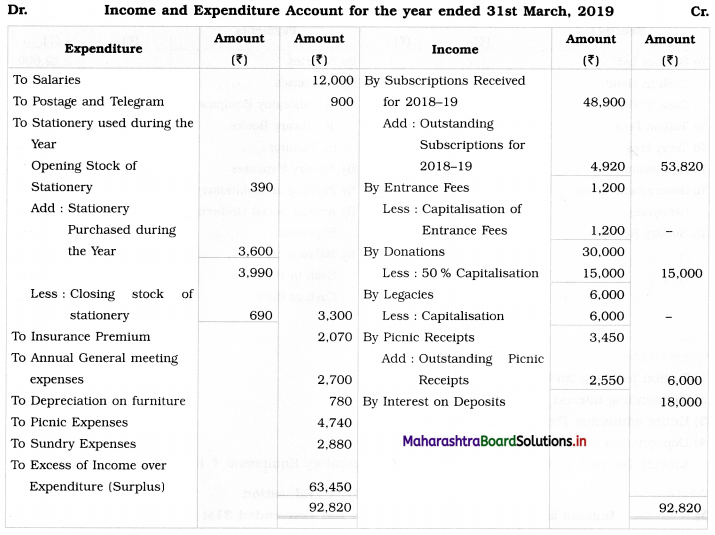
![]()
Question 4.
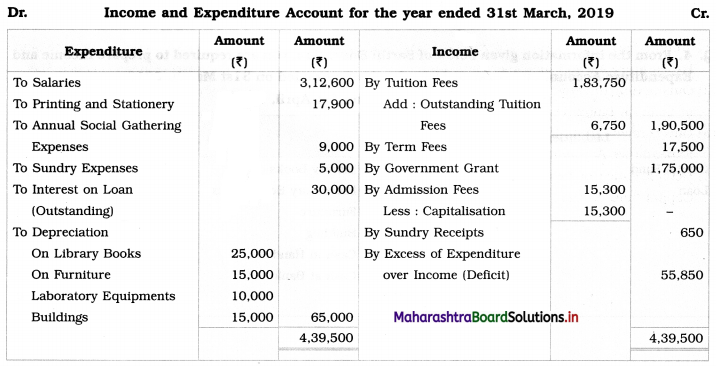
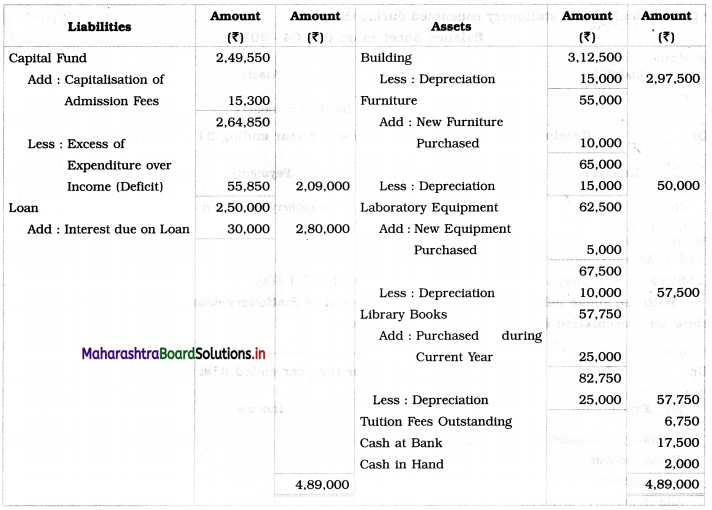
From the information given below of Sarthi Education, you are required to prepare Income and Expenditure Account and Balance Sheet for the year ended on 31st March, 2019:
Balance Sheet as on 1st April, 2018
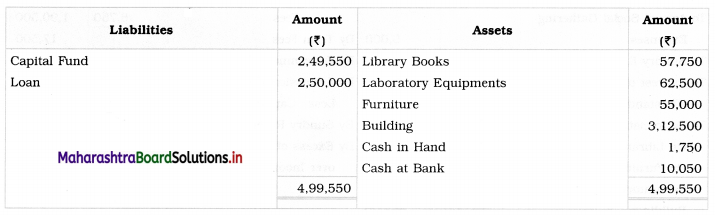
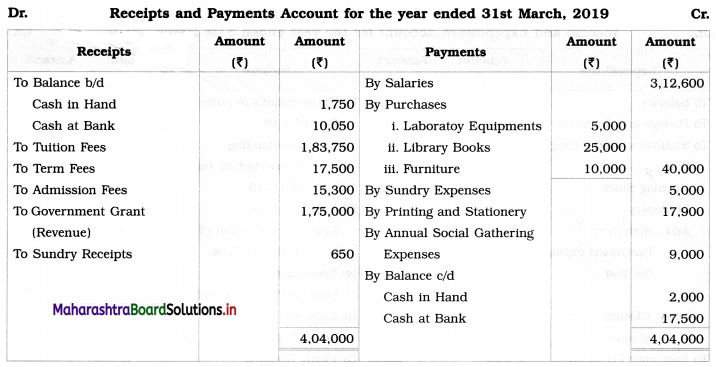
Adjustments:
1. Tuition fees outstanding ₹ 6,750.
2. Outstanding interest on loan ₹ 30,000.
3. Entire admission Fees are to be capitalized.
4. Depreciation is to be written off as under:
Library Books ₹ 25,000, Furniture ₹ 15,000, Laboratory Equipment ₹ 10,000, Building ₹ 15,000.
Solution:
In the books of Sarthi Education
Balance Sheet as on 31st March, 2019
Working Notes:
1. Tuition fees outstanding ₹ 6,750 are first added to Tuition Fees on the credit side of Income and Expenditure A/c and then such outstanding tuition fees are shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet.
2. Outstanding interest on Loan ₹ 30,000 is first debited to Income and Expenditure A/c and it is added to Loan on the Liabilities side of Balance Sheet.
3. Government grant (Revenue income) ₹ 1,75,000 is recorded on the credit side of the Income and Expenditure Account.
4. Debit balance of Income and Expenditure Account ₹ 55,850 indicates a deficit. It is deducted from the Capital fund on the Liabilities side of the Balance Sheet.