Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce Book Keeping & Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 5 Subsidiary Books Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Commerce BK Important Questions Chapter 5 Subsidiary Books
Objective Type Questions & Answers
1. Answer the following questions in one sentence.
Question 1.
Which transactions are recorded in the Return Outward Book?
Answer:
Return of goods purchased on credit to the suppliers is only recorded in the Return Outward Book.
Question 2.
Which transactions are recorded in the Return Inward Book?
Answer:
Goods sold on credit when returned by the customers due to certain reasons are only recorded in the Return Inward Book.
Question 3.
Who is a payee in case of cheque?
Answer:
A person to whom the amount of cheque is payable or paid is called a payee.
![]()
Question 4.
What is a dishonour of cheque?
Answer:
When the bank refuses to pay the amount of cheque on its presentation to the payee for certain reasons, the cheque is said to be dishonoured.
Question 5.
What is Pass Book?
Answer:
A bank passbook is a small booklet in which the details of all ledger entries in respect of banking transactions appearing in the books of the bank are entered for the knowledge of the account holder.
Question 6.
What is a Bank Book?
Answer:
A book maintained by businessmen to record only banking transactions is called Bank Book.
Question 7.
What do you mean by crossed cheque?
Answer:
A cheque on which two parallel transverse lines are drawn on its face at the left-hand top corner with or without any word is called crossed cheque.
Question 8.
What is meant by Bank Overdraft?
Answer:
The amount withdrawn by the account holder from his current account in excess of the balance standing in that account up to the specified limit is known as ‘Bank overdraft’.
Question 9.
What do you mean by analytical petty cash book?
Answer:
A petty cash book that had many sub-columns on the payment side for recording expenses that are repetitive in nature is called an analytical/columnar petty cash book.
![]()
Question 10.
What are opening entries?
Answer:
Entries passed at the beginning of the financial year to bring the assets and liabilities in the books of account are known as opening entries.
Question 11.
What are closing entries?
Answer:
Entries passed at the end of the financial year to close the accounts of expenses and incomes are called closing entries.
Question 12.
What are transfer entries?
Answer:
Entries passed to transfer the balance of one account to another account are known as transfer entries.
Question 13.
What are adjustment entries?
Answer:
The accounting entries are passed into the books of accounts to bring certain items which do not appear in the trial balance.
e.g. depreciation, further bad debts, closing stock, incomes receivable, etc. are called adjustment entries.
Question 14.
What is a cheque?
Answer:
A cheque is a written order given by the account holder to the bank to pay the sum of money specified there into himself or to the person in whose favour the cheque is issued.
Question 15.
What is a ‘Pay-in slip’?
Answer:
Pay-in-slip is a document used by the account holder for depositing cash as well as cheque into the bank.
![]()
Question 16.
What is a ‘Debit Note’?
Answer:
A document that is prepared to give debit if less debit is given earlier or to cancel the wrong credit or extra credit given is called a debit note.
Question 17.
What is a ‘Credit Note’?
Answer:
A document that is prepared to give credit if less credit is given earlier or to cancel the wrong debit or extra debit given is called a credit note.
2. Give a word/term or phrase for each of the following statements:
Question 1.
Signing on the backside of the cheque to transfer its ownership.
Answer:
Endorsement of Cheque
Question 2.
An extract of customer’s account maintained by the bank.
Answer:
Pass Book
Question 3.
A type of cheque whose payment is done across the counter of the bank.
Answer:
Bearer Cheque
Question 4.
Bank on whom a cheque is drawn.
Answer:
Drawee
![]()
Question 5.
Document used for depositing cash or cheque into the bank.
Answer:
Pay-in-slip
Question 6.
Subsidiary book in which only credit sale of goods is recorded.
Answer:
Sales Book
Question 7.
Subsidiary book in which return of goods purchased on credit is recorded.
Answer:
Purchase Return
Question 8.
Source document on the basis of which Purchase Book is prepared.
Answer:
Inward Invoice
Question 9.
Source document on the basis of which Sales Book is prepared.
Answer:
Outward Invoice
![]()
Question 10.
Source document on the basis of which Purchase Return Book is prepared.
Answer:
Debit Note
Question 11.
Source document on the basis of which Sales Return Book is prepared.
Answer:
Credit Note
Question 12.
Accounting entries passed in the journal proper in the beginning of the financial year.
Answer:
Opening Entries
Question 13.
Accounting entries are passed in the journal proper at the end of the financial year.
Answer:
Closing Entries
Question 14.
Bank’s refusal to pay the amount of cheque to the payee.
Answer:
Dishonour of Cheque
![]()
Question 15.
Book in which small payments are recorded.
Answer:
Petty Cash Book
Question 16.
Type of bank account in which money is deposited for a fixed period of time.
Answer:
Fixed Deposit Account
Question 17.
A written order is issued by the account holder to the bank to pay a certain amount from his account.
Answer:
Cheque
Question 18.
A cheque on which two parallel transverse lines are drawn on its face at the left-hand top corner with or without certain words.
Answer:
Crossed Cheque
Question 19.
A person who endorses the cheque.
Answer:
Endorser
![]()
Question 20.
A person in whose favour the cheque is endorsed.
Answer:
Endorsee
3. State whether the following statements are True or False with reasons:
Question 1.
The total of the payment side can be greater than the total of the receipt side in the case of the bank column.
Answer:
This statement is True.
It is an overdraft on the current account.
Question 2.
A cheque received and deposited into the bank on the same day is a contra entry.
Answer:
This statement is False.
A cheque received and deposited on the same day is not a contra entry.
Question 3.
Interest on overdraft charged by the bank is recorded in the cash column.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Interest on overdraft charged by the bank is recorded in the bank column.
Question 4.
It is not necessary to record dishonour of cheques in the cash book.
Answer:
This statement is False.
It is necessary to record dishonour of cheques in the cash book.
![]()
Question 5.
Businessman generally operates savings bank account.
Answer:
This statement is False.
Businessman generally operates a current account with the bank.
4. Do you agree with the following statements.
Question 1.
Issue of Bearer cheque record on payments side of cash book in Bank Column.
Answer:
Agree
Question 2.
Subsidiary books are the books of secondary entry.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 3.
Cash Discount is recorded in the cash book with cash and Bank columns.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 4.
Credit sale of goods to Mr. Harsh ₹ 12,000 at 5% cash discount recorded on the receipts side of cash book.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 5.
All Business transactions are recorded in the cash book only.
Answer:
Disagree
![]()
Question 6.
Subsidiary books are useful for small trades only.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 7.
The big amount of payment of the organization is recorded in Petty Cash Book.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 8.
Sale of the old computer on credit recorded in the sales journal.
Answer:
Disagree
Question 9.
Cashbook cash column debit side is always greater than credit side.
Answer:
Disagree
![]()
Question 10.
When goods are returned by the buyer to the seller, Seller sends a credit note.
Answer:
Agree
5. Complete the following sentences:
Question 1.
Cash book is a ___________ book.
Answer:
Subsidiary
Question 2.
Only ___________ transactions are recorded in Simple Cash Book.
Answer:
Cash
Question 3.
Purchase book always shows ___________ balance.
Answer:
Debit
Question 4.
Sales book shows ___________ balance.
Answer:
Credit
Question 5.
Cash column of cash book can never have a ___________ balance.
Answer:
Credit
![]()
Question 6.
The source document for recording sales book is ___________
Answer:
Outward Invoice
Question 7.
___________ columns of a cash book are never balanced.
Answer:
discount
Question 8.
Credit purchase of goods are recorded in ___________
Answer:
purchase book
Question 9.
A person who draws a cheque is called ___________
Answer:
drawer
Question 10.
All expenses are recorded on the ___________ side of Cashbook.
Answer:
payment
Question 11.
When a bank refuses to make the payment of the cheque, it is said to be ___________
Answer:
dishonoured
![]()
Question 12.
The person who keeps a record of small payments is known as ___________
Answer:
petty cashier
Question 13.
In ___________ small cash payment of expenses are recorded.
Answer:
petty cash book
Question 14.
In ___________ petty cash book, on payment side there are many sub columns.
Answer:
analytical
Question 15.
___________ advance is given to the petty cashier.
Answer:
Petty
![]()
Question 16.
___________ means fixed amount of petty advance.
Answer:
Imprest
Question 17.
___________ petty cash book is not popular in the business world.
Answer:
Simple
Question 18.
Petty cash book is balanced at the end of every ___________
Answer:
month
Question 19.
Only ___________ discount is recorded in the books of accounts.
Answer:
cash
Question 20.
Cash book is book of ___________ entry.
Answer:
prime
Question 21.
___________ book is an extract of customer’s account in the ledger of bank.
Answer:
pass
![]()
Question 22.
The debit side of the passbook is called ___________ side.
Answer:
receipt
Question 23.
To draw 2 parallel lines on the face of the cheque is called ___________ of the cheque.
Answer:
crossing
Question 24.
Discount received is recorded on ___________ side of cash book.
Answer:
credit
Question 25.
The documents from which the returns to suppliers are recorded is known as ___________
Answer:
debit note
Question 26.
Sales Return book is also called as ___________
Answer:
return inward book
Question 27.
Purchase of goods on credit basis are recorded in ___________
Answer:
purchase book
![]()
Question 28.
Account in which there is restriction on withdrawals are called ___________ account.
Answer:
savings
Question 29.
___________ Entry is recorded on both the sides of cash with and bank columns.
Answer:
Contra
Question 30.
In sale journal goods sold on ___________ are recorded.
Answer:
Credit
Question 31.
Machinery purchase on credit will be recorded in ___________ subsidiary book.
Answer:
Journal Proper
Question 32.
Return of goods sold on credit by the customers will be entered in ___________ journal.
Answer:
Sales Return
Question 33.
Cash discount is recorded in ___________ book.
Answer:
Journal Proper
Question 34.
___________ Note is prepared when goods are returned to supplier.
Answer:
Debit
![]()
Question 35.
___________ is used to deposit cash on cheque in the bank.
Answer:
Pay-in-slip
Question 36.
___________ Cheque is more safer for payments.
Answer:
Cross Account Payee
6. Correct the following sentences and rewrite them same.
Question 1.
Credit sale of goods recorded in cash book receipts side.
Answer:
Cash sale of goods recorded in cash book receipts side.
Question 2.
Journal proper book is used to record cash transactions.
Answer:
Cashbook is used to record cash transactions.
Question 3.
Pay-in-slip is us to withdraw money from Bank.
Answer:
Pay-in-slip is us to deposit the money into the Bank.
![]()
Question 4.
The dividend received is a loss for the business.
Answer:
The dividend received is profit for the business.
7. Complete the following Table.
Question 1.
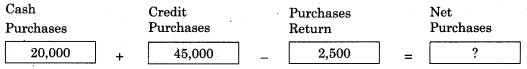
Answer:
62,500
Question 2.
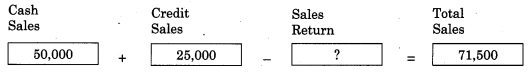
Answer:
3,500
Question 3.
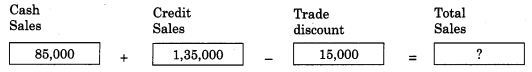
Answer:
2,05,000
Question 4.
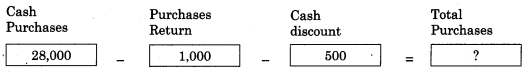
Answer:
26,500
![]()
Question 5.
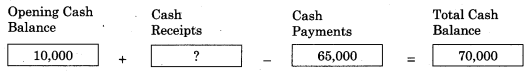
Answer:
1,25,000
Question 6.
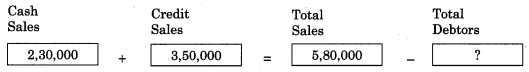
Answer:
3,50,000
Question 7.
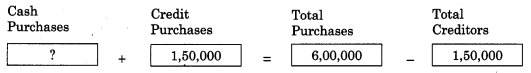
Answer:
4,50,000
Question 8.
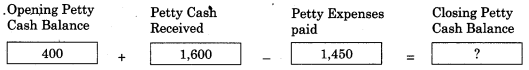
Answer:
550
![]()
Question 9.
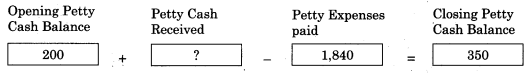
Answer:
1,990
Solved Problems
Simple/Single Column Cash Book
Question 1.
Prepare a simple cash book from the following information:
2019 January
1 Mr. Ashvin started the business with cash of ₹ 95,000.
3 Purchased furniture for office use ₹ 17,500.
4 Purchased goods worth ₹ 11,000.
7 Purchased machinery for ₹ 15,000.
10 Sold goods of ₹ 14,300 to Sandeep Traders for cash.
13 Received from Suyash ₹ 9,000.
15 Withdrew ₹ 2,500 from business for personal use.
19 Borrowed loan from Mr. Tilak ₹ 40,000.
22 Purchased goods of ₹ 14,000 at 5% trade discount.
26 Paid salary to staff ₹ 18,000.
29 Paid carriage on goods purchased ₹ 1,400.
30 Paid electricity bill ₹ 4,980.
31 Deposited into bank ₹ 7,000.
Solution:
In the books of Mr. Ashvin
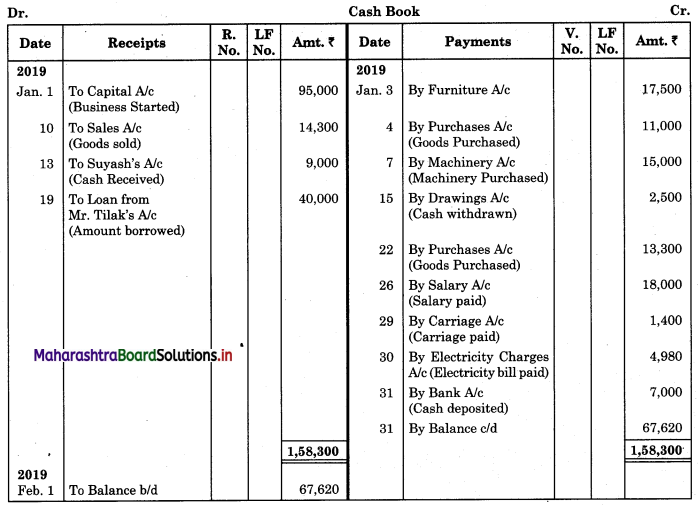
Working Notes:
1. 22nd Jan.:
Net Purchase Price = Purchase Price – 5% Trade Discount
= 14,000 – 5% of 14,000
= 14,000 – 700
= ₹ 13,300
2. Balance of Cash on 31st Jan. = Total of Receipt side – Total of Payment side
= 1,58,300 – 90,680
= ₹ 67,620
![]()
Question 2.
Prepare a simple cash book of Mr. Shriram from the following details:
2019 Feb.
1 Balance of cash ₹ 65,500.
2 Brought additional capital ₹ 12,000.
4 Received from Nilesh on account ₹ 3,800.
7 Purchased goods from United Ltd. ₹ 16,000 and paid half the amount immediately.
9 Received commission from Aarti Traders ₹ 2,650.
10 Paid to Prithviraj Traders on account ₹ 17,800.
13 Purchased stationery for office use ₹ 2,460.
17 Received rent ₹ 4,900.
20 Paid ₹ 1,750 for insurance premium.
22 Sold goods for cash ₹ 13,800.
25 Purchased 10% debentures of ₹ 20,000
27 Paid telephone bill ₹ 3,000 and electricity bill ₹ 2,340.
28 Deposited into the bank all cash in excess of ₹ 11,000.
Solution:
In the books of Mr. Shriram
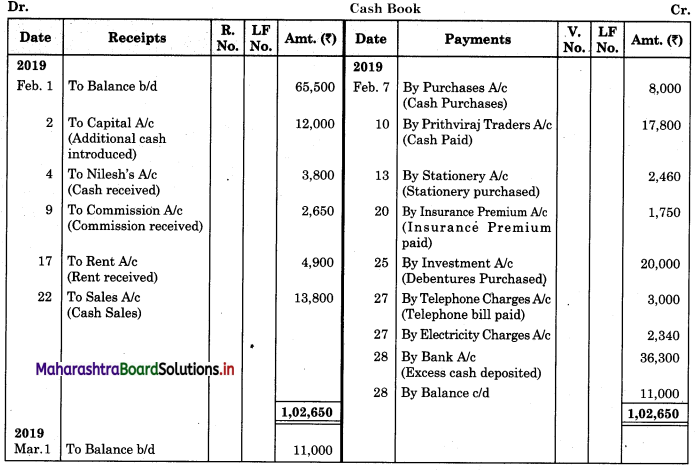
Working Note:
Dates: 28th February 2011:
Excess Cash Deposited = Total of Receipt Side – Total of Payment side including Closing Cash balance
= 1,02,650 – 66,350
= ₹ 36,300
Two Column Cash Book
Question 3.
Enter the following transaction in a cash book with cash and bank columns for the month of April 2019:
2019 April
1 Started business with cash ₹ 30,000.
2 Opened a current account with the bank and deposited ₹ 9,000.
5 Received ₹ 4,850 for Cash Sales and discount allowed ₹ 50.
6 Purchased goods of ₹ 3,000 @ 10% cash discount and half the amount was paid by cash and remaining by cheque.
9 Received a crossed cheque for ₹ 7,775 from Megha Associates and discount allowed ₹ 25.
12 Purchased machinery of ₹ 13,300 and paid for installation ₹ 700.
15 Received a bearer cheque of ₹ 735 from Rahul in full settlement of his account ₹ 800.
17 Deposited into the bank ₹ 2,000.
20 Transferred ₹ 8,000 from Savings Account to Current Account.
22 Received a hearer cheque from Vinod ₹ 2,230.
24 Deposited the cheque received from Vinod into the bank.
29 Bank informed that cheque received from Vinod is dishonoured.
30 Paid for printing bill book ₹ 660.
31 Withdrew from the bank for office use ₹ 1,000.
Solution:
In the books of ___________
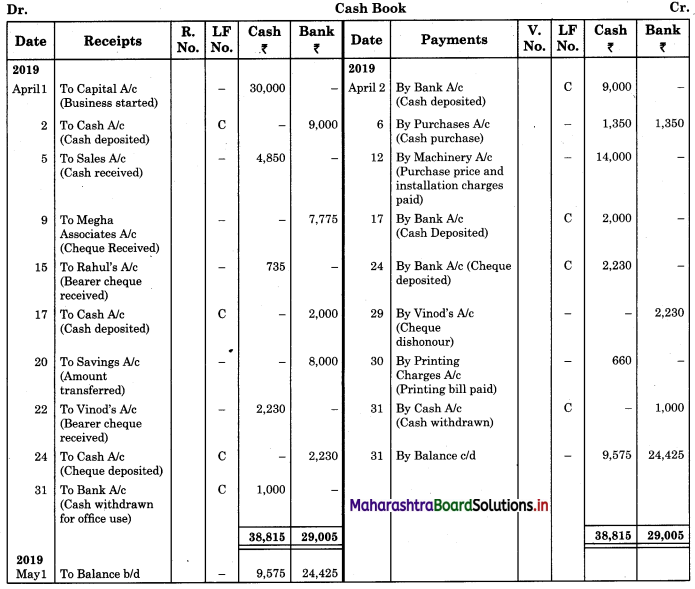
Working Notes:
1. Transaction dated 6th April 2019.
Cash Discount = 10% of Goods Purchased
= 10% of 3,000
= ₹ 300
Net Cash Payable = 3,000 – 300 = ₹ 2,700
Amount paid in cash = \(\frac{1}{2}\) of 2,700 = ₹ 1,350
Amount paid by cheque = \(\frac{1}{2}\) of 2,700 = ₹ 1,350
2. Dated: 12th April, 2019.
Cost of Machinery = Purchase Price + Installation Charges
= 13,300 + 700
= ₹ 14,000
![]()
3. Transaction dated: 29th April, 2019.
Entry for dishonour of Vinod’s Cheque:
Earlier Entries:


Question 4.
Enter the following transaction of Hariram Bros, in a cash book with cash and bank column for the month of May 2019.
2019 May
1 Cash Balance ₹ 33,000
Bank Balance ₹ 8,000
3 Received from Prerna cash ₹ 2,750 and a bearer cheque for ₹ 645.
6 Paid to Arjun ₹ 5,300 by cheque and discount received ₹ 125.
8 Cash sales ₹ 5,645 and discount allowed ₹ 55.
10 Cheque received on 3 May 2011 deposited into the bank for collection.
12 Deposited into bank ₹ 4,000.
15 Cheque received from Prerna returned dishonoured.
18 Purchased goods from Indrajit ₹ 4,000 at an 8% trade discount and paid half the amount immediately.
20 Bank paid insurance premium under our standing instruction ₹ 1,950 and collected interest on investment ₹ 3,650.
22 Cheque issued to Arjun was dishonoured.
24 Lucky Stores directly deposited into our bank ₹ 9,500.
25 Paid salaries by cheque ₹ 5,700.
26 Withdrew by cheque ₹ 2,000 for office use and ₹ 1,500 for personal use.
31 Deposited into the bank all cash in excess of ₹ 5,000.
Solution:
In the books of Hariram Bros.
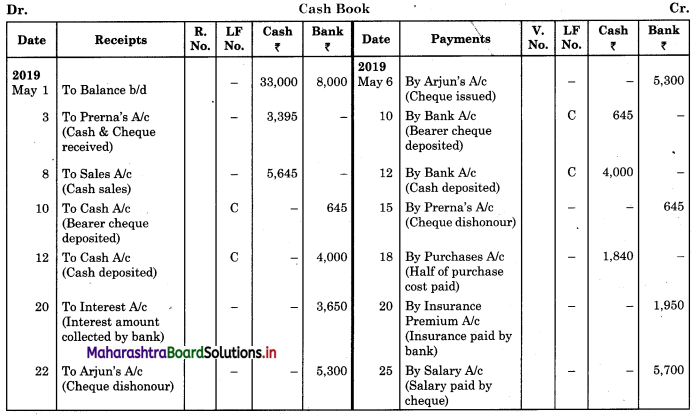
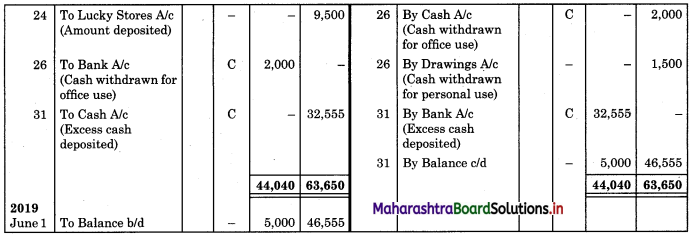
Working Notes:
1. Transaction dated 3rd May 2019:
Receipt of bearer cheque of ₹ 645 is debited to Cash A/c
Hence, Cash A/c is debited by 2,750 + 645 = ₹ 3,395
2. Transaction dated 10th May 2019:
Entry for deposit of cheque ₹ 645
Bank A/c ……………. Dr. 645
To Cash A/c 645
3. Transaction dated 15th May 2019:
Entry for dishonour of Prerna’s cheque.

When reverse entries are reconciled Cash A/c’s gets cancelled.
? Entry for dishonour of cheque is
Prerna’s A/c…………..Dr. 645
To Bank A/c 645
4. Transaction dated 18th May, 2019:
Net Price of goods purchased = Purchase Price – Trade discount
= 4,000 – 8% of 4,000
= 4,000 – 320
= ₹ 3,680
Amount Paid = \(\frac{1}{2}\) 3,680 = ₹ 1,840
5. Date: 31st May 2019:
Excess Cash deposited = Total of a debit column of cash – Total of credit column of cash including the closing balance
= 44,040 – 11,485
= ₹ 32,555
Question 5.
Enter the following transaction of Mr. Chavan in a cash book with cash and bank column for the month of April 2019.
2019 April
1 Cash Balance ₹ 56,000
Bank Overdraft ₹ 11,000
3 Purchased goods for ₹ 13,000 for cash at 2% cash discount and amount paid by cheque.
6 Received a bearer cheque for ₹ 13,250 in full settlement of ₹ 13,500 from Govind Traders.
9 Purchased 100 shares of Amar Ltd. of ₹ 100 each at ₹ 110 each and paid by cheque.
11 Sold goods of ₹ 7,000 at a 5% cash discount to Pramod and he paid half the amount immediately.
14 Deposited into bank ₹ 11,000.
17 Received a crossed cheque for ₹ 18,000 from Gajanan Traders.
20 Bank paid our telephone bill ₹ 3,230.
21 Bank charged ₹ 540 as interest on overdraft.
22 Paid by cheque to Urmila ₹ 8,000.
25 Deposited into the bank the cheque received from Govind Traders.
27 Received a bearer cheque for ₹ 3,460 for rent which was deposited into the bank.
29 Bank informed that the cheque received for rent was dishonoured.
30 Paid life insurance premium of Mr. Chavan ₹ 4,250 by cash and electricity bill ₹ 7,400 by cheque.
Solution:
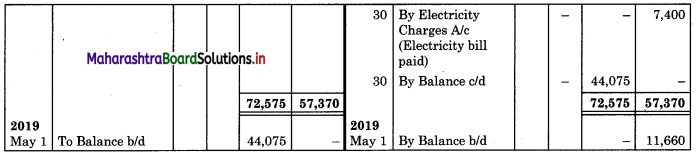
In the books of Mr. Chavan
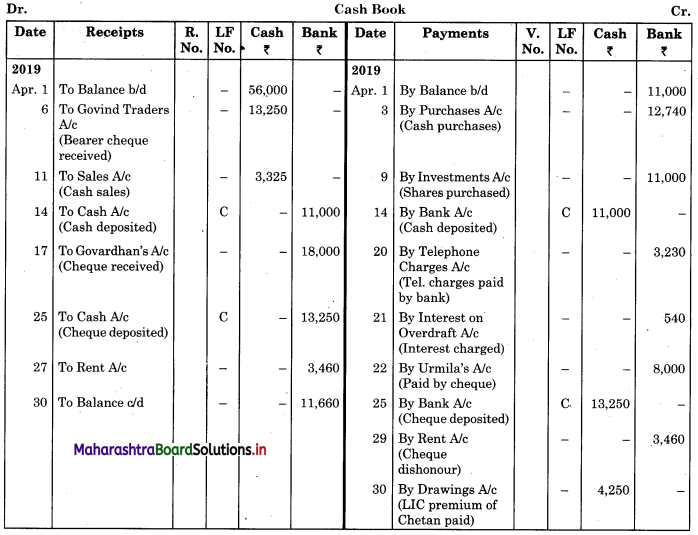
Working Notes:
1. Transaction dated 3rd April 2019:
Net payment made on cash purchases = Purchase Price – Cash discount
= 13,000 – 2% on 13,000
= 13,000 – 260
= ₹ 12,740
2. Transaction dated 9th April 2019:
Amount paid by cheque for purchase of shares = No. of shares purchased × Market value
= 100 × 110
= ₹ 11,000
![]()
3. Closing balance of Cash book
Cash balance = 72,575 – 28,500 = ₹ 44,075
Bank overdraft balance = 57,370 (Cr. column) – 45,710 (Dr. column)
Overdraft = ₹ 11,660
Petty Cash Book
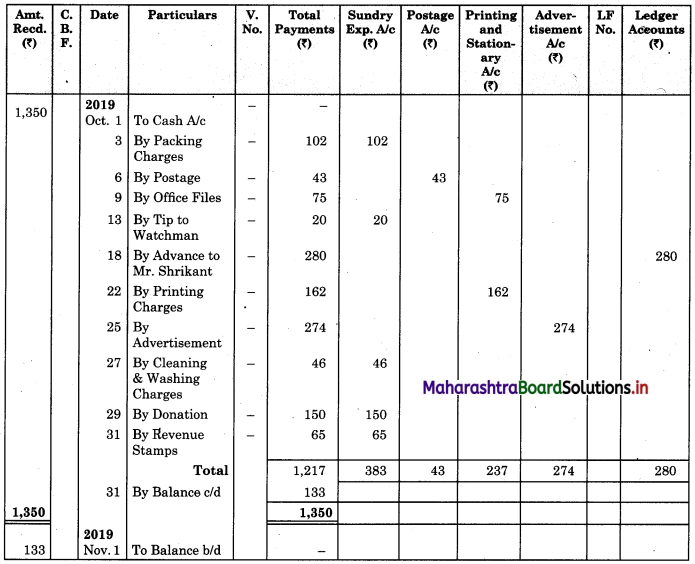
Question 6.
Enter the Following transaction in a petty cash book having analysis columns for the month of October 2019.
2019 Oct.
1 Received cash from head cashier ₹ 1,350.
3 Paid packing charges ₹ 102.
6 Paid for postage ₹ 43.
9 Purchased 3 office files of ₹ 25 each.
13 Gave a tip to watchman ₹ 20.
18 Gave advance to clerk Mr. Shrikant ₹ 280.
22 Paid for printing ₹ 162.
25 Paid for advertisement ₹ 274.
27 Paid cleaning and washing charges ₹ 46.
29 Gave donation for Diwali celebration ₹ 150.
31 Purchased revenue stamps ₹ 65.
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book of ___________
Question 7.
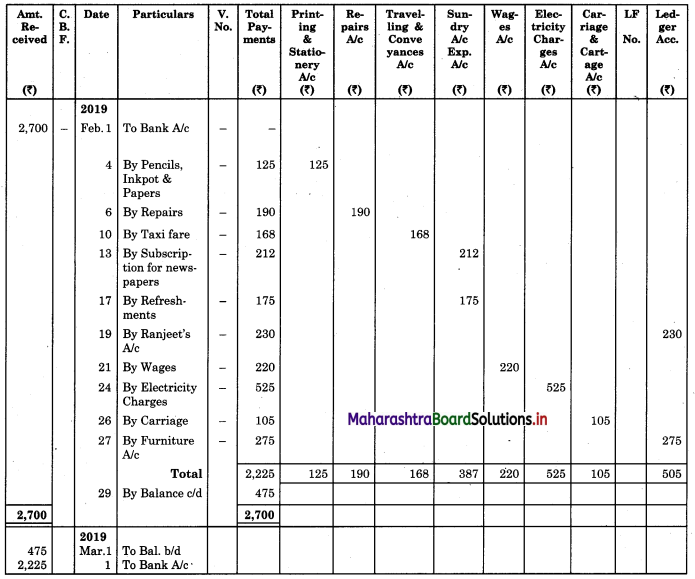
Enter the following transaction in an analytical petty cash book under the imprest system for the month of February 2019.
2019 Feb.
1 Received cheque from Head Cashier ₹ 2,700.
4 Purchased pencils for ₹ 45, inkpot ₹ 25, and papers ₹ 55.
6 Paid for repairs ₹ 190.
10 Paid taxi fare to Manager ₹ 168.
13 Paid subscription for newspaper ₹ 212.
17 Paid for refreshments to customers ₹ 175.
19 Paid to Ranjeet in settlement of his account ₹ 230.
21 Paid wages to casual labour ₹ 220.
24 Paid electricity bill ₹ 525.
26 Paid for carriage ₹ 105.
27 Purchase a wooden chair for ₹ 275.
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book of ___________
Question 8.
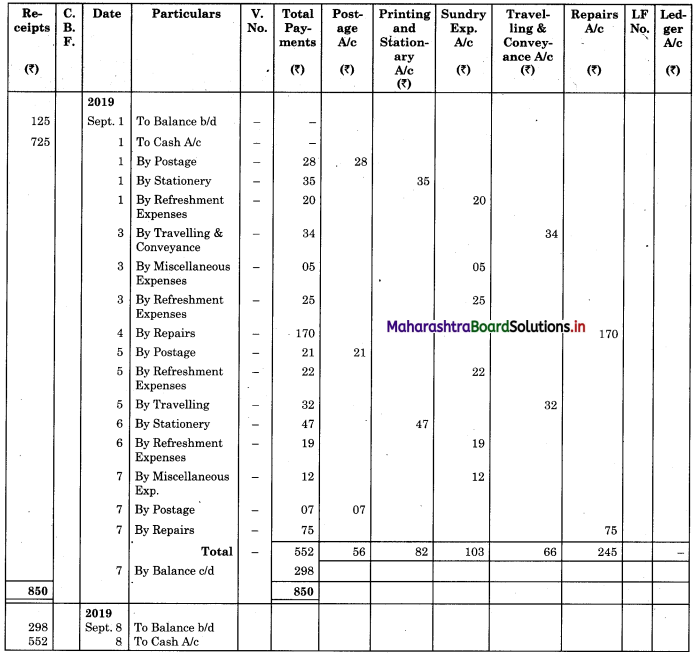
Mr. Shrinath maintains a columnar petty cash book on the Imprest system. The Imprest amount is ₹ 850. The following information, show how his Petty Cash Book would appear for the week ended 7th September. 2019.
2019 Sept.
1 Balance in hand ₹ 125.
Postage ₹ 28.
Stationery ₹ 35.
Refreshment expenses ₹ 20.
3 Travelling and Conveyance ₹ 34.
Miscellaneous Expenses ₹ 5.
Refreshment expenses ₹ 25.
4 Repairs charges ₹ 170.
Paid for Postage ₹ 21.
5 Refreshment expenses ₹ 22.
Travelling expenses ₹ 32.
Stationery ₹ 47.
6 Refreshment expenses ₹ 19.
7 Miscellaneous Expenses ₹ 12.
Paid for Postage ₹ 7.
Repair charges ₹ 75.
Solution:
Analytical Petty Cash Book of Mr. Shrinath
Purchase Book, Sales Book, Purchase Return Book, and Sales Return Book
Question 9.
Prepare Purchase Book and Sales Book, M/s. S.K. Traders dealer in ready-made garments, Mumbai.
2019 April
1 Purchased goods from M/s. Jalna Traders, Delhi for ₹ 10,000 at 10% T.D.
4 Sold goods to M/s Kalpana Stores, Ahmedabad for ₹ 15,000 at 5% T.D.
10 Bought goods from M/s. Raj Enterprise, Patna for ₹ 5,000.
15 Sold goods to M/s Sagar Traders, Kanpur for ₹ 20,000 at 20% T.D.
25 Bought goods from M/s. Rakesh Stores, Banglore for ₹ 12,000 @ 5% T.D.
Rate of GST applicable on ready made garments are CGST @ 9%, SGST @ 9% and IGST @ 18%.
Solution:
In the books of M/s. S.K. Traders, Mumbai
Purchase Book (Analytical)
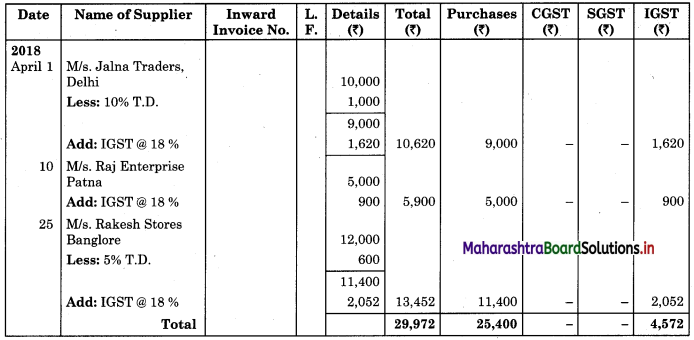
Sales Book (Analytical)
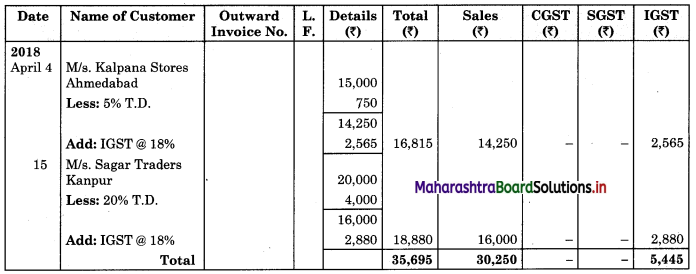
Note: In the case of inter-state sales IGST is used.
![]()
Journal Proper
Question 10.
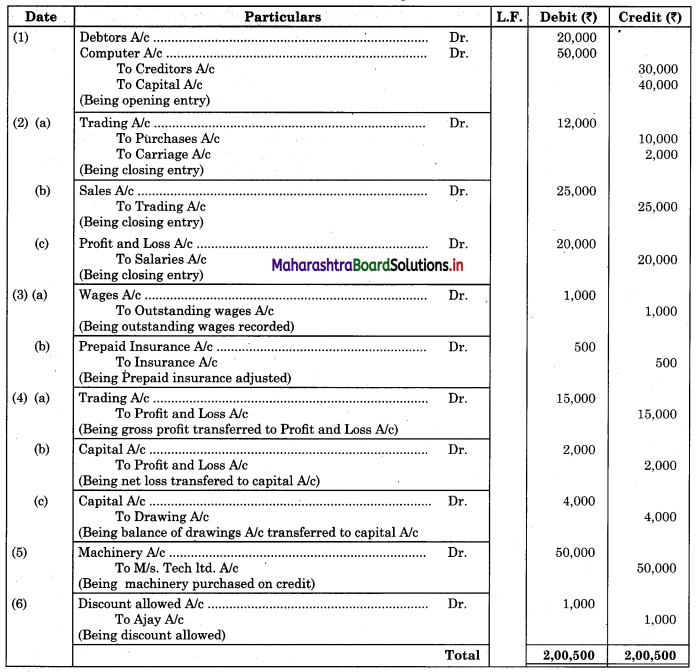
Journalise the following transactions in the Journal Proper of Mr. Mahadev.
1 Pass opening entries: Debtors ₹ 20,000; Creditors ₹ 30,000; Computer ₹ 50,000 and Capital ₹ 40,000.
2 Pass closing entries: Purchases ₹ 10,000; Sales ₹ 25,000; Salaries ₹ 20,000 and Carriage ₹ 2,000.
3 Pass adjustment entries: Outstanding Wages ₹ 1,000 and Prepaid Insurance ₹ 500.
4 Pass transfer entries: Gross Profit ₹ 15,000; Net loss ₹ 2,000 and Drawings ₹ 4,000
5 Bought Machinery on credit from M/s. Tech ltd. for ₹ 50,000.
6 Allowed cash discount of ₹ 1,000 to Ajay.
Solution:
In the books of Mr. Mahadev
Journal Proper