Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 11th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Question 1.
Write a note on nutrients.
Answer:
Nutrients:
- Nutrients are obtained from food and are used as a source of energy by the body.
- The main nutrients obtained from food are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals and water. Most nutrients are organic macromolecules.
- Along with providing energy, these nutrients also regulate various body functions like growth, repair of damaged body tissues, etc.
The following table consists of different types of nutrients and their major sources.
| Type of nutrient | Sources |
| Carbohydrates | Grains, fruits, vegetables, etc. |
| Proteins | Meat, fish. eggs, dairy products, pulses, etc. |
| Lipids | Dairy products, vegetable oil, animal fats, etc. |
| Vitamins | Grains, fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, pulses, etc. |
Question 2.
What happens when proteins and carbohydrates present in foods are digested in presence of enzymes?
Answer:
- Proteins and carbohydrates are organic polymeric macromolecules.
- When food is digested in presence of enzymes, the polymeric carbohydrates and proteins break down into monomers, i.e., glucose and α-amino acids, respectively.
Question 3.
Quality of food changes on shelving. Explain.
Answer:
- Enzymes are naturally present in all food materials.
- Quality of food changes on shelving mostly due to enzyme action, chemical reactions with the environment and due to the action of microorganisms.
Question 4.
Give two beneficial effects of shelving of food in day to day life.
Answer:
- Setting of milk into curd.
- Raising flour dough to make bread.
[Note: These changes are brought about by action of microorganisms.]
![]()
Question 5.
How are the chemical reactions of foodstuff with the environment controlled during storage?
Answer:
- Primarily the oxygen and microorganisms in air are responsible for adverse effects on stored food.
- The exposure of stored food to atmosphere is minimized by storing them in air tight container, evacuation or filling the container with N2 gas.
- Rate of a chemical reaction decreases with lowering of temperature. Thus, refrigeration is useful for controlling chemical reaction of foodstuff with environment.
- The reactions of foodstuff with environment are catalysed by enzymes. Due to boiling, the enzymes become denatured and the reactions are controlled.
Question 6.
What is the main aim of food preservation and food processing methods?
Answer:
Food preservation and food processing methods aim at prevention of undesirable changes and attempt to bring about desirable changes in food.
Question 7.
The melting points of unsaturated fats are lower. Give reason.
Answer:
- The long carbon chains of unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more C=C double bonds which produces one or more ‘kinks’ in the chain. This prevent the molecules from packing closely together.
- Also, the van der Waals forces between the unsaturated chains are weak.
Hence, the melting points of unsaturated fats are lower.
Question 8.
i. What are natural fats? Comment on their melting points.
ii. Explain how unsaturation affects the melting point and crystalline nature of fats.
Answer:
i. Natural fats are mixtures of triglycerides. They do not have sharp melting points and melt over a range of temperatures.
ii. Effect of unsaturation:
- The more unsaturated the fat (i.e., the presence of C=C bonds), lower is its melting point.
- Also, they will be less crystalline in nature.
Note: Naturals fats and their physical states
| Mainly saturated fats | Mainly monounsaturated fats | Mainly polyunsaturated fats |
| Coconut fat/oil, butterfat, lard, margarine, Vanaspati ghee | Olive oil, peanut oil, canola oil | Safflower oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil, com oil, fish oil |
| Solid | Liquid | Liquid |
Note: Molecular shapes of fats (A schematic representation):
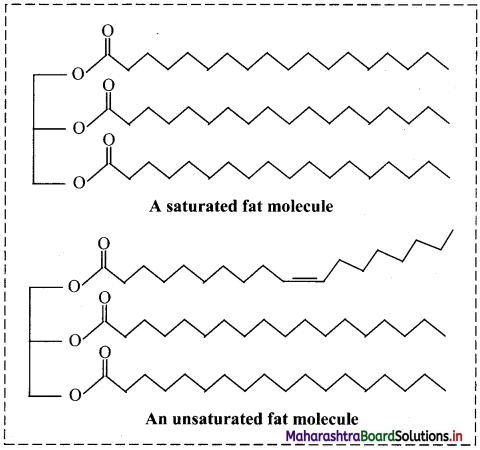
Question 9.
Write a note on cis and trans form of unsaturated fats.
Answer:
Due to the presence of C=C double bonds, unsaturated fats can have two geometrical isomers, i.e., cis form and transform.
i. Cis form:
- In the cis form of an unsaturated fatty acid, the two hydrogens on the two double bonded carbons are on the same side of the double bond.
- It is the most common form of unsaturated fats.
- Cis fats do not cause deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels and thus, decrease the chance of developing coronary heart disease.
ii. Transform:
- In the transform of an unsaturated fatty acid, the two hydrogens on the two double bonded carbons are on the opposite sides of the double bond.
- Trans fats are difficult to metabolize and may get deposited to dangerous levels in fatty tissues.
- Large amount of trans unsaturated fats, increase the tendency of cholesterol getting deposited in the blood vessels leading to increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
[Note: Transform occurs only in animal fats and processed unsaturated fats.]
![]()
Question 10.
In which form, fats are used to transport cholesterol in the body?
Answer:
Fats in the form of lipoprotein are used to transport cholesterol in the body.
Question 11.
Give reason: Excessive low-density lipoprotein (LDL) increases the risk of cardio vascular diseases.
Answer:
Excessive low-density lipoprotein (LDL) increases the risk of cardio vascular diseases because it causes deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels.
Question 12.
What does the term omega represent in unsaturated fatty acids? Explain with the help of an example.
Answer:
i. Omega denotes the last carbon of the carbon chain in unsaturated fatty acids.
ii. Depending upon the position of the double bond, there are several omega fatty acids such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
iii. These names are given for the position of the double bond in a long carbon chain of the unsaturated fatty acid.
iv. Omega-3 fatty acids have C = C bond between the third and fourth carbon from the end of a carbon chain.
e.g. Linolenic acid (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid).
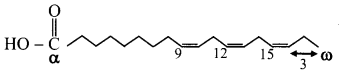
Question 13.
Do omega-3 and omega-6 fats have same effect on the body? Discuss the effects.
Answer:
No, omega-3 and omega-6 fats have different effects on the body.
Omega-3 fats are found to raise the high density lipoprotein, HDL (good cholesterol) level of blood whereas omega-6 fats are considered to increase the risk of high blood pressure.
Question 14.
State TRUE or FALSE. Correct the false statement.
i. Fats are triglycerides of fatty acids.
ii. Linolenic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid having four C = C double bonds in its structure.
iii. Omega-6 fats are considered to increase the risk of high blood pressure.
Answer:
i. True
ii. False
Linolenic acid is an omega-3 fatty acid having three C = C double bonds in its structure.
iii. True
![]()
Question 15.
Name few sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
Answer:
Foods like walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, soybean, cod liver oil are rich source of omega-3 fatty acids.
Question 16.
Draw the structure of vitamin E (tocopherol).
Answer:
Structure of vitamin E (tocopherol):
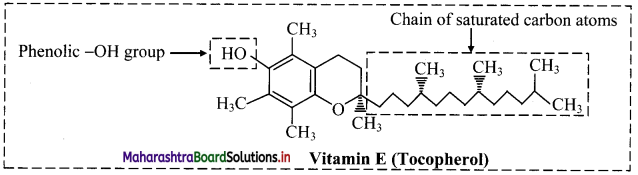
Question 17.
Give the sources of vitamin E.
Answer:
Vitamin E can be obtained from foods such as wheat germ, nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables and oils like safflower oil.
Question 18.
What are synthetic antioxidants? Give an example.
Answer:
Synthetic antioxidant:
- Synthetic antioxidants are chemicals that are synthesized in the laboratory and used as a substitute for natural antioxidants.
- They delay the onset of oxidant or slow down the rate of oxidation of foodstuff.
- They are added as additives to increase the shelf life of packed foods.
- Common structural units found in synthetic antioxidants are phenolic -OH group and tertiary butyl group.
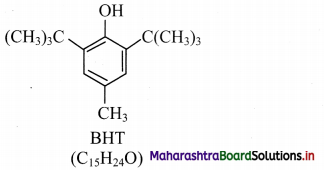
e.g. BHT, which is 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene.
Question 19.
Write a short note on BHT.
Answer:
1. BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) is a synthetic antioxidant.
2. It is used as an additive to increase the shelf life of packed foods.
3. Structure of BHT contains a phenolic – OH group (which is responsible for its antioxidant properties) and tertiary butyl group.
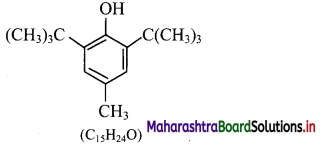
IUPAC name: 3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxytoluene
![]()
Question 20.
Define the term: Drug
Answer:
A chemical which interacts with biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nuclei acids and produces a biological response is called drug.
Question 21.
i. Which type of drug is used as medicine?
ii. What does a medicine contain?
iii. What are medicines used for?
Answer:
i. A drug having therapeutic and useful biological response is used as medicine.
ii. A medicine contains a drug as its active ingredient. Besides, it contains some additional chemicals which make the drug suitable for its use as medicine.
iii. Medicines are used in diagnosis, prevention and treatment of a disease.
[Note: Drugs being foreign substances in a body, often give rise to undesirable, adverse side effects.]
Question 22.
Explain the following terms:
i. Drug design
ii. Generic medicines
Answer:
i. Drug design is an important branch of medicinal chemistry which aims at synthesis of new molecules having better biological response. Now-a-days, there is an increasing trend in drug design to take cognizance of traditional medical knowledge such as Ayurvedic medicine or natural materials to discover new drugs.
ii. The drug manufacturing companies usually have a patent for drugs which are sold with the brand name. After the expiry of patent, the drug can be sold in the name of its active ingredient. These are called generic medicines.
Question 23.
What are analgesics? Explain their mode of action.
Answer:
Analgesics:
- Drugs which give relief from pain are called analgesics.
e.g. Aspirin, paracetamol - Most of the analgesics are anti-inflammatory drugs, which kill pain by reducing inflammation or swelling.
Question 24.
Mention the medicinal properties of salicylic acid.
Answer:
Salicylic acid has pain-killing and fever reducing properties.
Question 25.
i. What is aspirin? Write its use.
ii. Mention its side effect.
Answer:
i. Aspirin is acetyl derivative of salicylic acid.
It is widely used as an analgesic.
ii. It has a fewer side effects than salicylic acid. However, it retains stomach irritating side effects of salicylic acid.
![]()
Question 26.
Draw the structure of salicylic acid and write its IUPAC name.
Answer:
Structure of salicylic acid:

IUPAC name: 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid
Question 27.
Draw structures of following analgesics and write their molecular formula,
i. Aspirin
ii. Paracetamol
Answer:
i. Structure and molecular formula of aspirin:
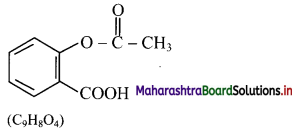
ii. Structure and molecular formula of paracetamol:
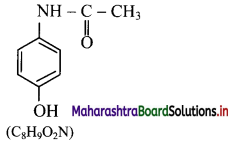
Question 28.
What are antimicrobial drugs?
Answer:
Any drug that inhibits or kills microbial cells that include bacteria, fungi and viruses, are called antimicrobial drugs.
Question 29.
Give a brief classification of antimicrobials.
Answer:
Antimicrobials are classified into the following three categories:
i. Disinfectants:
- Disinfectants are non-selective antimicrobials, which kill a wide range of microorganisms including bacteria.
- Disinfectants are used on non-living surfaces. For example, floors, instruments, sanitary ware, etc.
ii. Antiseptics:
Antiseptics are used to sterilise surfaces of living tissue when the risk of infection is very high, such as during surgery or on wounds.
iii. Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are a type of antimicrobial designed to target bacterial infections within or on the body.
Question 30.
Name the ingredients present in dettol.
Answer:
Chloroxylenol is the active ingredient of dettol. The other ingredients of dettol are isopropyl alcohol, pine oil, castor oil soap, caramel and water.
![]()
Question 31.
State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Correct the statement, if false.
i. A concentrated solution of boric acid is used as an antiseptic for eyes.
ii. Iodoform is a powerful antiseptic.
iii. The active ingredient present in dettol is chloroxylenol.
Answer:
i. False
A dilute aqueous solution of boric acid is used as an antiseptic for eyes.
ii. True
iii. True
Question 32.
Instead of phenol, it’s chloro derivatives are used as antiseptics. Explain.
Answer:
- A dilute aqueous solution of phenol has antiseptic properties but it is found to be corrosive in nature.
- Many chloro derivatives of phenol are more potent antiseptic and have less corrosive effects than phenol, if used in lower concentrations.
Thus, instead of phenol it’s chloro derivatives are used as antiseptics.
Question 33.
Draw the structures of the following compounds and name the class of antimicrobials to which they belong.
i. Thymol
ii. p-Chloro-o-benzylphenol
iii. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
Answer:
i. Thymol: It is an antiseptic.
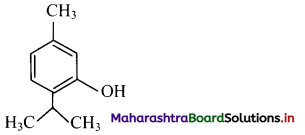
ii. p-Chloro-o-benzylphenol: It is a disinfectant. OH
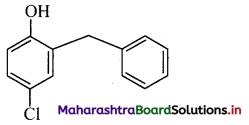
iii. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol: It is an antiseptic.
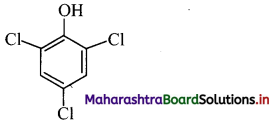
Question 34.
What are antibiotics?
Answer:
Antibiotics are drugs which are purely synthetic or obtained from microorganisms like bacteria, fungi or moulds.
e.g. Salvarsan, Prontosil
Question 35.
Name the first effective drug used in treatment of syphilis.
Answer:
Salvarsan was the first effective drug used in treatment of syphilis.
![]()
Question 36.
Name the following:
i. An effective diazo antibacterial drug.
ii. One example of a sulpha drug.
Answer:
i. Prontosil
ii. Sulphapyridine
Question 37.
Name the diazo antibacterial, which gets converted to sulphanilamide in the body.
Answer:
Prontosil is an effective diazo antibacterial, which gets converted to a simpler compound, sulphanilamide, in the body.
Question 38.
Draw the structure of the following:
i. An azodye
ii. Prontosil
iii. Sulphapyridine
iv. Sulphanilamide
Answer:

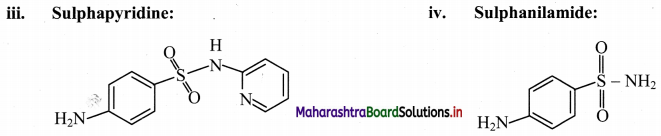
Question 39.
Draw the general structure of penicillin.
Answer:
General structure of penicillin:
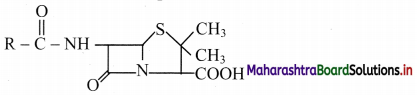
Question 40.
Draw the structure of chloramphenicol.
Answer:
Structure of chloramphenicol:
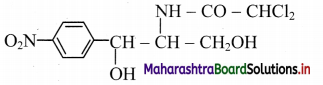
Question 41.
Give classification of antibiotics.
Answer:
Antibiotics can be of three types, which are as given below:
- Broad spectrum antibiotics: They are effective against wide range of bacteria.
- Narrow spectrum antibiotics: They are effective against one group of bacteria.
- Limited spectrum antibiotics: They are effective against a single organism.
[Note: Antibiotics can be synthetic, semisynthetic or of microbial origin.]
![]()
Question 42.
State the disadvantage of broad spectrum antibiotics.
Answer:
The disadvantage of broad spectrum antibiotics is that they also kill the useful bacteria in the alimentary canal.
Question 43.
Complete the following table.
| Plant | Medicinal property | Active ingredient |
| Cinnamon | Antimicrobial for cold | ———— |
| ———— | ———— | Eugenol |
| Citrus fruits | Antioxidant | ———— |
| Wintergreen | ———— | ———— |
| Indian gooseberry (amla) | Antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antioxidant | Vitamin C, Gallic acid |
Answer:
| Plant | Medicinal property | Active ingredient |
| Cinnamon | Antimicrobial for cold | Cinnamaldehyde |
| Clove | Antimicrobial and analgesic | Eugenol |
| Citrus fruits | Antioxidant | Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) |
| Wintergreen | Analgesic | Methyl salicylate |
| Indian gooseberry (amla) | Antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antioxidant | Vitamin C, Gallic acid |
Question 44.
Draw the structures of following:
i. Curcumin
ii. Methyl salicylate
iii. Cinnamaldehyde
iv. Eugenol
v. Vitamin C
vi. Gallic acid
Answer:
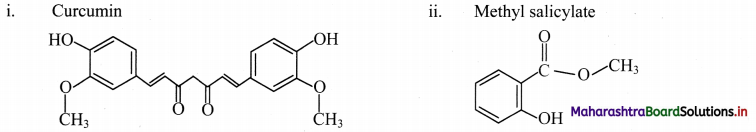


Question 45.
What are cleansing agents?
Answer:
Cleansing agents are substances which are used to remove stain, dirt or clutter on surfaces.
Question 46.
What are the different types of cleansing agents?
Answer:
Commercially cleansing agents are of the following two main types, depending on their chemical composition:
- Soaps
- Synthetic detergents
[Note: Cleansing agents may be natural or synthetically developed.]
![]()
Question 47.
What are soaps? How soaps are prepared?
Answer:
Soaps:
i. Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids.
ii. They are obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of natural oils and fats with NaOH or KOH. This is called saponification reaction.
iii. Chemically, oils are triesters of long chain fatty acids and propane-1,2,3-triol (commonly known as glycerol or glycerin).
iv. Saponification of oil produces soap and glycerol as shown in the reaction below:
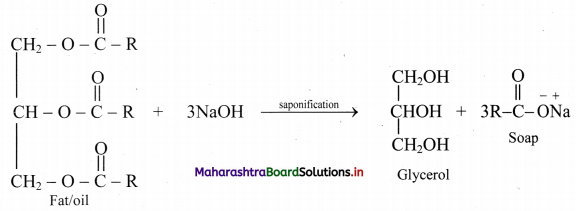
Question 48.
Give reason: Potassium soaps can be used for bathing purpose.
Answer:
- The quality of soap depends upon the nature of oil and alkali used.
- Potassium soaps (toilet soaps) are prepared by using better grades of oil and KOH. Therefore, they are soft to skin.
- Also, care is taken to remove excess of alkali which may otherwise cause skin irritation.
Hence, potassium soaps can be used for bathing purpose.
Question 49.
Laundry soaps are made using which alkali?
Answer:
Laundry soaps are made using alkali NaOH (sodium hydroxide).
Question 50.
Give examples of fillers used in making of laundry soaps.
Answer:
Laundry soaps contain fillers like sodium rosinate (a lathering agent), sodium silicate, borax, sodium and trisodium phosphate.
Question 51.
Explain why soaps become inactive in hard water.
Answer:
i. Soaps form scum in hard water and become inactive.
ii. This is because, hard water contains dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium. Soaps react with these salts to form insoluble calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids.
iii. This insoluble substance is termed as scum which sticks to the fabric.
iv. Reaction of soap with calcium salt (CaCl2) from hard water is given below:
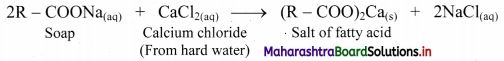
Question 52.
Which chemical can be used for softening of hard water? Why?
Answer:
- Washing soda (Na2CO3) can be used for softening of hard water.
- This is because, washing soda precipitates the dissolved calcium salts as carbonate and helps the soap action by softening of water.
![]()
Question 53.
i. What are synthetic detergents?
ii. Mention their different types.
Answer:
i. Synthetic detergents are manmade cleansing agents designed to use in soft water as well as in hard water.
ii. There are three types of synthetic detergents which are as follows:
- Anionic detergents
- Cationic detergents
- Nonionic detergents
Question 54.
Complete the following table:
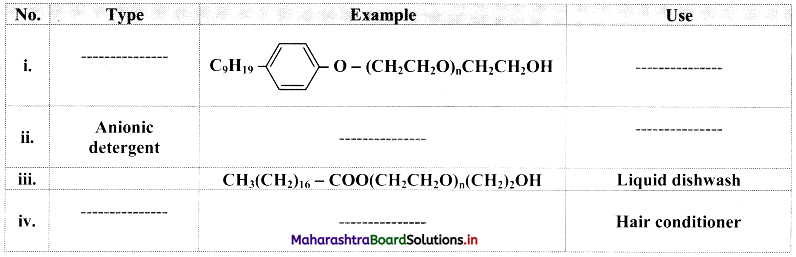
Answer:
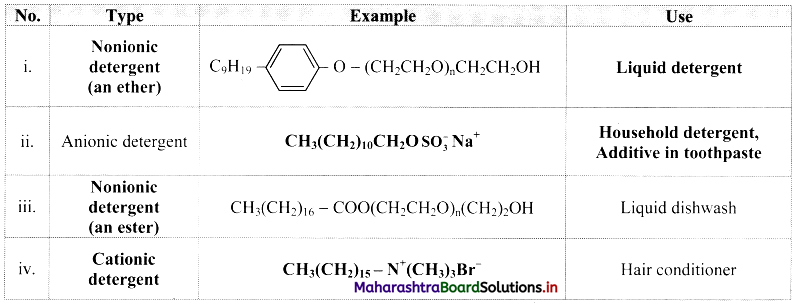
Question 55.
Give an example of detergent used as:
i. Additive in toothpaste
ii. Used as germicide
Answer:
i. Additive in toothpaste: Sodium lauryl sulphate, CH3(CH2)10CH2O\(\mathrm{SO}_{3}^{-}\)Na+
ii. Used as germicide: Ethyltrimethylammonium bromide, [CH3(CH5)15 – N+(CH3)3]Br–.
Question 56.
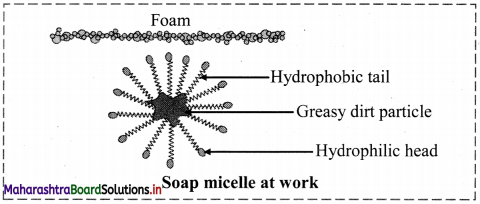
Explain cleansing mechanism of soaps and detergents.
Answer:
i. Soaps and detergents bring about cleansing of dirty, greasy surfaces by the same mechanism.
ii. Dirt is held at the surface by means of oily matter, and therefore cannot get washed with water.
iii. The molecules of soaps and detergent have two parts. One part is polar called head and the other part is long nonpolar chain of carbons called tail.
iv. The hydrophilic polar head can dissolve in water which is a polar solvent, while the hydrophobic nonpolar tail dissolve in oil/fat/grease.
v. The molecules of soap/detergent are arranged around the oily droplet such that the nonpolar tail points towards the central oily drop while the polar head is directed towards the water.
vi. Thus, micelles of soap/detergent are formed surrounding the oil drops, which are removed in the washing process.
Question 57.
Compound “X” having the following structure is used as synthetic antioxidant to increase the shelf life of packed foods.
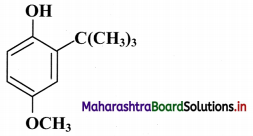
i. What is the molecular formula of compound “X”?
ii. Identify the structural unit responsible for antioxidant activity of “X”.
iii. Give one example of a compound with structure, similar to compound “X”, which is commonly used as synthetic antioxidant.
iv. Give the IUPAC name of compound “X”.
Answer:
i. Molecular formula: C11H16O2
ii. Structural unit responsible for antioxidant activity of compound “X” is phenolic -OH group.
iii. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) is commonly used synthetic antioxidant similar to compound “X”.
iv. The IUPAC name of compound “X” is 2-tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenol.
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions
1. BHT as a food additive act as …………….
(A) antioxidant
(B) flavouring agent
(C) colouring agent
(D) emulsifier
Answer:
(A) antioxidant
2. The structure of antioxidant BHT is …………….
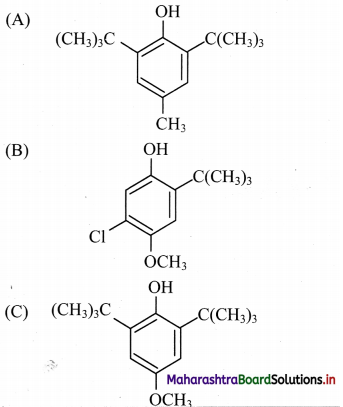
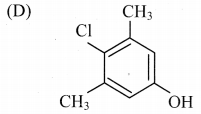
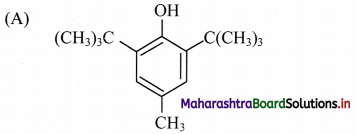
Answer:
3. The molecular formula of aspirin is …………….
(A) C8H8O3
(B) C9H8O4
(C) C9H10O4
(D) C9H8O3
Answer:
(B) C9H8O4
4. Aspirin is a/an …………….
(A) antibiotic
(B) analgesic
(C) antimicrobial
(D) disinfectant
Answer:
(B) analgesic
![]()
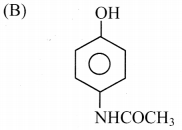
5. The CORRECT structure of the drug paracetamol is …………….
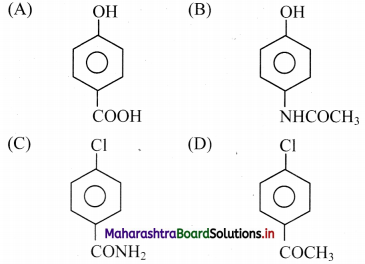
Answer:
6. Which of the following is used as a weak antiseptic for eyes?
(A) Tincture of iodine
(B) Dilute solution of dettol
(C) Iodoform
(D) Dilute aqueous solution of boric acid
Answer:
(D) Dilute aqueous solution of boric acid
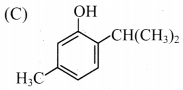
7. The structure of thymol is …………….
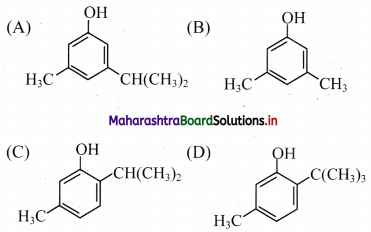
Answer:
8. Salvarsan is arsenic containing drug which was first used for the treatment of …………….
(A) syphilis
(B) typhoid
(C) ulcer
(D) dysentery
Answer:
(A) syphilis
![]()
9. The linkage present in salvarsan is …………….
(A) -N = N –
(B) – As = As –
(C) -S – S –
(D) – O – O –
Answer:
(B) – As = As –
10. Which of following contains – N = N – in its structure?
(A) Chloramphenicol
(B) Sulphapyridine
(C) Salvarsan
(D) Prontosil
Answer:
(D) Prontosil
11. Which of the following contains – As = As – linkage?
(A) Salvarsan
(B) Prontosil
(C) Sulphanilamide
(D) Sulphapyridine
Answer:
(A) Salvarsan
12. Which of the following element is NOT present in penicillin?
(A) O
(B) S
(C) P
(D) N
Answer:
(C) P
13. Methyl salicylate having analgesic properties is obtained from which of the following plant?
(A) Clove
(B) Indian gooseberry
(C) Wintergreen
(D) Cinnamon
Answer:
(C) Wintergreen
![]()
14. Hydrolysis of oil by aqueous alkali is called …………….
(A) esterification
(B) saponification
(C) acetylation
(D) carboxylation
Answer:
(B) saponification
15. Sodium lauryl sulphate is an example of …………….
(A) soap
(B) cationic detergent
(C) anionic detergent
(D) nonionic detergent
Answer:
(C) anionic detergent