Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 Civics Solutions Chapter 6 Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra Board Class 7 Civics Solutions Chapter 6 Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties
Class 7 Civics Chapter 6 Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties Textbook Questions and Answers
1. List the restrictions on the powers of the Government.

Answer:
Restrictions upon the powers of the Government are listed below:
- State should not discriminate between and among citizens on the basis of caste, religion, race, language or gender.
- State shall not deny anybody equality before the law and equal protection of the laws.
- No person shall be deprived of his life.
- State shall not impose any religious taxes.
![]()
2. Say ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.
Question 1.
The jobs advertised in the newspaper are for men and women both.
Answer:
Yes
Question 2.
Men and women doing the same work in a factory get different wages.
Answer:
No
Question 3.
Government implements various schemes for the improvement of public health.
Answer:
Yes
Question 4.
State shall protect all monuments of historic interest and national importance.
Answer:
Yes
![]()
3. Tell why:
Question 1.
The State shall protect all monuments of historic interest and national importance.
Answer:
- It is one of important Directive Principles of State policy.
- Monuments are a part of India’s rich cultural heritage. A rich source to learn history, it is our collective responsibility to protect them.
Question 2.
A pension scheme is implemented for old people.
Answer:
- The pension scheme is the State’s way of offering public assistance to citizens who have retired from work.
- This ensures that the retired person can lead a comfortable life.
- Hence a pension scheme is implemented for old people.
Question 3.
Free and compulsory education has been made available to children in the age group 6 to 14.
Answer:
- No child should be deprived of education. So it is made available.
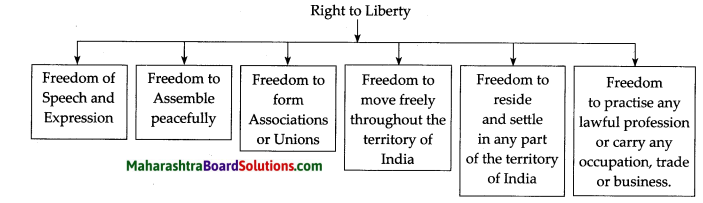
- Right to Liberty now also includes Right to Education and all children are entitled to get education as a Fundamental right.
4. Say right or wrong. Correct and write the wrong ones:
Question 1.
Not to let the National Flag fall down on the ground.
Answer:
Right: It is our Fundamental Duty to respect the National Flag.
Question 2.
To stand in attention while the National Anthem is playing.
Answer:
Right: It is our Fundamental Duty to respect our National Anthem.
![]()
Question 3.
To carve or paint our names on the walls of a historic place like a fort.
Answer:
Wrong: It is our Fundamental Duty to value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture.
Question 4.
To give lesser wages to women than to men for the same work.
Answer:
Wrong: Fundamental Rights put restrictions on the power of the government and one of the restriction states that the state should not discriminate between and among citizens on the basis of gender amongst other things.
Question 5.
To keep public places clean.
Answer:
Right: It is our Fundamental Duty to safeguard public property.
5. Write about the following:
Question 1.
The Directive Principles of the Constitution enumerated in the textbook.
Answer:
(i) The State should secure adequate means of livelihood to all citizens without any gender discrimination.
(ii) The State should secure equal pay for equal work for both men and women.
(iii) The State should secure the improvement of public health.
(iv) The State shall endeavour to protect and improve the environment and safeguard the forests and wild-life of the country.
(v) The State shall protect all monuments of historic interest and national importance.
(vi) The State shall promote with special care the educational and economic interests of the weaker sections of the people, especially the Scheduled Castes and Tribes.
(vii) The State shall offer public assistance to citizens in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness, etc.
(viii) The State shall secure a uniform civil code applicable to the entire country.
Question 2.
The provision of a Uniform Civil Code for citizens in the Directive Principles of the Indian Constitution.
Answer:
(i) The provision of a Uniform Civil Code for citizens in mentioned in the Constitution.
(ii) It aims to replace personal laws based on the customs and scriptures of the different religious communities living in India with a common set of laws, which is uniform to all the citizens of India.
![]()
Question 3.
Why is it said that the Directive Principles and Fundamental Rights are two sides of the same coin?
Answer:
(i) Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Rights are two sides of the same coin.
(ii) Due to Fundamental Rights, citizens get the most needed liberty, while Directive Principles of State Policy creates an atmosphere conducive to the growth of democracy.
6. What are the ways in which citizens can conserve the environment ? Write with examples.
Answer:
There are various ways in which citizens can conserve the environment:
(i) Citizens can support the endeavour of the State to protect and improve the environment and safeguard the forests and wild-life of the country.
(ii) Citizens should collectively take responsible actions to protect and improve the natural environment we are a part of.
(iii) Citizens should put to an end cruelty towards animals and have compassion for living creatures.
Activities
- Education is our right. Form groups and discuss our duties in this respect.
- The State shall protect all monuments of historic interest and national importance. This is one of the Directive Principles. Find out the efforts made by the State about the conservation and protection of forts and make a chart.
- Gather information about the schemes implemented by the Government for children’s health.
Class 7 Civics Chapter 6 Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the appropriate words from the options given below:
Question 1.
Due to citizens get the most needed liberty. (Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy, Fundamental Duties)
Answer:
Fundamental Rights
Question 2.
In order that the Indian citizens become conscious of their responsibilities ______ were included in the Constitution.
(Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy)
Answer:
Fundamental Duties
![]()
Question 3.
We should perform all the tasks that we have undertaken honestly always striving for ______. (excellence, progress, prosperity)
Answer:
excellence
Question 4.
Fundamental Rights restricts the power of the government to impose any ________. (laws, restrictions, religious taxes)
Answer:
religious taxes
Question 5.
Every citizen of India who is a parent or guardian should provide opportunities of education to his or her child or ward between the age of six and _______years. (eighteen, fourteen, seventeen)
Answer:
fourteen
Say ‘Yes’ or ‘No’:
Question 1.
The state should secure the improvement of public health.
Answer:
Yes
Question 2.
Public assistance is provided to citizens in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness etc.
Answer:
Yes
Name the following:
Question 1.
Put restriction on the power of the government.
Answer:
Fundamental Rights
Question 2.
Direction or guidelines in the Constitution about how to achieve the goals expressed in the Preamble of the Constitution.
Answer:
Directive Principles of the State Policy
Question 3.
Any two challenges faced by India after independence.
Answer:
Establishing order, carrying out smooth administration.
![]()
Question 4.
Any one directive which ensures that there is no gender discrimination.
Answer:
State should secure equal pay for equal work for both men and women.
Question 5.
It is our Fundamental Duty to respect these two national symbols.
Answer:
National Flag, National Anthem.
Question 6.
Any one practice we are expected to renounce according to the Fundamental Duties listed in our Constitution.
Answer:
Practices derogatory to the dignity of women.
Question 7.
It is our Fundamental Duty to develop these values.
Answer:
Scientific temper, Humanism, Spirit of inquiry and reform.
Say right or wrong with reason. Correct the write down the corrections:
Question 1.
To sacrifice our life for the sake of our motherland.
Answer:
Right: It is our Fundamental Duty .to defend the country, and to render national service when called upon to do so.
Question 2.
The State protects all monuments of historic interest and national importance.
Answer:
Right: It is one of the important Directive Principles of the State Policy.
![]()
Answer in one or two sentence:
Question 1.
Which restrictions on the power of the government by the Fundamental Rights ensure that no discrimination is practised by the State?
Answer:
Fundamental Rights restrains the State from discriminating between and among citizens on the basis of caste, religion, race, language or gender.
Question 2.
When India got independence, why was it necessary to draw up new policies?
Answer:
When India got independence the task of nation building had to be undertaken and for this new policies had to be drawn up.
Question 3.
What is included in the Directive Principles of the State Policy with respect to environment?
Answer:
It is included in the Directive Principles of the State Policy that the State shall endeavour to protect and improve the environment and safeguard the forest and wild-life of the country.
Question 4.
What is stated in the Directive Principles of State Policy with respect to weaker sections of the Society?
Answer:
It is stated in the Directive Principles of the State Policy that State shall promote with special care the educational and economic interest of the weaker sections of the people, especially the Scheduled Castes and Tribes.
Question 5.
What is the State expected to secure as per the Directive Principles of State Policy which is applicable to the entire country?
Answer:
The State is expected to secure a Uniform Civil Code applicable to the entire country according to the Directive Principles of State policy.
Question 6.
What can we do if a Directive is not implemented by the Government.
Answer:
If a Directive is not implemented by the Government, we can put pressure on the Government in various ways to make a policy in order to meet the goals.
Question 7.
When will the benefits of the various schemes of the Government not reach all the people?
Answer:
The benefits of the various schemes of the government cannot reach all the people if they do not fulfil their Fundamental Duties.
![]()
Question 8.
Why were the Fundamental Duties included in the Constitution?
Answer:
Fundamental Duties were included in the Constitution so that the Indian citizens become conscious of their responsibilities.
Question 9.
Why is it mentioned in our Fundamental Duties that we should strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity?
Answer:
It is mentioned in our Fundamental Duties that we should strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation can constantly rise to higher levels of endeavour and achievement.
Answer the following in brief:
Question 1.
What are the ways in which citizens can conserve the environment?
Answer:
There are various ways in which citizens can conserve the environment:
- Citizens can support the endeavour of the State to protect and improve the environment and safeguard the forests and wild-life of the country.
- Citizens should collectively take responsible actions to protect and improve the natural environment we are a part of.
- Citizens should put to an end cruelty towards animals and have compassion for living creatures.
Question 2.
State any five Fundamental Duties of the Indian citizens.
Answer:
Fundamental Duties of the Indian citizens are as follows:
- To abide by the Constitution and respect the National Anthem.
- To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom.
- To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
- To defend the country, and to render national service when called upon to do so.
- To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood transcending diversities; to renounce practices derogatory to the dignity of women.
![]()
Give reason:
Question 1.
The State shall protect all monuments of historic interest and national importance.
Answer:
- It is one of important Directive Principles of State policy.
- Monuments are a part of India’s rich cultural heritage. A rich source to learn history, it is our collective responsibility to protect them.
Question 2.
A pension scheme is implemented for old people.
Answer:
- The pension scheme is the State’s way of offering public assistance to citizens who have retired from work.
- This ensures that the retired person can lead a comfortable life.
Hence a pension scheme is implemented for old people.
Question 3.
Free and compulsory education has been made available to children in the age group 6 to 14.
Answer:
- No child should be deprived of education. So it is made available.
- Right to Liberty now also includes Right to Education and all children are entitled to get education as a Fundamental right.
Give your own response:
Question 1.
What else do you think the Government should do for students? Make a list of your demands. How would you convince others that your demands are just?
Answer:
The list of our demands are:
- Emphasis on skill training in school.
- Choice of a wide variety of subjects based on one’s interest.
- Compulsory training in a particular Sport.
- Making a foreign language compulsory in the curriculum.
- Better facilities in schools.
- Programme of mid-day meals should be implemented in all the schools in the rural areas.
- Inspection of schools from time to time to check the quality of education imparted.
- I will convince others through dialogues and discussion and go by the will of the majority.
![]()
Question 2.
Which improvements will be possible with the following facilities offered by the Government?
Answer:
- Public toilets: Maintenance from time to time and continuous water supply.
- Clean water supply: Ensuring that water treatment to remove contaminants is done before it reaches homes and other places for consumption.
- Vaccination of children:
- Create awareness among parents about different vaccinations through different media of communication.
- Organise vaccination drives from time to time.
Can you tell?
Question 1.
There is a directive to ensure ‘equal pay for equal work’.
Which principles and ideals of the Constitution will be realised with this directive? Why does it happen that inspite of doing the same work, women are paid less than men?
Answer:
(i) Right to Equality and the assurance that State shall not discriminate among citizens will be realised with this objective.
(ii) Due to lack of awareness of rights and no strict implementation of law, we witness gender discrimination at work.
Observe the Picture and answer the questions given below:

Which of the Fundamental Duties are not being followed in the situations above?
Question 1.
A boy scribbling on a historical structure.
Answer:
The duty to value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture.
Question 2.
Hanging lemon, chillies
Answer:
The duty to develop the scientific temper, humanism and spirit of inquiry and reform.
Question 3.
Damaging a public bus
Answer:
The duty to safeguard public property and to abjure violence.
Question 4.
A woman emptying a garbage can on the street.
Answer:
The duty to protect and improve the natural environment.
What do you think?
Question 1.
Girls and boys between the ages 6 and 14 have got the Right to Education. All the girls and boys in this age group should be in school. Yet many girls and boys are not able to go to school because of many reasons. They have to work to help their parents earn a living for the family. Do you think that it is unfair to such children to insist that they go to school?
Answer:
No I don’t think it is unfair to such children to insist that they go to school.
(i) Practising child labour is a form of exploitation and we have the Right against Exploitation which extends constitutional protection to children.
(ii) Similarly it is the Fundamental Duty of every citizen who is a parent or guardian to provide opportunities of education to his or her child or ward between the age of six and fourteen years.
![]()
Question 2.
Which improvements will be possible with the following facilities offered by the Government?
Answer:
(i) Public toilets :
- Public toilets will eradicate open defecation and will improve the overall public health
- As the availability of toilets at close proximity to highway will ensure that people do not face inconvenience while traveling.
(ii) Clean water supply:
- Water is our basic need hence providing clean water is very important
- It will prevent the spread of water borne diseases like cholera, jaundice, etc.
(iii) Vaccination of children:
- Vaccination will improve the health of infants
- Vaccination will reduce the occurrence of diseases like polio in infants