Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 12 Economics Important Questions Chapter 10 Foreign Trade of India Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 10 Foreign Trade of India
1. A. Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Before independence, India was exporting raw materials to –
(a) USA (b) Japan
(c) England (Britain)
(d) None of these
Options :
(1) a and b
(2) c and a
(3) d
(4) only c
Answer:
(4) only c
![]()
Question 2.
Internal trade also known as –
(a) Domestic trade
(b) Home trade
(c) External trade
(d) all of these
Options :
(1) a, b and c
(2) b and c
(3) a and b
(4) only d
Answer:
(3) a and b
Question 3.
International or External trade takes place between –
(a) two or more districts
(b) two or more states
(c) two or more countries
(d) none of these
Options :
(1) a and b
(2) a and c
(3) a, b and c
(4) only c
Answer:
(4) only c
Question 4.
Most important commodity in India’s import is –
(a) Petroleum, oil and lubricants
(b) Food grains .
(c) Engineering goods
(d) Readymade garments
Options :
(1) a and b
(2) b and c
(3) only a
(4) c and d
Answer:
(3) only a
Question 5.
According to Walter Krause definition of Balance of Payment, value of exchange of goods and services is considered among –
(a) the citizens and businessmen
(b) the firms
(c) the government
(d) none of these
Options :
(1) a, b and c
(2) b and c
(3) c and d
(4) only a
Answer:
(1) a, b and c
![]()
Question 6.
Trade surplus means –
(a) Export value > Import value
(b) Export value < Import value
(c) Export value = Import value
(d) All of these
Options :
(1) only a
(2) b and c
(3) only b
(4) only d
Answer:
(1) only a
Question 7.
Balance of trade includes –
(a) the value of imports of visible and invisible goods
(b) the value of imports of only visible goods
(c) the value of imports and exports of visible and invisible goods
(d) the value of exports of visible and invisible goods.
Options :
(1) a and d
(2) only b
(3) only c
(4) All of these
Answer:
(3) only c
Question 8.
International trade is important because –
(a) it helps in optimal utilisation of resources
(b) it brings stability in price level
(c) it helps to earn foreign exchange
(d) it encourages investment
Options :
(1) a and b
(2) b and c
(3) a and c
(4) all of these
Answer:
(4) all of these
Question 9.
The share of India’s foreign trade in Gross National Income during 2016-17 was –
(a) 25%
(b) 17.55
(c) 48.8 %
(d) None of these
Options :
(1) only a
(2) only b
(3) only c
(4) only d
Answer:
(3) only c
Question 9.
In recent years India’s leading trading partners are –
(a) USA, Germany, Japan, UK
(b) Britain
(c) Nepal, Sri Lanka, UK
(d) None of these
Options :
(1) only a
(2) b and c
(3) a and c
(4) only d
Answer:
(1) only a
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a benefit of international trade –
(a) provides multiple choices of imported goods
(b) leads to division of labour
(c) high wage levels for all domestic workers
(d) can earn reputation and goodwill in the international market
Options :
(1) a and d
(2) only c
(3) a, c and d
(4) a, b and d
Answer:
(2) only c
![]()
Question 11.
There is a change in the composition of India’s exports from –
(a) primary products to manufactured products
(b) manufactured products to primary products
(c) manufactured products to software
(d) All of these Options:
(1) a and b
(2) only a
(3) a, b and e
(4) only d
Answer:
(2) only a
(B) Complete the Correlation
(1) Internal trade : Home trade :: …………. : Foreign trade
Answer:
International trade
(2) Trade surplus: …………. :: Trade deficit: Export > Import
Answer:
Export > Import
(3) …………. : jute, cotton :: Manufactured goods: readymade garments
Answer:
Primary goods
(4) OECD : Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development :: …………. : Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries
Answer:
OPEC
(5) Import goods : …………. :: Export goods : Engineering goods
Answer:
Gold
(6) Trade within the country : Internal trade :: Trade between two or more countries : …………..
Answer:
External trade
(7) Highest share in export: Engineering goods :: Highest share in import: ………….
Answer:
Petroleum
(8) Old ports : Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai:: …………. : Kandla, Cochin, Vishakhapatnam
Answer:
New ports
(9) International trade : External trade :: Domestic trade : …………. :
Answer:
Internal trade
(10) Foreign trade before independence : …………. :: Foreign trade after independence : USA
Answer:
Britain / England
(11) Machinery : Capital goods :: Motor vehicles : ………….
Answer:
Consumer goods
(C) Give economic terms.
(1) To purchase goods and services by one country from another country.
Answer:
Import trade
(2) To sale goods and services by one country to another country.
Answer:
Export trade
![]()
(3) To purchase goods and services from one country and then selling them to another country after processing.
Answer:
Entrepot trade
(4) Exchange of goods and services.
Answer:
Trade
(5) Export value is greater than the import value.
Answer:
Trade surplus
(6) Import value is greater than the export value.
Answer:
Trade deficit
(7) The trade is by sea.
Answer:
Oceanic trade
(8) This leads division of labour and specialization.
Answer:
Foreign trade
(9) We can see or touch these goods.
Answer:
Visible / tangible goods
(10) We can’t see or touch these goods.
Answer:
Invisible / intangible goods
(D) Find the odd word out.
(1) Internal trade, Domestic trade, Foreign trade, Home trade.
Answer:
Foreign trade
(2) International trade, Internal trade, External trade, Foreign trade.
Answer:
Internal trade
(3) Types of foreign trade :
Import trade, Export trade, National trade, Entrepot trade.
Answer:
National trade
(4) Need of Foreign trade :
To earn foreign exchange, To earn rupees, To encourage investment,To stabilize price ; level
Answer:
To earn rupees
(5) Important features of India’s foreign trade :
Change in the composition of exports, ; Change in composition of imports, Change in composition of internal trade
Answer:
Change in composition of internal trade
(6) Trade relation with neighbouring countries :
Nepal, Afghanistan, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, England
Answer:
England
(7) New ports for foreign trade :
Mumbai, Kandla, Cochin, Vishakhapatnam ;
Answer:
Mumbai
(8) Major imported goods :
Gold, Fertilizers, Gems and Jewellery, Petroleum
Answer:
Gems and jewellery
(9) Major exported goods :
Iron and Steel, ‘ Engineering goods, Chemicals, Textiles and readymade garments
Answer:
Iron and steel
(10) Useful concept in foreign trade :
Balance of payment, Balance of trade, Balance budget
Answer:
Balance budget
(11) Organisation related to foreign trade : OECD, OPEC, EGEPC, NABARD
Answer:
NABARD
(12) Manufactured products :
Gems and jewellery, Electronic goods, s Computer hardware and software, Food grains
Answer:
Food grains
(13) Primary products :
Jute and cotton, Readymade garments, Oil seeds, Mineral products
Answer:
Readymade garments
(14) Visible goods :
Gold, Petroleum, Fertilizers, Communication
Answer:
Communication
(15) Invisible goods (service):
Banking, Communication, Engineering goods, Transport
Answer:
Engineering goods
(16) Cloth, Machinery, Technology, Fertilizers
Answer:
Cloth
![]()
(E) Complete the sentences.
(1) During the British rule …………………. industries suffered set back.
Answer:
handicraft
(2) In the post World War II, …………………. trade is considered as an investment.
Answer:
Foreign trade
(3) Buying and selling of goods and services within the boundaries of a nation are known as ………………….
Answer:
Internal trade
(4) Internal trade is also known as ………………….
Answer:
Domestic / Home trade
(5) The trade between Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, etc, is known as ………………….
Answer:
Internal trade
(6) International trade is also known as ………………….
Answer:
Foreign / External trade
(7) Trade which consists of transaction between residents of different countries is called ………………….
Answer:
International trade
(8) …………………. is a remarkable factor in expanding the market and encouraging the production of goods.
Answer:
Foreign trade
(9) …………………. helps to earn goodwill and reputation in the international market.
Answer:
Export trade
(10) After independence, there was change in the composition of imports from consumer goods to ………………….
Answer:
capital goods
(11) Share of …………………. trade-in-India is around 68%.
Answer:
Oceanic trade
(12) Goods such as cloth, motor vehicles, electrical goods, etc, are known as ………………….
Answer:
consumer goods
(13) Goods and services that are made in one country but purchased and consumed in another country is called ………………….
Answer:
export
(F) Choose the wrong pair ; (1 mark each)
I.
| Group‘A | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Internal trade | Between two or more countries |
| 2. Oceanic trade | Trade by sea |
| 3. Export trade | Sale of goods by one country to another country |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Internal trade – Between two or more countries
II.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Primary goods | Jute, cotton, tea |
| 2. Invisible goods | Cloth, medicine, car |
| 3. Capital goods | Machinery, technology, steel |
Answer:
Wrong pair : Invisible goods – Cloth, medicine, car
III.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Encourage investment | Foreign trade |
| 2. To earn foreign exchange | Internal trade |
| 3. International trade | Multiple choices of imported goods |
Answer:Wrong pair : To earn foreign exchange Internal trade
(G) Assertion and Reasoning:
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Trade is an engine of growth of an economy.
Reasoning (R) : It plays an important role for economic development.
(1) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : International trade consists of transaction between residents of different countries.
Reasoning (R): This is given by Wasserman and Hultman
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : During the British rule foreign trade did not permit industrialisation in India.
Reasoning (R) : India was a supplier of raw material to the England and importer of manufactured goods.
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Buying and selling of goods and services across the boundaries of a nation are known as internal trade. Reasoning (R) : Goods produced in
Maharashtra are sold to West Bengal then it is known as international trade.
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
Question 5.
Assertion (A) : Due to specialization resources are channelized for the production of only those goods which would give highest ( return.
Reasoning (R): There is rational allocation and specialization.
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii)(A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv)(A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
Question 6.
Assertion (A) : An increase in total investment leads to development of an economy. .
Reasoning (R) : Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets.
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv) (A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(i) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
Question 7.
Assertion (A) : Balance of payments is a summary statement of all the transaction between the residents of one country and the rest of the world.
Reasoning (R): This is given by Samuelson.
(i)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the
correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv)(A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
Question 8.
Assertion (A) : Balance of trade is the difference between the value of countries export and import for a given period. Reasoning (R) : Balance of trade is also referred to as international trade balance.
(i)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct reason for (A).
(ii) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct reason for (A).
(iii)(A) is true but (R) is false.
(iv)(A) and (R) both are false.
Answer:
(iii) (A) is true but (R) is false.
(H) Choose the right group of pairs :
I.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. Balance of Trade | (a)International trade balance |
| 2. OPEC | (b) Oil and Petrol Export Commission |
| 3. Trade | (c) Buying and selling of goods and services |
| 4. Invisible goods | (d) Banking, insurance |
| 5. WTO | (e) World Trade Organisation |
II.
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
| 1. OPEC | (a) Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries |
| 2. Trade deficit | (b) Value of export < Value of import |
| 3. Internal trade | (c) Trade within the country |
| 4. India’s imported goods | (d) Petroleum, Gold, fertilizer |
| 5. Entrepot Trade | (e) Re-export |
Answer:
II group is correct.
2.[A] Identify and explain the concept from given illustrations.
Question 1.
Antwerp city of Belgium imports raw diamonds and exports finished diamonds to other countries.
Answer:
Concept: Entrepot Trade
Explanation : It means purchase of goods and services from one country and selling them to another country after processing.
Question 2.
The country ‘A’ value of import was $200 billion and value of export was $150 billion.
Answer:
Concept: Trade deficit
Explanation : When value of import is greater than value of export it is called as trade deficit.
Question 3.
The country ‘X’ value of export was $500 billion and value of import was $200 billion.
Answer:
Concept: Trade Surplus
Explanation : When value of export is greater than value of import it is called as trade surplus.
Question 4.
Kashmir sold its apples to the other parts of country.
Answer:
Concept: Internal trade
Explanation : This trade is also known as home or domestic trade. It means buying and selling of goods and services within the country.
Question 5.
India is selling its spices to USA, China, Vietnam, etc.
Answer:
Concept: Export Trade
Explanation : It means selling of goods and services by one country to another country. It helps to earn foreign exchange.
Question 6.
India based Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) is selling their software and services to the USA.
Answer:
Concept: Export trade
Explanation : It means selling of goods and services by one country to another country. It helps to earn foreign exchange.
(B) Distinguish between
Question 1.
Import trade and Export trade.
Answer:
Import trade:
- It means to purchase of goods and services by one country from another country.
- E.g. India imports petroleum from Iraq, Kuwait
- It is inflow of goods and services.
Export trade:
- It means to the sale goods and services by one country to another country.
- E.g. India exports tea, rice, jute to China, Hong Kong, etc.
- It is outflow of goods and services.
Question 2.
Export trade and Entrepot trade.
Answer:
Export trade:
- Export trade means sale of goods by one country to another country.
- E.g. India selling its spices to USA, China, etc.
Entrepot trade:
- Entrepot trade means purchase of goods and services from one country and selling them to another country.
- E.g. Antwerp city of Belgium importing raw diamonds and exporting finished diamonds to other countries.
Question 3.
Trade surplus and Trade deficit.
Answer:
Trade surplus:
- When country’s exports are more than its imports, it is called as trade surplus.
- Generally, it is considered as a positive development.
Trade deficit:
- When country’s import are more than its exports, it is called as trade deficit.
- Generally, it is considered as a negative development.
![]()
3. Answer the following:
Question 1.
Explain the concepts of Balance of Trade.
Answer:
Balance of trade is the important concept of foreign trade. Balance of trade is the difference between the values of country’s exports and imports for a given period.
Balance of trade can be positive or negative.
(i) Trade surplus : When country’s value of export is more than its value of import, it is called trade surplus. It is also known as positive balance of trade.
(ii) Trade Deficit : When country’s value of import is more than its value of export, it is called as trade deficit. It is also known as negative balance of trade.
The formula for calculating balance of trade is as follows :
BOT = Total value of Exports – Total value of Imports.
4. State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements :
Question 1.
During British rule, indigenous handicraft suffered a severe blow.
Answer:
Yes, I do agree with this statement.
- During the British rule India was exporting raw materials to England and was importing final goods from England.
- Indian handicraft was unable to face competition with imported goods from England.
- An imported goods were cheaper as compared to handicraft goods.
- The demand for machine made cheap commodity had raised in Indian market.
- That’s why Indian handicraft industries suffered during the British rule.
Question 2.
Trade is an engine of growth for an economy.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
- Trade permits a more efficient allocation of national resources.
- Foreign trade provide foreign exchange which can be used to import modern machinery and technology from advanced countries.
- Foreign trade encourages producers to produce more goods for export.
- It leads to an increase in total investment in an economy.
- Thus, we can say, trade is an engine to growth for an economy.
Question 3.
Foreign trade leads to division of labour and specialisation at world level.
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this statement.
- Some countries have abundant natural resources.
- These countries should export raw material and import finished goods from countries which are advanced in skilled man power,
- Under specialisation specific work is given to the workers within a production process.
- Specialisation can increase the productivity of a firm or economy.
- Eg. Incase of car manufacturing company, some workers will design the cars, some workers will work on different section of assembly line, some workers will work on testing cars, some workers will work on marketing of cars.
Question 4.
Foreign trade is not playing an important role for economic development.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement.
- It helps to earn foreign exchange which can be used for productive purpose.
- It leads to an increase in a total investment in an economy.
- It helps to control the changes in the price level.
- It helps to maximum allocation and utlisation of resources at international level.
- Due to availability of imported goods, it helps to improve standard of living of the people in the country.
- During the natural calamities, foreign trade enables a country to import food grains and medicines from other countries to help the affected people.
- It promotes world peace by bringing countries closer.
Question 5.
During the pre and post independence period, India’s composition of import and export is the same.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement.
- Prior to independence, India used to export primary products like Jute, Cotton, Tea, Oil-Seeds etc.
- In the recent time India is exporting manufactured product like readymade garments, gems and jewellery, computer hardware and software, etc.
- Prior to independence India used to import consumer goods like medicines, cloth, motor vehicles, electrical goods, etc.
- In the recent time, India is importing capital goods like advanced technology and machinery, chemicals, fertilizers, steel, etc.
Question 6.
India is importing only petroleum from other countries.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement. India is importing many commodities like :
- Electronic goods : In the total import of country, share of electronic goods in 10.9% in the year 2016-17.
- Pearls and Gems : In the total import, share of peals and gems was 6.2% in the year 2016-17.
- Edible oils : India also imports edible oil from Malaysia and Indonesia and its share is 2.8% in the year 2016-17.
- Gold : There was growing demand for gold in the Indian market. In the year 2018-19, the value of gold imported was upto $32.8 billion.
- Fertilizers : India is importing fertilizers from China, US, Iraq, Russia. In the year 2016-17, the share of fertilizers was 1.3% in the total import of country.
Question 7.
India is exporting many commodities goods.
Answer:
Yes, I do agree with this statement. India exports many commodities like :
- Engineering goods : It has the large share in the export of India. The share of engineering goods was 25% in the total exports in 2017-18.
- Petroleum products : India turned as a net exporter of petroleum refinery products.
India’s export of petroleum product was 20.1% in 2013-14. - Chemicals and chemical product :
India is exporting chemicals and chemical products to many countries from last few years. In the year 2014-15 the share of chemicals was 10.4% in total exports of the country. - Gems and Jewellery : It is one of the major contributor which helps to earn foreign exchange. According to DGCI Kolkata, the value of Gems and Jewellery export was $38.96 billion in 2018-19.
5. Study the following table, chart, graph, passage and answer the questions.
1. India’s Merchandise Trade (US $ Billion)
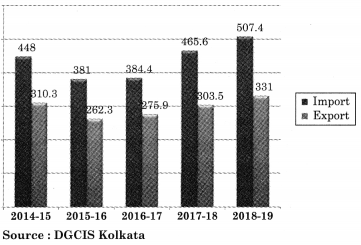
Question 1.
In the above bar diagram during which year export was maximum and how much was it?
The export was maximum in the year 2018¬19. It was $331billion.
Question 2.
In which year import was maximum and how much was it?
In the year 2018-19 import was maximum and it was $507.4 billion.
Question 3.
In which year import was least and how much was it?
In the year 2015-16 import was least and it was $381 billion.
Question 4.
Find out the trade deficit in the year 2017-18?
Trade deficit = Export – Import = 303.5 – 465.6
= $162.1 billion.
Question 5.
How much is the export increase in the year 2018-19 as compared to 2014-15?
Answer:
In the year 2018-19 export has increased by $20.7 billion as compared to 2014-15.
![]()
Question 6.
How much is the import increase in the year 2018-19 as compared to 2017-18?
Answer:
In the year 2018-19 imports has increased by $41.8 billion as compared to 2017-18.
Question 7.
Express your views on India’s merchandise trade.
Answer:
In the above bar diagram, India’s import is always greater then its export. India should take measures to reduce the imports. The Government of India should encourage the industries those are exporting goods by providing them various facilities such as availability of raw materials at cheaper rate, credit at low interest, etc.
(2) Share of top Five Commodities in India’s Export 2018-19
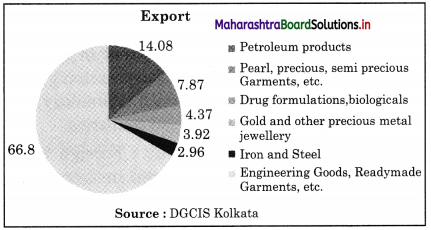
Question 1.
Name the second largest exported commodity in the year 2018-19.
Petroleum products are second largest exported commodity in the year 2018-19.
Question 2.
How much is the share of drug formulations, biologicals (chemical products) in total export of India.
Answer:
The share of chemical products is 4.37% in the total export of India.
Question 3.
Which commodity has least share in the total export of India and how much was it?
Answer:
Iron and Steel has least share and it is 2.96%.
Question 4.
Give your opinion on India’s export.
Answer:
India should focus on above five commodities to increase their export. The government of India should provide credit at low rate of interest, easy availability of raw materials required by above industries, as it will help to produce more goods.
3. Table A : Trade data for period 2009 – 10 to 2017 – 18
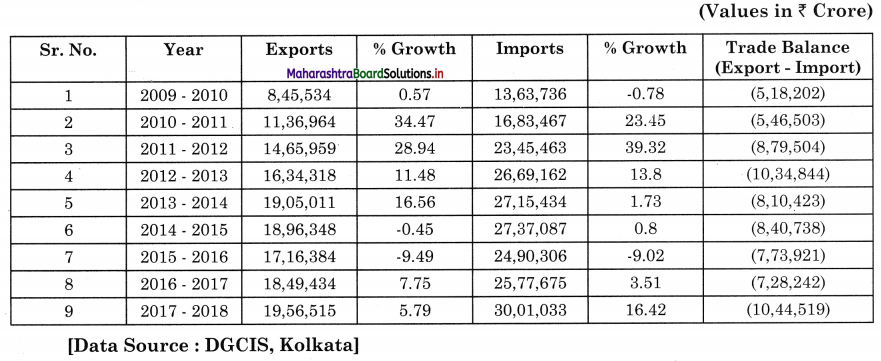
Question 1.
In which year export growth was least and how much?
Answer:
In the year 2015-16, export growth was least and it was -9.49%.
Question 2.
In which year import growth was maximum and how much?
Answer:
In the year 2011-12, import growth was maximum and it was 39.32%.
Question 3.
During which year trade balance was minimum?
Answer:
In the year 2009-10 trade balance was minimum.
Question 4.
Which concept of Balance of Trade is applicable here?
Answer:
The concept of trade deficit is applicable here, because in the above data every year India’s imports are more than its exports.
Question 5.
How much was India’s export value in the year 2017-18?
Answer:
In the year 2017-18 India’s export value was ? 19,56,515 crores.
![]()
Question 6.
Give your opinion on India’s foreign trade.
Answer:
Above data shows that every year India’s trade balance is deficit. It means imports are more than exports. The Government should formulate such policies that increases our export and reduces our imports.